英语中的十六种时态

英语中的十六种时态
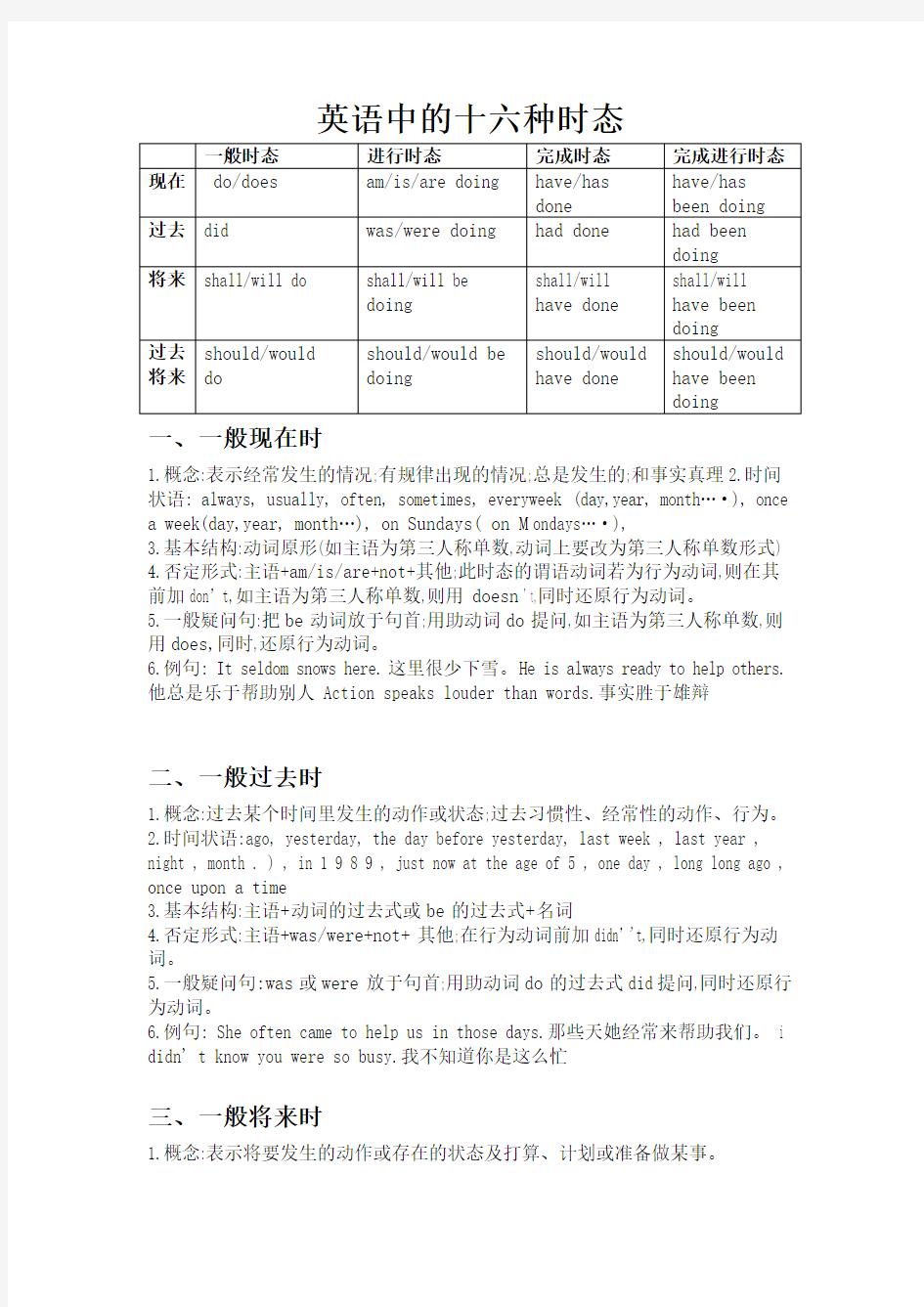
一般时态进行时态完成时态完成进行时态
现在do/does am/is/are doing have/has
done have/has been doing
过去did was/were doing had done had been
doing
将来shall/will do shall/will be
doing shall/will
have done
shall/will
have been
doing
过去将来should/would
do
should/would be
doing
should/would
have done
should/would
have been
doing
一、一般现在时
1.概念:表示经常发生的情况;有规律出现的情况;总是发生的;和事实真理
2.时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, everyweek (day,year, month…·), once
a week(day,year, month…), on Sundays( on M ondays…·),
3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式)
4.否定形式:主语+am/is/are+not+其他;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don’t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn’t,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
6.例句: It seldom snows here.这里很少下雪。He is always ready to help others.他总是乐于帮助别人Action speaks louder than words.事实胜于雄辩
二、一般过去时
1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week , last year , night , month . ) , in 1 9 8 9 , just now at the age of 5 , one day , long long ago , once upon a time
3.基本结构:主语+动词的过去式或be的过去式+名词
4.否定形式:主语+was/were+not+其他;在行为动词前加didn’'t,同时还原行为动词。
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词。
6.例句: She often came to help us in those days.那些天她经常来帮助我们。i didn' t know you were so busy.我不知道你是这么忙
三、一般将来时
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2时间状语: Tomorrow, next day(week, month,year…·) soon , in a few minutes , by , the day after tomorrow , etc .
3.基本结构:主语+am/is/are+ going to+do+其它;主语+wi1l/ shall+do+其它
4.否定形式:主语+am/is/ are not going to do;主语+will/ shall not do+其它
5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;wi1l/sha1l提到句首。{首字母大写
6 .例句: they are going to have a competition with us in studies It is going to rain.天要下雨了
四、一般过去将
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语: The next day( morning \,year……),the following
month(week…·),etc
3.基本结构:主语+Was/were+ going to+do+其它;主语+ would/ should+do+其它
4.否定形式:主语+was/were+not+ going to+do;主语+ would/ should
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首; would/ should提到句首
6.例句: He said he would go to beijing the next day.他说他第二天要去北京。asked who was going there.我问,谁要去那里。
五、现在进行时
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2时间状语:Now, at this time,days,etc.look, listen
3.基本结构:主语+be+ doing+其它
4.否定形式:主语+be+ not + doing+其它
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
6.例句: How are you feeling today?你今天感觉如何? He is doing well in his lessons.在课上他表现得很好。
六、过去进行时
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2时间状语: at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
3.基本结构主语+was/ were + doing+其它
4.否定形式:主语+Was/were+not+ doing+其它
5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。(第一个字母大写)
6.例句: At that time she was working in a pla unit.那段时间她在人民解放军部队工作。When he came in, i was reading a newspaper.他进来时,我正在读报纸。
七、将来进行时
1.概念:表示将来某一时间正在进行的动作,或表示要在将来某一时间开始,并继
续下去的动作。常用来表示询问、请求等。
2时间状语:Soon, tomorrow, this evening, on Sunday, by this time , in two days , tomorrow evening
3.基本结构:主语+ shall/will+be+现在分词+其它
4否定形式:主语+ shall/wi1l+not+be+现在分词+其它5.例句: This time next day they will be sitting in the cinema.下一天的这个时间,他们正坐在电影院。He won’ t be coming to the party.他不去参加聚会了。
八、过去将来进
1.概念:表示就过去某一时间而言,将来某一时刻或某一段时间正在进行的动作,
主要用于宾语从句中,尤其多用于间接引语中
2.基本结构: should/ would+be+现在分词
3.例句: They said they would be coming他们说了他们将要来。He said he could not come because he would be having a meeting .他说他不能来因为要开会
九、现在完成时
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:yet, already,just, never,ever, so far, by now,S1nce+时间点,for+时间段, recently, lately,ln the past few years , etc .
3.基本结构:主语
+have/has+p.p(过去分词)+其它
4.否定形式:主语+have/has+not+p.p(过去分词)+其它
5.一般疑问句:have或has放句首。
6.例句: I've written an article.我已经写了一篇论文。The countryside has changed a lot in the past few years在过去的几年,农村发生了巨大的变化
十、过去完成时
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之
前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2时间状语: Before, by the end of last year(term, month…·),etc.
3.基本结构:主语+had+pp(过去分词)+其它
4.否定形式:主语+had+not+p.p(过去分词)+其它
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6.例句: As soon as we got to the station, the train had left.当我们到车站的时候,火车已经开走了。By the end of last month , we had reviewed four books .到上个月底,我们已经复习了四本书。
7.基本结构:主语+had+p.p(过去分词)+其它
①肯定句:主语+had+p.p(过去分词)+其它②否定句:主语+had+not+p.p(过去分词)+其它
③一般疑问句:Had+主语+p.p(过去分词)+其它
④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
十一、将来完成时
1.概念:在将来某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态
2.时间状语: by the time of; by the end of+时间短语(将来); by the time+从句(将来)
3.基本结构:主语+ be going to/will/ shall+have+p.p(过去分词)+其它
4.例句:by the time you get back , great changes will have taken place in this area .到你回来的时候,就将发生巨大的变化。
十二、过去将来完成时
1.概念:表示在过去某一时间对将来某一时刻以前所会发生的动作,常用在虚拟语气中,表示与过去的事实相反。
2.基本结构: should/ would have done sth
3.例句: i thought you'’ d have left by this time.我想这会儿你已经走了。He told them he would have finished it by 8 o clock .他告诉他们他会在8点以前干完十三、现在完成进行时
1概念:表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到现在的动作。这一动作可能刚刚开始,也可能仍在继续,并可能延续到将来。
2.基本结构:主语+have/has+been+ doing+其它
3时间状语: Since+时间点,for+时间段等。
4.例子: i have been sitting here for an hour.我已经在这里坐了一个小时。The children have been watching tv since six o ' clock .从6点起,孩子们一直看电视十四、过去完成进行时
1.概念:表示某个正在进行的动作或状态,持续到过去某个时刻,还未完成,一直持续到之后的当前才结束。
2.基本结构:主语+had+been+ doing+其它
3.例子: She had been suffering from a bad cold when she took the exam。她在考试之前一直患重感冒。Had they been expecting the news for some time ?他们期待这个消息有一段时间了吧?
4.特殊含义:①尚未完成: He had been writing the novel.他已经在写小说了。(他没写完)
②企图: He had been studying the meaning of this proverb.他曾经学习过这个谚语。(他曾努力学习过它)
③未得结果: We had been studying what our enemy had said.我们一直致力于敌人所说的。(但是我们没有理解)
④最近情况: He had been quarreling with his wife.他和他的妻子吵了一场架。(最近)
⑤反复动作: He had been asking me the same question.他一直问我相同的问题。(屡次)⑥情绪: What had he been doing?他做了什么?(不耐烦)
十五、将来完成进行时
1.概念:表示动作从某一时间开始一直延续到将来某一时间是否继续下去,要视上
下文而定。
2.基本结构: shall/ will have been doing
3.例子:I shall have been working here in this factory for twenty years by the end of the year .到今年年底,我将在这个工厂工作20年了。
If we don ' t hurry up the store will have been closing before we get there .咱们如不快一点儿,等我们到了那儿,店门就会关了。
十六、过去将来完成进行时
1.概念:表示从过去某时看至未来某时以前会一直在进行的动
2.基本结构:should/ would+have+been+现在分词
3.例子: He told me that by the end of the year he would have been living there for thirty years .他告诉我,到年底时,他就在那住了30年了。
英语16种时态精彩分析
写在前面 时态是初中英语学习中最重要的语法内容。利用这个暑假,好好学习和揣摩各种时态的构成和用法,行动起来吧! 英语时态分为16种,如下表所示: 各时态结构及用法 1. 一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are) ①表示现在的情况、状态和特征。 例:He is a student. 他是一个学生。 ②表示经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. 他总是帮助别人。 ③客观事实和普遍真理。 例:The earth moves the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。 ④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。(常用于列车、客车、飞机或轮船时刻表) 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. 下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。
⑤主将从现:在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在表示将的来事情。例:If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home. 如果明天下雨,我们会待在家里。 2. 现在进行时(am/is/are doing) ①表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。 例:He is listning to the music now. 他现在正在听音乐。 ②表示目前一段时间内一直在做的事情,但不一定此时此刻正在做。 例:I am studying computer this term. 这个学期我一直在学习计算机。 ③现在进行时可以表示将来的含义。 瞬时动词的进行一定表将来。 例:I am leaving. 我要离开了。 持续动词的进行只有有将来的时间状语或有将来语境中才表将来。 例:I am travelling next month. 下个月我要去旅行。 ④现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。 例:He is always helping others. 他总是帮助别人。(褒义) 3. 过去进行时(was/ were doing) ①表示在过去一个具体的时间正在发生的动作。 例:Mary was listening to light music 10 minutes ago.
英语中的十六种时态
英语中的十六种时态 (1)一般现在时 基本形式(以do为例):第三人称单数:does(主语为非第三人称单数);肯定句:主语+动词原形+其他; He works for us. 否定句:主语+don't/doesn't+动词原形+其他; He doesn't work for us. 一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他。 肯定回答:Yes,(+主语+do/does). 否定回答:No,(+主语+don't/doesn't.) 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句语 Does he work for us? Yes, he does. No, he doesn't
What does he do for us? He works for us. (2)一般过去时 be动词+行为动词的过去式 否定句式:在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词,或was/were+not;was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词 例如: Did he work for us? He didn't work for us. He worked for us. (3)一般将来时 am/are/is+going to+do 或 will/shall+do am/is/are/about to + do
am/is/are to + do; 一般将来时的表达方法 be going to +动词原形 be +不定式,be to+动词原形,be about to +动词原形 be able to +不定式 be about to+动词原形 will + 动词原形; 例如:He is going to work for us. He will work for us; He is coming.这是特殊的用一般现在时表达将来时态的例子!! (4)过去将来时 be(was,were)going to+动词原形 be(was,were)about to+动词原形 be(was,were)to+动词原形
英语16种时态详解
英语的16种时态 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. 一般现在时 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。)2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法:A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging 全句的意思是:“虽然牛顿是个伟大的人物,但他的许多见解直到今天还在受到挑战,并且被现代科学家的工作所修正。”challenge是及物动词,在本句中应当是被动语态;其动作延续到今天,所以要用现在完成时态。可见答案是C) have been challenged。A) are to challenge和D) are challenging 都是主动语态,不可能是答案。B) may be challenged虽然是被动语态,但意思与全句内容不合,所以不对。 C) 表示发生在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常用点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose等。
英语中的十六种时态
英语中的十六种时态 一、一般现在时 1.概念:表示经常发生的情况;有规律出现的情况;总是发生的;和事实真理 2.时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, everyweek (day,year, month…·), once a week(day,year, month…), on Sundays( on M ondays…·), 3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4.否定形式:主语+am/is/are+not+其他;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don’t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn’t,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 6.例句: It seldom snows here.这里很少下雪。He is always ready to help others.他总是乐于帮助别人Action speaks louder than words.事实胜于雄辩 二、一般过去时 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week , last year , night , month . ) , in 1 9 8 9 , just now at the age of 5 , one day , long long ago , once upon a time 3.基本结构:主语+动词的过去式或be的过去式+名词 4.否定形式:主语+was/were+not+其他;在行为动词前加didn’'t,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词。 6.例句: She often came to help us in those days.那些天她经常来帮助我们。i didn' t know you were so busy.我不知道你是这么忙 三、一般将来时 1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。 2时间状语: Tomorrow, next day(week, month,year…·) soon , in a few minutes , by , the day after tomorrow , etc . 3.基本结构:主语+am/is/are+ going to+do+其它;主语+wi1l/ shall+do+其它
英语中的16种时态(全)
动词16个时态 —、一般现在时 1. 概念:表示经常发生的情况;有规律出现的情况;总是发生的;和事实真理。 2. 时间状语:Always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month once a …),week(day, year, month …)onS un days ( on Mon days …), 3. 基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4. 否定形式:主语+ am/is/are + no t + 其他;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't , 如主语为第三人称单数,则用does n't ,同时还原行为动词。 5?—般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 6.例句:It seldom sn ows here. 这里很少下雪。 He is always ready to help others. 他总是乐于帮助别人。 Action speaks louder tha n words. 事实胜于雄辩。 二、一般过去时 1. 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2. 时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week, last(year, night, month ), in 1989,just now, at the age of 5,one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 3. 基本结构:主语+动词的过去式或be的过去式+名词 4. 否定形式:主语+ was/were + not + 其他;在行为动词前加did n't ,同时还原行为动词。 5. 一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 6. 例句:She ofte n came to help us in those days. 那些天她经常来帮助我们。
英语16种时态总结
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。英语时态分为16种: 一. 一般现在时用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。B) 习惯用语。C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sund ays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二. 一般过去时用法: A) 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。 B) 表示过去习惯性动作。特别是由would/ used to do表达的句型,本身表示的就
高中16种英语时态总结归纳
时态 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。) 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法: A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging C) 表示发生在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常用点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose 等。 例:John has broken his left leg.(约翰摔断了左腿。) 注意事项 A) 现在完成时是联系过去和现在的纽带。现在完成时和过去时的区别在于:现在完成时强调动作的动态,或受动态的影响,是动态的结果,对现在有影响;过去时只表示过去的某个具体时间里发生的动作,与现在没有联系。 例:He worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他曾经在那家医院工作了8年。这只是讲述一个过去的事实,他现在已经不在那家医院了。) He has worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他已经在那家医院里工作了8年。表示他从过去开始工作,一直工作到现在,现在仍在那家医院工作。) B) 因为含有for加一段时间或since加一个时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有动态和延续性的特点,所以
英语中的16种时态(全)
动词16个时态 一、一般现在时 1.概念:表示经常发生的情况;有规律出现的情况;总是发生的;和事实真理。 2.时间状语:Always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…),once a week(day, year, month…),on Sundays(on Mondays …), 3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4.否定形式:主语 + am/is/are + no t + 其他;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时, 还原行为动词。 6.例句:It seldom snows here.这里很少下雪。 He is always ready to help others.他总是乐于帮助别人。 Action speaks louder than words.事实胜于雄辩。 二、一般过去时 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week, last(year, night, month…),in 1989,just now, at the age of 5,one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 3.基本结构:主语 + 动词的过去式或be的过去式+名词 4.否定形式:主语 + was/were + not + 其他;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 6.例句:She often came to help us in those days.那些天她经常来帮助我们。 I didn't know you were so busy.我不知道你是这么忙。 三、一般将来时 1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。 2.时间状语:Tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc. 3.基本结构:主语 + am/is/are + going to + do + 其它;主语 + will/shall + do + 其它 4.否定形式:主语 + am/is/are not going to do ;主语 + will/shall not do + 其它 5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。{首字母大写} 6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies. It is going to rain.天要下雨了。 四、一般过去将来时 1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。 2.时间状语:The next day (morning \, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
(完整版)英语16种英语时态解析
英语16种英语时态解析! 英语时态分为16种,如下表所示: 各时态结构及用法 1. 一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are) ①表示现在的情况、状态和特征。 例:He is a student. 他是一个学生。 ②表示经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. 他总是帮助别人。 ③客观事实和普遍真理。 例:The earth moves the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。(常用于列车、客车、飞机或轮船时刻表) 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. 下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。 ⑤主将从现:在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在表示将的来事情。 例:If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home. 如果明天下雨,我们会待在家里。 2. 现在进行时(am/is/are doing) ①表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。 例:He is listning to the music now. 他现在正在听音乐。 ②表示目前一段时间内一直在做的事情,但不一定此时此刻正在做。 例:I am studying computer this term. 这个学期我一直在学习计算机。 ③现在进行时可以表示将来的含义。 瞬时动词的进行一定表将来。 例: I am leaving. 我要离开了。 持续动词的进行只有有将来的时间状语或有将来语境中才表将来。例: I am travelling next month. 下个月我要去旅行。 ④现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
英语中的16种时态详解
全部16种英语动词时态的构成和使用规律 一、英语动词的四时、四态构成其全部时态,共16种。 态时一般态进行态完成态完成进行态过去时过去一般时过去进行时过去完成时过去完成进行时过去将来时过去将来一般时 过去将来进行时过去将来完成时过去将来完成进行时现在时现在一般时现在进行时现在完成时现在完成进行时将来时将来一般时 将来进行时 将来完成时将来完成进行时 二、英语四时的构成方式。 四时构成方式 过去时动词的过去式,助动词用do,have,be 的过去式did,had,were,was 等 过去将来时用助动词would (will 的过去式) 现在时用动词原形(第三人称单数加s),助动词用be (am,are,is),have (have,has)将来时用助动词will (第一人称常用shall) 三、英语四态的构成方式。 四、16种英语动词时态肯定式的构成。 综合英语四时、四态的构成方式,我们很容易使用三个基本时态助动词will(将来时)、be(进行态)、have(完成态)构成英语所有16种时态(注意:人称和数的变化永远在第一个动词): 五、16种英语动词时态否定式的构成。 除了过去一般时和现在一般时的否定式使用助动词do 的否定式构成外,其余的均只须在肯 四态构成方式 一般态现在时用动词原形(第三人称单数加s),其他时用相应的助动词进行态用助动词be +现在分词完成态用助动词用have +过去分词 完成进行态 用助动词have been +现在分词(be 的完成态+现在分词)16种时态构成方式(以动词make 为例) 过去一般时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)made 过去进行时I (He,She,It)was making,We (You,They)were making 过去完成时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)had made 过去完成进行时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)had been making 过去将来一般时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)would make 过去将来进行时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)would be making 过去将来完成时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)would have made 过去将来完成进行时 I (We,You,They,He,She,It)would have been making 现在一般时I (We,You,They)make ,He (She,It)makes 现在进行时I am making,We (You,They)are making,He (She,It)is making 现在完成时I (We,You,They)have made,He (She,It)has made 现在完成进行时I (We,You,They)have been making,He (She,It)has been making 将来一般时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)will make 将来进行时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)will be making 将来完成时I (We,You,They,He,She,It)will have made 将来完成进行时 I (We,You,They,He,She,It)will have been making
英语中的十六种时态
英语中的十六种时态 一般时态进行时态完成时态完成进行时态 现在do/does am/is/are doing have/has done have/has been doing 过去did was/were doing had done had been doing 将来shall/will do shall/will be doing shall/will have done shall/will have been doing 过去将来should/would do should/would be doing should/would have done should/would have been doing 一、一般现在时 1.概念:表示经常发生的情况;有规律出现的情况;总是发生的;和事实真理 2.时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, everyweek (day,year, month…·), once a week(day,year, month…), on Sundays( on M ondays…·), 3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4.否定形式:主语+am/is/are+not+其他;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don’t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn’t,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 6.例句: It seldom snows here.这里很少下雪。He is always ready to help others.他总是乐于帮助别人Action speaks louder than words.事实胜于雄辩 二、一般过去时 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week , last year , night , month . ) , in 1 9 8 9 , just now at the age of 5 , one day , long long ago , once upon a time 3.基本结构:主语+动词的过去式或be的过去式+名词 4.否定形式:主语+was/were+not+其他;在行为动词前加didn’'t,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词。 6.例句: She often came to help us in those days.那些天她经常来帮助我们。i didn' t know you were so busy.我不知道你是这么忙 三、一般将来时 1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
16种英语时态总结归纳
16种英语时态总结归纳 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 英语必考八大时态基本结构 一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时现在进行时 过去将来时过去进行时过去完成时现在完成时 1.一般现在时:一般现在时表示经常发生或习惯性的动作或状态及客观现实和普遍真理。 用法: A 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。B习惯用语C经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours. 等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。 注意:一般现在时通常与always , often , usually , every day , sometimes , once a week 等时间状语连用。 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法: A表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A didn't sell B sold C haven't sold D would sell 答案是C B表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for 加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A are to challenge C have been challenged B may be challenged D are challenging 全句的意思是:“虽然牛顿是个伟大的人物,但他的许多见解直到今天还在受到挑战,并且被现代科学家的工作所修正。”challenge是及物动词,在本句中应当是被动语态;其动作延续到今天,所以要用现在完成时态。可见答案是C) have been challenged。A) are to challenge和D) are challenging都是主动语态,不可能是答案。B) may be challenged虽然是被动语态,但意思与全句内容不合,所以不对。
英语的十六种时态汇总
英语的十六种时态汇总 Prepared on 22 November 2020
英语中的各种时态及用法包括要注意的,标志词等等 英语的时态是一种动词形式,不同的时态用以表示不同的时间与方式. 是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式.因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式. 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四 者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时 下面就英语中常见的八种基本时态进行阐述,其它的时态都是在这八种时态的基础上结合而成的. 一、一般现在时:? 1.概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况.? 2.时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays,? 3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4.否定形式:am/is/are+not; 此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词.? 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词.? 6.例句:. It seldom snows here.? He is always ready to help others.? Action speaks louder than words. 二、一般过去时:? 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为.? 2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week,last(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.? 3.基本结构:be动词;行为动词的过去式 4.否定形式:was/were+not; 在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词.? 5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词.? 6.例句:She often came to help us in those days.? I didn't know you were so busy. 三、现在进行时:? 1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为.? 2.时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.? 3.基本结构:am/is/are+doing? 4.否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing.? 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首. 6.例句: How are you feeling today? He is doing well in his lessons. 四、过去进行时:? 1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作.?
英语16种时态超经典整理
英语的16种时态 1.一般现在时the present tense 2.一般过去时the past tense 3.一般将来时the future tense 4.一般过去将来时the past future tense 5.现在进行时the present continuous tense 6.过去进行时the past Continuous Tense 7.将来进行时the future continuous tense 8.过去将来进行时the past future continuous tense 9.现在完成时the Present Perfect Tense 10.过去完成时the Past Perfect Tense 11.将来完成时the future perfect tense 12.过去将来完成时the past future perfect tense 13.现在完成进行时the present perfect continuous tense 14.过去完成进行时the past perfect continuous tense 15.将来完成进行时the future perfect continuous tense 16.过去将来完成进行时the past future perfect continuous tense
一、一般时态 1、一般现在时 (1)一般现在时表示没有时限的持久存在的动作或状态或现阶段反复发生的动作或状态,常和副词usually,often,always sometimes,regularly,near,occasionally,every year, every week 等连用。例如:1)The moon moves round the earth.. 2)Mr. Smith travels to work by bus every day. (2)在由after,until,before,once,when,even if,in case,as long as,as soon as,the moment 以及if,unless 等引导的时间状语从句或条件状语从句中,通常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如: 1)I will tell him the news as soon as I see him. 2)I will not go to countryside if it rains tomorrow. (3)某些表示起始的动词,可用一般现在时表示按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,这类动词有:be,go,come,start,depart,arrive,begin,leave 等。例如: 1)The plane leaves at three sharp. 2)The new teachers arrive tomorrow. (4)在由why,what,where,whoever,who,that,as 等引导的从句中,也常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如: 1)Free tickets will be given to whoever comes first. 2)You’ll probably be in the same train as I am tomorrow. 2.一般过去时 (1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。例如: We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film.
英语的16种时态
英语的16种时态 英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例) 一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时 现在 study be studying have studied have been studying 过去 studied be studying had studied had been studying 将来 will study wil be studying will have studied will have been studying 过去将来would study would be studying would have studied would have been studying 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. 一般现在时 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持 主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动 、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用 。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.(下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)
英语的16种时态归纳
英语共有十六种时态 其表现形式如下(以study为例) 一般时进行时完成时完成进行时 现在 study be studying have studied have been studying 过去 studied be studying had studied had been studying 将来 will study wil be studying will have studied will have been studying 过去将来would study would be studying would have studied would have been studying 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. 一般现在时 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 1)一般现在时 基本形式(以do为例):第三人称单数:does(主语为非第三人称单数); 肯定句:主语+动词原形+其他; He works for us. 否定句:主语+don't/doesn't+动词原形+其他; He doesn't work for us. 一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他。 肯定回答:Yes,(+主语+do/does). 否定回答:No,(+主语+don't/doesn't.) 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句语 Does he work for us? Yes, he does. No, he doesn't
