曼昆经济学原理英文版文案加习题答案8章

144
WHAT’S NEW IN THE S EVENTH EDITION:
A new In the News box on ―The Tax Debate ‖ has been added.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
how taxes reduce consumer and producer surplus.
the meaning and causes of the deadweight loss from a tax.
why some taxes have larger deadweight losses than others.
how tax revenue and deadweight loss vary with the size of a tax.
CONTEXT AND PURPOSE:
Chapter 8 is the second chapter in a three-chapter sequence dealing with welfare economics. In the
previous section on supply and demand, Chapter 6 introduced taxes and demonstrated how a tax affects the price and quantity sold in a market. Chapter 6 also described the factors that determine how the burden of the tax is divided between the buyers and sellers in a market. Chapter 7 developed welfare economics —the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being. Chapter 8 combines the lessons learned in Chapters 6 and 7 and addresses the effects of taxation on welfare. Chapter 9 will address the effects of trade restrictions on welfare.
The purpose of Chapter 8 is to apply the lessons learned about welfare economics in Chapter 7 to the issue of taxation that was addressed in Chapter 6. Students will learn that the cost of a tax to buyers and sellers in a market exceeds the revenue collected by the government. Students will also learn about the factors that determine the degree by which the cost of a tax exceeds the revenue collected by the government.
8
APPLICATION: THE COSTS OF
TAXATION
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?145
KEY POINTS:
? A tax on a good reduces the welfare of buyers and sellers of the good, and the reduction in consumer and producer surplus usually exceeds the revenue raised by the government. The fall in total surplus—the sum of consumer surplus, producer surplus, and tax revenue—is called the
deadweight loss of the tax.
?Taxes have deadweight losses because they cause buyers to consume less and sellers to produce less, and these changes in behavior shrink the size of the market below the level that maximizes total surplus. Because the elasticities of supply and demand measure how much market participants
respond to market conditions, larger elasticities imply larger deadweight losses.
?As a tax grows larger, it distorts incentives more, and its deadweight loss grows larger. Because a tax reduces the size of a market, however, tax revenue does not continually increase. It first rises with the size of a tax, but if the tax gets large enough, tax revenue starts to fall.
CHAPTER OUTLINE:
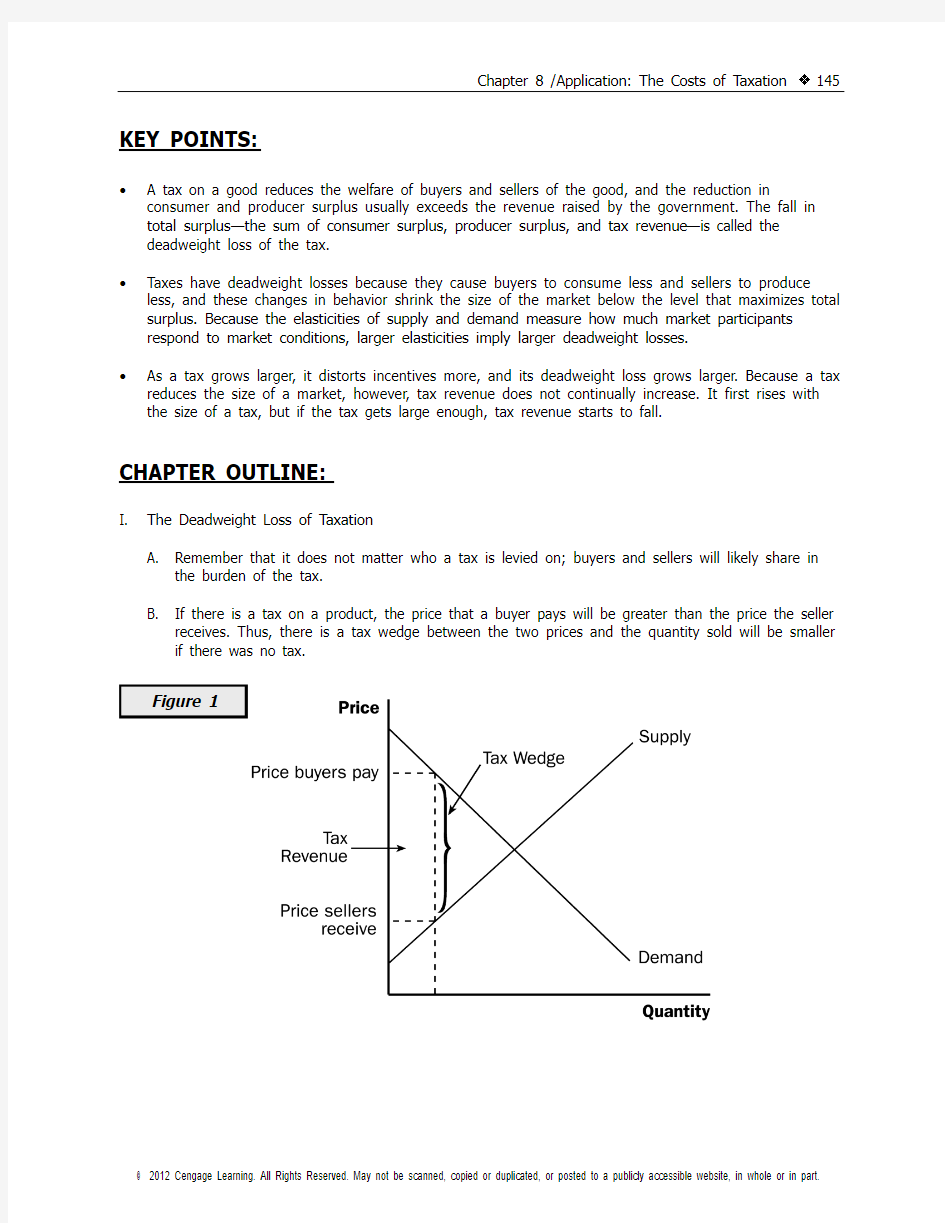
I. The Deadweight Loss of Taxation
A. Remember that it does not matter who a tax is levied on; buyers and sellers will likely share in
the burden of the tax.
B. If there is a tax on a product, the price that a buyer pays will be greater than the price the seller
receives. Thus, there is a tax wedge between the two prices and the quantity sold will be smaller if there was no tax.
146 ? Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation
C. How a Tax Affects Market Participants
1. We can measure the effects of a tax on consumers by examining the change in consumer
surplus. Similarly, we can measure the effects of the tax on producers by looking at the change in producer surplus.
2. However, there is a third party that is affected by the tax —the government, which gets total
tax revenue of T × Q. If the tax revenue is used to provide goods and services to the public, then the benefit from the tax revenue must not be ignored.
3. Welfare without a Tax
a. Consumer surplus is equal to: A + B + C.
b. Producer surplus is equal to: D + E + F.
c. Total surplus is equal to: A + B + C + D + E + F. 4. Welfare with a Tax
a. Consumer surplus is equal to: A.
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?147
b. Producer surplus is equal to: F.
c. Tax revenue is equal to: B + D.
d. Total surplus is equal to: A + B + D + F.
5. Changes in Welfare
a. Consumer surplus changes by: –(B + C).
b. Producer surplus changes by: –(D + E).
c. Tax revenue changes by: +(B + D).
d. Total surplus changes by: –(C + E).
6. Definition of deadweight loss: the fall in total surplus that results from a market
distortion, such as a tax.
D. Deadweight Losses and the Gains from Trade
1. Taxes cause deadweight losses because they prevent buyers and sellers from benefiting from
trade.
2. This occurs because the quantity of output declines; trades that would be beneficial to both
the buyer and seller will not take place because of the tax.
3. The deadweight loss is equal to areas C and E (the drop in total surplus).
4. Note that output levels between the equilibrium quantity without the tax and the quantity
with the tax will not be produced, yet the value of these units to consumers (represented by the demand curve) is larger than the cost of these units to producers (represented by the
supply curve).
148 ? Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation II. The Determinants of the Deadweight Loss
A. The price elasticities of supply and demand will determine the size of the deadweight loss that
occurs from a tax.
1. Given a stable demand curve, the deadweight loss is larger when supply is relatively elastic.
2. Given a stable supply curve, the deadweight loss is larger when demand is relatively elastic.
B. Case Study: The Deadweight Loss Debate
1. Social Security tax and federal income tax are taxes on labor earnings. A labor tax places a
tax wedge between the wage the firm pays and the wage that workers receive.
2. There is considerable debate among economists concerning the size of the deadweight loss
from this wage tax.
3. The size of the deadweight loss depends on the elasticity of labor supply and demand, and
there is disagreement about the magnitude of the elasticity of supply.
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?149
a. Economists who argue that labor taxes do not greatly distort market outcomes believe
that labor supply is fairly inelastic.
b. Economists who argue that labor taxes lead to large deadweight losses believe that labor
supply is more elastic.
III. Deadweight Loss and Tax Revenue as Taxes Vary
A. As taxes increase, the deadweight loss from the tax increases.
B. In fact, as taxes increase, the deadweight loss rises more quickly than the size of the tax.
1. The deadweight loss is the area of a triangle and the area of a triangle depends on the
square of its size.
150 ? Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation
2. If we double the size of a tax, the base and height of the triangle both double so the area of
the triangle (the deadweight loss) rises by a factor of four.
C. As the tax increases, the level of tax revenue will eventually fall.
D. Case Study: The Laffer Curve and Supply-Side Economics
1. The relationship between the size of a tax and the level of tax revenues is called a Laffer
curve.
2. Supply-side economists in the 1980s used the Laffer curve to support their belief that a drop
in tax rates could lead to an increase in tax revenue for the government.
3. Economists continue to debate Laffer’s argument.
a. Many believe that the 1980s refuted Laffer’s theory.
b. Others believe that the events of the 1980s tell a more favorable supply-side story.
c. Some economists believe that, while an overall cut in taxes normally decreases revenue,
some taxpayers may find themselves on the wrong side of the Laffer curve.
E. In the News: The Tax Debate
1. Recently, policymakers have debated the effects of increasing the tax rate, particularly on
higher-income taxpayers.
2. These two opinion pieces from The Wall Street Journal present both sides of the issue. ALTERNATIVE CLASSROOM EXAMPLE:
Draw a graph showing the demand and supply of paper clips. (Draw each curve as a 45-degree line so that buyers and sellers will share any tax equally.) Mark the equilibrium price as $0.50 (per box) and the equilibrium quantity as 1,000 boxes. Show students the areas of producer and consumer surplus.
Impose a $0.20 tax on each box. Assume that sellers are required to ―pay‖ the tax to the government. Show students that:
? the price buyers pay will rise to $0.60. ? the price sellers receive will fall to $0.40.
? the quantity of paper clips purchased will fall (assume to 800 units). ? tax revenue would be equal to $160 ($0.20 800).
Have students calculate the area of deadweight loss. (You may have to remind students how to calculate the area of a triangle.)
Show students that as the tax increases (to $0.40, $0.60, and $0.80), tax revenue rises and then falls, and the deadweight loss increases.
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?151
152 ? Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation
SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS:
Quick Quizzes
1. Figure 1 shows the supply and demand curves for cookies, with equilibrium quantity Q 1 and
equilibrium price P 1. When the government imposes a tax on cookies, the price to buyers
rises to P B , the price received by sellers declines to P S , and the equilibrium quantity falls to Q 2. The deadweight loss is the triangular area below the demand curve and above the supply curve between quantities Q 1 and Q 2. The deadweight loss shows the fall in total surplus that results from the tax.
Figure 1
2. The deadweight loss of a tax is greater the greater is the elasticity of demand. Therefore, a
tax on beer would have a larger deadweight loss than a tax on milk because the demand for beer is more elastic than the demand for milk.
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?153
3. If the government doubles the tax on gasoline, the revenue from the gasoline tax could rise
or fall depending on whether the size of the tax is on the upward or downward sloping
portion of the Laffer curve. However, if the government doubles the tax on gasoline, you can
be sure that the deadweight loss of the tax rises because deadweight loss always rises as the
tax rate rises.
Questions for Review
1. When the sale of a good is taxed, both consumer surplus and producer surplus decline. The
decline in consumer surplus and producer surplus exceeds the amount of government
revenue that is raised, so society's total surplus declines. The tax distorts the incentives of
both buyers and sellers, so resources are allocated inefficiently.
2. Figure 2 illustrates the deadweight loss and tax revenue from a tax on the sale of a good.
Without a tax, the equilibrium quantity would be Q1, the equilibrium price would be P1,
consumer surplus would be A + B + C, and producer surplus would be D + E + F. The
imposition of a tax places a wedge between the price buyers pay, P B, and the price sellers
receive, P S, where P B = P S + tax. The quantity sold declines to Q2. Now consumer surplus is
A, producer surplus is F, and government revenue is B + D. The deadweight loss of the tax is
C+E, because that area is lost due to the decline in quantity from Q1 to Q2.
Figure 2
3. The greater the elasticities of demand and supply, the greater the deadweight loss of a tax.
Because elasticity measures the responsiveness of buyers and sellers to a change in price,
higher elasticity means the tax induces a greater reduction in quantity, and therefore, a
greater distortion to the market.
4. Experts disagree about whether labor taxes have small or large deadweight losses because
they have different views about the elasticity of labor supply. Some believe that labor supply
is inelastic, so a tax on labor has a small deadweight loss. But others think that workers can
adjust their hours worked in various ways, so labor supply is elastic, and thus a tax on labor
has a large deadweight loss.
154 ?Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation
5. The deadweight loss of a tax rises more than proportionally as the tax rises. Tax revenue,
however, may increase initially as a tax rises, but as the tax rises further, revenue eventually
declines.
Quick Check Multiple Choice
1. a
2. b
3. c
4. a
5. b
6. a
Problems and Applications
1. a. Figure 3 illustrates the market for pizza. The equilibrium price is P1, the equilibrium
quantity is Q1, consumer surplus is area A + B + C, and producer surplus is area D + E +
F. There is no deadweight loss, as all the potential gains from trade are realized; total
surplus is the entire area between the demand and supply curves: A + B + C + D + E +
F.
Figure 3
b. With a $1 tax on each pizza sold, the price paid by buyers, P B, is now higher than the
price received by sellers, P S, where P B = P S + $1. The quantity declines to Q2, consumer
surplus is area A, producer surplus is area F, government revenue is area B + D, and
deadweight loss is area C + E. Consumer surplus declines by B + C, producer surplus
declines by D + E, government revenue increases by B + D, and deadweight loss
increases by C + E.
c. If the tax were removed and consumers and producers voluntarily transferred B + D to
the government to make up for the lost tax revenue, then everyone would be better off
than without the tax. The equilibrium quantity would be Q1, as in the case without the
tax, and the equilibrium price would be P1. Consumer surplus would be A + C, because
consumers get surplus of A + B + C, then voluntarily transfer B to the government.
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?155 Producer surplus would be E + F, because producers get surplus of D + E + F, then
voluntarily transfer D to the government. Both consumers and producers are better off
than the case when the tax was imposed. If consumers and producers gave a little bit
more than B + D to the government, then all three parties, including the government,
would be better off. This illustrates the inefficiency of taxation.
2. a. The statement, "A tax that has no deadweight loss cannot raise any revenue for the
government," is incorrect. An example is the case of a tax when either supply or demand is perfectly inelastic. The tax has neither an effect on quantity nor any deadweight loss,
but it does raise revenue.
b. The statement, "A tax that raises no revenue for the government cannot have any
deadweight loss," is incorrect. An example is the case of a 100% tax imposed on sellers.
With a 100% tax on their sales of the good, sellers will not supply any of the good, so
the tax will raise no revenue. Yet the tax has a large deadweight loss, because it reduces the quantity sold to zero.
3. a. With very elastic supply and very inelastic demand, the burden of the tax on rubber
bands will be borne largely by buyers. As Figure 4 shows, consumer surplus declines
considerably, by area A + B, but producer surplus decreases only by area C+D..
Figure 4 Figure 5
b.With very inelastic supply and very elastic demand, the burden of the tax on rubber
bands will be borne largely by sellers. As Figure 5 shows, consumer surplus does not
decline much, just by area A + B, while producer surplus falls substantially, by area C +
D. Compared to part (a), producers bear much more of the burden of the tax, and
consumers bear much less.
4. a. The deadweight loss from a tax on heating oil is likely to be greater in the fifth year after
it is imposed rather than the first year. In the first year, the demand for heating oil is
relatively inelastic, as people who own oil heaters are not likely to get rid of them right
away. But over time they may switch to other energy sources and people buying new
heaters for their homes will more likely choose gas or electric, so the tax will have a
greater impact on quantity. Thus, the deadweight loss of the tax will get larger over time.
156 ?Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation
b. The tax revenue is likely to be higher in the first year after it is imposed than in the fifth
year. In the first year, demand is more inelastic, so the quantity does not decline as
much and tax revenue is relatively high. As time passes and more people substitute away
from oil, the quantity sold declines, as does tax revenue.
5. Because the demand for food is inelastic, a tax on food is a good way to raise revenue
because it leads to a small deadweight loss; thus taxing food is less inefficient than taxing
other things. But it is not a good way to raise revenue from an equity point of view, because
poorer people spend a higher proportion of their income on food. The tax would affect them
more than it would affect wealthier people.
6. a. This tax has such a high rate that it is not likely to raise much revenue. Because of the
high tax rate, the equilibrium quantity in the market is likely to be at or near zero.
b. Senator Moynihan's goal was probably to ban the use of hollow-tipped bullets. In this
case, the tax could be as effective as an outright ban.
7. a. Figure 6 illustrates the market for socks and the effects of the tax. Without a tax, the
equilibrium quantity would be Q1, the equilibrium price would be P1, total spending by
consumers equals total revenue for producers, which is P1 x Q1, which equals area B + C
+ D + E + F, and government revenue is zero. The imposition of a tax places a wedge
between the price buyers pay, P B, and the price sellers receive, P S, where P B = P S + tax.
The quantity sold declines to Q2. Now total spending by consumers is P B x Q2, which
equals area A + B + C + D, total revenue for producers is P S x Q2, which is area C + D,
and government tax revenue is Q2 x tax, which is area A + B.
b. Unless supply is perfectly elastic or demand is perfectly inelastic, the price received by
producers falls because of the tax. Total receipts for producers fall, because producers
lose revenue equal to area B + E + F.
Figure 6
c. The price paid by consumers rises, unless demand is perfectly elastic or supply is
perfectly inelastic. Whether total spending by consumers rises or falls depends on the
price elasticity of demand. If demand is elastic, the percentage decline in quantity
exceeds the percentage increase in price, so total spending declines. If demand is
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?157 inelastic, the percentage decline in quantity is less than the percentage increase in price, so total spending rises. Whether total consumer spending falls or rises, consumer surplus declines because of the increase in price and reduction in quantity.
8. Figure 7 illustrates the effects of the $2 subsidy on a good. Without the subsidy, the
equilibrium price is P1 and the equilibrium quantity is Q1. With the subsidy, buyers pay price P B, producers receive price P S (where P S = P B + $2), and the quantity sold is Q2. The
following table illustrates the effect of the subsidy on consumer surplus, producer surplus, government revenue, and total surplus. Because total surplus declines by area D + H, the subsidy leads to a deadweight loss in that amount.
Figure 7
158 ?Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation
9. a. Figure 8 shows the effect of a $10 tax on hotel rooms. The tax revenue is represented by
areas A + B, which are equal to ($10)(900) = $9,000. The deadweight loss from the tax
is represented by areas C + D, which are equal to (0.5)($10)(100) = $500.
Figure 8 Figure 9
b. Figure 9 shows the effect of a $20 tax on hotel rooms. The tax revenue is represented by
areas A + B, which are equal to ($20)(800) = $16,000. The deadweight loss from the tax
is represented by areas C + D, which are equal to (0.5)($20)(200) = $2,000.
When the tax is doubled, the tax revenue rises by less than double, while the deadweight
loss rises by more than double. The higher tax creates a greater distortion to the market.
10. a. Setting quantity supplied equal to quantity demanded gives 2P = 300 –P. Adding P to
both sides of the equation gives 3P = 300. Dividing both sides by 3 gives P = 100.
Substituting P = 100 back into either equation for quantity demanded or supplied gives Q
= 200.
b. Now P is the price received by sellers and P +T is the price paid by buyers. Equating
quantity demanded to quantity supplied gives 2P = 300 ? (P+T). Adding P to both sides
of the equation gives 3P = 300 –T. Dividing both sides by 3 gives P = 100 –T/3. This is
the price received by sellers. The buyers pay a price equal to the price received by sellers
plus the tax (P +T = 100 + 2T/3). The quantity sold is now Q = 2P = 200 – 2T/3.
c. Because tax revenue is equal to T x Q and Q = 200 – 2T/3, tax revenue equals 200T?
2T2/3. Figure 10 (on the next page) shows a graph of this relationship. Tax revenue is
zero at T = 0 and at T = 300.
Chapter 8 /Application: The Costs of Taxation ?159
Figure 10 Figure 11
d. As Figure 11 shows, the area of the triangle (laid on its side) that represents the
deadweight loss is 1/2 × base × height, where the base is the change in the price, which is the size of the tax (T) and the height is the amount of the decline in quantity (2T/3).
So the deadweight loss equals 1/2 ×T × 2T/3 = T2/3. This rises exponentially from 0 (when T = 0) to 30,000 when T = 300, as shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12
e. A tax of $200 per unit is a bad policy, because tax revenue is declining at that tax level.
The government could reduce the tax to $150 per unit, get more tax revenue ($15,000 when the tax is $150 versus $13,333 when the tax is $200), and reduce the deadweight loss (7,500 when the tax is $150 compared to 13,333 when the tax is $200).
曼昆_微观经济学_原理_第五版_课后习题答案
第三章 6.下表描述了Baseballia国两个城市的生产可能性: 一个工人每小时生产的红补袜子量一个工人每小时生产的白袜子量 A.没有贸易,波士顿一双白袜子价格(用红袜子表示)是多少芝加哥11双白袜子价格是多少答:没有贸易时,波士顿1 双白袜子价格是1 双红袜子,芝加哥1 双白袜子价格是2 双红袜子。B.在每种颜色的袜子生产上,哪个城市有绝对优势哪个城市有比较优势 答:波士顿在生产红、白袜子上都有绝对优势。波士顿在生产白袜子上有比较优势,芝加哥在生产红袜子上有比较优势。 C.如果这两个城市相互交易,两个城市将分别出口哪种颜色的袜子 答:如果它们相互交易,波士顿将出口白袜子,而芝加哥出口红袜子。 D.可以进行交易的价格范围是多少 答:白袜子的最高价格是2 双红袜子,最低价格是1 双红袜子。红袜子的最高价格是1 双白袜子,最低价格是1/2 双白袜子。 7.假定一个美国工人每年能生产100件衬衣或20台电脑,而一个中国工人每年能生产100件衬衣或10台电脑。 A.画出这两个国家的生产可能性边界。假定没有贸易,每个国家的工人各用一半的时间生产两种物品,在你的图上标出这一点。 答:两个国家的生产可能性边界如图3 一4 所示。如果没有贸易,一个美国工人把一半的时间用于生产每种物品,则能生产50 件衬衣、10 台电脑;同样,一个中国工人则能生产50 件衬衣、5 台电脑。
图3 一4 生产可能性边界 B.如果这两个国家进行贸易,哪个国家将出口衬衣举出一个具体的数字例子,并在你的图上标出。哪一个国家将从贸易中获益解释原因。 答:中国将出口衬衣。对美国而言,生产一台电脑的机会成本是5 件衬衣,而生产一件衬衣的机会成本为1/5 台电脑。对中国而言,生产一台电脑的机会成本是10 件衬衣,而生产一件衬衣的机会成本为1/10 台电脑。 因此,美国在生产电脑上有比较优势,中国在生产衬衣上有比较优势,所以中国将出口衬衣。 衬衣的价格在1/5 到1/10 台电脑之间。两个国家都会从贸易中获益。例如,衬衣的价格为1/8 台电脑,换言这,中国出口8 件衬衣换回1 台电脑。中国专门生产衬衣(100 件),并出口其中的8 件,这样就有92 件衬衣和换回的1 台电脑。而没有贸易时,92 件衬衣和1 台电脑在中国是不可能得到的产出。美国专门生产电脑(20 台)并向中国出口其中的1 台换取8 件衬衣。这样,美国最后就有19 台电脑和8 件衬衣,这也是没有贸易时美国不可 能得到的产出。由此可见,贸易使中国和美国所能消费的产品增加,两国都获益了。 C.解释两国可以交易的电脑价格(用衬衣衡量)是多少。 答:一台电脑的价格将在5 到10 件衬衣之间。如果电脑价格低于5 件衬衣,美国将不会出口,因为在美国一件衬衣的机会成本为1/5 台电脑。如果电脑的价格高于10 件衬衣,中国将不会进口,因为在中国一台电脑的机会成本是10 件衬衣。 D.假设中国的生产率赶上了美国,因此,一个中国工人每年可以生产100件衬衣或20台电脑。你预期这时的贸易形式会是什么样的。中国生产率的这种进步将如何影响两国居民的经济福利 答:此时,中美双方将同时生产两种商品,然后进行贸易,不过此时的贸易被称为水平贸易,即生产率大致相同的两个国家进行的贸易。而中国在提高生产率之前,两国进行的是垂直贸易。垂直
经济学原理第五版中文曼昆 名词解释
23章 微观经济学:研究家庭和企业如何做出决策,以及它们如何在市场上相互影响。 宏观经济学:研究整体经济现象,包括通货膨胀,失业和经济增长。 国内生产总值(GDP ):在某一既定时期一个国家内生产的所有最终物品与劳务的市场价值。 消费:家庭除购买新住房之外用于物品与劳务的支出。 投资:用于资本设备、存货和建筑物的支出,包括家庭用于购买新住房的支出。 政府购买:地方、州和联邦政府用于物品与劳务的支出。 净出口:外国人对国内生产的物品的支出(出口)减国内居民对外国物品的支出(进口)。 名义GDP :按现期价格评价的物品与劳务的生产。 真实GDP :按不变价格评价的物品与劳务的生产。 GDP 平减指数:用名义GDP 与真实GDP 的比率乘以100计算的物价水平衡量指标。 100GDP GDP GDP ?=真实名义平减指数 %100GDP GDP -GDP ?=平减指数 第一年的平减指数第一年的平减指数第二年的第二年的通货膨胀率 24章 消费物价指数(CPI ):普通消费者所购买的物品与劳务的总费用的衡量指标。 100?=基年一篮子的价格 的价格当年一篮子物品与劳务消费物价指数 通货膨胀率:从前一个时期以来物价指数变动的百分比。 %100CPI CPI -CPI ?=第一年第一年第二年第二年的通货膨胀率 生产物价指数:企业购买的一篮子物品与劳务的费用的衡量指标。 年的物价水平 今天的物价水平年美元的数量今天的美元的数量T T ?= 指数化:根据法律或协议按照通货膨胀的影响对美元数量的自动调整。 名义利率:通常公布的、未根据通货膨胀的影响校正的利率。 真实利率:根据通货膨胀的英雄校正过得利率。 25章 生产率:每单位劳动投入所生产的物品与劳务的数量。 物质资本:用于生产物品与劳务的设备和建筑物存量。 人力资本:工人通过教育、培训和经验而获得的知识与技能。 自然资源:由自然界提供的用于生产物品和劳务的投入,如土地、河流和矿藏。 技术知识:社会对生产物品与劳务的最好方法的了解。 收益递减:随着投入量的增加,每一单位额外投入得到的收益减少的特性。 追赶效应:开始时贫穷的国家倾向于比开始时富裕的国家增长更快的特征。 26章 金融体系:经济中促使一个人的储蓄与另一个人的投资相匹配的一组机构。 金融市场:储蓄者可以借以直接向借款者提供资金的金融机构。
曼昆经济学原理英文版文案加习题答案8章
144 WHAT’S NEW IN THE S EVENTH EDITION: A new In the News box on ―The Tax Debate ‖ has been added. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: how taxes reduce consumer and producer surplus. the meaning and causes of the deadweight loss from a tax. why some taxes have larger deadweight losses than others. how tax revenue and deadweight loss vary with the size of a tax. CONTEXT AND PURPOSE: Chapter 8 is the second chapter in a three-chapter sequence dealing with welfare economics. In the previous section on supply and demand, Chapter 6 introduced taxes and demonstrated how a tax affects the price and quantity sold in a market. Chapter 6 also described the factors that determine how the burden of the tax is divided between the buyers and sellers in a market. Chapter 7 developed welfare economics —the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being. Chapter 8 combines the lessons learned in Chapters 6 and 7 and addresses the effects of taxation on welfare. Chapter 9 will address the effects of trade restrictions on welfare. The purpose of Chapter 8 is to apply the lessons learned about welfare economics in Chapter 7 to the issue of taxation that was addressed in Chapter 6. Students will learn that the cost of a tax to buyers and sellers in a market exceeds the revenue collected by the government. Students will also learn about the factors that determine the degree by which the cost of a tax exceeds the revenue collected by the government. 8 APPLICATION: THE COSTS OF TAXATION
曼昆经济学原理试题Chapter 08a
Chapter 8 Application: The Costs of Taxation Test A 1. A tax levied on the buyers of a product shifts the a. demand curve upward or to the right. b. demand curve downward or to the left. c. supply curve upward or to the left. d. supply curve downward or to the right. ANSWER: b. demand curve downward or to the left. TYPE: M KEY1: D SECTION: 1 OBJECTIVE: 1 RANDOM: Y 2. When a tax is levied on a good a. buyers are worse off but sellers are not. b. sellers are worse off but buyers are not. c. neither buyers nor sellers are worse off. d. both buyers and sellers are worse off. ANSWER: d. both buyers and sellers are worse off. TYPE: M KEY1: D SECTION: 1 OBJECTIVE: 1 RANDOM: Y 3. When a tax on a good is enacted, a. sellers always bear the full burden of the tax. b. buyers always bear the full burden of the tax. c. buyers and sellers share the burden of the tax regardless of which party it is levied on. d. sellers bear the full burden if the tax is levied on them, but buyers bear the full burden if the tax is levied on them. ANSWER: c. buyers and sellers share the burden of the tax regardless of which party it is levied on. TYPE: M KEY1: C SECTION: 1 OBJECTIVE: 1 RANDOM: Y 4. A tax placed on a good a. causes the price of the good to fall. b. causes the size of the market for the good to shrink. c. affects buyers of the good, but not sellers. d. is usually borne entirely by the seller of the good. ANSWER: b. causes the size of the market for the good to shrink. TYPE: M KEY1: C SECTION: 1 OBJECTIVE: 1 RANDOM: Y 5. When a tax is levied on a good a. the market price falls because demand declines. b. the market price falls because supply falls. c. the market price rises because demand falls. d. a wedge is placed between the price buyers pay and the price sellers receiv e. ANSWER: d. a wedge is placed between the price buyers pay and the price sellers receive. TYPE: M KEY1: C SECTION: 1 OBJECTIVE: 1 RANDOM: Y
曼昆《经济学原理》第五版宏观经济学习题答案(中文)
第 20 章货币制度 1、为什么银行不持有百分百的准备金?银行持有的准备金量和银行体系所创造的货币量 有什么关系? 参考答案: 银行不持有百分百的准备金是因为把存款用于放贷并收取利息比持有全部存款更有利 可图。银行持有的准备金量和银行体系通过货币乘数所创造的货币量是相关的。银行的准备金率越低,货币乘数越大,所以银行存款的每一元钱可以创造更多的货币 2、考察以下情况如何影响经济的货币制度。 a、假设雅普岛的居民发现了一种制造石轮的简单方法。这种发现如何影响石轮作为货 币的有用性呢?并解释之。 b、假设美国某个人发现了一种仿造100 美元钞票的简单办法。这种发现将如何影响美 国的货币制度呢?并解释之。 参考答案: a、如果有一种制造石轮的简单方法,雅普岛上的居民就会制造多余的石轮,只要每个 石轮的货币价值大于制造它的成本。结果,人们会自己制造货币,于是就有太多的货币被制 造出来。最有可能的是,人们会停止接受石轮作为货币,而转向其他资产作为交换的媒介 b.如果美国有人发现了伪造百元面值美钞的简单方法,他们就会大量地生产这种假 钞,而降低百元美钞的价值,结果可能是转为使用另一种通货。 3、伯列戈瑞德州银行(BSB)有 2.5 亿美元存款,并保持10%的准备率。 a)列出 BSB的 T 账户。 b) 现在假设BSB的大储户从其账户中提取了1000 万美元现金。如果 BSB决定通过减 少其未清偿贷款量来恢复其准备率,说明它的新T 账户。 c) 解释 BSB的行动对其他银行有什么影响? d) 为什么 BSB要采取 (b) 中所描述的行为是困难的?讨论BSB恢复其原来准备金率的 另一种方法。 参考答案: a. BSB的 T 账户如下: : 伯列戈瑞德州银行(BSB) 资产负债 准备金$25 million存款$250 million 贷款$225 million b.当 BSB的大储户提取了 1000 万美金现金,而 BSB通过减少其未清偿贷款量来恢复其 准备率,它的 T 账户如下:
曼昆经济学原理英文版文案加习题答案22章
WHAT’S NEW IN THE S EVENTH EDITION: A new Case Study on Left-Digit Bias has been added and a new In the News feature on "Can Brain Science Improve Economics" has been added. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand: how to examine problems caused by asymmetric information. the market solutions to asymmetric information. why democratic voting systems may not represent the preferences of society. why people may not always behave as rational maximizers. CONTEXT AND PURPOSE: Chapter 22 is the last chapter in the microeconomics portion of the text. It is the second of two unrelated chapters that introduce students to advanced topics in microeconomics. These two chapters are intended to whet their appetites for further study in economics. The purpose of Chapter 22 is to give students a taste of three topics on the frontier of microeconomic research. The first topic addressed is asymmetric information , a situation when one person in an economic relationship has more relevant knowledge than the other person does. The second topic is political economy , the application of economic tools to the understanding of the functioning of government. The third topic addressed is behavioral economics , the introduction of psychology into the study of economic issues. 22 FRONTIERS OF MICROECONOMICS
曼昆 经济学原理(第五版) 课后答案
第十二章税制的设计 复习题 1.在过去的几十年来,政府的增长比经济中的其他部分快还是慢? 答:在过去几十年间,政府的增长比经济中其他部分快。数据表明,美国经济中包括联邦、州和地方政府在内的政府收入在总收人中所占百分比的增长速度快于经济中其他部分。 2.美国联邦政府收入最重要的两个来源是什么? 答:美国联邦政府收入最重要的两个来源是个人收入所得税和用于社会保障的工薪税。 3.解释公司利润如何双重纳税。 答:当企业赚到利润时,它要按公司所得税交税;当企业用其利润向公司股东支付股息时,按个人所得税第二次交税。 4.为什么纳税人的税收负担大于政府得到的收入? 答:因为纳税人的税收负担除了向政府交纳的税收之外,还包括两种成本:一是税收改变了激励所引起的资源配置扭曲;二是遵守税法的管理负担。这两种成本没有政府的收入作为补偿。因此,纳税人的税收负担大于政府得到的收入。 5.为什么一些经济学家支持对消费征税,而不是对收入征税? 答:因为对收入征税扭曲了对人们储蓄的激励,鼓励人们少储蓄。如果政府采取消费税,储蓄起来的全部收入在最后支出前都不征税,就不会扭曲人们的储蓄决策。 6.举出富有的纳税人应该比贫穷纳税人多纳税的两种观点。 答:这方面的观点有受益原则和能力纳税原则。 受益原则认为:人们应该根据他们从政府服务中得到的利益来纳税。通常富人从公共服务中受益多,他们应该多纳税。 能力纳税原则认为:应该根据一个人所能承受的负担来对这个人征税。显然,富人的财务承受能力强于穷人,富人应该多纳税。 7.什么是横向平等概念。为什么运用这个概念是困难的? 答:横向平等是指主张有相似支付能力的纳税人应该缴纳等量税收的思想。这一原则面临的问题是什么决定两个纳税人是相似的。每个纳税人在许多方面不同,为了评价税收是不是横向平等,必须决定哪些差别对纳税人的支付能力是相关的,哪些是不相关的。这些相关关系的确定是复杂而困难的。它不仅涉及经济学问题,还涉及价值观问题,很难说确定的结果是否公平。 8.说明支持与反对用单一税率取代现行税制的观点。 答:单一税率的支持者认为:(1)单一税率税将取消现行所得税的许多税收减免。通过用这种方法扩大税基,固定税能够降低大多数人面临的边际税率。税率越低意味着经济福利越大。因此,单一税率支持者声称,这种改变将扩大经济馅饼的规模。(2)由于单一税率税如此简单,所以,赋税的管理负担将大大降低。(3)由于所有纳税人都面临相同的边际税率,所以可以按收入来源而不是按得到收入的人来收税。这种额外的简单化也降低了管理成本。 (4)单一税率税将取代个人所得税和公司所得税。所有收入无论是来自工作中的劳动还是来自公司中拥有的股份,都按相同的边际税率一次性纳税。单一税率将消除目前对公司利润的双重征税,这就可以鼓励企业投资于新工厂和设备。(5)在为纳税计算收入时,允许企业扣除所有合法的经营支出,包括新投资品的支出。这种投资扣除使单一税率税更像消费税而不像所得税。结果,变为单一税率税将提高对投资的激励。 单一税率税的反对者认为:这种税很少注意纵向平等的目标。他们声称,单一税率税的累进性要小于现在的税制,而且,特别是它会把一些税收负担从富人身上转移到中产阶级身上。
曼昆经济学原理答案30—34
曼昆经济学原理答案30—34
第十二篇短期经济波动 第三十一章总需求与总供给 复习题 1.写出当经济进入衰退时下降的两个宏观经济变量的名字。写出当经济进入衰退时上升的一个宏观经济变量的名字。 答:当经济进入衰退时,实际GDP和投资支出下降,失业率上升。 2.画出一个有总需求、短期总供给和长期 总供给的曲线的图。仔细地标出正确的轴。 答: 图31—1 经济的长期均衡 3.列出并解释总需求曲线向右下方倾斜的 三个原因。 答:为了理解总需求曲线向右下 方倾斜的原因,我们必须考察物价水平如何影响消费、投资和净出口的物品与劳务需求量。 (1)庇古的财富效应
物价水平下降使消费者感到更富裕,这又鼓励他们更多地支出,消费支出增加意味着物品与劳务的需求量更大。 (2)凯恩斯的利率效应 较低的物价水平降低了利率,鼓励了家庭和企业更多地支出于投资物品,从而增加了物品与劳务的需求量。 (3)蒙代尔——弗莱明汇率效应 当美国物价水平下降引起美国利率下降时,实际汇率贬值,而且这种贬值刺激了美国的净出口,从而增加了国外对美国物品与劳务的需求量。 由于这三个原因,总需求曲线向右下方倾斜。 4.解释为什么长期总供给曲线是垂线。 答:在长期中,一个经济的物品与劳务的供给取决于它资本与劳动的供给,以及用来把资本与劳动变为物品与劳务的生产技术。由于物价水平并不影响这些实际GDP的长期决定因素,所以长期总供给曲线是一条垂线,即经济的资本、劳动和技术决定了物品与劳务供给量,而且,无论物价水平如何变动,供给量都是相同的。
5.列出并解释为什么短期总供给曲线向右上方倾斜的三种理论。 答:在短期中,总供给曲线向右上方倾斜,也就是说,在一个一两年的时期中,经济中物价总水平的上升增加了物品与劳务的供给量,而物价水平下降倾向于减少物品与劳务供给量。什么因素引起物价水平与产量之间的正相关关系呢?宏观经济学家提出了三种理论说明短期总供给曲线的向右上方倾斜。在每一种理论中,一种特殊的市场不完全性引起经济中供给一方的短期状况与长期不同。虽然每一种理论在细节上不同,但它们具有共同的内容:当物价水平背离了人们预期的物价水平时,供给量就背离了其长期水平或“自然水平”。当物价水平高于预期水平时,产量就高于其自然率。当物价水平低于预期水平时,产量就低于其自然率。 (1)新古典的错觉理论 根据这种理论,物价总水平的变动会暂时误导供给者对他们出售其产品的市场发生的变动的看法。由于这些短期的错觉,供给者对物价水平的变动作出了反应,而这种反应引起了向右上方倾斜的总供给曲线。假设物价总水平降到低于
曼昆经济学原理第五版宏观经济学习题答案中文
1 / 5 第20xx货币制度 1、为什么银行不持有百分百的准备金?银行持有的准备金量和银行体系所创造的货币量有什么关系? 参考 答案: 银行不持有百分百的准备金是因为把存款用于放贷并收取利息 比持有全部存款更有利可图。银行持有的准备金量和银行体系通过货币乘数所创造的货币量是相关的。银行的准备金率越低,货币乘数越大,所以银行存款的每一元钱可以创造更多的货币 2、考察以下情况如何影响经济的货币制度。 a、假设雅普岛的居民发现了一种制造石轮的简单方法。这种发现如何影响石轮作为货币的有用性呢?并解释之。 b、假设美国某个人发现了一种仿造100美元钞票的简单办法。这种发现将如何影响美国的货币制度呢?并解释之。 参考 答案: a、如果有一种制造石轮的简单方法,雅普岛上的居民就会制造多余的石轮,只要每个石轮的货币价值大于制造它的成本。结果,人们会自己制造货币,于是就有太多的货币被制造出来。最有可能的是,人们会停止接受石轮作为货币,而转向其他资产作为交换的媒介
b.如果美国有人发现了伪造百元面值美钞的简单方法,他们就会大量地生产这种假钞,而降低百元美钞的价值,结果可能是转为使用另一种通货。 3、xx瑞德州银行(BSB)有 2.5亿美元存款,并保持10%的准备率。 2 / 5 a)列出BSB的T账户。 b)现在假设BSB的大储户从其账户中提取了1000万美元现金。如果BSB决定通过减少其未清偿贷款量来恢复其准备率,说明它的新T账户。 c)解释BSB的行动对其他银行有什么影响? d)为什么BSB要采取(b)中所描述的行为是困难的?讨论BSB恢复其原来准备金率的另一种方法。 参考 答案: a. xx瑞德州银行(BSB) 资产 准备金 贷款 b.当BSB的大储户提取了1000万美金现金,而BSB通过减少其未清偿贷款量来恢复其准备率,它的T账户如下: $25 million存款
曼昆经济学原理第五版课后练习答案word精品
第一篇导言 第一章经济学十大原理 1.列举三个你在生活中面临的重要权衡取合的例子。 答:①大学毕业后.面临着是否继续深造的选择,选择继续上学攻读研究生学位,就意味着在今后三年中放弃参加工作、赚工资和积累社会经验的机会;2、在学习内容上也面临 着很重要的权衡取舍,如果学习《经济学》,就要减少学习英语或其他专业课的时间,③对 于不多的生活费的分配同样面临权衡取舍,要多买书.就要减少在吃饭、买衣服等其他方面的开支。 2、看一场电影的机会成本是什么? 答:看一场电影的机会成本是在看电影的时间里做其他事情所能获得的最大收益,例如:看书、打零工。 3、水是生活必需的。一杯水的边际利益是大还是小呢? 答:这要看这杯水是在什么样的情况下喝.如果这是一个人五分钟内喝下的第五杯水.那么他的边际利益很小.有可能为负;如果这是一个极度干渴的人喝下的第一杯水,那么他的边际利益将会极大。 4、为什么决策者应该考虑激励? 答:因为人们会对激励做出反应。如果政策改变了激励,它将使人们改变自己的行为,当决策者未能考虑到行为如何由于政策的原因而变化时.他们的政策往往会产生意想不到的效果。 5 为什么各国之间的贸易不像竞赛一样有赢家和输家呢? 答:因为贸易使各国可以专门从事自己最擅长的话动,并从中享有更多的各种各样的物品与劳务。通过贸易使每个国家可供消费的物质财富增加,经济状况变得更好。因此,各 个贸易国之间既是竞争对手,又是经济合作伙伴。在公平的贸易中是“双赢”或者“多赢” 的结果。 6.市场巾的那只“看不见的手”在做什么呢,答:市场中那只“看不见的手”就是商品价格,价格反映商品自身的价值和社会成本, 市场中的企业和家庭在作出买卖决策时都要关注价格。因此.他们也会不自觉地考虑自己行为的(社会)收益和成本。从而,这只“看不见的手”指引着干百万个体决策者在大多数情况下使社会福利趋向最大化。 7 解释市场失灵的两个主要原因,并各举出一个例子。答:市场失灵的主要原因是外部性和市场势力。外部性是一个人的行为对旁观者棉利的影响。当一个人小完全承担(或享受)他的行为所造成的成本(或收益)时,就会产生外部性。举例:如果一个人不承担他在公共场所吸烟的全部成本,他就会毫无顾忌地吸烟。在这种情况下,政府可以通过制定禁止在公共场所吸烟的规章制度来增加经济福利。 市场势力是指一个人(或一小群人)不适当地影响市场价格的能力。例如:某种商品的垄断生产者由于几乎不受市场竞争的影响,可以向消费者收取过高的垄断价格。在这种情况下,规定垄断者收取的价格有可能提高经济效率。 8.为什么生产率是重要的? 答:因为一国的生活水平取决于它生产物品与劳务的能力,而对这种能力的最重要的 衡量度就是生产率。生产率越高,一国生产的物品与劳务量就越多。 9 什么是通货膨胀,什么引起了通货膨胀? 答:通货膨胀是流通中货币量的增加而造成的货币贬值生活中价格总水平上升。货币量增长引起了通货膨胀。 10.短期中通货膨胀与失业如何相关? 答:短期中通货膨胀与失业之间存在着权衡取台,这是由于某些价格调整缓慢造成的。政府为了抑制通货膨胀会减少流通中的货币量,人们可用于支出的货币数量减少了,但是商品价格在短期内是粘性的,仍居高不下.于是社会消费的商品和劳务量减少,消费量减少又引起企业解雇工人。在短期内.对通货膨胀的抑制增加了失业量。 问题与应用
经济学原理名词解释(英文版)
经济学原理名词解释 CHAPTER 1 Scarcity : the limited nature of society’s resources. Economics : the study of how society manages its scarce resources. Efficiency : the property of society getting the most it can from its scarce resources. Equity : the property of distributing economic prosperity fairly among the members of society. Opportunity cost : whatever must be given up to obtain some item. Marginal changes : small incremental adjustments to a plan of action. Market economy : an economy that allocates resources through the decentralized decisions of many firms and households as they interact in markets for goods and services. Market failure : a situation in which a market left on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently. Externality : the impact of one person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander. Market power : the ability of a single economic actor (or small group of actors) to have a substantial influence on market prices. Productivity : the quantity of goods and services produced from each hour of a worker’s time. Inflation : an increase in the overall level of prices in the economy. Phillips curve : a curve that shows the short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. Business cycle : fluctuations in economic activity, such as employment and production. CHAPTER 2 Circular-flow diagram : a visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms.
曼昆经济学原理试题及答案
一、名词解释(每小题5分,共50分) 1.机会成本 2.科斯定理 3.搭便车 4.囚徒困境 5.菲利普斯曲线 6.供应学派 7.凯恩斯革命 8.看不见的手 9.比较优势 10.外部性 二、简述题(第11、12、13题各12分,14题14分,共50分) 1.简述银行存款的创造过程。 2.简述失业的根源及其类型。 3.简述节俭的是非。 4.根据有关经济学原理,简析我国森林减少、珍稀动物来绝的原因及解决的措施。 三、论述题(每小题25分,共计50分) 1.论述人民币升值对中国经济的影响。 2.论述政府公共投资对国民经济的作用。 一、名词解释(每小题5分,共50分) 1.机会成本:指人们利用一定资源获得某种收入时所放弃的在其他可能的用途中所能够获取的最大收入。生产一单位的某种商品的机会成本是指生产者所放弃的使用相同的生产要素在其他生产用途中所能得到的最高收入。机会成本的存在需要三个前提条件。第一,资源是稀缺的;第二,资源具有多种生产用途;第三,资源的投
向不受限制。从机会成本的角度来考察生产过程时,厂商需要将生产要素投向收益最大的项目,而避免带来生产的浪费,达到资源配置的最优。机会成本的概念是以资源的稀缺性为前提提出的。从经济资源的稀缺性这一前提出发,当一个社会或一个企业用一定的经济资源生产一定数量的一种或者几种产品时,这些经济资源就不能同时被使用在其他的生产用途方面。这就是说,这个社会或这个企业所能获得的一定数量的产品收入,是以放弃用同样的经济资源来生产其他产品时所能获得的收入作为代价的。这也是机会成本产生的缘由。因此,社会生产某种产品的真正成本就是它不能生产另一些产品的代价。所以,机会成本的含义是:任何生产资源或生产要素一般都有多种不同的使用途径或机会,也就是说可以用于多种产品的生产。但是当一定量的某种资源用于生产甲种产品时,就不能同时用于生产乙种产品。因此生产甲种产品的真正成本就是不生产乙种产品的代价,或者是等于该种资源投放于乙种产品生产上可能获得的最大报酬。一种资源决定用于甲种产品,就牺牲了生产其他产品的机会;从事生产甲种产品的收入,是由于不从事或放弃其他产品生产的机会而产生的。 2.科斯定理:指一种产权理论。科斯本人并未将科斯定理写成文字,科斯定理的提出是由其好友斯蒂格勒首先根据科斯于20世纪60年代发表的《社会成本问题》这篇论文的内容概括出来的。其内容是:只要财产权是明确的,并且其交易成本为0或者很小,则无论在开始时财产权的配置是怎么样的,市场均衡的最终结果都是有效率的。科斯定理进一步扩大了“看不见的手”的作用。按照这个定理,只要那些假设条件成立,则外部影响就不可能导致资源配置不当。或者以另一角度来说,在所给条件下,市场力量足够强大,总能够使外部影响以最经济的办法来解决,从而仍然可以实现帕累托最优状态。西方学者认为,明确的财产权及其转让可以使得私人成本(或利益)与社会成本(或利益)趋于一致。以污染问题为例,科斯定理意味着,一旦所需条件均被满足,则污染者的私人边际成本曲线就会趋于上升,直到与边际社会成本曲线完全重合,从而污染者的利润最大化产量将下降至社会最优产量水平。 科斯定理解决外部影响问题在实际中并不—定真的有效。资产的财产权不一定总是能够明确地加以规定;已经明确的财产权不一定总是能够转让;分派产权会影响收入分配,而收入分配的变动可以造成社会不公平,引起社会动乱。在社会动乱的情况下,就谈不上解决外部效果的问题了。 3.搭便车:指不付成本或支付很低的成本而消费公共产品的行为。公共产品的特点决定了私人厂商不愿自动提供这种产品。这是因为在公用产品消费中存在“搭便车”问题,即每个人都想不付任何成本,或只支付很低的代价,来享受公共产品的服务。由于公共物品具有消费的非竞争性和受益的非排他性,人们可以在不付费的情况下享受公共物品所带来的效益。因此公共产品覆盖的消费者人数越多,搭便车问题就越严重,公共产品由私人厂商提供出来的可能性就越小。例如:1970年美国通用汽车公司研制出了一种汽车污染物排放控制装置,每个售价20美金,如果每个车尾都装上这一装置,可使汽车排放的污染下降30%至50%。然而,污染的降低是一种公共产品,每个人呼吸空气质量是否改善并不取决于自己的车上是否装上这个新发明,而是取决于该地区大多数车主的选择,于是大多数人都不想多花20美元而只是试图搭便车,结果,在私人市场上,这种公共产品的产量总难以达到最佳水平。私人不能提供公共产品,就只能由政府出面担当此项职能。事实上,私人经济中的政府,最初就是为了提供公共产品(法律、国防、公安等等)的目的由众多私人共同建立起来的。政府这一职能具体体现为:①尽可能正确地估价社会对公用产品的实际需求;②按照社会福利最大化的原则确定税收比率,并用税收收入购置公用产品,为公众提供服务。 4.囚徒困境:指两个被捕获的囚犯之间的一种特殊“博弈”,说明为什么甚至在合作对双方有利时,保持合作也是困难的。囚犯两难处境的故事包含着一个一般性的结论,这个结论适用于任何一个力图维持其成员合作的集团。这是博弈论中的一个经典例证,同一市场上的寡头在力图达到垄断结果时的博弈类似于两个处于两难处境的囚犯的博弈。具体情况如下:两囚徒被指控是一桩罪案的同案犯。他们被分关在不同的牢房且无法互通信息。各囚徒都被要求坦白罪行。如果两囚徒都坦白,各将被判入狱5年;如果两人都不坦白,则很难对他们提起刑事诉讼,因而两囚徒可以期望被从轻发落为入狱2年;另一方面,如果一个囚徒坦白而另一个囚徒不坦白,坦白的囚徒就只需入狱1年,而另一个将被判入狱10年。那么囚徒将会怎么选择呢?下表归纳了各种可能的结果。(其中“得益”是负的,表格右下角单元格意思是两个囚徒各2年徒刑)。该表说明,这两个囚徒面临着一种困境。如果他们都不坦白(以一种会遵守的方法),那么两人只需入狱仅仅2年。但他们不能相互讲话,如果囚徒A不坦白,他就冒着被B利用的危险。因为不管囚徒A怎么选择,囚徒B坦白总是最优方案。
曼昆经济学原理英文版第11章
Examine why people tend to use common r esour ces too much Consider some of the impor tant common r esour ces in our economy Consider some of the impor tant public goods in our economy Lear n t he def ini ng characteristics of public goods and common r esour ces Examine why private markets fail to pr ovide public goods See why the cost-benefit analysis of public goods is both necessar y and dif ficult An old song lyric maintains that “the best things in life are free.” A moment’s thought reveals a long list of goods that the songwriter could have had in mind. Na-ture provides some of them, such as rivers, mountains, beaches, lakes, and oceans.The government provides others, such as playgrounds, parks, and parades. In each case, people do not pay a fee when they choose to enjoy the benefit of the good.Free goods provide a special challenge for economic analysis. Most goods in our economy are allocated in markets, where buyers pay for what they receive and sellers are paid for what they provide. For these goods, prices are the signals that guide the decisions of buyers and sellers. When goods are available free of charge,however, the market forces that normally allocate resources in our economy are absent. In this chapter we examine the problems that arise for goods without market prices. Our analysis will shed light on one of the Ten Principles of Economics P U B L I C G O O D S A N D C O M M O N R E S O U R C E S 225
