英语词汇学作业答案
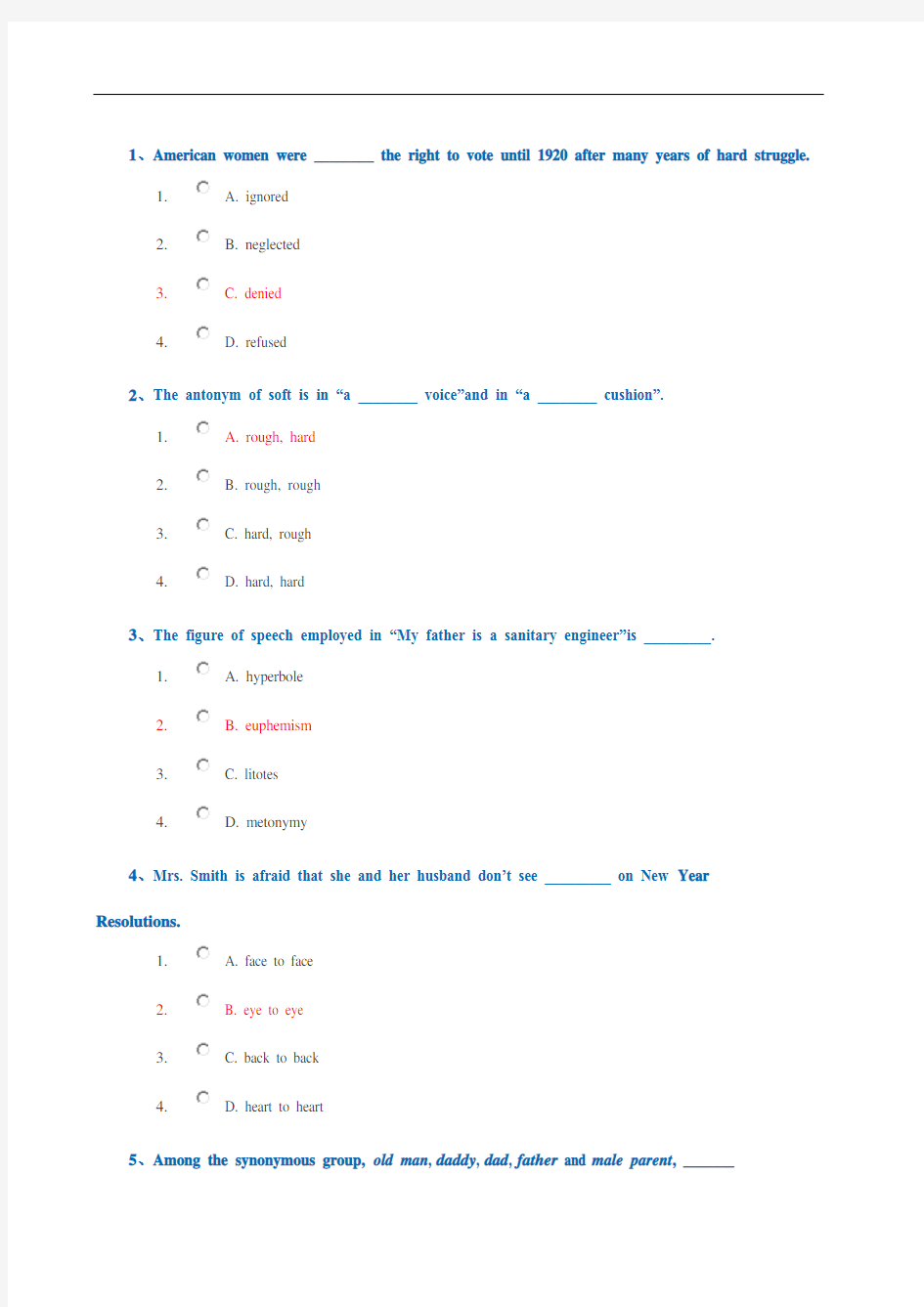

1、American women were ________ the right to vote until 1920 after many years of hard struggle.
1. A. ignored
2. B. neglected
3. C. denied
4. D. refused
2、The antonym of soft is in “a ________ voice”and in “a ________ cushion”.
1. A. rough, hard
2. B. rough, rough
3. C. hard, rough
4. D. hard, hard
3、The figure of speech employed in “My father is a sanitary engineer”is _________.
1. A. hyperbole
2. B. euphemism
3. C. litotes
4. D. metonymy
4、Mrs. Smith is afraid that she and her husband don’t see _________ on New Year Resolutions.
1. A. face to face
2. B. eye to eye
3. C. back to back
4. D. heart to heart
5、Among the synonymous group, old man, daddy, dad, father and male parent, _______
would most probably used by a lawyer in the court.
1. A. dad
2. B. old man
3. C. father
4. D. male parent
6、Our teacher is now not with us. Aha! When the ________ is away, the ________ will play.
1. A. tiger, monkeys
2. B. cat, mice
3. C. hawk, birds
4. D. old, young
7、I could give an opinion ________, but I would rather think about it.
1. A. off the sleeve
2. B. off the cuffs
3. C. off the cuff
4. D. off the sleeves
8、Choked traffic has been a(n) ________ to urban transportation system.
1. A. archenemy
2. B. primary enemy
3. C. main enemy
4. D. major enemy
9、Which one of the following abbreviations means “and so on”? ________.
1. A. i.e.
2. B. e.g.
3. C. etc.
4. D. viz.
10、“ex-”in ex-husband reads ________ and means _______.
1. A. /iks/, “out”
2. B. /iks/, “former”
3. C. /eks/, “out”
4. D. /eks/, “former”
11、Our work calls for mutual support. We shouldn’t ________ each other's efforts.
1. A. activate
2. B. interact
3. C. counteract
4. D. active
12、I am not sure whether I should fly to London or take the train. I’m really caught between two ________.
1. A. choices
2. B. options
3. C. alternatives
4. D. stools
13、Hey! Don’t sit there and count your ________. You need to work really hard.
1. A. chicken
2. B. chickens
3. C. duck
4. D. ducks
14、The figure of speech employed in “The past is a bucket of ashes”is _________.
1. A. metaphor
2. B. euphemism
3. C. irony
4. D. litotes
15、When the crowd saw the prize-fighter stretched out on the canvas, shouts and cheers ________ from it.
1. A. broke up
2. B. b roke forth
3. C. broke through
4. D. break upon
16、persona non grata means ________.
1. A. someone who is not acceptable or welcome
2. B. someone who is slim
3. C. someone who does not take the leading role
4. D. someone who has graduated with no degree
17、The figure of speech employed in “I haven’t seen you for ages”is ________.
1. A. metaphor
2. B. hyperbole
3. C. irony
4. D. metonymy
18、Communication is the process of ________ a message from a source to an audience via a channel.
1. A. transmitting
2. B. submitting
3. C. transforming
4. D. switching
19、Johnson had already ________ in an intimate book.
1. A. thrown out the beans
2. B. thrown out his beans
3. C. spilled the beans
4. D. spilled his beans
20、Free medical treatment in this country covers sickness of mind as well as ________ sicknesses.
1. A. normal
2. B. ordinary
3. C. average
4. D. regular
21、For an English word, the shift of stress may indicate a change of part of speech; export is a perfect example
T
22、dies, died, dying, dead, etc. are different word forms of the same lexeme DIE.
F
23、The figurative use of words is an important cause for words to develop new meanings
T
24、An idiom is semantically integrated, thus an idiom cannot be understood even if you know all its components
F
25、In the sentence, “More hands are needed on the farm”, metonymy is employed
T
26、air-conditioner is a word derived from adding -er to air-condition
F
27、house is the superordinate of wall, roof, floor, etc.
F
28、According to cognitive semantics, our mind can be explored via the study of linguistic meanings
T
29、Word equivalents are a necessary part for lexicology and all phrases fall within the range of lexicology
T
30、Compared with horse, gee-gee is stylistically more formal.
F
31、In standard AmE, the letter r is pronounced wherever it appears as in bar, board, park, etc
T
32、The most important role for derivation is word class transformation.
T
33、Lexical semantics is not only a subset of lexicology, but also a subset of semantics.
T
34、“sense”, as a term in semantics, denotes the relationship between words within language.
T
36、Celtic is a branch of the Indo-European Language Family.
F
37、de-urbanization is a word composed of 5 morphemes, all of which are bound ones
F
38、Human languages have originated from human’s natural cries for pain, anger and joy, etc
F
39、The word nice has gone through a semantic change called “generalization
F
40、Answering the question “Will you marry me?”with “Yes, I will”, the speaker is using
substitution
F
35、Absolute synonyms are not easy to found in any language
41、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
lexeme
Lexeme is an abstract unit of meaning with all its grammatical inflectional endings wiped out. Most of the words listed in the dictionary are lexemes
42、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
grammar
Grammar is a set of rules or regularities applied to form complex expressions via simpler ones.
43、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
polysemy
Polysemy refers to semantic phenomenon where a single word or phrase has several meanings.
44、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
generalization
Generalization refers to the extension of the word range, or the widening of the semantic scope.
45、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
context of situation
Context of situation refers to the immediate environment of the text.
46、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
function word
A function word is a word that contributes to the major structure of a sentence. It belongs to the close-class
elements of the vocabulary of a given language in the sense that their numbers is small and fixed.
47、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
clipping
Clippings are forms abbreviated from larger words but share a common function with words they are clipped
from.
48、Define the following term and give examples when needed.
affix
An affix is the morpheme added to a root and contributes to the meaning of a word as a whole.For
example,"dis-" in "dishonest" is an affix.
49、Answer the following question with appropriate illustration.
What are the characteristics of native element in English vocabulary?
The following are the 7 general characteristics of native (Aglo-Saxon) elements:
1. All-national character. Native element is shared by all the native speakers, regardless of whether he is a king under the crown, a fisherman on the sea or a vagrant on the street.
2. Monosyllabicity. Most of the native element in Modem English has only one syllable. e.g. sun, cow, go, run, etc.
3. Productivity. Most of the native elements are monosyllabic or root words and are semantically basic. Thus, they are productive in the sense that clusters of words are derived or compounded from them. For example, the word hand, has brought such derivatives and compounds as handy, handle, handkerchief, handiwork, handicraft, handful, handbook, handbarrow, handcuff, etc.
4. Collocational extensiveness. The native element has a wide range of collocation. Many native words enter quite a number of expressions, idioms, phrases and proverbial sayings. For example, the word heel is found in the following units: Achilles’ heel (a vulnerable point), heel over head or head over heels (upside down), cool one’s heels (be kept waiting), show a clean pair of heels, take to one’s heels (run away), turn on one’s heels (turn sharply round), etc.
5. Semantic polysemy. The native words are highly polysemic because they have gone
through semantic changes due to their frequent use in daily life. For example, the verb tell conveys the following meanings: make known, express, explain, utter, confide in order, distinguish, count, reveal, scold, etc.
6. High-frequency value. The native element forms the bulk of the most frequent elements used in any style of speech. Every writer uses considerably more native words than borrowed ones. Corpus investigations show that about 90 percent of the words in Shakespeare’s works and 94 percent of words in King James Bible are native words.
7. Stylistic neutrality. Most native words are stylistically neutral and are equally fit to be used in a lecture, a poem, or when speaking to a child. This can be observed by a simple comparison, for example begin (neutral) vs. commence (formal).
50、Answer the following question with appropriate illustration.
What is the context and its role in shaping word meaning?
Word meaning is sensitive to context, speakers and hearers usually rely heavily on context in constructing and interpreting word meaning. Contextual information can exert two major effects. More specifically, it influences the interpretation of a word, on the one hand, and speeds up lexical access, on the other. In most cases, the contextual aspect plays a crucial role in recognizing the specific meaning of a word.
1. Context has the crucial role to resolve ambiguity.
e.g. Please give me a hamburger, a cup of cola, and some chips.
[a small piece of wood, the potato chip, or electronic circuit]
I saw a tattoo of dragon on the back of that naked young guy,
The big John has been accustomed to the constant tattoos,
Hearing the sound of tattoo, soldiers returned to the quarter as quickly as possible.
[tattoo1 a signal sounded on a drum or bugle to summon soldiers or sailors to their quarters at night;
tattoo2 a display of military exercises offered as evening entertainment;
tattoo3 a design that is drawn on someone’s skin using needles to make little holes and filling them with colored dye.]
2. Context gives rise to the joking effect of puns.
e.g. A: Why can’t a bicycle stand on its own?
B: Because it is two-tired.
[a thick piece of rubber of vehicles, to having used a lot of energy and wanting a rest]
3. Context is beneficial to the understanding of deixis.
There are three major kinds of deixis, that is, person deixis (I, you, we), spatial deixis (here, there), and temporal deixis (now, yesterday).
e.g. I didn’t see her yesterday. It only with the contextual information can the reader know whom the personal deixis her refers to. And the same is the case with the deixises in the following example:
Only contextual information can provides clues to the understanding of I, her and yesterday.
51、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
His behavior means that you should stay a bit longer
他的行为表明,你得再呆一段时间。
52、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
Brave it out, no matter how difficult it is.
无论那有多困难,你都应勇敢面对。
53、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
Let’s cash in on the fine weather and go for an excursion.
54、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
Be polite, but don’t kowtow to him.
对他,你应以礼相待,但也没必要卑躬屈膝。
55、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
He that sups with the devil must have a long spoon.
与恶人交往,必须小心谨慎。
56、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
You don’t have to go to Oxbridge to receive a good university education
接受良好的大学教育,你不需要非去牛津剑桥不可。
57、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part. Spare the rod and spoil the child.
丢了棍子,坏了孩子。
58、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
Nothing venture, nothing have.
不入虎穴焉得虎子
59、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
I don’t like him. He speaks with too many “ifs”, “ands”and “buts”.
我不喜欢他。说话时满口“假设”、“况且”和“但是”。
60、Translate the following into Chinese and pay special attention to the bold typed part.
A politician thinks of the next election. A statesman, of the next generation.
政客们思考的是下一届竞选,政治家思考的是下一代人民。
英语词汇学教程参考题答案(杨信彰)
《英语词汇学教程》参考答案 Chapter 1 1. The three definitions agree that lexicology studies words. Yet, they have different focuses. Definition 1 focuses on the meaning and uses of words, while definition 2 on the overall structure and history. Definition 3 regards lexicology as a branch of linguistics and focuses on the semantic structure of the lexicon. It is interesting to note that the three definitions use different names for the object of study. For Definition 1, it is words, for Definition 2 the vocabulary of a language, and for Definition 3 the lexicon. 2. (1) They can go into the room, and if they like, shut the door. (2) You boys are required to give in your homework before 10 o’clock. (3) I watch the football match happily and find it very interesting. 3. (1) W hen it follows ‘-t’ and ‘-d’, it is pronounced as [id]; (2) When it follows voiceless consonants, it is pronounced as [t]; (3) When it follows voiced consonants and vowels, it is pronounced as [d]. 4. (1) They are words that can be included in a semantic field of “tree”. (2) They represent the forms of the verb “fly” and have a common meaning. (3) They belong to a lexical field of “telephone communication”. (4) They are synonyms, related to human visual perception. Specifically, they denote various kinds of “looking”. 5. (a) 'blackboard: a board with a dark smooth surface, used in schools for writing with chalk (the primary stress in on black); 'blackbird: a particular kind of bird, which may not necessarily be black in color (the primary stress in on black); 'greyhound: a slender, swift dog with keen sight (the primary stress in on black); 'White House: the residence of the US President in Washington (the primary stress in on black). (b) 'black 'board: any board which is black in color (both words receive primary stress); 'black 'bird: any bird which is black in color (both words receive primary stress); 'grey 'hound: any hound that is grey in color (both words receive primary stress); 'white 'house: any house that is painted white (both words receive primary stress). 6. There are 44 orthographic words, i.e. sequences of letters bounded by space. There are 24 open class words and 20 closed class words. 7. (a) The ‘bull’ is literal, referring to a male bovine animal. (b) ‘Take the bull by the horn’is an idiom, meaning (having the courage to) deal with someone or something directly. (c) ‘Like a bull in a china shop’is an idiom, meaning doing something with too much enthusiasm or too quickly or carelessly in a way that may damage things or upset someone.
英语词汇学考试重点整理
Explain the following terms 一1) free morpheme/ A free morpheme is one that can be uttered发出,表达alone with meaning. It can exist on its own without a bound morpheme. In the traditional sense, a free morpheme is a word. 例如hand ,eat, get 2) bound form/never used as sentences. – ess in countess, lioness and duchess –ish in boyish, childish and greenish –s in hats, books and cups 3) function words/ function words are often short words, they do not have much lexical meaning and some of them have no lexical meaning of their own; They are often short words such as determiners限定词, conjunctions连词, prepositions介词, auxiliaries辅助物, and so forth. 如to, the , of , by 4) content words实词/ They are used to name objects, qualities, actions, processes or states, and have independent lexical meaning. They are the nouns, main verbs, adjectives形容词and adverbs副词of a language. 二1) syntheti c综合的language / inflectional grammatical markers, French, German and Russian. 2) analytic language/word order, prepositions or auxiliary verbs , English and Chinese 3) Indo-European family of languages/ Europe and parts of Southern Asia Eight groups 三1) morphemes /The morpheme is the smallest meaningful linguistic unit of language, not divisible可分的or analyzable into smaller forms. 2) allomorphs/variants变体of the same morphem如im-, ir-, il- : allomorphs of the morpheme in- 3) root / is the basic unchangeable part of a word, and it conveys the main lexical meaning of the word. work able, work er, work ed, and work ing 4) stem /A stem is of concern only when dealing with inflectional morphology. Inflectional (but not derivational) affixes are added to it. It is the part of word-form which remains when all inflectional affixes have been removed. 如undesirables, undesirable; desired, desire 5) base / A base is any form to which affixes of any kind can be added. Desirable, desire - base and root, not stem; undesirable, desirable-base, not root and stem 6) inflectional affixes/A inflectional affix serves to express such meanings as plurality复数, tense, and the comparative比较的or superlative 最高的degree. 如-s, -ed, -er, -est 7) derivational affixes / When they are added to another morpheme, they derive a new word. re+write, mini+car, super+market, modern+ize, work+er 8) compounding 复合法/Compounding is a word-formation process consisting of combining two or more bases to form a compound word 9) derivation 派生法/Derivation or affixation is generally defined as a word-formation process by which new words are created by adding a prefix or a suffix or both to the base 10) conversion 转化法/Conversion is a word-formation process in which a word of a certain word-class is shifted into a word of another word-class without the addition of an affix. 11) initialism/It is a type of shortening, using the first letters of words to form a proper name, a technical term, or a phrase. 12) acronym首字母缩略词/Acronyms are words formed from the initial letters of the name of an organization or a scientific term, etc. Acronyms differ from initialisms in that they are pronounced as words rather than as sequences of letters. 13) blending拼缀/Blending is a process of word-formation in which a new word is formed by
(完整版)英语词汇学英语词汇学习题3及答案
试题三 第一部分选择题 I. Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers. Choose the one that would best complete the statement and put the letter in the bracket.(30%) 1.According to the degree of similarity, homonyms can be classified into ( ) A. perfect homonyms B. homonyms C. homophones D. all the above 2.Transfer as a mode of semantic change can be illustrated by the example ( ) A. ad for “advertisement” B. dish for “food" C. fond for “affectionate” D. an editorial for “an editorial article" 3.It is a general belief that the meaning does not exist in the word itself, but it rather spreads over ( ) A. the reader’s interpretation B. the neighbouring words C. the writer's intention D. the etymology of the word 4.Which of the following is a prefix of time and order? A. extra- B. pro- C. re- D. semi- 5.Which of the following dictionaries is not a specialized dictionary? A. The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology B. Chamber's Encyclopedic English Dictionary C. Longmont Dictionary of Phrasal Verbs D. Webster's New Dictionary of Synonyms 6.Which of the following statements is Not true? A. Reference is the relationship between language and the world. B. The relationship between a word and its referent is arbitrary. C. Concept is universal to all men alike. D. Sense denotes the relationships outside the language. 7.The words which occur before or after a word and may affect its meaning form ( ) A. physical context B. grammatical context C. lexical context D. linguistic context 8."Smith is an architect. He designed World Trade Center. "The clue provided in the context is ( ) A. definition B. explanation C. example D. hyponym 9.The term "vocabulary" is used in different ways because of all the following reasons EXCEPT that ( ) A. it can refer to the common core of a language B. it can refer to the total number of the words in a language C. it can represent all the words used in a certain historical period D. it can stand for words in given dialect or field 10.The idiom "a dark horse" is a ( ) A. simile B. metaphor
英语词汇学教程(练习答案)(1)解析
《英语词汇学教程》(2004 年版)练习答案 Chapter 1 7. Choose the standard meaning from the list on the right to match each of the slang words on the left. a. tart: loose woman b. bloke: fellow c. gat: pistol d. swell: great e. chicken: coward f. blue: fight g. smoky: police h. full: drunk i. dame: woman j. beaver: girl 8. Give the modern equivalents for the following archaic words. haply = perhaps albeit = although methinks = it seems to me eke = also sooth = truth morn = morning troth = pledge ere = before quoth = said hallowed = holy billow = wave / the sea bade = bid 12. Categorize the following borrowed words into denizens, aliens, translation loans, and semantic loans. Denizens: kettle, die, wall, skirt, husband Aliens: confrere, pro patria, Wunderkind, mikado, parvenu Translation loans: chopstick, typhoon, black humour, long time no see Semantic loans: dream Chapter 2 1. Why should students of English lexicology study the Indo-European Language Family? The Indo-European Language Family is one of the most important language families in the world. It is made up of most of the languages of Europe, the Near East and India. English belongs to this family and the other members of the Indo-European have more or less influence on English vocabulary. Knowledge of the Indo-European Language Family will help us understand English words better and use them more appropriately. 2. Make a tree diagram to show the family relations of the modern languages given below.
(完整word版)英语词汇学复习大纲整理
1 B a s i c C o n c e p t s 基本概念 1.1 the definition of a word ( alone in a sentence. A word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function.) 1.2 sound and meaning :symbolic connection is almost always arbitrary and conventional . A dog is called a dog not because the sound and the three letters that make up the word just automatically suggest the animal in question. 1.3 sound and form : 1.4 vocabulary 1.5 classification of words 词汇分类 basic word stock 基本词汇 nonbasic vocabulary 非基本词汇 by use frequency 按使用频率分: basic word stock and nonbasic vocabulary 基本词汇和非基本词汇 by notion 按概念分: content words and functional words 实义词和功能词 by origin 按起源分: native words and borrowed words 本地词和外来词 all national character 全民性 stability 稳定性 productivity 多产性 polysemy 一词多义 collocability 搭配性 terminology 术语 jargon 行话 slang 俚语 argon 黑话 dialectal words 方言词 archaism 古语词 neologism 新词 neutral in style 文体上中性 frequent in use 使用频繁 native words 本地词 borrowed words 外来词 denizens 同化词 aliens 异形词 translation-loans 译借词 1. No enough letters: alphabet from Latin 2. Pronunciation changed more rapidly 3. Early scribes: change spelling for easier recognition 4. Borrowing: different rules of pronunciation and spelling obvious characteristics 明显的特点 (Functional words do not have notions of their own and their main function is to express the relation between notions, words, etc.)
(完整版)全国英语词汇学(00832)高等教育自学考试试题与答案
全国高等教育自学考试 英语词汇学试题 课程代码:00832 Ⅰ.Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers. Choose the one that best completes the statement and put the letter in the bracket.(30%)1.According to semanticists, a word is a unit of ______.() A.meaning B.Sound C.combination of sounds D.Group 2.The pronunciation has changed ______ spelling over the years.() A.more slowly than B.As quickly as C.more rapidly than D.Not so quickly as 3.Words may fall into the basic word stock and nonbasic vocabulary by ______.()A.use frequency B.notion C.origin D.sound 4.Rapid growth of science and technology breeds such new words as the following EXCEPT______.() A.green revolution B.fast food C.moon walk D.space shuttle 5.Semantic change means an old form which takes on a new ______ to meet the new need. ()A.form B.meaning C.look D.pronunciation 6.Reviving archaic words also contribute to the growth of English vocabulary. For instance, in American English “fall” means ______ in British English.() A.four B.fell C.for D.autumn 7.The plural morpheme “-s” is realized by /s/after the following sounds EXCEPT ______. ()A./t/ B./g/ C./p/ D./k/ 英语词汇学试卷第 1 页共9 页
大学英语词汇学教程参考答案
《英语词汇学教程》参考答案 (注:参考答案仅供参考。有些题目的答案并非是唯一的) Chapter 1 1. The three definitions agree that lexicology studies words. Yet, they have different focuses. Definition 1 focuses on the meaning and uses of words, while definition 2 on the overall structure and history. Definition 3 regards lexicology as a branch of linguistics and focuses on the semantic structure of the lexicon. It is interesting to note that the three definitions use different names for the object of study. For Definition 1, it is words, for Definition 2 the vocabulary of a language, and for Definition 3 the lexicon. 2. (1) They can go into the room, and if they like, shut the door. (2) You boys are required to give in your homework before 10 o’clock. (3) I watch the football match happily and find it very interesting. 3. (1) when it follows ‘-t’ and ‘-d’, it is pronounced as [id]; (2) when it follows voiceless consonants, it is pronounced as [t]; (3) when it follows voiced consonants and vowels, it is pronounced as [d]. 4. (1)They are words that can be included in a semantic field of “tree”.
大学英语词汇学期末考试 重点复习资料整理 权威版 后附试题
2012词汇学复习资料 The development of the English Vocabulary 1.Indo-European Language Family The Indo-European Language Family is considered as one of the most important language families. It includes most languages of Europe, the Near East, and India. Those languages, which are believed to have originated from this language family and developed alone different lines, show various degrees of similarity to one another. They fall into eight principal groups, which can be grouped into an Eastern Set东部诸语族: Balto-Slavic波罗的-斯拉夫语, Indo-Iranian印度伊朗语族, Armenian 亚美尼亚语族and Albanian阿尔巴尼亚语族; a Western Set: 西部诸语族Celtic凯尔特语族, Italic 意大利语族, Hellenic希腊语族, Germanic日尔曼语族. All the languages in both sets shed some influence on English to a greater or lesser extent because each has lent words into the English vocabulary. Prussian普鲁士语 Lithuanian立陶宛语 Polish波兰语 Balto-Slavic波罗的-斯拉夫语Czech捷克斯洛伐克语 Bulgarian保加利亚语 Slovenian斯洛文尼亚语 Russian Albanian阿尔巴尼亚 Persian波斯语 Hindi北印度语 Indo-Iranian印度伊朗语系Bengali孟加拉语 Romany,吉卜赛语 Armenian亚美尼亚语 Portuguese Spanish Italic意大利语族Italian Roumanian罗马尼亚语 French Indo-European Language Family Irish Celtic凯尔特语Breton Scottish Norwegian挪威语 Icelandic,冰岛语 Danish丹麦语 Germanic Swedish瑞典语 日尔曼语言English Dutch Flemish German Hellenic,古希腊语- Greek
(完整版)英语词汇学试题
英语词汇学试题 Introduction and Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Words and Vocabula ry(练习1) I.Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers. Choose the one that would best complete the statement. 1.Morphology is the branch of grammar which studies the structure or forms of words, primarily through the use of _________construct. A. word B. form C. morpheme D. root 2.________ is traditionally used for the study of the origins and history of the form and meaning of words. A. Semantics B. Linguistics C. Etymology D. Stylistics 3.Modern English is derived from the language of early ______ tribes. A. Greek B. Roman C. Italian D. Germanic 4. Semantics is the study of meaning of different _________ levels: lexis, syntax, utterance, discourse, etc. A. linguistic B. grammatical C. arbitrary D. semantic 5.Stylistics is the study of style . It is concerned with the user’s choices of linguistic elements in a particular________ for special effects A. situation B. context C. time D. place 6.Lexicography shares with lexicology the same problems: the form , meaning, origins and usages of words, but they have a _______ difference. A . spelling B. semantic C. pronunciation D. pragmatic 7. Terminology consists of _______ terms used in particular disciplines and academic areas. A. technical B. artistic C. different D. academic 8. __________refers to the specialized vocabularies by which members of particular arts, sciences, trades, and professions communicate among themselves. A. Slang B. Jargon C. Dialectal words D. Argot 9 ._________ belongs to the sub-standard language, a category that seems to stand between the standard general words including informal ones available to everyone and in-group words. A. Jargon B. Argot C. Dialectal words D. Slang 10. Argot generally refers to the jargon of _______.Its use is confined to the sub-cultural groups and outsiders can hardly understand it. A. workers B. criminals C. any person D. policeman 11.________ are words used only by speakers of the dialect in question. A. Argot B. Slang C. Jargon D. Dialectal words 12. Archaisms are words or forms that were once in _________use but are now restricted only to specialized or limited use. A. common B. little C. slight D. great 13. Neologisms are newly-created words or expressions, or words that have taken on ______meanings. A. new B. old C. bad D. good 14. Content words denote clear notions and thus are known as_________ words. They include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs and numerals. A. functional B. notional C. empty D. formal 15. Functional words do not have notions of their own. Therefore, they are also called _______words. Prepositions, conjunctions, auxiliaries and articles belong to this category. A. content B. notional C. empty D. new
最新英语词汇学期末复习资料资料
1、选择题(2 ×15=30) 2、填空题(2×5=10 ) 3、搭配题(1×10=10) 4、名词解释题(4×5=20) 5、问题回答(5×3=15) 6、论述题(第39题7分,第40题8分) 选择题: 1. Which of the following is an initialism ? D. UN 2. The following are all nominal suffixes EXCEPT A. –ful . 3.Both English and B. Danish belong to the Germantic branch of the Indo-European language family. 4.Affixes added to the end of words to indicate grammatik relationships are known as C. inflectional morphemes. 5.Motiation accounts for the connection between word-form and C.its meaning. 6.Ambiguity often arises due to polysemy and C.homonymy. 7.Affixes attached to other morphemes to create new words are known as B .derivational affixes. 8.The semantic unity of idioms is reflected in the A.illogical relationship between the literal meaning of each word and the meaning of the idiom as in rain cats and dogs. https://www.360docs.net/doc/543032829.html,ually a small number of languages have been designated official languages for an organization’s activities ,for example, the UN was established with five official languages English, French, A.Spanish Russian, and Chinese.中英俄法西
英语词汇学 英语词汇学习题2及答案
试题二 第一部分选择题 I. Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers Choose the one that would best complete the statement and put the letter in the bracket(30%) 1. Degradation can be illustrated by the following example A. lewd → ignoran t B. silly → foolish C. last → pleasure D. knave → boy 2. Homophones are often employed to create puns for desired effects of: A. humour B. sarcasm C. ridicule D. all the above 3. The four major modes of semantic change are _____. A. extension, narrowing, elevation and degradation B. extension, generalization, elevation and degradation C. extension, narrowing, specialization and degradation D. extension, elevation, amelioration and degradation 4. The use of one name for that of another associated with it is rhetorically called _____. A. synecdoche B. metonymy C. substitution D. metaphor 5. Idioms adjectival in nature function as _____. A. adjectives B. attributes C. modifiers D. words 6. Grammatical context refers to _____ in which a word is used. A. vocabulary B. grammar C. semantic pattern D. syntactic structure 7. In the idiom 'in good feather', we change 'good' into 'high, full' without changing meaning. This change of constituent is known as _____ . A. addition B. replacement C. position-shifting D. variation 8. The word "laconic" is _____. A. onomatopoeically motivated B. morphologically motivated
