药用丁基胶塞---四大药典检测标准异同
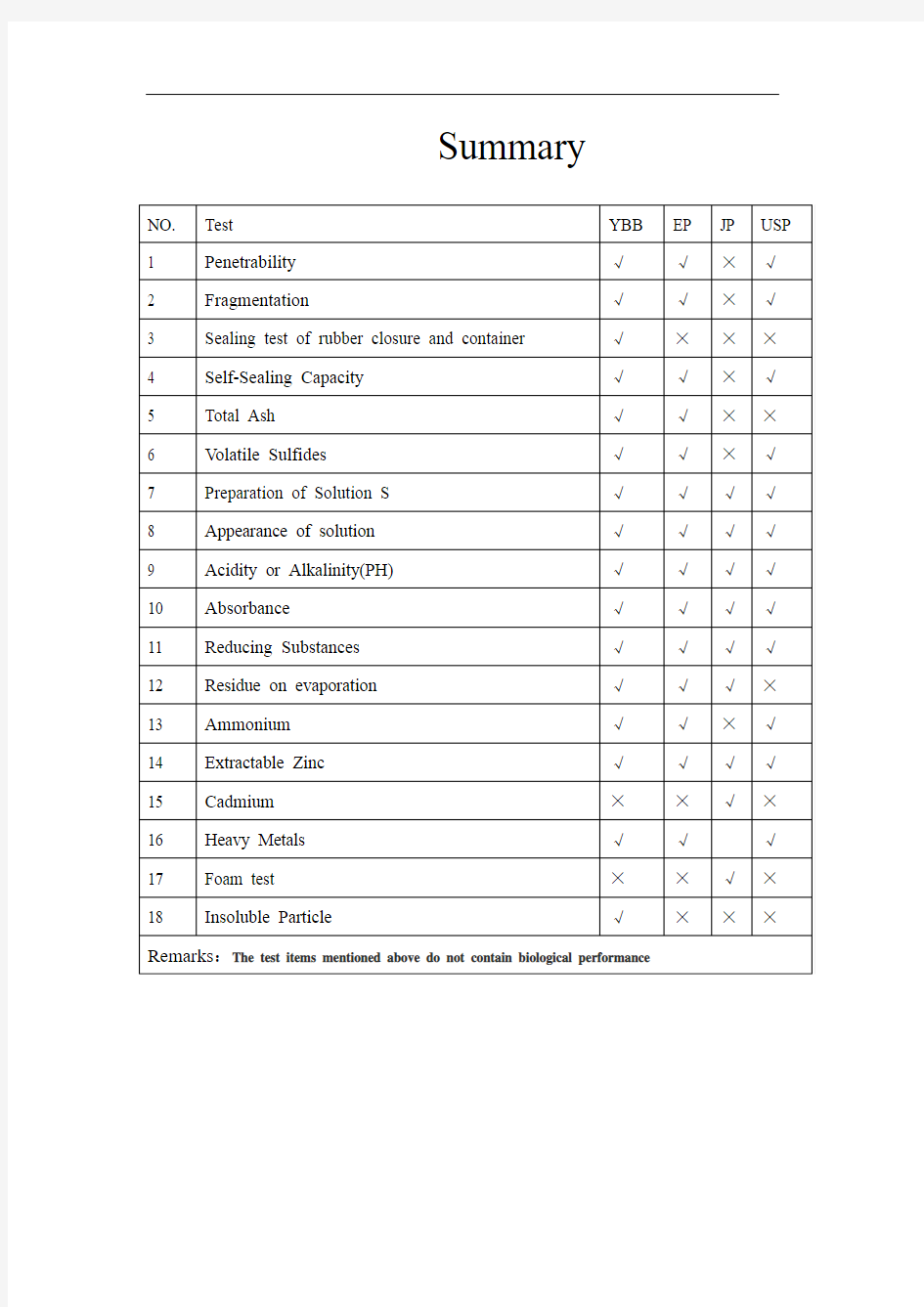

Summary
1、Penetrability
[YBB]Take 10 rubber closures, test according to the second method of YBB60072012, the average puncture force does not exceed 10N.
[EP] Fill 10 suitable vials to the nominal volume with water R, fit the closures to be examined and secure with a cap. Using for each closure a new, lubricated long-bevel(1) (bevel angle 12 ± 2°) hypodermic needle with an external diameter of 0.8 mm, pierce the closures with the needle perpendicular to the surface. The force required for piercing, determined with an accuracy of ± 0.25 N (25 gf), is not greater than 10 N (1 kgf) for each closure.
[JP]None
[USP]Fill 10 suitable vials to the nominal volume with water, fit the closures to be examined, and secure with a cap. Using a new hypodermic needle as described above for each closure, pierce the closure with the needle perpendicular to the surface.
Requirement—The force for piercing is no greater than 10 N (1 kgf) for each closure, determined with an accuracy of ± 0.25 N (25 gf).
2、Fragmentation
[YBB]Take 10 rubber closures, test according to the second method of YBB60082012, The total number of fragments does not exceed 5.
[EP] For closures intended to be pierced by a hypodermic needle, carry out the following test. If the closures are to be used for aqueous preparations, place in
12 clean vials a volume of water R corresponding to the nominal volume minus
4 ml, close the vials with the closures to be examined, secure with a cap and
allow to stand for 16 h. If the closures are to be used with dry preparations, close 12 clean vials with the closures to be examined. Using a lubricated long-bevel(1) (bevel angle 12 ±2°) hypodermic needle with an external diameter of 0.8 mm fitted to a clean syringe, inject into the vial 1 ml of water R and remove 1 ml of air ; carry out this operation 4 times for each closure, piercing each time at a different site. Use a new needle for each closure and check that the needle is not blunted during the test. Pass the liquid in the vials through a filter having approxi mately 0.5 μm pores. Count the fragments of rubber visible to the naked eye. The total number of fragments does not exceed
5. This limit is based on the assumption that fragments with a diameter equal to
or greater than 50 μm are visible to the naked eye; in cases of doubt or dispute, the fragments are examined with a microscope to verify their nature and size. [JP] None
[USP] Closures for Liquid Preparations— Fill 12 clean vials with water to 4 mL less than the nominal capacity. Fit the closures to be examined, secure with a
cap, and allow to stand for 16 hours.
Closures for Dry Preparations— Fit closures to be examined into 12 clean
vials, and secure each with a cap.
Procedure— Using a hypodermic needle as described above fitted to a clean
syringe, inject into each vial 1 mL of water while removing 1 mL of air. Repeat this procedure 4 times for each closure, piercing each time at a different site.
Use a new needle for each closure, checking that it is not blunted during the test.
Filter the toatal volume of liquid in all the vials through a single filter with a nominal pore size no greater than 0.5 μm. Count the rubber fragments on the surface of the filter visible to the naked eye.
Requirement— There are no more than 5 fragments visible. This limit is based on the assumption that fragments with a diameter >50 μm are visible to the naked eye. In case of doubt or dispute, the particles are examined microscopically to verify their nature and size.
3、Sealing test of rubber closure and container
[YBB] Take 10 rubber closures into the beaker, boil for 5 min , take out and dry 1h at 70℃ and ready to use. Fill 10 suitable vials to the nominal volume with water, fit the closures to be examined and secure with a cap. Heat in an autoclave so that a temperature of 121 ± 2 °C and maintain at this temperature for 30 min.
Cool to room temperature and then place 24h, Immerse the vials upside down in
a 10% solution of methylene blue R and reduce the external pressure by 25 kPa
for 30 min. Restore atmospheric pressure and leave the vials immersed for 30 min. Rinse the outside of the vials. None of the vials contains any trace of colored solution.
[EP]None
[JP]None
[USP] None
4、Self-Sealing Capacity
[YBB]Take the samples from sealing test of rubber closure and container, using for a hypodermic needle (YBB60082012 method 2), pierce each closure 3 times, change the hypodermic needle after it is used 10 times ,piercing each time at a different site.The vials upside down in a 10% solution of methylene blue R and reduce the external pressure by 25 kPa for 30 min. Restore atmospheric pressure and leave the vials immersed for 30 min. Rinse the outside of the vials. None of the vials contains any trace of colored solution.
[EP]For closures intended to be used with multidose containers, carry out the following test. Fill 10 suitable vials to the nominal volume with water R, fit the closures to be examined and secure with a cap. Using for each closure a new hypodermic needle with an external diameter of 0.8 mm, pierce each closure 10 times, piercing each time at a different site. Immerse the vials upright in a 1 g/l solution of methylene blue R and reduce the external pressure by 27 kPa for 10 min. Restore atmospheric pressure and leave the vials immersed for 30 min.
Rinse the outside of the vials. None of the vials contains any trace of coloured solution.
[JP]None
[USP]Procedure—Fill 10 suitable vials with water to the nominal volume. Fit the closures that are to be examined, and cap. Using a new hypodermic needle as described above for each closure, pierce each closure 10 times, piercing each time at a different site. Immerse the 10 vials in a solution of 0.1% (1 g per L) methylene blue, and reduce the external pressure by 27 kPa for 10 minutes.
Restore to atmospheric pressure, and leave the vials immersed for 30 minutes.
Rinse the outside of the vials.
Requirement—None of the vials contain any trace of blue solution.
5、Total Ash
[YBB] Take the rubber closures, test according to YBB600212012, should be comply with the standard.
[EP]The total ash (2.4.16) is within ± 10 per cent of the result obtained with the type sample.
[JP]None
[USP] None
6、Volatile Sulfides
[YBB]Take the rubber closures, according to the YBB60052012, should be comply with the standard.
[EP] Place closures, cut if necessary, with a total surface area of 20 ± 2 cm2 in a 100 ml conical flask and add 50 ml of a 20 g/l solution of citric acid R. Place a piece of lead acetate paper R over the mouth of the flask and maintain the paper in position by placing over it an inverted weighing bottle. Heat in an autoclave at 121 ± 2℃ for 30 min. Any black stain on the paper is not more intense than that of a standard prepared at the same time in the same manner using 0.154 mg of sodium sulphide R and 50 ml of a 20 g/l solution of citric acid R.
[JP]None
[USP] Procedure— Place closures, cut if necessary, with a total surface area of 20 ± 2 cm2 in a 100-mL flask, and add 50 mL of a 20 g per L citric acid solution. In the same manner and at the same time, prepare a control solution in a separate 100-mL flask by dissolving 0.154 mg of sodium sulfide in 50 mL of a 20 g per L citric acid solution. Place a piece of lead acetate paper over the mouth of each flask, and hold the paper in position by placing over it an inverted weighing bottle. Heat the flasks in an autoclave at 121 ± 2℃for 30minutes.
Requirement—Any black stain on the paper produced by Solution S is not more intense than that produced by the control solution.
7、Preparation of Solution S
[YBB] Put a number of uncut closures corresponding to a surface area of about 200 cm2 in a suitable glass container, cover with purified water( sample: water=1:2), boil for 5 min and rinse 5 times with the same volume of purified water. Place the washed closures in a conical flask, add the same volume of water and weigh.
Cover the mouth of the flask with a borosilicate-glass beaker. Heat in an autoclave so that a temperature of 121 ± 2 °C is reached within 20 min to 30 min and maintain at this temperature for 30 min. Cool to room temperature.
Make up to the original mass with purified water. Shake and immediately separate the solution from the rubber by decantation. Shake solution S before each test Blank. Prepare a blank in the same manner using 400 mL of water for purified water.
[EP] Solution S.Introduce a number of uncut closures corresponding to a surface area of about 100 cm2in a suitable glass container, cover with water for injections R, boil for 5 min and rinse 5 times with cold water for injections R.
Place the washed closures in a wide-necked flask (glass type I, 3.2.1), add 200 ml of water for injections R and weigh. Cover the mouth of the flask with a borosilicate-glass beaker. Heat in an autoclave so that a temperature of 121 ±
2 °C is reached within 20 min to 30 min and maintain at this temperature for 30
min. Cool to room temperature over about 30 min. Make up to the original mass with water for injections R. Shake and immediately separate the solution from the rubber by decantation. Shake solution S before each test
Blank. Prepare a blank in the same manner using 200 ml of water for injections R.
[JP] Wash the rubber closures with water, and dry at room temperature. Place them in a glass container, add water exactly 10 times the mass of the test material, close with a suitable stopper, heat at 121℃ for 1 hour in an autoclave, take out the glass container, allow to cool to room temperature,then take out immediately the rubber closures, and use the remaining solution as the test
solution. Prepare the blank solution with water in the same manner. Perform the following tests with the test solution and the blank solution
[USP] Place whole, uncut closures corresponding to a surface area of 100 ± 10 cm2 into
a suitable glass container. Cover the closures with 200 mL of Purified Water or
Water for Injection. If it is not possible to achieve the prescribed closure surface area (100 ± 10 cm2) using uncut closures, select the number of closures that will most closely approximate 100 cm2, and adjust the volume of water used to the equivalent of 2 mL per each 1 cm2 of actual closure surface area used. Boil for 5 minutes, and rinse five times with cold Purified Water or Water for Injection
Place the washed closures into a Type I glass wide-necked flask (see Containers—Glass 660 ), add the same quantity of Purified Water or Water for Injection initially added to the closures, and weigh. Cover the mouth of the flask with a Type I glass beaker. Heat in an autoclave so that a temperature of 121 ± 2℃ is reached within 20 to 30 minutes, and maintain this temperature for
30 minutes. Cool to room temperature over a period of about 30 minutes. Add
Purified Water or Water for Injection to bring it up to the original mass. Shake, and immediately decant and collect the solution. [NOTE—This solution must be shaken before being used in each of the tests]
Prepare a blank solution similarly, using 200 mL of Purified Water or Water for Injection omitting the closures
8、Appearance of solution
[YBB]According to the part 2 of Chinese pharmacopoeia, 2010 edition of appendixⅨB and appendix IX A, standard solution is not more opalescent than reference suspension II. Standard solution is not more intensely coloured than No.5 reference solution
[EP] Solution S is not more opalescent than reference suspension II for type I closures and is not more opalescent than reference suspension III for type II closures
(2.2.1). Solution S is not more intensely coloured than reference solution GY5
(2.2.2, Method II).
[JP] Place 5 mL of the test solution in a glass-stoppered test tube of about 15 mm in inner diameter and about 200 mm in length, and shake vigorously for 3 minutes.
The foam arisen disappears almost completely within 3 minutes.
[USP] Determination of Turbidity (Opalescence)
Procedure A: Visual Comparison— Use identical test tubes made of colorless, transparent, neutral glass with a flat base and an internal diameter of 15 to 25 mm. Fill one tube to a depth of 40 mm with Solution S, one tube to the same depth with water, and four others to the same depth with Reference Suspensions A, B, C,and D. Compare the solutions in diffuse daylight 5 minutes after preparation of the Reference Suspensions, viewing vertically against a black background. The light conditions shall be such that Reference Suspension A can be readily distinguished from water and that Reference Suspension B can be readily distinguished fromReference Suspension A.
REQUIREMENT—Solution S is not more opalescent than Reference Suspension B for Type I closures, and not more opalescent than Reference Suspension C for Type II closures. Solution S is considered clear if its clarity is the same as that of water when examined as described above, or if its opalescence is not more pronounced than that of Reference Suspension A (refer to Table 3).
Procedure B: Instrumental Comparison—Measure the turbidity of the
Reference Suspensions in a suitable calibrated turbidimeter (see Spectrophotometry and Light Scattering 851 ). The blank should be run and the results corrected for the blank. Reference Suspensions A, B, C, and D represent 3, 6, 18 and 30 Nephelometric Turbidity Units (NTU), respectively. Measure the turbidity of Solution S using the calibrated turbidimeter. REQUIREMENT—The turbidity of Solution S is not greater than that for Reference Suspension B (6 NTU FTU) for Type I closures, and is not greater than that forReference Suspension C (18 NTU FTU) for Type II closures (refer to Table 3).
Determination of Color
Color Standard— Prepare a solution by diluting 3.0 mL of Matching Fluid O (see Color and Achromicity 631 ) with 97.0 mL of diluted hydrochloric acid. Procedure—Use identical tubes made of colorless, transparent, neutral glass with a flat base and an internal diameter of 15 to 25 mm. Fill one tube to a depth of 40 mm with Solution S, and the second with Color Standard. Compare the liquids in diffuse daylight, viewing vertically against a white background. Requirement—Solution S is not more intensely colored than the Color Standard.
9、Acidity or Alkalinity(PH)
[YBB]Take each of 20 ml blank solution and solution S, respectively with KCl solution
1 ml, According to the part
2 of Chinese pharmacopoeia, 2010 edition of
appendixⅥH, the difference between the two may not be over 1.0.
[EP] To 20ml of solution S add 0.1ml of bromothymol blue solution R1. Not more than 0.3ml of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide or 0.8 ml of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required to obtain either a blue or a yellow colour, respectively.
[JP] To 20 mL each of the test solution and the blank solution add 1.0 mL each of potassium chloride solution, prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of potassium chloride in water to make 1000 mL. The difference of pH between the two solutions is not more than 1.0
[USP] Bromothymol Blue Solution—Dissolve 50 mg of bromothymol blue in a mixture of 4 mL of 0.02 M sodium hydroxide and 20 mL of alcohol. Dilute with water to 100 mL.
Procedure— To 20 ml of Solution S add 0.1 ml of Bromothymol Blue Solution.
If the solution is yellow, titrate with 0.01 N sodium hydroxide until a blue endpoint is reached. If the solution is blue, titrate with 0.01 N hydrochloric acid until a yellow endpoint is reached. If the solution is green, it is neutral and no titration is required.
Blank Correction—Test 20 mL of Blank similarly. Correct the results obtained for Solution S by subtracting or adding the volume of titrant required for the Blank, as appropriate. (Reference Titrimetry 541 .)
Requirement— Not more than 0.3 ml of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide produces a blue color, or not more than 0.8 ml of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid produces a yellow color, or no titration is required.
10、Absorbance
[YBB] Filter solution S on a membrane filter having approximately 0.45 μm pores.
Measure the absorbance of the filtrate at wavelengths from 220 nm to 360 nm using the blank as compensation liquid. At these wavelengths, the absorbance does not exceed 0.1(according to the part 2 of Chinese pharmacopoeia, 2010 edition of appendixⅣA).
[EP] Carry out the test within 5 h of preparation of solution S. Filter solution S on a membrane filter having approximately 0.45 μm pores rejecting the first few milliliters of filtrate. Measure the absorbance (2.2.25) of the filtrate at wavelengths from 220 nm to 360 nm using the blank (see solution S) as compensation liquid. At these wavelengths, the absorbance does not exceed 0.2 for type I closures or 4.0 for type II closures. If necessary, dilute the filtrate before measurement of the absorbance and correct the result for the dilution. [JP] Read the absorbance of the test solution between 220 nm and 350 nm against the blank solution as directed under Ultraviolet-visible Spectrophotometry <2.54>: it is not more than 0.20.
[USP] Procedure — [NOTE—Perform this test within 5 hours of preparing Solution S.] Filter Solution S through a 0.45-μm pore size filter, discarding the first few mL of filtrate. Measure the absorbance of the filtrate at wavelengths between 220 and 360 nm in a 1-cm cell using the blank in a matched cell in the reference beam. If dilution of the filtrate is required before measurement of the absorbance, correct the test results for the dilution.
Requirement—The absorbances at these wavelengths do not exceed 0.2 for Type I closures or 4.0 for Type II closures.
11、Reducing Substances
[YBB] To 20.0 mL of solution S add 1 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R and 20.0 mL of
0.002 M potassium permanganate. Boil for 3 min. Cool. Add 0.1 g of potassium
iodide R and titrate immediately with 0.01 M sodium thiosulfate until the color
turned light brown , using 5 drops of starch solution R as indicator. Carry out a
titration using 20.0 mL of the blank. The difference between the titration
volumes is not greater than7.0mL.
[EP] Carry out the test within 4 h of preparation of solution S. To 20.0 ml of solution S add 1 ml of dilute sulphuric acid R and 20.0 ml of 0.002 M potassium permanganate. Boil for 3min. Cool. Add 1 g of potassium iodide R and titrate immediately with 0.01 M sodium thiosulphate, using 0.25 ml of starch solution R as indicator. Carry out a titration using 20.0 ml of the blank. The difference between the titration volumes is not greater than 3.0 ml for type I closures and
7.0 ml for type II closures.
[JP] Measure 100 mL of the test solution in a glass-stoppered,Erlenmyer flask, add
10.0 mL of 0.002 mol/L potassium permanganate VS and 5 mL of dilute
sulfuric acid, and boil for 3 minutes. After cooling, add 0.10 g of potassium iodide,stopper, mix by shaking, then allow to stand for 10 minutes,and titrate
<2.50> with 0.01 mol/L sodium thiosulfate VS(indicator: 5 drops of starch TS).
Perform the blank test in the same manner, using 100 mL of the blank solution.
The difference in mL of 0.002 mol/L potassium permanganate VS required between the tests is not more than 2.0 mL.
[USP] Procedure— [NOTE—Perform this test within 4 hours of preparing Solution S.] To 20.0 mL of Solution S add 1 mL of diluted sulfuric acid and 20.0 mL of
0.002 M potassium permanganate. Boil for 3 minutes. Cool, add 1 g of
potassium iodide, and titrate immediately with 0.01 M sodium thiosulfate, using
0.25 mL of starch solution TS as the indicator. Perform a titration using 20.0
mL of blank and note the difference in volume of 0.01 M sodium thiosulfate
required.
Requirement—The difference between the titration volumes is not greater than 3.0 mL for Type I closures and not greater than 7.0 mL for Type II closures.
12、Residue on evaporation
[YBB]Evaporate 100 mL of solution S and blank solution to dryness on a water-bath and dry at 100 °C to 105 °C. The residue weighs not more than 4.0 mg. [EP]Evaporate 50.0 ml of solution S to dryness on a water-bath and dry at 100 °C to 105 °C. The residue weighs not more than 2.0 mg for type I rubber and not
more than 4.0 mg for type II rubber.
[JP]Measure 100 mL of the test solution, evaporate on a water bath to dryness, and dry the residue at 1059 C for 1 hour.The mass of the residue is not more
than 2.0 mg.
[USP]None
13、Ammonium
[YBB] Precision measuring 10 ml of solution S, adding alkaline potassium iodide solution 2 ml, place 15 minutes, should not be color; if it colored , compare with reference solution (with 2.0 ml ammonium chloride solution (take ammonium
chloride 31.5 mg, add right amount chlorine free water and dissolve diluted to
1000 ml), 8 ml blank reference solution, 2ml alkaline potassium mercuric iodide solution for mixing), should not be more intensely colored (0.0002%)
[EP] maximum 2 ppm.
Dilute 5 ml of solution S to 14 ml with water R. The solution complies with limit test A.
[JP]None
[USP] Alkaline Potassium Tetraiodomercurate Solution— Prepare a 100 mL solution containing 11 g of potassium iodide and 15 g of mercuric iodide in water.
Immediately before use, mix 1 volume of this solution with an equal volume of
a 250 g per L solution of sodium hydroxide.
Test Solution— Dilute 5 mL of Solution S to 14 mL with water. Make alkaline if necessary by adding 1 N sodium hydroxide, and dilute with water to 15 mL.
Add 0.3 mL of Alkaline Potassium Tetraiodomercurate Solution, and close the container.
Ammonium Standard Solution— Prepare a solution of ammonium chloride in water (1 ppm NH4). Mix 10 mL of the 1 ppm ammonium chloride solution with
5 mL water and 0.3 mL of Alkaline Potassium Tetraiodomercurate Solution.
Close the container.
Requirement—After 5 minutes, any yellow color in the Test Solution is no darker than the Ammonium Standard Solution (no more than 2 ppm of NH4 in Solution S).
14、Extractable Zinc
[YBB] Filter solution S on a membrane filter having approximately 0.45μm pores, Precision measuring filtrate 10 ml, add 1 ml 2 mol/L of hydrochloric acid and 3 drops of potassium ferrocyanide test solution(weight 4.2 g potassium ferrocyanide trihydrate, dissolve and diluted with water to 100 ml, shake evenly, this product should be new prepared) for mixing, should not be color; if it colored, compare with reference solution( with 3 ml standard zinc solution (weight 44.0g Zinc sulfate seven hydrated compounds, with new boiled and cooled purified water dissolved and diluted to 1000 ml, this product should be new prepared), shall not be deeper(0.0002%),7ml blank reference solution, 1ml 2mol/L hydrochloric acid and 3 drops of potassium ferrocyanide solution for mixing), should not be more intensely colored.(0.0003%)
[EP] maximumof 5 μg of extractable Zn per millilitre of solution S.
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.23, Method I). Test solution. Dilute
10.0 ml of solution S to 100 ml with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid.
Reference solutions. Prepare the reference solutions using zinc standard solution
(10 ppm Zn) R diluted with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid.
Source: zinc hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength: 213.9 nm.
Flame: air-acetylene.
[JP]To 10.0 mL of the test solution add diluted dilute nitric acid (1 in 3) to make 20 mL, and use this solution as the sample solution. Further, to 1.0 mL of Standard Zinc Solutionfor atomic absorption spectrophotometry add diluted nitricacid (1 in 3) to make exactly 20 mL, and use this solution asthe standard solution. Perform the tests according to the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry <2.23>,using these solutions, under the following conditions.
The absorbanceof the sample solution is not more than that of the standardsolution.
Gas: Combustible gasóAcetylene.
Supporting gasóAir.
Lamp: Zinc hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength: 213.9 nm.
Standard Zinc Solution for atomic absorption spectrophotometry: Measure exactly 10 mL of the Standard Zinc Stock Solution, and add water to make exactly 1000 mL. Prepare before use. One mL of this solution contains 0.01 mg of zinc(Zn).
[USP] Test Solution—Prepare a Test Solution by diluting 10.0 mL of Solution S to 100 mL with 0.1N hydrochloric acid. Prepare a test blank similarly, using the Blank forSolution S.
Zinc Standard Solution— Prepare a solution (10 ppm Zn) by dissolving zinc sulfate in 0.1 N hydrochloric acid.
Reference Solutions—Prepare not fewer than 3 Reference Solutions by diluting the Zinc Standard Solution with 0.1 N hydrochloric acid. The concentrations of zinc in these Reference Solutions are to span the expected limit of the Test Solution.
Procedure—Use a suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light Scattering 851 ) equipped with a zinc hollow-cathode lamp and an air–acetylene flame. An alternative procedure such as an appropriately validated inductively coupled plasma analysis (ICP) may be used.
Test each of the Reference Solutions at the zinc emission line of 213.9 nm at least 3 times. Record the steady readings. Rinse the apparatus with the test blank solution each time, to ensure that the reading returns to initial blank value.
Prepare a calibration curve from the mean of the readings obtained for each Reference Solution. Record the absorbance of the Test Solution. Determine the ppm zinc concentration of the Test Solution using the calibration curve.
Requirement— Solution S contains not more than 5 ppm of extractable zinc.
一致性评价案例展示——奥美拉唑肠溶胶囊-片
一致性评价案例展示奥美拉唑肠溶胶囊/片 达4年的“酝酿-争议-探讨”拉锯战之后,国家层面力推的仿制药质量和疗效一致性评价工作终于要快马加鞭向前开进了。CFDA于5月26日再次发文明确了评价对象和实施阶段,同时还公布了289个必须在2018年底前完成一致性评价的品种清单。 由于289个品种将涉及上千家药企手中的上万个生产批文,各药企在艰难做出“哪些品种需要做一致性评价”这一生死抉择后,紧接着面临的就是具体品种如何做一致性评价的问题。医药魔方将在未来一段时间连载与289个品种有关的案例,以便为制药企业开展一致性评价的相关工作提供参考。今天为大家展示的是一份关于奥美拉唑肠溶胶囊/片的一致性评价资料。 原研药学信息综述 国内上市情况 目前国内奥美拉唑肠溶胶囊10mg规格有10个文号(文号即发文字号,是由发文机关代字、发文年份和文件顺序号三个部分组成。);20mg规格有101个文号;40mg规格有4个文号。 奥美拉唑肠溶片在国内有16个文号。有进口本地化产品上市,国药准字 H20030412,商品名:洛赛克;阿斯利康制药有限公司。 有韩美和香港正美两家公司在中国进口上市。 国外上市情况 目前美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)上市的奥美拉唑肠溶胶囊三个规格共有51个文号;
FDA橙皮书参比制剂为ASTRAZENECA生产的奥美拉唑肠溶胶囊,规格20mg、40mg。 日本橙皮书中参比制剂为阿斯利康和田边三菱的片剂,规格20mg 原料药理化性质 性状:本品为白色结晶性粉末 溶解度:易溶于N,N-二甲基甲酰胺中,微溶于乙醇(95%)溶液,几乎不溶于水。 解离常数(室温):pKa1(一般来说,较大的Ka值(或较少的pKa值)代表较强的酸,这是由于在同一的浓度下,离解的能力较强。) = 4.5(针对吡啶环、采用吸光度法测定);pKa1 = 8.9(针对苯并咪唑环、采用吸光度法测定在各溶出介质中的溶解度(37℃): pH 1.2:33.0mg/ml pH 6.0:0.079mg/ml pH 6.8:0.078mg/ml 水:0.091mg/ml 在各溶出介质的稳定性: 水:37℃条件下,2小时降解14%,6小时降解43%。 在各pH值溶出介质中:在pH1.2、pH6.0和pH6.8各溶出介质中,37℃/2小时分别降解83%、97%和8%。 光:未测定。 熔点:约150℃
塑胶件外观检验标准ok
塑胶件外观检验标准 1.制定目的: 确定检验作业条件,确定抽样水准,明确检验方法,建立判定标准,以确保产品品质。 2.适用范围: 本检验规范适用我司塑胶件产品检验作业。 3.权责单位: 本检验规范由品管单位制定,事业部总经理核准后发行; 所制定之规格,如有修改时,须经原制定单位同意后修改之。 4.应用文件: MIL-STD-105E II 抽样计划表(国家标准GB2828-87一般检查水平II)、工程图纸、工程样板。 5.检验标准: 1、MIL-STD-105E II表(国家标准GB2828-87一般检查水平II),正常检验、单次抽样计划,AQL订定为CRI=0 、MAJ=0.65 、MIN=1.5。 2、相关抽样标准或判定标准,可视品质状况或客户要求等做修正。 6.定义 6.1缺点分类: a.严重缺陷(CRI):可能对机器或装备的操作者造成伤害;潜在危险性的效应,会导致与安全有关的失效或不符合政府法规;影响机械或电气性能,产品在组装后或在客户使用时会发生重大品质事件的。 b.主要缺陷(MAJ):性能不能达到预期的目标,但不至于引起危险或不安全现象;导致最终影响产品使用性能和装配;客户很难接受或存在客户抱怨风险的。 c.次要缺陷(MIN):不满足规定的要求但不会影响产品使用功能的;客户不易发现,发现后通过沟通能使客户接受的。 6.2塑胶不良描述: 6.2.1、异色点:与本身颜色不同的杂点或混入树脂中的杂点暴露在表面上。 6.2.2、气纹:由于种种原因,气体在产品表面留下的痕迹。 6.2.3、缩水:材料冷却收缩造成的表面下陷。 6.2.4、水纹:射胶时留在产品表面的水波浪的纹路。 6.2.5、拉伤:开模时分模面或皮纹拖拉产品表面造成的划痕。 6.2.6、变形:产品出现的弯曲、扭曲、拉伸现象。 6.2.7、顶白:颜色泛白,常出现在顶出的位置。 6.2.8、烧焦:塑胶燃烧变质,通常颜色发黄,严重时碳化发黑。 6.2.9、塌坑:由于材料收缩,使产品局部整体表面下陷。 6.210、熔接缝:产品在成型过程中,二股以上的融熔料相汇合的接线,目视及手感都有感觉。 6.2.11、缺料:产品某个部位不饱满 6.2.12、混色:由于内应力,在产品表面产生与产品本色不同的颜色。 6.2.13、滋边(毛刺):由于种种原因,产品非结构部分产生多余的料。 6.2.14、封堵:应该通透的地方由于滋边造成不通。 6.2.15、断裂:塑料理局部断开后的缺陷 6.2.16、拉毛:因摩擦而产生的细皮,附在塑料表面的现象。 6.2.17、油污(油痕):由于种种原因,在产品表面留下的痕迹(包括脱模式剂),使该部位发光并带有流动样 6.2.18、气泡:透明产品内部形成的在中空。 6.2.19、划痕:由于硬物摩擦而造成的塑胶件表面线形痕迹。 6.3喷涂件不良描述: 6.3.1、漆点:涂层厚度比周围涂层厚的部分。
药用包装材料质量标准ISO15378(中文)
精心整理 ISO15378:2006标准的中文版内容 国际标准化组织/第76技术委员会(IS0/TC76)于2003年制定了1S015378国际标准草案(Draftofinterrfationalstandard ,D1S),标题是:《药品初包装材料ISO9001:2008应用的专用要求,包含生产质量管理规范(GMP)》。2006年,形成了借鉴ISO9001:2008质量体系的《药用包装材料质量标准ISO15378:2006》初稿。这个国际标准的制定说明了国际社会对药包材生产企业实施质量管理的重视。此处择其(一) 0.1领会GMP 采用0.2(1)理解并满足要求; (2)需要从增值的角度考虑过程; (3)获得过程业绩和有效性的结果; (4)基于客观的测量,持续改进过程。 ISO15378引用了以过程为基础的QMS 模式图,展示了有关的过程联系(可参见ISO9001:2008)。 此外,称之为“PDCA ”的(Plan 计划,D0执行,Check 检查,Action 处理)的方法可
适用于所有过程。 0.3与ISO9004的关系 ISO9001与ISO9004为一对协调一致的QMS标准,它们相对补充,但也可单独使用。 ISO9001规定了QMS要求,可供组织内部使用,也可用于认证或合同目的。在满足顾客要求方面,ISO_9001,所关注的是QMS的有效性。 与ISO9001相比,ISO9004为QMS更宽范围的目标提供了指南。除了有效性,该标准还特别关注持续改进组织的总体业绩与效率。对于最高管理者希望通过追求业 0.4 这些 )、OHSMS( (二) 1.范围 1.1 认为该项要求“适当”:初包装材料满足所规定的要求;和(或)组织实施纠正措施。 1.2应用 1S015378是一个药品初包装材料的应用标准。该标准也适用于第三方对此类产品的认证。 2.规范性引用文件 ISO9000:2008质量管理体系基础和术语 ISO9001:2008质量管理体系要求
注射用奥美拉唑钠-标准
征求意见稿注射用奥美拉唑钠 Zhusheyong Aomeilazuona Omeprazole Sodium for Injection 本品为奥美拉唑钠的无菌冻干品。含奥美拉唑钠以奥美拉唑(C 17H 19N 3O 3S )计应为标示量的93.0%~107.0%。 【性状】 本品为白色或类白色疏松块状物或粉末。 【鉴别】(1)在含量测定项下记录的色谱图中,供试品溶液主峰的保留时间应与对照品溶液主峰保留时间一致。 (2)取本品,加0.1mol/L 氢氧化钠溶液制成每1ml 中约含奥美拉唑20μg 的溶液,照紫外-可见分光光度法(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅳ A )测定,在305nm 与276nm 的波长处有最大吸收,其吸光度比值应为1.6~1.8。 (3)本品的水溶液显钠盐鉴别(1)的反应。(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅲ)。 【检查】 溶液的澄清度与颜色 取本品5瓶,加水或所附专用溶剂适量使溶解并制成每1ml 中含奥美拉唑4.0mg 的溶液,溶液应澄清,如显浑浊,与1号浊度标准液(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅸ B )比较,不得更浓;取溶液,照紫外-可见分光光度法(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅳ A ),在440nm 的波长处测定,吸光度不得过0.1。 碱度 取溶液的澄清度与颜色项下的溶液,依法测定(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅵ H ),pH 值应为10.1~11.1。 有关物质 避光操作。取奥美拉唑磺酰化物(5-甲氧基-2-{[4-甲氧基-3,5-二甲基-2-吡啶基]-甲基]-磺酰基}-1H -苯并咪唑)对照品约6mg ,精密称定,置100ml 量瓶中,加乙腈5ml 使溶解,用溶剂(同含量测定项下)稀释至刻度,摇匀,精密量取适量,加溶剂制成每1ml 中约含0.6μg 的溶液,作为杂质对照品溶液。另精密量取含量测定项下的供试品溶液1ml ,置100ml 量瓶中,用溶剂稀释至刻度,作为对照溶液。照含量测定项下的色谱条件,量取对照溶液20μl 注入液相色谱仪,调节检测灵敏度,使主成分色谱峰的峰高约为满量程的20%。精密量取杂质对照品溶液、对照溶液和含量测定项下的供试品溶液(配制后15分钟内进样)各20μl ,分别注入液相色谱仪,记录色谱图至主成分色谱峰保留时间的3倍。供试品溶液的色谱图中如有杂质峰(包括奥美拉唑磺酰化物),单个杂质峰面积均不得大于对照溶液的主峰面积;如奥美拉唑磺酰化物的峰面积大于对照溶液主峰面积的0.3倍,按外标法以峰面积计算,不得过奥美拉唑标示量的1.0%;各杂质峰面积的和不得大于对照溶液主峰面积的1.5倍。 含量均匀度 (20mg 规格) 避光操作。取本品1瓶,加0.01mol/L 四硼酸钠溶液适量使内容物溶解,定量转移至100ml 量瓶中并稀释至刻度,摇匀,精密量取2ml ,置50ml 量瓶中,用含20%乙醇的0.01mol/L 四硼酸钠溶液稀释至刻度,摇匀,照紫外-可见分光光度法(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅳ A ),在305nm 的波长处测定吸光度;另精密称取奥美拉唑钠对照品 适量, 用含20%乙醇的0.01mol/L 的四硼酸钠溶液制成每1ml 中约含奥美拉唑8μg 的溶液,同法测定吸光度,计算含量,应符合规定(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅹ E )。 细菌内毒素 取本品,依法检查(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅺ E ),每1mg 奥美拉唑中含内毒素的量应小于2.0EU 。 水分 取本品,照水分测定法(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅷ M 第一法)测定,含水分不得过7.0%。 无菌 取本品,分别加灭菌注射用水(或0.1%的蛋白胨水溶液)制成每1ml 中约含奥美拉唑8mg 的溶液,用薄膜过滤法处理后,依法检查(中国药典2010年版二部附录Ⅺ H ),应符合规定。
药用丁基胶塞与药物相容性研究现状和展望_张宇
36:5167 2许培,王勇.多囊卵巢综合征的病因学及诊断研究进展.徐州医学院学报,2009,29(2):123 3肖承.现代中医妇科治疗学.北京:人民卫生出版社,2004.135 4周夫群,杨松涛,康建颖,等.补肾法治疗多囊卵巢综合征的疗效研究.山东中医杂志,2009,28(6):377 5金维新,孙少霞,王长墉.罗勒治疗女性排卵功能障碍研究.福建中医学院学报,1986,10(2):11 6邵明霞.中西医结合治疗多囊卵巢综合征所致不孕的临床观察.四川中医,2006,24(1):90 7庄静,许良智,康德英,等.去氧孕烯炔雌醇治疗多囊卵巢综合征的系统评价.中华妇幼临床医学杂志(电子版),2009,5(1):54 8麻海英,刘复权.复方口服避孕药治疗多囊卵巢综合征.国外医学#妇幼保健分册,2005,16(3):170 9王海娜.复方醋酸环丙孕酮联合二甲双胍治疗多囊卵巢综合征疗效观察.中国妇幼保健,2009,24(18):256910ChristyNA,Franks A S,C ross L B.Sp irono l actone f or h irsuti s m i n poly-cys tic ovary s yndro m e.Ann Phar m acother,2005,39(9):1517 11迟贞旎,洪洁.多囊卵巢综合征的治疗方法.上海交通大学学报(医学版),2008,28(3):133 12章汉旺,陈丽萍,岳静.环丙孕酮与螺内酯辅助治疗多囊卵巢综合征65例.医药导报,2008,27(3):591 13王婧,张跃辉,胡敏,等.胰岛素增敏方法在多囊卵巢综合征中的应用.世界中西医结合杂志,2008,3(6):364 14O rbets ova M,Ka m en ov Z,Ko l arov G,et a l.E ffect of6-m on t h trea-t m en tw i th oral an tiandrogen al on e and i nco m b i nation w it h i n s u li n sens i t-i zers on body compositi on,hor m onal and m etabolic para m et ers i n w o m en w it h pol ycysti c ovary syndro m e(PCOS)i n order to deter m i n eherapeu tic strategy.Aku s h G i nerol(Sofii a),2006,45(7):16 15袁园.溴隐亭治疗难治性多囊卵巢综合征的观察.西昌学院学报#自然科学版,2008,22(1):99 药用丁基胶塞与药物相容性研究现状和展望* 张宇 (天津市药品检验所,天津300070) 摘要本文对药用丁基橡胶塞在使用中经常出现的问题及药用丁基橡胶塞与药物相容性研究中所采用的分析技术等进行了初步的归纳,并对药用丁基橡胶塞与药物相容性研究未来的发展方向进行展望。 关键词药用丁基橡胶塞,药物相容性研究 中图分类号:R94文献标识码:A文章编号:1006-5687(2010)01-0072-03 丁基橡胶瓶塞是医药包装材料的升级换代产品,主要用于替代传统的天然橡胶瓶塞。丁基橡胶瓶塞是一种有诸多优越性能的医药包装材料,具有比天然橡胶瓶塞更好的使用性,其气体透过率约为天然橡胶的1/20,丁基橡胶的耐热性、耐候性和耐臭氧氧化性都很突出,最高使用温度可达200e,能长时间暴露于阳光和空气中而不易损坏。丁基橡胶耐化学腐蚀性好,耐酸碱和极性溶剂。此外,丁基橡胶的电绝缘性和耐电晕性能比一般合成橡胶好;耐水性能优异,水渗透率极低;减震性能好,在-30~50e具有良好的减震性能;在玻璃化温度(-37e)时仍具有屈挠性。卤化丁基橡胶是丁基橡胶的改性产品,目的是卤代后提高了丁基橡胶的活性,使之与其他不饱和橡胶产生相容性,提高自黏性和互黏性,以及硫化交联能力,同时保持了丁基橡胶的原有特性。常用的卤化丁基橡胶塞有氯化丁基橡胶塞和溴化丁基橡胶塞两类。另外一种胶塞的分类是按照国际上对卤化丁基橡胶塞洁净度的要求分为四类[1]:需洗涤的胶塞、需漂洗的胶塞、需灭菌的胶塞、即用胶塞。目前全世界90%的药用橡胶瓶塞是由丁基橡胶为基材制造的。日本早在1965年就淘汰了天然橡胶瓶塞,美国和西欧等经济发达国家也在上世纪70年代实现了药用瓶塞的丁基化。我国于上世纪80年代开始药用丁基橡胶瓶塞的研究开发,直到1992年才批量生产,并在1995年由原国家医药管理局下达5关于淘汰部分天然橡胶抗生素瓶盖的通知6,如今已在部分药物和出口药物中使用。但是随着近来的使用观察,发现丁基胶塞质量的稳定对药品质量的稳定有着明显的影响,所以药用丁基橡胶塞与药物相容性研究也随之展开。 1药用丁基胶塞在使用过程中存在的问题 一般情况下药用丁基胶塞在使用过程中直接与药物接触,虽然丁基橡胶具有良好的气密性和化学惰性,但在使用过程中,仍然存在与药物的相互作用,甚至影响药物的物化性质和药理作用。试验表明,橡胶塞与注射液接触时,可能会出现橡胶塞吸收注射剂中的有效成分或者橡胶塞中的成分也可能被浸出至溶液中。 72天津药学T i anji n P harmacy2010年第22卷第1期*收稿日期:2009-12-16
GMP包装材料质量标准(1)
一、目的:制定通用纸箱的质量标准,规范公司通用纸箱的采购、检验、使用。 二、标准依据:《中华人民共和国国家标准》GB6543-86。 三、适用范围:适用于公司通用纸箱的采购、检验。 四、责任者:质保部全体人员、仓库管理员、采购员。 五、内容: 通用纸箱 B-01、B-02、B-03、B-45 【材质】本品材质为卡面纸、瓦楞纸板。 【外观】合拢摇盖,离缝重叠不得大于3mm。 箱体方正,表面没有明显的损坏和污迹,切断口表面裂损宽度不超过8mm。 箱面印刷文字、图案清晰深浅一致,位置准确,色泽鲜艳,颜色均匀。 纸箱接头钉合搭接舌边宽度35~50mm,金属钉应沿搭接部分中线钉合,箱钉应排列整齐、均匀,单排钉距不大于80mm,钉距均匀,头尾钉距底面压痕边线不超过20mm。 纸箱接头粘合搭接舌边宽度不小于30mm,粘合接缝的粘合剂涂布应均匀充分。 瓦楞纸箱的压痕线宽度,单瓦楞纸箱不大于12mm,双瓦楞纸箱不大于17mm,折
线居中,不得有破裂断线,箱壁没有多余的压痕线。 瓦楞纸箱摇盖经开、合180o往复5次,不得有裂缝。 粘合纸箱用乙酸乙烯乳液或具有同等效果的其它黏合剂。 纸箱附件纸箱附件应与纸箱配套。 规格箱子的基本尺寸符合下表要求: 允许误差±5mm、±5g
一、目的:制定塑料瓶的质量标准,规范公司塑料瓶的采购、检验、使用。 二、标准依据:《国家药品包装容器(材料)》标准、《中华人民共和国国家标准》 GB5009·60—85。 三、适用范围:适用于公司口服液药用瓶、液体消毒剂和杀虫剂用塑料瓶的采购、检验。 四、责任者:质保部全体人员、采购员、仓库管理员。 五、内容: 塑料瓶 【材质】口服液药用瓶的材质为聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯塑料;液体消毒剂和杀虫剂用瓶材质为聚丙烯塑料。 【外观】表面应清洁、光滑、无破损。 无污迹、卫生、洁净。 瓶盖应清洁、无破损、硬度好,与塑料瓶结合良好,气密性好。 规格尺寸:允许误差±2mm、±0.5g 口服液药用瓶应按下述方法进行微生物限度检测。 【微生物限度】按照微生物限度检查法检测,将口服液药用瓶用50ml0.9%灭菌氯化钠液冲洗内壁,作为供试液。取适宜的连续的2-3个稀释级的供试液1:10、1:100、1:1000的稀释液各1ml,置直径约90mm的平皿中,再注入约45℃的培养基约15ml,混匀,待凝固后,倒置培养,每稀释级作2个平皿。
注射用奥美拉唑钠分析报告
注射用奥美拉唑钠质量对比分析报告 上海医药工业研究院 二〇一三年五月
目录 目录 (1) 概述 (2) 一、质量标准 (3) 二、检测结果与统计分析 (3) 三、风险评估 (9) 四、总体评价 (9) 附件1 注射用奥美拉唑钠样品情况 (11) 附件2 注射用奥美拉唑钠碱度测定结果 (12) 附件3 注射用奥美拉唑钠溶液的澄清度与颜色测定结果 (13) 附件4 注射用奥美拉唑钠水分测定结果 (16) 附件5 注射用奥美拉唑钠有关物质 (17) 附件7 注射用奥美拉唑钠含量测定结果 (20) 附件8 注射用奥美拉唑钠风险评估 (21)
概述 奥美拉唑钠(Omeprazole Sodium)为胃壁细胞质子泵抑制剂,化学名:5-甲氧基-2-{[(4-甲氧基-3,5-二甲基-2-吡啶基)-甲基]-亚磺酰基}-1H-苯并咪唑钠盐一水合物,分子式:C17H18N3NaO3S·H2O;该药是苯并咪唑类衍生物,具有亚磺酰基苯并咪唑化学结构,化学性质不稳定,对光、热、湿、酸等条件均十分敏感,易降解变色。 奥美拉唑钠是阿斯利康制药有限公司(AstraZeneca,以下简称“阿斯利康”)首先研制,于1987年以商品名“Antra”在瑞士上市,1989年通过美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准在美国上市,商品名:“洛赛克”(LOSEC?)。 注射用奥美拉唑钠现行标准为国家药品标准WS1-(X-350)-2004Z-2011,浙江亚太药业股份有限公司(以下简称“亚太药业”)产品与阿斯利康制药有限公司(AstraZeneca,以下简称“阿斯利康”)产品均执行此标准;此标准为2011年 4 月10 日起实施的新国家标准,对原标准WS1-(X-350)-2004Z中的溶液的澄清度与颜色、有关物质和含量测定等项目进行了修订,更好的保证了注射用奥美拉唑钠安全有效、质量可控。 重要质控项目分析检测和统计分析结果显示,亚太药业12批样品之间的碱度、溶液的澄清度与颜色、水分、装量差异、有关物质、含量测定结果无显著差异,其产品具有良好的批内、批间均一性及稳定性;与阿斯利康公司原研产品相比,杂质个数较少、杂质总量相近,其余质量指标均无显著差异。 参照国家食品药品监督管理局国家药品评价性抽验工作中药品质量风险评估方法,依据国家药品标准WS1-(X-350)-2004Z-2011评估,亚太药业产品质量风险指数结果:批质量风险指数为57~65,企业单品种质量风险指数为61;阿斯利康公司原研产品质量风险指数结果:批质量风险指数为61~78,企业单品种质量风险指数为69。 从质量标准对比分析、样品检测与结果统计分析以及风险评估情况看,亚太药业产品执行的药品注册标准较完善,有利于产品的质量控制;其产品均一、稳定;质量不低于阿斯利康公司原研产品,达到国际先进水平。
药用丁基胶塞质量标准[指南]
药用丁基胶塞质量标准[指南] 药用丁基胶塞质量标准 药用氯化丁基橡胶塞标准(试行) YBB 00042002 本标准适用于直接与注射剂接触的氯化丁基橡胶塞。 【外观】取本品数个,目视检测,表面色泽应均匀,不得有污点、杂质、气泡、裂纹、缺胶、粗糙、胶丝、胶屑、海绵状、毛边;不得有除边造成的残缺或锯齿现象;不得有模具造成的明显痕迹。 【鉴别】(1)称取本品5,20g,置于干燥的试管中,将长约4毫米的钠片一片置于固定并倾斜的试管中,使其恰好位于试样之上,用火焰的尖端加热试管,将钠融化在试样上,继续加热2分钟,使呈深红色,冷却后加入乙醇,将过剩的钠醇化,加水约10ml溶解,过滤,滤液备用。 A:取滤液1.5ml置于试管中,加硝酸酸化,煮沸1,2分钟,加入硝酸银1滴,应产生白色沉淀。 B:取滤液0.2ml,置于微量试管中,加氯仿1滴,加稀硫酸1滴,加薪配置的氨水1滴(或3,H2O2溶液2,3滴),经振荡混匀后,静止5分钟,氯仿层应不显色。 (2)红外光谱取本品约3g切成3mm×3mm小块置索氏抽提器中用丙酮或适宜的溶剂回流浸提8小时,取残渣80?烘干,取0.1,0.2g置于裂解管的底部,然后用试管夹水平的将裂解管移到酒精灯上加热,当出现裂解产物冷凝在裂解管冷端时,再继续加热至裂解基本完全但没碳化为止,取少许裂解物滴在溴化钾片上,在80?烘干,照分光光度法(《中华人民共和国药典》2000年版二部?C)测定,应与对照图谱基本一致。
【穿刺落屑】输液瓶用胶塞:取10只被测胶塞和10只已知穿落屑数的胶塞分别装在与其相配的输液瓶上,每只瓶中注入半瓶水。加上铝盖,用手动封盖机封口,打开铝盖穿刺部位。按先被测胶塞再已知穿刺落屑数胶塞的顺序交替穿刺胶塞。穿刺时,胶塞保持直立,握持金属穿刺器(见图1)垂直向胶塞标记区域内穿刺,晃动数秒后拨出穿刺器。每次穿刺前用丙酮或甲基—异丁基酮擦拭穿刺器。 穿刺器不得有损坏,并保持锋利(如穿器损坏,须换用新的)。直至所有胶塞胶被穿刺一次。取下被测胶塞,将瓶中水全部通过快速滤纸过滤,确保瓶中不残留落屑。在一般条件下,眼与滤纸距离为25cm,用肉眼观察快速滤纸上的穿刺落屑数。对已知穿刺落屑数的胶 塞同法操作。被测胶塞落屑总数不得过20粒(注:如果已知穿刺落屑数胶塞的结果与先前测得的结果具有一致性,则应判被测胶塞测得的结果有效。反之,则无效)。 抗生素瓶用胶塞:胶塞预处理:取适量胶塞加二倍胶塞总表面积(Acm2)的水 (2Aml)。煮沸5min,用水冲洗5次,将胶塞放入三角烧瓶中,加2Aml水,用铝箔或一只硅硼酸盐烧杯将烧杯瓶口盖住,放入高压蒸汽消毒器中加热,在30分钟内升温至121??2?,保持30分钟,于20,30分钟内冷却至室温,取出,在60?条件下烘60min,贮存于密封的玻璃容器中备用。 选择50只与被测胶塞相配的注射剂瓶,每只瓶中注入半瓶水。将被测胶塞装在25只瓶上,将25只已知穿刺落屑数的胶塞装在另25只瓶上,胶塞均预处理过。加上铝盖,用手动封盖机封口,打开铝盖穿刺部位。按先被测胶塞再已知穿刺落屑数胶塞的顺序交替穿刺胶塞。穿刺时,胶塞保持直立,将注射器充水并除去注射针头(外径0.8mm)上的水,垂直向胶塞标记区域内穿刺,再重复三次,最后一次拔出针头前,将1ml水注入瓶内。每次穿刺前用丙酮或甲基—异丁基酮擦拭注射针。
奥美拉唑-欧洲8.0药典
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0 Omeprazole 04/2013:0942OMEPRAZOLE Omeprazolum C 17H 19N 3O 3S M r 345.4 [73590-58-6] DEFINITION 5-Methoxy-2-[(RS )-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sul?nyl]-1H -benzimidazole.Content :99.0per cent to 101.0per cent (dried substance).CHARACTERS Appearance :white or almost white powder.Solubility :very slightly soluble in water,soluble in methylene chloride,sparingly soluble in ethanol (96per cent)and in methanol.It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.It shows polymorphism (5.9).IDENTIFICATION Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).Comparison :omeprazole CRS .If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences,dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in methanol R ,evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues. TESTS Solution S .Dissolve 0.50g in methylene chloride R and dilute to 25mL with the same solvent. Appearance of solution .Solution S is clear (2.2.1). Impurities F and G :maximum 350ppm for the sum of the contents. The absorbance (2.2.25)of solution S determined at 440nm is not greater than 0.10. Related substances .Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).Prepare the solutions immediately before use . Test solution .Dissolve 3mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 25.0mL with the mobile phase.Reference solution (a).Dissolve 1mg of omeprazole CRS and 1mg of omeprazole impurity D CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0mL with the mobile phase. Reference solution (b).Dilute 1.0mL of the test solution to 100.0mL with the mobile phase.Dilute 1.0mL of this solution to 10.0mL with the mobile phase. Reference solution (c).Dissolve 3mg of omeprazole for peak identification CRS (containing impurity E)in the mobile phase and dilute to 20.0mL with the mobile phase.Column : –size :l =0.125m,?=4.6mm; –stationary phase :octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5μm). Mobile phase :mix 27volumes of acetonitrile R and 73volumes of a 1.4g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R previously adjusted to pH 7.6with phosphoric acid R .Flow rate :1mL/min. Detection :spectrophotometer at 280nm.Injection :40μL. Run time :5times the retention time of omeprazole. Identification of impurities :use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a)to identify the peak due to impurity D;use the chromatogram supplied with omeprazole for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c)to identify the peak due to impurity E. Relative retention with reference to omeprazole (retention time =about 9min):impurity E =about 0.6;impurity D =about 0.8. System suitability :reference solution (a): –resolution :minimum 3.0between the peaks due to impurity D and omeprazole;if necessary,adjust the pH of the aqueous part of the mobile phase or the concentration of acetonitrile R ;an increase in the pH will improve the resolution.Limits : –impurities D,E :for each impurity,not more than 1.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.15per cent); –unspecified impurities :for each impurity,not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.10per cent);–total :not more than 5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b)(0.5per cent); –disregard limit :0.5times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05per cent).Loss on drying (2.2.32):maximum 0.2per cent,determined on 1.000g by drying under high vacuum at 60°C for 4h.Sulfated ash (2.4.14):maximum 0.1per cent,determined on 1.0g.ASSAY Dissolve 0.250g in a mixture of 10mL of water R and 40mL of ethanol (96per cent)R .Titrate with 0.1M sodium hydroxide ,determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).1mL of 0.1M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 34.54mg of C 17H 19N 3O 3S. STORAGE In an airtight container,protected from light,at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C. IMPURITIES Specified impurities:D,E,F,G . Other detectable impurities (the following substances would,if present at a suf?cient level,be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph.They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspeci?ed impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034).It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance.See also 5.10.Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use ):A,B,C,H,I . A.5-methoxy-1H -benzimidazole-2-thiol, B.2-[(RS )-[(3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sul?nyl]-5-methoxy-1H -benzimidazole, General Notices (1)apply to all monographs and other texts 2911
橡胶制品检验标准
橡胶制品进料检验标准 一目的明确橡胶制品进料品质验收标准,规范检验动作,使检验、判定标准能达到一致性 二范围本标准规定了橡胶制品进料检验的技术要求、包装要求、检验规则。本标准适用于本公司所有橡胶制品的进料检验。 三检验项目及规则 外观检验 ●制品表面应整洁,无飞过,毛剌等,且不允许有杂质,无明显划痕,泡状突起.表面纹路自然,表面无可见的微粒,无折射缺陷及浇注口印迹,流痕等. 目测和手感 尺寸检查 ●橡胶件尺寸必须按规定程序批准的产品设计图纸和各相关的国家标准制造,必须符合产品图样或技术文件的要求. 卷尺和卡尺 耐汽油性检查 ●在40OC的环境温度下,放在汽油中浸泡48h后,其本积变化率应小于10%,硬度变化为-25RHD以内,拉断强度变化率应在-35%以内,拉伸变化率在-20%以内。
耐润滑油性检查 ●在70OC的环境温度下,放在润滑油中浸泡72h后,其体积变化率在-10%~+15%之间,硬度变化为-5~+10RHD之间,拉断强度变化率应在10%以内,伸长变化率在-30%以内。 硬度检查 ●橡胶件硬度应符合产品图纸或技术文件的要求。常用橡胶件的材质及硬度值,仅作为一般批产件验收参考,如有特殊要求时,请以经确认的技术要求执行。 耐老化性能检查 ●橡胶件必须具有一定的耐老化性。橡胶件在70OC温度试验下,经72h热空气老化试验后,其硬度变化不超过±15%IRHD,拉伸强度变化率不超过±30%,拉断伸长率变化不超过-50%。 耐温性能检查 ●低温试验后试样敲击无破现象,高温试验后试样弹性良好,弯折无龟裂现象。 裂缝试验 ●根据样品具体形状,用样品的全部或者取其中的一部分呈长条型,将其拉长10%,在变形的情况下,呈南北或东西方向放置三个月,在
药用包装材料质量标准ISO15378(中文)
ISO 15378: 2006 标准的中文版内容 国际标准化组织 /第76技术委员会 (IS0/TC76) 于2003年制定了 1S0 15378国际标准草案 (Draft of interrfational standard ,D1S),标题是:《药品初包装材料 ISO 9001:2008 应用的专用要求,包含生产质量管理规范(GMP) 》。2006 年,形成了借鉴 ISO 9001:2008 质量体系的《药用包装材料质量标准 ISO 15378 : 2006 》初稿。这个国际标准的制定说明了国际社会对药包材生产企业实施质量管理的重视。此处择其要简介其主要内容 (略去的有些内容可参见 ISO 9001: 2008 标准) ( 一 ) 引言 引言部分包括 :总则;过程方法;与 ISO 9004 的关系;与其他管理体系的相容性。 0.1 总则 本标准把 GMP原理和 QMS质量管理体系规定的要求应用于药品的初包装材料。由于初包装材料与药品直接接触,组织 (企业) 对初包装材料的生产和质量控制中的领会 GMI'原理对于患者使用药品时的安全性是非常重要的。药用包装材料应用 GMP应能确保这些材料满足制药工业的需求。 采用 QMS应当是组织的一项战略性决策。一个组织 QMS的设计和实施受各种需求、具体目标、所提供的产品、所采用的过程以及该组织的规模和结构的影响。 . ISO 15378 的主要目的是规定协商的初包装材料的要求。它包括一些初包装材料的专用要求,这些要求出自药品生产、控制等生产质量管理规范。 0.2 过程方法 本标准鼓励在建立、实施 QMS以及改进其有效性时采用过程方法,通过满足顾客要求,增强顾客满意。 过程方法在 QMS中应用时,强调以下方面的重要性: (1)理解并满足要求 ;
MSDS奥美拉唑镁
OMEPRAZOLE MAGNESIUM CRS êX Xi : Irritant Trade name:OMEPRAZOLE MAGNESIUM CRS Use:For laboratory tests and assays only, as described in the European Pharmacopoeia. Directions for use:For any questions: www.edqm.eu/hd (HelpDesk) Company identification:EDQM 7, Allée Kastner CS 30026 F-67081 Strasbourg FRANCE Tel. +33 (0)3 88 41 20 35 Fax. + 33 (0)3 88 41 27 71 Risk Phrases:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. - May cause sensitization by skin contact. - Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. Adverse human health effects:Metabolism and nutrition disorders. Breathing difficulties. Gastrointestinal disorders. Fever. Sore throat. Nausea. Vomiting. Exposure may produce an allergic reaction. Components:This product is hazardous. Substance name Contents CAS No EC No Annex No Classification Omeprazole magnesium:95382-33-5---------------Xi; R36/37/38 R43 R52-53 First aid measures - Inhalation:Assure fresh air breathing. Rest. If you feel unwell, seek medical advice. - Skin contact:Remove affected clothing and wash all exposed skin area with mild soap and water, followed by warm water rinse. - Eye contact:Rinse immediately with plenty of water. Obtain medical attention if pain, blinking, tears or redness persist. - Ingestion:Rinse mouth. If swallowed, seek medical advice immediately and show this container or label. In case of reactions described in hazards identification or other severe, immediate or persisting symptoms seek medical advice and call the nearest poison centre. Show the label and this safety data sheet. Extinguishing media
