fluent噪声培训资料(中)
Tutorial:Broadband Noise Modeling
Purpose
The purpose of this tutorial is to provide guidelines and recommendations for the basic setup and solution procedure for solving an acoustics?eld generated from a sedan car using the broadband noise model.The problem is initially solved for steady state,and then the broadband acoustic model is included in the calculation to perform postprocessing.
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes that you are familiar with the user interface,basic setup and solution procedures in FLUENT.This tutorial does not cover mechanics of using the broadband noise model,but focuses on setting up the problem for a sedan car and performing postprocessing.
It also assumes that you have a basic understanding of aeroacoustic physics.
If you have not used FLUENT before,it would be helpful to?rst review FLUENT6.2User’s Guide and FLUENT6.2Tutorial Guide.
Problem Description
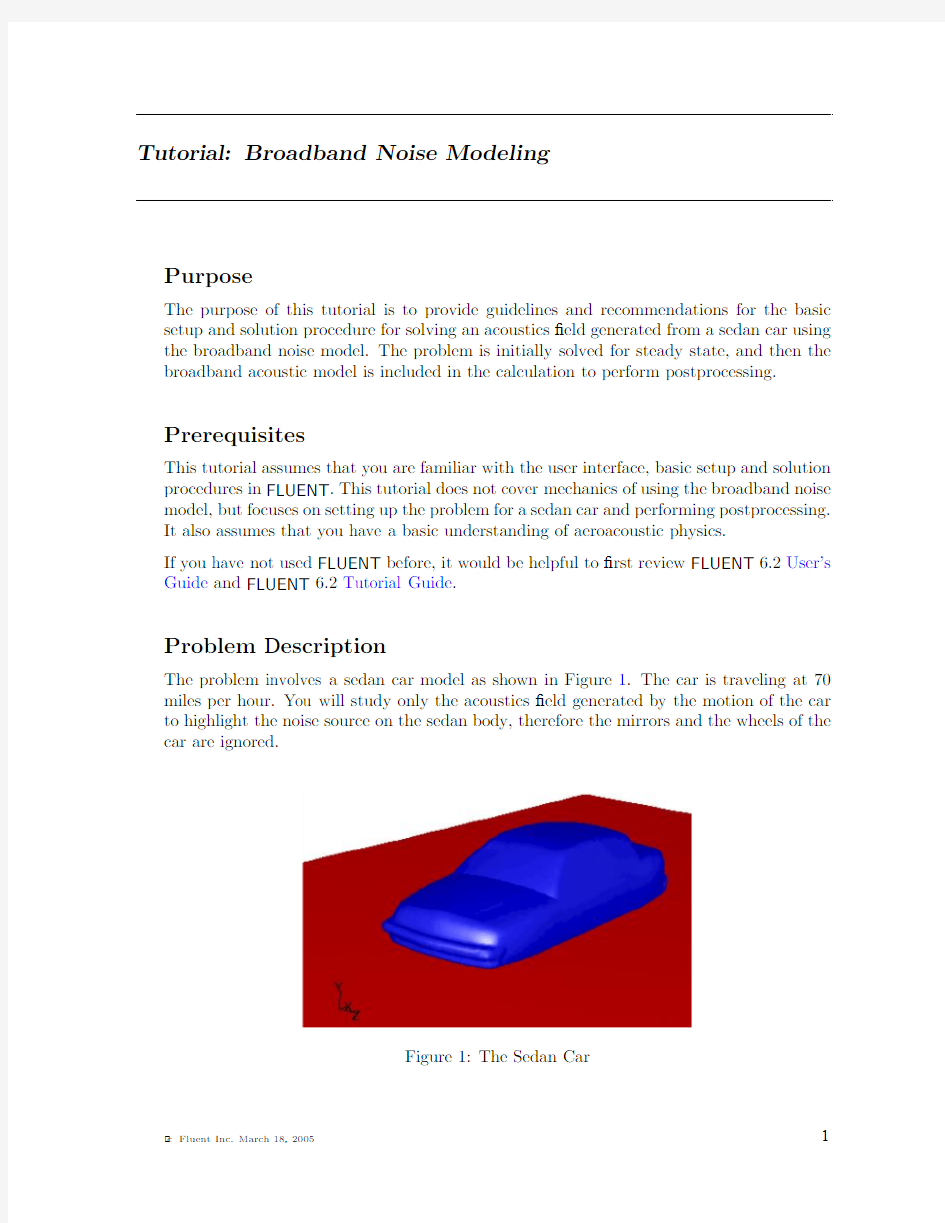
The problem involves a sedan car model as shown in Figure1.The car is traveling at70 miles per hour.You will study only the acoustics?eld generated by the motion of the car to highlight the noise source on the sedan body,therefore the mirrors and the wheels of the car are ignored.
Figure1:The Sedan Car
Broadband Noise Modeling
Preparation
1.Copy the mesh?le,sedan-acoustics.msh from the input?le into your working di-
rectory.
2.Start the3D version of FLUENT.
Setup and Solution
Step1:Grid
1.Read the mesh?le,sedan-acoustics.msh.
File?→Read?→Case...
2.Check the grid.
Grid?→Check...
3.Keep default scale for the grid.
Grid?→Scale...
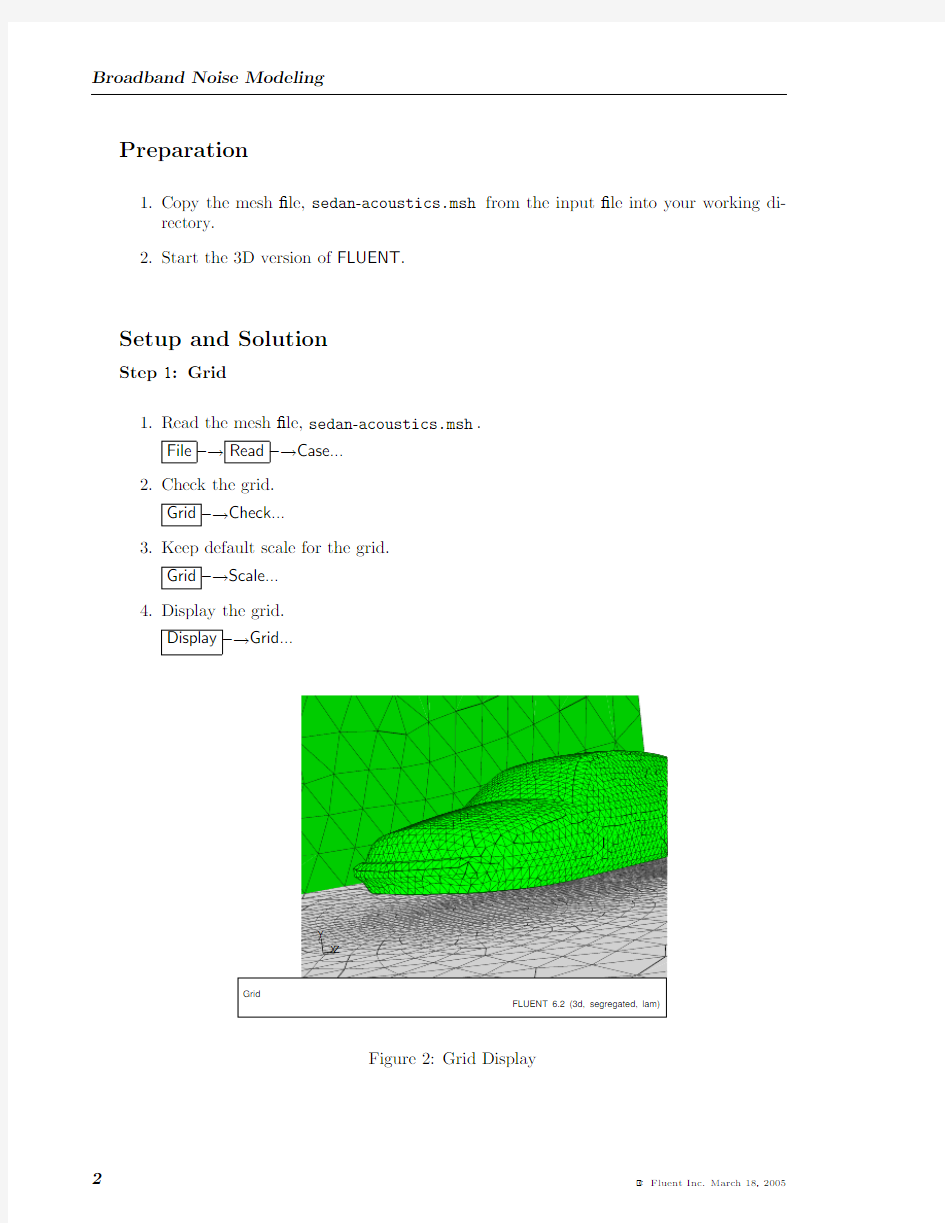
4.Display the grid.
Display?→Grid...
Figure2:Grid Display
Broadband Noise Modeling Step2:Models
1.Keep the default solver settings.
De?ne?→Models?→Solver...
2.Enable the standard k-epsilon turbulence model.
De?ne?→Models?→Viscous...
Step3:Materials
De?ne?→Materials...
1.Keep the default selection of air in the Materials panel.
Step4:Operating Conditions
De?ne?→Operating Conditions...
1.Keep the default operating conditions.
Step5:Boundary Conditions
De?ne?→Boundary Conditions...
1.Set the boundary conditions for velocity inlet(inlet).
(a)Under Zone,select inlet.
The Type will be reported as velocity-inlet.
(b)Click Set...to open the Velocity Inlet panel.
Broadband Noise Modeling
i.Specify a value of31for Velocity Magnitude.
ii.Select Intensity and Length Scale in the Turbulence Speci?cation Method drop-down list.
iii.Specify a value of2and0.35for Turbulence Intensity and Turbulence Length Scale respectively.
2.Set the boundary conditions for pressure outlet(outlet)as shown in the panel.
3.Keep the default boundary conditions for other walls.
Broadband Noise Modeling Step6:Solution
1.Retain the default under-relaxation factors and discretization schemes.
Solve?→Controls?→Solution...
2.Enable the plotting of residuals during the calculation(Figure3).
Solve?→Monitors?→Residual...
3.Initialize the solution.
Solve?→Initialize?→Initialize...
(a)Select inlet in the Compute From drop-down list and click Init.
4.Write the case?le(sedan.cas.gz).
5.Start the calculation by requesting70iterations.
Solve?→Iterate...
6.Write the data?le(sedan.dat.gz).
Broadband Noise Modeling
Figure3:Scaled Residuals
Step7:Enable the Broadband Acoustic Model
De?ne?→Models?→Acoustics...
1.Under Model,select Broadband Noise Sources.
(a)Specify a value4e-10for Reference Acoustic Power(w).
(b)Set the Number of Realizations to50.
Broadband Noise Modeling
(c)Retain the default values for the rest of the model constants and click OK to
close the panel.
Step8:Postprocessing
1.Display the?lled contours of Acoustics Power Level(dB)on the surfaces of the sedan
car,i.e.,front,rear,and cabinet(Figure4).
Display?→Contours...
(a)Under Options,select Filled.
(b)Select Acoustics...and Acoustic Power Level(dB)from the Contours of drop-down
lists.
(c)Under Surfaces,select front,rear,and cabinet.
(d)Click Display.
2.Similarly,display the?lled contours of Surface Acoustics Power Level(dB)(Figure5),
and Lilley’s Total Noise Source(Figure6)on the surfaces of the sedan car.
Broadband Noise Modeling
Figure4:Contours of Acoustic Power Level
Figure5:Contours of Surface Acoustics Power Level
Broadband Noise Modeling
Figure6:Contours of Lilley’s Total Noise Source
Summary
This tutorial demonstrated the use of FLUENT’s broadband noise acoustic model to solve an acoustics?eld generated from a sedan car.You have learned how to set up the relevant parameters and postprocess the noise signals to highlight the source of noise on the sedan car body.
fluent噪声培训资料(上)
Tutorial:Modeling Flow-Induced(Aeroacoustic)Noise Problems Using FLUENT Introduction This tutorial demonstrates how to model2D turbulent?ow across a circular cylinder using large eddy simulation(LES)and compute?ow-induced(aeroacoustic)noise using FLUENT’s acoustics model. You will learn how to: ?Perform a2D large eddy simulation. ?Set parameters for an aeroacoustic calculation. ?Save acoustic source data for an acoustic calculation. ?Postprocess aeroacoustic results. Prerequisites This tutorial assumes that you are familiar with the FLUENT interface and that you have a good understanding of basic setup and solution procedures.Some steps will not be shown explicitly. In this tutorial you will use the acoustics model.If you have not used this feature before,?rst read Chapter21,Predicting Aerodynamically Generated Noise,of the FLUENT6.2 User’s Guide
