(完整word版)初中英语被动语态(精讲+精练)
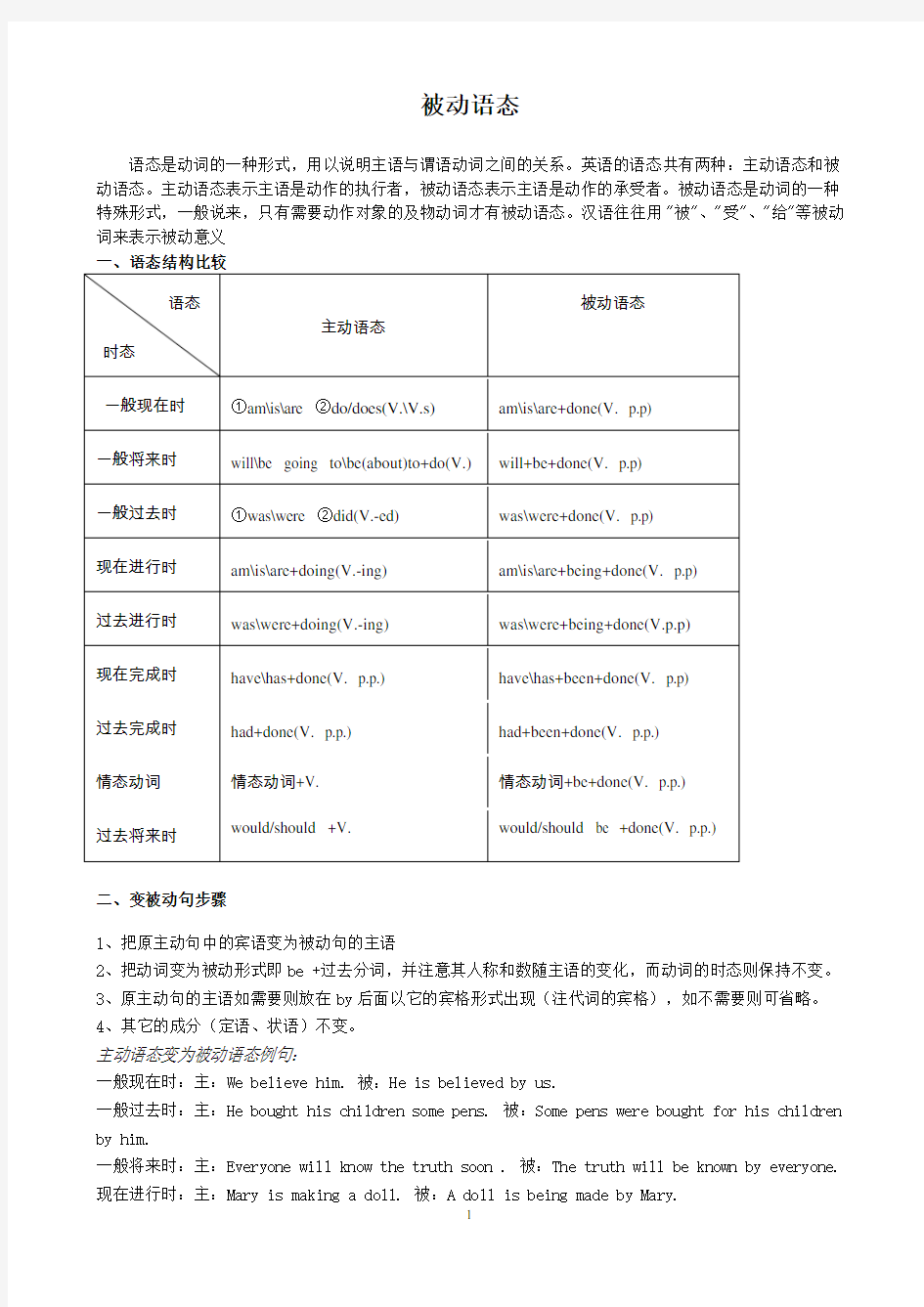

被动语态
二、变被动句步骤
1、把原主动句中的宾语变为被动句的主语
2、把动词变为被动形式即be +过去分词,并注意其人称和数随主语的变化,而动词的时态则保持不变。
3、原主动句的主语如需要则放在by后面以它的宾格形式出现(注代词的宾格),如不需要则可省略。
4、其它的成分(定语、状语)不变。
主动语态变为被动语态例句:
一般现在时:主:We believe him. 被:He is believed by us.
一般过去时:主:He bought his children some pens. 被:Some pens were bought for his children by him.
一般将来时:主:Everyone will know the truth soon . 被:The truth will be known by everyone. 现在进行时:主:Mary is making a doll. 被:A doll is being made by Mary.
过去进行时:主:They were carrying the hurt player. 被:The hurt player was being carried by them .
现在完成时:主:He has received the letter. 被:The letter has been received by him.
过去完成时:主:They had built ten bridges. 被:Ten bridges had been built by them.
三、一般用法
1.一般现在时的被动语态构成:is / am / are +及物动词的过去分词
Our classroom is cleaned everyday.
I am asked to study hard by my mother.
Knives are used for cutting things.
2.一般过去时的被动语态构成:was / were + 及物动词的过去分词
The new shop was built last year.
Dinosaur eggs were laid long long ago.
3.现在完成时的被动语态构成:has / have + been +及物动词的过去分词
This book has been translated into many languages.
Many man-made satellites have been sent up into space by many countries.
4.一般将来时的被动语态构成:will+ be + 及物动词的过去分词
A new hospital will be built in our city.
Many more trees will be planted next year.
5.含有情态动词的被动语态构成:情态动词+ be + 及物动词的过去分词
Young trees must be watered often.
Your mistakes should be corrected right now.
The door may be locked inside.
Your homework can be handed in tomorrow.
6.现在进行时的被动语态构成:am / is / are + being +及物动词的过去分词
Uncl e Wang is mending my bike now.→
My bike is being repaired by Tom now.
They are planting trees over there. →
Trees are being planted over there by them.
7.不定式的被动语态:to + be + 及物动词的过去分词
There are two books to be read. →
There are twenty more trees to be planted.
四、特殊用法
1.不及物动词无被动语态。如:happen, break down, come out......
What will happen in 100 years.
The dinosaurs disappeared about 65 million years ago.
2.有些动词用主动形式表示被动意义。如: write, sell, ride.....
This pen writes well.
This new book sells well.
3.感官动词或使役动词使用省略to的动词不定式,主动语态中不带“to”,但变为被动语态时,须加上“to”。
例:make somebody do something→somebody+ be +made to do something
see somebody do something→somebody +be +seen to do something
A girl saw my wallet drop when she passed by.→My wallet was seen to drop by a girl when she passed by.
The boss made the little boy do heavy work.→The little boy was made to do heavy work by the boss.
4.如果是接双宾语的动词改为被动语态时,直接宾语(物)作主语,那么动词后要用介词,这个介词是由与其搭配的动词决定。
He gave me a book.→A book was given to me by him.
He showed me a ti cket.→A ticket was shown to me by him.
My father bought me a new bike. →A new bike was bought for me by my father.
5.一些动词短语用于被动语态时,动词短语应看作一个整体而不能丢掉其中的介词或副词。
We can’t laugh at him. →He can’t be laughed at by us.
He listens to the radio every day. →The radio is listened to by him every day.
The nurse is taking care of the sick man. →The sick man is being taken care of by the nurs e.
五、带双宾语
在用于被动结构时,有些动词可以带双宾语。在这种情况下,主动结构中的间接宾语变为主语时,直接宾语仍然保留在谓语后面;直接宾语变为主语时,间接宾语前通常加上介词for/to, etc.。
即:S+V+IO+DO→IO+ be done +DO→DO+ be done + prep. +IO
1.g. 1) My uncle gave me a gift on my birthday.
→I was given a gift on my birthday.
→A gift was given to me on my birthday.
1.We often hear him play guitar.
→He is often heard to play guitar.
→It is often heard from him to play guitar.
六、新兴形式
Get+过去分词也可以构成被动语态,用这种结构的句子侧重于动作的结果而不是动作本身。如: The man got hurt on his way home. 那个男人在回家的路上受伤了。 How did the glass get broken? 杯子怎么破了?
Get+过去分词的被动语态是一种新兴的被动语态形式;相对来说它的使用还没有Be+过去分词构成的被动语态那么广泛,一般限于口语和非正式书面语;但它却有着用得愈来愈多的趋势,是一种生气蓬勃的语言现象。
七、特别提醒
有些动词后跟不带to的不定式作宾语补足语,但改为被动结构后要加上“to”。
We heard him sing in his room just now.
---He was heard to sing in his room just now.
need doing something也表示被动
被动语态专项练习
一、将下列句子变为被动语态。
1.He often helps his brother.
2.People all over the world know the Great Wall.
3.They founded that hospital in 1996.
4.He was doing his homework at this time yesterday.
5.He asked me to work on the farm with him.
6.My father is mending my bike.
7.The writer has written many stories for that magazine.
8.We’re going to hold a meeting this afternoon.
9. His mother had told him not to waste time on fishing.
10. They should do it at once.
二、单选
( ) 1 The People's Republic of China ___ on October 1, 1949.
A. found
B. was founded
C. is founded
D. was found
( ) 2 English ____ in Canada.
A. speaks
B. are spoken
C. is speaking
D. is spoken
( )3 This English song___ by the girls after class.
A. often sings
B. often sang
C. is often sang
D. is often sung
( ) 4 This kind of car ___ in Japan.
A, makes B. made C. is making D. is made
( ) 5 New computers ___ all over the world.
A. is used
B. are using
C. are used
D. have used
( ) 6 Our room must ___ clean.
A. keep
B. be kept
C. to be kept
D. to keep
( ) 7 -I'd like to buy that coat.
-I'm sorry. ___. A. it sold B. it's selling C. It's been sold D. it
had been sold
()8A new house ___ at the corner of the road.
A. is building
B. is being built
C. been built
D. be building
( ) 9 The key ___ on the table when I leave.
A. was left
B. will be left
C. is left
D. has been left
( ) 10 Doctors ___ in every part of the world.
A. need
B. are needing
C. are needed
D. will need
( )11 His new book___ next month.
A.will be published
B. is publishing
C. is being published
D. has been published
( ) 12 Japanese ___ in every country.
A. is not spoken
B. are spoken
C. is speaking
D. is not speaking
() 13 These papers___yet.
A.have not written
B. have not been written
C. has not written
D. has not been written
( ) 14 The sports meet ___ be held until next week.
A. didn't
B. won't
C. isn't
D. doesn't
( ) 15 -My shoes are worn out.
A. Can't they be mended?
B. Let me have a look at it.
C. How much do they cost?
D. Can't they mended?
() 16 ___ the watch been repaired yet? I badly need it.
A. Does
B. Has
C. Is
D. Are
() 17___ these desks be needed?A. Will B. Are C. Has D. Do
() 18 Why ___ to talk about it yesterday?
A. didn't a meeting hold
B. wasn't a meeting held
C. wasn't held a meeting
D. a meeting wasn't held
() 19 Who was the book___?
A. write
B. wrote
C. written
D. written by
() 20 Where ___ these boxes
A. was
B. were
C. is
D. am
()21 The flowers___often.
A. must be water
B. must be watered
C. must watered
D. must water
() 22 The books may___ for two weeks.
A. be kept
B. be borrowed
C. keep
D. borrow
() 23 The broken bike____ here by Mr Smith.
A. can mend
B. can mended
C. can be mend
D. can be mended
() 24 The old bridge in my hometown___ next month.
A.is going to be rebuilt
B. will rebuilt
C. are going to be rebuilt
D. are going to rebuilt
( ) 25 The play ___ at the theatre next Sunday.
A. is going to be shown
B. will shown
C. will show
D. is shown
() 26 The old stone bridge ___ next week.
A.is going to be rebuilt
B. will be rebuild
C. are going to be rebuilt
D. will rebuild
( )27Now these magazines___ in the library for a long time.
A. have kept
B. are keeping
C. have been keeping
D. have been kept
( ) 28The pot ___ for ___ hot water.
https://www.360docs.net/doc/d316459288.html,ed; keeping
B. was used; keeping
C. is used; to keep
D. are used; keep
( )29Tea ___ in the south of China.
A. grows
B. is grown
C. were grown
D. will grow
( ) 30 The bridges___ two years ago.
A. is built
B. built
C. were built
D. was built
Key:
1---5 BDDDC6—10 BCBBC11---15AABBA16--20BABDB21---25BADAA 26---30ADBBC
人教版初中英语初中英语语法之一名词(通用版)
初中英语语法之一名词 名词可以分为专有名词(Proper Nouns)和普通名词 (Common Nouns),专有名词是某个(些)人,地方,机构等专有的名称,如Beijing,China等。普通名词是一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词,如:book,sadness 等。普通名词又可分为下面四类: 1)个体名词(Individual Nouns):表示某类人或东西中的个体,如:gun。 2)集体名词(Collective Nouns):表示若干个个体组成的集合体,如:family。 3)物质名词(Material Nouns):表示无法分为个体的实物,如:air。 4)抽象名词(Abstract Nouns):表示动作、状态、品质、感情等抽象概念,如:work。 个体名词和集体名词可以用数目来计算,称为可数名词(mCountable Nouns),物质名词和抽象名词一般无法用数目计算,称为不可数名词(Uncountable Nouns)。归纳一下,名词的分类可以下图表示:||专有名词 || | 名| | 个体名词 | | || || 可数名词| || | 集体名词 || ||普通名词 || | | 词 | | 物质名词 | | || || 不可数名词| || | 抽象名词 || 1.1 名词复数的规则变化 ___________________________________________________ 情况构成方法读音例词 _________________________________________________ _ 一般情况加 -s 1.清辅音后读/s/;map-maps 2.浊辅音和元音后读 /z/;bag-bags car-cars __________________________________________________ _ 以s,sh,ch, x等结尾的词加 -es读 /iz/bus-buses watch-watches ______________________________________________ __ __ 以ce,se,ze, (d)ge等结尾的词加 -s读 /iz/license-licenses __________________________________________________ _ 以辅音字母+y变y 为i 结尾的词再加es读 /z/baby---babies 1.2 其它名词复数的规则变化 1) 以y结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y 结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数: 如:two Marys the Henrys monkey---monkeys holiday---holidays 比较:层楼:storey ---storeys story---stories 2) 以o 结尾的名词,变复数时: a. 加s,如: photo---photos piano---pianos radio---radios zoo---zoos; b. 加es,如:potato--potatoes tomato--tomatoes c. 均可,如:zero---zeros / zeroes 3) 以f或fe 结尾的名词变复数时: a. 加s,如: belief---beliefs roof---roofs safe---safes gulf---gulfs; b. 去f,fe 加ves,如:half---halves knife---knives leaf---leaves wolf---wolves wife---wives life---lives thief---thieves; c. 均可,如:handkerchief: handkerchiefs / handkerchieves
初中英语被动语态讲解与练习
初中被动语态语法讲解 (一) 语态分类 英语动词有两种语态,主动语态和被动语态。主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者。如: They will build a new bridge over the river. (主动) A new bridge will be built over the river. (被动) 汉语中常用“被”、“给”、“由”、“受”等词用来表示被动,而英语用: 助动词be + 及物动词的过去分词构成。 (二) 被动语态的时态、人称和数的变化 主要体现在be的变化上,其形式与系动词be的变化形式完全一样。不同时态的被动语态,列表如下:一般现在时:am / is / are + done 一般过去时:was / were + done 一般将来时:shall / will + be done 一般过去将来时:should / would + be done 现在进行时:am / is / are + being + done 过去进行时:was / were + being + done 现在完成时:have / has + been + done 过去完成时:had + been + done 将来完成时:shall / will + have been + done 过去将来完成时:should / would + have been + done [注]被动语态没有将来进行时和过去将来进行时。 (三)常见的八种时态中的被动语态 1. 一般现在时: (1)People grow rice in the south of the country. Rice is grown in the south of the country. (2)The school doesn't allow us to enter the chemistry lab without a teacher. We are not allowed to enter the chemistry lab without a teacher. 2. 一般过去时: (1)They agreed on the building of a new car factory last month. The building of a new car factory was agreed on last month. (2)The students didn't forget his lessons easily. His lessons were not easily forgotten 3. 一般将来时: (1)They will send cars abroad by sea. Cars will be sent abroad by sea. (2)They will give plenty of jobs to school-leavers. Plenty of jobs will be given to school-leavers. 4. 过去将来时: (1)The manager said they would complete the project by the end of the year. The manager said the project would be completed by the end of the year. (2) The workers told me they would mend the car as soon as possible. The workers told me that the car would be mended as soon as possible. 5. 现在进行时:
2020年初中英语被动语态深度讲解、练习及答案
2020年初中英语被动语态深度讲解、练习及 答案 the bridge、 The bridge was built by them、 (一)被动语态的构成被动语态由“助动词be+及物动词的过去分词”构成。人称、数和时态的变化是通过be的变化表现出来的。现以teach为例说明被动语态在各种时态中的构成。 1一般现在时:am/is/are+taught She often watersthe flowers、The flowers are often watered by her’English is spoken by lots of people in the world2一般过去时:was/were+taught Was/were doneWe visited a form yesterday、A form was visited yesterday by us、the cup was broken by the boy、He was saved at last、My bike was stolen,Some new computers were stolen last night、This book was published in198 1、这本书出版于1981年3一般将来时:will/shall be+taught Am/ is /are going to be doneShe will plant some trees this week、some trees will be planted this week、our class is going to hold a party this morning、A party is going to be held this evening by our classA new road will be built next year4现在进行时:am/is/are being+
初中英语语法精讲全(教师版)
初中英语语法 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before . 10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足 语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如: I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名 词、代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间 接宾语。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他 给我写了一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接 宾语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信)
初中英语语法精讲精练
David
一名词的分类: 1.名词可以分为专有名词和普通名词,专有名词是某个(些)人,地方,机构等专有的名称,如Beijing,China等。普通名词是一类人或东西或是一个抽象概念的名词,如:book,sadness等。普通名词又可分为下面四类:1)个体名词:表示某类人或东西中的个体,如:gun。 2)集体名词:表示若干个个体组成的集合体,如:family。 3)物质名词:表示无法分为个体的实物,如:air。 4)抽象名词:表示动作、状态、品质、感情等抽象概念,如:work。 二,名词变复数: 2 名词复数的不规则变化1)child---children foot---feet tooth---teeth mouse---mice man---men woman---women 注意:由一个词加man 或woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是-men 和-women,如an Englishman,two Englishmen。但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans;Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。 2)单复同形,如deer,sheep,fish,Chinese,Japanese ,li,jin,yuan,two li,three mu,four jin等。但除人民币的元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:a dollar, two dollars; a meter, two meters。 3)集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。例如: people police cattle 等本身就是复数,不能说a people,a police,a cattle,但可以说a person,a policeman,a head of cattle, the English,the British,the French,the Chinese,the Japanese,the Swiss 等名词,表示国民总称时,作复数用,如The Chinese are industries and brave.中国人民是勤劳勇敢的。 4)以s结尾,仍为单数的名词,如: a. maths,politics,physics等学科名词,一般是不可数名词,为单数。 b. news 为不可数名词。 c. the United States,the United Nations 应视为单数。 The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。 d. 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。例如: "The Arabian Nights" is a very interesting story-book. 《一千零一夜》是一本非常有趣的故事书。 5)表示由两部分构成的东西,如:glasses (眼镜)trousers,clothes等,若表达具体数目,要借助数量词pair(对,双);suit(套); a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers等。 6)另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods货物,waters水域,fishes(各种)鱼。 物质名词和抽象名词可以借助单位词表一定的数量,如a glass of water 一杯水/ a piece of advice一则建议。 5. 定语名词的复数 名词作定语一般用单数,但也有以下例外。 1) 用复数作定语。例如: sports meeting 运动会students reading-room 学生阅览室talks table 谈判桌the foreign languages department 外语系2)man, woman, gentleman等作定语时,其单复数以所修饰的名词的单复数而定。 例如:men workers women teachers gentlemen officials 3)有些原有s结尾的名词,作定语时,s保留。例如: goods train (货车)arms produce武器生产customs papers 海关文件clothes brush 衣刷4)数词+名词作定语时,这个名词一般保留单数形式。例如: two-dozen eggs两打鸡蛋 a ten-mile walk 十英里路two-hundred trees 两百棵树 a five-year plan.一个五年计划
初中英语被动语态精讲
动词语态 英语的语态是通过动词的形式表现出来的,用来表明主语与谓语动词之间的关系,英语的动词有两种语态形式,即主动语态和被动语态。 如果主语是动作的执行者,谓语动词用主动语态。如果主语是动作的对象,谓语动词用被动语态。如: They speak English.他们讲英语。 主语“他们”是“讲”这一行为的执行者,是主动句,动词用主动语态来表示; English is spoken by them.英语由他们讲。 主语“英语”是“讲”的承受者,是被动句,动词用被动语态的形式。 He opened the door.他打开了这扇门。(主动语态) The door was opened.这扇门被打开了。(被动语态) 一、被动语态的构成 1、助动词be+(及物动词的)过去分词构成动词的被动语态的形式。助动词be有人称、数和 时态的变化,其变化规则与be作为系动词的变化完全一样。 二、主动语态变被动语态 1、主动语态变为被动语态的步骤: (1)将主动句的宾语变为主语: 注意:如果主动句的宾语是代词,需将其由宾格变为主格。如: Tom killed him. →He was killed by Tom. 主动结构的主语变为介词by的宾语,组成介词短语,放在被动结构中谓语动词之后。在动作的执行者无须说明或不必要强调时,by短语可以省略。主动语态、被动语态两种时态要保持一致。 (2)将动词改为"be+过去分词"。 They held a meeting yesterday. →A meeting was held by them yesterday. 他们昨天开会了。 (3)将主动语态的主语改为be…放在谓语动词后。 注意:如果原主语是代词,则应由主格变为宾格。 He sang a song. →A song was sung by him. 2、主动语态变为被动语态的注意事项: 含有双宾语,即直接宾语(常指事物)和间接宾语(常指人)的句子,每个宾语都可变为被动语态的主语,即其被动语态有两种形式。但多以间接宾语作主语。 Jack told us the truth.杰克告诉了我们真相。 We were told the truth by Jack. The truth was told (to) us by Jack. 三、各种时态的被动语态 1、一般现在时:am/is/are +过去分词 We are taught English by her.由她教我们英语。 2、一般过去时:was/were+过去分词 A present was given to me by Mary.玛丽给了我一件礼物。 3、一般将来时:will be+过去分词 The desk will be mended by him.这张桌子将由他修理。 4、现在进行时:am/is/are +being + 过去分词 The walls are being painted now.正在粉刷墙壁。 5、过去进行时:was/were +being + 过去分词
初中英语语法精讲动词不定式用法(教案)
动词不定式用法 动词不定式没有人称和数的变化,在句中不能独立作谓语。但动词不定式具有名词、形容词和副词特征,在句中可以作主语、宾语、宾语补足语、定语、表语和状语等多种成分。另外,动词不定式具有动词特点,可以有自己的宾语和状语,组成动词不定式短语。动词不定式的肯定形式是to+do;其否定形式是not to+do。 下面以动词不定式在句中的作用来予以详细说明。 1.作主语 可以直接作主语。如:To see is to believe. 但在英语中,常用it作形式主语,真正的主语即动词不定式放在后面。如: It's wrong to play tricks on other people. It's our duty to keep our environment clean and tidy. 点击规律:动词不定式在句中作主语时,常放在It is +adj +(for sb.)+(not)to do sth句型中,表示说话人对客观事件的决断,意为:做…..是……的,it仅作形式主语,真正的主语是to do sth It is very interesting to read.读书是有趣的 It is useful to read.看书是有用的 It is healthy to run every day.每天跑步是健康的 It is a little difficulty for me to work out this question.解出这道题对我来说有点难 It is bad not to finish homework.不完成作业是糟糕的 It is bad to be late for school.迟到是糟糕的 It is+adj+of sb +(not)to do sth该句型通常表示说话人对客观事件的惊讶、兴奋、懊悔、难过等感叹情绪,与It is +adj +(for sb.)+(not)to do sth的意义不同。 It is very kind of you to tell me the truth.你能告诉我事实,真是太好了 It is stupid of him to do such a silly thing.他做那件傻事,真是太笨了 It is very clever of you to work out this question. 你能解出这道题目,真是太聪明了 It is very wise of you to read this novel. 你看这本小说,真是太明智了 这个句型中用介词of而不是for的原因是这里的形容词是用来形容人的品质性格的。 类似的词有:careless,careful,clever,considerate,foolish,good,impolite,kind,naughty,nice,silly,stupid,friendly 因此区分是用It is +adj +(for sb.)+(not)to do sth还是It is+adj+of sb +(not)to do sth,要
1初中英语名词用法精讲精练公开课
初中英语名词用法精讲精练 A.名词的意义 从英语语法角度来讲,表示人物、时间、地点、事物或抽象概念的词,我们通常称为名词。例如:teacher,desk,Japanese,milk,physics等。B.名词的种类 总的来说,英语中的名词可以分为专有名词和普通名词两类。 A.专有名词:表示人、地方、组织、事物、机构、等专有名称的名词。专有名词的第一个字母要大写。例如:Lucy,Shanghai,the Communist Party of China,the United States等。 B.普通名词:表示某一类人或事物或表示一个抽象概念的名称的名词。例如:worker,boy,machine等。普通名词又可分为以下四类: 1.个体名词:表示个体的人或事物的名词。例如:man ,pencil,chair,cat 等。 2.集体名词:表示一群人或一些事物的总称的名词。例如:class,police,family, furniture, team等。 3.物质名词:表示无法分为个体的物质或材料的名词。例如:rice,glass,grass, water,porridge等。 4.抽象名词:表示状态、品质、动作、情感等抽象概念的名词。例如:life,love, safety,happiness等。 C.名词的数 名词的数是数量概念的语法表现,具体说来,是指名词的单数和复数两种形式,名词按其所表示的事物的性质可分为可数名词和不可数名词两种。个体名词和大多数集体名词一般是可数名词;物质名词和抽象名词是不可数名词,表示可以计数的事物的名词叫可数名词,一般有单数和复数两种形式;表示不可以计数的事物的名词叫不可数名词,一般不分单数和复数,初中阶段学过的不可数名词有:news,paper,milk,orange(桔子汁),bread,chalk (粉笔),truth(事实),water,rice(米),work,housework,homework,luck,ink,meat,money ,sugar,grass,ice等等。不可数名词 一般没有复数形式,不可以个数计算,要表示这类名词的个体性质应用单位词。 1.例如:a piece of bread/cake/chalk/ice/meat/music/news /paper/work/sugar; a bit of bread/grass/news/trouble/wood ; a bottle of ink/milk/orange juice; a glass of beer/milk,a cup of tea等。 D. 名词的复数 可数名词由单数变为复数形式,其构成方法分为规则和不规则两种。 A)规则变化: (1)一般情况下,在词尾加-s,例如:boy-boys ,car- cars,book- books, train-trains,girl- girls. (2)以s,x, ch, sh结尾的单词,在词尾加-es,例如: bus-buses,box-boxes,watch-watches,wish-wishes. (3)以辅音字母加y结尾的单词,把y变成i再加-es,例 如:country-countries,factory-factories. (4)以元音字母加y结尾的单词,直接在词尾加-s,例如: day-days ,boy-boys.
初中英语语法时态精讲版
初中英语语法时态精讲版 Prepared on 24 November 2020
初中英语动词时态精讲 一般现在时 一、动词的第三人称词尾变化: 当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词需加-s或-es: 注意:动词have的第三人称单数是has. 二. 一般现在时的用法 1)表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的副词连用。常用的频度副词有: always、often、 usually、seldom、never。频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer.他夏天经常游泳。 I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 2)表示现在的状态。 例如:My father is at is very busy. 我父亲在工作,他很忙。 The boy is twelve. 这男孩十二岁。 3)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football .我全家人都喜欢足球。My sister is always ready to help others . 我妹妹总是乐于助人。 Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不 错,讲的可不行。
4)表示客观真理,客观存在,自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。 Shanghai lies in the east of China. 上海位于中国东部。 5)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。 He comes back tonight. 他今晚回来。 6)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。 例如: I'll tell him the news when he comes back. 他回来时,我将告诉他这个消息。 If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 如果你接受这份工作,他们将和你谈谈细节。 一般过去时 1)表示过去某个时间所发生的动作或存在的状态。常和表示过去的时间状语yesterday, last week, an hour ago,just now, the other day, in 1982等连用。在一般过去式中,要表达“过多少时间之后”,一般用after。几年后。例如:Where did you go just now 刚才你上哪儿去了
初中英语被动语态练习题
被动语态 1. The PRC (found) in 1949. 2. Edison’s mother (save) after the operation. 3. I (tell) the good news yesterday. I was pleased to hear that. 4. Dr. Bethune went on with the operation though he (ask) to leave. 5. Very little (know) about the universe thousands of years ago. 6. —Where is Peter? —He (tell) to meet some foreign friends just now. 7. He (live) in this house since it (build). 8. Trees must (put) in the hole so that it is straight. 9. Old people must (speak) to politely. 10. Let’s (go) home if your homework (do). 11. Miss Zhao usually (ask) us some questions in class but yesterday she (ask) a lot of questions by us. 12. Tom (catch) a bad cold. He (must take) good care of. 13. —Look! I (buy) a new dictionary. —When it (buy)? —The day before yesterday. 14. I can’t mend the machine. Uncle Wang should (send) for at once. 15. He showed me the kite as soon as it (make). 16. —this kind of flower (water) every day? —Certainly. It (need) much more water than the others. 17. —Which does Li Lei prefer, the long jump or the high jump? —Of course, the high jump. He (know) to be good at it. 18. Sometimes Tom (take) to school by bike, but now he (walk) to school by himself every morning. 19. No more bread (need) because my mother (buy) so much of it. 20. Stamps can (use) to send and receive letters. 21. My bike (not work) now. It must (mend). I (use) it tomorrow. 22. Your shoes (wear) out. But they can (mend) here. 被动语态专项练习 将下列句子变成被动语态(A) 1.They produce silk in Suzhou. _____________________________. 2. We take good care of our textbooks. ____________________________. 3. Many young people don’t speak Russian. ______________________________. 4. Do you often make lanterns for the traditional Lantern Festival in China?______________. 5. His mother gave him a present for his birthday.________________________________. 6. They didn’t choose me this term. _____________________________________. 7. I often hear him sing in his room. __________________________________. 8. The story made us laugh. ____________________________________. 9. We are going to build a school in the small village. ____________________________. 10. When will you held the match? _______________________________. 11. We should plant many trees on the mountains. ________________________________. 12. His mother told him not to waste time on fishing. _________________________________. 13. Father gave me a toy at Christmas. ______________________________________.
初中英语语法-----主谓一致---(附练习题和答案)
初中英语语法-----主谓一致---(附练习题和答案)
初中英语语法精讲精练:主谓一致 主谓一致是指谓语动词与主语在人称和数上保持一致。表现在三个方面:语法 一致;意义一致;就近一致(就近原则)。 一、语法一致(意义一致):主语复数---- 谓语复数;主语单数----- 谓语单数 1、主语复数的情况---- 谓复 ⑴people, police, staff, crowd, sheep, cattle等集体名词作主语,谓语动词用复数形式。 The police are waiting for the boy. The staff are dressed as clowns. ⑵由both…and…连接两个单数名词作主语时,谓语动词用复数形式; Both his father and his mother are both teachers. 他的爸爸和妈妈都是 老师。 ⑶“定冠词+姓氏复数形式”表示一家人时,谓语一般用复数。 The Smiths are having dinner. ⑷the +a. 表一类人,做主语,谓语用复数;但表示抽象概念时,用单数形式: The poor aren’t always very sad, while the rich aren’t always happy. The beautiful lives forever. 美是永存的。 2、主语单数的情况----- 谓单 ⑴单数名词(代词),不可数名词作主语时,谓语用单数形式: Some water is in the bottle. The boy is playing football on the playground. ⑵many a+单数名词作主语,意义虽为“许多”,但谓语要用单数形式: Many a student has been to Shanghai.
初中英语被动语态的教案
被动语态 授课人:授课时间: 一、语态概述 英语中有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。 主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者。巧记为:主动、主动、主去动。 例如:Many people speak English. 谓语:speak的动作是由主语many people来执行的。 被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者,即行为动作的对象。巧记为:被动、被动、主被动。例如:English is spoken by many people.主语English是动词speak的承受者。 He opened the door.他开了门。(主动句) The door was opened.门被开了。(被动句) 判断:你来判断哪个是主动哪个是被动? We call the doctor. People don’t play football here. The truck was cleaned yesterday. Mr Chen teaches us English. The classroom was cleaned. 二、被动语态的构成:be+动词的过去分词+by sb(be+done) 一般现在时:am/is/are+taught 一般过去时:was/were+taught 一般将来时:will/shall be+taught 现在进行时:am/is/are being+taught 过去进行时:have/has been+taught 现在完成时:have/has been+taught 含有情态动词的被动语态:can/may/must/should... +be done
歌诀是:被动语态be字变,过去分词跟后面。 三、主动变被动的方法 口诀:主变宾,宾变主,By 句尾跟 Be 字变,Vpp跟后面 一、选择题(2×15=30分) 一、选择题(2×15=30分) ( )1._____ a new library _____ in our school last year? A. Is; built B. Was; built C. Does; build D. Did ; build ( )2. An accident ____ on this road last week. A. has been happened B. was happened C. is happened D. happened ( )3.Cotton(棉花)____ in the southeast of China. A. is grown B. are grown C. grows D. grow ( )4.So far, the moon ____ by man already.A. is visited B. will be visited C. has been visited D. was visited ( )5.A talk on Chinese history _____ in the school hall next week. A. is given B. has been given C. will be given D. gives ( )6.How many trees ____ this year? A. are planted B. will plant C. have been planted D. planted ( )7.A lot of things ____ by people to save the little girl now.
(完整word版)初中英语被动语态(精讲+精练).pdf
被动语态 语态是动词的一种形式,用以说明主语与谓语动词之间的关系。英语的语态共有两种:主动语态和被 动语态。主动语态表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者。被动语态是动词的一种 特殊形式,一般说来,只有需要动作对象的及物动词才有被动语态。汉语往往用"被"、"受"、"给"等被动词来表示被动意义 一、语态结构比较 语态 时态主动语态 被动语态 一般现在时①am\is\are ②do/does(V.\V.s) am\is\are+done(V. p.p) 一般将来时will\be going to\be(about)to+do(V.) will+be+done(V. p.p) 一般过去时①was\were ②did(V.-ed) was\were+done(V. p.p) 现在进行时am\is\are+doing(V.-ing) am\is\are+being+done(V. p.p) 过去进行时was\were+doing(V.-ing) was\were+being+done(V.p.p) 现在完成时have\has+done(V. p.p.) have\has+been+done(V. p.p) 过去完成时had+done(V. p.p.) had+been+done(V. p.p.) 情态动词情态动词+V. 情态动词+be+done(V. p.p.) 过去将来时would/should +V. would/should be +done(V. p.p.) 二、变被动句步骤 1、把原主动句中的宾语变为被动句的主语 2、把动词变为被动形式即be +过去分词,并注意其人称和数随主语的变化,而动词的时态则保持不变。 3、原主动句的主语如需要则放在by后面以它的宾格形式出现(注代词的宾格),如不需要则可省略。 4、其它的成分(定语、状语)不变。 主动语态变为被动语态例句: 一般现在时:主:We believe him. 被:He is believed by us. 一般过去时:主:He bought his children some pens. 被:Some pens were bought for his children by him. 一般将来时:主:Everyone will know the truth soon . 被:The truth will be known by everyone. 现在进行时:主:Mary is making a doll. 被:A doll is being made by Mary.
