定语从句知识结构图解
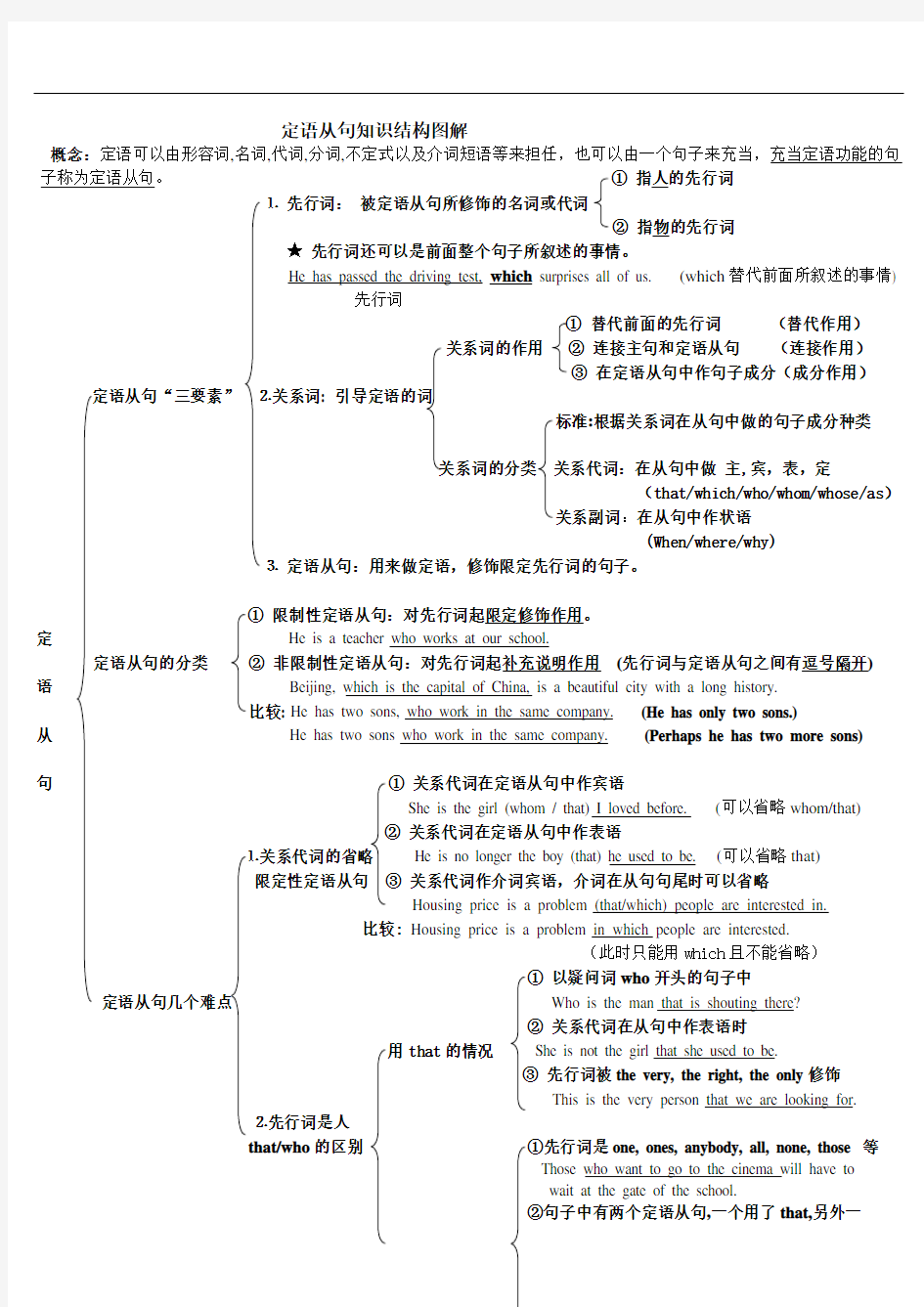

定语从句知识结构图解
概念:定语可以由形容词,名词,代词,分词,不定式以及介词短语等来担任,也可以由一个句子来充当,充当定语功能的句子称为定语从句。①指人的先行词
⒈先行词:被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词
②指物的先行词
★先行词还可以是前面整个句子所叙述的事情。
He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us. (which替代前面所叙述的事情)
先行词
①替代前面的先行词(替代作用)
关系词的作用②连接主句和定语从句(连接作用)
③在定语从句中作句子成分(成分作用)
定语从句“三要素”⒉关系词: 引导定语的词
标准:根据关系词在从句中做的句子成分种类
关系词的分类关系代词:在从句中做主,宾,表,定
(that/which/who/whom/whose/as)
关系副词:在从句中作状语
(When/where/why)
⒊定语从句:用来做定语,修饰限定先行词的句子。
①限制性定语从句:对先行词起限定修饰作用。
定He is a teacher who works at our school.
定语从句的分类②非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明作用(先行词与定语从句之间有逗号隔开)
语Beijing, which is the capital of China, is a beautiful city with a long history.
比较: He has two sons, who work in the same company. (He has only two sons.)
从He has two sons who work in the same company. (Perhaps he has two more sons)
句①关系代词在定语从句中作宾语
She is the girl (whom / that) I loved before. (可以省略whom/that)
②关系代词在定语从句中作表语
⒈关系代词的省略He is no longer the boy (that) he used to be. (可以省略that)
限定性定语从句③关系代词作介词宾语,介词在从句句尾时可以省略
Housing price is a problem (that/which) people are interested in.
比较:Housing price is a problem in which people are interested.
(此时只能用which且不能省略)
①以疑问词who开头的句子中
定语从句几个难点Who is the man that is shouting there?
②关系代词在从句中作表语时
用that的情况She is not the girl that she used to be.
③先行词被the very, the right, the only修饰
This is the very person that we are looking for.
⒉先行词是人
that/who的区别①先行词是one, ones, anybody, all, none, those 等
Those who want to go to the cinema will have to
wait at the gate of the school.
②句子中有两个定语从句,一个用了that,另外一
用who的情况个用who
Who is the boy that won the gold medal?
③在there be 结构中
There are many young men who are against him.
④在非限定性定语从句当中
Tom, who is my best friend, has gone abroad to study.
①在非限定性定语从句中.
She lost the game, which depressed her greatly.
②关系词置于介词之后,作宾语.
The pen with which you write is Jack’s.
用which的情况③先行词是that或定语从句中套定语从句,一个关系
词用that,另一个用which.
Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from the
library which is newly open to us.
①先行词是不定代词如all, little, few, much,
⒊先行词是物anything, everything, nothing, none, no one等
that / which的区别She did all that she could to help us.
②先行词被all, every, no, some, little, much, the only,
the very, the right,the last等所修饰时
This is the very book that I want.
③先行词中既有人又有物时
She described in her compositions the people and
用that的情况the places that impressed her most.
④先行词前有序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。
This is the best book that I have ever read.
This is the first film that I’ve seen since I came here.
⑤定语从句中套定语从句,其中一个关系词以用
which, 另外一个用that
He built a factory which produced things that had
never been seen before.
定⑥当主句的主语是疑问词which,另一个用that
Who is the person that is standing at the gate?
语定语从句10个难点①As 既可以引导限制性定语从句也可以用于非限定性定
句中充当主语,宾语,表语等。常用于以下句型当中
从★Such/so….. as…. 像…..一样the same …. as…和…...同样的
A computer is so useful a machine as we can use everyday.
句⒋As引导定语从He is not the same man as he was.
句的用法②引导非限制性定语从句,此时
译为“正如,像”等。可以放在句首,句中或句末。
As I remember, there were a net bar here.
Taiwan is an inseparable part of China, as is known to all.
★the same as...和the same that...引导定语从句的区别
This is the same bike that I lost yesterday. (同一事物)
This is the same bike as I lost yesterday. (同类事物)
①When 在定语从句中做时间状语,先行词为表示时间的time, day等
I still remember the day when I first came to Beijing. (when=on which)
②Where 在定语从句中做地点状语,先行词为表地点的place, spot等
Can you tell me the office where he works? (where = in which)
③Why 在定语从句中做原因状语,先行词只有reason.
⒌关系副词的运用I don’t want to listen to any reason why you were absent. (why = for which)
★
★case(情形),situation,
position(位置),stage (阶段),point(地步)等
What are the situations where body language is the only form of communication?
在哪些情况下身体语言是唯一的沟通方式。(此时where = in which)
① way that / in which / 不填
The way in which / that / 不填he explains the sentence to us is quite simple.
比较: The way which /that/不填he told to us was quite simple.
(★way在定语中作tell的宾语)
表示“次数”时,用关系代词that引导定语从句
⒍几个特殊②先行词time This is the first time that the president has visited the country.
的先行词time作“一段时间”讲时,应用关系副词when
This was the time when there were no radios, no telephones or no
TV sets. (★此时when = during which 在..期间)
③先行词reason4种引导方式
why/for which/that/不填
This is the reason why/for which/that/不填he can not come here.
比较:Is this the reason that/which/不填he explained to us for his absence from the
conference. (★reason 在定语从句中做explain的宾语)
★该结构的关系代词只有两种即介词+which(指物)介词+whom(指人)
★该结构介词的选用原则:
①根据定语从句中谓语动词的习惯搭配
This is the book on which I spent $ 8.
This is the book for which I paid $ 8.
②根据先行词的搭配习惯
I remember the days during which I lived there.
I remember the day on which I graduated from university.
⒎介词+关系代词③根据整个句子所表达的意思来决定
The colorless gas without which we can’t live is called oxygen.
④英语中为了强调某一名词,不定式前面也可以加上关系代词。
Here is the money with which to buy the piano.
She is the right person on whom to depend.
定注意:Ⅰ如果介词后移,关系代词可以省略
The person (whom/who/that) you will write to is Todd.
语定语从句10个难点Ⅱ有些含有介词的动词短语介词不能提前如
look for/after; take care of; send for; hear from/of/about deal with等从This is the baby that you will look after.
句①当先行词是one of + 复数名词,定语从句的位于动词要用复数形式
⒏定语从句的every year.
主谓一致②当先行词是 the only + one of +复数名词,从句谓语用单数形式
moon.
③先行词如果是整个句子,定语从句的谓语动词用单数
Great changes have taken place in China, as is known to all.
He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us.
定语从句可以转换为–ing或-ed形式
⒐定语从句的The girl (who is) dancing now just returned from Taiwan.
转化I love the stories (which were) written by Hemingway.
The man (who stands) standing there is my friend.
①判断从句是否为定语从句(先行词,关系词,定语从句)
②准确判断先行词在定语从句中的成分(主、宾、表、定、状)
10.定语从句的从而正确选定使用关系代词或关系副词
解题方法例:Is this the museum ___ you visited a few days ago?
Is this the museum ____ the exhibition was held?
A. where
B. that
C. on which
D. what
注意:Ⅰ.关系代词whose的用法。Whose在定语从句中做定语。
Do you know the boy whose parents / the parents of whom are on holiday?
I’d like a room whose window / the window of which faces the sea.
Ⅱ.That引导定语从句,名词性从句和强调句型的区别
定语从句中的that: 关系代词,在后面的定语从句中做句子成分。
名词性从句中的that: 从属连词,只起连接主从句的作用,在从句中不做句子成分。
强调句中的that, 运用于it is/was…that..结构;判断标准:去掉强调句型结构,成分仍然完整。
(that 引导定语从句)
(that和前面的it is构成强调句型)
(that 引导名词性从句--同位语从句)
(that引导名词性从句--主语从句)
(that引导名词性从句--宾语从句) The reason for your failure is that you lack confidence in yourself. (that 引导名词性从句--表语从句)
定语从句练习题:
1. They will fly to Washington, _______ they plan to stay for two or three days.
A. where
B. there
C. which
D. when
2. The growing speed of a plant is influenced by a number of factors, _______ are beyond our control.
A. most of them
B. most of which
C. most of what
D. most of that
3. I will give you my friend’s home address, _____ I can be reached most evenings.
A. which
B. when
C. whom
D. where
4. All the neighbors admire this family, _______ the parents are treating their child like a friend.
A. why
B. where
C. which
D. that
5. Villagers here depend on the fishing industry, _______ there won’t be much work.
定语从句知识结构图解
定语从句知识结构图解 概念:定语可以由形容词,名词,代词,分词,不定式以及介词短语等来担任,也可以由一个句子来充当,充当定语功能的句子称为定语从句。①指人的先行词 ⒈先行词:被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词 ②指物的先行词 ★先行词还可以是前面整个句子所叙述的事情。 He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us. (which替代前面所叙述的事情) 先行词 ①替代前面的先行词(替代作用) 关系词的作用②连接主句和定语从句(连接作用) ③在定语从句中作句子成分(成分作用) ⒉关系词: 引导定语的词 标准:根据关系词在从句中做的句子成分种类 关系词的分类关系代词:在从句中做主,宾,表,定 (that/which/who/whom/whose/as) 关系副词:在从句中作状语 (When/where/why) ⒊定语从句:用来做定语,修饰限定先行词的句子。 ①限制性定语从句:对先行词起限定修饰作用。 定He is a teacher who works at our school. 定语从句的分类②非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明作用(先行词与定语从句之间有逗号隔开) 语Beijing, which is the capital of China, is a beautiful city with a long history. 比较: He has two sons, who work in the same company. (He has only two sons.) 从He has two sons who work in the same company. (Perhaps he has two more sons) 句①关系代词在定语从句中作宾语 She is the girl (whom / that) I loved before. (可以省略whom/that) ②关系代词在定语从句中作表语 ⒈关系代词的省略He is no longer the boy (that) he used to be. (可以省略that) 限定性定语从句③关系代词作介词宾语,介词在从句句尾时可以省略 Housing price is a problem (that/which) people are interested in. 比较:Housing price is a problem in which people are interested. (此时只能用which且不能省略) ①以疑问词who开头的句子中 定语从句几个难点Who is the man that is shouting there? ②关系代词在从句中作表语时 用that的情况She is not the girl that she used to be. ③先行词被the very, the right, the only修饰 This is the very person that we are looking for. ⒉先行词是人 that/who的区别①先行词是one, ones, anybody, all, none, those 等 Those who want to go to the cinema will have to wait at the gate of the school. ②句子中有两个定语从句,一个用了that,另外一 用who的情况个用who Who is the boy that won the gold medal? ③在there be 结构中 There are many young men who are against him. ④在非限定性定语从句当中 Tom, who is my best friend, has gone abroad to study.
定语从句专项知识点总结汇总
定语从句专项知识点总结汇总 - 定语从句(Attributive Clauses)在句中做定语,修饰一个名词或代词,有时也可以修饰部分或整个句子。 被修饰的名词,词组或代词即先行词。定语从句通常出现在先行词之后,由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引出。 关系代词有:who, whom, whose, that, which, as。 关系副词有:when, where, why, how。 关系代词和关系副词放在先行词和定语从句之间,起连接作用,同时又可做定语从句的一个成分。当关系代词做宾语时可以省略。 定语从句中的谓语动词必须在人称上和数量上和先行词保持一致。 定语从句分为限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。 1 关系代词引导的定语从句 1) who, whom, that 这些词代替的先行词是人的名词或代词,在从句中所起作用如下:
Is he the man who/that wants to see you? (who/that在从句中作主语) He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday. (whom/that在从句中作宾语) 2) whose 用来指人或物,(只用作定语,若指物,它还可以同of which互换). 例如: Please pass me the book whose (of which) cover is green. 3) which, that 它们所代替的先行词是事物的名词或代词,在从句中可作主语、宾语等. 例如: A prosperity which / that had never been seen before appears in the countryside. (which / that在句中作宾语) The package (which / that) you are carrying is about to come unwrapped. (which / that在句中作宾语) 关系代词that和which 都可以指物,that 和Who 都可以指人,其用法区别:
高中英语定语从句知识点及练习复习过程
高中英语定语从句知识点及练习
高中英语---定语从句 一定义及相关术语 1.定语从句:修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。定语从句一般紧跟在它所修饰的词之后。 2.先行词:被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词。 3.关系词:引导定语从句的词叫关系词。关系词有关系代词和关系副词。关系代词有that, which, who, whom, whose, as等;关系副词有when, where, why等关系词在定语从句中有三大作用 1. 连接作用——连接先行词和定语从句。 2. 替代作用——在定语从句中替代从句所修饰的先行词。 3. 成分作用——在定语从句中作主语、宾语、定语或状语。 The man who is shaking hands with my father is a policeman. 二关系代词引导的定语从句 引导定语从句的关系代词主要有who, whom, whose, which, that等。它们分别代替前面的先行词,并在定语从句中作主语、宾语或定语。 1. who 指人,在定语从句中作主语。 That is the teacher who teaches us physics. 2. whom 指人,在定语从句中做宾语,可省略,在口语或非正式文体中常可用who 来代替。 Li Ming is just the boy (whom) I want to see. 3. which 指物,在定语从句中做主语或宾语,做宾语时常可省略。 Football is a game which is liked by most boys.
4. that 指人时,相当于who 或whom;指物时,相当于which.。在定语从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时常可省略。 He is the man that/who lives next door. Where is the man (that/whom) I saw this morning? 、 The season that/which comes after spring is summer. The dress (that/which) Ann bought doesn’t fit her very well. 5. whose 指人、物皆可,与后面的名词有所属关系,在定语从句中做定语。 I visited a scientist whose name is known all over the country. 注意:指物时,常用以下结构来代替: The house whose windows are broken is empty. =The house the windows of which are broken is empty. Do you like the book whose cover is yellow? =Do you like the book the cover of which is yellow? 三“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句 关系代词在从句中作介词宾语时,可以跟介词一起放在从句与主句之间(that, who不可以),也可以把介词放在从句中有关动词的后面,使关系代词紧跟它所修饰的先行词。 The school (which/that) he once studied in is very famous. =The school in which he once studied is very famous. This is the boy (whom/who/that) I played tennis with yesterday. =This is the boy with whom I played tennis with yesterday. 注意:1. 含有介词的短语动词一般不拆开,介词仍放在短语动词的后面。如:look for, look after, take care of 等。 2. 介词后的关系代词不可用that和who,若介词放在关系代词前,关系代词指人时只可用whom指物时只可用which;关系代词是所有格时用whose。
知识结构图
九年级第六单元知识结构图 一、单元分析与提示 1.本单元共四篇文章,三篇史传篇幅较长,囊括了初中文言文学习的多种要求,五首词是古代诗词中的经典词作,从内容、风格、艺术上都各具典型性和代表性。 2.在本单元的学习过程中,学生不但可以积累重要的文言文知识,还可以增长历史知识并受到古人智慧、勇气和节操方面的感染和激励。 3.学习这个单元的内容,引导学生去同古人作心灵对话,理解他们特殊的思想情感,从这些历史资料中去发现和领会中华民族那种为追求理想、报效国家,而甘于“鞠躬尽瘁,死而后已”的传统精神,弘扬中华民族的传统美德。 4.指导学生用历史唯物主义观点去认识历史事件和历史人物,引导学生结合时代背景、社会风貌,体会历史人物的思想感情和历史作用,脱离特定环境审视人物的做法是不足取的。树立正确的偶像观、英雄观人生观和远大抱负;帮助学生学会运用历史唯物主义的观点和方法评价历史人物。 5.朗读在文言文的教学中具有特别重要的作用,因此,教学时应该采用多种朗读方式。如齐读、散读、个人朗读、分组朗读等方式,既加深学生对课文的理解,又让学生尽可能在课堂上识记相关名句。书读百遍,其义自见。 6.培养学生自主、合作、探究式学习,鼓励学生通过自己的思考,去掌握知识,掌握学习知识的方法。在教学中,可以让学生互相质疑,“有疑而问”或是“明知故问”,互相取长补短,从而掌握文章的大意,进一步熟悉学习文言文的方法。 二、单元教学目标 1.反复地诵读,熟悉并背诵重要的篇章,提高阅读能力,学会一些阅读技巧。 了解有关作者、文体及相关知识,积累文言词语,培养文言语感。 2.借助注释和工具书理解文意,进一步培养学生把文言文翻译成现代文的能力。 3.积累古今异义词,揣摩、品味精彩文句,提高语言运用能力。 4.欣赏古代诗词,体会作者表达的思想感情,并与作者产生思想共鸣。 5.从文章中学到历史人物的勇气、魄力和智慧,并从他们身上汲取精华,传承美德,砥砺意志,自强不息。 三、单元教学重点 1.了解一些文学常识及中国几大历史著作的有关知识。 2.反复地诵读,熟悉并背诵重要的篇章,提高阅读能力,学会一些阅读技巧。 3.培养学生把文言文翻译成现代文的能力。掌握文言实词和虚词。 4.欣赏古代诗词,体会作者表达的思想感情,并与作者产生思想共鸣。 四、单元教学难点 1.学生对特定的历史背景难以理解。 2.对古今异义词的理解和掌握有较大的难度,应重点训练。 3.文言文的一些语法知识与现代文的有所不同,学生难以理解和把握。 4.指导学生,从文章中学到历史人物的勇气、魄力和智慧,并受到思想教育。 五、单元教学设想 1.熟读成诵法:古代诗文教学中,诵读是十分关键的环节,学生能流畅诵读,对课文内容才能真正掌握,而且诵读本身就能够使学生感受到作品的美,受到美的熏陶和感染。 2.疏通文意法:借助注释和工具书掌握浅显的文言词语,归纳积累重要词语,掌握疏通文言文内容的技巧和方法。
高中定语从句知识结构图解(答案解析版)
图解定语从句 概念:定语可以由形容词,名词,代词,分词,不定式以及介词短语等来担任,也可以由一个句子来充当,充当定语功能的句子称为定语从句。 ①指人的先行词 ⒈先行词:被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词 ②指物的先行词 ★先行词还可以是前面整个句子所叙述的事情。 He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us. 先行词(which替代前面所叙述的事情) 替代前面的先行词(替代作用) 关系词的作用②连接主句和定语从句(连接作用) ③在定语从句中作句子成分(成分作用) 定语从句 “三要素”⒉关系词: 引导定语的词 标准:根据关系词在从句中做的句子成分种类 关系词的分类关系代词:在从句中做主,宾,表,定 (that/which/who/whom/whose/as) 关系副词:在从句中作状语 (When/where/why) ⒊定语从句:用来做定语,修饰限定先行词的句子。 ①限制性定语从句:对先行词起限定修饰作用。 定He is a teacher who works at our school. 定语从句②非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明作用 的分类 (先行词与定语从句之间有逗号隔开) 语Beijing, which is the capital of China, is a beautiful city with a long history. 比较:He has two sons, who work in the same company. (He has only two sons.) 从He has two sons who work in the same company. (Perhaps he has two more sons) 句
定语从句最全面的知识点整理
定语从句整理 定语从句分为限定性和非限定性 1.定语从句修饰先行词 2.关系代词:that, who, whom, whose, which, as 关系副词:where, when, why 3.关系词在句中的作用1. 引导定语从句 2. 代替先行词3.在定语从句中担当一个成分 4.关系代词在从句中做主语或者宾语; 5.关系副词做状语,相当于:介词+which。 when是时间状语,where是地点状语,一些特殊先行词后面也用where,比如 point, situation, part, condition,case 表示到了某种地步,某种程度也用where. * where和when都可以换成介词+which,但是不是所有介词+which都可以换成where或者when。 *不是所有介词都可以放在which或者whom前面,一些动词短语比如:look for, look after,take care of turn in, pay attention to, depend on, listen to就不能拆开使用,且介词后面不能用who或者that 关于关系词的省略 1)who, whom, that, which, 做宾语时可省。 2)that做表语可省 be动词后 3)that做宾补可省 4)*关系副词when在time, year, day后面可省,也可换成that,但不 普遍 5)*关系副词where在place, 和anywhere, somewhere这种--where 的后面时候可以省略,也可换成that但不普遍 6)*关系副词why放在the reason后面,即可换成 for which, that 又可省略,此较普遍。但放在a reason后面可省,但貌似不可以换成that 7)the way后面可以用in which, that 也可省略 关于that 可以用that的情况; that 在定语从句中的功能非常多 1.可以代词关系代词 who, whom, which, 既可以做主语又可以做宾语,做宾语时可以省略;限从中可以说遇到关系代词就可以换成that, whose除外,因为whose的名词所有格(。。。的)whose= of which 2.关系副词why修饰the reason可换成that,也可省。 Notice:见到the reason不一定非要选why, 做宾语时候选which/that, 也可省。 3.that在某些特殊情况下代替 where, when但不普遍。 4.the way后面可以用in which, that 也可省略 必须用that的情况 (做宾语依旧可省) 1.先行词是不定代词 everything, anything, nothing, 等不定代词 *不含something 2.先行词被every, any, all, some, no, little, few, much等限定词修饰 3.先行词被序数词修饰 the first, the second..... 4.先行词被最高级修饰 the best, the most 5.先行词被the very, the most修饰时
圆中知识结构图
关于《圆》的知识结构整理 一.主要定理及其作用: 1.圆心角, 弧,弦,弦心距之间的关系定理: 在同圆或等圆中,如果①两个圆心角②两条弧,③两条弦④两条弦心距中,有一组量相等,那么它们所对应的其余各组量都分别相等:(等弧---等角---等弦……) 用的最多的依据: ①在同圆或等圆中,如果两个圆心角相等,那么它们所对的两条弧相等 ②等弧所对的圆心角相等: ③在同圆或等圆中,如果两条弦相等,那么它们所对的两条弧相等 ④等弧所对的两条弦相等 2.垂径定理: 如果一条直线①过圆心;②垂直于弦;③平分弦;④平分劣弧;⑤平分优弧.只要具备其中两个条件,就可推出其余三个结论. (直角三角形---等弧……)用的最多的依据: ①垂直于弦的直径平分弦,并且平分弦所的两条弧 ②平分弦(非直径)的直径垂直于这条弦,并且平分这条弦所对的两条弧. ③一条弦的垂直平分线||经过圆心,并且平分这条弦所对的两条弧 ④平分弧的直径过圆心的直线垂直平分这条弧所对的弦. 3.圆周角定理: (1)直径所对的圆周角是直角; (2)90°的圆周角所对的弦是直径。 (3)一条弧所对的圆周角等于它所对的圆心角的一半; (4)同弧所对的圆周角相等; (5)等弧所对的圆周角相等; (6)在同圆或等圆中,相等的圆周角所对的弧相等; (等弧---等角---直角三角形) 4.切线的性质定理: 圆的切线垂直于经过切点的半径(直径)。(垂直关系) 5.切线的判定定理: 经过半径的外端,并且垂直于这条半径的直线是圆的切线。 6.切线长定理: 从圆外一点引圆的两条切线,它们的切线长相等,这一点和圆心的连线平分两条切线的夹角。(等弦---等弧---等角) 7.相切和相交两圆的性质定理: 如果两圆相切,连心线必过切点。如果两圆相交,连心线垂直平分公共弦 二.主要辅助线及其作用: 1.作弦心距:弦的中点.弧的中点。 2.过某一点作弦:构造相等的圆周角。 3.作直径:构造直角三角形和同弧所对的圆周角。 4.连结过切点的半径:“题中若有圆切线圆心切点连一连”。 5.两圆相切和两圆相交时,作连心线和公共弦。
最新定语从句知识结构图解
1 2 定语从句知识结构图解 3 概念:定语可以由形容词,名词,代词,分词,不定式以及介词短语等来担任,也可以由一个句子来充当,4 充当定语功能的句子称为定语从句。①指 5 人的先行词 6 ⒈先行词:被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词 7 ②指物的先行词 8 ★先行词还可以是前面整个句子所叙述的事情。 9 He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us. 0 (which替代前面所叙述的事情) 1 先行词 2 ①替代前面的先行词 3 (替代作用) 4 关系词的作用②连接主句和定语从 5 句(连接作用) 6 ③在定语从句中作句子成分 7 (成分作用) 8 定语从句“三要素”⒉关系词: 引导定语的词 9 标准:根据关系词在从句中做的 句子成分种类 1 2 关系词的分类关系代词:在从句中做主,宾,表,
3 定 4 5 (that/which/who/whom/whose/as) 6 关系副词:在从句中作状语 7 (When/where/why) 8 ⒊定语从句:用来做定语,修饰限定先行词的句子。 9 ①限制性定语从句:对先行词起限定修饰作用。 1 定 He is a teacher who works at our school. 2 定语从句的分类②非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明作用 (先行词与定语从句之3 间有逗号隔开) 4 语Beijing, which is the capital of China, is a beautiful city with 5 a long history. 6 比较: He has two sons, who work in the same company. (He has only 7 two sons.) 8 从He has two sons who work in the same company. (Perhaps he 9 has two more sons) 1 句①关系代词在定语从句中作宾语 2 She is the girl (whom / that) I loved before. (可以省略whom/that) 3 ②关系代词在定语从句中作表语
【初中英语】定语从句知识点总结
【初中英语】定语从句知识点总结 一、定语从句 1.This is the most beautiful picture __________ I have ever seen. A.that B.which C.what D.who 【答案】A 【解析】 句意:这是我见过的最漂亮的画。考查定语从句。先行词被最高级修饰时,引导词应用that。 结合句意和语境可知选A。 点睛:限制性定语从句中只能用that 引导定语从句的几种情况: 当先行词是everything, anything, nothing (something 除外), all, none, few, little, some等不定代词时,或当先行词受every, any, all, some, no, little, few, much等词修饰时。如: Have you set down everything that Mr Li said? There seems to be nothing that is impossible to him in the world. 注意:当先行词指人时,偶尔也可用关系代词who。如: Any man that / who has a sense of duty won’t do such a thing. 任何有责任感的人都不会做这样的事。 All the guests that / who were invited to her wedding were important people. 所有被邀请参加婚礼的 客人都是重要人物。2. 当先行词被序数词修饰时。如:The first American movie that I watched was the Titanic. 3. 当先行词被形容词最高级修饰时。如: This is the best museum that I have visited all my life. 4. 当先行词被the very, the only, the first / last等修饰时。如:She is the only person that understands me. 注意:当先行词指人时,偶尔也可以用关系代词who。如: Wang Hua is the only person in our school who will attend the meeting. 5. 当先行词前面有who, which等疑问代词时。如:Who is the man that is standing in front of the crowd? 站在人群前 面的那个人是谁?Which is the room that Mr Wang lives in? 哪一间是王先生住的房间? 当先行词人与物时。如:Look at the man and his donkey that are walking up the street. 当先行词是reason, way(方法)等词时,关系代词常用that代替in which, for which, why, 也常可省略。如:She admired the way (that) they solved the questions. 2.Mr.Brown is a teacher is strict with all is students. A.which B.who C.where 【答案】B 【解析】 【详解】 句意“布朗是一个对所有的学生都严格的老师”。 本题考查定语从句。A.指物,在从句中作主语或宾语;B.指人,在从句中作主语或宾语;C.表示地方,在从句中作地点状语。本句话中先行词为a teacher,指人,在从句中作主语,故选B。 【点睛】 做定语从句的题时,可先将先行词还原到句中。其次选择关系词,要先看先行词指人、指
(完整版)完整全面定语从句知识点
The Attributive Clause 定语从句:在英语复合句中,由关联词引导,修饰句中的名词、代词,有时也修饰主句的一部份或整个句子的从句称为定语从句。 它分为:限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句。 被定语从句所修饰的那个词称为先行词。 关系代词:which, that, who, whom, whose,as(在句中充当成分,可作主语,宾语,表语,定语)引导词 关系副词:when, where, why,在句中只作状语。 e.g. She is an English teacher who likes singing songs. 先行词定语从句 引导词(从句中做主语) 关系词的作用: 1.引导定语从句; 2. 代替先行词; 3. 在从句中担当一个成分 e.g. This is the best film that I have seen. Ⅰ关系代词 (1)who, whom引导的定语从句 who 指人作主语/宾语(可省略)介词在前不可使用 whom 指人宾语(可省略)介词后不可省略 a. What’s the name of the girl who just came in? b. Do you know the student to whom Jane is talking?(不能用who) (2)that 引导的定语从句 that 人或物主语 宾语 表语 不引导非限制性定语 从句,不位于介词后。 a. Here is the money that/which will be given to you. b. Do you like the book (that/which) you borrowed yesterday? c. He is no longer the boy that he used to be. (3).which引导的定语从句 which 指物主语或宾语(可省略) 在介词后不可省略 a. The building which /that stands near the river is our school. b. The room in which there are a lot of books is a reading room. (4)whose引导的定语从句 whose是关系代词who与which的所有格形式,用作名词的限定语,whose 指人或物,在从句中作定语。Have you seen a dictionary whose cover is blue? (the cover of which is blue)? ▲whose经常后接名词,这结构可以用the+名词+of+whom/which来替换,意义不变。也就是说,表示所属关系, whose + n. = of which/ whom + the + n. = the + n. + of which/ whom e.g. He is an whose daughter studies abroad. excellent teacher,the daughter of whom studies abroad.
最完整七年级下册历史知识点总结结构图(精华版)
七年级下册历史知识点总结结构图 七年级历史教材为中国古代史内容,隐含着丰富的历史知识,由于受到教材篇幅的限制等原因,编写者往往会将其情感隐匿于教材之 中。下面由为你提供的七年级下册历史知识点总结结构图,希望大 家喜欢。 七年级下册历史知识点总结结构图欣赏一、隋朝的建立、统一和灭亡 1 、隋的建立:581 年,杨坚(隋文帝)夺取北周政权,建立隋朝,定都长安。 2 、隋的统一: 时间:589 年,隋朝灭陈,统一南北。 隋实现重新统一的原因:①长期的分裂和战乱,人民渴望统一; ②北方:经过南北朝的民族大融合,民族界限缩小,为南北统一创造 了条件;南方:江南经济的发展,南北人民要求结束分裂局面,加强 双方的经济交流。③隋朝励精图治,国力强盛;陈朝统治腐败,力量衰弱。 意义:结束了西晋末年以来二百七十多年的分裂、对峙局面,开 创隋唐时期三百二十余年的“大一统”局面,为经济文化的繁荣发展 奠定了基础。 3 、隋的灭亡:暴政引起农民起义,公元618 年,隋炀帝在江都
被部将杀死,隋朝灭亡。 二、隋朝经济的繁荣──“开皇之治” 1 、表现:人口激增,垦田扩大、粮仓丰实。 2 、原因:①国家统一,社会安定;②隋文帝励精图治,发展生产; ③统治者提倡节俭。 3 、隋文帝在位时期,国家统一、安定,人民负担较轻,经济繁 荣发展,史称隋文帝的统治为“开皇之治”。 七年级下册历史知识点二三、大运河的开通 1 、目的:为了加强南北交通,巩固隋王朝对全国的统治。 2 、开通原因:①隋文帝在位的二十多年里,国家治理得比较好,出现了经济繁荣的景象,这就使隋炀帝开通大运河具备了经济实力。 ②隋朝国家统一,使隋炀帝有征发几百万人的可能性。③有前代开凿的几段古运河为基础。 3 、时间、人物:隋炀帝从605 年起,开通了一条纵贯南北的大 运河。 4 、中心、起始点:以洛阳为中心,北达涿郡,南至余杭。 5 、长度及地位:全长两千多公里,是古代世界最长的运河。 6 、四个组成部分(自北向南):永济渠、通济渠、邗沟、江南河。 7 、连接五条河流(自北向南):海河、黄河、淮河、长江、钱塘江。 8 、流通七省区:(略) 9 、开通的作用:有利于维护国家统一和中央集权,大大促进了
定语从句语法知识点基本汇总
定语从句 一、that引导的定语从句 1. that指人时,相当于who或whom;指物时,相当于which。 在定语从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时常可省略。 He is the man that/who lives next door.他就是住在隔壁的那个人。 Where is the man(that/whom) I saw this morning? 我今天早上看到的那个人在哪儿?The person (that/whom) you introduced to me is very kind. 你介绍给我的那个人很友好。The season that/which comes after spring is summer.春天之后的季节是夏季。 I don’t like stories that/which have unhappy endings. 我不喜欢结尾悲伤的故事。 The dress(that/which) Ann bought doesn’t fit her very well.安买的衣服不太合身。 2.限制性定语从句中只能用that引导定语从句的情况 (1)当先行词为all, much, little, something, everything, anything, nothing, none, few, some, the one等词时。 Everything that he said was true. 他所说的一切都是真的。 There seems to be nothing that is impossible to him in the world. 对他来说似乎世界上没有什么不可能的事。 Is there anything that I can do for you? 有我能为你效劳的事吗? That’s all that I know. 我知道的就这么多。 (2)当先行词被the very(恰恰,正好)the only, any, few, little, no, all修饰时。 This is the very grammar book (that) I want to buy. 这正是我要买的语法书。 The only thing that is constant is change. 唯一不变的是变化。 There was little that we could do to help her. 我们没有什么能帮助她的。 (3)当先行词是形容词最高级或被形容词最高级修饰时。 This is the best that has been used against pollution.这是曾经用过的最好的抗污染的办法。This is the most interesting film that I've ever seen. 这是我看过的最有趣的电影。 (4)当先行词是first,last,next等序数词或被序数词修饰时。 The first place that they visited in London was the Big Ben. 在伦敦他们参观的第一个地方是大本钟。 What is the first American film that you have seen? 你看过的第一部美国电影是什么?(5)当主句的主语是疑问词who或which时。 Who that has common sense will believe such nonsense? 有常识的人谁会相信这种无聊的
定语从句 知识结构图
指代对象 人 事物 人+事物 主格 who/that which/that that 宾格 who/that/whom which/that that 所有格 Whose whose/of which 1.只用that 不用which ?(1)介词+which+从句,在此结构中因介词提前不能用that 代替which ,当介词不提前时方可。此结构可用关系副词代替“介词+which ”,如: The chair on which she sat is made of wood. The chair which /that she sat on is made of wood.?(2)先行词本身是that /those What’s that which flashed in the sky just now 定语从句在复合句中作定语,由关系代词和关系副词引导,被修饰的词为先行词。 一. 关系代词的用法 语法专题五:定语从句 2.关系代词只能用that 的情况 ?(1)先行词为“all ”,“everything ”,“nothing ”,“little ”,“much ”等不定代词。 ?eg. There is something that you can borrow. ?(2)先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last 修饰。?eg.This is the very place that I want to find. ?The last place that we visited was a factory. ?(3)先行词被形容词的最高级修饰。 ?eg.This is the best book that I have ever read. ?(4)先行词为两种或两种以上不同的事物。先行词若为分别表示人和事物的名词,也只能用that 引导定语从句。?eg.She gave me some books and a pen that I need. ?(5)先行词被序数词修饰。 ?eg.This is the second article that I wrote in English.?(6)主句是以who 或which 开头的特殊问句时。?eg.Who is the person that is standing at the door?
高考高中定语从句知识点汇总
定语从句知识点汇总 一、先行词 二、关系词 1.关系代词: 2.关系副词: 三、分类 1.限制性定语从句:对先行词有限制,区分的作用,并与先行词有着不可分割的关系,不能省略 2.非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明的作用,可省略不会影响主句的意思,与主句用逗号隔开 3.区别: 4.非限制性定语从句的特殊情况 4.1有些既可以做限制性,又可以做非限制性的定语从句,其含义不同
There are 20 students in this class who are from the north of China. There are 20 students in this class,who are from the north of China. 5.关系代词that和关系副词why不能引导非限制性定语从句 四、关系词的用法 1.which,that which指物,在从句中作主语,宾语 that指人或物,指人可与who,whom互换;指物可与which互换 2.who,whom 从句中的介词提到关系代词词前,whom作宾语,不能用who代替 In our class there are 46 students, of whom half wear glasses. 先行词为指人的one,ones,anyone或those时,关系代词用who;双重定语从句中一个定语从句的关系代词是that,另一个指人的关系代词用who。 3.whose 表示“……的”。可指人或物。用来指物时, whose+名词=限定词+名词+of which=of which+限定词+名词 The house whose windows face south is ours. The house the window of which face south is ours.=The house of which the window face south is ours. 4.as 作为关系代词可指人或物,在从句中作主语,宾语或表语。 一般用于such...as 、the same...as 、as...as结构中,表示“像”的意思 We have found such materials as are used in their factory.
各个专题知识结构图
各个专题知识结构图 专题一:珍爱生命、保护自己、学做生活的主人: (七上三、八、九课) 1、本专题记忆的知识(来自中考说明)、 (1)了解身边的诱惑:认清不良诱惑的危害。【黄赌毒】 身边的诱惑有:金钱的诱惑、电子游戏的诱惑、毒品的诱惑、赌博的诱惑、不健康信息的诱惑。不良诱惑危害参考指导书本P13 ★毒品的诱惑:毒品具有极大的社会危害性。我国法律规定:吸毒违法、贩毒有罪。《预防未成年人犯罪法》把未成年人“吸食注射毒品”列为严重的不良行为之一。消除毒害,人人有责。【劝解身边的人不吸毒的理由】 拓展:【禁毒宣传标语】消除毒害人人有责珍爱生命、远离毒害远离毒害莫入虎口 ★赌博的危害:【奉劝别人不赌博的原因】赌博是一种不正当的娱乐,一种恶习。是社会公害之一,“参与赌博、屡教不改”是未成年人的严重不良行为之一 ★不健康信息的危害:色情、暴力等不良信息混合在一起给涉世未深,分辨能力较差的青少年造成很大的危害。我们要遵守网络法律和道德,安全文明上网。 (2)了解青少年身边受侵害的表现。身边的侵害主要来自意外伤害、家庭侵害、学校侵害、社会侵害。这些侵害不仅对青少年身体,还有心理和精神等方面带来伤害,最严重的是对生命的剥夺。青少年要学会自我保护。自我保护是人的本能,剧本自我保护意识是未成年人迈向成熟的重要一步。 2、知识结构图: 专题二:知法守法、自立自强、学过安全的生活 (七下七、八课) 1、本专题记忆的知识(来自中考说明) (1)知道刑罚的含义,了解刑罚的种类。 ★刑罚的含义:刑罚又叫刑事处罚、刑事处分,是指人民法院对犯罪分子实行惩罚的一种强制方法。 ★刑罚的种类:根据我国刑法的规定,刑罚种类分为主刑和附加刑两大类。 主刑有:管制、拘役、有期、无期徒刑和死刑 附加刑有:罚金、剥夺政治权利、没收财产三种。 注意区别:罚款是行政处罚,罚金是刑罚,拘留是行政处罚,罚金是刑罚。 2、预防未成年人犯罪法规定的不良行为和严重不良行为。【指导书P21记熟】 A、未成年人的不良行为: ①旷课、夜不归宿;②携带管制刀具;③打架斗殴、辱骂他人;④强行向他人索要财物;⑤偷窃、故意毁坏财物;⑥参与赌博或者变相赌博;⑦观看、收听色情、淫秽的音像制品、读物等;⑧进入法律、法现规定未成年人不适宜进入的营业性歌舞厅等场所;⑨其他严重违背社会公德的不良行为。 B、未成年人的严重不良行为:“严重不良行为”,是指下列严重危害社会,尚不够刑事处罚的违法行为: ①纠集他人结伙滋事,扰乱治安;②携带管制刀具,屡教不改;③多次拦截殴打他人或者强行索要他人财物;④传播淫秽的读物或者音像制品等;⑤进行淫乱或者色情、卖淫活动; ⑥多次偷窃;⑦参与赌博,屡教不改;⑧吸食、注射毒品;⑨其他严重危害社会的行为。 3、未成年人受法律保护的基本内容。 ★四个保护:家庭、学校、社会、司法保护。 四个保护的内容:P21-22 ★家庭保护:父母和其他监护人的监护职责和抚养义务;尊重未成年人的接受教育的权利;
