英语动词时态归纳总结对照表

英语动词时态归纳总结对照表
;
英语时态专项练习
1、一般现在时。
通常用“usually, often, every day, sometimes”。
一般现在时基本用法介绍
一、一般现在时的功能
1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。
2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。
3.表示客观现实。如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
二、一般现在时的构成:
、
肯定句:
1).主语+系动词be(is, am, are )+名词(形容词,介词短语)
2) .其他主语+动词原形+其它
第三人称单数+动词-s+其它
如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。
We study English.我们学习英语。Mary likes Chinese.玛丽喜欢汉语。
三、一般现在时的变化
否定句: 1)主语+ be (is,am,are)+ not +其它。如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。
2)其他主语+do not(don’t)动词原形+其它 I don't like bread
第三人称单数+does not(doesn’t)动词原形+其它He doesn't often play.
《
一般疑问句:1)Be(Is,Are)+主语+其它如:-Are you a student -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.
2)Do其他主语+动词原形+其它
Does+第三人称单数+动词原形+其它+
注意:遇I/we—you, my—your, some—any.
Does she go to work by bike - Yes, she does. / No, she doesn't.
Do you often play football- Yes, I do. / No, I don't.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。如:Where is my bike
How does your father go to work
2、现在进行时。
通常用“now/look/listen”.
(
1.现在进行时表示现在正在进行或发生的动作,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。
2.现在进行时的结构:.
肯定句:主语+be(is,am,are )+动词现在分词-ing
eg: I am(not) doing my homework.
You/We/They are(not) reading.
He/She/It is(not) eating.
否定句:主语+be(is,am,are )+not + 动词现在分词-ing
一般疑问句:Is(Are)+主语+动词现在分词-ing
特殊疑问:疑问词+ be + 主语+ 动词ing
3.动词加ing的变化规则
-
1)一般情况下,直接加ing,如:cook-cooking
2)以不发音的e结尾,去e加ing,如:make-making, taste-tasting
3)如果末尾是一个元音字母和一个辅音字母,双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing,
如:run-running, stop-stopping,swim—swimming
3、一般过去时态
一般过去时通常用“a moment ago, just now, yesterday, last…”等。
1.一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。一般过去时也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作感谢。
2.Be动词在一般过去时中的变化:
⑴am 和is在一般过去时中变为was。(was not=wasn’t)
⑵are在一般过去时中变为were。(were not=weren’t)
}
⑶带有was或were的句子,其否定、疑问的变化和is, am, are一样,即否定句在was或were 后加not,一般疑问句把was或were调到句首。
3.行为动词的一般过去时变化
4.动词过去式的变化:
规则动词的变化:
不规则动词的变化:
》
原形
过去式原形过去式原形过去式原形过去式
sweep swept (
teach
taught have had go went
keep kept think thought {
do
did find found
sleep slept buy bought eat ate.said
say
feel felt drink drank is/am was take took }
read
read give gave are were mean meant
put put ~
sing
sang drive drove meet met
cut cut begin began !
speak
spoke make made
let let ring rang write wrote ¥
see
saw
fly flew run ran ride rode come came …
draw
drew sit sat hear heard tell told
grow grew 、
learn
learned/ learnt get got know knew
5.特殊疑问句:
⑴疑问词+did+主语+动词原形如:What did Jim do yesterday
⑵疑问词当主语时:疑问词+动词过去式如:Who went to home yesterday
4、一般将来时
—
概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。句中一般有以下时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, the day after tomorrow(后天)等。
1.基本结构:①主语+be (is,am,are)going to +动词原形.
②主语+will+ 动词原形.
2.否定句:①主语+be (is,am,are)+not +going to +动词原形.
②主语+will +not(won’t)+ 动词原形.
例如:I’m going to have a picnic this afternoon.→ I’m not going to have a picnic this afternoon.
3.一般疑问句:①Is(Are)+主语+going to +动词原形.+
②Will+主语+动词原形+
例:We are going to go on an outing this weekend.
→ Are you going to go on an outing this weekend Yes,we are. No, we aren’t.
)
Will he go to Beijing next week Yes,he will. No,he won’t.
4.对划线部分提问。一般情况,一般将来时的对划线部分有三种情况。
1). 问人。Who 例如:I’m going to New York soon. →Who’s going to New York soon.
2). 问干什么。Wha t … do.例如:My father is going to watch a race with me this afternoon. →What is your father going to do with you this afternoon.
3). 问什么时候。When.例如:She’s going to go to bed at nine. →When is she going to bed
5同义句:be going to = will I am going to go swimming tomorrow(明天). = I will go swimming tomorrow.
5.过去进行时:
肯定句:主语+助动词be (was,were)+动词现在分词-ing+其它
否定句:主语+助动词be (was,were)+not+动词现在分词-ing+其它
一般疑问句:Was(Were)+主语+动词现在分词-ing+其它
】
特殊疑问句:疑问词+was(were)+动词现在分词-ing+其它
用法:
1、表示在过去某一时间正在进行的动作,往往有表示过去的时间状语then, at that time, this time yesterday等,或与过去发生的某事同时发生的动作(即与when, while引出的时间状语从句连用)。例:They were talking about a film at six yesterday evening. 昨晚6点他们正在谈论一部电影。
What were you doing at this time last week 上周的这个时候你在干什么?
When the teacher came in, they were talking. 老师进来时,他们在讲话。
2、表示在过去某一段时间内进行的动作。
例:They were swimming from two to three yesterday afternoon. 昨天下午2点到3点他们在游泳。
She was watching TV the whole morning. 她整个上午在看电视。
3、表示过去将要发生的动作。
例:He said he was leaving on Tuesday. 他说他周二动身。
Tom said he was going tomorrow. 汤姆说他明天去。
4、用过去进行时描写故事背景。
例:It was getting dark. The wind was rising. 天渐渐黑了下来,风势增强了。
The procession was going. He was standing among the crowd looking on. 队伍在前进。他站在人群中观看。
6.现在完成时
构成:肯定句:主语+助动词have(has)+动词过去分词-ed
否定句:主语+助动词have(has)+not(ha ven’t,hasn’t)+动词过去分词-ed
一般疑问句:Have(Has)+ 主语+动词过去分词-ed+
特殊疑问句:疑问词+have(has)+ 主语+动词过去分词-ed+
用法:
1、表示说话之前已完成的动作,而且这个动作的结果对现在是情况仍有影响。常被
just,already,yet 等副词修饰。
Mr. Wang has just come back from America. 王先生刚从美国回来。
2.现在完成时还可用来表示过去发生的动作一直延续到现在,常带有for或since 等表示一段时间的状语。
如:Mr Wang has lived here since 1983.
《
3.现在完成时瞬间动词即终止性动词不能与表示一段时间的状语连用。
常见终止性动词与延续性动词(或状态动词) 的对应关系如下:
come / go / arrive / get / reach / move--- be in/at
open --- be open die --- be dead
close --- be closed become ---be
borrow --- keep put on --- wear
buy --- have leave ----- be away (from)
begin / start ----- be on fall asleep ---- be asleep
end/finish ----- be over catch a cold ----- have a cold
join the army ---- be in the army, be a soldier
、
join the Party---- be in the Party , be a Party member
例:吉姆买这支已有两年了。
Jim bought this pen two years ago.
Jim has had this pen for two years.
Jim has had this pen since two years ago.
Jim has had this pen since 2007
It is two years since Jim bought this pen.
4.在表示“最近几世纪/ 年/ 月以来……”时间状语中,谓语动词用现在完成时。
in the past few years/months/weeks/days;over the past few years; during the last three months; for the last few centuries, through centuries; throughout history 等
5.表示“第几次做某事,”或在“It is the best (worst, most interesting ) +名词+that” 后面跟现在完成时。
…
例:This is my first time that I have visited China.
This is the most interesting film I have ever seen.
That is the only book that he has written.
6. have / has been to + 地点意为“曾去过某地”,暗含目前已不在该地,仅表示当事人的一种经历而已。
have / has gone to + 地点“到了某地去了”,暗含“已离开原地去了某地”之意,但是否到达了某地尚不确定。
如:He has gone to Shanghai. 他去了上海。
He has been to Shanghai. 他去过了上海。
7.现在完成进行时
表示一个动作从过去某时开始,延续或重复地出现至今,或将继续延续至将来。。常与表示一段时间的状语,如:for two hours,since early morning,these few days 等连用。
构成:
肯定句:主语+助动词have(has)+been+动词现在分词-ing
否定句:主语+助动词have(has)+not+been+动词现在分词-ing
一般疑问句:Have(Has)+ 主语+ been+动词现在分词-ing+
特殊疑问句:疑问词+ have(has)+ 主语+ been+动词现在分词-ing+
例:It has been raining for three hours.
We have been waiting here since an hour ago.
How long has it been raining 雨下多久了?
She has been sitting there for more than 2 hours. 他已经在那坐了两个小时了。
We’ve been seeing quite a lot of each other recently. 最近我们常见面。
He has been telephoning me several times in two days. 这两天他打好几次电话给我。
注意事项:与现在完成时相比,现在完成进行时更强调:在从过去到现在的时间里,动作或状态一直持续或一直反复出现。
8.过去完成时
构成:
肯定句:主语+助动词had +动词过去分词-ed+其它
否定句:主语+助动词had +not(hadn’t)+动词过去分词-ed+其它
一般疑问句; Had+主语+动词过去分词-ed+其它+
特殊疑问句:疑问词+had +主语+动词过去分词-ed+其它+
例:There had been 25 parks in our city up till 2000.
By the end of last term we had finished the book.
They finished earlier than we had expected.
用法:
1、表示在过去某一时间或动作之前已完成或延续到某一过去时间的动作或状态,即“过去的过去“。这一动作可以是一直持续到过去这一时刻或将继续下去。这个过去的时间常用by,before after,)等介词短语或一个时间状语从句表示,也可以用一个表示过去的动作或上下文来表示。例:The train had left before she got to the station. 在她到车站以前,火车已开走了。
We had learned about 500 English words by the end of mine. 到上个月为止,我们已经学了约500个英文单词。
Mr. Smith died yesterday. He had been a good friend of mine. 史密斯先生昨天去世了,他曾是我的一位好友。
2、用于以连词when, as soon as, as…as, before, after, until, now that引导的状语从句中或一些宾语从句中以表示动作发生的时间早于主句所表示的动作,可表示原因、动作先后等关系。如:
例:After I had finished my homework, I watched TV last night. (表时间先后)
We took a taxi home, as the last bus already gone. 由于最后一班公车已开走,所以,我们就乘出租车回家。(表原因)
He got to the airport and suddenly realized that he had forgotten to bring his ticket. 他赶到机场时突然意识到他忘了带机票。
3、用在一般过去时之后的间接引语中。
He told me that he had been seen the film the day before. 他跟我说他前一天看过那个电影了。
注意:过去完成时的句子中,终止性动词不能与一段时间连用,而状态动词的过去完成时必须和一段时间连用。如:
He had already died. 他已经死了。
He had been dead for an hour. 他已经死了一个小时了。
9.过去将来时
构成:
肯定句:主语+助动词would+动词原形。
主语+助动词was(were) going to+动词原形。
否定句:主语+助动词would+not(wouldn’t)+动词原形。
.主语+助动词was(were)+not+ going to+动词原形
一般疑问句:Would+主语+动词原形+
Was(Were) +主语+ going to+动词原形+
特殊疑问句:疑问词+would+主语+动词原形+
was(were) +主语+ going to+动词原形+
例:I hoped she would succeed.
用法
过去将来时表示从过去某一时间看将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。这种时态常用于宾语从句或间接引语中。主要有以下几种形式:
1、would + 动词原形
这一形式表示过去将来时间,通常带有表示过去将来的时间状语,多见于从句或间接引语中。
I wanted to know when you would finish the article. 我想知道你什么时候写完论文。
He said he would wait for me at the gate. 他说他将在校门口等我。
2、was / were going to +不定式
They told me they were going to plaint trees. 他们告诉我他们打算去植树。
3、was / were to + 不定式
这一形式通常指按过去的计划,安排将在某个过去将来时间发生的事。
The reporter said the sports meeting was to take place soon. 记者称运动会不久将举行。
实用文档之100道题!初中英语八大时态专项练习题(含答案)
实用文档之"100道题!初中英语八大时态专 项练习题(含答案)" 100道题!初中英语八大时态专项练习题(含答案) 1. The sun ________ in the east. A. is always rising B. always is rising C. rises always D. always rises 2. He often ________ his clothes on Sundays. A. washing B. washes C. has washed D. wash 3. I’m Japanese. Where ________ from? A. do you come B. you are coming C. you come D. are you coming 4. A mother who ________ her son will do everything for his happiness. A. is loving B. loves C. loved D. has loved 5. ________ at a higher temperature than water?
A. Has milk boiled B. Is milk boiling C. Does milk boil D. Was milk boiling 6. He signed to us with his hand, “The lesson is over. You ________.” A. dismissed B. are dismissed C. have dismissed D. were dismissed 7. I haven’t met him for ages, but his mother ________ him sometimes. A. had still seen B. still sees C. has still seen D. still saw 8. We will start as soon as our team leader________ . A. comes B. will come C. come D. is coming 9. I think Jack ________ the answer. A. has known B. does know C. is knowing D. knows 10. My father ________ George quite well; they were introduced at a party. A. is knowing B. was knowing C.
初中考英语八大时态总结
巧用英语时态表,掌握英语谓语形式 一、英语时态名称的记忆 二、英语时态形式的记忆:(以动词work为例) 可以分两个步骤记忆: 1、一般现在时: work(当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词也要用第三人称单数形式。) 现在进行时: be + working (be随主语人称和数的变化而变化。) 现在完成时: have + worked (have随主语人称和数的变化而变化,worked 是work的过去分词。) 这三种基本时态形式位于时态表的中心位置,是必须首先记住的。其它形式可推导而出。
2、记住了上面三种时态的形式后,可以设想把时间提前至过去,这三种时态的形式就相应地左移一格成为一般过去时:worked (worked是work的过去式);过去进行时was / were + working;过去完成时had + worked (worked是work 的过去分词)。 把时间错后至将来,这三种时态的形式也就相应地右移一格成为 一般将来时: shall / will + work; 将来进行时: shall / will + be working; 将来完成时: shall / will + have worked。(shall仅用于主语是第一人称时,will可用于主语是任何人称时。)当然,根据shall / will 的用法要求,紧随其后的动词或助动词要用原形形式。 简而言之,把这三种现在时态形式左移变成三种过去时态形式,只需把第一个动词变成过去式即可(一般现在时谓语只有一个动词,也可把它看成为第一个动词)。与此类似,过去将来时的变化是在一般将来时的基础上把第一个动词变成过去式。把这三种现在时态形式右移变成三种将来时态形式,只需在前面加一助动词shall / will (紧随其后的动词或助动词用原形形式)即可。 三、英语被动语态形式的记忆(以动词ask为例)
初中英语八种时态(超详细)
动词的时态 在英语中,不同时间里以不同方式发生的动作或存在的状态,要用不同的动词形式来表示,动词的这种不同形式称为动词的时态。 时态从时间上划分,可分为四大类:现在时、过去时、将来时和过去将来时;从行为上,每一类可以分为四种形式:一般式、进行式、完成式和完成进行式。这样英语的动词合起来,总共有十六种时态,初中只需掌握其中的八种时态。 以动词work为例: 一、一般现在时 1、概念:表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态。 2、构成: (1)当动词是be动词时,第一人称单数用am,第二人称或复数名词、代词用are,第三人称单数、单数名词或不可数名词用is。 (2)当动词是实义动词时,一般用动词原形。但如果主语是第三人称单数时,动词必须用第三人称单数形式,其变化规则如下: 助动词do(第三人称单数用does)构成否定句、疑问句及答语,但要注意助动词后原来的谓语动词要恢复原形。如: I like music. 我喜欢音乐。
I don’t like music. 我不喜欢音乐。 Do you like music?你喜欢音乐吗? Yes, I do. / No, I don’t. 是的,我喜欢/不,我不喜欢。 3、用法 (1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态。常和often, usually, every day, sometimes, always , once a week (month , year , etc.) , seldom, ever, never, now and then, from time to time,nowadays等时间状语连用。如:He goes to school by bus every day. 他每天坐公交去学校。 They often play football. 他们经常踢足球。 (2)表示主语的状态、性质、特征、性格、职业、能力等。这里的目的是为了"描述现阶段的动作或状态",其重点"不是强调动作发生的时间、或进行的状态"。如: Miss Gao teaches English. 高小姐教英语。 Do you speak Japanese? 你讲日语吗? He can speak five foreign languages. 他能说五种外语。 My sister is always ready to help others . 我妹妹总是乐于助人。 (3)陈述客观事实、普遍真理。顾名思义,客观的情况是"没有时间概念"的;也"不会在意动作进行的状态"。如: The sun rises in the east. 日出东方。 The earth goes around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。 Ten minus two is eight. 十减二等于八。 Light travels faster than sound. 光的速度比声音的速度快。 The United States lies by the west coast of the Pacific Ocean. 美国位于太平洋西岸。 Time and tide wait for no man. 时不我待。 (4)在时间状语和条件状语从句中,或在谈到计划、规定、安排或时刻表时,主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表示将要发生的动作。如:If I see him, I’ll tell him to give you a call. 如果我见到他,我将告诉他给你回个电话。 We’ll wait until he comes back.我们将等着直到他回来。 The plane takes off at7:30. 飞机在7:30起飞。 Classes begin at 8:00. 8:00开始上课。 【注意】 a.现在进行时有时用来代替一般现在时,表示一个经常性的重复的动作或状态。这时句中常带always, forever以表示说话人的某种感情,如赞叹、厌烦等。如:He is always thinking of others. 他总是为别人考虑。 The boy is always asking for money.这个男孩总是要钱。
中考初中英语语法八大时态总结(附答案)
中考初中英语语法八大时态总结(附答案) 初中英语语法八大时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词) don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有: always、often、 usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。 例如: I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他
初中英语八大时态练习题
初中英语八大时态练习题 一般现在时1)在条件时间等状语从句中用一般现在时表将来 1.If it _____ tomorrow, I will go to school by car. A. rain B. will rain C. rains D. would rain 2.Don’t forget to ask him to write to me. -- I won’t. As soon as he ___, I’ll ask him to write to you. A. will come B. came C. comes D. is coming 2)在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,若表示客观事实真理,从句要用一般现在时。 The teacher told us that light ______ much faster than sound. A. travels B. traveled C. was D. will be 一般过去时 get-- go-- eat -- do--- cut--- say --- take-- swim-- drink-- come-- put—See-- drink--- stop-- regret-- forget-- make-- have-- hit-- 1.Li Ming didn’t understand what American people said,_____? (2004北京) A.couldn’t he B.could he C.didn’t he D.did he 2. Oh, it’s you. I’m sorry I ____know you _____ here. A. don’t; are B. didn’t; are C. didn’t; were D. don’t; were 3.Jane ___a new dress every month when she was in Shanghai. A. buys B. is buying C. bought D. will buy 4.He turned off the light and then _______. A. leaves B. has left C. will leave D. left 一般将来时 1.There___twomeetingstomorrowafternoon. A.are going to be B.are going to have C.is going to be D.will have 2.The twins____to the cinema with their parents tonight. A.will go B.would go C.are go D.went 3.---When____we have the meeting? ---At 8. A.are B.shall C.would D.will 4.--When___you___for London? --Next week. A.will;leaving B.are;leaving C.shall;leave D.have;left 现在完成时考点1:考查基本概念。2:考查时间状语。3:考查与一般过去时的区别。4:考查非延续性动词的用法。5:考查词组have/has been to , have/has gone to与have/has been in/at的区别 1.for+时间段 2.since+时间点(过去) 3.since+一段时间+ago=for+时间段 4.since+从句(常用一般过去时) borrow--- buy-- close-- die-- begin/start---- open--- leave--
(完整版)初中英语语法八大时态总结,推荐文档
初中英语语法八大时态 一.一般现在时 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有:always、often、usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将 来要发生的动作。 例如:I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 二.一般过去时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Did+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+did (否)No,主语+did not 基本结构否定句一般疑问句
(完整版)初中英语八种时态总结归纳
初中英语八种时态总结归纳 一、大凡现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:often,usually,always,sometimes,everyweek(day,year,month...),once a week,on sundays,etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don“t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn“t,同时还原行为动词。 大凡疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二、大凡过去时: 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语:ago,yesterday,the day before yesterday,last week(year,night,month...),in 1989,just now,at the age of 5,one day,long long ago,once upon a time,etc.基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn“t,同时还原行为动词。 大凡疑问句:①was或were放在句首;②用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词。 三、现在进行时: 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 时间状语:now,at this time,these days,etc. 基本结构:am/is/are+doing
否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing 大凡疑问句:把be动词放在句首 四、过去进行时: 概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。 时间状语:at this time yesterday,at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是大凡过去时的时间状语等。 基本结构:was/were+doing 否定形式:was/were+not+doing 大凡疑问句:把was或were放在句首 五、现在完成时: 概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。 时间状语:recently,lately,since...,for...,in the past few years,etc. 基本结构:have/has+done 否定形式:have/has+not+done 大凡疑问句:have/has放于句首 六、过去完成时: 概念:以过去某一时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。 时间状语:before,by the end of last year(term,month...),etc. 基本结构:had+done
初中英语八大基本时态详解
初中英语八大基本时态详解 时态无疑是初中英语最重要的语法内容,学好时态基本就拿下了语法的半壁江山。今天老师加油总结的八种时态是大家在初中阶段必学必考的,期中复习时一定要加倍重视哦! 英语八大时态表: 1 一般现在时 标志:动词原形 1. 表示经常性或习惯性动作,常与表频度的时间状语连用: She often speaks English. I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2. 表示现在的状态、特征、职业、能力、感觉等: He seems to feel a bit down today. He works as a driver.
3. 表示真理、客观存在、科学事实或用于格言警句中: Shanghai lies in the east of China. Columbus proved that the earth is round. Where there is a will, there is a way. 4. 表示现在瞬间的动作: Here comes the bus! 5. 表示将来1) 表按规定、计划、安排将要发生的动作(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的趋向动词),可以与表示未来的时间状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通状况。如: The next train leaves at 3 o’clock this afternoon. How often does the shuttle bus run? 2) 在时间和条件状语从句中常使用一般现在时表示将来发生的事情:When Bill comes (不用will come), ask him to wait for me. I shall go there tomorrow unless I’m too busy. 2 一般过去时标志:动词过去式
初中英语八大时态总结
英语八大时态总结 一、一般现在时: 基本结构:①动词原形②主语三单:动词原形 +s/es 三种常考基本用法:1、经常性和习惯性动作 Eg. I always get up early. 2、客观事实和普遍真理 Eg. The earth goes around the sun. 3、在时间状语从句及条件状语从句中,一般现 在表将来 If it doesn't rain, we will have a picnic. 其中,第三种用法就是学生们熟知的"主将从现"的原则,这一点大家务必掌握,此知识点会在初二,同时也是中考重要考点。 常见时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every day, on Sundays, at weekends, once a week, twice a month, etc. 二、一般过去时: 基本结构:动词的过去式
基本用法: 1、过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态 Eg. I got up late yesterday. 2、过去习惯性、经常性的动作 Eg. When I was in the countryside, I often swam in the river. 常见时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week (year, night, month…), in 1986, just now, at the age of 10, at that time, once upon a time, etc. 三、一般将来时: 基本结构:①am/is/are/going to + do;②will/shall + do. 基本用法: am/is/are/going to + do 1、(人)计划打算做某事 Eg. I'm going to go shopping with my mom tomorrow. 2、(事)即将发生 Eg. Look at the clouds, it's going to rain.
初中英语语法八大时态总结
初中英语语法八大时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有:always、often、usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。 例如:I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Did+主语+动词原形+其他
初中英语八种时态整理
一、一般现在时 (一)定义 表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或存在的状态,还表示主语具备的性格和能力及客观真理。 例:I get up at 6:30 in the morning . She is at home . (二)构成 主要用动词原形表示,当主语是第三人称单数时,在动词词尾加s/es。 (三)句型 1、肯定句:主语+谓语+其他。 She reads English everyday . 2、否定句:主语+don’t/doesn’t+谓语+其他。 He doesn’t get up at 6:30 in the morning . 3、一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+V原+其他? Do you like English ? Yes ,I do ./No, I don’t . 4、特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+do/does+主语+V原+其他? What time do you get up every morning ? (四)用法 1、表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或存在的状态,带与表示频率的时间状语如:often , sometimes, usually, always, everyday year, month...), once/twice a week (month, year, etc.), seldom, on Sunday等连用。 I leave home for school at seven every morning . 2、表示客观真理,科学事实、格言警句。 The earth goes around the sun .地球绕着太阳转。 Ten minus two is eight.十减二等于八。 3、根据英文语法规定,当主句的谓语动词是一般将来时,那么时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。
初中英语八种时态归纳复习 详解
Ⅰ. 初中英语八种时态归纳复习 英语时态是一种表示动作或状态发生的时间的动词形式,而汉语动词没有时态形式。 一、一般现在时: 1. 概念:表示经常性的习惯动作,现在的特征或状态,和普遍真理的时候,谓语动词用一般现在时。 2. 构成:一般现在时主要由动词原形构成,但第三人称单数后要加词尾-s , 另外 动词be 和 have 有特殊的人称变化形式。 列表如下: 3.在词尾加-s 时要注意: 4.词尾-s 的读音, 与名词复数词尾-s 读音一样: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 例句:I go to school every day. 7. 否定形式:①动词be: am/is/are+not;②行为动词:在其前加don't, 如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't ,助动词后动词一概用原形。 例句:Jerry is not a student. Sally doesn ’t like animals. 8. 一般疑问句:①把be 动词放于句首;②用助动词do 提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does ,同时,还原行为动词。 例句: Is Jerry a student? Does sally like animals?
二、一般过去时 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态,现在已经不再继续;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.构成:一般过去时由动词的过去式表示, 1) 动词be有 was, were 两个过去式,was 用于第一、第三人称, were 用于第二人称和第一、二、三人称的复数形式。 动词表。 读音规则: 3. 与一般过去式经常搭配的时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 4.否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加助动词didn't,助动词后加动词原形。 5.一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,助动词后用动词原形。
初中英语八大时态总结
初中英语八大时态总结 一、一般现在时 具体情况(主要用于下面几情况) 1) 描述当前时间内经常出现、反复发生的动作或存在的状态。 在这种情景中,句子常带有表示频率的时间状语:always , everyday , often , once a week (month , year , etc.) , sometimes , seldom , usually等等,以表示句中的动作或状态是习惯性的、经常性的。例如: They raise ducks as a sideline .他们以养鸭为副业。 It seldom rains here .这儿很少下雨。 2)仅为了描述状态、性质、特征、能力等等。 这里的目的是为了"描述现阶段的动作或状态",其重点"不是强调动作发生的时间、或进行的状态"。例如: He can speak five foreign languages .他能说五种外语。 That is a beautiful city .那是座美丽的城市。 3) 陈述客观事实、客观真理。 顾名思义,客观的情况是"没有时间概念"的;也"不会在意动作进行的状态"。例如: The sun rises in the east .日出东方。 4) 根据英文语法规定,当主句的谓语动词是一般将来时,那么时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。例如: I'll tell him the news when he comes back. 他回来时,我将告诉他这个消息。 *【用于一般现在时的副词,除了上面提到的一些表示频率的以外,常见的还有:now, today , nowadays等等】 二、一般过去时 具体情况(主要用于下面几情况) 1.主要是用来描述在过去某个时候发生的动作或存在的状态。它也可以用来表示在过去某段时间里经常发生的习惯性动作。 例:I was very thin in my childhood. 2.一般过去时由谓语动词的过去式表示,也就是说动词词末要加-ed(除不规则动词外)。常和一般过去时连用的过去时间状语有:last night (week ,month , year , century , etc.) , yesterday , the day before yesterday , yesterday morning ( afternoon , evening ) , in 1999 , two hours ago ( one week ago , tree years ago , …)等等。 例:Did you meet yesterday? He left just now. 3.使用一般过去时,在某种意义上说就是要强调动作或状态发生或存在于过去的某个时候。"过去"的时间概念有两层意思:一是指"现在某个时间"以前的时间;二是指"说话、写文章的那个时间点"以前的时间 He got his driving license last month. 他上个月拿到了驾照。
初中英语八种时态讲解
一般现在时 一.要点提示 一般现在时主要用动词原形表示,但是当主语是第三人称单数或者单数名词时,动词的形式要发生变化,其变化规律是:1. 一般动词后加-s, 如:wears, reads, plays, likes, 2.以s, x, ch, sh结尾,后加-es, 如:watches, brushes, 3.以辅音字母+o结尾,一般加-es, 如:goes, does, 4.辅音字母+y 结尾,变y为i,再加-es, 如:worries, carries. Be动词一般现在时的特殊形态是:am, is, are。Have的第三人称单数是has。 二.用法指南 一般现在时的用法 1) 表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。 时间状语:always总是, often经常,usually通常, seldom很少, never从不, sometimes有时(以上频度副词位置放于行为动词之前), every…每…(放于句首或者句末均可) I leave home for school at 7 every morning. It often snows here. 2) 表示现在的状态、特征、能力、性格等。 I know him very well. Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well. 3) 表示格言或警句中。 Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 Failure is the mother of success. 失败是成功之母。 4) 表示客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。 The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 三. 一般现在时态的肯定形式,否定形式及疑问形式 肯定形式是用动词原形,be动词用am, is, are, 注:动词的第三人称单数形式的变化; 否定形式是在be动词后加否定词not(缩写成isn’t, aren’t, am与not不能缩写),或者添加助动词do/does加not再加动词原形(缩写成don’t/doesn’t). 疑问形式是把be动词或助动词do/does提置句首, 动词还原,句末问号,人称上第一人称变第二人称,第二人称变第一人称,第三人称不变。 一般将来时 一.要点提示 一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或反复发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用(tomorrow, tomorrow morning, next week (year, term…), in (two days…), soon, the day after tommorrow等。 二.用法指南 一般将来时的结构及用法
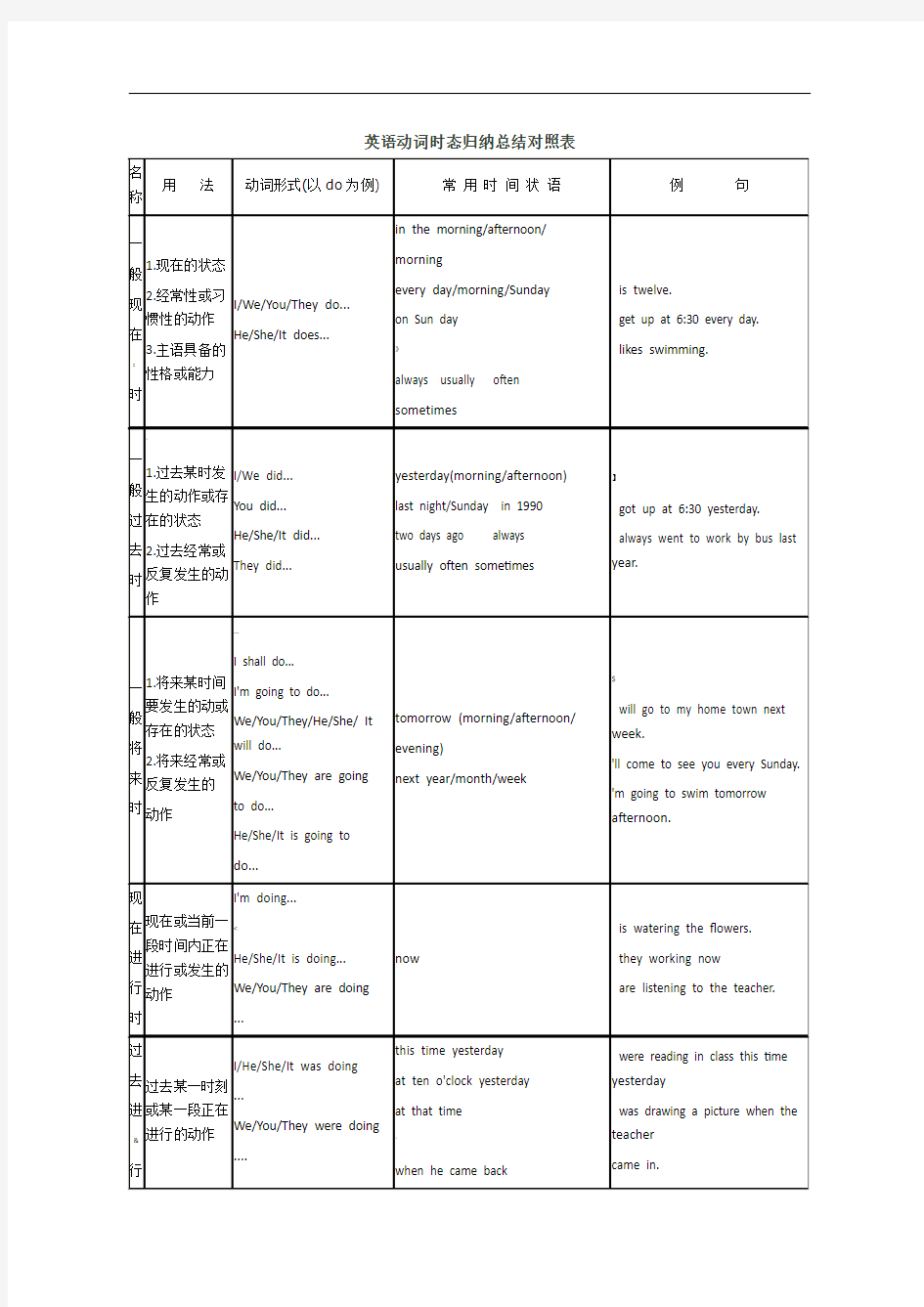
(完整版)英语动词时态归纳总结对照表
英语动词时态归纳总结对照表
英语时态专项练习 1、一般现在时。 通常用“usually, often, every day, sometimes”。 一般现在时基本用法介绍 一、一般现在时的功能 1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。 2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。 3.表示客观现实。如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。 二、一般现在时的构成: 肯定句: 1).主语+系动词 be(is, am, are )+名词(形容词,介词短语) 2) .其他主语+动词原形+其它 第三人称单数+动词-s+其它 如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。 We study English.我们学习英语。Mary likes Chinese.玛丽喜欢汉语。
三、一般现在时的变化 否定句:1)主语+ be (is,am,are)+ not +其它。如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。 2)其他主语+do not(don’t)动词原形+其它I don't like bread 第三人称单数+does not(doesn’t)动词原形+其它He doesn't often play. 一般疑问句:1)Be(Is,Are) +主语+其它?如:-Are you a student? -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not. 2)Do其他主语+动词原形+其它? Does+第三人称单数+动词原形+其它+? 注意:遇I/we—you, my—your, some—any. Does she go to work by bike? - Yes, she does. / No, she doesn't. Do you often play football?- Yes, I do. / No, I don't. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。如:Where is my bike? How does your father go to work? 2、现在进行时。 通常用“now/look/listen”. 1.现在进行时表示现在正在进行或发生的动作,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。 2.现在进行时的结构:. 肯定句:主语+be(is,am,are ) +动词现在分词-ing eg: I am(not) doing my homework. You/We/They are(not) reading. He/She/It is(not) eating. 否定句:主语+be(is,am,are )+not + 动词现在分词-ing 一般疑问句:Is(Are)+主语+动词现在分词-ing? 特殊疑问:疑问词+ be + 主语 + 动词ing? 3.动词加ing的变化规则 1)一般情况下,直接加ing,如:cook-cooking 2)以不发音的e结尾,去e加ing,如:make-making, taste-tasting 3)如果末尾是一个元音字母和一个辅音字母,双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing, 如:run-running, stop-stopping,swim—swimming 3、一般过去时态 一般过去时通常用“a moment ago, just now, yesterday, last…”等。 1.一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。一般过去时也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作感谢。 2.Be动词在一般过去时中的变化: ⑴am 和is在一般过去时中变为was。(was not=wasn’t)
初中英语8种时态的例句各10个
初中英语8种时态的例句各10个 每个时态我只给了你两个例题,相信你自己可以继续的。顺便我也把各个时态的用法给你说下。 1.一般现在时现在的事或者既成事实 1) He goes to school at seven o’clock everyday. 2) The sun rises in the east. 2.一般过去时过去的事 1) he was born in 1989. 2) I used to play football when I was young. 3.一般将来时表示打算啊,现在的推测之类的 1) We will visit the science museum next week. 2) We are going to discuss the problem tomorrow. 4.现在进行时现在正在发生的事或动作 1) The boy is playing video games. 2) His father is writing a novel these days. 5.现在完成时过去发生并持续到现在或对现在有影响 1) Great changes have taken place in China since 1980. 2) I have finished my task. 6.过去进行时过去正在发生的事,一般有一个明确的过去的时间点 1) He was reading an interesting book this time yesterday. 2) When I came in, they were having supper. 7.过去完成时过去的过去发生的事对过去有影响 1) He was reading an interesting book this time yesterday. 2) When I came in, they were having supper.
