临床试验英语词汇

专业术语、缩略语中英对照表
缩略语英文全称中文全称
ABE Average Bioequivalence 平均生物等效性
AC Active control 阳性对照
ADE Adverse Drug Event 药物不良事件
ADR Adverse Drug Reaction 药物不良反应
AE Adverse Event 不良事件
AI Assistant Investigator 助理研究者
ALB Albumin 白蛋白
ALD Approximate Lethal Dose 近似致死剂量
ALP Alkaline phosphatase 碱性磷酸酶
ALT Alanine aminotransferase 丙氨酸转氨酶ANDA Abbreviated New Drug Application 简化新药申请ANOV A Analysis of variance 方差分析
AST Aspartate aminotransferase 天冬氨酸转氨酶ATR Attenuated total reflection 衰减全反射法
BA Bioavailability 生物利用度
BE Bioequivalence 生物等效性
BMI Body Mass Index 体质指数
BUN Blood urea nitrogen 血尿素氮
CA TD Computer-assisted trial design 计算机辅助试验设计CDER Center of Drug Evaluation and Research 药品评价和研究中心CFR Code of Federal Regulation 美国联邦法规
CI Co-Investigator 合作研究者
CI Confidence Interval 可信区间
COI Coordinating Investigator 协调研究者
CRC Clinical Research Coordinator 临床研究协调者
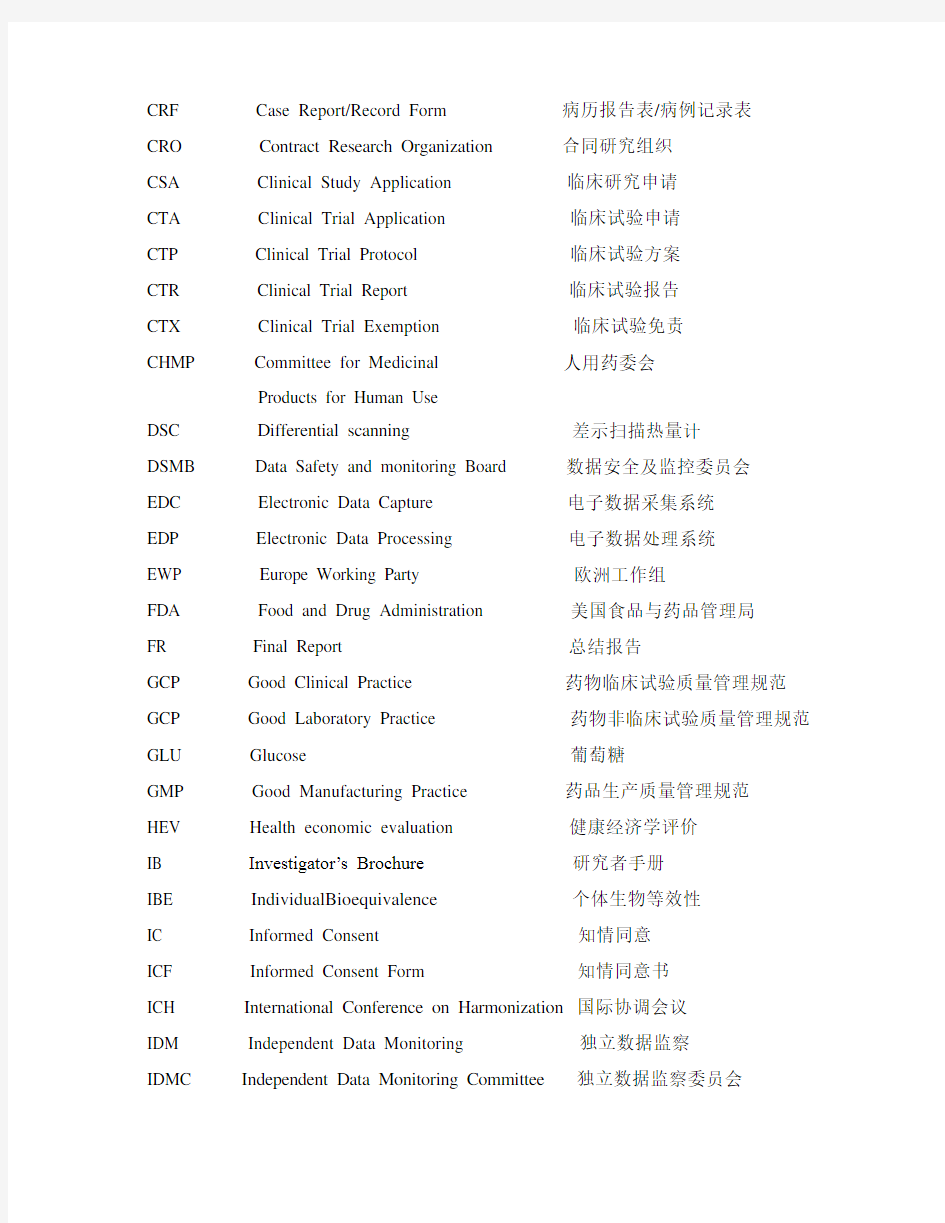
CRF Case Report/Record Form 病历报告表/病例记录表
CRO Contract Research Organization 合同研究组织
CSA Clinical Study Application 临床研究申请
CTA Clinical Trial Application 临床试验申请
CTP Clinical Trial Protocol 临床试验方案
CTR Clinical Trial Report 临床试验报告
CTX Clinical Trial Exemption 临床试验免责
CHMP Committee for Medicinal 人用药委会
Products for Human Use
DSC Differential scanning 差示扫描热量计
DSMB Data Safety and monitoring Board 数据安全及监控委员会
EDC Electronic Data Capture 电子数据采集系统
EDP Electronic Data Processing 电子数据处理系统
EWP Europe Working Party 欧洲工作组
FDA Food and Drug Administration 美国食品与药品管理局
FR Final Report 总结报告
GCP Good Clinical Practice 药物临床试验质量管理规范GCP Good Laboratory Practice 药物非临床试验质量管理规范GLU Glucose 葡萄糖
GMP Good Manufacturing Practice 药品生产质量管理规范
HEV Health economic evaluation 健康经济学评价
IB Investigator’s Brochure研究者手册
IBE IndividualBioequivalence 个体生物等效性
IC Informed Consent 知情同意
ICF Informed Consent Form 知情同意书
ICH International Conference on Harmonization 国际协调会议
IDM Independent Data Monitoring 独立数据监察
IDMC Independent Data Monitoring Committee 独立数据监察委员会
IEC Independent Ethics Committee 独立伦理委员会
IND Investigational New Drug 新药临床研究
IRB Institutional Review Board 机构审查委员会
ITT Intention-to –treat 意向性分析
IVD In Vitro Diagnostic 体外诊断
IVRS Interactive Voice Response System 互动语音应答系统
LD50 Medial lethal dose 半数致死剂量
LLOQ Lower Limit of quantitation 定量下限
LOCF Last observation carry forward 最接近一次观察的结转LOQ Limit of Quantitation 检测限
MA Marketing Approval/Authorization 上市许可证
MCA Medicines Control Agency 英国药品监督局
MHW Ministry of Health and Welfare 日本卫生福利部
MRT Mean residence time 平均滞留时间
MTD Maximum Tolerated Dose 最大耐受剂量
ND Not detectable 无法定量
NDA New Drug Application 新药申请
NEC New Drug Entity 新化学实体
NIH National Institutes of Health 国家卫生研究所(美国)NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance 核磁共振
PD Pharmacodynamics 药效动力学
PI Principal Investigator 主要研究者
PK Pharmacokinetics 药物动力学
PL Product License 产品许可证
PMA Pre-market Approval (Application) 上市前许可(申请)
PP Per protocol 符合方案集
PSI Statisticians in the Pharmaceutical Industry 制药业统计学家协会QA Quality Assurance 质量保证
QAU Quality Assurance Unit 质量保证部门
QC Quality Control 质量控制
QWP Quality Working Party 质量工作组
RA Regulatory Authorities 监督管理部门
REV Revision 修订
SA Site Assessment 现场评估
SAE Serious Adverse Event 严重不良事件
SAP Statistical Analysis Plan 统计分析计划
SAR Serious Adverse Reaction 严重不良反应
SD Source Data/Document 原始数据/文件
SD Subject Diary 受试者日记
SDV Source Data Verification 原始数据核准
SEL Subject Enrollment Log 受试者入选表
SFDA State Food and Drug Administration 国家食品药品监督管理局SI Sponsor-Investigator 申办研究者
SI Sub-investigator 助理研究者
SIC Subject Identification Code 受试者识别代码
SOP Standard Operating Procedure 标准操作规程
SPL Study Personnel List 研究人员名单
SSL Subject Screening Log 受试者筛选表
T&R Test and Reference Product 受试和参比试剂
T-BIL Total Bilirubin 总胆红素
T-CHO Total Cholesterol 总胆固醇
TG Thromboglobulin 血小板球蛋白
Tmax Time of maximum concentration 达峰时间
TP Total proteinum 总蛋白
UAE Unexpected Adverse Event 预料外不良事件
WHO World Health Organization 世界卫生组织
WHO- WHO International Conference WHO 国际药品管理当局会议ICDR A of Drug Regulatory Authorities
Aberrant result 异常结果
Absorption phase 吸收相
Absorption 吸收
Accuracy 准确度
Accurate 精密度
Administer 给药
Amendment修正案
Approval 批准
Assess 估计
Audit Report 稽查报告
Audit 稽查
Auditor 稽查员
Analytical run/batch:分析批
Benefit 获益
Bias 偏性,偏倚
Bioequivalence 生物等效
Biosimilar /Follow-on biologics 生物仿制药
Blank Control 空白对照
Blind codes 编制盲底
Blind review 盲态检查/盲态审核
Blinding method 盲法
Blinding/masking 盲法/设盲
Block size 每段的长度
Block 层/分段
BCS 生物药剂学分类系统
Carryover effect 延滞效应
Case history 病历
Clinical equivalence 临床等效性
Clinical study 临床研究
Clinical Trial Report 临床试验报告
Comparison 对照
Compensation 补偿,赔偿金
Compliance 依从性
Concomitant 伴随的
Conduct 行为
Confidence level 置信水平
Consistency test 一致性检验
Contract/ agreement 协议/合同
Control group 对照组
Coordinating Committee 协调委员会
Crossover design 交叉设计
Cross-over Study 交叉研究
Cure 痊愈
Data management 数据管理
Descriptive statistical analysis 描述性统计分析
Dichotomies 二分类
Dispense 分布
Diviation 偏差
Documentation 记录/文件
Dosage forms 剂型
Dose dumping 剂量倾卸(药物迅速释放入血而达到危险浓度)Dose-reaction relation 剂量-反应关系
Double blinding 双盲
Double dummy 双模
Drop out 脱落
Effectiveness 疗效
Elimination phase 消除相
Emergency envelope 应急信件Enantiomers 对映体
End point 终点
Endpoint criteria/ measurement 终点指标Enterohepatic recycling 肠肝循环Essential Documentation 必需文件Ethical 伦理的
Ethics committee 伦理委员会
Evaluate 评估
Exclusion Criteria 排除标准
Excretion 排泄
Expedite 促进
Extrapolated 外推的
Essentially similar product:基本相似药物Factorial design 析因设计
Failure 无效,失败
Finacing 财务,资金
Final point 终点
First pass metabolism 首过代谢
Fixed-dose procedure 固定剂量法
Full analysis set 全分析集
GC-FTIR 气相色谱-傅利叶红外联用GC-MS 气相色谱-质谱联用
Generic drug 通用名药
Gene mutation 基因突变
Genotoxicity tests 生殖毒性试验
Global assessment variable 全局评价变量Group sequential design 成组序贯设计Hypothesis test 假设检验
Highly permeable:高渗透性
Highly soluble:高溶解度
Highly variable drug:高变异性药物Highly:Variable Drug 高变异性药物HVDP:高变异药物制剂
Identification 鉴别,身份证Improvement 好转
In vitro 体外
In vivo 体内
Inclusion Criteria 入选表准
Information Gathering 信息收集
Initial Meeting 启动会议
Inspection 检察/视察
Institution Inspection 机构检察Instruction 指令,说明
Integrity 完整,正直
Intercurrent 中间发生的,间发的
Inter-individual variability 个体间变异性Interim analysis 期中分析Investigational Product 试验药物Investigator 研究者
Involve 引起,包括
IR 红外吸收光谱
Innovator Product:原创药
Ka 吸收速率常
LC-MS 液相色谱-质谱联用
logarithmic transformation 对数转换
Logic check 逻辑检查
Lost of follow up 失访
Mask 面具,掩饰
Matched pair 匹配配对
Metabolism 代谢
Missing value 缺失值
Mixed effect model 混合效应模式
Modified release products 改良释放剂型Monitor 监查员
Monitoring Plan 监察计划
Monitoring Report 监察报告
MS-MS 质谱-质谱联用
Multi-center Trial 多中心试验
Negative 阴性,否定的
Non-clinical Study 非临床研究
Non-inferiority 非劣效性
Non-Linear Pharmacokinetics 非线性药代动力学Non-parametric statistics 非参数统计方法NTID:窄治疗指数制剂
Obedience 依从性
Open-blinding 非盲
Open-label 非盲
Original Medical Record 原始医疗记录Outcome Assessment 结果评价
Outcome measurement 结果指标
Outlier 离群值
OIP 经口服吸收药物
Parallel group design 平行组设计Parameter estimation 参数估计
Parametric statistics 参数统计方法
Patient file 病人档案
Patient History 病历
Per protocol,PP 符合方案集Permeability 渗透性
Pharmacodynamic characteristics 药效学特征Pharmacokinetic characteristics 药代学特征Placebo Control 安慰剂对照
Placebo 安慰剂
Polytomies 多分类
Post-dosing postures 给药后坐姿
Potential 潜在的
Power 检验效能
Precision 精密度
Preclinical Study 临床前研究
Precursor 母体前体
Premature 过早的,早发
Primary endpoint 主要终点
Primary variable 主要变量
Prodrug 药物前体
Protocol amendment 方案补正
Protocol Amendments 修正案
Protocol 试验方案
Quality Control Sample:质控样品
Rapidly dissolving:快速溶出
Racemates 外消旋物
Randomization 随机/随机化
Range check 范围检
Rating scale 量表
Recruit 招募,新会员
Replication 可重复
Retrieval 取回,补修
Revise 修正
Risk 风险
Run in 准备期
Safety evaluation 安全性评价
Safety set 安全性评价的数据集
Sample Size 样本量、样本大小
Sampling schedules 采血计划
Scale of ordered categorical ratings 有序分类指标Secondary variable 次要变量
Sequence 试验次序
Seriousness 严重性
Severity 严重程度
Significant level 检验水准
Simple randomization 简单随机
Single Blinding 单盲
Site audit 试验机构稽查
Solubility 溶解度
Specificity 特异性
Specify 叙述,说明
Sponsor-investigator 申办研究者
Standard curve 标准曲线
Statistical model 统计模型
Statistical tables 统计分析表
Steady state 稳态
Storage 储存
Stratified 分层
Study Audit 研究稽查
Study Site 研究中心
Subgroup 亚组
Sub-investigator 助理研究者
Subject Enrollment Log 受试者入选表
Subject Enrollment 受试者入选
Subject Identification Code List 受试者识别代码表
Subject Recruitment 受试者招募
Subject Screening Log 受试者筛选表
Subject 受试者
Submit 交付,委托
Superiority 检验
Supplemental 增补的
Supra-bioavailability 超生物利用度(试验药的生物利用度大于对照药)Survival analysis 生存分析
System Audit 系统稽查
SmPC:药品说明书
Standard Sample:标准样品
Target variable 目标变量
Treatment group 试验组
Trial error 试验误差
Trial Initial Meeting 试验启动会议
Trial Master File 试验总档案
Trial Objective 试验目的
Trial site 试验场所
Triple Blinding 三盲
Two one-side test 双单侧检验
Therapeutic equivalence:治疗等效性
Un-blinding 破盲/揭盲
Verify 查证、核实
Visual analogy scale 直观类比打分法
Vulnerable subject 弱势受试者
Wash-out Period 洗脱期
Well-being 福利,健康
Withdraw 撤回,取消
药代动力学参数
Ae(0-t):给药到t时尿中排泄的累计原形药。
AUC: 血浆浓度-时间曲线下面积
AUCτ:
AUC(0-t):从给药到时间t时血药浓度曲线下面积
AUC(0-∞):从给药到所有原形药物全部被消除的血药浓度曲线下面积
AUC(0- ):达稳态时一个剂量间隔期间的血药浓度曲线下面积
AUC(0-72h):从开始给药到给药后72小时血药浓度曲线下面积
AUC0-:血药浓度-时间曲线从时间0到无穷远的曲线下面积
AUC0-tau:血药浓度-时间曲线在稳态时,从时间0到T的曲线下面积( T为给药间隔时间)
AUCss:稳态药时曲线下面积
C max:最大血药浓度
C max,ss:最大稳态血药浓度
C min,ss:最小稳态血药浓度
Cmin:给药间隔末的浓度
Ct:最后一次可测量到的药物浓度
Cav:平均稳态血药浓度Cav=AUCss/τ
残留面积:外推面积((AUC(0-∞) - AUC(0-t))/ AUC(0-∞))R max:最大尿排泄速率
t max:达峰时间
t max,ss:最大稳态血药浓度达峰时间
t1/2:血药浓度半衰期(Elimination half life)
τ:给药时间间隔
F:相对生物利用度:
λz:终末速率常数
Z:终末或消除速率常数
CL:clearance清除率CL h 肝清除率CL r肾清除率CI:confidence interval 可信区间
DF:波动系数
CV:个体内变异系数
[U,L]=exp[±k*s WR]
S WR:为参比制剂C max值经对数转换后的个体内标准差U:指可接受的上限值
L:为可接受的下限值
θ:个体差别
f2-test / f2:相似因子(体外溶出试验)
速记英语单词的好方法及口诀
各门科都正是打基础的时候,如果基础没有打好,不要说想学好这门科了。今天为大家整理了英语单词速记法,希望这些英语单词对提高同学们英语成绩有所帮助。 英语单词速记口诀 1、冲出黄眉老怪巢穴 偷他的car(小汽车) 冲挡路bar(栏杆) 加速跑far(遥远) 天上出star(星星) 2、猪八戒探路 误闯入airport(飞机场) 向唐僧report(报告): 大鸟爱sport(运动) 腿圆且short(短的) 3、猪八戒思念高翠兰 天空是clear(晴朗的) 叫一声dear(亲爱的) 你可能hear(听见) 我还是near(近的) 即将新year(年) 寄回个pear(梨) 4、孙悟空回忆深山学艺时 一个class(班) 坐在grass(草地)
手拿glass(玻璃杯) 挨个pass(传) 5、牛魔王听说小红孩被杀 小红孩的dad(爸爸) 听到消息bad(坏的) 内心里面sad(悲伤的) 知道是谣言glad(高兴的) 大口吃着salad(沙拉) 6、八戒重回高老庄见小孙子左手牵grandpa(爷爷) 右手牵grandma(奶奶) 走进了cinema(电影院) 坐下吃banana(香蕉) 屏幕看China(中国) 7、二郎神的哮天犬 颜色是yellow(黄色) 把主人follow(跟随) 天将要snow(下雪) 能提前know(知道) 8、孙悟空和六耳猕猴到如来前风吹动air(空气) 来猴子a pair(一对)
对如来chair(椅子) 一起喊sir(先生) 请把他repair(修理) 回荡声音their(他们的)(请如来“修理”对手。)9、唐僧出长安独行荒山 行走在road(路) 把经书read(读) 感觉是tired(累的) 水和饭need(需要) 黑夜里afraid(害怕的)野狼一hundred(百) 牙齿是pointed(尖的)10、洞穴发现妖怪 头发是red(红色的) 睡一张bed(床) 巨大的head(头) 枕一个bread(面包)11、光屁股哪吒闹海 淘气的child(孩子) 永远不old(老的) 也不觉cold(冷的)
现代英语词汇学概论最强版复习资料chapter
现代英语词汇学概论最强版复习资料c h a p t e r 文件管理序列号:[K8UY-K9IO69-O6M243-OL889-F88688]
Chapter 9 Changes in Word Meaning 9.1 Causes of Changes in Word Meaning 9.2 Four Tendencies in Semantic Change 9.3 Semantic Development or Change Resulting from the Figurative Use of Words Definition: Change of meaning refers to the alteration of the meaning of existing words, as well as the addition of new meaning to established words. 9.1 Causes of Changes in Word Meaning A.Historical cause 历史原因 It often happens that though a word retains its original form ,its meaning has changed because the object which it denotes has changed . *Changes of meaning because of increased knowledge of the object described are common in the history of science. Eg. pencil ==is from a Latin word meaning “a little tail” or “a fine brush”, like our Chinese “pen”毛笔.Later, when it was made of wood and graphite ,it was still called a “pencil”. atom ==It was borrowed though Latin and French from Greek arouos,invisible. Thus atom meant originally “an particle too small to be divided”. This meaning is now out-of-date, because scientist have found out that atom can be split.
(完整版)英语词汇学英语词汇学习题3及答案
试题三 第一部分选择题 I. Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers. Choose the one that would best complete the statement and put the letter in the bracket.(30%) 1.According to the degree of similarity, homonyms can be classified into ( ) A. perfect homonyms B. homonyms C. homophones D. all the above 2.Transfer as a mode of semantic change can be illustrated by the example ( ) A. ad for “advertisement” B. dish for “food" C. fond for “affectionate” D. an editorial for “an editorial article" 3.It is a general belief that the meaning does not exist in the word itself, but it rather spreads over ( ) A. the reader’s interpretation B. the neighbouring words C. the writer's intention D. the etymology of the word 4.Which of the following is a prefix of time and order? A. extra- B. pro- C. re- D. semi- 5.Which of the following dictionaries is not a specialized dictionary? A. The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology B. Chamber's Encyclopedic English Dictionary C. Longmont Dictionary of Phrasal Verbs D. Webster's New Dictionary of Synonyms 6.Which of the following statements is Not true? A. Reference is the relationship between language and the world. B. The relationship between a word and its referent is arbitrary. C. Concept is universal to all men alike. D. Sense denotes the relationships outside the language. 7.The words which occur before or after a word and may affect its meaning form ( ) A. physical context B. grammatical context C. lexical context D. linguistic context 8."Smith is an architect. He designed World Trade Center. "The clue provided in the context is ( ) A. definition B. explanation C. example D. hyponym 9.The term "vocabulary" is used in different ways because of all the following reasons EXCEPT that ( ) A. it can refer to the common core of a language B. it can refer to the total number of the words in a language C. it can represent all the words used in a certain historical period D. it can stand for words in given dialect or field 10.The idiom "a dark horse" is a ( ) A. simile B. metaphor
2017年在职研究生考研英语二真题及答案解析
2017年在职研究生考研英语二真题及答案解析 考研教育英语教研室 Section I Use of English Directions: Read the following text. Choose the best word (s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on the ANSWER SHEET. (10 points) People have speculated for centuries about a future without work.Today is no different,with academics,writers,and activists once again 1 that technology is replacing human workers. Some imagine that the coming work-free world will be defined by 2 . A few wealthy people will own all the capital,and the masses will struggle in an impoverished wasteland.. A different and not mutually exclusive 3 holds that the future will be a wasteland of a different sort,one 4 by purposelessness:Without jobs to give their lives 5 ,people will simply become lazy and depressed. 6 today’s unemployed don’t seem to be having a great time. One Gallup poll found that 20 percent of Americans who have been unemployed for at least a year report having depression,double the rate for 7 Americans. Also,some research suggests that the 8 for rising rates of mortality,mental-health problems,and addicting9 poorly-educated middle-aged people is shortage of well-paid jobs. Perhaps this is why many 10 the agonizing dullness of a jobless future. But it doesn’t 11 follow from findings like these that a world without work would be filled with unease. Such visions are based on the 12 of being unemployed in a society built on the concept of employment. In the 13 of work,a society designed with other ends in mind could 14 strikingly different circumstances for the future of labor and leisure. Today,the 15 of work may be a bit overblown. “Many jobs are boring,degrading,unhealthy,and a waste of human potential,” says John Danaher,a lecturer at the National University of Ireland in Galway. These days,because leisure time is relatively 16 for most workers,people use their free time to counterbalance the intellectual and emotional 17 of their jobs. “When I come home from a hard day’s work,I often feel 18 ,” Danaher says,adding,“In a world in which I don’t have to work,I might feel rather different”—perhaps different enough to throw himself 19 a hobby or a passion project with the intensity usually reserved for 20 matters.
初中英语词汇辨析的知识点总复习含解析(5)
一、选择题 1.I’d like to________the mall because it’s crowded and noisy. A.visit B.hang out C.walk D.go off 2.It’s ________ of the soldiers to rush into the fire to save people. A.stupid B.proud C.honest D.brave 3.In modern life, shopping online is________ used by many people, especially for teenagers. A.exactly B.badly C.heavily D.widely 4.—Oh, my God! I have ________ five pounds after the Spring Festival. —All of the girls want to lose weight, but easier said than done. A.given up B.put on C.got on D.grown up 5.— Sorry, I can't afford to go abroad. — What about having a country travel with a little________ price? A.cheaper B.higher C.lower D.less 6.My sister Nancy often gets lost because of her bad _____ of direction. A.sense B.feeling C.experience D.information 7.—Help yourselves! The drinks are ________ me. —Thank you. You’re always so generous. A.above B.in C.on D.over 8.Her only problem, ________ you can call it a problem, is that she expects to be successful all the time. A.if B.because C.though D.since 9.We should learn_______ each other. A.to B.from C.for D.of 10.We loved the food so much, ________the fish dishes. A.special B.especial C.specially D.especially 11.— Is your home close to the school, Tom? — No, it's a long way, but I am________ late for school because I get up early daily. A.always B.usually C.never D.sometimes 12.Remember to return the book to the school library in time, ________ you will be fined(罚款). A.or B.and C.but D.so 13.—Billy, you are very confident all the time, how do you make it? —I think confidence is more than just an attitude, it comes from a strong ________ to take responsibility rather than just let life happen. A.present B.care C.promise D.protect 14.—Does she have a ________? — Yes, she ________ in a food shop. A.job; work B.job; works C.work; job
(完整版)全国英语词汇学(00832)高等教育自学考试试题与答案
全国高等教育自学考试 英语词汇学试题 课程代码:00832 Ⅰ.Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers. Choose the one that best completes the statement and put the letter in the bracket.(30%)1.According to semanticists, a word is a unit of ______.() A.meaning B.Sound C.combination of sounds D.Group 2.The pronunciation has changed ______ spelling over the years.() A.more slowly than B.As quickly as C.more rapidly than D.Not so quickly as 3.Words may fall into the basic word stock and nonbasic vocabulary by ______.()A.use frequency B.notion C.origin D.sound 4.Rapid growth of science and technology breeds such new words as the following EXCEPT______.() A.green revolution B.fast food C.moon walk D.space shuttle 5.Semantic change means an old form which takes on a new ______ to meet the new need. ()A.form B.meaning C.look D.pronunciation 6.Reviving archaic words also contribute to the growth of English vocabulary. For instance, in American English “fall” means ______ in British English.() A.four B.fell C.for D.autumn 7.The plural morpheme “-s” is realized by /s/after the following sounds EXCEPT ______. ()A./t/ B./g/ C./p/ D./k/ 英语词汇学试卷第 1 页共9 页
在职博士英语考试大纲
在职博士英语考试大纲 迅速发展的经济带来越来越重的经济压力,很多在职人员通过提升自己已获得更高的薪资,博士学位作为最高的学历,在职博士首当其冲成为首选,而当再一次面对英语考试,更多的是陌生和迷茫,国家统一考试规定的具体内容是什么呢?下面就为大家介绍一下在职博士英语考试大纲。 考试对象: 报考开设在职博士专业所属院校拟攻读博士学位的考生(全国统一试题)。 考试目的: 检验考生是否具有进入攻读博士学位阶段的英语水平和能力。 考试共有五个部分:词汇(占10%)、完形填空(占15%)、阅读理解(占40%)、英译汉占(15%),写作(占20%)。试卷分为:客观试题,包括前三个部分,共75题,顺序排号;主观试题,包括英译汉和写作两个部分。 一、词汇: 主要测试考生是否具备一定的词汇量和根据上下文对词和词组意义判断的能力。词和词组的测试范围基本以考试大纲词汇表为参照依据。 共20题。每题为一个留有空白的英文句子。要求考生从所给的四个选项中选出可用在句中的最恰当词或词组。
二、完形填空: 主要测试考生在语篇层次上的理解能力以及对词汇表达方式和结构掌握的程度。考生应具有借助于词汇、句法及上下文线索对语言进行综合分析和应用的能力。要求考生就所给篇章中15处空白所需的词或短语分别从四个选项中选出最佳答案。 三、阅读理解: 本部分共分两节。要求考生能: 1)掌握中心思想、主要内容和具体细节; 2)进行相关的判断和推理; 3)准确把握某些词和词组在上下文中的特定含义; 4)领会作者观点和意图、判断作者的态度。 A节:主要测试考生在规定时间内通过阅读获取相关信息的能力。考生须完成1800-2000词的阅读量并就题目从四个选项中选出最佳答案。 B节:主要测试考生对诸如连贯性和一致性等语段特征的理解。考生须完成700-900词的阅读量(2篇短文),并根据每篇文章(约400词)的内容,从文后所提供的6段文字中选择能分别放进文章中5个空白处的5段。 四、英译汉:
一种趣味无穷的英语单词记忆方法——顺口溜
一种趣味无穷的英语单词记忆方法——顺口溜 英语有大量的单词需要记忆,据说国内很多大学毕业生甚至研究生和博士生词汇量严重不足(本人也有同感),连简单的英文日报阅读起来都非常吃力,说明传统的教学方法有很大需要改进的余地。尤其在是知识信息和爆炸的时代,效率和时效性已经成为一个衡量学习效果的重要杠杆。如果我们改变传统的记忆方式,学习效果可能会更好。比如把这些单词编成顺口溜,请看下列一组单词: 猫和老鼠- 有一个rat(老鼠)* 非常地fat(肥胖) 跳进了vat(缸) 偷吃了salt(盐) 变成了bat(蝙蝠) 气坏了cat(猫) 咬破了hat(帽子) 经过国内外许多代学者的努力,从英语词汇的结构角度上所做的研究已经非常充分了,而且很多学习者已经对此非常熟悉了,在这种情况下,把结构相似的单词系统、完整地联系在一起。我们看下面的内容: -猴王出世- 花果山的back(背部) 有块石头black(黑色的) 突然中间crack(裂开) *
飞出一个sack(口袋) * 天兵天将attack(攻击) 却找不到track(行踪) (口袋里是刚出生的猴王。) 这里就把冷冰冰的单词联系在一起了。同时又把这些单词和鲜活的形象"猴王"联系起来了--猴王是每一个中国人都熟悉的形象,很亲切而且容易接受和记忆,最重要的是容易回想起来,从而有利于复习。 但相似的单词聚集一起,也有一个问题,就是容易搞混淆了,鄙人给出一个简单思考和解决的办法,仅供参考。 我们再看: -珍珠港战士- 海洋非常vast(广阔) 抓颗手雷cast(投掷) 速度非常fast(快) 从天空中past(穿过) 打中敌舰last(最后一个) 炸坏舰上mast(桅杆) * 如何记忆vast这个单词,本书告诉你,主要是第一字母v与别的单词不同,而把“v”无限放大成“V”的形状,就显得非常广阔了,这样就和词义"广阔的"联系起来了;而cast第一个字母“c”,向右旋转90度,就像投掷出的东西在空中的轨迹,这样也和单词的词义联系起来了;而mast起首字母是“m”,发音似“木”,桅杆多是木头做的,于是又和词义联系起来了。 另外,用“珍珠港”这么个重大事件发生的地方做背景,虽然所述故事可能是莫须有的,但几乎每个学生都知道“珍珠港”,无疑也可以很容易想到“珍珠港”这个地方,并把整个内容连带回忆出来。
自考英语词汇学复习大纲自己整理
11 C h a p t e r 1 B a s i c C o n c e p t s 基本概念 1.1 the definition of a word (he definition of a word comprises the following points: (1) a minimal free form of a language; (2) a sound unity; (3) a unit of meaning; (4) a form that can function alone in a sentence. A word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic function.) 1.2 sound and meaning :symbolic connection is almost always arbitrary and conventional. A dog is called a dog not because the sound and the three letters that make up the word just automatically suggest the animal in question. 1.3 sound and form : 1.4 vocabulary 1.5 classification of words 词汇分类 basic word stock 基本词汇 nonbasic vocabulary 非基本词汇 by use frequency 按使用频率分: basic word stock and nonbasic vocabulary 基本词汇和非基本词汇 by notion 按概念分: content words and functional words 实义词和功能词 by origin 按起源分: native words and borrowed words 本地词和外来词 all national character 全民性 stability 稳定性 productivity 多产性 p ol ysemy 一词多义 collocability 搭配性 terminology 术语 jargon 行话 slang 俚语 argon 黑话 dialectal words 方言词 archaism 古语词 neologism 新词 neutral in style 文体上中性 frequent in use 使用频繁 native words 本地词 borrowed words 外来词 denizens 同化词 aliens 异形词 translation-loans 译借词 semantic-loans 借义词 1. No enough letters: alphabet from latin 2. Pronunciation changed more rapidly 3. Early scribes: change spelling for easier recognition 4. Borrowing: different rules of pronunciation and spelling obvious characteristics 明显的特点
(完整版)英语词汇学试题
英语词汇学试题 Introduction and Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Words and Vocabula ry(练习1) I.Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers. Choose the one that would best complete the statement. 1.Morphology is the branch of grammar which studies the structure or forms of words, primarily through the use of _________construct. A. word B. form C. morpheme D. root 2.________ is traditionally used for the study of the origins and history of the form and meaning of words. A. Semantics B. Linguistics C. Etymology D. Stylistics 3.Modern English is derived from the language of early ______ tribes. A. Greek B. Roman C. Italian D. Germanic 4. Semantics is the study of meaning of different _________ levels: lexis, syntax, utterance, discourse, etc. A. linguistic B. grammatical C. arbitrary D. semantic 5.Stylistics is the study of style . It is concerned with the user’s choices of linguistic elements in a particular________ for special effects A. situation B. context C. time D. place 6.Lexicography shares with lexicology the same problems: the form , meaning, origins and usages of words, but they have a _______ difference. A . spelling B. semantic C. pronunciation D. pragmatic 7. Terminology consists of _______ terms used in particular disciplines and academic areas. A. technical B. artistic C. different D. academic 8. __________refers to the specialized vocabularies by which members of particular arts, sciences, trades, and professions communicate among themselves. A. Slang B. Jargon C. Dialectal words D. Argot 9 ._________ belongs to the sub-standard language, a category that seems to stand between the standard general words including informal ones available to everyone and in-group words. A. Jargon B. Argot C. Dialectal words D. Slang 10. Argot generally refers to the jargon of _______.Its use is confined to the sub-cultural groups and outsiders can hardly understand it. A. workers B. criminals C. any person D. policeman 11.________ are words used only by speakers of the dialect in question. A. Argot B. Slang C. Jargon D. Dialectal words 12. Archaisms are words or forms that were once in _________use but are now restricted only to specialized or limited use. A. common B. little C. slight D. great 13. Neologisms are newly-created words or expressions, or words that have taken on ______meanings. A. new B. old C. bad D. good 14. Content words denote clear notions and thus are known as_________ words. They include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs and numerals. A. functional B. notional C. empty D. formal 15. Functional words do not have notions of their own. Therefore, they are also called _______words. Prepositions, conjunctions, auxiliaries and articles belong to this category. A. content B. notional C. empty D. new
英语词汇记忆口诀
词汇记忆口诀(一)记忆口诀------排骨抢劫案 教堂旁边的shop(商店) 大声播放pop(流行音乐) 卖美味红烧chop(排骨) 口水好像要drop(滴下) 无奈没有钱shop(买东西) 抢一盘朝外hop(跳跃) 越过绊脚的mop(拖把) 猛地撞上了bishop(主教) 被抓住交给cop(警察) 记忆口诀------童话版9.11 有一只pest(害虫) 穿一件vest(背心) 飞向southwest(西南) 撞树上nest(巢穴) 世道不公我protest(抗议) 记忆口诀------八戒怨唐僧 总住破烂hut(小屋) 门都没得shut(关闭) 餐餐吃peanut(花生) 一年没haircut(理发) 老指俺的nut(坚果,头) 说等妖怪cut(砍,剪) 记忆口诀------冬日找工记 空气中透着chill(寒意) 感觉就要fall ill(生病) 吞下了两颗pill(药丸) 手拿着一瓶milk(牛奶) 出门走去woolen will(毛纺厂)
决心去学门skill(技能) 一定把梦想fulfill(实现)心里激动身体thrill(发抖) 牛奶不慎被spill(洒落) 唉!天不从人will(意愿) 还是卖肉回家grill(烧烤) 先把肚子fulfill(填满) 记忆口诀------午夜凶铃 阴森森的well(井) 井边铺满shell(贝壳) 井底是个hell(地狱) 贞子在里dwell(居住) 邪气被人smell(闻到) 她被抓去cell(小牢房) 身体开始swell(肿胀) 爬出电视yell(叫喊) 记忆口诀------超级噩梦 我变成了hare(兔子) 土著上身bare(赤裸的) 个个对我glare(瞪眼) 他们围在square(广场) 说要把我share(分享) 挣扎无人care(在意) 突然间I’m aware(意识到) It’s a nightmare(噩梦)记忆口诀------犒劳自己鼓起极大的nerve(勇气)把豪华酒店reserve(预定)享受专人来serve(伺候)这一切我都deserve(值得)记忆口诀------讨厌的国家
(完整版)英语词汇学复习题。。。。
Key to chapter 1 1 .What is a word? 1.A word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound, meaning and syntactic function. 2.In what way are words related to vocabulary? V ocabulary refers to the sum total of all the words in a language. In other words, vocabulary is composed of words and words make up vocabulary. If we compare vocabulary to a family, words are family members. 3.Illustrate the relationship between sound and meaning with examples . Sound is the physical aspect of a word and meaning is what the sound refers to. Sound and meaning are not intrinsically related and their collection is arbitrary and conventional. For example, tree/tri:/ means 树in English because the English-speaking people have agreed to do so just as Chinese people use/shù/ (树) to refer to the same thing. This explains why people of different languages use different sounds to express the same concept. However, in the same languages, the same sound can denote different meanings, e.g. /rait/ can mean right, rite, and write. 4 .Enumerate the causes for the differences between sound and form of english words There are generally four major causes of the differences between sound and form. ⑴ There are more phonemes than letters in English, so there is no way to use one letter to represent one phoneme. ⑵ The stabilization of spelling by printing, which breaks the synchronized change of sound and spelling. ⑶ Influence of the work of scribes, who deliberately changed the spelling of words and ⑷ borrowing, which introduces many words which are against English rules of pronunciation and spelling. 5 .Give examples to show the influence of early scribes on english spelling Early scribes changed the spelling of many words while copying things for others because the original spelling forms in cursive writing were difficult for people to recognize, such as sum, cum, wuman, munk and so on. Later, the letter u with vertical lines was replaced with o, resulting in the current spelling forms like some, come, woman, monk. The changed spelling forms are more distinguishable to readers. 6.What are the characteristics of basic word stock Words of the basic word stock form the common core of the English language. They are the words essential to native speakers’ daily communication. Such words are characterized by all national character, stability, polysemy, productivity and collocability. 7.choose the standard meaning form from the list on the right to match each of the slang words on the left A tart loose woman b. bloke fellow c.gat pistol d. swell great e. chicken coward F .blue fight g. smoky police h full drunk i. dame woman j. beaver girl 8.given the modern equivalents for the following archaic words haply = perhaps albeit= although methinks = it seems to me eke= also bade= bid smooth= truth morn= morning troth= pledge ere= before quoth = said hallowed= holy billow= wave/ the sea 9.Explain neologisms with examples Neologisms refer to newly-coined words or old words with new meanings. For example, euro(欧元), e-book(电子书), SARS(非典), netizen(网民), are newly-coined words. Words like mouse(鼠标),web(网络),space shuttle(航天飞机) etc. are old words which have acquired new meanings. 10.What is the fundamental difference between content and functional words By notion, words fall into content words and functional words. Content words include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs and numerals, which have clear notions; whereas functional words are void of notions but are mainly used to connect content words into sentences. Content words are numerous and changing all the time, while functional words are small in number and stable. But functional words have much higher frequency in use than content words. 11.How do you account for the role of native words in english in relation to loan words ? Native words form a small portion of the English vocabulary, but they make up the mainstream of the basic word-stock which belongs to the common core of the English language. Compared with most loan-words, native words are mostly essential to native speakers’ daily communication and enjoy a much higher frequency in actual use.
