Android仿照Launcher的Workspace实现左右滑动切换
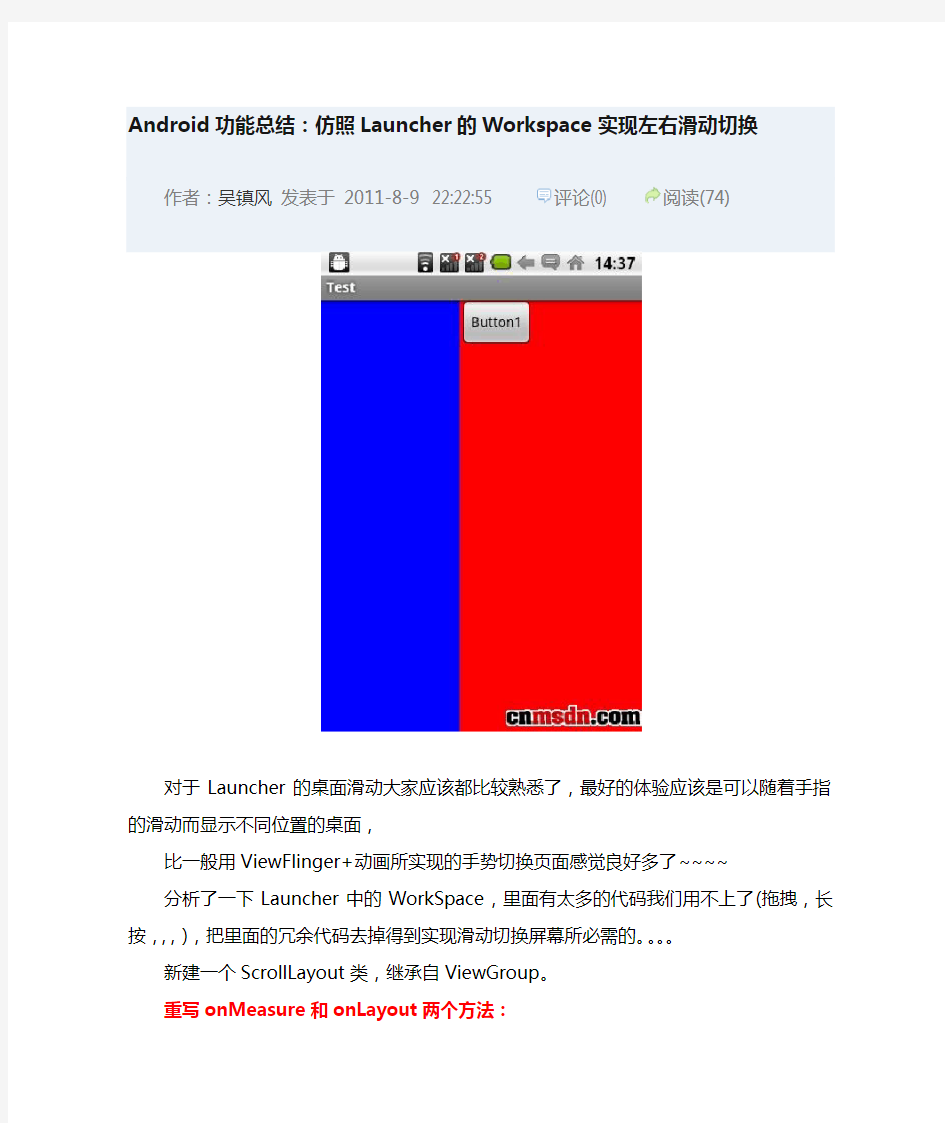

Android功能总结:仿照Launcher的Workspace实现左右滑动切换
作者:吴镇风发表于2011-8-9 22:22:55 评论(0) 阅读(74)
对于Launcher的桌面滑动大家应该都比较熟悉了,最好的体验应该是可以随着手指的滑动而显示不同位置的桌面,
比一般用ViewFlinger+动画所实现的手势切换页面感觉良好多了~~~~
分析了一下Launcher中的WorkSpace,里面有太多的代码我们用不上了(拖拽,长按,,,),把里面的冗余代码去掉得到实现滑动切换屏幕所必需的。。。。
新建一个ScrollLayout类,继承自ViewGroup。
重写onMeasure和onLayout两个方法:
其中onMeasure方法中,得到ScrollLayout的布局方式(一般使用FILL_PAR ENT),然后再枚举其中所有的子view,设置它们的布局(FILL_PARENT),这样在ScrollLayout之中的每一个子view即为充满屏幕可以滑动显示的其中一页。
在onLayout方法中,横向画出每一个子view,这样所得到的view的高与屏幕高一致,宽度为getChildCount()-1个屏幕宽度的view。
添加一个Scroller来平滑过渡各个页面之间的切换,
重写onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent来响应手指按下划动时所需要捕获的消息,例如划动的速度,划动的距离等。再配合使用scrollBy (int x, i nt y)方法得到慢速滑动小距离的时候,所需要显示的内容。最后当手指起来时,
根据划动的速度与跨度来判断是向左滑动一页还是向右滑动一页,确保每次用户操作结束之后显示的都是整体的一个子view.
ScrollLayout源码:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
package com.yao_guet.test;
import Android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.VelocityTracker;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewConfiguration;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Scroller;
/**
* 仿Launcher中的WorkSapce,可以左右滑动切换屏幕的类
* @author Yao.GUET
* blog: https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,/Yao_GUET
* date: 2011-05-04
*/
public class ScrollLayout extends ViewGroup {
private static final String TAG = "ScrollLayout";
private Scroller mScroller;
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
private int mCurScreen;
private int mDefaultScreen = 0;
private static final int TOUCH_STATE_REST = 0;
private static final int TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING = 1;
private static final int SNAP_VELOCITY = 600;
private int mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST;
private int mTouchSlop;
private float mLastMotionX;
private float mLastMotionY;
public ScrollLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public ScrollLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
mCurScreen = mDefaultScreen;
mTouchSlop =
ViewConfiguration.get(getContext()).getScaledTouchSlop();
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (changed) {
int childLeft = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i=0; i final View childView = getChildAt(i); if (childView.getVisibility() != View.GONE) { final int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth(); https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,yout(childLeft, 0, childLeft+childWidth, childView.getMeasuredHeight()); childLeft += childWidth; } } } } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { L og.e(TAG, "onMeasure"); super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); final int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) { throw new IllegalStateException("ScrollLayout only canmCurScreen run at EXACTLY mode!"); } final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); if (heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) { throw new IllegalStateException("ScrollLayout only can run at EXACTLY mode!"); } // The children are given the same width and height as the scrollLayout final int count = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { getChildAt(i).measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } // Log.e(TAG, "moving to screen "+mCurScreen); scrollTo(mCurScreen * width, 0); } /** * According to the position of current layout * scroll to the destination page. */ public void snapToDestination() { f inal int screenWidth = getWidth(); f inal int destScreen = (getScrollX()+ screenWidth/2)/screenWidth; s napToScreen(destScreen); } public void snapToScreen(int whichScreen) { // get the valid layout page w hichScreen = Math.max(0, Math.min(whichScreen, getChildCount()-1)); i f (getScrollX() != (whichScreen*getWidth())) { final int delta = whichScreen*getWidth()-getScrollX(); mScroller.startScroll(getScrollX(), 0, delta, 0, Math.abs(delta)*2); mCurScreen = whichScreen; invalidate(); // Redraw the layout } } public void setToScreen(int whichScreen) { w hichScreen = Math.max(0, Math.min(whichScreen, getChildCount()-1)); m CurScreen = whichScreen; s crollTo(whichScreen*getWidth(), 0); } public int getCurScreen() { r eturn mCurScreen; } @Override public void computeScroll() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if (https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,puteScrollOffset()) { scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY()); postInvalidate(); } } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if (mVelocityTracker == null) { mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain(); } mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event); final int action = event.getAction(); final float x = event.getX(); final float y = event.getY(); switch (action) { Log.e(TAG, "event down!"); if (!mScroller.isFinished()){ mScroller.abortAnimation(); } mLastMotionX = x; break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: int deltaX = (int)(mLastMotionX - x); mLastMotionX = x; scrollBy(deltaX, 0); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: Log.e(TAG, "event : up"); // if (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING) { final VelocityTracker velocityTracker = mVelocityTracker; https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,puteCurrentVelocity(1000); int velocityX = (int) velocityTracker.getXVelocity(); Log.e(TAG, "velocityX:"+velocityX); if (velocityX > SNAP_VELOCITY && mCurScreen > 0) { // Fling enough to move left Log.e(TAG, "snap left"); snapToScreen(mCurScreen - 1); } else if (velocityX < -SNAP_VELOCITY && mCurScreen < getChildCount() - 1) { // Fling enough to move right Log.e(TAG, "snap right"); snapToScreen(mCurScreen + 1); } else { snapToDestination(); } if (mVelocityTracker != null) { mVelocityTracker.recycle(); mVelocityTracker = null; } // } mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST; break; mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST; break; } return true; } @Override public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Log.e(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent-slop:"+mTouchSlop); final int action = ev.getAction(); if ((action == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE) && (mTouchState != TOUCH_STATE_REST)) { return true; } final float x = ev.getX(); final float y = ev.getY(); switch (action) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: final int xDiff = (int)Math.abs(mLastMotionX-x); if (xDiff>mTouchSlop) { mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING; } break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: mLastMotionX = x; mLastMotionY = y; mTouchState = mScroller.isFinished()? TOUCH_STATE_REST : TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING; break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST; break; } return mTouchState != TOUCH_STATE_REST; } } ScrollLayoutTest.Java package com.yao_guet.test; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; public class ScrollLayoutTest extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,yout.main); } } 通信实训报告 -Android移动平台开发 学院:信息工程学院 班级: 学号: 姓名: 实训内容: 一.1.Andriod的简介 Android一词的本义指“机器人”,同时也是Google于2007年11月5日宣布的基于Linux平台的开源手机操作系统的名称,该平台由操作系统、中间件、用户界面和应用软件组成,号称是首个为移动终端打造的真正开放和完整的移动软件。目前,最新版本为Android 2.4 Gingerbread 和Android 3.0 Honeycomb。 Android是基于Linux开放性内核的操作系统,是Google公司在2007年11月5日公布的手机操作系统。 Android早期由原名为"Android"的公司开发,谷歌在2005年收购"Android.Inc"后,继续对Android系统开发运营,它采用了软件堆层(software stack,又名软件叠层)的架构,主要分为三部分。底层Linux内核只提供基本功能,其他的应用软件则由各公司自行开发,部分程序以Java编写。2011年初数据显示,仅正式上市两年的操作系统Android已经超越称霸十年的塞班系统,使之跃居全球最受欢迎的智能手机平台。现在,Android系统不但应用于智能手机,也在平板电脑市场急速扩张,在智能MP4方面也有较大发展。采用Android系统主要厂商包括台湾的HTC,(第一台谷歌的手机G1由HTC生产代工)美国摩托罗拉,SE等,中国大陆厂商如:魅族(M9),华为、中兴、联想、蓝魔等。 2.Android构架图 二.1软件下载 Android SDK,网址是https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,. JDK的下载地址https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,/javase/downloads/widget/jdk6.jsp。Eclipse的下载网址是https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,/downloads/ 2.Android开发环境搭建 视图组件的使用模式 常用组件 高级组件 提示框与警告对话框 就是Android应用程序的开发过程。一般过程是先通过XML布局文件或Java代码创建界面布局,设定组件显示样式,随后获取UI组件对象,并处理组件事件响应。 视图组件的定义 资源的访问 生成视图组件资源标识 视图组件的引用 视图组件的事件响应 组件的常用属性 1.1视图组件的定义 使用XML布局文件定义视图组件 使用Java代码定义视图组件(不推荐) 1.1视图组件的定义 使用XML布局文件定义视图组件 Android平台为大多数视图组件以及其子类提供了XML标记,可通过XML布局文件中的标记来定义视图组件。XML中的每个元素代表了一个组件,即元素名称对应相应的Java类。 1.1视图组件的定义 这样的话就比较容易实现了,再看一下整体的Layout布局情况: xml布局文件如下:注意层次的嵌套。先是一个RelativeLayout,它有两个子布局,RelativeLayout和LinearLayout。 android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:padding="10.0dip" android:singleLine="true" android:text="设置" android:textColor="@color/white" android:textSize="15dp" /> 基于Android系统的App界面设计 智能手机时代的来临改变了大多数人的生活习惯,时至今日智能手机已经成为了人们工作生活中的一部分,在工作生活中发挥着重要的作用。App作为智能手机应用程序的核心,构建以用户体验为核心的页面设计是智能手机App设计的核心与要点,同时也是满足用户使用需求的重要途径与方式。现今的智能手机App主要分为IOS与Android两大市场,与IOS的封闭不同的是Android系统具有极强的开放性,而这一开放性在为Android系统App带来无限可能的同时也使得基于Android系统所开发的App界面本身缺乏统一的规范,从而造成基于Android系统所开发的App界面具有极大的开放性。新时期为做好基于Android 系统App的设计需要从情感、认知以及感官三个层面入手做好基于Android系统的App界面的开发设计,使之具有良好的用户使用体验。 标签:Android系统;App;界面设计 Abstract:The advent of the smart phone era has changed the habits of most people. Today,smart phone s have become a part of people’s work and life,and play an important role in the work and life. As the core of smart phone applications,App plays an important role in the work and life. The design of page based on user experience is the core and key point of the App design of smart phone,and it is also an important way and way to meet the needs of users. Today’s smartphone App is mainly divided into IOS and Android two major markets,Different from the closure of IOS,Android system has a very strong openness,and this openness not only brings infinite possibility to App of Android system,but also makes the App interface based on Android system lack of unified specification. As a result,the App interface based on Android system is very open. In order to do well the design of App based on Android system in the new period,it is necessary to develop and design the App interface based on Android system from the three aspects of emotion,cognition and sense organ,to make it have a good user experience. Keywords:Android system;App;interface design 前言 Android系统是与IOS系统所并行的应用于智能手机中的两大智能系统,在基于Android系统App界面开发的过程中受多种因素的影响使得一些App的界面具有很大的不协调性,从而影响了广大用户的使用体验。本文在分析影响智能手机App界面设计因素的基础上对如何做好基于Android系统的App界面设计进行分析阐述。 1 影响智能手机App界面设计的因素分析 智能手机App是智能手机的灵魂,用户结合自身需求可以下载安装自身所 https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,/cmdn/bbs/viewthread.php?tid=18736&page=1 #pid89255 Android UI开发专题(一) 之界面设计 近期很多网友对Android用户界面的设计表示很感兴趣,对于Android UI开发自绘控件和游戏制作而言掌握好绘图基础是必不可少的。本次专题分10节来讲述,有关OpenGL ES相关的可能将放到以后再透露。本次主要涉及以下四个包的相关内容:android.content.res 资源类 android.graphics 底层图形类 android.view 显示类 android.widget 控件类 一、android.content.res.Resources 对于Android平台的资源类android.content.res.Resources可能很多网友比较陌生,一起来看看SDK上是怎么介绍的吧,Contains classes for accessing application resources, such as raw asset files, colors, drawables, media or other other files in the package, plus important device configuration details (orientation, input types, etc.) that affect how the application may behave.平时用到的二进制源文件raw、颜色colors、图形drawables和多媒体文件media的相关资源均通过该类来管理。 int getColor(int id) 对应res/values/colors.xml Drawable getDrawable(int id) 对应res/drawable/ XmlResourceParser getLayout(int id) 对应res/layout/ String getString(int id) 和CharSequence getText(int id) 对应res/values/strings.xml InputStream openRawResource(int id) 对应res/raw/ void parseBundleExtra (String tagName, AttributeSet attrs, Bundle outBundle) 对应res/xml/ String[] getStringArray(int id) res/values/arrays.xml float getDimension(int id) res/values/dimens.xml 二、android.graphics.Bitmap 作为位图操作类,Bitmap提供了很多实用的方法,常用的我们总结如下: boolean compress(https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,pressFormat format, int quality, OutputStream stream) 压缩一个Bitmap对象根据相关的编码、画质保存到一个OutputStream中。其中第一个压缩格式目前有JPG和PNG void copyPixelsFromBuffer(Buffer src) 从一个Buffer缓冲区复制位图像素 void copyPixelsToBuffer(Buffer dst) 将当前位图像素内容复制到一个Buffer缓冲区 我们看到创建位图对象createBitmap包含了6种方法在目前的Android 2.1 SDK中,当然他们使用的是API Level均为1,所以说从Android 1.0 SDK开始就支持了,所以大家可以放心使用。 Android UI开发专题(一) 之界面设计 发帖日期:2010-02-09 10:49:28 标签:ophone 近期很多网友对Android用户界面的设计表示很感兴趣,对于Android UI开发自绘控件和游戏制作而言掌握好绘图基础是必不可少的。本次专题分10节来讲述,有关OpenGL ES相关的可能将放到以后再透露。本次主要涉及以下四个包的相关内容: android.content.res 资源类 android.graphics 底层图形类 android.view 显示类 android.widget 控件类 一、android.content.res.Resources 对于Android平台的资源类android.content.res.Resources可能很多网友比较陌生,一起来看看SDK上是怎么介绍的吧,Contains classes for accessing application resources, such as raw asset files, colors, drawables, media or other other files in the package, plus important device configuration details (orientation, input types, etc.) that affect how the application may behave.平时用到的二进制源文件raw、颜色colors、图形drawables和多媒体文件media的相关资源均通过该类来管理。 int getColor(int id) 对应res/values/colors.xml Drawable getDrawable(int id) 对应res/drawable/ XmlResourceParser getLayout(int id) 对应res/layout/ String getString(int id) 和CharSequence getText(int id) 对应 res/values/strings.xml InputStream openRawResource(int id) 对应res/raw/ void parseBundleExtra (String tagName, AttributeSet attrs, Bundle outBundle) 对应res/xml/ String[] getStringArray(int id) res/values/arrays.xml float getDimension(int id) res/values/dimens.xml 二、android.graphics.Bitmap 作为位图操作类,Bitmap提供了很多实用的方法,常用的我们总结如下: boolean compress(https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,pressFormat format, int quality, OutputStream stream) 压缩一个Bitmap对象根据相关的编码、画质保存到一个OutputStream中。其中第一个压缩格式目前有JPG和PNG void copyPixelsFromBuffer(Buffer src) 从一个Buffer缓冲区复制位图像素 实验2 android的界面设计(控件与布局) 学时:4学时 一、实验目的: 1、了解Android编程原理 2、掌握界面控件设计 3、了解和熟悉常用控件的使用、界面布局等内容。 二、实验内容: 1.基本控件的制作: (1)TextView的制作: a)体会Autolink,依次更换属性:web/phone/all/email/ b) 制作跑马灯效果 android:ellipsize 设置当文字过长时,该控件该如何显示。有如下值设置:”start”—-省略号显示在开头;”end”——省略号显示在结尾;”middle”—-省略号显示在中间;”marquee”——以跑马灯的方式显示(动画横向移动) android:marqueeRepeatLimit 在ellipsize 指定marquee 的情况下,设置重复滚动的次数,当设置为marquee_forever 时表示无限次。 android:focusableInTouchMode:是否在触摸模式下获得焦点。 android:focusable 控件是否能够获取焦点 (2)EditView制作 (a) maxLength:最大输入长度属性 (b) singleLine:多行文本框 (c) inputType:限制输入文本类型 (d) hint:设置提示信息 2.布局设计 (1) LinearLayout布局: (2)Relative Layout: (3)Table Layout 3.建立一个如图所示的图形界面: 4.用ListView制作如图界面(图片自定) (将该题以你的学号命名,发给你班的学习委员,以班为单位统一发给我,我的邮箱为:610083060@https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,): 5.用expandablelistview制作如下界面: 一、Android设计常识 开始介绍之前先帮大家梳理一下Android常用单位,方便各位亲们更好的掌握并了解Android端设计规范。 1.1 Android常用单位 1.1.1. PPI(pixels per inch):数字影像的解析度,也就是每英寸所拥有的像素数,即像素密度; PPI计算公式:ppi=√(长度像素数2 + 宽度像素数2)/屏幕对角线英寸数1.1.2. DPI(dots per inch):是指印刷上的计量单位,也就是每英寸上能印刷的网点数,我们设计用于显示器的默认为(72像素/英寸)就好了; 1.1.3. 屏幕尺寸(Screen Size):一般我们所说的手机屏幕尺寸,比如3英寸、5.5英寸等,都是指对角线的长度,而不是手机的面积; 1.1.4. 分辨率(Resolution):是指手机屏幕垂直和水平方向上的像素个数,比如分辨率为:720*1280,是指设备水平方向有720个像素点,垂直方向有1280个像素点 1.1.5. px( pixels):像素,不同设备显示效果相同 1.1.6. pt( point):一个标准的长度单位,ios的逻辑单位,1Pt=1/72英寸,用于印刷业,非常简单易用;标注字体大小(72是早期台式机的DPI) 1.1.7. sp(Scaled-independentpixels):放大像素,安卓的字体单位; 1.1.8. Dp(Density-independentpixels):是指设备的独立像素,不同的设备有不同的显示效果,它与设备硬件有关系; sp和dp基本一样,是android开发里特有的单位,都是为了保证文字在不同密度的显示屏上显示相同的效果;dp与设备硬件有关,与屏幕密度无关,sp与屏幕密度和设备硬件均无关; 软件设计开发本栏目责任编辑:谢媛媛Computer Knowledge and Technology 电脑知识与技术第5卷第29期(2009年10月)基于Android 技术的界面设计与研究 赵亮1,张维2 (徐州建筑职业技术学院,江苏徐州221000) 摘要:详细介绍了google 发布的新一代智能手机平台Android 的基本架构,通过对其应用程序构成框架的分析,分析了构成An -droid 应用程序的四种架构块的功能。最后通过对视图和布局的介绍,给出一种使用Android 技术的界面设计实现方案,并通过数据绑定实现了用户事件映射。 关键词:Android ;view ;viewgroup ;数据绑定;布局 中图分类号:TP311文献标识码:B 文章编号:1009-3044(2009)29-8183-03 Research and Design of Interface Based on Android Technology ZHAO Liang 1,ZHANG Wei 2 (Department of Electrionic Information,Xuzhou Institute of Architectural Technology,Jiangsu 221000,China) Abstract:Described in detail the Android that was the basic structure of a new generation smart phones platform of google.By the analysis of its application constitution,we analyze the function of the four kinds of block that compose the Android architecture.Finally through the introduction of the view and layout,present an interface implementation using Android technology and realize the user event mapping by data binding. Key words:Android;view;viewgroup;data binding;layout 随着3G 网络的使用,移动终端不再仅是通讯网络的终端,还将成为互联网的终端。因此,移动终端的应用软件和需要的服务将 会有很大的发展空间。Google 为此于2007年11月推出了一个专为移动设备设计的软件平台——— Android 。Android 是一个针对移动设备的程序集,其中包括一个操作系统,一个中间件和一些关键性应用。 1Android 平台的架构 Android 平台自底向上由以下四个层次组成:Linux 内核层、运行时库和其他库层、应用框架层、应用程序层。如图1所示。 1)Linux 内核层:Android 底层是一个基于Linux 内核来开发的独立操作系统,主要是添加了一个名为Goldfish 的虚拟CPU 以及Android 运行所需的特定驱动代码。该层用来提供系统的底层服务,包括安全机制、内 存管理、进程管理、网络堆栈及一系列的驱动模块。作为一个虚拟的中间层,该层位于硬件 与其它的软件层之间。需要注意的是,这个内核操作系统并非类GNU/Linux 的,所以其系 统库、系统初始化和编程接口都和标准的Linux 系统有所不同的。它没有采用虚拟内存文 件系统,而是采用YAFFS2文件系统。YAFFS2(Yet Another Flash File System)文件系统是一 个开源的专门为NAND Flash 设计的文件系统,具有很好的可移植性,同时也是一种日志 型文件系统。2)Android 运行时库和其他库层:Android 运行时库包含一组核心库和Dalvik 虚拟机 同时Android 提供了丰富的库类支持且大部分为开源代码。 3)应用框架层:在应用框架层Android 开发人员可以跟那些核心应用一样拥有访问框架APIs 的全部权限。应用的系结构化设计简化了各组件之间的重用,任何应用都可以分发自己的组件,任何应用也可以使用这些分发的组件。 4)应用程序层:Android 本身会附带一些核心的应用程序,包括e-mail 客户端、短信程序、日历、地图、浏览器、通讯录等,目前所有的应用程序都是由Java 语言开发的。 2Android 应用程序的构成 对于一个Android 应用程序来说,是由四种构造块组织而成:Activity 、Intent Receiver 、Service 、Content Provider 。但是,并不是每一个Android 应用程序都需要这四种构造块,我们对四种构造块做一些说明: 1)Activity 。Activity 是Android 构造块中最基本的一种。一个activity 通常就是一个单独的屏幕。每一个activity 都被实现为一个独立的类,并且继承于Activity 这个基类。这个activity 类将会显示由几个Views 控件组成的用户接口,并对事件做出响应。大部份的应用都会包含多个的屏幕。Android 使用了Intent 这个特殊类,实现在屏幕与屏幕之间移动。通过解析各种intent ,从一个屏幕导航到另一个屏幕是很简单的。当向前导航时,activity 将会调用startActivity(Intent myIntent)方法。然后,系统会在所有安装的应用程序中定义的IntentFilter 中查找,找到最匹配myIntent 的Intent 对应的activity 。新的activity 接收到myIntent 的通知后,开始运行。当startActivity 方法被调用将触发解析myIntent 的动作,这个机制提供了两个关键好处:能够重复利用从其它组件中以Intent 的形式产生的一个请求和可以在任何时候被一个具有相同IntentFilter 的新的Activity 取代。 收稿日期:2009-09-16 作者简介:赵亮(1982-),男,江苏徐州人,主要研究方向:移动开发,计算机网络。 图1Android 平台的架构 ISSN 1009-3044Computer Knowledge and Technology 电脑知识与技术Vol.5,No.29,October 2009,pp.8183-8185E-mail:xsjl@https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html, https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html, Tel:+86-551-569096356909648183 【目的】And 【要求】 1、2、3、4、5、【原理】 1、实验】 roid程序设计】 了解Android 掌握各种UI控 掌握UI设计完成课堂练完成课后作业 】 掌握各种基本验二、An 计基础;熟悉d程序设计基控件的基本功的方法 习 业,并且提交 本控件的基本ndroid 程悉各种UI控件基础 功能和用法交实验报告 本功能和用法程序UI 件并且进行U 法,常用的控界面设计UI设计。 控件包括: 计 2、Abs Grid ListL Tabl 【参考过1、2、换到UI 设 1所示。选择“C 框,在此“Linear 3、 了解各种布局oluteLayout dView 、 Layout 、 leLayout 过程】 新建一个名为双击Layout 设计界面(默在此屏幕上Change Layou 此对话框的“rLayout (Vert 将Form Wid 局Layout 的基、 Fram Linea Radi … 为Lab02的A →activity_m 默认布局为R 上点击鼠标右t…”,出现““New Layout tical )”修改 dgets 中的 Bu 基本功能和用meLayout 、arLayout 、oGroup 、 Android Proje ain.xml 文件 RelativeLayou 右键,在弹出“Change Layo t Type ”下拉布局。 utton 拖入屏图 2用法 ect 件,即可切ut ),如图出式窗口中 out ”对话拉框中选择 屏幕中,如图 2所示。 图1 4、见在代码 5、z Bac 键,如图2所示在码中已经新增修改控件属性方法一: 单击Butto kground 、Te 选择“ Show 在屏幕下端从增了Button 性 on ,在窗xt 等。如果没w In ”→“ P 从Graphical 的xml 代码,图3口右边的pr 没有出现Pro roperties ”即图 4Layout 切换至如图3所示 roperties 窗operties 窗口即可,如图 至activity_m 示。 口中修改口,选中Butt 4所示。 main.xml ,可相应的属性,ton ,点击鼠标以看如 标右 1、android分辨率 Android的多分辨率,一向是设计师和开发者非常头疼的事儿。尽管如此,对于多分辨造成的复杂问题,也是大家要优先解决的。Android支持多种不同的dpi模式:ldpi 、mdpi 、hdpi 、xhdpi 、xxhdpi 、xxxhdpi 注意,ppi、dpi 是密度单位,不是度量单位: * ppi (pixels per inch):图像分辨率(在图像中,每英寸所包含的像素数目) * dpi (dots per inch):打印分辨率(每英寸所能打印的点数,即打印精度) dpi主要应用于输出,重点是打印设备上;ppi对于设计师应该比较熟悉,photoshop 画布的分辨率常设置为72像素/英寸,这个单位其实就是ppi 。尽管概念不同,但是对于移动设备的显示屏,可以看作ppi=dpi 。 ppi的运算方式是:PPI = √(长度像素数2 + 宽度像素数2)/ 屏幕对角线英寸数。即:长、宽各自平方之和的开方,再除以屏幕对角线的英寸数。 以iphone5为例,其ppi=√(1136px2 + 640px2)/4 in=326ppi(视网膜Retina屏)对于android手机,一个不确切的分法是,720 x 1280 的手机很可能接近320 dpi (xhdpi 模式),480 x 800 的手机很可能接近240 dpi (hdpi模式),而320 x 480 的手机则很接近160 dpi(mdpi模式)。 来自友盟指数2014年3月份的数据: 480 x 800的手机占比最高为31.9%,720 x 1280的手机占比为16.5%位居第二,而240 x 320的手机占比最少为1.0% 。xxdhpi模式的高分辨率1080 x 1920手机占比也越来越高,目前为6.1% 。 2、单位换算方法 android开发中,文字大小的单位是sp,非文字的尺寸单位用dp,但是我们在设计稿用的单位是px。这些单位如何换算,是设计师、开发者需要了解的关键。 * dp:Density-independent pixels,以160PPI屏幕为标准,则1dp=1px。dp和px的换算公式:dp*ppi/160 = px。对于320ppi的屏幕,1dp x 320ppi/160 = 2px。 * sp:Scale-independent pixels,它是安卓的字体单位,以160PPI屏幕为标准,当字体大小为100%时,1sp=1px。sp 与px 的换算公式:sp*ppi/160 = px。对于320ppi 的屏幕,1sp x 320ppi/160 = 2px。 简单理解的话,px(像素)是我们UI设计师在PS里使用的,同时也是手机屏幕上所显示的,dp是开发写layout的时候使用的尺寸单位。 为什么要把sp和dp代替px?原因是他们不会因为ppi的变化而变化,在相同物理尺寸和不同ppi下,他们呈现的高度大小是相同。也就是说更接近物理呈现,而px则不行。 近期很多网友对Android用户界面的设计表示很感兴趣,对于Android UI开发自绘控件和游戏制作而言掌握好绘图基础是必不可少的。本次专题分10节来讲述,有关OpenGL ES相关的可能将放到以后再透露。本次主要涉及以下四个包的相关内容: android.content.res 资源类 android.graphics 底层图形类 android.view 显示类 android.widget 控件类 一、android.content.res.Resources 对于Android平台的资源类android.content.res.Resources可能很多网友比较陌生,一起来看看SDK 上是怎么介绍的吧,Contains classes for accessing application resources, such as raw asset files, colors, drawables, media or other other files in the package, plus important device configuration details (orientation, input types, etc.) that affect how the application may behave.平时用到的二进制源文件raw、颜色colors、图形drawables和多媒体文件media的相关资源均通过该类来管理。 int getColor(int id) 对应res/values/colors.xml Drawable getDrawable(int id) 对应res/drawable/ XmlResourceParser getLayout(int id) 对应res/layout/ String getString(int id) 和CharSequence getText(int id) 对应res/values/strings.xml InputStream openRawResource(int id) 对应res/raw/ void parseBundleExtra (String tagName, AttributeSet attrs, Bundle outBundle) 对应res/xml/ String[] getStringArray(int id) res/values/arrays.xml float getDimension(int id) res/values/dimens.xml 二、android.graphics.Bitmap 作为位图操作类,Bitmap提供了很多实用的方法,常用的我们总结如下: boolean compress(https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,pressFormat format, int quality, OutputStream stream) 压缩一个Bitmap对象根据相关的编码、画质保存到一个OutputStream中。其中第一个压缩格式目前有JPG和PNG void copyPixelsFromBuffer(Buffer src) 从一个Buffer缓冲区复制位图像素 void copyPixelsToBuffer(Buffer dst) 将当前位图像素内容复制到一个Buffer缓冲区 我们看到创建位图对象createBitmap包含了6种方法在目前的Android 2.1 SDK中,当然他们使用的是API Level均为1,所以说从Android 1.0 SDK开始就支持了,所以大家可以放心使用。 static Bitmap createBitmap(Bitmap src) static Bitmap createBitmap(int[] colors, int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config) static Bitmap createBitmap(int[] colors, int offset, int stride, int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config) 作者:Bruce Lee 出处:https://www.360docs.net/doc/373857316.html,/BruceLee521 样式 设备和显示器 Android有百万计的手机、平板电脑和其他设备,这些设备都有各种屏幕尺寸。利用Android 的灵活的布局系统,您可以创建小到手机大到平板的各种应用程序。 变通 拉伸和压缩布局,以适应不同的高度和宽度。 优化布局 在大型设备中有额外的屏幕空间利用。但在移动手持设备上需要创建复合的视图,结合多个视图来显示更多的内容,并且是这些视图易于导航。 所有的资源 提供不同的屏幕分辨率(DPI)的资源,以确保您的应用程序在任何设备上看上去都很好,比如32*32,64*64。 策略 那么设计这些多尺寸的屏幕,应该从哪个规格开始?一种方法是先设计标准设备的(正常大小和MDPI),然后设计向上和向下比例的尺寸。另一种方法是从最大屏幕尺寸的开始,然后缩减,并找出我们需要使在小屏幕上的折中的UI。 主题 主题是Android机器应用统一样式到应用程序或活动的一。样式指定用户界面元素的视觉属性,如颜色,高度,填充和字体大小。为了促进更大的平台上的所有应用程序之间的凝聚力,Android 提供了三个系统的主题,你可以从中选择来构建应用程序: 全亮主题 全暗主题 全亮与全暗动作条主题 Gmail是使用全亮的主题。Settings是使用全暗主题. Talk使用全亮与全暗动作条主题. 触摸反馈 使用颜色和明亮来响应触摸,强化行为的手势,并表明什么样的动作是允许的什么样的是不允许的。 当用户触摸可操作的区域,应用程序需要可视化的反应。这让用户知道哪些对象被触摸了,你的应用程序是“听”到触摸了。 状态 Android的UI元素具有内置的触摸反馈,包括状态,用于指示触摸元素是否会产生什么反应。 通讯 Android用户界面设计 Android用户界面设计:使用片段 Android 3.0引入的新的片断(Fragment)API,让我们更容易地创建动态用户界面。在这个教程中,我们学习如何将一个两屏的ListView转换成WebView流,以适应大屏幕的单屏流设计,比如在平板设备中。 这篇文章的节奏将比我们的入门教程更快一些。如果你对基本的Android控件或概念不熟悉你可能需要复习这个网站上我们其它的一些教程,甚至是Android API参考。最终的开源代码可以在Google code上下载到。 片段简介 在我们开始之间,让我们在更高的层次上定义一下什么是片段。通常来说,片段是一大块用户界面,它具有自己的生存周期。如果它听起来像一个Activity,那是因为它确实很像一个Activity。然而,片段与Activity不同,片段必须存在于Activity之内。片段不须要在它每次初始化的时候与同一个Activity配对,这使它具有一些灵活性。与Activity一样,片段也无需包含任何用户界面。 步骤0:开始 这个教程假设你读过我们的列表视图教程,你可以下载那个教程的代码,并完成一些任务,然后开始,也可以直接下载这个教程的代码直接开始。 步骤1:重新设计界面 下图示意了我上在列表视图教程中所提到的文章阅读应用,我们还没有考虑并使用片段: 这个流程在相对小屏幕上运行得很不错。然而,在大屏幕上,比如Motorola Xoom平板的10寸屏幕上,在列表视图上却浪费了很多空间。WebView看起来正常,但是有点枯燥。 这就是要引入片段的地方:在大屏幕上,我们可以提供更有效的用户界面,如果我们可以在同一屏上显示ListView和WebView。当用户点击左边“面板”的列表视图中的某一项时,右边的WebView更新显示相应的内容。Android简单的登陆界面的设计开发
第4章 Android用户界面设计
Android界面设计教程
基于Android系统的App界面设计
Android UI开发专题
android UI界面设计
实验2 android的界面设计(控件与布局)
APP界面设计规范二(Android版)
基于Android技术的界面设计与研究
实验二_Android程序UI界面设计
Android界面设计规范
Android UI开发专题(一) 之界面设计
Android的界面设计规范
Android用户界面设计
