中小企业融资偏好SME外文文献翻译2014年译文4500字

文献出处
Mac an Bhaird C. SME Owners’ Financing P references[J]Resourcing Small and Medium Sized Enterprises., 2014,(5): 77-103.
原文
SME owners’ financing preferences
Mac an Bhaird C. SME
Academic studies investigating the financing of SMEs commonly examine the subject by conducting multivariate regression analysis employing panel data sets consisting of accounting and finance data (see Appendix B for a comprehensive review of this literature). Researchers adopting this approach seek to explain financing choice in terms of firm characteristics such as firm size, age, asset structure, profitability, growth opportunities, and legal organisation. This methodology, whilst beneficial in theory testing and preliminary benchmark studies, neglects one of the most important aspects of small business and entrepreneurship: the central role of the SME owner. Given the primary decision making role of the firm owner, this method excludes a fundamental element of the financing and finance provision in SMEs. The approach adopted in this chapter is to record SME owners’ views on financing their businesses, and the reasons why they choose one type of finance over another, or why they avoid some forms of financing entirely. Whilst this approach may appear self-evident or overly simplistic, it can reveal explanations for observed capital structures and how financial markets and institutions might better respond to the needs of the small business community.
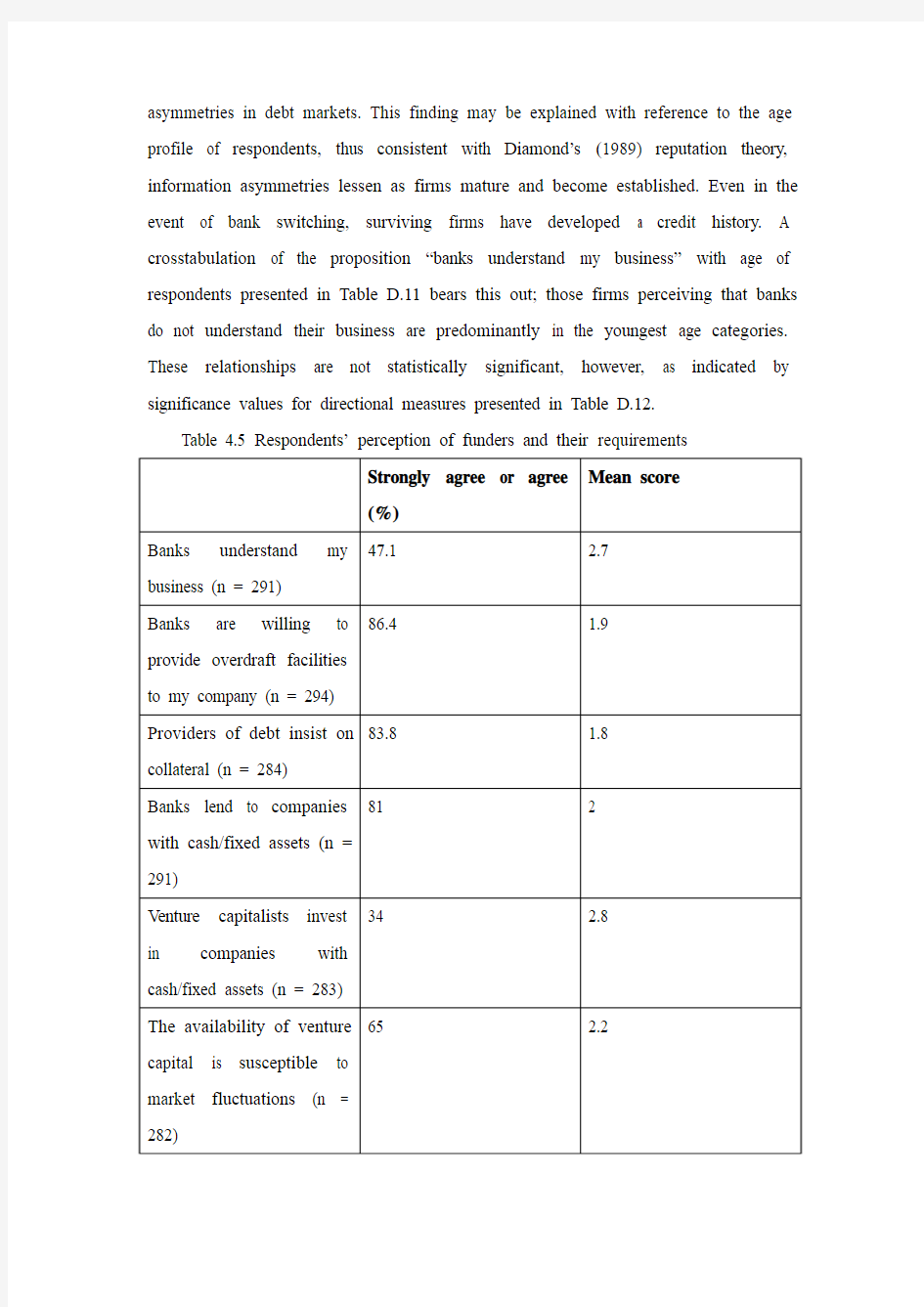
Respondents’ perceptions concerning issues related to funders and their lending practices are reported in Table 4.5. Almost 50% of respondents are of the perception that “banks understand their business,” with 20% disagreeing with this proposition. This result indicates that respondents generally do not perceive information
asymmetries in debt markets. This finding may be explained with reference to the age profile of respondents, thus consistent with Diamond’s (1989) reputation theory, information asymmetries lessen as firms mature and become established. Even in the event of bank switching, surviving firms have developed a credit history. A crosstabulation of the proposition “banks understand my business” with age of respondents presented in Table D.11 bears this out; those firms perceiving that banks do not understand their business are predominantly in the youngest age categories. These relationships are not statistically significant, however, as indicated by significance values for directional measures presented in Table D.12.
Table 4.5 Respondents’ perception of funders and their requirements
Results explain preferences and patterns of financing reported in earlier sections. Respondents’ preference for debt when seeking external finance expressed in Tables 4.1 and 4.2 may be partly explained by firms not perceiving information asymmetries in debt markets. Greater perception of information asymmetries among firms in the youngest age categories is exacerbated by the concentration of 50% of these firms in sectors typified by a high proportion of intangible assets. This finding may also explain the high use of external equity (37% of total financing) by this group reported in Table 2.2, and partly explains the provision of personal assets to secure debt by firm owners in the youngest age category.
A sectoral cross tabulation of the proposition “banks understand my business” presented in Table D.13 reveals that almost 30% of respondents perceiving information asymmetries in debt markets are in the “computer software development and services” sector. This may arise from a relatively young age profile, as over 60% of firms in this sector are under 10 years old. Another relevant factor is the technological nature of the sector, confirming the finding of Hogan and Hutson (2005), that firms in this sector do not perceive information asymmetries in venture capital markets to the same extent that they perceive asymmetries in the bank-client relationship. This may be due to the technical knowledge and specialist skills of venture capitalists in assessing technologically complicated investment projects, and the lack of specialised knowledge by loan assessors in banks.
Almost 90% of respondents believe that “banks are willing to provide overdraft facilities” to their company, as shown in Table 4.5. This result is consistent with empirical evidence highlighting the reliance of SMEs on short-term bank debt (Chittenden et al. 1996), which is even greater in the Irish context (Ayadi 2008). The effect of respondents’ perception may perpetuate this reliance, as firms are more likely to apply for additional short-term debt if they perceive their application will be successful. Respondents’ perception partly explains patterns of financing reported in Table 2.2, indicating that short-term debt was the second most important source of finance after retained profits, comprising an average 22% of capital structures. This
result also supports the contention that financial institutions advance short-term debt facilities more readily, as they usually involve smaller amounts than long-term debt or mortgage finance, and can be recalled at short notice (Esperanca et al. 2003). Additionally, banks may seek to reduce their exposure by advancing debt with a shorter maturity. Respondents’ perception may therefore result from a combination of demand-side and supply-side factors.
Respondents’ perception of the procli vity of financial institutions to seek collateral as security for debt finance is evident from responses to propositions three and four presented in Table 4.5. Eighty five per cent of respondents perceive that “providers of debt insist on collateral,” and 81% perceive that banks lend to firms with tangible assets, such as cash and fixed assets. Respondents’ perceptions may be due to experiences in contracting with financial institutions (results from multivariate models presented in Table 3.10 indicate statistically significant positive relationships between use of short-term, long-term, and total debt, and provision of collateral). Additionally, results from SUR models presented in Table 3.19 indicate statistically significant positive relationships between use of debt and provision of firm assets as collateral for all models, apart from firms in the “other” sector. These results confirm findings of previous studies emphasising the importance of lien-free collateralisable assets in securing debt finance (Heyman et al. 2008). Thus, consistent with Myers (1997), firms whose assets consist primarily of intangibles have most difficulty in accessing bank loans.
Respondents’ perceptions highlight a number of issues for SME financing. Firstly, firms without access to adequate collateralisable assets may be discouraged from applying for debt capital on the basis that they believe it will be unsuccessful (Kon and Storey 2003), which may lead to underinvestment. Secondly, these perceptions may result in overreliance on short-term debt (Chittenden et al. 1996), rather than a more appropriate source, such as long-term debt. This may increase the cost of capital for the firm, as short-term debt is generally more expensive than the latter. Additionally, dependence on short-term debt exposes the firm to liquidity problems if the bank restricts or withdraws this facility at short notice. Furthermore, SMEs may
be compelled to employ more expensive sources of financing, such as debt factoring, invoice discounting or use of trade credit.
Respondents’ perceptions on propositions concerning venture capital funders are also reported in Table 4.5. Venture capital comprises 5% of the capital structures of respondents (as shown in Table 2.2), and this is reflected in responses to questions on venture capital funding. Whilst 34% of respondents agreed with the proposition that “venture capitalists invest in companies with cash/fixed assets,” over 50% expressed no opinion and 15% disagreed. This result suggests that respondents are generally inexperienced with, or ambivalent about venture capital finance. Of those firms in disagreement with this statement, over 50% are in sectors typified by a lack of collateralisable assets, namely the “computer software development and services” and “other services” sectors. This finding suggests that respondents in these sectors are more acquainted or experienced in contracting with venture capitalists.
Sixty five per cent of respondents agree with the statement “the availability of venture capital is su sceptible to market fluctuations,” whilst 32% express no opinion. This result indicates that respondents are aware of fluctuations in venture capital investment activity. One third of those in agreement with this proposition comprise firms in sectors typif ied by a lack of collateralisable assets, namely the “computer software development and services” and “other services” sectors. Once again, this result suggests that respondents in these sectors are more experienced in contracting with venture capitalists. Whilst respondents appear cognisant of the workings of venture capital markets in general, they do not have strong opinions about proposed statements. This may be explained by the relatively small percentage of respondents seeking venture capital. Respond ents in the “computer software development and services” and “other services” sectors appear to have more definite opinions on venture capitalists.
In summary, respondents’ answers to propositions presented in Table 4.5 partially explain motivations behind observed capital structures and stated financing preferences. In general, respondents do not perceive information asymmetries in debt markets. This perception may be partly explained by the age profile of respondents, as
reputation effects (Diamond 1989) overcome these asymmetries. Information asymmetries in debt markets may be higher in practice, however, because the views of non-surviving firms are not reported in this survey. The latter firms may have perceived higher asymmetries in debt markets. Respondents perceive a requirement for collateral to secure debt finance, confirming evidence from previous studies detailing financial institutions’ proclivity for collateral to overcome potential agency problems of moral hazard (Coco 2000; Heyman et al. 2008). An implication of this perception is that firms lacking adequate collateralisable assets may be reluctant to apply for debt finance. Respondents report that financial institutions are willing to advance short-term debt facilities, which may partly explain reliance on this source as the second most important means of financing. Relatively few firms in the sample employ external equity, which is reflected in the ambivalence of respondents to questions on the requirements of venture capitalists.
In this chapter, agency and pecking order theories of capital structure are further explored by consideration of evidence in the form of respondents’ replies to direct questions, and statements proposed in the form of Likert scales. A number of interrelated questions are asked in addressing two primary issues; “What are the financing preferences of respondents?,” and “Why do respondents maintain these preferences?” Replies to these questions facilitate examination of the relevance of theoretical propositions in explai ning respondents’ capital structures, and stated financing preferences.
Respondents’ preferred source of financing is retained profits. Almost 50% indicate a willingness to employ long-term debt finance when required. Eighty per cent of respondents indicate an aversion to raising additional external equity. These preferences are consistent with propositions of the pecking order theory (Myers 1984; Myers and Majluf 1984), although the expressed aversion to external equity suggests that the majority of respondents may adhere to a truncated pecking order. Investigation of the perceived greatest internal growth constraints and primary considerations when raising debt emphasise the importance of profitability in financing investment, and suggest that adherence to a preferred pecking order is
contingent on the profitability of the firm.
Explanations for stated financing preferences of respondents are threefold. The primary reason is desire to retain control of the firm and maintain managerial independence, which is stronger in closely held private limited firms than in firms with wider ownership. Secondly, the main financial objectives of respondents are to maximise profits and sales, which reaffirms financing preferences and emphasises respondents’ primary goal o f maintaining control of the firm. There are sectoral differences in pursuit of this objective; firms in the “computer software development and services” sector are twice as willing to relinquish control as firms in all other sectors, and they consider maximisation of the value of the firm as their primary financial objective. Thirdly, respondents generally do not perceive information asymmetries in debt markets, and believe that financial institutions are willing to provide short-term debt facilities. This is not an unexpected finding given the age profile of respondents, suggesting that information asymmetries are alleviated by reputation effects (Diamond 1989). The majority of firms perceiving information asymmetries in debt markets are in the “computer s oftware development and services” and “other services” sectors. This may be due to a combination of the age profile and technological characteristics of firms in this sector.
Respondents highlighted a number of issues they consider most important when raising external finance that partly explain stated financing preferences and indicate the conditions under which they would consider raising additional finance. By taking these factors into account, funders can improve the efficiency of supply of funds to th e sector. Respondents’ primary concern when raising debt is the cost of finance, highlighting the influence of supply-side factors in the financing decision. An implication of this belief is that firm owners may avoid raising debt in times of high interest rates, resulting in underinvestment. As respondents also express an aversion to external equity, firm growth will be limited to the return on investment of retained profits, leading to lower growth rates. Additionally, as respondents do not believe in accumulating financial slack they may encounter financing problems during an economic recession, particularly if there is a credit squeeze.
Another belief held by respondents is the requirement for collateral to secure debt finance. Respondents in sectors in which asset structures are typified by a high proportion of tangible assets are more likely to apply for debt finance, and are more confident in securing the finance required than respondents in sectors with asset structures typified by a high proportion of intangible assets. The practice of financial institutions in providing debt finance based on collateral rather than profitability is inefficient, and may have a number of adverse consequences for SMEs. Firstly, perception of a lack of sufficient collateralisable assets may result in a reduction of applications for long-term debt finance, leading to underinvestment. Secondly, this belief may result in over-reliance on other sources of finance which are less appropriate and more costly, such as short-term debt, for example. Investigation of respondents’ views on signalling, debt tax shields, timing considerations, and the accumulation of financial slack indicate that these issues are not primary concerns when making the financing decision. Respondents appear more concerned with the issue of raising adequate capital to finance their firm than what they may consider ancillary issues.
译文
中小企业融资偏好
伯哈德
在调查研究中小型企业融资的学术研究中,通常通过多元回归分析来审查这个主题。这一分析利用由会计和财务资料组成的面板数据集(参见本文献的全面回顾附录B)。研究人员利用这种方法,设法据公司特征来解释融资选择。例如,公司规模,企业年龄,资产结构,盈利能力,发展机会和法定组织。这种方法虽然有益于理论检验和初步基准研究,却忽略了小企业和创业中一个最重要的方面。那就是中小型企业业主的核心作用。鉴于企业所有者的主要决策作用,这种方法排除了在中小型企业融资和资金供给的基本要素。本章采用这个方法,是为了记录中小型企业业主对融资的看法,以及他们完全避开有些形式的融资而只选择选择其中一种融资的理由。这种方法可能不证自明地或过于简单地出现,并揭示关于实测资本结构的解释。也可以对金融市场和机构怎样更好的回应小企业的需求做出做更好的解释。
表4.5是受访者对投资者和他们借贷行为的看法。几乎50%的受访者认为“银行了解他们的业务”,而还有20%不同意这一主张。这一结果表明,受访者并没有察觉到债务市场的信息不对称。这一发现可以根据受访者的年龄分布做解释。与黛蒙德(1989)的名誉理论一致,信息不对称性将会随着公司的成熟和成立逐渐降低。即便是在银行转换的情况下,幸存的公司已开发出一种信用记录。表D.11是关于“银行了解我们的业务”的观点和受访者年龄的交叉表。那些认为银行不了解他们业务的公司,是以最年轻的年龄组为主。这个表证实了这一点。如表D.12所示的方向性实施意义上,这些关系在统计上并怎么不重要。
表4.5 投资者中受访者的看法和他们的要求
这些结果可以解释在前章节提到的融资偏好和形式。我们在表 4.1 和 4.2可以看到,受访者为债务寻求外部资金时的优先权。这可以解释在债务市场上没有感知到信息不对称的公司部分解释。将拥有高比例无形资产的领域的50%公司集中了起来。最年轻的年龄组公司之间的信息不对称感知力,因这些公司的集中而更加加重。正如在表2.2看到的那样,这一发现解释了此集团对外部股权(融资总额的37%)的使用高。也部分解释个人资产由公司提供,以确保业主在最年轻年龄组的债务。
在表D.13看到的一样,一个跨领域的“银行了解我们的业务”命题制表显示,几乎30%的受访者察觉到债务市场的信息不对称在“计算机软件开发和服务”的领域。这可能由企业创立史相对比较年轻的状况引起。因为在这个领域,60%以上的公司创立历史都在10年以下。霍根和赫特森(2005年)发现,在这个领域的公司没有察觉到风险资本市场的信息不对称。不像他们察觉银行和顾客关系的不对称那样。另一个相关要素是该领域的技术性质,这实例证实了他们的这一发现。这可能跟风险投资家在评估技术复杂的投资项目时使用的技术知识和专业技能有关,也可能是银行贷款评审们缺乏专业知识所导致的。
如表4.5所示,将近90%的受访者认为,“银行愿意为他们的公司提供透支”。这一结果与强调中小型企业对短期银行债务(奇滕登等。1996年)的依赖是一致。这一依赖在爱尔兰语境(艾亚迪2008)更大,受访者的看法表明这种依赖
中英文文献翻译
毕业设计(论文)外文参考文献及译文 英文题目Component-based Safety Computer of Railway Signal Interlocking System 中文题目模块化安全铁路信号计算机联锁系统 学院自动化与电气工程学院 专业自动控制 姓名葛彦宁 学号 200808746 指导教师贺清 2012年5月30日
Component-based Safety Computer of Railway Signal Interlocking System 1 Introduction Signal Interlocking System is the critical equipment which can guarantee traffic safety and enhance operational efficiency in railway transportation. For a long time, the core control computer adopts in interlocking system is the special customized high-grade safety computer, for example, the SIMIS of Siemens, the EI32 of Nippon Signal, and so on. Along with the rapid development of electronic technology, the customized safety computer is facing severe challenges, for instance, the high development costs, poor usability, weak expansibility and slow technology update. To overcome the flaws of the high-grade special customized computer, the U.S. Department of Defense has put forward the concept:we should adopt commercial standards to replace military norms and standards for meeting consumers’demand [1]. In the meantime, there are several explorations and practices about adopting open system architecture in avionics. The United Stated and Europe have do much research about utilizing cost-effective fault-tolerant computer to replace the dedicated computer in aerospace and other safety-critical fields. In recent years, it is gradually becoming a new trend that the utilization of standardized components in aerospace, industry, transportation and other safety-critical fields. 2 Railways signal interlocking system 2.1 Functions of signal interlocking system The basic function of signal interlocking system is to protect train safety by controlling signal equipments, such as switch points, signals and track units in a station, and it handles routes via a certain interlocking regulation. Since the birth of the railway transportation, signal interlocking system has gone through manual signal, mechanical signal, relay-based interlocking, and the modern computer-based Interlocking System. 2.2 Architecture of signal interlocking system Generally, the Interlocking System has a hierarchical structure. According to the function of equipments, the system can be divided to the function of equipments; the system
中小企业融资外文翻译
本科毕业论文(设计) 外文翻译 原文: Financing of SMEs Abstract The main sources of financing for small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs) are equity, trade credit paid on time, long and short term bank credits, delayed payment on trade credit and other debt. The marginal costs of each financing instrument are driven by asymmetric information and transactions costs associated with nonpayment. According to the Pecking Order Theory, firms will choose the cheapest source in terms of cost. In the case of the static trade-off theory, firms choose finance so that the marginal costs across financing sources are all equal, thus an additional Euro of financing is obtained from all the sources whereas under the Pecking Order Theory the source is determined by how far down the Pecking Order the firm is presently located. In this paper, we argue that both of these theories miss the point that the marginal costs are dependent of the use of the funds, and the asset side of the balance sheet primarily determines the financing source for an additional Euro. An empirical analysis on a unique dataset of Portuguese SME’s confirms that the composition of the asset side of the balance sheet has an impact of the type of financing used and the Pecking Order Theory and the traditional Static Trade-off theory are https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, For SME’s the main sources of financing are equity (internally generated cash), trade credit, bank credit and other debt. The choice of financing is driven by the costs of the sources which is primarily determined by costs of solving the asymmetric information problem and the expected costs associated with non-payment of debt. Asymmetric information costs arise from collecting and analysing information to support the decision of extending credit, and the non-payment costs are from
1外文文献翻译原文及译文汇总
华北电力大学科技学院 毕业设计(论文)附件 外文文献翻译 学号:121912020115姓名:彭钰钊 所在系别:动力工程系专业班级:测控技术与仪器12K1指导教师:李冰 原文标题:Infrared Remote Control System Abstract 2016 年 4 月 19 日
红外遥控系统 摘要 红外数据通信技术是目前在世界范围内被广泛使用的一种无线连接技术,被众多的硬件和软件平台所支持。红外收发器产品具有成本低,小型化,传输速率快,点对点安全传输,不受电磁干扰等特点,可以实现信息在不同产品之间快速、方便、安全地交换与传送,在短距离无线传输方面拥有十分明显的优势。红外遥控收发系统的设计在具有很高的实用价值,目前红外收发器产品在可携式产品中的应用潜力很大。全世界约有1亿5千万台设备采用红外技术,在电子产品和工业设备、医疗设备等领域广泛使用。绝大多数笔记本电脑和手机都配置红外收发器接口。随着红外数据传输技术更加成熟、成本下降,红外收发器在短距离通讯领域必将得到更广泛的应用。 本系统的设计目的是用红外线作为传输媒质来传输用户的操作信息并由接收电路解调出原始信号,主要用到编码芯片和解码芯片对信号进行调制与解调,其中编码芯片用的是台湾生产的PT2262,解码芯片是PT2272。主要工作原理是:利用编码键盘可以为PT2262提供的输入信息,PT2262对输入的信息进行编码并加载到38KHZ的载波上并调制红外发射二极管并辐射到空间,然后再由接收系统接收到发射的信号并解调出原始信息,由PT2272对原信号进行解码以驱动相应的电路完成用户的操作要求。 关键字:红外线;编码;解码;LM386;红外收发器。 1 绪论
零售企业营销策略中英文对照外文翻译文献
零售企业营销策略中英文对照外文翻译文献(文档含英文原文和中文翻译)
译文: 零售企业的营销策略 Philip Kotlor 今天的零售商为了招徕和挽留顾客,急欲寻找新的营销策略。过去,他们挽留顾客的方法是销售特别的或独特的花色品种,提供比竞争对手更多更好的服务提供商店信用卡是顾客能赊购商品。可是,现在这一切都已变得面目全非了。现在,诸如卡尔文·克连,依佐和李维等全国性品牌,不仅在大多数百货公司及其专营店可以看到,并且也可以在大型综合商场和折扣商店可以买到。全国性品牌的生产商为全力扩大销售量,它们将贴有品牌的商品到处销售。结果是零售商店的面貌越来越相似。 在服务项目上的分工差异在逐渐缩小。许多百货公司削减了服务项目,而许多折扣商店却增加了服务项目。顾客变成了精明的采购员,对价格更加敏感。他们看不出有什么道理要为相同的品牌付出更多的钱,特别是当服务的差别不大或微不足道时。由于银行信用卡越来越被所有的商家接受,他们觉得不必从每个商店赊购商品。 百货商店面对着日益增加的价格的折扣店和专业商店的竞争,准备东山再起。历史上居于市中心的许多商店在郊区购物中心开设分店,那里有宽敞的停车场,购买者来自人口增长较快并且有较高收入的地区。其他一些则对其商店形式进行改变,有些则试用邮购盒电话订货的方法。超级市场面对的是超级商店的竞争,它们开始扩大店面,经营大量的品种繁多的商品和提高设备等级,超级市场还增加了它们的促销预算,大量转向私人品牌,从而增加盈利。 现在,我们讨论零售商在目标市场、产品品种和采办、服务以及商店气氛、定价、促销和销售地点等方面的营销策略。 一、目标市场 零售商最重要的决策时确定目标市场。当确定目标市场并且勾勒出轮廓时,零售商才能对产品分配、商店装饰、广告词和广告媒体、价格水平等作出一致的决定。如沃尔玛的目标市场相当明确:
英文文献翻译
中等分辨率制备分离的 快速色谱技术 W. Clark Still,* Michael K a h n , and Abhijit Mitra Departm(7nt o/ Chemistry, Columbia Uniuersity,1Veu York, Neu; York 10027 ReceiLied January 26, 1978 我们希望找到一种简单的吸附色谱技术用于有机化合物的常规净化。这种技术是适于传统的有机物大规模制备分离,该技术需使用长柱色谱法。尽管这种技术得到的效果非常好,但是其需要消耗大量的时间,并且由于频带拖尾经常出现低复原率。当分离的样本剂量大于1或者2g时,这些问题显得更加突出。近年来,几种制备系统已经进行了改进,能将分离时间减少到1-3h,并允许各成分的分辨率ΔR f≥(使用薄层色谱分析进行分析)。在这些方法中,在我们的实验室中,媒介压力色谱法1和短柱色谱法2是最成功的。最近,我们发现一种可以将分离速度大幅度提升的技术,可用于反应产物的常规提纯,我们将这种技术称为急骤色谱法。虽然这种技术的分辨率只是中等(ΔR f≥),而且构建这个系统花费非常低,并且能在10-15min内分离重量在的样本。4 急骤色谱法是以空气压力驱动的混合介质压力以及短柱色谱法为基础,专门针对快速分离,介质压力以及短柱色谱已经进行了优化。优化实验是在一组标准条件5下进行的,优化实验使用苯甲醇作为样本,放在一个20mm*5in.的硅胶柱60内,使用Tracor 970紫外检测器监测圆柱的输出。分辨率通过持续时间(r)和峰宽(w,w/2)的比率进行测定的(Figure 1),结果如图2-4所示,图2-4分别放映分辨率随着硅胶颗粒大小、洗脱液流速和样本大小的变化。
中小企业融资的英文文献
中小企业融资的英文文献 Automatically translated text: The definition of lease financing Finance leases (Financial Leasing) also known as the Equipment Leasing (Equipment Leasing), or modern leasing (Modern Leasing), and is essentially transfer ownership of the assets of all or most of the risks and rewards of the lease. The ultimate ownership of assets to be transferred, or may not transfer. It refers to the specific content of the lessee to the lessor under the lease object and the specific requirements of the supplier selection, vendor financing to purchase rental property, and the use of leased to a lessee, the lessee to the lessor to pay instalments rent, the lease term lease ownership of objects belonging to the lessor of all, the tenant has the right to use the leased items. Term expired, and finished the lessee to pay rent under the lease contract financing to fulfil obligations in full, leasing objects that vesting ownership of all the lessee. Despite the finance lease transactions, the lessors have the identity of the purchase of equipment, but the substantive content of the purchase of equipment suppliers such as the choice of the specific requirements of the equipment, the conditions of the purchase contract negotiations by the lessee enjoy and exercise, lessee leasing object is essentially the purchaser. , Is a finance lease extension of loans and trade and technology updates in the new integrated financial industry. Because of its extension of loans and combination of features, there is a problem in leasing companies can recycling, treatment of leasing, and
毕业论文英文参考文献与译文
Inventory management Inventory Control On the so-called "inventory control", many people will interpret it as a "storage management", which is actually a big distortion. The traditional narrow view, mainly for warehouse inventory control of materials for inventory, data processing, storage, distribution, etc., through the implementation of anti-corrosion, temperature and humidity control means, to make the custody of the physical inventory to maintain optimum purposes. This is just a form of inventory control, or can be defined as the physical inventory control. How, then, from a broad perspective to understand inventory control? Inventory control should be related to the company's financial and operational objectives, in particular operating cash flow by optimizing the entire demand and supply chain management processes (DSCM), a reasonable set of ERP control strategy, and supported by appropriate information processing tools, tools to achieved in ensuring the timely delivery of the premise, as far as possible to reduce inventory levels, reducing inventory and obsolescence, the risk of devaluation. In this sense, the physical inventory control to achieve financial goals is just a means to control the entire inventory or just a necessary part; from the perspective of organizational functions, physical inventory control, warehouse management is mainly the responsibility of The broad inventory control is the demand and supply chain management, and the whole company's responsibility. Why until now many people's understanding of inventory control, limited physical inventory control? The following two reasons can not be ignored: First, our enterprises do not attach importance to inventory control. Especially those who benefit relatively good business, as long as there is money on the few people to consider the problem of inventory turnover. Inventory control is simply interpreted as warehouse management, unless the time to spend money, it may have been to see the inventory problem, and see the results are often very simple procurement to buy more, or did not do warehouse departments . Second, ERP misleading. Invoicing software is simple audacity to call it ERP, companies on their so-called ERP can reduce the number of inventory, inventory control, seems to rely on their small software can get. Even as SAP, BAAN ERP world, the field of
文献翻译英文原文
https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html,/finance/company/consumer.html Consumer finance company The consumer finance division of the SG group of France has become highly active within India. They plan to offer finance for vehicles and two-wheelers to consumers, aiming to provide close to Rs. 400 billion in India in the next few years of its operations. The SG group is also dealing in stock broking, asset management, investment banking, private banking, information technology and business processing. SG group has ventured into the rapidly growing consumer credit market in India, and have plans to construct a headquarters at Kolkata. The AIG Group has been approved by the RBI to set up a non-banking finance company (NBFC). AIG seeks to introduce its consumer finance and asset management businesses in India. AIG Capital India plans to emphasize credit cards, mortgage financing, consumer durable financing and personal loans. Leading Indian and international concerns like the HSBC, Deutsche Bank, Goldman Sachs, Barclays and HDFC Bank are also waiting to be approved by the Reserve Bank of India to initiate similar operations. AIG is presently involved in insurance and financial services in more than one hundred countries. The affiliates of the AIG Group also provide retirement and asset management services all over the world. Many international companies have been looking at NBFC business because of the growing consumer finance market. Unlike foreign banks, there are no strictures on branch openings for the NBFCs. GE Consumer Finance is a section of General Electric. It is responsible for looking after the retail finance operations. GE Consumer Finance also governs the GE Capital Asia. Outside the United States, GE Consumer Finance performs its operations under the GE Money brand. GE Consumer Finance currently offers financial services in more than fifty countries. The company deals in credit cards, personal finance, mortgages and automobile solutions. It has a client base of more than 118 million customers throughout the world
市场营销_外文翻译_外文文献_英文文献_顾客满意策略与顾客满意
顾客满意策略与顾客满意营销 原文来源:《Marketing Customer Satisfaction 》自20世纪八十年代末以来, 顾客满意战略已日益成为各国企业占有更多的顾客份额, 获得竞争优势的整体经营手段。 一、顾客满意策略是现代企业获得顾客“货币选票”的法宝随着时代的变迁, 社会物质财富的极大充裕, 顾客中的主体———消费者的需求也先后跨越了物质缺乏的时代、追求数量的时代、追求品质的时代, 到了20世纪八十年代末进入了情感消费时代。在我国, 随着经济的高速发展,我们也已迅速跨越了物质缺乏时代、追求数量的时代乃至追求品质的时代, 到今天也逐步迈进情感消费时代。在情感消费时代, 各企业的同类产品早已达到同时、同质、同能、同价, 消费者追求的已不再是质量、功能和价格, 而是舒适、便利、安全、安心、速度、跃动、环保、清洁、愉快、有趣等,消费者日益关注的是产品能否为自己的生活带来活力、充实、舒适、美感和精神文化品位, 以及超越消费者期望值的售前、售中、售后服务和咨询。也就是说, 今天人们所追求的是具有“心的满足感和充实感”的商品, 是高附加值的商品和服务,追求价值观和意识多元化、个性化和无形的满足感的时代已经来临。 与消费者价值追求变化相适应的企业间的竞争, 也由产品竞争、价格竞争、技术竞争、广告竞争、品牌竞争发展到现今的形象竞争、信誉竞争、文化竞争和服务竞争, 即顾客满意竞争。这种竞争是企业在广角度、宽领域的时空范围内展开的高层次、体现综合实力的竞争。它包括组织创新力、技术创新力、管理创新力、产业预见力、产品研发力、员工向心力、服务顾客力、顾客亲和力、同行认同力、社会贡献力、公关传播沟通力、企业文化推动力、环境适应力等等。这些综合形象力和如何合成综合持久的竞争力, 这就是CSft略所要解决的问题。CS寸代,企业不再以“自己为中心”,而是以“顾客为中心”;“顾客为尊”、“顾客满意”不再是流于形式的口号, 而是以实实在在的行动为基础的企业经营的一门新哲学。企业不再以质量达标, 自己满意为经营理念, 而是以顾客满意, 赢得顾客高忠诚度为经营理念。企业经营策略的焦点不再以争取或保持市场占有率为主, 而是以争取顾客满意为经营理念。因此, 营销策略的重心不再放在竞争对手身上而是放在顾客身上, 放在顾客现实的、潜在的需求上。当企业提供的产品和服务达到了顾客事先的期望值, 顾客就基本满意;如果远远超越顾客的期望值, 且远远高于其他同行, 顾客才真正满意;如果企业能不断地或长久地令顾客满意, 顾客就会忠诚。忠诚的顾客不仅会经常性地重复购买, 还会购买企业其它相关的产品或服务;忠诚的顾客不仅会积极向别人推荐他所买的产品, 而且对企业竞争者的促销活动具有免疫能力一个不满意的顾客会将不满意告诉16-20个人, 而每一个被告知者会再传播给12-15个人。这样, 一个不满意者会影响到二、三百人。在互联网普及的今天, 其影响则更大。据美国汽车业的调查, 一个满意者会引发8笔潜在的生意, 其中至少有一笔会成交。而另一项调查表明, 企业每增加5%的忠诚顾客, 利润就会增长25%-95%。一个企业的80%的利润来自20%的忠诚顾客;而获取一个新顾客的成本是维持一个老顾客成本的6倍。所以,美国著名学者唐?佩 珀斯指出: 决定一个企业成功与否的关键不是市场份额, 而是在于顾客份额。 于是, 企业纷纷通过广泛细致的市场调研、与消费者直接接触、顾客信息反馈等方式来了解顾客在各方面的现实需求和潜在需求。依靠对企业满意忠诚的销售、服务人员, 定期、定量地对顾客满意度进行综合测定, 以便准确地把握企业经营中与“顾客满意” 目标的差距及其重点领域, 从而进一步改善企业的经营活动。依靠高亲和力的企业文化、高效率的人文管理和全员共同努力, 不断地向顾客提供高附加值的产品, 高水准的亲情般的服
英文文献及中文翻译
毕业设计说明书 英文文献及中文翻译 学院:专 2011年6月 电子与计算机科学技术软件工程
https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Overview https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, is a unified Web development model that includes the services necessary for you to build enterprise-class Web applications with a minimum of https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, is part of https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Framework,and when coding https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, applications you have access to classes in https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Framework.You can code your applications in any language compatible with the common language runtime(CLR), including Microsoft Visual Basic and C#.These languages enable you to develop https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, applications that benefit from the common language runtime,type safety, inheritance,and so on. If you want to try https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html,,you can install Visual Web Developer Express using the Microsoft Web Platform Installer,which is a free tool that makes it simple to download,install,and service components of the Microsoft Web Platform.These components include Visual Web Developer Express,Internet Information Services (IIS),SQL Server Express,and https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Framework.All of these are tools that you use to create https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Web applications.You can also use the Microsoft Web Platform Installer to install open-source https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, and PHP Web applications. Visual Web Developer Visual Web Developer is a full-featured development environment for creating https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Web applications.Visual Web Developer provides an ideal environment in which to build Web sites and then publish them to a hosting https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html,ing the development tools in Visual Web Developer,you can develop https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Web pages on your own computer.Visual Web Developer includes a local Web server that provides all the features you need to test and debug https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Web pages,without requiring Internet Information Services(IIS)to be installed. Visual Web Developer provides an ideal environment in which to build Web sites and then publish them to a hosting https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html,ing the development tools in Visual Web Developer,you can develop https://www.360docs.net/doc/b012883428.html, Web pages on your own computer.
中小企业融资问题与对策外文资料翻译
淮阴工学院 毕业设计(论文)外文资料翻译 学院: 专业: 姓名: 学号: 外文出处:Facts for You (用外文写) 附件: 1.外文资料翻译译文;2.外文原文。 注:请将该封面与附件装订成册。
附件1:外文资料翻译译文 中小型企业融资决策 企业的产生、生存及发展均离不开投资与融资活动。随着我国加入WTO 组织,市场经济体制的逐步完善,金融市场的快速发展,投资与融资效率也越来越成为企业发展的关键。对于中小型企业而言,应要根据自身发展需求,认真考虑如何选择自己需要和适合自己发展阶段的融资方式以及各种融资方式的利用时机、条件、成本和风险,确定合适的融资规模以及制定最佳融资期限等问题。要解决这些问题,需要中小型企业制定适当的融资策略,以作出最优化的融资决策。 一、企业融资决策概述 (一)企业融资决策概述 企业融资决策,是企业根据其价值创造目标需要,利用一定时机与渠道,采取经济有效的融资工具,为公司筹集所需资金的一种市场行为。它不仅改变了公司的资产负债结构,而且影响了企业内部管理、经营业绩、可持续发展及价值增长。典型的融资决策包括出售何种债务和股权(融资方式)、如何确定所要出售债务和股权的价值(融资成本)、何时出售些债务和股权(融资时机)等等。而其中最主要的包括融资规模的决策和融资方式的决策。融资规模应为企业完成资金使用目的的最低需要量。而企业的融资方式则多种多样,常见的以下几种: 1.财政融资。财政融资方式从融出的角度来讲,可分为:预算内拨款、财政贷款、通过授权机构的国有资产投资、政策性银行贷款、预算外专项建设基金、财政补贴。 2.银行融资。从资金融出角度即银行的资金运用来说,主要是各种代款,例如:信用贷款、抵押贷款、担保贷款、贴现贷款、融资租凭、证券投资。 3.商业融资。其方式也是多种多样,主要包括商品交易过程中各企业间发生的赊购商品、预收货款等形式。
外文文献翻译——参考格式
广东工业大学华立学院 本科毕业设计(论文) 外文参考文献译文及原文 系部经济学部 专业经济学 年级 2007级 班级名称 07经济学6班 学号 16020706001 学生姓名张瑜琴 指导教师陈锶 2011 年05月
目录 1挑战:小额贷款中的进入和商业银行的长期承诺 (1) 2什么商业银行带给小额贷款和什么把他们留在外 (2) 3 商业银行的四个模型进入小额贷款之内 (4) 3.1内在的单位 (4) 3.2财务子公司 (5) 3.3策略的同盟 (5) 3.4服务公司模型 (6) 4 合法的形式和操作的结构比较 (8) 5 服务的个案研究公司模型:厄瓜多尔和Haiti5 (9)
1 挑战:小额贷款中的进入和商业银行的长期承诺 商业银行已经是逐渐重要的运动员在拉丁美洲中的小额贷款服务的发展2到小额贷款市场是小额贷款的好消息客户因为银行能提供他们一完整类型的财务的服务,包括信用,储蓄和以费用为基础的服务。整体而言,它也对小额贷款重要,因为与他们广泛的身体、财务的和人类。如果商业银行变成重的运动员在小额贷款,他们能提供非常强烈的竞争到传统的小额贷款机构。资源,银行能廉宜地发射而且扩张小额贷款服务rela tively。如果商业广告银行在小额贷款中成为严重的运动员,他们能提出非常强烈的竞争给传统的小额贷款机构。然而,小额贷款社区里面有知觉哪一商业银行进入进入小额贷款将会是短命或浅的。举例来说,有知觉哪一商业银行首先可能不搬进小额贷款因为时候建立小额贷款操作到一个有利润的水平超过银行的标准投资时间地平线。或,在进入小额贷款,银行之后可能移动在-上面藉由增加贷款数量销售取利润最大值-或者更坏的事,退出如果他们是不满意与小额贷款的收益性的水平。这些知觉已经被特性加燃料商业银行的情形进入小额贷款和后来的出口之内。在最极端的,一些开业者已经甚至宣布,”降低尺度死!”而且抛弃了与主意合作的商业银行。 在最 signific 看得到的地方,蚂蚁利益商业银行可能带给小额贷款,国际的ACCION 发展发射而且扩张的和一些商业银行的关系小额贷款操作。在这些情形的大部分方面, ACCION 和它的合伙人正在使用方法,已知的当做服务公司模型,表演早答应当做一个能工作的方法克服真正的。 商业银行的障碍进入和穿越建立长命的小额贷款操作一个商业银行 这论文描述如何服务公司模型、住址商业银行中的主要议题进入进小额贷款,监定成功建立的因素动作井小额贷款服务公司,和礼物结果和小额贷款的课servic e 公司用最长的经验,在海地和审判官席 del 的 SOGEBANK│ SOGESOL 初期结果指出那这服务公司模型表现一重要的突破在促成商业银行进入和留在小额贷款。在厄瓜多尔的 Pichincha│ CREDIFE。初期结果指出服务公司模型在促成商业广告中表现一次重要的突破银行进入而且留在小额贷款。
外文文献及翻译
文献翻译 原文 Combining JSP and Servlets The technology of JSP and Servlet is the most important technology which use Java technology to exploit request of server, and it is also the standard which exploit business application .Java developers prefer to use it for a variety of reasons, one of which is already familiar with the Java language for the development of this technology are easy to learn Java to the other is "a preparation, run everywhere" to bring the concept of Web applications, To achieve a "one-prepared everywhere realized." And more importantly, if followed some of the principles of good design, it can be said of separating and content to create high-quality, reusable, easy to maintain and modify the application. For example, if the document in HTML embedded Java code too much (script), will lead the developed application is extremely complex, difficult to read, it is not easy reuse, but also for future maintenance and modification will also cause difficulties. In fact, CSDN the JSP / Servlet forum, can often see some questions, the code is very long, can logic is not very clear, a large number of HTML and Java code mixed together. This is the random development of the defects. Early dynamic pages mainly CGI (Common Gateway Interface, public Gateway Interface) technology, you can use different languages of the CGI programs, such as VB, C / C + + or Delphi, and so on. Though the technology of CGI is developed and powerful, because of difficulties in programming, and low efficiency, modify complex shortcomings, it is gradually being replaced by the trend. Of all the new technology, JSP / Servlet with more efficient and easy to program, more powerful, more secure and has a good portability, they have been many people believe that the future is the most dynamic site of the future development of technology. Similar to CGI, Servlet support request / response model. When a customer submit a request to the server, the server presented the request Servlet, Servlet responsible for handling requests and generate a response, and then gave the server, and then from the server sent to
