湖南电大2014年1月高级商务英语试题

湖南广播电视大学外语教研室试卷代号:7660
湖南广播电视大学2014年1月开放教育期末考试
高级商务英语试题
2013年12月
注意事项
一、将你的准考证号、学生证号、姓名及分校(工作站)的名称填
写在答题纸的规定栏内。考试结束后,把试卷和答题纸放在桌上。
试卷和答题纸均不得带出考场;
二、仔细读懂题目的说明,并按题目的要求答题。答案一定要写在
答题纸的指定位置上,写在试卷上的答案无效;
三、用蓝、黑圆珠笔或钢笔答题,使用铅笔无效。
Part I Vocabulary and Structure ( 30 分)
Section 1 (1-10 题,每题1分,共10分)
Match the words on the left with their definitions on the right.
Section 2(11-20题,每题2分,共20分)
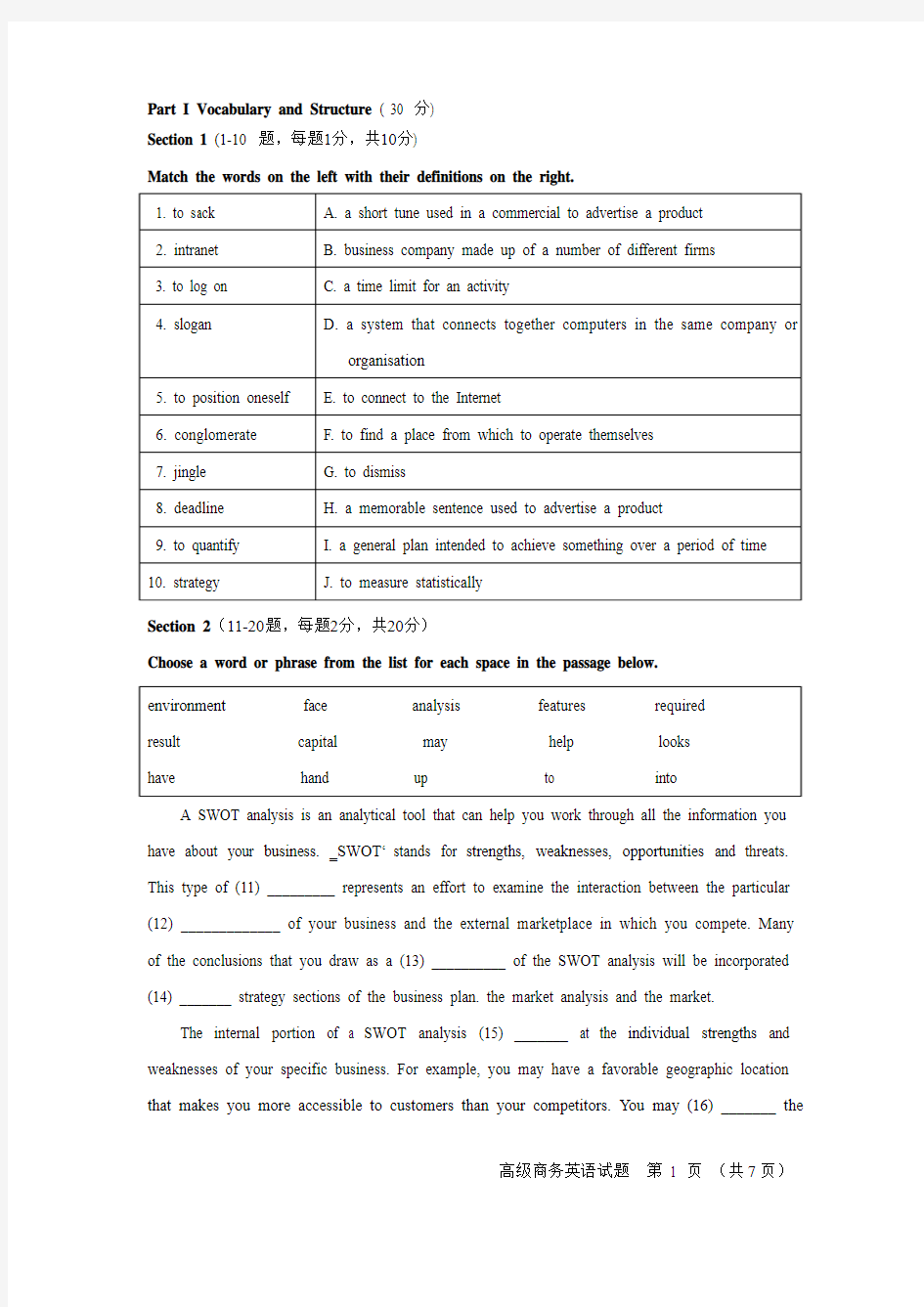
Choose a word or phrase from the list for each space in the passage below.
A SWOT analysis is an analytical tool that can help you work through all the information you have about your business. ?SWOT‘stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. This type of (11) _________ represents an effort to examine the interaction between the particular (12) _____________ of your business and the external marketplace in which you compete. Many of the conclusions that you draw as a (13) __________ of the SWOT analysis will be incorporated (14) _______ strategy sections of the business plan. the market analysis and the market.
The internal portion of a SWOT analysis (15) _______ at the individual strengths and weaknesses of your specific business. For example, you may have a favorable geographic location that makes you more accessible to customers than your competitors. You may (16) _______ the
other (17) _______ invested in state-of-art equipment that only recently became available. On the other (18) ________, you may have problems managing your inventory or you may have employees who just are not (19) _______ to the tasks that will be required to implement your plan.
Similarly, the external analysis looks at the opportunities presented by the marketplace and the threats that you face in your chosen market. Be as accurate as possible in assessing the market (20) ______ in which you do business. Identify those areas in which your competitors pose a threat.
Part 2 Reading (35 分)
Section 1 (21-30题,每题2分,共20分)
Choose the best answer according to the information provided in the 2 passages.
Passage One
What is the purpose of a marketing system in a society? One very common view is that it should encourage consumption. In theory, if more people buy more things, the demand for goods will increase. And if demand increases , this will result in higher production , more employment and more ―wealth‖—the main indicators of a healthy economy. Finally it is generally believed that the more people consume –the more goods and services they buy the happier they will be.
But, some experts disagree with this view. They feel that increasing consumer satisfaction is more important than making consumers buy more. They say that manufacturers should concentrate on producing goods that suit the tastes and needs of consumers. If customers find goods that suit their tastes and needs , this will help to improve their lifestyles , and they will feel satisfied.
Unfortunately, increasing the amount of choice also has some disadvantages. Firstly, when a company increases the variety of products this also increases the cost of production. So, goods and services tend to become more expensive. And higher prices lead to decreasing sales.
Secondly, greater variety of products means that more money needs to be spent on market research, to find exactly what the customers want.
Thirdly, consumers themselves have to spend more time and effort looking at a variety of products, before they decide which one suits their needs. If there wasn‘t so much choice, the
customers would have more time, and this time could be spent buying more things.
Finally, having more products to choose from does not necessarily increase the consumer‘s real choice, because such products may be very similar to other brands of the same product. Advertisers would like us to believe that their washing powder is better than any other.
They are always telling us that their brand gives us a ―white wash‖than that of their competitors. But, in fact, one detergent powder is very much the same as any other, and it really doesn‘t matter which one we buy. This same problem can occur with all kinds of products from beer and cigarettes to toothpaste and toilet soap.
Perhaps the most important purpose of a marketing system is to improve the quality of our lives. We have to consider not just the amount we buy, but also about how easily available products are , whether we can afford them , and whether we are satisfied by their quality.
For a company the most important thing is whether the people really like the product. No matter how much marketing a company does , if in the end people don't enjoy using the product, then the marketing has failed.
21. Most people think that the purpose of a marketing system is ______.
A. to keep consumers happy by providing more choice
B. to improve customer satisfaction by improving quality
C. to satisfy people's needs by selling them more products
D. to increase consumption
22. We know that an economy is doing well if ______.
A. people buy more things
B. people own more things
C. production and employment rise and more money circulates
D. people seem satisfied
23. Besides choice, the three things which are important in improving people's lives are ______.
A. quantity, quality and satisfaction
B. quality, availability and affordability
C. suitability, satisfaction and quantity
D. necessity, cost and quality
24. Beer, cigarettes and face cream are all examples of ______.
A. products which everybody needs
B. products which are very similar, whichever brand you choose
C. products of which the consumer has little choice
D. products for which it is not necessary to provide choice
25. The most important factor which influences the choice of products is ________.
A. whether people like them
B. whether they have been marketed properly
C. how much time it takes to choose them
D. whether there are enough of them Passage Two
Getting the Most Out of Meetings
One aspect of business life which many managers are unhappy with is the need to attend meetings. Research indicates that managers well spend between a third and a half of their working lives in meetings. Although most managers would agree that it is hard to think of an alternative to meetings, as a means of considering information and making collective decisions, their length and frequency can cause problems with the workload of even the best-organised executives.
Meetings work best if they take place only when necessary and not as a matter of routine. One example of this is the discussion of personal or career matters between members of staff and their line and personnel manager. Another is during the early stages of a project when the team managing it needs to learn to understand and trust one another.
Once it has been decided that a meeting is necessary, decisions need to be taken about who will attend and about the location and length of the meeting. People should only be invited to attend if they are directly involved in the matters under discussion and the agenda should be distributed well in advance. An agenda is vital because it acts as a road map to keep discussion focused and within the time limit allocated. This is also the responsibility of the person chairing the meeting, who should encourage those who say little to speak and stop those who have a great deal to say from talking too much.
At the end of a well organised meeting, people will feel that the meeting has been a success and be pleased they were invited. They will know not only what decisions were made but also the reasons for these decisions. Unfortunately, at the end of a badly organised meeting those present will leave feeling that they have wasted their time and that nothing worthwhile has been achieved.
Much thought has been given over the years to ways of keeping meetings short. One man who has no intention of spending half his working life in meetings is Roland Winterson, chief executive of a large manufacturing company. He believes that meetings should be short, sharp and infrequent. ?I try to hold no more than two or three meetings a week, attended by a maximum of three people for no longer than half an hour,‘he says. ?They are clearly aimed at achieving a specific objective, such as making a decision or planning a strategy, and are based on careful preparation. I draw up the agenda for every meeting and calculate it in advance; those attending are expected to study it carefully and should be prepared to both ask and answer questions. Managers are best employed carrying out tasks directly connected with their jobs not attending endless meetings. In business, time is money and spending it in needless meetings that don‘t achieve anything can be very costly. Executives should follow the example of lawyers and put a cost on each hour of their time and then decide whether attending a long meeting really is the best way to spend their time.‘
26. What do most managers think about meetings?
A. Meetings take up most of their working life.
B. Meetings allow them to monitor decision-making.
C. Meetings prevent them from establishing a routine.
D. Meetings are the only way they know of achieving certain objectives.
27. According to the writer, the agenda is important because it ________.
A. is seen by everybody before the meeting
B. helps to give direction to the discussions
C. contains items of interest to all those present
D. shows who should speak at each stage of the meeting
28. The writer says that people leaving a well-organised meeting will understand ________.
A. the reason for their invitation to attend
B. how the decisions taken were relevant to them
C. the importance of proposals under discussion
D. why certain courses of action were agreed upon
29. What does Roland Winterson say about the meetings that he organises?
A. He aims to hold them on a regular basis.
B. He ensures that they have a definite purpose.
C. He uses them to make decisions about strategy.
D. He requires his managers to draw up the agenda.
30. What is Roland Winterson‘s opinion about meetings?
A. They can be a bad use of a manager‘s time.
B. Their importance is often underestimated.
C. They frequently result in wrong decisions.
D. Their effectiveness could be improved with better plans.
Section 2 (31-35题,每题3分,共15分)
Read the following text and answer questions.
Passage Three
It’s a Small World after All …
Take some of the world's best known brand names-Coca Cola, British Airways, The Times of London. What do they all have in common? Each one of them is run by an Australian. In fact, the World Bank is run by an Australian too. As Dame Edna would say—spooky!
We may conclude, therefore, that the Australians run the world. Except, of course, they don‘t. So who does? Democratically elected political leaders, answerable to their own voters? Or powerful global corporations, answerable to their own shareholders, and interested only in profit?
Ever since the violent public protests at the World Trade Organisation meeting in Seattle in the autumn of 1999, the word ―globali s ation‖has come to be used as a weapon in the war of words over the way the world is developing. It is a wonderfully vague, all encompassing term,
which can mean more or less whatever you want it to mean. My favourite definition is ―globalisation = everything that is happening.‖
Imagine a high school kid playing basketball—he‘s wearing a sports shirt with the name of his favourite team on it. Probably an American team, on a shirt that may well have been designed in Europe and manufactured in Southeast Asia. The same goes for the shoes on his feet, the designer sunglasses on his nose as he saunters home, and the funky sports bag slung over his shoulder. It doesn‘t matter if you‘re in Cape Town, Copacabana, Cologne or Kowloon—that‘s globalisation.
And what‘s made it all possible is the communications revolution. Little more than 100 years ago, if I had designed a shirt here in London, the only way to have had it made in Hong Kong would have been to send the designs, by courier, using horses and ships, halfway round the world. If I‘d wanted to pay someone to make it, the money would have gone the same way. Now, with a click of my computer mouse, my designs can be in Hong Kong, Helsinki and Houston in an inst ant. So can my money. That‘s globalisation.
And yet, t hree quarters of all the world‘s telephone lines are in the richest countries where only one-fifth of the world‘s population live. Whereas 40 years ago, the people living in the richest countries earned on average 30 times more than those in the poorest, now they earn 80 times more. According to the World Bank, two billion people have been left behind by the globalisation revolution, most of them in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East and the countries of the former Soviet Union.
And although everyone now seems to pay lip service to the notion of free trade, it‘s not free yet. The international development charity Oxfam says that the rich countries of the northern hemisphere still have trade barriers in place that cost the developing nations US$700 billion a year in lost exports. Most of this is in agriculture and textiles, which means that millions of poor farmers are still far from seeing the supposed benefits of the new global economy.
As for the global corporations , every time we buy our washing powder (Unilever) , fill our cars with petrol (Shell) , or wear a pair of blue jeans (Levi‘s),perhaps we should pause for just a moment to think of those who have sweated to manufacture the product we‘re buying. So, is globalisation good for us? It depends on who you mean by ?us‘.
31. Why may one conclude that the Australians run the world?
32. What does the example of the high school kid tell us about globalisation?
43. What has changed with the communications revolution?
34. What evidence is given to show that globalisation hasn‘t benefited poor countries?
35. What is the writer‘s opinion of globalisation?
Part III Short-Answer Questions (15分)
Answer the following questions based on what you have learned from the textbook. You should use complete sentences. (36-38题,每题5分,共15分)
36. List at least five kinds of market research.
37. What is the SMART action plan?
38. What does the term TQM mean?
Part IV Translation (20分)
Translate the following passage into Chinese. (1题,20分)
39.
China Backs EU Bailout Measures
Chinese Vice Premier Wang Yang said Tuesday that China supports the measures taken by the European Union and International Monetary Fund to bail out certain European countries and stabilize the financial markets. Speaking at the third EU-China High Level Economic and Trade Dialogue, Mr. Wang said China hopes th e effects of the European Union‘s measures to address the Euro-zone debt crisis become apparent as soon as possible. Mr. Wang‘s statement is the latest China‘s leaders over the past year expressing support for measures taken to address the Euro-zone crisis. The comments gave the Euro positive momentum in currency markets during the Asia day, though the currency later fell after ratings firm Moody's Investors Service warned of a possible debt downgrade to Portugal.
试卷代号:7660
湖南广播电视大学2014年1月开放教育期末考试
高级商务英语试题答题纸
Part I Vocabulary and Structure ( 30 分)
Section 1 (1-10 题,每题1分,共10分)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Section 2 (11-20题,每题2分,共20分)
11. 12. 13. 14. 15.
16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
Part II Reading (35 分)
Section 1(21-30题,每题2分,共20分)
Passage One
21. 22. 23. 24. 25.
Passage Two
26. 27. 28. 29. 30.
Section 2(31-35题,每题3分,共15分)
Passage Three
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
Part III Short-Answer Questions (15分) Answer the following questions (36-38题,每题5分,共15分) 36.
37.
38.
Part IV. Translation (20分)
Translate the following passage into Chinese. (1题,20分)
39.
试卷代号:7660
湖南广播电视大学2014年1月开放教育期末考试
高级商务英语试题参考答案及评分标准
Part 1 Vocabulary and Structure ( 30 分)
Section 1 (1-10 题,每题1分,共10分)
Match the words on the left with their definitions on the right.
1. G
2. D
3. E
4. H
5. F
6. B
7. A
8. C
9. J 10. I
Section 2 (11-20题,每题2分,共20分)
11. analysis 12. features 13. result 14. into 15. looks
16. have 17. capital 18. hand 19. up 20. environment
Part 2 Reading (35 分)
Section 1 (21-30题,每题2分,共20分)
Passage One
21. D 22. C 23. B 24. B 25. A
Passage Two
26. D 27. B 28. D 29. B 30. A
Section 2 (31-35题,每题3分,共15分)
Passage Three
31. Beca use they run some of the world‘s most important companies and organisations such as
Coca Cola, British Airways, Times and the World Bank.
32. Manufactured goods may have been designed and made in different parts of the world.
33. The flow of information and money can go much faster than before.
34. They have only one-fourth of the world‘s telephone lines. Their citizens earn about 80 times
less than the citizens of rich countries. Their exports, mainly agricultural products and
textiles, are subject to trade barriers.
35. On the whole, globalisation benefits the rich more than the poor.
Part 3 Short-Answer Questions(15分)
Answer the following questions based on what you have learned from the textbook. You should use complete sentences. (36-38题,每题5分,共15分)
36. They are attitude research, motivational research, qualitative market research , desk research ,
market communications research , omnibus survey , and quantitative market research etc. (If five of these are listed, 5 full points can be offered. )
37. SMART, a planning tool, stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timed.
They are a set of criteria by which marketing objectives are assessed.
38. TQM, total quality management, is an approach to management which involves a complete
dedication to the idea of quality. Total means that everyone in the organisation is involved in the final product or service to the customer. Quality concerns the objective, measurable and manageable criteria that everyone must understand and commit to. Management is a proactive rather than a reactive process, recognising that TQM is a managed process which involves people, systems and supporting tools and techniques.
Part IV. Translation (20分)
Translate the following passage into Chinese. (1题,20分)
39.
中国支持欧盟救市计划
中国国务院副总理汪洋周二说,中国支持欧盟(European Union)和国际货币基金组织(IMF)为救助某些欧洲国家以及稳定金融市场而采取的举措。汪洋在第三次中欧经贸高层对话中说,中国希望欧盟为解决欧元区债务危机而采取的措施能尽快产生明显效果。汪洋的讲话是中国领导人在过去一年中最近一次对为解决欧元区危机而采取的措施表示支持。这番言论在汇市亚洲交易时段中为欧元提供了上行动能,但欧元随后下跌,因为评级机构穆迪投资者服务公司(Moody‘s Investors Service)警告说可能下调葡萄牙的债务评级。
评分细则:
本题为英译汉,计20分。评分分为5个档次;先根据译文整体结构和内容确定基本档次,再以该档次要求来衡量、确定最后得分。
2019电大网考计算机应用基础统考试题真题及答案必考重点
电大计算机应用基础1 一、单选题 1、第一台电子计算机是1946年在美国研制成功的,该机的英文 缩写名是 _______ 。答案:A A : ENIAC B : EDVA C C : EDSAC D : MARK 2、关于计算机的分类方法有多种,下列选项中不属于按计算机 处理数据的方式进行分类的是 ________ 。答案:B A:电子数字计算机B :通用计算机 C :电子模拟计算机 D :数模混合计算机 3、以下不属于电子数字计算机特点的是 __________ 。答案:C A :运算快速 B :计算精度高 C :形状粗笨 D :通用性强 4、利用计算机来模仿人的高级思维活动称为____。答案:D A :数据处理 B :自动控制 C :计算机辅助系统 D :人工智能 5、在计算机领域,客观事物的属性表示为__________ 。答案:A A :数据 B :数值 C :模拟量 D :信息 6、组成计算机主机的主要是 _____ 。答案:B A :运算器和控制器 B :中央处理器和主存储器 C :运算器和外设 D :运算器和存储器 7、指令的操作码表示的是 ________ 。答案:A A :做什么操作 B :停止操作 C :操作结果 D :操作地址 8、某单位的人事管理程序属于 ______ 。答案:C A :系统程序 B :系统软件 C :应用软件 D :目标软件 9、冯?诺依曼结构计算机的五大基本构件包括运算器、存储器、 输入设备、输岀设备和 ________ 。答案:B A :显示器 B :控制器 C :硬盘存储器 D :鼠标器 10、绘图仪是计算机的输岀图形的输岀设备,同属于输岀设备的还有_______ 。答案:A A :打印机和显示器 B :键盘和显示器 C :鼠标和显示器 D :扫描仪和打印机 11、计算机的主频即计算机的时钟频率,较高的主频用吉赫来表示。其英文缩略语为 ________ 。答案:B A : MHz B : GHz C : GDP D : MIPS 12、下列四组数应依次为二进制、八进制和十六进制,符合这个要求的是 _____。答案:D A : 11, 78, 19 B : 12, 77, 10 C: 12, 80, 10 D: 11, 77, 19 13、下列字符中ASCII码值最小的是 _____ 。答案:B A : a B : A C : f D : Z 14、微型计算机的显示器有阴极射线型的及液晶型两大类。关于它们的使用范围的描述,错误的是_________ 。答案:D A :台式机目前大都采用阴极射线型的 B :笔记本式微型机大都采用液晶型的 C :液晶型的正逐步取代阴极射线型的 D :阴极射线型的正逐步取代液晶型的 15、计算机的主频是它的主要性能指标之一。主要性能指标还包括下列四项中的________ 。答案:D A :键盘键数的多少 B :有无喷墨打印机 C :有无绘图功能 D :字长 16、在Word中,创建表格不应该使用的方法是_____ 。答案:A A :用绘图工具画一个 B :使用工具栏按钮创建 C :使用菜单命令创建 D :使用"表格和边框”工具栏绘制表格 17、在Word的编辑状态下,要在文档中添加符号"①"、"②"、"③"等,应该使用的命令安排 _________ 。答案:D A :"文件”菜单中 B :"编辑”菜单中 C :"格式"菜单中 D :"插入"菜单中 18、在Excel的电子工作表中建立的数据表,通常把每一列称为一 个 _________ 。答案:C A :记录 B :元组 C :属性 D :关键字 19、假定单元格D3中保存的公式为"=B$3+C$3",若把它复制到E4 中,则E4中保存的公式为_________ 。答案:B A : =B$3+C$3 B : =C$3+D$3 C : =B$4+C$4 D : =C&4+D&4 20、当Windows的任务栏在桌面屏幕的底部时,其右端的"指示器"显示的是_______ 。答案:D A :"开始"按钮 B :用于多个应用程序之间切换的图标 C :快速启动工具栏 D :网络连接状态图标、时钟等 21、当一个记事本窗口被关闭,该记事本文件将—。答案:A A :保存在外存中 B :保存在内存中 C :保存在剪贴板中 D :既保存在外存也保存在内存中 22、W indows菜单操作中,如果某个菜单项的颜色暗淡,则表示_D_。A:只要双击,就能选中B :必须连续三击,才能选中 C单击被选中后,还会显示出一个方框要求操作者进一步输入信息 D在当前情况下,这项选择是没有意义的,选中它不会有任何反应 23、屏幕保护程序的主要作用是________ 。答案:A A :保护计算机系统的显示器 B :保护用户的身体 C :保护用户的眼睛 D :减低能耗 24、 __________________________________________ 在查找文件时,通配符*与?的含义是 __________________________________ 。答案:A A : *表示任意多个字符,?表示任意一个字符 B : ?表示任意多个字符,*表示任意一个字符 C : *和?表示乘号和问号 D :查找*.?与?.*的文件是一致的 25、当我们在搜索引擎中输入"申花",想要去查询一些申花企业 的资料时却搜索出了很多申花足球队的新闻,为此我们可以在搜索的时候键入 ____ 。答案:C A :申花&足球 B :申花+足球 C :申花—足球 D :申花OR足球 26、 __________________________________________ 在Internet上收发E-mail的协议不包括 ______________________________ 。答案:C A : SMTP B : POP3 C : ARP D : IMAP 27、在对PowerPoint幻灯片进行自定义动画设置时,可以改变 C o A :幻灯片片间切换的速度 B :幻灯片的背景 C :幻灯片中某一对象的动画效果 D :幻灯片设计模板 28、若要将当前幻灯片全部打印到文件,应进行的操作是_C o A :"文件"T "保存"-"打印文件"
电大网考计算机应用基础统考答案7(00001)
计算机应用基础1 一、单选题 1、第一台电子计算机是1946年在美国研制成功的,该机的英文缩写名是_A:ENIAC 2、关于计算机的分类方法有多种,下列选项中不属于按计算机处理数据的方式进行分类的是B:通用计算机。 3、以下不属于电子数字计算机特点的是______。 A:运算快速 B:计算精度高 C:形状粗笨 D:通用性强 答案: C 4、利用计算机来模仿人的高级思维活动称为____。 A:数据处理 B:自动控制 C:计算机辅助系统 D:人工智能 答案: D 5、在计算机领域,客观事物的属性表示为______。 A:数据 B:数值 C:模拟量 D:信息 答案: A 6、组成计算机主机的主要是____。 A:运算器和控制器 B:中央处理器和主存储器 C:运算器和外设 D:运算器和存储器 答案: B 7、指令的操作码表示的是______。 A:做什么操作 B:停止操作 C:操作结果 D:操作地址 答案: A 8、某单位的人事管理程序属于____。 A:系统程序 B:系统软件 C:应用软件 D:目标软件 答案: C 9、冯·诺依曼结构计算机的五大基本构件包括运算器、存储器、输入设备、输出设备和______。 A:显示器 B:控制器 C:硬盘存储器 D:鼠标器 答案: B 10、绘图仪是计算机 的输出图形的输出设 备,同属于输出设备 的还有______。 A:打印机和显示 器 B:键盘和显示器 C:鼠标和显示器 D:扫描仪和打印 机 答案: A 11、计算机的主频即 计算机的时钟频率, 较高的主频用吉赫来 表示。其英文缩略语 为______。 A:MHz B:GHz C:GDP D:MIPS 答案: B 12、下列四组数应依 次为二进制、八进制 和十六进制,符合这 个要求的是____。 A:11,78,19 B:12,77,10 C:12,80,10 D:11,77,19 答案: D 13、下列字符中ASCII 码值最小的是____。 A:a B:A C:f D:Z 答案: B 14、微型计算机的显 示器有阴极射线型的 及液晶型两大类。关 于它们的使用范围的 描述,错误的是 ______。 A:台式机目前大 都采用阴极射线型的 B:笔记本式微型 机大都采用液晶型的 C:液晶型的正逐 步取代阴极射线型的 D:阴极射线型的 正逐步取代液晶型的 答案: D 15、计算机的主频是 它的主要性能指标之 一。主要性能指标还 包括下列四项中的 ______。 A:键盘键数的多 少 B:有无喷墨打印 机 C:有无绘图功能 D:字长 答案: D 16、在Word中,创建 表格不应该使用的方 法是____。 A:用绘图工具画 一个 B:使用工具栏按 钮创建 C:使用菜单命令 创建 D:使用"表格和边 框"工具栏绘制表格 答案: A 17、在Word的编辑状 态下,要在文档中添 加符号"①"、"②"、" ③"等,应该使用的命 令安排______。 A:"文件"菜单中 B:"编辑"菜单中 C:"格式"菜单中 D:"插入"菜单中 答案: D 18、在Excel的电子工 作表中建立的数据 表,通常把每一列称 为一个________。 A:记录 B:元组 C:属性 D:关键字 答案: C 19、假定单元格D3中 保存的公式为"=B$3+C$3",若把它复制到 E4中,则E4中保存的公式为________。 A:=B$3+C$3 B:=C$3+D$3 C:=B$4+C$4 D:=C&4+D&4 答案: B 20、当Windows的任务栏在桌面屏幕的底 部时,其右端的"指示器"显示的是____。 A:"开始"按钮 B:用于多个应用程序之间切换的图标 C:快速启动工具栏 D:网络连接状态图标、时钟等 答案: D 21、当一个记事本窗口被关闭,该记事 本文件将______。 A:保存在外存中 B:保存在内存中 C:保存在剪贴板中 D:既保存在外存也保存在内存中 答案: A 22、Windows菜单操作中,如果某个菜单 项的颜色暗淡,则表示____。 A:只要双击,就能选中 B:必须连续三击,才能选中 C:单击被选中后,还会显示出一个方 框要求操作者进一步输入信息 D:在当前情况下,这项选择是没有意 义的,选中它不会有任何反应 答案: D 23、屏幕保护程序的主要作用是 ______。 A:保护计算机系统的显示器 B:保护用户的身体 C:保护用户的眼睛 D:减低能耗 答案: D 24、在查找文件时,通配符*与?的含义 是____。 A:*表示任意多个字符,?表示任意 一个字符 B:?表示任意多个字符,*表示任意 一个字符 C:*和?表示乘号和问号 D:查找*.?与?.*的文件是一致的 答案: A 25、当我们在搜索引擎中输入"申花", 想要去查询一些申花企业的资料时却搜索 出了很多申花足球队的新闻,为此我们可 以在搜索的时候键入____。 A:申花&足球 1 / 4
电大本科计算机统考网考操作题题库小抄最新
WINDOWS 1、请在考生文件夹下完成如下操作: (1)在考生文件夹下建立“图片2”文件夹; (2)在考生文件夹下查找所有的jpg文件,并将文件移动到“图片2”文件夹中; (3)将名为“2.jpg”文件设为只读文件。 操作提示: ①打开考生文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“新建”→“文件夹”,修改新文件夹的默认名称“新建文件夹”为“图片2”。 ②找到考生文件夹下的所有.jpg文件,选择这些文件单击鼠标右键,选择“剪切”;打开“图片2”文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“粘贴”,完成移动文件操作。 ③选择“2.jpg”文件,单击鼠标右键,选择“属性”,在打开的“属性”窗口中选中“只读”复选按钮,最后单击“确定”按钮。 2、请在考生文件夹下完成如下操作: (1)在考生文件夹下建立“WORD文档”文件夹; (2)在考生文件夹下查找“文件操作.doc”文件,将它复制到“WORD 文档”文件夹中。 操作提示: ①打开考生文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“新建”→“文件夹”,修改新文件夹的默认名称“新建文件夹”为“WORD文档”。 ②打开考生文件夹,在上方的工具栏中单击“搜索”按钮,选择“文件或文件夹”命令,打开“搜索”对话框,键入要查找的文件的名字“文件操作.doc”,搜索范围选择考生文件夹所在位置,单击“立即搜索”按钮。 ③在“搜索结果”窗口中单击工具栏中的“文件夹”按钮,左窗格显示整个系统的文件夹树,在右窗格显示搜索结果,选择位于考生文件夹下的“文件操作.doc”文件,执行“编辑”→“复制”命令,通过左窗格打开考生文件夹下“WORD文档”文件夹,执行“编辑”→“粘贴”命令。 3、请在考生文件夹下完成如下操作: (1)在考生文件夹下创建名为“MYFILE”的文件夹;(2)将“MYFILE”文件夹复制到考生文件夹下的“ME”文件夹中,并 将“ME”文件夹改名为“我的文件夹”; (3)查找考生文件夹下的“我的文档.ppt”文件,并为其创建桌面 快捷方式,快捷方式名称为“我的文档.ppt”。 操作提示: ①打开考生文件夹,单击右键选择“新建”→“文件夹”,并且修改文 件夹名称为“MYFILE”。 ②选择“MYFILE”文件夹,单击右键选择复制,打开考生文件夹下的 “ME”文件夹,单击右键选择“粘贴”。并将“ME”文件夹改名为“我的 文件夹”。 ③打开考生文件夹,在上方的工具栏中单击“搜索”按钮,选择“文 件或文件夹”命令,打开“搜索”对话框,键入要查找的文件的名字 “我的文档.ppt”,搜索范围选择考生文件夹所在位置,单击“立即 搜索”按钮。 ④在“搜索结果”窗口中单击工具栏中的“文件夹”按钮,左窗格显示 整个系统的文件夹树,在右窗格显示搜索结果,选择位于考生文件 夹下的“我的文档.ppt”文件。单击右键选择“创建快捷方式”,将快 捷方式剪切并粘贴到桌面,并修改快捷方式名称为“我的文 档.ppt”。 4、请在考生文件夹下完成如下操作: (1)在考生文件夹下建立“日志”文件夹; (2)在考生文件夹下建立“报告”文件夹; (3)在考生文件夹下的“报告”文件夹中建立“进货”、“出售”两个 文件夹; (4)新建一个名为“简历.DAT”的文件,输入内容“销售报告”,并 将其保存在“出售”文件夹中。 (5)在考生文件夹下建立“出售”的快捷图标,快捷方式名为“出 售”。 操作提示: ①打开考生文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“新建”→“文件夹”,修改 新文件夹的默认名称“新建文件夹”为“日志”。 ②打开考生文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“新建”→“文件夹”,修改 新文件夹的默认名称“新建文件夹”为“报告”。 ③打开考生文件夹下的“报告”文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“新建” →“文件夹”,建立“进货”、“出售”两个文件夹。 ④打开“出售”文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“新建”→“文本文档”, 并输入文字“销售报告”,单击“文件”菜单,选择“保存”,修改文件 的名称为“简历”,后缀名改为“.DAT”。 ⑤选中“出售”文件夹,单击鼠标右键选择“复制”;返回考生文件夹 下,单击鼠标右键,选择“粘贴快捷方式”,并修改快捷方式名称为 “出售”。 5、请在考生文件夹下完成如下操作: (1)在考生文件夹下建立“计算机基础练习”文件夹; (2)在“计算机基础练习”文件夹下建立“文字”、“图片”和“多媒体” 三个子文件夹; (3)在考生文件夹下查找一个名为“1.BMP”的图片文件,将它复制 到“图片”文件夹中。 操作提示: ①打开考生文件夹,单击鼠标右键,选择“新建”→“文件夹”,修改 新文件夹的默认名称“新建文件夹”为“计算机基础练习”。双击“计 算机基础练习”文件夹图标,打开该文件夹,分别创建“文字”、“图 片”、“多媒体”三个子文件夹。 ②打开考生文件夹,在上方的工具栏中点击“搜索”按钮,选择“文 件或文件夹”命令,打开“搜索”对话框,键入要查找的文件的名字 “1.BMP”,搜索范围选择考生文件夹所在位置,单击“立即搜索”按 钮。 ③在“搜索结果”窗口中单击工具栏中的“文件夹”按钮,左窗格显示 整个系统的文件夹树,在右窗格显示搜索结果,选择位于考生文件 夹下的“1.BMP”文件,执行“编辑”→“复制”命令,通过左窗格打开 考生文件夹下“计算机基础练习”中的子文件夹“图片”,执行“编辑” →“粘贴”命令。 6、请在考生文件夹下完成如下操作: (1)在考生文件夹下建立“user1”、“user2”两个文件夹; (2)通过资源管理器,打开考生文件夹下的“program”文件夹,将 文件夹中的“张三.zip”、“李四.zip”和“王五.zip”文件复制到 “user1”文件夹中。
新剑桥商务英语高级习题答案
新剑桥商务英语高级习题 答案 Last revision date: 13 December 2020.
English for Business Studies Key to Unit 01: The three sectors of the economy This unit covers a lot of basic vocabulary concerning developed economies much of it in an extract from a well-known British novel. It also discusses the evolution of the economy of most of the older industrialized countries, with the decline of manufacturing industry and its replacement by services. There is an extract from a magazine interview with an economist and an interview with a British Member of Parliament on this issue. 1a Vocabulary p09 Identify the most prominent features in this photograph, which illustrates various important elements of the infrastructure of a modern industrialized country. The photo clearly shows a large factory (the Unilever factory in Warrington, England) in the center, with more factories, industrial units, or warehouses in the top right-hand corner. The large factory seems to include some office buildings. Also visible are agricultural land (in the background; the land in the foreground doesn’t appear to be cultivated), a river, a railway and several roads, and housing, perhaps with a school in the center of the housing estate top left. 1b Reading p10 What is the key point that this extract is making about economies? The text suggests that most people take for granted the amazing complexity of the economic infrastructure. 1c Comprehension p11 lines 4-7, Robyn sees examples of all three. What are they? Tiny fields (the primary sector), factories (the secondary sector), and railways, motorways, shops, offices, and schools (the tertiary sector). long sentence from lines 12-28 lists a large number of operations belonging to the different sectors of the economy. Classify the 18 activities from the passage Primary sector: digging iron ore, mining coal. Secondary sector: assembling, building, cutting metal, laying cables, milling metal, smelting iron, welding metal. Tertiary sector: advertising products, calculating prices, distributing added value, maintenance, marketing products, packaging products, pumping oil, transportation. you think of three important activities to add to each list (not necessarily in relation to the kettle) Primary sector: farming (agriculture), fishing and forestry Secondary sector: manufacturing, transforming and processing Tertiary sector: financing, designing, retailing
中央电大网考计算机年月题库
电大网考试卷 标红的为答案: 1.当前的计算机一般被认为是第四代计算机,它所采用的逻辑元件是 O A.晶体管 B.大规模集成电路 C.电子管 D. 集成电路 2.一个完备的计算机系统应该包含计算机的_____ 。 A.主机和外设/ B.硬件和软件/ C.控制器和运算器进一步记忆:软件又必须 包括 _____________________________ 。(A.系统软件/ B. 应用软 件) 3. ________________________ 微软的Ofice软件属于。(还可以看p.26-27第51、52、53、54 题)。 A操作系统B 编译系统C 应用软件D系统软件 4.现代计算机之所以能够自动、连续地进行数据处理,主要是因为__________ 。 A.采用了开关电路 B.具有存储程序的功能 C.采用了二进制 “存储程序”原理是科学家冯?诺依曼提出来(参考p.7倒数第1段),再看下一题目: 时至今日,计算机仍采用程序内存(或称存储程序原理),原理的提出者是 O —A.莫尔/ B. 比尔?盖茨/ C.冯?诺依曼/ D.科得(E.F.Codd) 5.以下不属于外部设备是 ______ 。A.输入设备B.中央处理器和主存储器C. 输出设备D .外存— 提示:参考p.7---图1-1,计算机硬件系统的组成…. 6.个人计算机简称PC机这种计算机属于 ____ 。 A.微型计算机/ B.小型计算机/ C. 超级计算机/ D.巨型计算机 7.当前气象预报已广泛采用数值预报方法,这主要涉及计算机应用中的 A.科学计算与辅助设计 B.数据处理和辅助设计 C.科学计算和数据处理 8.计算机当前的应用领域广泛,但据统计其应用最广泛的领域是_________ 。 A.数据处理 B.科学计算 C.辅助设计 D.过程控制 9.计算机辅助教案的英文缩写是________ 。 A.CAD B.CAI C.CAM D.CAT (计算机辅助设计、计算机辅助制造、计算机辅助教案----请你自己对 号入座) 10.利用计算机来模仿人的高级思维活动称为 ____ 。 A.人工智能 B.自动控制 C. 计算机辅助系统 D.数据处理 11.在Win dows中,排列桌面图标顺序 种方法分别按名字、按类型、按大 按 _____ 。 提示,在桌面空白处点右键,如 A.地点 B.修改时间 C.任务 D.属性 正确的说法是的4 小 和 右图。
2018年电大计算机网考统考机考试题及答案-按字母新排版
2018年电大计算机网考统考机考试题及答案-按字母新排版一、计算机基础知识 A:1、ASCII码可以表示的字符个数是______C、128 B:1、保持微型计算机正常运行必不可少的输入/输出设备是______。C、键盘和显示器 C: 1、磁盘和磁盘驱动器是微型计算机的外存储设备,可实现对信息的_____C、输入和输出 2、超市收款台检查货物的条形码,这属于对计算机系统的信息。A、输入 3、采用超大规模集成电路的计算机是计算机发展中的______。A、第4代 D: 1、当前微型计算机采用的外存储器中,大部分不包括______。 D、磁带 2、当运行某个程序时,如果发现存储容量不够,最直接和有效的解决办法是 D、扩充内存 3、当前计算机已应用于各种行业、各种领域,而计算机最早的设计是应用于__ B、科学计算 4、当前计算机的应用领域极为广泛,但其应用最早的领域是____。 B、科学计算 5、当前气象预报已广泛采用数值预报方法,这种预报方法会涉及计算机应用中的____。A、科学 计算和数据处理 6、当前的计算机一般被认为是第四代计算机,它所采用的逻辑元件是__。D、大规模集成电路 7、打印机是计算机系统的常用输出设备,当前输出速度最快的是_____。C、激光打印机 8、第一代计算机体积大、耗电多、性能低、其主要原因是受制于。B、元器件 9、第二代电子计算机的主要元件是。B、晶体管 10、第三代计算机采用的主要电子器件为______。B、小规模集成电路 11、电子计算机按使用范围分类,可以分为______。C、通用计算机和专用计算机 12、电子数字计算机的运算对象是______。D、不连续量(也称数字量) 13、电子计算机按规模划分,可以分为_____。D、巨型计算机、小型计算机和微型计算机 14、第一台电子计算机是1946年在美国研制成功的,该机的英文缩写名是_____。A、ENIAC 15、对磁盘极其驱动器的叙述中有许多专业术语,而与其无关的是_____D、光标 16、对输入到计算机中的某种非数值型数据用二进制数来表示的转换规则被称为_____A、编码 17、对于信息,下列说法错误的是。D、信息可以不依附于某种载体而存在 E;二进制数10110001相对应的十进制数应是_____D、77 F:冯?诺依曼结构计算机的五大基本构件包括运算器、存储器、输入设备、输出设备和____。B、控制器1、冯?诺依曼计算机的基本原理是______。 D、程序存储 G: 1、固定在计算机主机箱箱体上的、起到连接计算机各种部件的纽带和桥梁作用的是_____ B、主 板 2、个人计算机(PC)必备的外部设备是____。B、显示器和键盘 3、构成计算机物理实体的部件被称为____。 B、计算机硬件 4、个人计算机属于_____。A、微型计算机 5、关于计算机的分类方法有多种,下列选项中不属于按计算机处理数据的方式进行分类的是 ______。B、通用计算机 H:衡量计算机存储能力的指标是。D、存储容量 I:、Inte!公司使用Lsl率先推出微处理器4004,宣布第四代计算机问世是在 D、1971年 J: 1、计算机的技术指标有多种,而最主要的应该是______。 B、主频、字长和内存容量 2、计算机配置的内存的容量为128MB或128MB以上,其中的128MB是指 D、128×1024×1024 个字节 3、计算机断电后,会使存储的数据丢失的存储器是______。A、RAM 4、计算机存储单元中存储的内容______。A、可以是数据和指令 5、计算机鼠标器具有简单、直观、移动速度快等但下列四项中不能用鼠标点击的是。A键盘 6、计算机显示器画面的清晰度决定于显示器的。C分辨率 7、计算机的内存容量可能不同,而计算容量的基本单位都是______。C、字节 8、计算机系统应包括硬件和软件两部分,软件又必须包括______。 B、系统软件 9、计算机执行某种操作的命令被称为______。A、指令 10、计算机的硬件系统由五大部分组成,下列各项中不属于这五大部分的是___B、软件 11、计算机中,运算器的主要功能是完成。C、算术和逻辑运算 12、计算机系统中用来保存程序的数据, 以及运算的中间最后结果的装置是 . B、内存和外存 13、计算机中,完成程序指令指定的基于二进制数的算术运算或逻辑运算的部分是__D、运算器 14、计算机内部用于处理数据和指令的编码是______。B、二进制码 15、计算机一次能处理数据的最大位数称为该机器的______。 B、字长 16、计算机软件分为系统软件和应用软件两大类,下列各项中不属于系统软件的是__ B、办公软件 17、计算机操作系统是一种______。A、系统软件 18、计算机能解决有大量数据和程序语句的问题.起主要作用的因素是。 C、大容量内外存储器 19、计算机系统由硬件系统和软件系统两部分组成,下列选项中不属于硬件系统的是______。 D、
2015年中央电大计算机网考统考机考试题及答案
2015年中央电大计算机网考统考机考试题及答案
2015年中央电大计算机网考统考机考试题及答案 一、计算机基础知识 1、保持微型计算机正常运行必不可少的输入/输出设备是______。C、键盘和显示器C: 1、磁盘和磁盘驱动器是微型计算机的外存储设备,可实现对信息的 _____C、输入和输出2、超市收款台检查货物的条形码,这属于对计算机系统的信息A、输入3、采用超大规模集成电路的计算机是计算机发展中的______。A、第4代 4、个人计算机属于_____。A、微型计算机 5、关于计算机的分类方法有多种,下列选项中不属于按计算机处理数据的方式进行分类的是 ______。B、通用计算机 H:衡量计算机存储能力的指标是。D、存储容量I:、Inte!公司使用Lsl 率先推出微处理器4004,宣布第四代计算机问世是在、1971年J: 1、计算机的技术指标有多种,而最主要的应该是______。B、主频、字长和内存容量 2、计算机配置的内存的容量为128MB或128MB以上,其中的128MB 是指D、128×1024×1024 个字节 3、计算机断电后,会使存储的数据丢失的存储器是______。A、RAM 4、计算机存储单元中存储的内容______。A、可以是数据和指令 5、计算机鼠标器具有简单、直观、移动速度快等但下列四项中不能用鼠标点击的是A键盘 6、计算机显示器画面的清晰度决定于显示器的C分辨率
7、计算机的内存容量可能不同,而计算容量的基本单位都是______。C、字节8、计算机系统应包括硬件和软件两部分,软件又必须包括______。 B、系统软件9、计算机执行某种操作的命令被称为______。A、指令 10、计算机的硬件系统由五大部分组成,下列各项中不属于这五大部分的是___B、软件11、计算机中,运算器的主要功能是完成。C、算术和逻辑运算 12、计算机系统中用来保存程序的数据, 以及运算的中间最后结果的装置是B、内存和外存13、计算机中,完成程序指令指定的基于二进制数的算术运算或逻辑运算的部分是__D、运算器14、计算机内部用于处理数据和指令的编码是______。B、二进制码15、计算机一次能处理数据的最大位数称为该机器的______。B、字长 16、计算机软件分为系统软件和应用软件两大类,下列各项中不属于系统软件的是__ B、办公软件17、计算机操作系统是一种______。A、系统软件 18、计算机能解决有大量数据和程序语句的问题.起主要作用的因素是。C、大容量内外存储器19、计算机系统由硬件系统和软件系统两部分组成,下列选项中不属于硬件系统的是______。D、 系统软件 20、计算机系统由两大部分组成,它们是____。C、硬件系统和软件系统 21、计算机系统中运行的程序、数据及相应的文档的集合称为_______。 B、软件系统 22、计算机系统应包括硬件和软件两个子系统,硬件和软件又必须依次分别包括______。B、中央 处理器和系统软件 23、计算机应用中最诱人、也是难度大且目前研究最为活跃的领域之一是___A、人工智能 1 D:
高级商务英语模拟试题1(可编辑修改word版)
全国职业能力测评考试 高级商务英语模拟试题(一) 第一部分模拟试题 I.In each of the following questions and select a different 1.A、bread B、dream C、lead D、team 2.A、hole B、none C、old D、fold 3.A、house B、south C、touch D、mouth 4.A、bush B、must C、rub D、truck 5.A、ease B、mean C、head D、heat II.The following example from the sentence chosen the right answer 6 、Adults sometimes envy children who play all the time they themselves have to work.rain or shine. A、while B、once C、since D、though 7、Talking to foreigners is fun if you the right time and place. A、locate B、consider C、choose D、decide
8、A person with the blood type AB can any type of blood. A、apply B、recognize C、receive D、absorb 9、In a second-hand bookshop ,Billy came across a book which he thought was certainly a edition. A、rare B、scarce C、seldom D、hardly 10、The red color can stimulate all our ,including appetite. A、thoughts B、worries C、senses D、desires 11、While I was waiting for her ,I killed time looking in the show windows. A、by B、with C、in D、over 12、Mrs.London has that she is unable to get a job. A、such small education B 、so little education C、a such little education D、a so small education 13、I come yesterday ,but I could not. A、was to have B、must C、ought D、have to 14、He treats it a request for information. A、for B、as C、like D、by 15、They promised each other when they went to work. A、get in touch with B、getting in touch with C、to get in touch with D、to get touch with 16、She was too shy to speak . A、in public B、in the public C、in a public D、at public 17、I often thought of my childhood, I lived on a farm. A、when B、which C、where D、who 18、I don’t like this hat.Please show me . A、another B、the other C、others D 、both 19、They shopping,when someone knocked at the door. A、are about to B、are to go C、were about to go D、were to go 20、He gained his by printing of famous writers. A、wealth; work B、wealthy ; works C、wealthy; work D、wealth;works III.The following example from the short space select the right answer Nobody wants to be 21 .Unfortunately our bodies can 22 problems.When we aren’t 23 ,our bodies tell us .Sometimes a part of our bodies hurts. When a part of our bodies 24 ,we say we have aches and pains. We can have aches and pains in 25 parts of the body. We call some simple 26 proplems“aches”.For example, we can have a headache,a toothache,an earache,a backache or a stomachache.Other simple problems are not 27 aches,so we describe them in different ways. For example,we can 28 a sore throat,a sore leg ,a sore toe. “Pain”is another word that we use to 29 a problem.We can have a pain in the chest, a pain in the shoulder or a pain 30 the back.A pain is strong. Also, a pain hurts in a specific place. When aches and pains aren’t too31 ,we can buy medicine in the drugstore . Usually small aches go away 32 .When pain is more serious ,we 33 to visit the doctor(or the dentist).The doctor asks us what our 34 are.The doctor may have to do tests or take Xrays to 35 what is wrong .Then he or she will tell us what to do. 21、A、sleep B、bad C、cold D、sick
电大网考计算机最全题库+操作指南完美版
电大本科《计算机应用基础》网考模拟试卷1 一、单选题 1、第一台电子计算机是1946年在美国研制成功的,该机的英文缩写名是______。 A、ENIAC B、EDV AC C、EDSAC D、MARK 参考答案:A 解析: 一般认为,世界上第一台电子数字计算机于1946年在美国宾夕法尼亚大学研制成功。该计算机的名称为ENIAC。 2、为了实现自动控制处理,需要计算机具有的基础条件是______。 A、存储程序 B、高速度与高精度 C、可靠性与可用性 D、连网能力 参考答案:A 解析: 计算机具有自动控制处理能力。存储程序是计算机工作的一个重要原则,这是计算机能自动控制处理的基础。 3、当前计算机已应用于各种行业、各种领域,而计算机最早的设计是应用于______。 A、数据处理 B、科学计算 C、辅助设计 D、过程控制 参考答案:B 解析: 计算机已普及到各行各业、各种领域,已经无所不在。但早期的电子数字计算机的设计目的是用于快速计算,着重用于军事。而随着计算机技术的发展与应用需求的增加,计算机从主要用于科学和工程计算发展到从事数据处理、辅助设计和过程控制以及人工智能等。 4、在计算机领域,信息是经过转化而成为计算机能够处理的______。 A、数据 B、符号 C、图形
D、数字 参考答案:A 解析: 信息是人们由客观事物得到的。在计算机领域,信息是经过转化而成为计算机能够处理的数据,同时也是经过计算机处理后作为问题解答而输出的数据。 5、将计算机分为通用计算机和专用计算机的分类标准是______。 A、计算机处理数据的方式 B、计算机的使用范围 C、计算机的规模和处理能力 D、计算机出现的时间 参考答案:B 解析: 空 6、计算机中,完成程序指令指定的基于二进制数的算术运算或逻辑运算的部分是______。 A、内存储器 B、输入输出设备 C、外存储器 D、运算器 参考答案:D 解析: 空 7、下列四个计算机存储容量的换算公式中,错误的是______。 A、1KB=1024MB B、1KB=1024B C、1MB=1024KB D、1GB=1024MB 参考答案:A 解析: 空 8、计算机操作系统是一种______。 A、系统软件 B、应用软件 C、工具软件 D、调试软件 参考答案:A 解析: 空 9、计算机系统由硬件系统和软件系统两部分组成,下列选项中不属
历届电大计算机-英语-网考真题答案
但从09年12月份的考试来看,许多题目已经更新了.请大家灵活答题,同时计算机光盘的题目,特别是针对后面exce,word,ppt光盘中的内容,一定要反复做,坚持每天做一次,做错的,看答案后,再来一次,如果光盘里内容每次能做到80分以上,考试100%通过—小语 1.当前的计算机一般被认为是第四代计算机,它所采用的逻辑元件是______。 A.晶体管 B. 大规模集成电路 C.电子管 D. 集成电路 2.一个完备的计算机系统应该包含计算机的____。 A.主机和外设/ B.硬件和软件/ C.控制器和运算器 进一步记忆:软件又必须包括______。(A. 系统软件/ B. 应用软件) 3.微软的Office软件属于______。(还可以看p.26-27第51、52、53、54题)。 A 操作系统 B 编译系统 C 应用软件 D 系统软件 4.现代计算机之所以能够自动、连续地进行数据处理,主要是因为______。 A.采用了开关电路 B.具有存储程序的功能 C.采用了二进制 “存储程序”原理是科学家冯·诺依曼提出来(参考p.7倒数第1段),再看下一题目:时至今日,计算机仍采用程序内存(或称存储程序原理),原理的提出者是____。 A.莫尔/ B.比尔·盖茨/ C.冯·诺依曼/ D.科得( E. F.Codd) 5.以下不属于外部设备是______。 A.输入设备 B.中央处理器和主存储器 C.输出设备D.外存储器 提示:参考p.7---图1-1,计算机硬件系统的组成…. 6.个人计算机简称PC机,这种计算机属于___。 A.微型计算机/ B.小型计算机/ C.超级计算机/ D.巨型计算机 7.当前气象预报已广泛采用数值预报方法,这主要涉及计算机应用中的______。 A.科学计算与辅助设计 B.数据处理和辅助设计 C.科学计算和数据处理 8.计算机当前的应用领域广泛,但据统计其应用最广泛的领域是______。 A.数据处理 B.科学计算 C.辅助设计 D.过程控制 9.计算机辅助教学的英文缩写是______。
