英语16种时态表

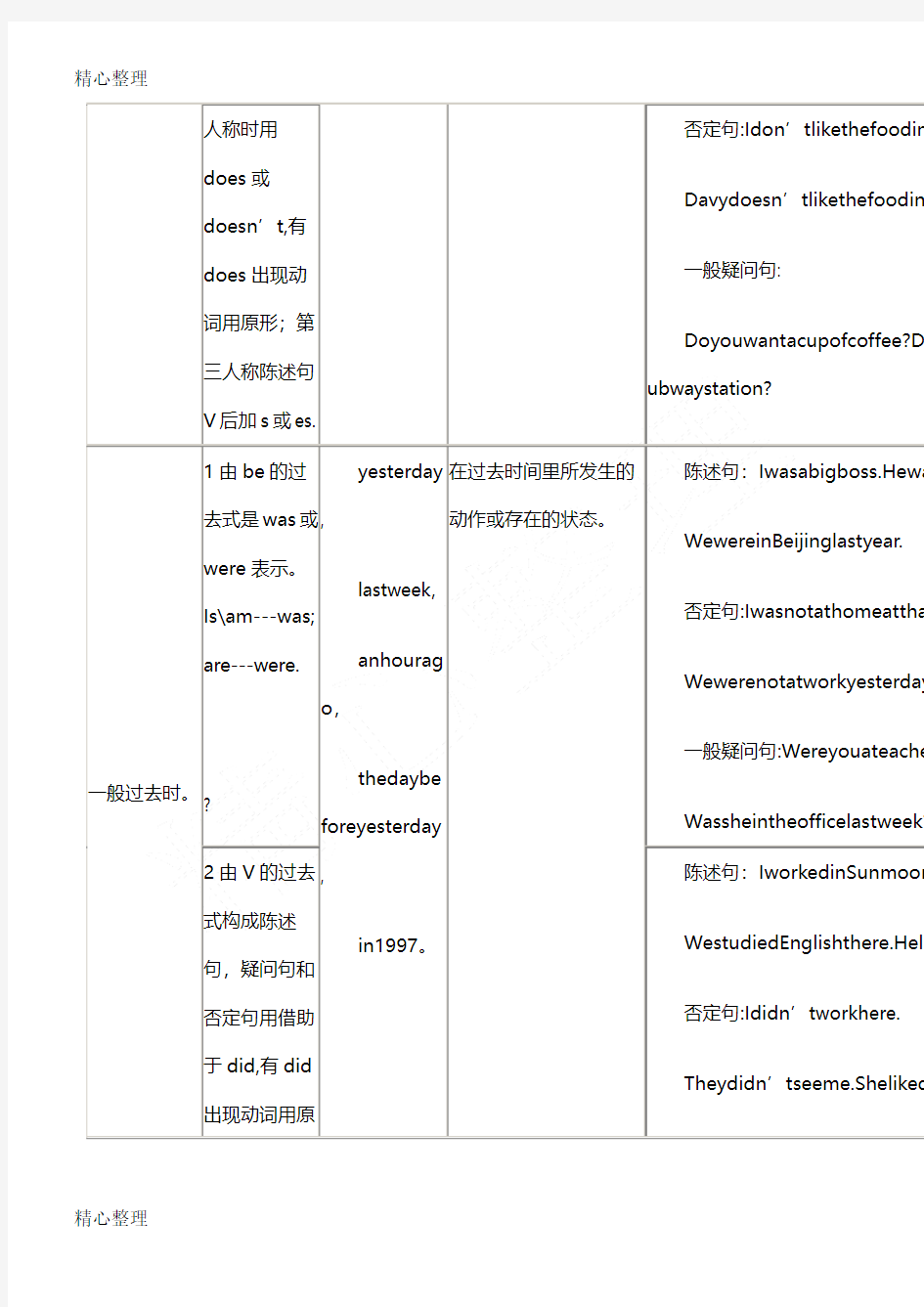
精心整理|?英语16种时态表
英语时态表
英语时态表
时态
名称
结构常连用的词主要用法例句
一般现在时1由be的
isamare表
示,之后接名
词,形容词或
介词。
every…,
sometime
s,
always,ne
ver,
often,usu
ally等。
一般现在时表示没有时
限的持久存在的习惯性
的动作或状态,或现阶段
反复发生的动作或状态
陈述句:Iamanofficeworker.
Heissolazy. Theyareathome
否定句:IamnotTim.
Sheisnotverybeauiful.
Theyarenotintheoffice.
一般疑问句:Areyouanofficea
Isshebeautiful?
2由实意动词
V构成,引导
疑问句和否定
句,用do或
don’t。第三
陈述句:IworkinShanghai.
Heworksathome.
DavyneverwatchesTVathome
人称时用does或doesn’t,有does出现动词用原形;第三人称陈述句V后加s或es.
否定句:Idon’tlikethefoodinK
Davydoesn’tlikethefoodinK
一般疑问句:
Doyouwantacupofcoffee?Do ubwaystation?
一般过去时。1由be的过
去式是was或
were表示。
Is\am---was;
are---were.
?
yesterday
,
lastweek,
anhourag
o,
thedaybe
foreyesterday
,
in1997。
在过去时间里所发生的
动作或存在的状态。
陈述句:Iwasabigboss.Hewa
WewereinBeijinglastyear.
否定句:Iwasnotathomeatthat
Wewerenotatworkyesterday
一般疑问句:Wereyouateacher
Wassheintheofficelastweek? 2由V的过去
式构成陈述
句,疑问句和
否定句用借助
于did,有did
出现动词用原
陈述句:IworkedinSunmoon
WestudiedEnglishthere.Heliv
否定句:Ididn’tworkhere.
Theydidn’tseeme.ShelikedE
形。? 一般疑问句:DidyougotoAmer DidheworkinSunmoon?
时
态
名
称
结构常连用的词主要用法例句
一般将来时1任何人称+will+
动词原形.
tomorrow,
nextyear,
themonthaft
ernext,
intwohours.
?
即将发生动作或状态。陈述句:IwillflytoKongKongt
Hewillgowithus.
WewillarriveinShanghainextw
否定句:Iwillneverbelieveyoua
Hewillnotcometonight.
Wewillnotbuyacarnextyear.
一般疑问句:Willyougothereby
Willhecometomorrow?
Willtheyliveafive-starhotel?
2is/am/are+goin gto+V原形,表示计划打算做什么事情。陈述句:I’mgoingtogotoKo 否定句:Wearenotgoingtobuy 一般疑问句:Aretheygoingtoch 特殊疑问句:Howareyougoing
过去将来时was/weregoingto
+V原形
在过去将会发生的动作。陈述句:Iwasgoingtobuyaco
Theytoldmethattheywerenot
否定句:Iwasnotgoingtobuyac 任何人称
+would+V原形
HesaidhewouldcomeininSha
IsaidIwouldbuyyouacaroned
?
时
态
名
称
结构常连用的词主要用法例句
现在进is/am/are+Ving now,
atthe(this)
表示现在(指说话
人说话时)正在发
生的事情。
陈述句:I’mwaitingformybo
Heisdoingthehouseworkatho
行时? moment
Look!(放在句首)
Listen!(放在句首)
Weareenjoyingourselves.
否定句:Heisnotplayingtoys.
一般疑问句:Areyouhavingdin
IsTimcookinginthekitchen?
特殊疑问句:Whatareyoudoing
Wherearetheyhavingameal?
过去进行时was/were+Ving
?
atthattime
at10o’
clocklastnight
atthatmoment等过
去具体的时间
过去一段时间正在
发生的动作。
陈述句:Iwasdoingmyhomew
Wewerehavingapartywhilehe
否定句:Hewasnotsleepingat1
一般疑问句:Wereyouwatching
特殊疑问句:Whatwereyoudoi 时
态
名
称
结构常连用的词主要用法例句
现在have/has+
done(过去
already;用来表示之前已发
生或完成的动作或
陈述句:
IhavealreadytoldDavy.Davyhaskn
完成时分词)just(notjustnow)
yet;ever;never;
fortwoweeks;
forayear;
forseveraldays;
since2004
sincelastweek
状态,其结果的确
和现在有联系。动
作或状态发生在过
去但它的影响现在
还存在;也可表示
持续到现在的动作
或状态。简单的说,
就是动作已经发生
对现在造成明显的
影响。
Hehaslivedherefornearly10ye
否定句:Ihaven’tfinishedmyh
Timhasn’tcomeyet.
Wehaven’theardanynewsab
一般疑问句:Hasheworkedhere
特殊疑问
句:Howlonghaveyouworkedinthis 特别注意:1.have/hasalwaysbeen+名词/形容词/介词:总是或一直是什么样子。。。
Hehasalwaysbeenagoodfather.Ihavealwaysbeenbusy.
TheyhavealwaysbeeninAmerica.
2.have/hasgoneto:去
了。。。
HehasgonetoBeijing.
Theyhavegonetothe
cinema.
3.have/hasbeento:表示去过或到过。。。
IhavebeentoCanada.HaveyoubeentoHongkong?
Wherehaveyoubeen?Ihaveneverbeenhere.
过去had+done
(过去分
bytheen
doflastyear
动作发生在
过去的过去。
陈述句:HesaidhehadtoldDavy.
完成时词)bylastye
ar
?
?
Theytoldustheyhadfinishedthework.
HelefttheofficeafterhehadcalledDavy.
否定句:Shehadn’thaddinnerbeforeshewentout.
一般疑问句:HadshelearntEnglishbeforeshemovedhe
特殊疑问句:howmanyEnglishwordshadhelearntbyth 补充:
一、情态动词can,must,may。may没有否定形式。
陈述句:Icandriveacar.Hemusttellthetruth.Wemaygetthereonfoot.
否定句:Ican’tswimatall.Youmustn’t(表示禁止)smokeintheoffice.
一般疑问句:Canyouwaitaminute?MustIstayathome?MayIuseyourphone?
特殊疑问句:HowcanIgetthere?WhatmustIdonow?
由情态动词的过去式构成,can—could. Shecouldwalkwhenshewasoneyearold. IcouldnotspeakEnglishoneyearago.
二、各种时态用法补充:
1、一般现在时
(1)在由after,until,befor,once,when,evenif,incase,aslongas,assoonas,themomen 引导的时间状语从句或条件状语从句中,通常用一般现在时代替将来时。
例:IwilltellhimthenewsassoonasIseehim.
我一看见他,就把消息告诉他。
(2)某些表示起始的动词,可用一般现在时表示按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,这come,start,depart,arrive,begin,leave等。
(3)在由why,what,where,whoever,who,that,as等引导的从句中,也常用一般现在时
例:Tomorrowatthistimewe’llgive$500toanyonewhobringshimtojustice.
2、一般将来时
(1)begoingto+v在口语中广泛使用,表示准备做或即将发生的事情。
例:I’mgoingtobuyahousewhenwe’vesavedenoughmoney.
(2)beto+v表示计划安排将要做的事。
例:ThereistobearailstrikeonJuly18th.
(3)beaboutto+v表示即将发生的事情。
例:Weareabouttostart.
(4)bedueto+v表示预先确定了的、必定要发生的事。
例:HisbookisduetobepublishedinOctober.
他的书预定10月份出版。
(5)beonthepoint/vergeof+(v-ing)sth.强调即将发生的某种事态。
例:Thecountryisonthevergeofcivilwar.
这个国家就要打内战了。
3、现在进行时
(1)表示现阶段经常发生的动作,常与always,continually,constantly等连用(多表示赞
例:Johnisalwayscominglate.??约翰总是迟到。
(2)表示根据计划或安排在最近要进行的事情。具有这种语法功能的动词仅限于过渡性个状态或位置转移到另一个状态或位置上去的动词。常用的有;go,come,leave,start,arrive
例:TheyareleavingforHongkongnextmonty.
他们下个月去香港。
(3)有些动词一般不能使用进行时,这是一类表示“感觉”、“感情”、“存在”、“如:see,hear,smell,taste,feel,notice,look,appear(表示感觉的动词);hate,love,fear,like
refuse,forgive(表示感情的动词);be,exist,remain,stay,obtain(表示存在状态的动词);h contain,belong,consistof,form(表示占有与从属的动词);understand,know,belive,thin member(表示思考、理解的动词)。但是如果它们词义改变,有时也可使用进行时态。
例:Janelookspale.What’swrongwithhim?
珍妮看上去脸色苍白,她怎么了?(look在此为联系动词)
例:Janeislookingforhisbooks.
珍妮正在寻找她的书。(look在此为实义动词)
4.完成进行时
完成进行时是完成时的强调形式。
5.完成时态
(1)现在完成时与与一般过去时的区别:现在完成时强调过去发生的动作与现在的关系影响等;而一般过去时只表示动作发生在过去表示某一时刻,不表示与现在的关系。
(2)完成时态可用在下列结构中:
This(That,it)is(was)thefirst(second….)time+定语从句:
This(That,It)is(was)theonly(last)+名词+定语从句;This(This,It)is(was)+形容词最高句。如果主句的谓语动词是一般将来时,从句的谓语动词动词通常用现在完成时;如果主句去时,从句的谓语动词通常用过去完成时。
例1:Thisisthefirsttime(that)I’vedrunkCalifornianchampagne.
这是我第一次喝加利福尼亚香槟酒。
例2:Therewasaknockatthedoor.Itwasthesecondtimesomeonehadinterrupted
有人敲门,这是当天晚上第二次有人打扰我了。
6.动词expect,hope,mean,intend,plan,suppose,wish,want,desire等用过去完成时预期,意图或愿望等没有实现。
例1:IhadmeanttoleavetoonMonday,buthavestayedon.
我本来打算星期一离开,但最终还是继续留下来了。
另外两种表示“过去想做而未做的事”的表达方式是:
7.was/were+tohavedonesth.
例1:Weweretohavecomeyesterday,butwecouldn’t.
我们本想昨天来的,但我们来不了。
8.intended(expected,hoped,meant,planned,supposed,wished,wanted,desired)+
例:1Imeantohavetoldyouaboutit,butIforgottodoso.
我本想告诉你这件事,但我忘掉了。
9.过去完成时常用于以下固定句型:
(1)hardly/scarcely/barely+过去完成时(倒装形式)+when+过去时
例1:HardlyhadIarrivedwhenIhadanewproblemtocopewith.
我一到达就有新问题要处理。
(2)nosooner+过去完成时(倒装形式)+than+过去时。
例1:Nosoonerhadthewordsbeenspokenthanherealizedthatheshouldhaverem 这话刚说出口,他就意识到他本该保持沉默的。
(3)by(theendof)+过去时间,主句中谓语动词用过去完成时。
例1:BytheendofthatyearHenryhadcollectedmorethanathousandforeignstamp 到那年年底,亨利已收集了一千多张外国邮票
英语八种时态一览表
金山??编写整理?
八种时态介绍:
一?一般现在时态:表示现在经常发生或习惯性的动作。时间状语:every…,sometimes, al ways,never,often,?usually等。
1由be的isamare表示,之后接名词,形容词或介词。
陈述句:Iamanofficeworker.?Heissolazy.?Theyareathomenow.
否定句:IamnotTim.Sheisnotverybeauiful.Theyarenotintheoffice.
一般疑问句:Areyouanofficeassistant?Isshebeautiful?
特殊疑问句:Whatisyourjob?Whatcolourisyourbag?Whereareyounow?
2由实意动词V构成,引导疑问句和否定句,用do或don’t。第三人称时用does或does n’t,有does出现动词用原形;第三人称陈述句V后加s或es.
陈述句:IworkinShanghai.Heworksathome.DavyneverwatchesTVathome.
否定句:Idon’tlikethefoodinKFC.Davydoesn’tlikethefoodinKFCeither.
一般疑问句:Doyouwantacupofcoffee?Doesshelivenearthesubwaystation?
特殊疑问句:Whatdoyouwant?Wheredoesshelive?Howdotheygotowork?
?3由情态动词can,must,may构成。may没有否定形式。
陈述句:Icandriveacar.Hemusttellthetruth.Wemaygetthereonfoot.
否定句:Ican’tswimatall.Youmustn’t(表示禁止)smokeintheoffice.
一般疑问句:Canyouwaitaminute?MustIstayathome?MayIuseyourphone?
特殊疑问句:HowcanIgetthere?WhatmustIdonow?
二一般过去时态。在过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。
时间状语有:yesterday,lastweek,anhourago,thedaybeforeyesterday,in1997。
1由be的过去式是was或were表示。Is\am---was;are---were.
陈述句:Iwasabigboss.Hewasbeautiful.WewereinBeijinglastyear.
否定句:Iwasnotathomeatthatmoment.Wewerenotatworkyesterday.
一般疑问句:Wereyouateacher?Wassheintheofficelastweek?
特殊疑问句:Wherewereyoulastnight?Whenwereyouinthatcompany?
2由V的过去式构成陈述句,疑问句和否定句用借助于did,有did出现动词用原形。
陈述句:IworkedinSunmoon.WestudiedEnglishthere.HelivedinHongKong.
否定句:Ididn’tworkhere.Theydidn’tseeme.ShelikedEnglishalot.
一般疑问句:DidyougotoAmerica?DidheworkinSunmoon?
特殊疑问句:Wheredidyouwork?Whatdidhesaytoyou?Howdidyouknowmyname?
3由情态动词的过去式构成,can—could.
Shecouldwalkwhenshewasoneyearold.IcouldnotspeakEnglishoneyearago.
三一般将来时态:即将发生动作或状态。时间状语有:tomorrow,nextyear,themonthafter next,intwohours.
1任何人称+will+动词原形.
IwillflytoKongKongtomorrow.Hewillgowithus.WewillarriveinShanghainextweek.
Iwillneverbelieveyouagain.Hewillnotcometonight.Wewillnotbuyacarnextyear.
Willyougotherebytrain?Willhecometomorrow?Willtheyliveafive-starhotel?
Whatwillyoudoafterclass?Wherewillhelive?Howwilltheycomehere?
2is/am/are+goingto+V原形,表示计划打算做什么事情。
I’mgoingtogotoKongkongbyair.?Wearenotgoingtobuyahousehere.
Aretheygoingtochangetheirjobs??Howareyougoingtotellhim?
四过去将来时态;在过去将会发生的动作。
构成:任何人称+would+V原形
?????was/weregoingto+V原形
HesaidhewouldcomeininShanghai.?IsaiIwouldbuyyouacaroneday.
Theytoldmethattheywerenotgoingtogoabroad.
五现在进行时态:表示现在(指说话人说话时)正在发生的事情。常用的时间的动作:now,att he(this)moment
构成:is/am/are+Ving?
I’mwaitingformyboyfriend.Heisdoingthehouseworkathomenow
Heisnotplayingtoys.Weareenjoyingourselves.
Areyouhavingdinnerathome?IsTimcookinginthekitchen?
Whatareyoudoingnow?Wherearetheyhavingameal?
六过去进行时态:过去一段时间正在发生的动作。
构成:was/were+Ving
Iwasdoingmyhomeworkatthattime.Hewasnotsleepingat11o’clocklastnight.
Whatwereyoudoingatthatmoment?
Wewerehavingapartywhilemyneighbourissleeping.
七现在完成时态:用来表示之前已发生或完成的动作或状态,其结果的确和现在有联系。动作或状态发生在过去但它的影响现在还存在;也可表示持续到现在的动作或状态。简单的说,就是动作已经发生对现在造成明显的影响。常用的时间for two/weeks/years;for several days;sinc e2004/Apr. 23/last week /the accident
?构成:have/has+done(过去分词)
IhavealreadytoldDavy.Davyhasknownthismatter.Hehaslivedherefornearly10years.
Ihaven’tfinishedmyhomework.Timhasn’tcomeyet.Wehaven’theardanynewsabout him
Howlonghaveyouworkedinthiscompany?
?特别注意:
?1.have/hasalwaysbeen+名词/形容词/介词:总是或一直是什么样子。。。Hehasalwaysbeenagoodfather.Ihavealwaysbeenbusy. TheyhavealwaysbeeninAmerica.
?2have/hasbeento:表示去过或到过。。。
IhavebeentoCanada.HaveyoubeentoHongkong? Wherehaveyoubeen?Ihaveneverbeenhere.
?3have/hasgoneto:去了。。。
HehasgonetoBeijing.Theyhavegonetothecinema.
八过去完成时态:发生在过去的过去。
构成:had+done
HesaidhehadtoldDavy.Theytoldustheyhadfinishedthework. Shehadhaddinnerbeforeshewentout. HelefttheofficeafterhehadcalledDavy. ?
(完整版)英语中的十六种时态
英语中的十六种时态 (1)一般现在时 基本形式(以do为例):第三人称单数:does(主语为非第三人称单数);肯定句:主语+动词原形+其他; He works for us. 否定句:主语+don't/doesn't+动词原形+其他; He doesn't work for us. 一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他。 肯定回答:Yes,(+主语+do/does). 否定回答:No,(+主语+don't/doesn't.) 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句语 Does he work for us? Yes, he does.
No, he doesn't What does he do for us? He works for us. (2)一般过去时 be动词+行为动词的过去式 否定句式:在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词,或was/were+not;was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词 例如: Did he work for us? He didn't work for us. He worked for us. (3)一般将来时 am/are/is+going to+do 或 will/shall+do am/is/are/about to + do
am/is/are to + do; 一般将来时的表达方法 be going to +动词原形 be +不定式,be to+动词原形,be about to +动词原形 be able to +不定式 be about to+动词原形 will + 动词原形; 例如:He is going to work for us. He will work for us; He is coming.这是特殊的用一般现在时表达将来时态的例子!! (4)过去将来时 be(was,were)going to+动词原形 be(was,were)about to+动词原形
高考英语十六时态表格总结(很全面)
英语时态表 —— 一般现在时、一般过去时 时态 名称 结构 常连用的词 主要用法 例句 一般 现在时 1 动词用表示,之后接名词,形容词或介词。 ; ; …; ; ; ; … a ; ….; 一般现在时表示没有时限的持久存在的习惯性的 动作或状态,或现阶段反复发生的动作或状态 陈述句:I . . . 否定句: I . . . 一般疑问句: ? ? 2行为动词用V 原形或,引导疑 问句和否定句,用或’t ;第三人称时用或’t,有出现动词用原形;第三人称陈述句V 后加s 或. 陈述句:I . . . 否定句: I ’t . ’t . 一般疑问句: a ? ? 一般过去时 1.动词用过去 式或 表示。 ; ; ….; … ; a ; ; 过去的时间; 在过去时间里所 发生的动作或存 在的状态。 陈述句:I a . . 否定句: I . . 一般疑问句: a ? ? 2行为动词用,陈述句,疑问句和否定句借助 于,有出现动词 用原形。 陈述句:I . . . 否定句: I ’t . ’t . a . 一般疑问句: ? ?
英语时态表——现在进行时、过去进行时 时态 名称 结构常连用的词主要用法例句 现在进行时; ; ; !(放在句首); ! (放在句首); 表示现在 ( 指说话人 说话时) 正 在发生的事 情。 陈述句:I’m . . . 否定句 . 一般疑问句? ? 特殊疑问句? a ? 过去进行时 ; ; 时间点; ; 过去一段时 间正在发生 的动作。 陈述句:I . a . 否定句11 o’ . 一般疑问句: ? 特殊疑问句: ? 英语时态表——现在完成时、过去完成时 时态 名称 结构常连用的词主要用法例句 现在完成时 (过去分词) ;;; (否定句中);;;… 一段时间; +时间点; 一段时间; 现在时间; ; ; ; ; ; …. 用来表示之 前已发生或 完成的动作 或状态,其结 果的确和现 在有联系。动 作或状态发 生在过去但 它的影响现 在还存在;也 可表示持续 到现在的动 作或状态。简 单的说,就是 动作已经发 生对现在造 成明显的影 响。 陈述句:I . . 10 . 否定句’t .. ’t . ’t 一般疑问句: ? 特殊疑问句: ? 特别注意: 1名词/形容词/介词:总是或一直是什么样子。。。 a . I . .
英语十六种时态表格分析情况总结
一般将来时、过去将来时
现在进行时、过去进行时
现在完成时 句子结构:主语+have/has done I have studied English in several different countries.在一些国家,我已经学习了英语. 句子结构:主语+had done I had studied a little English before I moved to the U.S. 在我搬去美国之前,我已经学习了 一点英语. 句子结构:主语+will+have done I will have studied every tense by the time I finish this course. 在我完成这个课程的时候,我已经能 完成英语时态的学习了. 句子结构:主语+be going to+have done I’m going to have studied every tense by the time I finish this course. 同上. Present Perfect Continuous 现在完成进行时Past Perfect Continuous 过去完成进行时 Future Perfect Continuous 将来完成进行时 句子结构:主语+have/has been doing I have been studying English for ten years. 我已经学习英语有十年的时间了. 句子结构:主语+had been doing I had been studying English for ten years before I moved to the U.S. 在我搬去美国之前,我已经学习了 十年的英语了. 句子结构:主语+will have been doing I will have been studying English for over three hours by the time you arrive. 明晚你来的时候,我已经学习英语3 个小时了. 句子结构:主语+be going to have been doing I’m going to have been studying English for over three hours by the time you arrive 同上. 详细讲解-一般现在时 通常以动词原形表示。主语为第三人称单数时,用现单三形式。
英语16种时态表
精心整理|?英语16种时态表 英语时态表 英语时态表 时态 名称 结构常连用的词主要用法例句 一般现在时1由be的 isamare表 示,之后接名 词,形容词或 介词。 every…, sometime s, always,ne ver, often,usu ally等。 一般现在时表示没有时 限的持久存在的习惯性 的动作或状态,或现阶段 反复发生的动作或状态 陈述句:Iamanofficeworker. Heissolazy. Theyareathome 否定句:IamnotTim. Sheisnotverybeauiful. Theyarenotintheoffice. 一般疑问句:Areyouanofficea Isshebeautiful? 2由实意动词 V构成,引导 疑问句和否定 句,用do或 don’t。第三 陈述句:IworkinShanghai. Heworksathome. DavyneverwatchesTVathome
人称时用does或doesn’t,有does出现动词用原形;第三人称陈述句V后加s或es. 否定句:Idon’tlikethefoodinK Davydoesn’tlikethefoodinK 一般疑问句: Doyouwantacupofcoffee?Do ubwaystation? 一般过去时。1由be的过 去式是was或 were表示。 Is\am---was; are---were. ? yesterday , lastweek, anhourag o, thedaybe foreyesterday , in1997。 在过去时间里所发生的 动作或存在的状态。 陈述句:Iwasabigboss.Hewa WewereinBeijinglastyear. 否定句:Iwasnotathomeatthat Wewerenotatworkyesterday 一般疑问句:Wereyouateacher Wassheintheofficelastweek? 2由V的过去 式构成陈述 句,疑问句和 否定句用借助 于did,有did 出现动词用原 陈述句:IworkedinSunmoon WestudiedEnglishthere.Heliv 否定句:Ididn’tworkhere. Theydidn’tseeme.ShelikedE
英语16种时态详解
英语的16种时态 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. 一般现在时 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。
C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。)2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法:A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging 全句的意思是:“虽然牛顿是个伟大的人物,但他的许多见解直到今天还在受到挑战,并且被现代科学家的工作所修正。”challenge是及物动词,在本句中应当是被动语态;其动作延续到今天,所以要用现在完成时态。可见答案是C) have been challenged。A) are to challenge和D) are challenging 都是主动语态,不可能是答案。B) may be challenged虽然是被动语态,但意思与全句内容不合,所以不对。 C) 表示发生在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常用点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose等。
英语十六时态表格完整总结
英语十六时态表格总结(很全面) 目录 一般现在时、一般过去时 ........................................................................................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。一般将来时、过去将来时?错误!未定义书签。 现在进行时、过去进行时 ........................................................................................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。现在完成时、过去完成时?错误!未定义书签。 英语时态表—英语时态举例!?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-一般现在时?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-现在进行时、一般过去时 ....................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 现在进行时?错误!未定义书签。 一般过去时?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-过去进行时、过去完成时、 ................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 过去进行时?错误!未定义书签。 过去完成时?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-过去完成进行时、一般将来时 ............................................................................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 过去完成进行时............................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 一般将来时....................................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。详细讲解-将来进行时?错误!未定义书签。 将来进行时....................................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。详细讲解-过去将来时、将来完成时 ....................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 过去将来时?错误!未定义书签。 将来完成时....................................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
英语十六种时态表格总结
一般现在时、一般过去时 时态 名称 结构 常连用的词 主要用法 例句 一般现在时 1 be 动词用 am/is/are 表示,之后接名词,形容词或介词。 often; usually; every…; sometimes; always; never; once/twice/… a week/month/year; on Sundays/Mondays/….; 一般现在时 表示没有时限的持久存在的习惯性 的动作或状 态,或现阶段 反复发生的动作或状态,或一般真理 陈述句:I am an office worker. He is so lazy. They are at home now. 否定句: I am not Tim. She is not very beautiful. They are not in the office. 一般疑问句:Are you an officeassistant? Is she beautiful? 2行为动词用V 原形或V-s/es ,引导疑问句和否定句,用do 或don’t ;第三人称时用does 或doesn’t,有does 出现动词用原形;第三人称陈述句V 后加s 或es. 陈述句:I work in Shanghai. He works at home. Davy never watches TV at home. 否定句: I don’t like the food in KFC. Davy doesn’t like the food in KFC either. 一般疑问句: Do you want a cup of coffee? Does she live near thesubway station? 一般过去时。 1.be 动词用 过去式was 或 were 表示。 yesterday; the day before yesterday; last week/month/year/….; … ago; a moment ago; just now; on/in+过去的时间; 在过去时间 里所发生的 动作或存在 的状态。 陈述句:I was a big boss.He was beautiful. We were in Beijing last year. 否定句: I was not at home at that moment. We were not at work yesterday. 一般疑问句: Were you a teacher? Was she in the office last week? 2行为动词用V-ed ,陈述句,疑问句和 否定句借助 于did,有did 出现动词用原形。 陈述句:I worked in Sunmoon. We studied English there. He lived inHongKong. 否定句: I didn’t work here. They didn’t see me. She liked English a lot. 一般疑问句: Did you go to America? Did he work in Sunmoon?
英语16种时态总结
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。英语时态分为16种: 一. 一般现在时用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。B) 习惯用语。C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sund ays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二. 一般过去时用法: A) 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。 B) 表示过去习惯性动作。特别是由would/ used to do表达的句型,本身表示的就
英语16种时态及被动语态_表格打印版2
英语16种时态及例句 ★动词的五种基本形式:1.动词原型(V.) 2.第三人称单数(V-S) 3.现在分词(V-ing) 4.过去式(V-ed) 5.过去分词(V-ed) 例词be is being was/were been 例如 study 一般时进行时完成时完成进行时 现在I study English everyday.I am studying English now.I have studied English in several different countries. I have been studying English for ten years. 过去Two years ago, I studied English in America. I was studying English when you called yesterday. I had studied a little English before I moved to the U.S. I had been studying English for ten years before I moved to the U.S. 将来I’m going to study English next year. I will be studying English when you arrive tonight. I’m going to be studying English when you arrive tonight. I will have studied every tense by the time I finish this course. I’m going to have studied every tense by the time I finish this course. I will have been studying English for over three hours by the time you arrive. 过去将来 I would study English the next day. I would be studying English that night. I should have studied English harder before I failed to pass the exam S hould have been studying would have been studying ★被动语态变化:即把表一里的动词V 用be动词的对应形式代替+ 动词的过去分词(v-ed) 例:一般将来时:Will+ V 的被动语态:现在进行时be+ V-ing 的被动语态 Will+ be + 过分be+ be-ing + 过分
(完整版)英语16种英语时态解析
英语16种英语时态解析! 英语时态分为16种,如下表所示: 各时态结构及用法 1. 一般现在时(do/does; is/am/are) ①表示现在的情况、状态和特征。 例:He is a student. 他是一个学生。 ②表示经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. 他总是帮助别人。 ③客观事实和普遍真理。 例:The earth moves the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。(常用于列车、客车、飞机或轮船时刻表) 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. 下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。 ⑤主将从现:在时间、条件和让步状语从句中经常用一般现在表示将的来事情。 例:If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home. 如果明天下雨,我们会待在家里。 2. 现在进行时(am/is/are doing) ①表示此时此刻正在发生的事情。 例:He is listning to the music now. 他现在正在听音乐。 ②表示目前一段时间内一直在做的事情,但不一定此时此刻正在做。 例:I am studying computer this term. 这个学期我一直在学习计算机。 ③现在进行时可以表示将来的含义。 瞬时动词的进行一定表将来。 例: I am leaving. 我要离开了。 持续动词的进行只有有将来的时间状语或有将来语境中才表将来。例: I am travelling next month. 下个月我要去旅行。 ④现在进行时与频度副词连用,表示说话者或褒义或贬义的感情色彩。
英语16种时态表格
英语16种时态表格篇(1):一张图看懂英语的16个时态 一张图看懂英语的16个时态 英语时态的系统学习和复习 英语与汉语最大之不同就是英语具有时态的语法特点,而汉语则无此项语法内容。此种区别也恐是广大中国学生学习英语的最大障碍之一。莱曼英语始终认为,任何一个庞杂,混乱,使人感到困惑的事物,只要找到其内在的规律,就会较为容易地驾驭和掌握它。英语的时态也不例外。事实上,人人都懂得这个道理。但是,发现一个事物的内在规律就不是嘴上说说那么容易了。 一.时态概论 所谓的英语时态就是动作发生的时间不同,要用不同的动词形式来表达。因而,英语时态的驾驭和掌握必须以动作发生的时间为根本,进行判断,从而来进行时态的选择。英语中,常用的时态共计十种。根据现行的学校教材安排,英语时态被分成下列三个阶段 小学四种 初中四种(兼顾复习小学所学的四种) 高中二种 重难点在于各种时态之间的区别,综合运用以及动词形式的记忆。 二.时态分类 英语时态按下列名称分类为 现在时态过去时态 一般现在时一般过去时 现在将来时过去将来时 现在进行时过去进行时 现在完成时过去完成时
现在将来进行时 现在完成进行时 以上各时态平起平坐,无任何顺序排列而言。也即,它们是同等的重要和常用,不应厚此薄彼。 三.学习方法 莱曼英语在多年的教学实践中,一直奉行方法领先的教学原则。在教授英语时态时也不例外。只有这样,才能使学生概念清晰,才能使学生在学完时态以后,娴熟地将其转化为能力。莱曼英语根据英语时态的内在规律,推出英语时态的“五点论”学习方法 含义每一种时态独有反映其内在规律的含义。 中文线索每一种英语时态都会有相应的中文时间定位。 构成每一种时态都有其独特的构成,或被称为时态句型。 助动词时态不同,助动词也就不同。帮助构成问句和否定句。 时态例句通过例句,掌控不同的时态,使其娴熟起来,区别于其他时态。 四.各时态例句展示 一般现在时 I always swim in the afternoon.It is usually sunny. He always swims in the afternoon.He feels very relaxed. 现在将来时 I will swim tomorrow afternoon.I am not going to have any classes. He will swim tomorrow afternoon.He is going to have a swimming test. 现在进行时 I am swimming in the gym with my classmates now.I want to improve my swimming skill. He is swimming in the gym with his classmates now.He likes swimming very much.
英语的16种时态
英语的16种时态 英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例) 一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时 现在 study be studying have studied have been studying 过去 studied be studying had studied had been studying 将来 will study wil be studying will have studied will have been studying 过去将来would study would be studying would have studied would have been studying 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. 一般现在时 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 用法:A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持 主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动 、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用 。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon.(下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)
英语十六时态表格总结(很全面)
英语时态表——一般现在时、一般过去时 时态 名称 结构常连用的词主要用法例句 一般现在时1 be动词用 am/is/are表示, 之后接名词,形 容词或介词。often; usually; every…; sometimes; always; never; once/twice/… a week/month/year; on Sundays/Mondays/….; 一般现在时表示 没有时限的持久 存在的习惯性的 动作或状态,或 现阶段反复发生 的动作或状态 陈述句:I am an office worker. He is so lazy.They are at home now. 否定句:I am not Tim. She is not very beautiful. They are not in the office. 一般疑问句:Are you an officeassistant? Is she beautiful? 2行为动词用V 原形或V-s/es, 引导疑问句和 否定句,用do 或don’t;第三 人称时用does 或doesn’t,有 does出现动词 用原形;第三人 称陈述句V后加 s或es. 陈述句:I work in Shanghai. He works at home. Davy never watches TV at home. 否定句: I don’t like the food in KFC. Davy doesn’t like the food in KFC either. 一般疑问句: Do you want a cup of coffee? Does she live near thesubway station? 一般过去时。1.be动词用过 去式was或 were表示。 yesterday; the day before yesterday; last week/month/year/….; … ago; a moment ago; just now; on/in+过去的时间; 在过去时间里所 发生的动作或存 在的状态。 陈述句:I was a big boss.He was beautiful. We were in Beijing last year. 否定句: I was not at home at that moment. We were not at work yesterday. 一般疑问句: Were you a teacher? Was she in the office last week? 2行为动词用 V-ed,陈述句, 疑问句和否定 句借助于did,有 did出现动词用 原形。 陈述句:I worked in Sunmoon. We studied English there. He lived inHongKong. 否定句: I didn’t work here. They didn’t see me. She liked English a lot. 一般疑问句: Did you go to America? Did he work in Sunmoon? 英语时态表——一般将来时、过去将来时 时态 名称 结构常连用的词主要用法例句 一般 将来 时 1 任何人称+will+V原形. tomorrow, the day after tomorrow; soon; next week/month/year/...; the 即将发生动 作或状态。 陈述句:I will fly to KongKong tomorrow. He will go with us. We will arrive in Shanghai next week. 否定句:I will never believe you again. He will not come tonight. We will not buy a car next year. 一般疑问句:Will you go there by train? Will he come tomorrow?
英语十六时态表格总结
英语时态表 —— 英语时态举例! Simple Present 一般现在时 Simple Past 一般过去时 Simple Future 一般将来时 句子结构:主语+V I?study ?English everyday. 我每天都学习英语. 句子结构:主语+V-ed Two years ago, I?studied ?English in America. 两年前,我在美国学英语. 句子结构:主语+will+V. ? If you are having problems, I?will help ?you study English. 如果你在学习英语当中,遇到问题,我将帮 助你. 句子结构:主语+be going to+V I’m going to study ?English next year. 我明年将开始学习英语. Present Continuous 现在进行时 Past Continuous 过去进行时 Future Continuous 将来进行时 句子结构:主语+be+doing I?am studying English now. 我正在学习英语. 句子结构:主语+was/were+doing I?was studying ?English when you called yeaterday. 你昨天给我打电话的时候,我正在学习 英语. 句子结构:主语+will be+doing I?will be studying ?English when you arrive tonight. 明晚你来的时候,我会正在学习英语. 句子结构:主语+be going to+be+doing I’m going to be studying ?English when you arrive tonight. 同上.
英语十六时态表格总结很全面
下面用表格的形式给罗列出来,便于记忆英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例):
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。英语时态分为16种: 一. 一般现在时 用法:
A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。B) 习惯用语。C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等 定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为
英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例):精编版
英语共有十六种时态,其表现形式如下(以study为例): 一般时进行时完成时完成进行时 现在 study studies am studying is studying are studying have studied has studied have been studying has been studying 过去studied was studying were studying had studied had been studying 将来shall study will study shall be studying will be studying shall have studied will have studied shall have been studying will have been studying 过去将来should study would study should be studying would be studying should have studied would have studied should have been studying would have been studying 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 一. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。B) 习惯用语。C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情 时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二. 一般过去时 用法: A) 表示过去某个时间发生的动作或情况。
