Exam1_solutions

Physics 140, Winter 2011
First Midterm Exam
Physics Department, University of Michigan
February 3, 2011FORM 1
Please print your name: ____SAUL LOU SHEN______________
Your INSTRUCTOR:_________________________
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1.Fill in YOUR NAME, INSTRUCTOR and the EXAM FORM NUMBER on the scantron.
2.RECORD YOUR ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON USING A #2 PENCIL.
3.Turn in this exam copy with your scantron answer sheet.
4.This is a 90-minute, closed book exam. You may use one 3” x 5” card on which you have your
favorite equations. You also may use a calculator but please do not share calculators.
5.All cell phones and other communication devices must be shut off and out of sight.
6.There are altogether 20 multiple choice questions. All questions are of equal value.
Equations/values that you may find useful:
s f = s i + v0t + ? a t2
v f = v0 + at
a rad = v2/r
F = m a
F k = μk N
g = 9.8 m/s2
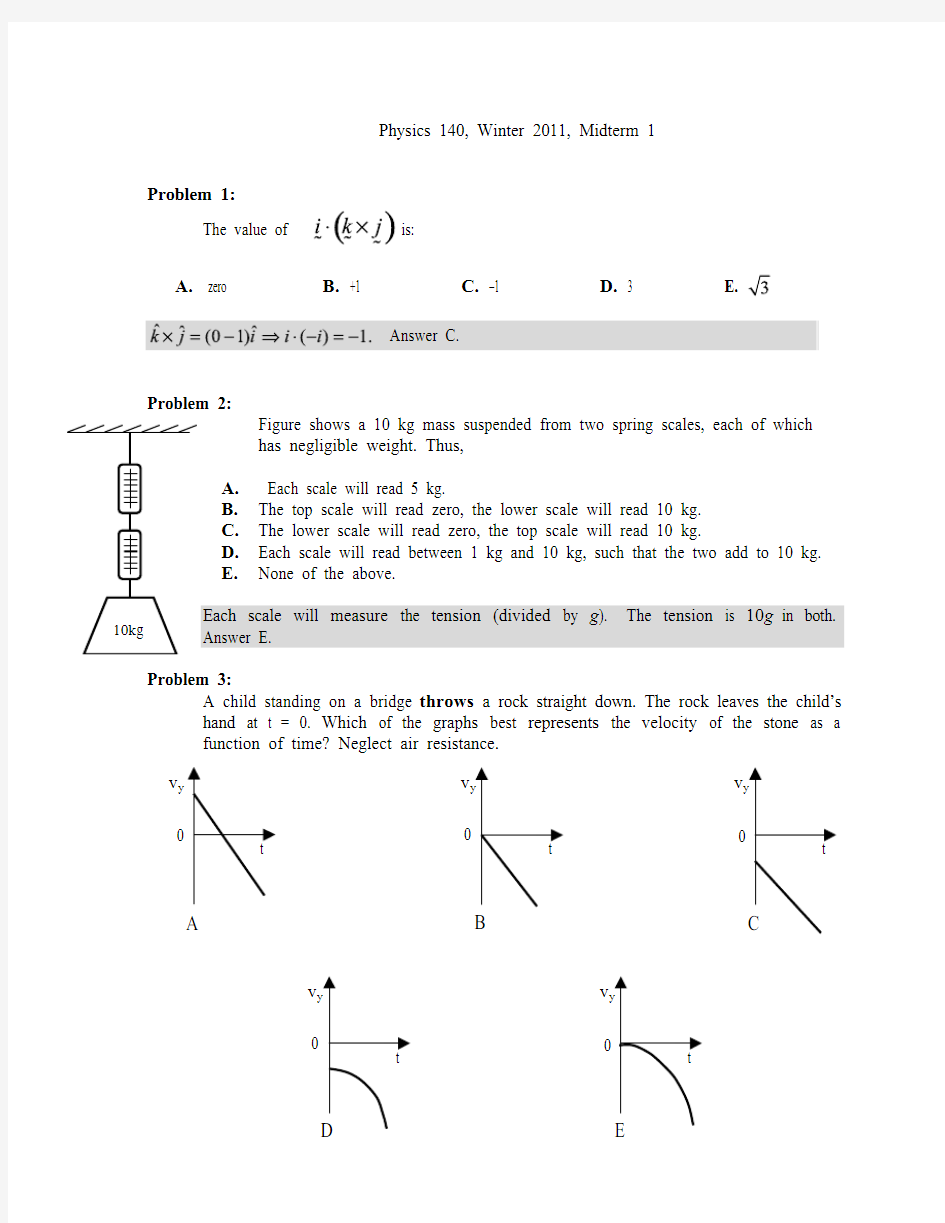
Physics 140, Winter 2011, Midterm 1
Problem 1: The value of is:
A. zero
B. +1
C. –1
D. 3
Answer C.
Problem 2:
Figure shows a 10 kg mass suspended from two spring scales, each of which has negligible weight. Thus,
A. Each scale will read 5 kg.
B. The top scale will read zero, the lower scale will read 10 kg.
C. The lower scale will read zero, the top scale will read 10 kg.
D. Each scale will read between 1 kg and 10 kg, such that the two add to 10 kg.
E. None of the above.
Each scale will measure the tension (divided by g ). The tension is
10g in both. Answer E.
Problem 3:
A child standing on a bridge throws a rock straight down. The rock leaves the child’s hand at t
= 0. Which of the graphs best represents the velocity of the stone as
a function of time? Neglect air resistance.
If we take up positive then . The initial velocity is down so it’s negative too. A line with a negative intercept and a slope of –g. Answer C.
Problem 4:
Three boxes with mass m1= 1kg, m2= 2kg, and m3= 3kg are hanging from
strings as shown in figure. You are pulling the top string with the force of 100N.
What is the tension T12 in the string connecting boxes m1 and m2?
A.20 N
B. 49 N
C. 59 N
D. 72 N
E. 83 N
Problem 5:
A small remote-control car with mass 1.60 kg moves at a constant speed of 12.0 m/s
in a vertical circle inside a hollow metal cylinder that has a radius of 5.00 m. What is the magnitude of the normal force exerted on the car by the walls of the cylinder at the top of the vertical circle?
A.15.7 N
B. 22.4 N
C. 30.4 N
D. 39.6 N
E. 46.1 N At the top the FBD is a normal force (N) down and mg down. The centripetal direction is down too, so call down positive. = 30.4 N. Answer C.
Problem 6:
Buttons are lined up along the diameter of a circular platter that rests on a horizontal table. As the platter is spun up to a rate of 33 revolutions per minute, the buttons lying a distance greater than 0.1 m from the center are observed to fly off. What is the coefficient of static friction between the platter and the buttons?
A.0.12
B. 0.18
C. 0.24
D. 0.30
E. 0.36
Problem 7:
You are riding in a friend’s plush car admiring the cheap pine-scented air
freshener hanging from the rear view mirror. As the car rounds a 45 m radius
horizontal curve on level road at 22 m/s, at what angle with respect to vertical does the air freshener hang?
A. 12 deg
B. 25 deg
C. 38 deg
D. 48 deg
E. 56 deg
Problem 8:
A baseball is hit by a bat. The ball is launched at 32 m/s, at an angle 30° above the horizontal. The ball travels towards a 5m high wall 70 m away. How high is the ball when it passes over the wall? (You can ignore the effects of any possible air friction….)
A. It doesn’t reach the wall
B. It strikes the wall 2.2 m above the ground
C. It passes over the wall 5.4 m above the ground
D. It passes over the wall 9.2 m above the ground
E. It passes over the wall 24.5 m above the ground
Problem 9:
A skydiver falling at 39.0 m/s opens her parachute 322 m above the ground. Her mass is 61.0 kg. Just before she hits the ground her speed is 5.00 m/s. The work done on her by the parachute is: (neglect air resistance on the skydiver directly)
A. –238 kJ
B. –190 kJ
C. –4.56 kJ
D. –4.63kJ
E. +190 kJ
70m
5 m
Problem 10:
A particle is moving along the x-axis with positive velocity at position
x=0. A force given by acts on the particle, where c is a constant. At
what position will the particle's velocity be zero?
A.
B.
C.
Problem 11:
You push a 21 kg crate for 52 m at constant velocity across a warehouse floor.
The coefficient of friction between the crate and the floor is 0.33. The force you exert is horizontal. How much work have you done on the crate?
A.–10700 J
B. –3530 J
C. 0 J
D. 3530J
E. 10700 J Since the velocity is constant the total work is zero. The two forces doing work on the crate are your push and friction. The work done by friction is . Since the total work is zero the work done by you must be 3530 J. Answer D.
Problem 12:
A block of mass M is attached to a massive uniform rope with a mass m. The
block rests on a frictionless table. A force F to the right is applied to the end of
the rope as shown. What is the tension at a point 1/3rd of the rope’s length from
the right end of the rope?
A. F
B. FM / (M + m)
C. FM / (M + m /3)
D. F (M + m / 3) / (M + m)
E. F (M + 2m / 3) / (M + m)
Problem 13:
A pebble stuck in a tire follows a path called a cycloid. The horizontal and
vertical positions of the pebble as a function of time are given by
and , respectively. ω is constant.
What is the angle between the velocity and acceleration vectors when
radians?
A.0 degrees
B. 45 degrees
C. 90 degrees
D. 135 degrees
E. 180 degrees
Problem 14:
The picture below shows an upper block of mass m A and a lower block of mass
m B connected by a light string wrapped around a massless and frictionless pulley.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and between the block B
and the table is μk. For the blocks to move at constant speed what force F must
you apply?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Problem 15:
A hiker walks 5.0 km due east, then 4.0 km due south, then 2.0 km due west. What is
the ratio of the total distance she walks to the magnitude of her net displacement?
A. 1.0
B. 1.4
C. 1.8
D. 2.2
E. 2.6
The distance is 5+4+2 = 11 km. The displacement is the vector sum of the displacements, which is 4.0 km south and 5.0 – 2.0 = 3.0 east. The magnitude of the displacement is 5 km. The ratio is 11/5 = 2.2. Answer D.
Problem 16:
A motorcyclist racing at 30.0 m/s suddenly sees an armadillo standing 120 meters
ahead on the road, slams on his brakes, and goes into a skid. If he skids to a stop right
at the feet of the frightened animal, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between
the motorcycle tires and the road?
A.0.18
B. 0.28
C. 0.38
D. 0.48
E. 0.58
In the vertical direction the normal force and the weight are equal and opposite. In the horizontal direction the frictional force is . (Minus because it’s opposite the displacement, which I call positive). To get a from the kinematic information use eg. –3.75 m/s2. Solving for
0.383. Answer C.
Problem 17:
A boater heads due east across a river that flows southward at 2.50 m/s. If the
river is 400 m wide and the total distance the boat travels in crossing the river is
500 m (as seen by a person standing on the riverbank), what is the boat’s speed
with respect to the water?
Problem 18:
A boater wishes to cross a river to a point directly opposite on the other bank. The
river flows downstream at 2.0 m/s. If the boat’s speed with respect to the water is
3.5 m/s, at what upstream angle (relative to the direction of straight across) should
the boater head?
A.5.0°
B. 15.°
C. 25.°
D. 35.°
E. 45.°
Read B for boat, W for water, and G for ground. Using the graphical addition method (tip-to-tail) we can see that degrees. Answer D.
Problem 19:
A cannon fires two shells in succession, both at an initial speed of V0from
ground-level. The first shell is launched at an angle 30° above the horizontal, and
the second shell is launched 60° above the horizontal. Both land at ground level.
If air resistance can be neglected, which of the following statements is false?
A.The two shells travel the same distance through the air.
B.The two shells land at the same horizontal distance away from the launch point.
C.The 2nd shell spends a longer time in the air than the 1st shell spends.
D.The 1st shell has a greater average horizontal velocity than the 1st shell has.
E.The 2nd shell reaches a greater maximum height than the 1st shell.
Problem 20:
Two identical masses M1 = M2 = 2.0 kg are attached to a massless string wrapped
around a massless and frictionless pulley, as shown. M1slides up a ramp that
makes an angle θ= 30.0°with the horizontal. M1is observed to move up the
ramp at a constant acceleration a = 1.0 m/s2. What is the coefficient of kinetic
friction between M1 and the ramp?
