SI_quantities&units

SI quantities and units
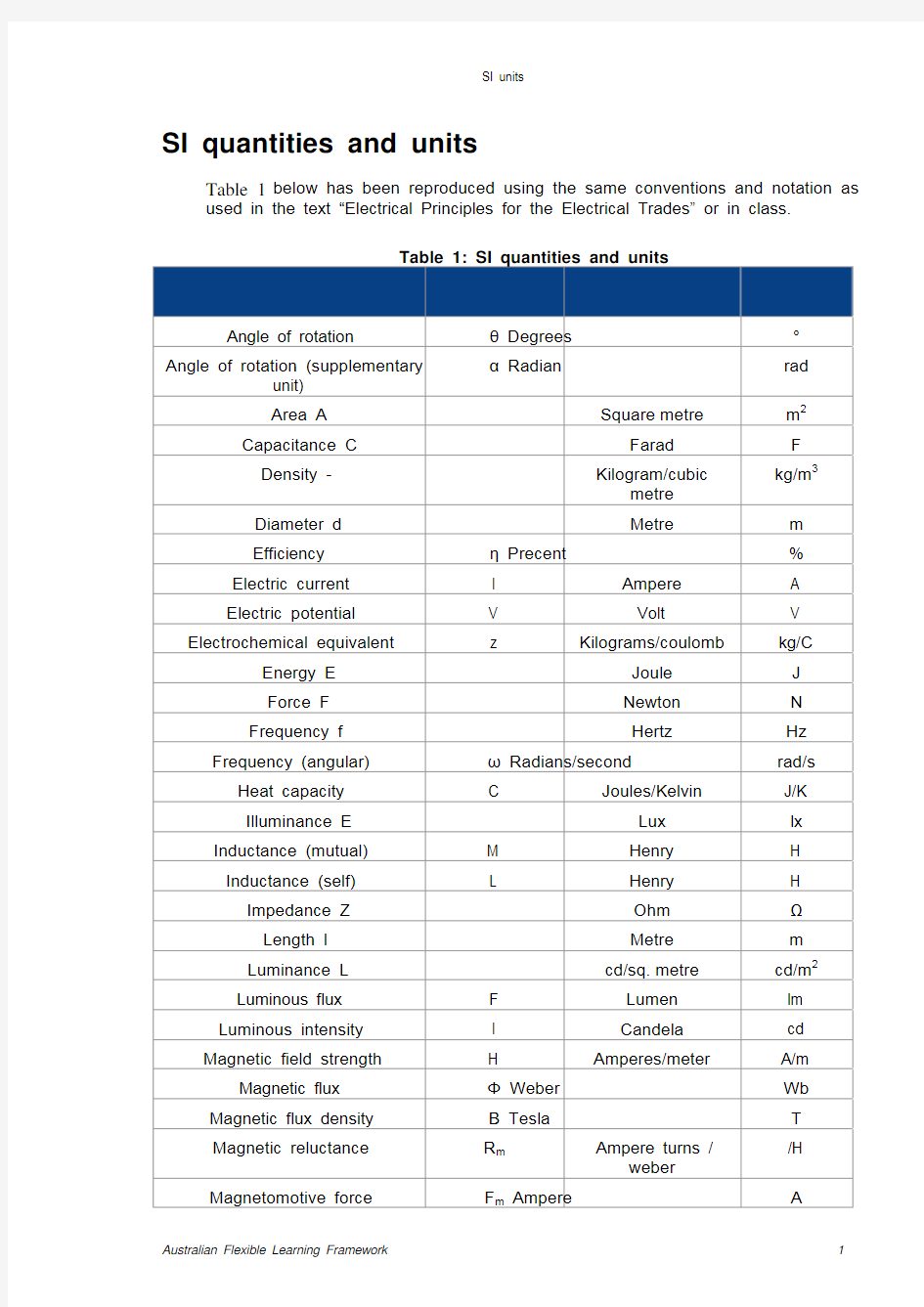
Table 1 below has been reproduced using the same conventions and notation as used in the text “Electrical Principles for the Electrical Trades” or in class.
Table 1: SI quantities and units
Name of quantity Quantity
symbol Name of unit Unit
symbol
Angle of rotation θ Degrees °
Angle of rotation (supplementary
unit) α Radian
rad
Area A
Square
metre
m2
Capacitance C
Farad
F Density -
Kilogram/cubic
metre
kg/m3
Diameter d
Metre
m Efficiency η Precent % Electric current I Ampere A
Electric potential V Volt V
Electrochemical equivalent z Kilograms/coulomb kg/C
Energy E
Joule
J Force F
Newton
N Frequency f
Hertz
Hz Frequency (angular) ω Radians/second
rad/s Heat capacity C Joules/Kelvin J/K
Illuminance E Lux
lx Inductance (mutual) M Henry H
Inductance (self) L Henry H
Impedance Z
Ohm
?
Length l
Metre
m Luminance L
cd/sq.
metre
cd/m2
Luminous flux F Lumen lm
Luminous intensity I Candela cd
Magnetic field strength H Amperes/meter A/m
Magnetic flux Φ Weber
Wb Magnetic flux density Β Tesla T Magnetic reluctance R m Ampere turns /
weber
/H Magnetomotive force F m Ampere A
Name of quantity
Quantity symbol
Name of unit
Unit symbol
Mass m Kilogram kg Number of poles p - - Number of turns N
-
-
Permeability actual μ - - Permeability absolute μ0 Henry/metre H/m
(7104?×π) Permeability relative
μr - (ratio)
Permittivity ε Farads/metre F/m Power apparent S Volt ampere VA Power reactive Q Volt ampere reactive
var Power true P
Watt
W
Power factor λ Ratio cos φ Pressure P Pascal Pa
Quantity of charge
Q
Coulomb
C
Radius r Metre m Reactance X Ohm ? Resistance R Ohm ? Resistivity ρ Ohm metre ?m Rotational speed n
-
rpm
rps
Solid angle ω Steradian sr Slip s Percent %
Specific heat capacity C Jouls/kg.kelvin
J/kg.K Temperature absolute T Kelvin K Temperature customary
t
Degrees Celsius
°C
Time t Second s
Time constant τ Second s
Torque T Newton metre Nm
Transformation ratio
(instrument transformer)
K - -
Turns t - -
Turns ratio (transformer)
n - -
Work W Joule J
SI Units
What does SI mean? It stands for Systeme International d’Unites (the International
System of Units) which is abbreviated in many languages to SI units.
This system is international and uses common units for mechanical, thermal, and
electrical values. Table 2 shows the basic SI units.
Table 2: Base SI units
Quantity Units
Physical Quantity Quantity Symbol Unit Name Unit Symbol
length l metre m mass m kilogram
kg
s time t second
electric current I ampere A
temperature t kelvin K
Luminous intensity I candela cd
rad Angle of rotation α radian
Definitions
Table 3: Unit definitions
Unit Definition
Metre The length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum
during a time interval of 1/299,792,458 second.
Kilogram The mass of the international Prototype of the Kilogram
(Platinum - Iridium)
Second The time interval corresponding with 9,192,631,770
oscillations of a caesium 133 atom at 0°K
Ampere The current required to flow in 2 parallel conductors,
placed 1 metre apart in a vacuum to produce a force of 2
x 10-7 Newton metres between the conductors.
Kelvin 1/273.16 of the (Triple point) of water (Ice Point)
Candela The luminous intensity, in a given direction of a source
that emits monochromatic radiation of 54,012 Hz and has
a radian intensity of 1/683 watts per steradian.
Radian The angle between 2 radii of the same circle, which mark
off, on the circumference of the circle, an arc equal in
length to the radius of the circle.
