项目管理CH05(英文)
工程项目管理英文版本

Engineering project management is a critical discipline that involvesthe application of project management principles, methodologies, andtools to effectively plan, execute, and control engineering projects. This article aims to provide an overview of engineering project management, its key components, and its significance in the successful completion of engineering projects.1. Definition and ScopeEngineering project management is the application of project management concepts, techniques, and skills to engineering projects. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of a project, from conception to completion. The scope of engineering project management includes the planning, executing, and controlling of engineering projects to ensure they are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.2. Key Components of Engineering Project Managementa. Project PlanningProject planning is the process of defining the project objectives, scope, and deliverables. It involves creating a detailed project planthat outlines the activities, resources, and timelines required to complete the project. Key components of project planning include:- Project charter: A document that authorizes the project and definesits objectives, scope, and stakeholders.- Work breakdown structure (WBS): A hierarchical decomposition of the project scope into smaller, manageable components.- Schedule: A timeline that shows the sequence of activities and their durations.- Budget: An estimate of the costs required to complete the project.- Risk management plan: A document that identifies, assesses, and prioritizes risks associated with the project.b. Project ExecutionProject execution is the process of carrying out the project plan. It involves coordinating resources, managing stakeholders, and monitoring progress. Key components of project execution include:- Resource allocation: Assigning resources, such as personnel, equipment, and materials, to project activities.- Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about project progressand issues.- Change management: Managing changes to the project scope, schedule,and budget.- Quality management: Ensuring that project deliverables meet the required quality standards.c. Project ControlProject control is the process of monitoring and controlling the project to ensure it is on track to achieve its objectives. Key components of project control include:- Progress tracking: Monitoring the actual progress of the project against the planned schedule and budget.- Performance measurement: Assessing the project's performance in terms of quality, cost, and time.- Change control: Managing changes to the project scope, schedule, and budget.- Risk management: Identifying, assessing, and responding to risks that may impact the project.3. Significance of Engineering Project ManagementEngineering project management is essential for the successfulcompletion of engineering projects. It helps organizations to:- Reduce project costs and improve profitability.- Enhance project quality and customer satisfaction.- Mitigate risks and uncertainties.- Improve project efficiency and productivity.- Develop and maintain stakeholder relationships.In conclusion, engineering project management is a vital discipline that ensures the successful completion of engineering projects. By applying project management principles, methodologies, and tools, organizations can achieve their project objectives and deliver high-quality outcomes within the specified time and budget constraints.。
工程项目管理英文解释

Engineering project management is a professional discipline that involves the application of project management principles, tools, and techniques to successfully execute and deliver engineering projects. It is a comprehensive process that encompasses planning, organizing, leading, and controlling the activities of a project to achieve specific goals and objectives within the defined constraints of time, budget, and quality.The primary objective of engineering project management is to ensurethat the project is completed on time, within budget, and meets the required quality standards. This involves managing various aspects of the project, such as scope, schedule, cost, quality, human resources, communication, risk, and procurement.Scope management involves defining, documenting, verifying, and controlling the project scope to ensure that the project deliverables meet the agreed-upon requirements. It includes activities such as scope planning, scope definition, scope verification, and scope control.Schedule management is the process of planning, scheduling, and controlling the project activities to ensure that the project is completed on time. This involves activities such as schedule planning, schedule development, schedule control, and schedule updates.Cost management involves planning, budgeting, and controlling theproject costs to ensure that the project is completed within the allocated budget. It includes activities such as cost estimation, cost budgeting, cost control, and variance analysis.Quality management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling quality policies to ensure that the project deliverables meet the required quality standards. It includes activities such as quality planning, quality assurance, quality control, and continuous improvement.Human resource management involves planning, acquiring, developing, and managing the project team to ensure that the project is executed effectively. It includes activities such as human resource planning,staffing, training and development, performance management, and conflict resolution.Communication management involves planning, implementing, andcontrolling the project communication to ensure that the relevant information is effectively communicated to the stakeholders. It includes activities such as communication planning, communication tools and techniques, and stakeholder management.Risk management involves identifying, analyzing, and responding to risks that may impact the project objectives. It includes activities such as risk identification, risk analysis, risk response planning, and risk monitoring and control.Procurement management involves obtaining goods and services from external sources to meet the project requirements. It includesactivities such as procurement planning, solicitation, supplier selection, contract administration, and contract closure.Engineering project management also involves several key processes, such as project initiation, project planning, project execution, project monitoring and controlling, and project closing. Each of these processes has specific objectives, activities, and outputs that contribute to the successful completion of the project.Project initiation involves identifying and defining the project, as well as obtaining approval for the project. It includes activities such as project charter development, feasibility study, and business case preparation.Project planning involves developing the project management plan, which includes the project scope statement, schedule, budget, quality management plan, human resource plan, communication plan, risk management plan, and procurement plan.Project execution involves implementing the project management plan to execute the project activities and deliver the project outputs. It includes activities such as resource allocation, task execution, and project coordination.Project monitoring and controlling involves tracking, reviewing, and managing the project performance to ensure that the project objectives are achieved. It includes activities such as progress reporting, performance measurement, variance analysis, and corrective actions.Project closing involves completing all project activities, documenting lessons learned, and transitioning the project deliverables to the stakeholders. It includes activities such as project closure documentation, project review, and project handover.In conclusion, engineering project management is a complex and dynamic process that requires a comprehensive understanding of project management principles and techniques. Effective engineering project management can lead to the successful completion of projects, ensuring that the desired outcomes are achieved within the defined constraints.。
项目管理英文对照

项目管理术语中英文对照项目管理术语中英文对照ACWP Actual Cost of Work Performed 已执行工作实际成本AD Activity Description 工作描述ADM Arrow Diagramming Method 箭线图示解法AF Actual Finish Date 实际完成日期AOA Activity-On-Arrow 双代号网络图AON Activity-On-Node 单代号网络图AS Actual Start Date 实际开始日期BAC Budget At Completion 在完成时的预算BCWP Budgeted Cost of work Performed 已执行工作预算成本BCWS Budgeted Cost of work Scheduled 计划完成工作预算成本CCB Change Control Board 变更控制委员会CPFF Cost Plus Fixed Fee 成本加固定费用(合同)CPIF Cost Plus Incentive Fee 成本加奖励费用(合同)CPI Cost Performance Index 成本执行指数CPM Critical Path Method 关键线路法CV Cost Variance 成本偏差DD Data Date 数据日期DU Duration 持续时间,工期EAC Estimate At Completion 在完成时的估算EF Early Finish date 最早完成日期ES Early Start date 最早开始日期ETC Estimate (or Estimated) To Complete 到完成时的估算EV Earned Value 挣值法FF Free Float or Finish-to-Finish 自由时差,或完成到完成关系FFP Firm Fixed Price 完全固定总价合同FPIF Fixed Price Incentive Fee 固定价加奖励费用FS Finish-to-Start 完成到开始关系GERT Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique 图示评审技术IFB Invitation For Bid 邀标LF Late Finish Date 最晚完成日期LOE Level of Effort 投入水平LS Late Start date 最晚开始日期MPM Modern Project Management 现代项目管理OBS Organization(al) Breakdown Structure 组织分解结构PC Percent Complete 完成百分比PDM Precedence Diagramming Method 优先图示法PERT Program Evaluation and Review Technique 计划评审技术PF Planned Finish date 计划完成日期PM Project Management or Project Manager 项目管理或项目经理PMBOK Project Management Body of Knowledge 项目管理知识体系PMP Project Management Professional 项目管理专业人员PS Planned Start date 计划开始日期QA Quality Assurance 质量保障QC Quality Control 质量控制RAM Responsibility Assignment Matrix 责任分配矩阵RDU Remaining DUration 剩余工期RFP Request For Proposal 请求建议书RFQ Request For Quotation 请求报价单SF Scheduled Finish date or Start-to-Finish 计划完成日期或开始到完成关系SOW Statement of Work 工作说明SPI Schedule Performance Index 进度执行指数SS Scheduled Start date or Start-to-Start 计划开始日期或开始到开始关系SV Schedule Variance 进度偏差TC Target Completion date 目标完成日期TF Total Float or Target Finish date 总时差,或目标完成日期TS Target Start date 目标开始日期TQM Total Quality Management 全面质量管理WBS Work Breakdown Structure 工作分解结构定义这里定义的许多词,在词典的定义中具有更广泛的意义,在某些情况下具有不同的意义。
项目管理知识体系(英文)(ppt 33页)
R is k Response
S o lic ia tio n
Form al Acceptance
P ro p o s a ls
Source
C ontrol Budget Updates
Corrective Action Plan
C o n tro l
S e le c tio n
S c h e d u le C o n tro l
R isk Q uantification
R isk Response D evelopm ent
D istribution
P ro je c t Records
Q uality M gm t Plan Com m un Sources of Risk
O perational Defn M gm t Plan Potential RiskEvents
O ve ra ll Change C o n tro l
C lo s in g
C o n tra ct C lo s e o u t
Contract File Form al Acceptance
& Closure
Adm inistrative C lo s u re
Project Archives Form al Acceptance Lessons Learned
Project M anagem ent Processes G roups
In itia tin g
F a c ilita tin g
E x e c u tin g
P la n n in g
Inform ation
Q uality P la n n in g
ch05物料需求计划(MRP)

库存信息说明物料清单中列出的每个项目的如下数据: 物料可用数据和编制订单数据.
1、 物料可用数据
(1)现有库存量:
指仓库中实际存放的可用库存量。
(2)计划入库量(或计划接收量)
指在将来某个时间某项目的入库量。该入库量一般来 源于正在执行中的采购订单或生产订单。
(3)已分配量
指已经分配给某使用者,但还没有从仓库中领走的项
Ch5 物料需求计划(MRP)
整理ppt
1
物料需求计划(MRP)的编制
1 MRP的概念 2 MRP的工作原理 3 MRP处理过程 4 MRP的编制案例 5 MRP的更新方法
整理ppt
2
1.1 什么是物料需求计划
物料需求计划(MRP ,Material Requirement Planning)是对主生产计划 (MPS)的各个项目所需的全部制造件和全部采 购件的网络支持计划和时间进度计划。
MRP是生产管理的核心,它将主生产计划排产 的产品分解成自制零部件的生产计划和采购件 的采购计划。
整理ppt
4
MRP主要解决以下五个问题:
(1)要生产(含采购或制造)什么?生产(含采购或 制造)多少?(这些数据从MPS获得)
(2)要用到什么?(这些数据根据BOM表展开获得)
(3)已经有了什么?(这些数据根据物料库存信息、 即将到到货信息或产出信息获得)
整理ppt
13
库存信息(3/3)
(4)批量规则(批量政策)
实际计划生产或采购的交付数量和订货数量并非等于 净需求量,这是由于在实际生产或订货中,准备加工、 订货、运输、包装等都必须是按照一定的数量来进行 的,这 一定的数量 称为生产或订货的批量。批量规 则是库存管理人员根据库存管理的要求和目标权衡利 弊后选择的。
CH-GC05工程管理工作策划(电 梯)
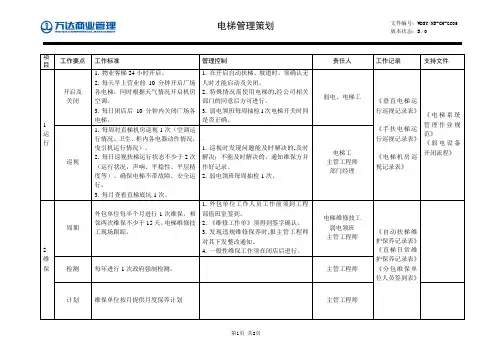
项目工作要点工作标准管理控制责任人工作记录支持文件1 运行开启及关闭1.物业客梯24小时开启。
2.每天早上营业前10分钟开启广场各电梯,同时根据天气情况开启机房空调。
3.每日闭店后10分钟内关闭广场各电梯。
1.在开启自动扶梯、坡道时,须确认无人时才能启动及关闭。
2.特殊情况需使用电梯的,经公司相关部门的同意后方可进行。
3.弱电领班每周抽检1次电梯开关时间是否正确。
弱电、电梯工《垂直电梯运行巡视记录表》《手扶电梯运行巡视记录表》《电梯机房巡视记录表》《电梯系统管理作业规范》《弱电设备开闭流程》巡视1.每周对直梯机房巡视1次(空调运行情况、卫生、柜内各电器动作情况,曳引机运行情况)。
2.每日巡视扶梯运行状态不少于2次(运行状况,声响、平稳性、平层精度等)。
确保电梯不带故障、安全运行。
3.每月查看直梯底坑1次。
1.巡视时发现问题能及时解决的,及时解决;不能及时解决的,通知维保方并作好记录。
2.弱电领班每周抽检1次。
电梯工主管工程师部门经理2 维保周期外包单位每半个月进行1次维保,相邻两次维保不少于15天,电梯维修技工现场跟踪。
1.外包单位工作人员工作前须到工程部值班室签到。
2.《维修工作单》须得到签字确认。
3.发现违规维修保养时,报主管工程师对其下发整改通知。
4.一般性维保工作须在闭店后进行。
电梯维修技工弱电领班主管工程师《自动扶梯维护保养记录表》《直梯日常维护保养记录表》《分包维保单位人员签到表》检测每年进行1次政府强制检测。
主管工程师计划维保单位按月提供月度保养计划主管工程师项目工作要点工作标准管理控制责任人工作记录支持文件安全控制1.维修保养人员在对电梯进行保养、检修时,应先在各层厅门前挂上“电梯保养、检修”告示牌。
2.检修完成,经试运行正常后交付使用。
3.完成维修现场卫生清理工作。
1.由维保单位提供维修记录。
2.由弱电领班确认维修效果。
弱电领班主管工程师《电梯安全操作规程》3 电梯紧急故障处理措施1.电、扶梯停机进行重新启动。
项目管理专用中英文术语词汇
项目管理专用中英文术语词汇1、活动,Activity2、活动定义,Activity Definition3、活动描述/说明,AD=Activity Description4、活动历时估算,Activity Duration Estimating5、箭线网络图(双代号网络图),AOA=Activity-On-Arrow6、节点式网络图(单代号网络图),AON=Activity-on-Node7、已执行工作实际成本,ACWP=Actual Cost of Work Performed8、实际完成日期,AF=Actual Finish Date9、实际开始日期,AS=Actual Start Date10、行政收尾,Administrative Closure11、箭线,Arrow12、箭线图示法,ADM=Arrow Diagramming Method13、逆推计算法,Backward Pass14、横道图,Bar Chart15、基准计划,Baseline16、完工预算,BAC=Budget At Completion17、概算,Budget Estimate18、已执行预算成本,BCWP=Budgeted Cost of Work Performed19、计划执行预算成本,BCWS= Budgeted Cost of Scheduled20、日历单位,Calendar Unit21、变更控制委员会,CCB=Chang Control Board22、沟通规划,Communications Planning23、并行工程,Concurrent Engineering24、意外费用,Contingencies25、意外准备金,contingency Allowance26、意外规划,Contingency Planning27、意外储备,Contingency Reserve28、合同,Contract29、合同管理,Contract Administration30、合同收尾,Contract Close-out31、控制,Control32、控制图,Control Chart33、纠正措施,Corrective Action34、费用预算,Cost Budgeting35、费用控制,Cost Control36、费用做算,Cost Estimating37、质量成本,Cost of Quality38、费用绩效指数,CPI=Cost Performance Index39、费用偏差,CV=Cost Variance40、赶工,Crashing41、关键工序,Critical Activity42、关键路线,Critical Path43、关键路线法,CPM=Critical Path Method44、当前完成日期,Current Finish Date45、当前开始日期,Current Start Date46、数据日期,DD=Data Date47、交付物,Deliverable48、依赖关系,Dependency49、虚活动,Dummy Activity50、延续时间,DU=Duration51、延续时间压缩,Duration Compression52、最早完工日期,EF=Early Finish Date53、最早开始日期,ES=Early Start Date54、挣值法,EV=Earned Value55、挣值分析,Earned Value Analysis56、人工量,Effort57、估算,概算,Estimate58、在完成时的费用估算,EAC=Estimate At Completion59、到完成时的估算,ETC=Estimate To Complete60、单节点事件图,Event-on-Node61、例外报告,Exception Report62、完成日期,Finish Date63、完成到完成关系,FF=Finish-to-Finish64、完成到开始关系,FS=Finish-to-Start65、时差,机动时间,浮动时间,Float66、顺推计算法,Forward Pass67、自由时差,FF=Free Float68、职能经理,Functional Manager69、职能组织,Functional Organization70、甘特图,Gantt Chart71、图解评审技术,GERT=Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique72、集合工作,Hammock73、悬摆,Hanger74、信息分发,Information Distribution75、立项,Initiation76、成本/进度综合报告,Integrated Cost/Schedule Reporting77、邀标,IFB= Invitation for Bid78、关键事件进度计划,Key Event Schedule79、滞后量,Lag80、最晚完成日期,LF=Late Finish Date81、最晚开始日期,LS=Late Start Date82、提前量,Lead83、全生命期成本估算,Life-cycle Costing84、产品经理,Line Manager85、逻辑图,Logic Diagram86、逻辑关系,Logical Relationship87、回路,Loop88、管理储备量,Management Reserve89、主进度计划,Master Schedule90、矩阵型组织,Matrix Organization91、里程碑,Milestone92、里程碑进度计划,Milestone Schedule93、现代项目管理,MPM=Modern Project Management94、监控,Monitoring95、蒙托卡罗分析,Monte Carlo Analysis96、次关键工作,Near-Critical Activity97、网络,Network98、网络分析,Network Analysis99、网络逻辑,Network Logic100、网络路线,Network Path101、节点,Node102、组织分解结构,OBS=Organizational Breakdown Structure 103、组织规划,Organizational Planning104、整体变更控制,Overall Change Control105、重叠,Overlap106、参数估算法,Parametric Estimating107、线路,Path108、线路时差,Path Float109、完成百分比,PC=Percent Complete110、执行报告,Performance Reporting111、执行机构,Performing organization112、计划评审技术图,PERT Chart113、计划的完成日期,PF=Planned Finish Date114、计划的开始日期,PS=Planned Start Date115、优先图示法,PDM=Precedence Diagramming Method116、优先关系,Precedence Relationship117、紧前工作,Predecessor Activity118、采购规划,Procurement Planning119、工程,Program120、计划评审技术,PERT=Program Evaluation and Review Technique 121、项目,Project122、项目许可证,Project Charter123、项目沟通管理,Project Communication Management124、项目费用管理,Project Cost Management125、项目人力资源管理,Project Human Resource Management126、项目综合管理,Project Integration Management127、项目生命周期,Project Life Cycle128、项目管理,PM=Project Management129、项目管理知识体系,PMBOK=Project Management Body of Knowledge 130、项目管理软件,Project Management Software131、项目管理团队,Project Management Team132、项目经理,PM=Project Manager133、项目网络图,Project Network Diagram134、项目阶段,Project Phase135、项目计划,Project Plan136、项目计划开发,Project Plan Development 137、项目计划实施,Project Plan Execution138、项目规划,Project Planning139、项目采购管理,Project Procurement Management 140、项目质量管理,Project Quality Management 141、项目风险管理,Project Risk Management142、项目进度计划,Project Schedule143、项目范围管理,Project Scope Management 144、项目团队成员,Project Team Member145、项目时间管理,Project Time Management 146、项目型组织,Project Organization147、质量保证,QA=Quality Assurance148、质量控制,QC=Quality Control149、质量规划,Quality Planning150、剩余持续时间,RDU=Remaining Duration 151、请求建议书,RFP=Request for Proposal152、请求报价单,RFQ=Request for Quotation153、储备量,Reserve154、资源平衡,Resource Leveling155、资源约束进度计划,Resource-Limited Schedule156、资源规划,Resource Planning157、责任分配矩阵,RAM=Responsibility Assignment Matrix 158、责任图,Responsibility Chart159、责任矩阵,Responsibility Matrix160、保留金,Retain age161、突发事件,Risk Event162、风险识别,Risk Identification163、风险应对控制,Risk Response Control164、风险应对开发,Risk Response Development165、S曲线,S-Curve166、进度计划,Schedule167、进度计划分析,Schedule Analysis168、进度计划压缩,Schedule Compression169、进度计划控制,Schedule Control170、进度执行指数,SPI=Schedule Performance Index 171、进度偏差,SV=Schedule Variance172、计划完成日期,SF=Scheduled Finish Date173、计划开始日期,SS=Scheduled Start Date174、范围,Scope175、范围基准计划,Scope Baseline176、范围变更,Scope Change177、范围变更控制,Scope Change Control 178、范围定义,Scope Definition179、范围规划,Scope Planning180、范围验证,Scope Verification181、时差,Slack182、询价,Solicitation183、询价规划,Solicitation184、工作人员招募,Staff Acquisition185、项目相关者,Stakeholder186、开始日期,Start Date187、开始到完成关系,Start-to-Finish188、开始到开始关系,Start-to-Start189、工作说明,SOW=Statement of Work190、子网,Subnet191、子网络,Subnet Work192、后续工作,Successor Activity193、目标完成日期,TC=Target Completion Date 194、目标时度计划,Target Schedule195、任务,Task196、团队建设,Team Development197、团队成员,Team members198、时标网络图,Time-Scaled Network Diagram 199、目标完成日期,TF=Target Finish Date200、目标开始日期,Ts=Target Start Date201、总时差,TF=Total Float202、全面质量管理,TQM=Total Quality Management 203、权变措施,Workaround204、工作分解结构,WBS=Work Breakdown Structure 205、工作包,Work Package。
项目管理英语Project Management
Finance
Electron Military
军事
Medicine
Communication
State organs The world financial group
Professional development
In the development of professional , the division of the project management has been refined gradually in this period, and then it formed a series professional of project management. For instance, Professional project manager, cost engineer, architectural engineer, master builder and so on. At the same time, a series of project management professional certification system were born in this period. Now, project manager is no longer considered as the executor of the project, they have a formal title and greater power and responsibility.
Keywords:Management, skill and tool
The past of the Project Managemen
Embryonic(萌芽) development period: in fact, there is a long history of project management, a lot of the key projects no matter in ancient times or in modern world are applied to the project management in the implementation process(实施 过程), while without specialiaed course name , however, some methods has also laid the foundation for the development of project management theory
项目管理中常用英语
项目管理中常用英语(转载学习)工程项目管理常用英语工艺包 process package工艺设计 process design工艺发表 process release工艺预发表 initial process release工作范围;项目任务范围 scope of work ; project scope工作包 work package工作项 work item任务单项 line item分解结构 breakdown structure工作分解结构 work breakdown structure组织分解机构 organizational breakdown structure项目大项工作分解结构 project summary work breakdown structure承包商标准工作分解结构;工程公司标准工作分解结构 contractor's standard work breakdown structure责任分工矩阵 responsibility assignment matrix风险 risk风险分析 risk analysis风险备忘录 risk memorandum公司本部 home office公司本部服务 home office service公用工程 utility计划 plan项目计划 project plan(项目)设计计划 (project)engineering plan (项目)采购计划 (project)procurement plan (项目)施工计划 (project)construction plan (项目)开车计划 (project)start-up plan专利 patent专利权 patent right产权技术 proprietary technology专利技术 licensed technology专有技术;技术诀窍 know-how许可证 license专利商;许可方 licensor受许可放;受让方 licensee(技术)转让费;提成费 royalty许可证费 license fee专有技术费 know-how fee专业 discipline工艺 process design ; process engineering 系统 systems engineering设备 equipment engineering布置 plant layout engineering管道设计 piping design管道机械 piping mechanical engineering仪表 instruments engineering电气 electrical engineering建筑 architectural engineering土建 civil engineering开车 start-up试车 commissioning投料试车 start-up ; test run ; initial operations性能考核,生产考核 performance test run ; performance guarantee tests用户验收 client acceptance支付条件;付款条件 terms of payment ; conditions of payment ; terms and conditions of payment预付款 advance payment ; down payment按实物进度付款 progress payment按日工程进度付款 schedule payment保留金;扣留款 retention money最终付款 final payment代码;编码 code ; number组码 group code标准分类记帐码;记帐码 standard classification of accountnumbers[SCAN];account codes ; code of accounts可编码 variable code ; optional variable code通用型活动码 generic activity type(numbers)[GAT]不可预见费 contingency发表 issue ; release汇票 bill of exchange ; draft议付汇票 bill for negotiation业主 owner用户;客户 client设计;工程设计 design ; engineering设计阶段 engineering phase工艺设计阶段 process design phase基础工程设计阶段 basic engineering phase分析设计阶段 analytical engineering phase平面设计阶段 planning engineering phase详细工程设计阶段 detailed engineering phase ; final engineering phase ; production engineering phase会议 meeting开工会议 kick-off meeting报价开工会议 proposal kick-off meeting用户开工会议 client kick-off meeting项目开工会议 project kick-off meeting设计开工会议 project kick-off meeting施工动员会议 construction mobilization meeting审核会 review meeting合同;承包 contract合同生效日期 effective date of the contract合同终止 termination of contract合同失效 frustration of contract总价合同 lump-sum contract[L-S](固定)单价合同 (fixed) unit price contract偿付合同;成本加抽筋合同 (cost) reimbursable contract ; cost-plus (fee) contract [C-P]成本加固定酬金合同 cost plus fixed fee contract [CPFF]成本加浮动酬金合同 cost plus fluctuating fee contract ; cost plus sliding scale fee contract目标成本加奖罚合同 (target) cost plus fee contract , with bonus or penalty conditions限定最高价偿付合同;限定最高成本加抽筋合同 reimbursable guaranteed maximum price contract [RGMP] ; guarantee maximum cost plus fee contract承包商 contractor分包商 subcontractor合营企业 joint venture [JV]交货 delivery交货日期 delivery date ; date of delivery交货周期 lead time交货到现场 delivery to job-site交货单 delivery note提货单 delivery order提单 bill of lading交货条件 delivery terms离岸价 free on board [FOB]铁路交货(价);敞车上交货(价) free on rail [FOR] ; free on truck [FOT]成本加运费(价) cost and freight [CFR] or [C&F]到岸价 cost insurance and freight ; cost insurance freight [CIF]船边交货(价) free alongside ship [FAS]货交承运人(价) free carrier [FCA]工厂交货(价) ex works [EXW]估算;费用估算 estimate ' cost estimate估算方法类别 types of estimate详细估算(发) detailed estimate ; defined estimate设备详细估算(发);确切估算(发) defined equipment estimate ; definitive estimate设备估算 equipment estimate分析估算 analysis estimate报价估算 proposal estimate控制估算 control estimate初期控制估算 interim control estimate ; initial control estimate [ICE]批准的控制估算 initial approved cost [IAC]核定估算 check estimate首次核定估算 first check estimate [FCE]二次核定估算 production check estimate [PCE]人工时估算 man-hour estimate证书;证明书 certificate产地证明书 certificate of origin机械竣工证书 mechanical completion certificate用户验收证书;合同项目验收证书 client acceptance certificate (of plant)材料 material设备 equipment散装材料 bulk materials ; commodities材料分类 material class材料统计 material take-off [MTO]材料表;材料清单 bill of materials [BOM]材料管理 material management材料控制 material control进度;进度表;进度计划 schedule进展;进度;实物进度 progress ; physical progress编制进度计划 scheduling ; time scheduling(项目)初期工作进度计划 starter schedule ; early work schedule项目主进度计划 project master schedule ; master project schedule 详细进度计划;详细进度表 detailed schedule网络(图);网络(进度)计划 network (diagram)里程碑网络图 milestone network详细网络图 detailed network关键线路法 critical path method [CPM]关键工序;关键活动 critical activity工序;活动 activity里程碑 milestone进度控制 schedule control ; progress control进度曲线;S曲线 progress curve ; "S" curve资源负荷曲线 resource loading curve ; Bell curve进度提前 ahead of schedule进度拖延 schedule delay违约 default违约通知 default notice(违约)罚款条款 penalty clause违约罚金 liquidated damages运费 freight [Frt.] ; carriage运费付讫 freight paid ; carriage free ; carriage paids运费待收;货到收运费 freight collect ; freight to be collected ; freight payable at destination运费预付 freight prepaid ; advance(d) freight货到付运费;运费未付 freight forward ; carriage forward运费担保函 freight indemnity运费单 freight note运输商;承运商 forwarding agent采购 procurement采买 purchasing催交 expediting检验 inspection运输 traffic ; transport报关单 bill of entry报告 report费用和进展月报告 monthly cost and progress report(项目)进展月报 (job) monthly progress report设计进展月报 engineering monthly progress report项目费用汇总报告 project cost summary report项目实施费用状态报告 project operation cost status report进度报告 schedule report控制索引 control index执行效果报告 performance report劳动生产率报告 productivity report异常报告 exception report材料异常报告 material exception report [MER] ; equipment & materials exception report采购状态报告 procurement status report材料状态报告 material status report请购单和订单状态报告 purchase order and requisition status report供货厂商图纸状态报告 vendor drawing status report ; vendor data scheduling status report检验报告 inspection report(项目)完工报告 close-out report报价;投标 bid ; quotation ; proposal ; tender ; offer讯价文件评审委员会 inquiry review committee [IRC]报价策略会议 bid strategy meeting报价经理 proposal manager投标书;标书;建议书 proposal ; quotation ; bid ;tender ;offer标书评审;报价评审 bid evaluation标书评选表;报价评选表 bid tabulation form ; tabulation of bids谈判 negotiation厂商协调会议;协调会议 vendor coordination meeting [VCM] ; coordination meeting订货合约;定约;成交 commitment订货电传;订货通知 telex order ; notification of commitment订单(即定单);采买订单;订货合同 purchase order签订合同;合同签约 contract award询价;招标 inquiry ; invitation to bid资格预审 pre-qualification合格投标商表;合格供货商表 qualified bidders list ; qualified vendors list询价书;招标文件 inquiry(package) ; request for quotation(package) [RFQ]; request for proposal [RFP] ; invitation to bid [ITB]请购文件;请购单 requisition (package) ; requisition documents采购规格书;采购说明书 purchasing specification [PS]投标者须知;报价须知 instructions to bidders [ITB]变更 change用户变更;合同变更 client change ;contract change待定的用户变更 pending client change认可的用户变更 approved client change用户变更(通知)单;合同变更(通知)单 client change notice [CCB] ; contract change order [CCO]项目变更;内部变更 project change ; internal change项目变更(通知)单;内部变更(通知)单 project change notice[PCN] ;internal change order [ICO]变更申请单;偏差通知单 change request ; deviation notice [DN]质量 quality质量方针 quality policy质量管理 quality management质量策划 quality planning质量控制 quality control [QC]质量保证 quality assurance [QA]质量体系 quality system质量改进 quality improvement质量手册 quality manual质量计划 quality plan图纸 drawing工艺流程图 process flow diagram [PFD]工艺控制图 process control diagram [PCD]管道仪表流程图 piping and instrument diagram [PID] [P&ID]装置布置图 plot plan管道平面设计图 piping planning (drawing)管道平面布置图 piping layout drawing**sort out here)z O G {/e a+M 管段图;管道空视图 isometric drawing |.X$h }7v C ^ s7s"批准用于详细工程设计"图纸 drawing issued "Approved for Design" [AFD])Y$Q L u d"批准用于施工"图纸 drawings issued "Approved for construction" [AFC]供货厂商先期确认图(纸) advanced certified final drawings [ACF] ; advanced certified vendors' drawings ; preliminary vendor drawings [PD]供货厂商最终确认图(纸) certified final drawings [CF] ; certified vendor drawings[CD]图表 diagram ; chart直方图 histogram横道图 bar ; bar-chart ; Gantt chart进度趋势展示图 schedule trend display chart费用趋势展示图 cost trend display chart项目;工程项目 project项目实施费用状态报告 project execution项目实施阶段 project phase项目初始阶段 initial phase of project execution施工阶段 construction phase开车阶段 start-up phase项目建设周期 project duration's项目管理 project management项目控制 project control项目组 project team专责项目组 task force项目经理 project manager项目设计经理 project engineering manager项目采购经理 project procurement manager项目施工经理 project construction manager项目工艺经理 project process manager项目控制经理 project controls manager项目进度计划工程师 project scheduling engineer ; project scheduler项目估算师 project estimator项目费用控制工程师 project cost control engineer ; project cost engineer项目材料控制工程师 project material control engineer项目财务经理 project financial manager项目质量经理 project quality manager项目开车经理 project start-up manager项目安全工程师 project safety engineer项目秘书 project secretary项目控制手段 project controlling ; tools for project control控制基准;执行效果测量基准;实物进度基准 control baseline ; performance measurement baseline ; progress baseline偏差;差异 deviation ; variance执行效果;效绩;性能 performance跟踪 tracking ; follow up监控 monitoring趋势分析;趋势预测 trending ; trend projection偏差预测值 projected deviations预测 projection ; forecasting纠正措施 corrective action ; corrective measures项目综合控制 integrated project control赢得值原理 earned value concept [EVC]计划工作量的预算费用 budgeted cost for work scheduled [BCWS]已完工作量的预算费用 budgeted cost for work performed [BCWP]已完工作量的实耗费用 actual cost for work performed [ACWP]费用差异 cost variance [CV]进度差异 schedule variance [SV]费用指数 cost index [CI]进度指数 schedule index [SI]费用执行效果指数 cost performance index [CPI]进度执行效果指数 schedule performance index [SPI]竣工差异 at completion variance [ACV]竣工预算费用 budgeted cost at completion [BAC]竣工预测费用 estimated cost at completion [EAC]费用;成本 cost建设总费用 total installed cost [TIC]材料费用;直接材料费用 material cost ; direct material cost设备费用;设备购买费用 equipment cost ; purchased cost of equipment散装材料费用;散装材料购买费用 bulk materials cost ; purchased cost of bulk materials ; commodities cost(直接)材料相关费用(运费和保险费等) cost of material related freight ; insurance , etc.施工费用 construction cost施工人工费用;施工劳力费用 labor cost ; erection labor cost ; construction force cost设备安装人工费用 labor cost associated with equipment散装材料施工人工费用 labor cost associated with bulk materials人工时估算定额;施工人工时估算定额;标准工时定额 standard man-hours ; standard labor man-hours ; standard construction man-hours ; standardhours劳动生产率;劳动生产率系数 labor productivity ; productivity factor ; productivity ratio修正的人工事估算值 adjusted man-hours人工时单价 man-hour rate施工监督费用;施工监督和管理费用cost of construction supervision ; cost of construction management and supervision ; field administration and direct supervision cost施工间接费用 cost of construction indirect分包合同费用;现场施工分包合同费用 subcontract cost ; field subcontract cost公司本部(服务)费用 home office cost ; cost of home office servers公司管理费 overhead ; home office overheads非工资费用 non-payroll ; home-office expenses试车费用 commissioning activities cost投料试车费用 start-up cost其他费用 other costs利润;预期利润 profit ; expected profit服务酬金 service gains内部费用转换 internal transfer认可的预计费用 anticipated approved cost费用控制;成本控制 cost control预算(值);项目控制预算 budget ; project control budget预算结余(值);费用结余(值) under-run ; cost under-run预算超支(值);费用超支(值) over-run ; cost over-run施工 construction施工工种 construction craft试车准备 pre-commissioning机械竣工 mechanical completion [MC]界区 battery limit [BL]工艺界区 process battery limit ; inside battery limit [ISBL]界外设施区;辅助设施界区 offsite battery limit工艺装置 process section ; process unit界外设施;辅助设施;通用设施 offsite section ; offsite unit ; offsite facilities ; general facilities保证;担保 guarantee ; warranty性能保证 performance guarantees绝对保证 absolute guarantees违约罚款保证 penaltiable guarantees工作质量保证 workmanship guarantees机械保证;机械担保 mechanical guarantees ; mechanical warranties保函;担保(书) bond投标保函 bid bond履约保函;履约担保(书);为履约出具的银行保证书 performance bond ; performance bank guarantee预付款保函;为预付款出具的银行保证书 advance payment bond ; bank guarantee for advance payment保证书;保险公司出具的保函 surety bond银行保证书;信用保证书 bank guarantee ; letter of guarantee安慰信 letter of comfort保密协议 secrecy agreement保险 insurance ; assurance保险单 insurance policy保险证书 insurance certificate保险费 insurance premium保税货物 bonded goods保税仓库 bonded warehouse信用证 letter of credit [L/C]不可撤销信用证 irrevocable L/C可撤销信用证 revocable L/C即期信用证 sight credit ; sight L/C L 远期信用证 term credit ; term L/C保兑信用证 confirmed L/C可转让信用证 transferable L/C备用信用证 stand-by L/C信用证提款 drawing on L/C]信贷 CREDIT卖方信贷 SUPPLIER'S CREDIT [S/C]买方信贷 buyer's credit [B/C]信贷额度 line of credit项目融资;工程项目筹资 project finance 贷款 loan即期贷款 demand loan索赔 claim ; claim indemnity培训 training税;税金 tax(es)所得税 income taxes关税 duties合法避税 tax avoidance程序 procedure项目协调程序 project coordination procedure项目实施程序 project execution procedure项目设计程序 project engineering procedure项目采购程序 project procurement procedure项目检验程序 project inspection procedure项目控制程序 project control procedure变更控制程序 change control procedure预算变更程序 budget change procedure项目试车程序;项目开车程序 project commissioning procedure ; project start-up procedure ; project test run procedure化学清洗程序 chemical cleaning procedure性能考核程序;生产考核程序 performance test run procedure ; performance guarantee test procedure装置验收程序 plant acceptance procedure数据 data条件数据;设计条件 supporting data返回的条件数据;返回的设计条件 resultant feedback of data 意向书 letter of intent。
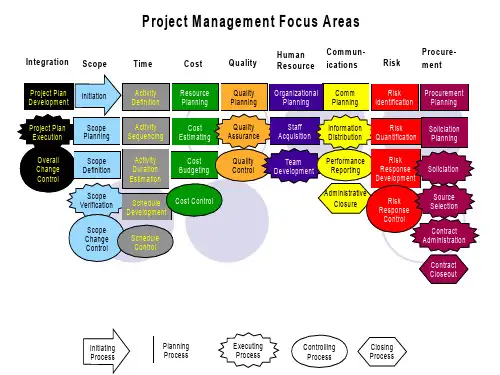
项目管理知识体系概览(英文版)
Initiating Process
Planning Process
Executing Process
Controlling Process
Closing Process
Initiating
Project Management Processes Groups
Planning
Executing Controlling Closing
Controlling
Performance Reporting
Performance Reports Change Requests
Overall Change Control
Closing
Contract Closeout
Contract File Formal Acceptance
& Closure
Risk
Distribution
Response Development
Project Records
Team
Risk Mgmt Plan
Development
Inputs to other processes
Contingency Plans
Performance Improvements
Reserves
Risk Response
Soliciation
Formal Acceptance
Proposals
Source
Control Budget Updates
Corrective Action Plan Control
Selection
Schedule Control
Corrective Action Plan Estimate at Completion Lessons Learned
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
Preparing the Network Diagram (Cont.)
• • • • • Should flow from left to right. Not drawn to a time scale. Can vary in how detailed the diagram should be. AIB vs. AOA is a matter of personal preference. AIB is the most common in project management software packages.
14
Activity on the Arrow (AOA) (Cont.)
• Activities are linked by circles called events. • An event represents the finish of activities entering it and the start of activities leaving it. • Each event is assigned a unique activity number.
Chapter 5 Planning
Learning Objectives
Clearly define the project objective Develop a work breakdown structure Develop a network diagram Utilize a project management methodology called the systems development life cycle for information systems development projects
9
பைடு நூலகம்
Gantt Charts
• Gantt charts, or bar charts, are popular due to their simplicity. • Activities are listed down the left-hand side. • A time scale is shown along the bottom.
15
Dummy Activities
• • • • Used in the AOA format. Consumes zero time. Represented by a dashed arrow. Needed for: – Helping in the unique identification of activities. – Showing certain precendential relationships.
11
Network Principals
• Different formats can be used to draw the diagram: – Activity in the box (AIB) • a.k.a. activity on the node (AON) – Activity on the arrow (AOA)
20
Information System, Defined
• An information system (IS) is a computer-based system that accepts data as input, processes the data, and produces useful information for users.
21
Planning for Information Systems Development
• The systems development life cycle (SDLC) is used to help plan, execute and control IS development projects. • Many people view the SDLC as a classic problemsolving approach.
4
Project Objective
• Planning is an essential part of project management. • In essence, the plan is a roadmap. • The first step is to define the project objective. • The objective must be clear, attainable, specific, and measurable. • The objective is usually defined in terms of scope, schedule and cost.
2
Real World Example
• Vignette: Trojan Reactor Vessel • Project: Remove, transport, and dispose of a full-sized commercial nuclear reactor weighing more than two million pounds • Numerous planning studies were done on worker safety, public safety, transportation safety, and costs. • The project was completed at a cost of $21.9 million, which was $4.2 million under budget, and $19 million less than conventional disposal methods. • Effort won the International Project of the Year Award
12
Activity in the Box (AIB)
• • • • • Each activity is represented by a box. The activity description is written in the box. Each box is assigned a unique activity number. Activities have a precedential relationship. Some activities may be done concurrently.
16
Loops
• Not allowed because it portrays a path of activities that perpetually repeats itself.
17
Laddering
• Used for projects that have a set of activities that are repeated several times.
6
Responsibility Matrix
• Displays in tabular format the individuals responsible for the work items. • “X” can be used to indicate who is responsible. • “P” indicates who has primary responsibility. • “S” indicates who has secondary responsibility.
7
Activities, Defined
• An activity is a piece of work that consumes time.
8
Developing the Network Plan
• After all activities have been defined, they are graphically portrayed in a network diagram. • Two network planning techniques were developed in the 1950’s: – Program evaluation and review technique (PERT) – Critical path method (CPM)
5
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
• The second step is to determine what activities need to be performed. • A list of all the activities must be developed. • The WBS is a hierarchical tree of end items to be accomplished. • A work item is one small piece of the project. • A work package is the lowest-level item.
13
Activity on the Arrow (AOA)
• Each activity is represented by an arrow. • The activity description is written above the arrow. • The tail of the arrow designates the start of the activity. • The head of the arrow designates the completion of the activity.
3
Real World Example
• Vignette: Planning for Risk • During the planning phase risks need to be identified, classified, and weighed. • Some risk classifications include: technological, resource, organizational, and market risks. • The severity of each risk should be investigated and measured. • The probability of each risk should be considered. • A contingency plan should be developed.
