四级语法知识点总结(上)
四级语法知识点总结(上)
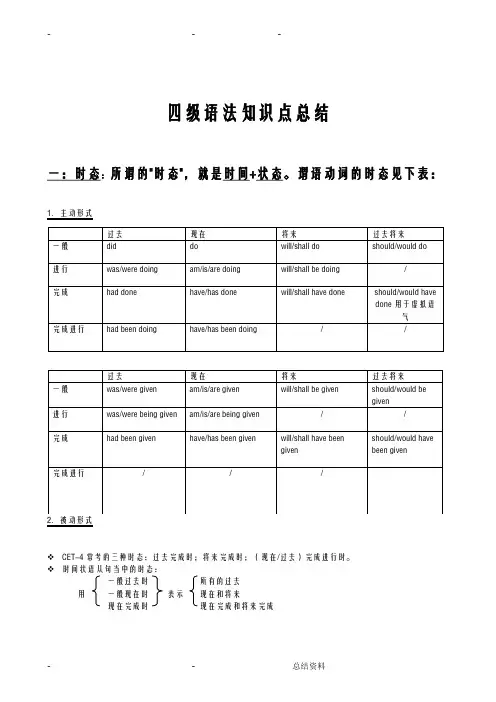
四级语法知识点总结一:时态:所谓的"时态",就是时间+状态。
谓语动词的时态见下表:1.主动形式2.被动形式❖CET-4 常考的三种时态:过去完成时;将来完成时;(现在/过去)完成进行时。
❖时间状语从句当中的时态:一般过去时所有的过去用一般现在时表示现在和将来现在完成时现在完成和将来完成二:非谓语动词1.不定式:一)不定式的常考形式:1)一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up with the others.被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavier work to do.语法功能:表示与谓语动词同步发生2)完成形式:He pretended not to have seen me.被动形式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages.语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前二)不定式常考的考点:1)不定式做定语----将要发生2)不定式做状语----目的3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe.三)不定式的省略感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel + do 表示动作的完整性,真实性;+ doing表示动作的连续性,进行性I saw him work in the garden yesterday.昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。
(强调"我看见了"这个事实)I saw him working in the garden yesterday.昨天我见他正在花园里干活。
(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)❖感官动词后面接形容词而不是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels comfortable.使役动词 have bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原toI ‘d like to have John do it.I have my package weighed.Paul doesn’t have to be made to learn.help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan, offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to doforce sb to do. be more likely to do love to do warn sb to do be able to dobe ambitious to do. begin to do . start to do五) 有的时候to后面要接-ing形式accustom (oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; in addition to; look forward to; object to; be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort to; sink to; be used to; be alternative to; be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; be opposition/opposed to; be similarity/similar to.2. 动名词:具有动作性特征的名词1)是名词 seeing is believing2)具有动词性特征可以带宾语 starving troops is necessary.一)动名词的形式:一般形式:I don't like you smoking.完成形式:I regret not having taken your advice.被动形式:This question is far from being settled.二) 动名词常考的点1)动名词做主语谓语动词为单数2)在动名词和不定式中,做为介词的宾语是动名词3)动名词的否定直接在其前加否定词,通过代词的宾格或所有格形式给出逻辑主语.I would appreciate_______ back this afternoon.A.you to call B.you call C.you calling D.you're calling(Key:C your calling 也对)I regret not having taken your advice.4)有些词后只能接动名词admit; appreciate; avoid; celebrate; consider; contemplate; defer; delay; deny; detest; discontinue; dislike; dispute; enjoy; it entails; escape; excuse; explain; fancy; feel like; finish; forgive; can't help; hinder; imagine; it involves; keep; it means; mention; mind; miss; it necessitates; pardon; postpone; practice; prevent; recall; report; resent; resist; risk; suggest; understand...另外还有一些接-ing形式的常用说法:it's no good; it's no/little/hardly any/ use; it's not/hardly/scarcely use; it's worthwhile; spend money/time; there's no; there's no point in; there's nothing worse than; what's the use/point...5)有些词后加不定式和动名词均可remember, forget, try, stop, go on, cease, mean后面用不定式和-ing形式,意义截然不容。
四级语法重点

四级语法重点一、主谓一致主语与谓语在人称和数上要一致。
1. 单数主语+动词+s/ es例如:- The cat eats fish.(猫吃鱼。
)- He watches TV every day.(他每天看电视。
)2. 复数主语+动词(去除s/ es)例如:- The cats eat fish.(猫吃鱼。
)- They watch TV every day.(他们每天看电视。
)3. 主语为第三人称单数(he、she、it)时,动词要加s/ es 例如:- She reads a book.(她读一本书。
)- It rains heavily.(天下起了大雨。
)二、时态1. 一般现在时表示经常性动作或普遍事实。
肯定句:主语+动词原形(不加s/ es)例如:- I like swimming.(我喜欢游泳。
)否定句:主语+do/ does not +动词原形例如:- He does not like swimming.(他不喜欢游泳。
)疑问句:Do/ Does +主语+动词原形+其他?例如:- Do you like swimming?(你喜欢游泳吗?)2. 一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态。
肯定句:主语+动词过去式例如:- I ran in the park yesterday.(昨天我在公园里跑步。
)否定句:主语+did not +动词原形例如:- He did not eat dinner last night.(昨晚他没有吃晚饭。
)疑问句:Did +主语+动词原形+其他?例如:- Did you go to the cinema last week?(上周你去电影院了吗?)3. 一般将来时表示将要发生的动作或预测的事情。
肯定句:主语+will +动词原形例如:- We will have a meeting tomorrow.(明天我们将开会。
)否定句:主语+will not +动词原形例如:- She will not go to the party.(她不会去参加派对。
大学英语四级语法词汇基础知识

大学英语四级语法词汇基础知识大学英语四级语法词汇基础知识知之者不如好之者,好之者不如乐之者。
以下是店铺为大家搜索整理的大学英语四级语法词汇基础知识,希望能给大家带来帮助!学习笔记:第一部分:分类句中性词,突破相关语法一、分类局中词性,突破相关语法动词部分1、谓语动词1)关于时态A、一般现在时代替一般将来时B、在时间、条件或让步状语从句中:C、在下列句型中常用一般现在时:D、现在完成时E、英语中通常有四类动词不宜用进行式F、一般过去时和现在完成时的区别G、前后时态的呼应H、过去完成时今天背诵内容:◆21. Eliminating problems by transferring the blame to others is often called scape-goating.21.用怪罪别人的`办法来解决问题通常被称为寻找替罪羊。
◆22. The chief foods eaten in any country depend largely on what grows best in its climate and soil.22.一个国家的主要食物是什么,大体取决于什么作物在其天气和土壤条件下生长得最好。
◆23. Over a very large number of trials, the probability of an event’s occurring is equal to the probability that it will not occur.23.在大量的实验中,某一事件发生的几率等于它不发生的几率。
◆24. Most substance contract when they freeze so that the density of a substance’s solid is higher than the density of its liquid.24.大多数物质遇冷收缩,所以他们的密度在固态时高于液态。
四级语法考点总结

四级语法考点总结语法是学习一门外语时必不可少的一部分,对于英语学习者来说,掌握语法规则和考点是提高语言能力的关键。
以下是四级考试常见的语法考点总结。
一、时态与语态1. 一般现在时:表示经常或习惯性的动作,句子结构为主语+谓语动词原形。
2. 现在进行时:表示现阶段正在进行的动作,句子结构为主语+be 动词+动词-ing形式。
3. 一般过去时:表示过去发生的动作或状态,句子结构为主语+谓语动词过去式。
4. 过去进行时:表示过去某个时间点正在进行的动作,句子结构为主语+was/were+动词-ing形式。
5. 一般将来时:表示将来要发生的动作,句子结构为主语+will+动词原形。
6. 现在完成时:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,句子结构为主语+have/has+动词过去分词。
7. 被动语态:表示句子的主语是动作的承受者,句子结构为主语+be动词+过去分词。
二、名词与代词1. 可数名词与不可数名词:可数名词表示可以数的事物,可以与冠词或数词连用;不可数名词表示不能数的物质或抽象概念,不能与冠词连用。
2. 可数名词的单复数形式:大部分名词在尾部加-s或-es构成复数形式,但也有很多名词有不规则的复数形式。
3. 代词的使用:代词用于代替名词,可以避免重复使用,例如人称代词、指示代词、不定代词等。
4. 反身代词:反身代词用于强调动作的主体同时也是动作的承受者,例如myself、yourself等。
三、形容词与副词1. 形容词的比较级与最高级:形容词比较级用于比较两个事物的性质,最高级用于比较三个或以上事物的性质。
2. 副词的用法:副词用于修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,例如slowly、very等。
四、介词与连词1. 常用介词的使用:介词用于表示时间、地点、原因、方式等,例如at、in、on等。
2. 连词的使用:连词用于连接短语、从句或并列句,例如and、but 等。
五、从句与句型1. 名词性从句:名词性从句用于替代名词的作用,包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
四年级上册英语语法总结

四年级上册英语语法总结四种时态的重点掌握内容一、一般现在时:主体构成:主语sh/ch/s/x 尾 +es,辅音字母 +Y 尾把+be+名词 / 形容词主语 +动词动词变化:一般词尾Y 变 i+es,辅音字母 +o 结 +es.+S,标志词:usually, often, sometimes ,always, every morning/night/evening/day/week,二、现在进行时:主体构成:主语+be+动词 ing 标志性词语:look now listen ing形式变化:①直接+ing ②去掉 e+ing③双写最后一个字母+ing get sit shop swim run三、一般过去时态表示过去某一时间所发生的动作或存在的状态。
谓语动词要用一般过去式。
经常与 yesterday(昨天) , last week (上周) , last month (上个月) , last year(去年)two months ago (两个月前) , the day before yesterday (前天), in 1990 (在 1990年), in those days (在那些日子里)等表示过去的时间状语连用。
动词过去式变化规则:1.一般在动词末尾加-ed,如: pull-pulled, cook-cooked 2 .结尾是 e 加 d,如: taste-tasted 3.末尾是辅音字母加一个元音字母和一个辅音字母的重读闭音节,应双写末尾的辅音字母,再加 -ed,如:stop-stopped 4 .以“辅音字母 +y”结尾的,变 y 为 i ,再加 -ed,如:study-studied 5 .不规则动词过去式:am,is-was, are-were , do-did , see-saw, say-said, give-gaveget-got, go-went , come-ca me,have-had,eat-ate,take-took ,run-ran ,sing-sang,put-put ,make-made ,read-read, write-wrote , draw-drew , drink-drank , swim-swam, sit-sat四、一般将来时:主体构成: 1、主语 +be+going+动词原形2、 will+ 动词原型标志性词语:tomorrow , tomorrow morning / afternoon, this morning/afternoon, next year /month, fromnow on (从现在开始 ), in an hour ( 一小时后 )1)肯定句:主语+be going to + 动词原形 +其他。
英语四级考试语法结构与词汇

英语四级考试语法结构与词汇一、语法结构部分。
1. 时态。
- 一般现在时。
- 用法:表示经常发生的动作、存在的状态或客观事实。
- 结构:主语 + 动词原形(第三人称单数主语时动词加 -s或 -es)。
例如:I play football every Sunday.(play,动词原形,[pleɪ])He plays football every Sunday.(plays,动词第三人称单数形式,[pleɪz])- 一般过去时。
- 用法:表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
- 结构:主语+动词的过去式。
例如:I saw a movie yesterday.(saw,see的过去式,[sɔː],动词)- 现在进行时。
- 用法:表示现在正在进行的动作。
- 结构:主语+be动词(am/is/are)+动词的 -ing形式。
例如:She is reading a book.(is,be动词第三人称单数形式,[ɪz];reading,动词的 -ing形式,['ri ːdɪŋ])- 过去进行时。
- 用法:表示过去某个时刻正在进行的动作。
- 结构:主语+be动词(was/were)+动词的 -ing形式。
例如:He was watching TV at 8 o'clock last night.(was,be动词第一、三人称单数过去式,[wɒz];watching,动词的 -ing形式,['wɒtʃɪŋ])2. 从句。
- 定语从句。
- 概念:在句中作定语,修饰名词或代词。
- 关系代词:who(指人,主格,[huː]),whom(指人,宾格,[huːm]),which(指物,[wɪtʃ]),that(指人或物,[ðæt])。
例如:The boy who/that is standing there is my brother.(这里who/that引导定语从句修饰the boy)- 名词性从句。
大学英语4级语法笔记
大学英语4级语法笔记
1. 主谓一致
- 主语和谓语在人称和数上保持一致。
- 当主语是单数第三人称时,谓语动词要加s。
- 当主语是复数时,谓语动词不加s。
2. 动词时态
- 一般现在时:表示经常性或惯性的动作。
- 现在进行时:表示现在正在进行的动作。
- 一般过去时:表示过去某个时间发生的动作。
- 过去进行时:表示过去某一段时间内正在进行的动作。
- 现在完成时:表示过去某个时间发生的动作对现在造成的影
响或结果。
- 过去完成时:表示过去某个时间发生的动作对过去的另一个
时间或动作造成的影响或结果。
3. 形容词和副词的比较级和最高级
- 比较级:注意形容词和副词在比较级前面要加上more或less。
- 最高级:注意形容词和副词在最高级前面要加上the most或the least。
4. 名词所有格
- 表示属于关系时,在名词后面加's。
- 表示复数名词所有格时,在名词后面加'。
5. 祈使句和感叹句
- 祈使句表示命令、请求或建议,一般用动词原形。
- 感叹句表示惊讶、赞叹等情感,常以What、How等引导。
6. 介词的用法
- 介词用于表示位置、时间、方式等关系。
- 常用的介词有in、on、at、under、over等。
以上是大学英语4级语法的一些基础知识点,请在学习和写作时注意运用。
四年级上册英语语法点滴-外研版
四年级上册英语语法点滴-外研版第一章:名词1.1 名词的分类- 专有名词:表示人、地点、事物等的专有名称,如:Beijing, China, Sun Yat-sen University等。
- 普通名词:表示一类事物,如:book, pen, student等。
1.2 名词的数- 单数名词:以一个单词表示,如:cat, dog, desk等。
- 复数名词:以两个单词表示,如:cats, dogs, desks等。
1.3 名词的所有格- 单数名词的所有格:在单词末尾加上's,如:John's book。
- 复数名词的所有格:在单词末尾加上's,如:the students' books。
第二章:代词2.1 代词的分类- 人称代词:表示人,如:I, you, he, she, it, we, they等。
- 物主代词:表示所有关系,如:my, your, his, her, its, our, their 等。
- 反身代词:表示动作的反射,如:myself, yourself, himself等。
2.2 代词的数和格- 单数代词:与单数名词一致,如:he, she, it等。
- 复数代词:与复数名词一致,如:they等。
第三章:形容词和副词3.1 形容词- 形容词用来描述名词,如:big, small, tall, short等。
- 形容词的位置:位于名词之前或之后,如:a big house, the house is big。
3.2 副词- 副词用来描述动词、形容词或其他副词,如:quickly, slowly, loudly等。
- 副词的位置:位于动词、形容词或其他副词之前,如:She sings beautifully.第四章:动词4.1 动词的分类- 行为动词:表示动作,如:eat, drink, read等。
- 状态动词:表示状态,如:be, have, do等。
英语四级语法重点整理
英语四级语法重点整理英语四级考试中,语法是非常重要的一部分内容。
掌握好语法规则不仅有助于理解阅读材料,还能提高写作和口语的表达准确性。
下面是英语四级语法的重点整理。
一、时态1. 一般现在时:表示经常性动作、客观真理等。
2. 现在进行时:表示现在正在进行的动作。
3. 一般过去时:表示过去某个具体时间发生的动作。
4. 过去进行时:表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作。
5. 一般将来时:表示将来某个时间会发生的动作。
二、被动语态被动语态由助动词be加上动词的过去分词构成,用于强调动作的承受者而非执行者。
被动语态的时态和主动语态保持一致。
三、倒装句1. 全部倒装:把助动词或情态动词放在主语之前,用于表示强调、条件、地点状语等情况。
2. 部分倒装:将助动词、情态动词或系动词放在句首,用于表示否定、否定含义的副词、状语从句等情况。
四、条件句1. 第一类条件句:表示对未来某种条件的假设,主句用一般现在时,从句用一般现在时。
2. 第二类条件句:表示对现在某种不可能实现的假设,主句用would/could/might + 动词原形,从句用过去完成时。
3. 第三类条件句:表示对过去某种不可能实现的假设,主句用would/could/might + have + 过去分词,从句用过去完成时。
五、比较级和最高级1. 比较级:表示两个人或物之间的比较,一般在形容词或副词前加-er,或在词前加more。
2. 最高级:表示三个或三个以上人或物之间的比较,一般在形容词或副词前加-est,或在词前加most。
六、名词1. 可数名词:表示可以计数的名词,可以与a/an或数字等连用。
2. 不可数名词:表示无法计数的名词,不能与a/an或数字等连用。
3. 复数形式:一般在词尾加-s,或变音,或保持不变。
七、冠词1. 不定冠词:用于特指单数可数名词前,表示泛指。
2. 定冠词:用于特指单数或复数名词前,表示特指。
八、动词1. 动词的时态和语态变化规律。
四级语法要点总结
四级语法要点总结语法是英语学习的基础和核心要素之一,它对于英语的正确表达和理解至关重要。
在四级考试中,语法知识所占比重也是相当大的。
下面将对四级考试中的一些重要的语法要点进行总结。
一、时态1. 一般现在时一般现在时表示经常性的动作、习惯、真理等。
结构:主语 + 动词原形(+ 其他成分)2. 一般过去时一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构:主语 + 动词过去式(+ 其他成分)3. 一般将来时一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
结构:主语 + will + 动词原形(+ 其他成分)4. 现在进行时现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作。
结构:主语 + am/is/are + 现在分词(+ 其他成分)5. 过去进行时过去进行时表示过去某个时间正在进行的动作。
结构:主语 + was/were + 现在分词(+ 其他成分)6. 将来进行时将来进行时表示将来某个时间正在进行的动作。
结构:主语 + will be + 现在分词(+ 其他成分)7. 现在完成时现在完成时表示过去某个时间发生并且对现在有影响的动作或状态。
结构:主语 + have/has + 过去分词(+ 其他成分)8. 过去完成时过去完成时表示过去某个时间已经发生并且对过去某个时间有影响的动作或状态。
结构:主语 + had + 过去分词(+ 其他成分)9. 将来完成时将来完成时表示将来某个时间已经发生并且对将来某个时间有影响的动作或状态。
结构:主语 + will have + 过去分词(+ 其他成分)二、语态1. 被动语态被动语态表示动作的承受者在句子中作主语的一种语态。
结构:主语 + be + 过去分词(+ 其他成分)2. 完成被动语态完成被动语态表示动作的承受者在句子中作主语的一种完成语态。
结构:主语 + have/has been + 过去分词(+ 其他成分)三、倒装1. 完全倒装完全倒装句是指将助动词或情态动词提到主语之前的句子结构。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
四级语法知识点总结一:时态:所谓得"时态",就就是时间+状态。
谓语动词得时态见下表:1.主动形式2.被动形式:过去完成时;将来完成时;(现在/过去)完成进行时。
❖时间状语从句当中得时态:一般过去时 所有得过去用 一般现在时 表示 现在与将来现在完成时 现在完成与将来完成二:非谓语动词1.不定式:一)不定式得常考形式:1) 一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up with the others 、被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavier work to do 、语法功能: 表示与谓语动词同步发生2)完成形式:He pretended not to have seen me、被动形式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages、语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前二)不定式常考得考点:1)不定式做定语将要发生2)不定式做状语目得3)不定式充当名词功能To see is to believe、三)不定式得省略感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel+ do 表示动作得完整性,真实性;+ doing表示动作得连续性,进行性I saw him work in the garden yesterday、昨天我瞧见她在花园里干活了。
(强调"我瞧见了"这个事实)I saw him working in the garden yesterday、昨天我见她正在花园里干活。
(强调"我见她正干活"这个动作)❖感官动词后面接形容词而不就是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels fortable、使役动词 have bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原toI ‘d like to have John do it、I have my package weighed、Paul doesn’t have to be made to learn、help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan,offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to doforce sb to do、 be more likely to do love to do warn sb to do be able to dobe ambitious to do、 begin to do 、 start to do五) 有得时候to后面要接ing形式accustom (oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; inaddition to; look forward to; object to; be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort to; sink to; be used to; be alternative to; be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; be opposition/opposed to; be similarity/similar to、2、动名词: 具有动作性特征得名词1)就是名词 seeing is believing2)具有动词性特征可以带宾语 starving troops is necessary、一)动名词得形式:一般形式:I don't like you smoking、完成形式:I regret not having taken your advice、被动形式:This question is far from being settled、二) 动名词常考得点1)动名词做主语谓语动词为单数2)在动名词与不定式中,做为介词得宾语就是动名词3)动名词得否定直接在其前加否定词,通过代词得宾格或所有格形式给出逻辑主语、I would appreciate_______ back this afternoon.A.you to callB.you callC.you callingD.you're calling(Key:C your calling 也对)I regret not having taken your advice、4)有些词后只能接动名词admit; appreciate; avoid; celebrate; consider; contemplate; defer; delay; deny; detest; discontinue; dislike; dispute; enjoy; it entails; escape; excuse; explain; fancy; feel like; finish; forgive; can't help; hinder; imagine; it involves; keep; it means; mention; mind; miss; it necessitates; pardon; postpone; practice; prevent; recall; report; resent; resist; risk; suggest; understand、、、另外还有一些接ing形式得常用说法:it's no good; it's no/little/hardly any/ use; it'snot/hardly/scarcely use; it's worthwhile; spend money/time; there's no; there's no point in; there's nothing worse than; what's theuse/point、、、5)有些词后加不定式与动名词均可remember, forget, try, stop, go on, cease, mean后面用不定式与ing形式,意义截然不容。
I remembered to post the letters、 (指未来/过去未来得动作)I remembered posting/having posting the letters (我记得这个动作)forgot与remember得用法类似。
I regret to inform you that… 我很遗憾地通知您…I regretted having left the firm after twenty years、为了"二十年前得离开"而遗憾。
try to 努力 You really must try to overe your shyness、try –ing 试验Try practicing five hours a day、I mean to go, but my father would not allow me to、 [打算、想]我想去,但我父亲不让我去。
To raise wage means increasing purchasing power、 [意味着]赠加工资意味着增加购买力。
prefer得用法:我宁愿在这里等。
I prefer to wait here、(所以啊,您不介意得话,我就等下去。
)I prefer waiting here、(我正在这里等,我就喜欢这么做。
)I prefer swimming to cycling、(这个句子里面就不能用不定式了。
)3 分词:现在分词主动进行,过去分词被动状态现在分词得形式:1)一般式: Do you see the man talking to the dean(主任)?(与谓语动词同步发生)2)完成形式:Not having made adequate preparations, they failed、(发生谓语动词之前)3)完成被动形式:Having been adapted, the script seems perfect、(发生谓语动词之前且表示被动)过去分词1)过去分词表示被动:Fight no battle unprepared、2)过去分词得进行形式:You'll find the topic being discussed everywhere、 (强调正在被做)这三种非谓语动词,都可以构成复合结构,非谓语动词所修饰得成分就是这些非谓语动词得逻辑主语。
她们之间得一致关系——主动还就是被动,往往就就是考点。
独立主格结构中,要注意得就是分词与她前面得逻辑主语之间得主动被动得关系。
三:虚拟语气情态动词所表达得可能性程度:must/can't → should/shouldn't →might/may (not)另外两个"类情态词得形式:"need/needn't; have to/don't have to ❖最自然得虚拟状态:由should/would+原型时态(不含时间只含状态) 本质上就是过去将来时:这时"虚拟语气"得产生往往就是因为我们要表达"本来应该……"(而现在却还没有……)(本来可以……,本来能……)I should go! (… but I'm still here!)(一般)I should be working now! (进行)I should have practiced more (than I did)! (完成)我应该多多练习!(言下之意,现在我练习得不多。
)I shouldn't dream away my time too much! (完成得否定)(actually I did dream away my time too much!)It shouldn't have been leaking for such a long time! (完成进行)I may/might/could have finished! (完成)一些常见得句型中,就会出现这种虚拟语气,而处于从句之中,should 常常被省略掉o suggest, advise, propose, remend, plan;o demand, order, direct, arrange, mand, decide;o require, request;o think, expect, believe, insist, suspect、由于她们得含义中包含"建议,假设,应该"这类得含义,所以,由她们引起得从句中,就会包含有should+原型时态构成得虚拟语气。
