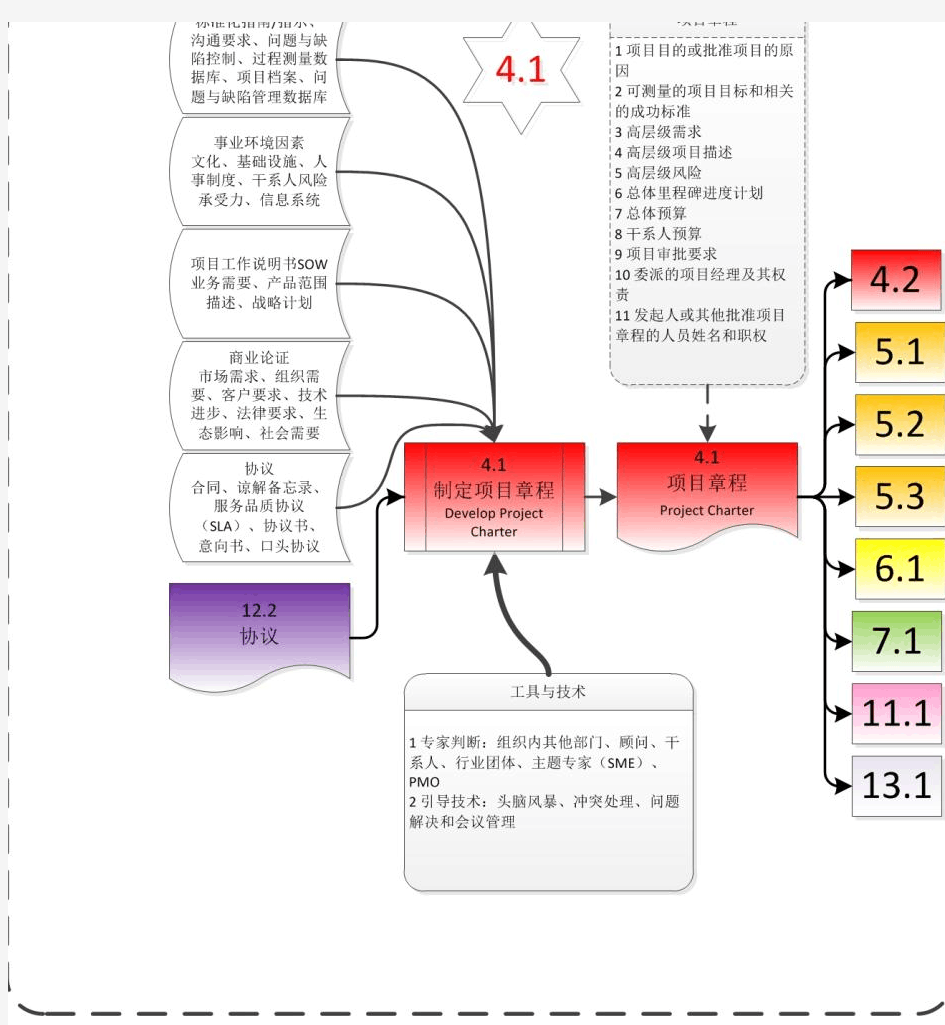
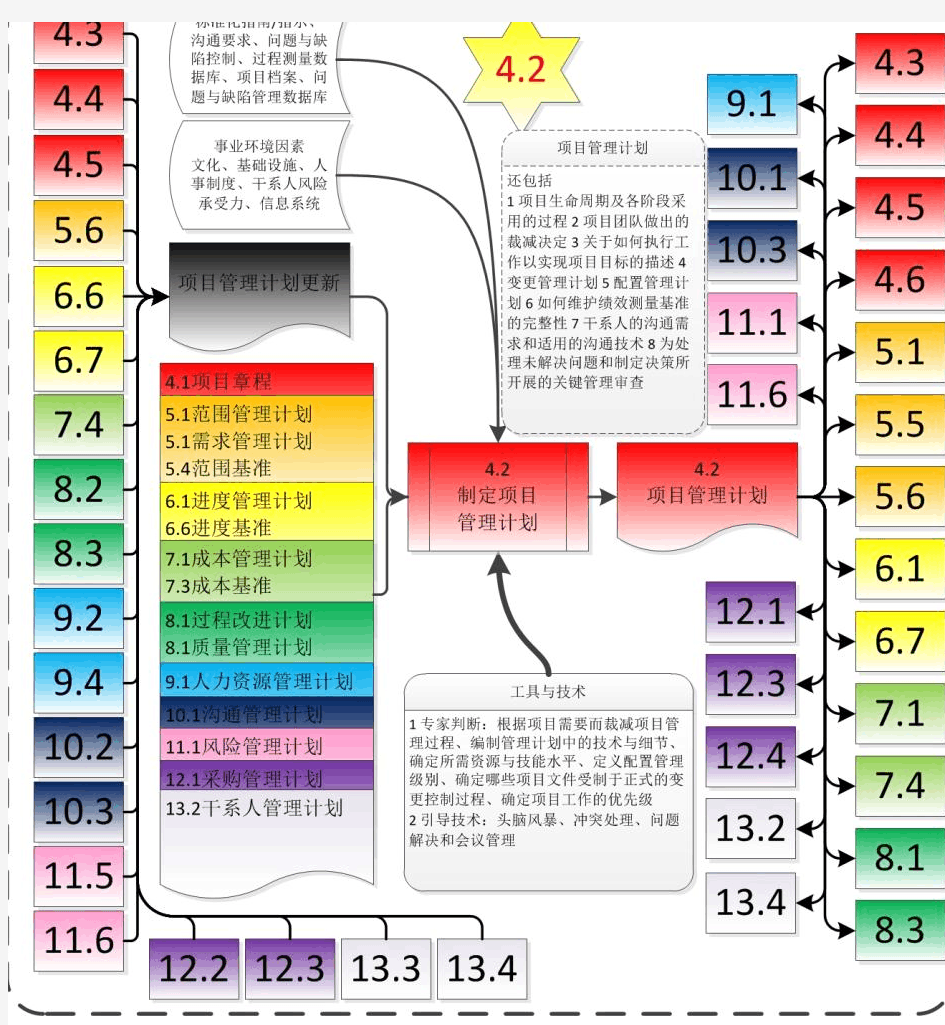
PMP PMBOK(第五版中文)要素记忆卡片
公司理财(英文版)题库2
CHAPTER 2 Financial Statements & Cash Flow Multiple Choice Questions: I. DEFINITIONS BALANCE SHEET b 1. The financial statement showing a firm’s accounting value on a particular date is the: a. income statement. b. balance sheet. c. statement of cash flows. d. tax reconciliation statement. e. shareholders’ equity sheet. Difficulty level: Easy CURRENT ASSETS c 2. A current asset is: a. an item currently owned by the firm. b. an item that the firm expects to own within the next year. c. an item currently owned by the firm that will convert to cash within the next 12 months. d. the amount of cash on hand the firm currently shows on its balance sheet. e. the market value of all items currently owned by the firm. Difficulty level: Easy LONG-TERM DEBT b 3. The long-term debts of a firm are liabilities: a. that come due within the next 12 months. b. that do not come due for at least 12 months. c. owed to the firm’s suppliers. d. owed to the firm’s shareholders. e. the firm expects to incur within the next 12 months. Difficulty level: Easy NET WORKING CAPITAL e 4. Net working capital is defined as: a. total liabilities minus shareholders’ equity. b. current liabilities minus shareholders’ equity. c. fixed assets minus long-term liabilities. d. total assets minus total liabilities. e. current assets minus current liabilities. Difficulty level: Easy LIQUID ASSETS d 5. A(n) ____ asset is on e which can be quickly converted into cash without significant loss in value.
完整word版公司理财英文版题库8
CHAPTER 8 Making Capital Investment Decisions I. DEFINITIONS INCREMENTAL CASH FLOWS a 1. The changes in a firm's future cash flows that are a direct consequence of accepting a project are called _____ cash flows. a. incremental b. stand-alone c. after-tax d. net present value e. erosion Difficulty level: Easy EQUIVALENT ANNUAL COST e 2. The annual annuity stream o f payments with the same present value as a project's costs is called the project's _____ cost. a. incremental b. sunk c. opportunity d. erosion e. equivalent annual Difficulty level: Easy SUNK COSTS c 3. A cost that has already been paid, or the liability to pay has already been incurred, is a(n): a. salvage value expense. b. net working capital expense. c. sunk cost. d. opportunity cost. e. erosion cost. Difficulty level: Easy OPPORTUNITY COSTS d 4. Th e most valuable investment given up i f an alternative investment is chosen is a(n): a. salvage value expense. b. net working capital expense.
英文版罗斯公司理财习题答案
CHAPTER 8 MAKING CAPITAL INVESTMENT DECISIONS Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. In this context, an opportunity cost refers to the value of an asset or other input that will be used in a project. The relevant cost is what the asset or input is actually worth today, not, for example, what it cost to acquire. 2. a.Yes, the reduction in the sales of the company’s other products, referred to as erosion, and should be treated as an incremental cash flow. These lost sales are included because they are a cost (a revenue reduction) that the firm must bear if it chooses to produce the new product. b. Yes, expenditures on plant and equipment should be treated as incremental cash flows. These are costs of the new product line. However, if these expenditures have already occurred, they are sunk costs and are not included as incremental cash flows. c. No, the research and development costs should not be treated as incremental cash flows. The costs of research and development undertaken on the product during the past 3 years are sunk costs and should not be included in the evaluation of the project. Decisions made and costs incurred in the past cannot be changed. They should not affect the decision to accept or reject the project. d. Yes, the annual depreciation expense should be treated as an incremental cash flow. Depreciation expense must be taken into account when calculating the cash flows related to a given project. While depreciation is not a cash expense that directly affects c ash flow, it decreases a firm’s net
公司理财(英文版)题库15
CHAPTER 15 Capital Structure: Basic Concepts Multiple Choice Questions: I. DEFINITIONS HOMEMADE LEVERAGE a 1. The use of personal borrowing to change the overall amount of financial leverage to which an individual is exposed is called: leverage. a. homemade recapture. b. dividend c. the weighted average cost of capital. d. private placement. debt offset. e. personal Difficulty level: Easy MM PROPOSITION I b 2. The proposition that the value of the firm is independent of its capital structure is called: a. the capital asset pricing model. b. MM Proposition I. c. MM Proposition II. d. the law of one pric e. e. the efficient markets hypothesis. Difficulty level: Easy MM PROPOSITION II c 3. The proposition that the cost of equity is a positive linear function of capital structure is called: a. the capital asset pricing model. b. MM Proposition I. c. MM Proposition II. d. the law of one pric e. e. the efficient markets hypothesis. Difficulty level: Medium INTEREST TAX SHIELD a 4. The tax savings of the firm derived from the deductibility of interest expense is called the: a. interest shield. tax basis. b. depreciable umbrella. c. financing d. current yield. e. tax-loss carryforward savings. Difficulty level: Easy
公司理财期末整理(英文版)
一、***是什么意思? 1)Capital budgeting 资金预算 2)Capital Structure 资金结构 3)Net working capital 二、组织结构图谁负责谁? 三、The corporate firm Forms of Business Organization ●Attributes: ●It is the cheapest business to form. ●It pay no corporate income taxes. ●The owner has unlimited liability. ●Its life is limited. ●It has difficulty in raising funds. 1)The sole proprietorship 独资企业特点P7 2)The Partnership 合伙企业(The business is owned by two or more persons.)Attributes:特征 @Initiation @Liability @ Life @ Ability to raise funds @Taxation @Controlling (1)General Partnership @ All partners agree to provide fraction of the work and cash and to share the profit and loss. @Each partner is liable for all of the debts . (2)Limited Partnership One or more partners are designated general partners and other partners are designated limited partners. 3)The Corporation: 公司 A corporation is owned by individuals who normally are not active in the day –to –day operation of that business. It is by far the most important form of business. Features:特征 1.Starting @Starting a corporation is more complicated @Preparing articles of incorporation and a set of by laws: Name of corporation Intended life Business purpose
(公司理财)英文版罗斯公司理财习题答案C
CHAPTER 20 INTERNATIONAL CORPORATE FINANCE Answers to Concepts Review and Critical Thinking Questions 1. a.The dollar is selling at a premium because it is more expensive in the forward market than in the spot market (SFr 1.53 versus SFr 1.50). b.The franc is expected to depreciate relative to the dollar because it will take more francs to buy one dollar in the future than it does today. c.Inflation in Switzerland is higher than in the United States, as are nominal interest rates. 2.The exchange rate will increase, as it will take progressively more pesos to purchase a dollar. This is the relative PPP relationship. 3. a.The Australian dollar is expected to weaken relative to the dollar, because it will take more A$ in the future to buy one dollar than it does today. b.The inflation rate in Australia is higher. c.Nominal interest rates in Australia are higher; relative real rates in the two countries are the same. 4. A Yankee bond is most accurately described by d. 5. No. For example, if a country’s currency strengthens, imports become cheaper (good), but its exports become more expensive for others to buy (bad). The reverse is true for currency depreciation. 6.Additional advantages include being closer to the final consumer and, thereby, saving on transportation, significantly lower wages, and less exposure to exchange rate risk. Disadvantages include political risk and costs of supervising distant operations. 7.One key thing to remember is that dividend payments are made in the home currency. More generally, it may be that the owners of the multinational are primarily domestic and are ultimately concerned about their wealth denominated in their home currency because, unlike a multinational, they are not internationally diversified. 8. a.False. If prices are rising faster in Great Britain, it will take more pounds to buy the same amount of goods that one dollar can buy; the pound will depreciate relative to the dollar. b.False. The forward market would already reflect the projected deterioration of the euro relative to the dollar. Only if you feel that there might be additional, unanticipated weakening of the euro that isn’t reflected in forward rates today, will the forward hedge protect you against additional declines.
公司理财相关知识(英文版)
Chapter 8: Strategy and Analysis in Using Net Present Value Concept Questions - Chapter 8 8.1 ?What are the ways a firm can create positive NPV. 1.Be first to introduce a new product. 2.Further develop a core competency to product goods or services at lower costs than competitors. 3.Create a barrier that makes it difficult for the other firms to compete effectively. 4.Introduce variation on existing products to take advantage of unsatisfied demand 5.Create product differentiation by aggressive advertising and marketing networks. https://www.360docs.net/doc/dc3440789.html,e innovation in organizational processes to do all of the above. ?How can managers use the market to help them screen out negative NPV projects? 8.2 ?What is a decision tree? It is a method to help capital budgeting decision-makers evaluating projects involving sequential decisions. At every point in the tree, there are different alternatives that should be analyzed. ?What are potential problems in using a decision tree? Potential problems 1) that a different discount rate should be used for different branches in the tree and 2) it is difficult for decision trees to capture managerial options.
公司理财期末试题及答案(英文版)
EXAM PAPER 1 I. True(T) or False(F). Please fill in the bracket with T or F. (15%) 1. In financial management, the more appropriate goal of the firm is maximization of shareholder wealth. ( ) 2. The component cost of preferred stock must be adjusted for taxes which the stockholders must pay on the dividends. ( ) 3. If an investment project has a profitability index of 1.15, the project’s internal rate of return exceeds its net present value. ( ) 4. With an annuity due the payments occur at the end of each period. ( ) 5. If the firm decides to impose a capital constraint on investment projects, the appropriate decision criterion is to select the set of projects with the highest NPV subject to the capital constraint. ( ) 6. Business risk refers to the relative dispersion in the firm’s EBIT. ( ) 7. Net working capital equals current assets less current liabilities. ( ) 8. Under MM’s model with corporate taxes, the benefits of debt financing stem solely from the tax deductibility of interest payments. ( ) 9. Investors can only expect to receive a return for incurring unsystematic risk. ( ) 10. The Security Market Line is a risk-return trade-off for combinations of the market portfolio and the riskless asset. ( ) II. Multiple Choice (15%) 1. Dorset Ltd wishes to calculate its weighted average cost of capital for use in investment appraisal. The company is financed by 150 million $1 ordinary shares, which have a current market value of $2, and $100 million 12 per cent irredeemable debentures, which are currently quoted at $150 per $100 nominal value. The cost of ordinary share capital is 11 per cent and the rate of corporation tax is 25 per cent. What is the weighted average cost of capital for Dorset Ltd? (To one decimal place) A. 9·0 per cent
