热处理手册第三版全四卷
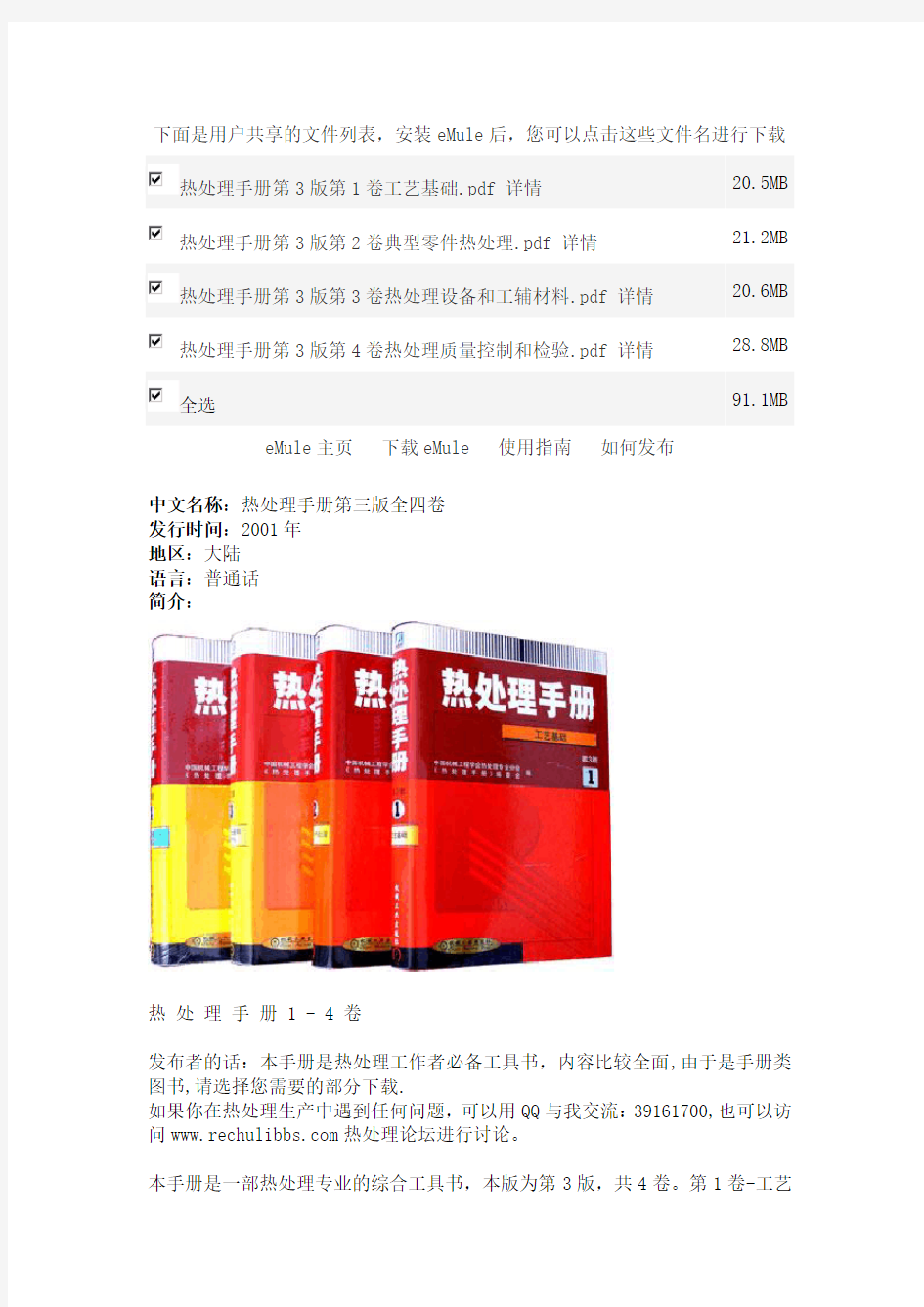

中文名称:热处理手册第三版全四卷
发行时间:2001年
地区:大陆
语言:普通话
简介:
热处理手册 1 - 4 卷
发布者的话:本手册是热处理工作者必备工具书,内容比较全面,由于是手册类图书,请选择您需要的部分下载.
如果你在热处理生产中遇到任何问题,可以用QQ与我交流:39161700,也可以访问https://www.360docs.net/doc/ac7391439.html,热处理论坛进行讨论。
本手册是一部热处理专业的综合工具书,本版为第3版,共4卷。第1卷-工艺
基础,第2卷-典型零件热处理,第3卷-热处理设备和工辅材料,第4卷-热处理质量控制和检验。
第1卷,共10章。内容包括金属的热处理加热和冷却、钢铁热处理及表面热处理、非铁金属和合金的热处理、铁基粉末合金件和硬质合金的热处理、功能材料的热处理等。邮购单价:72元。
第2卷,共19章。内容包括齿轮、滚动轴承零件、弹簧、紧固件、大型铸锻件、工模量具、汽车拖拉机零件、金属切削机床零件、气动工具及钻探机械零件、液压元件、轻工产品零件和飞机零件等的热处理。此外,还论述了热处理工艺制订原则和程序及零件的热处理工艺性。邮购单价:72元。
第3卷,共15章。内容包括设备分类、筑炉材料、燃烧加热器和电热元件、耐热金属构件、炉子配套器件、热工仪表、传感器、各种热处理炉结构、热处理工辅材料等。邮购单价:80元。
第4卷,共11章。内容包括金属化学成分检验、宏观组织和断口分析、显微组织分析、力学性能试验、无损检测、内应力测定、物理性能测试及试验研究方法、金属腐蚀试验、金属制品的失效分析方法、热处理质量的管理与控制和常用数据及单位换算等。邮购单价:80元。
精装B5(683页+696页+827页+797页),全套手册邮购价:304元。
详细目录:
第1卷工艺基础
第1章基础资料
1.1 金属热处理分类及代号
1.1.1 基础分类
1.1.2 附加分类
1.1.3 常用热处理工艺及代号
1.2 合金相图
1.2.1 铁碳系合金相图
1.2.2 其他铁基合金相图
1.2.3 铝基\铜基及钛基合金相图
1.3 现有热处理标准题录
参考文献
第2章金属热处理的加热
2.1 金属热处理的加热
2.1.1 珠光体-奥氏体转变
2.1.2 铁素体-珠光体向奥氏体的等温转变
2.1.3 连续加热时的奥氏体形成过程
2.1.4 钢加热时的奥氏体晶料长大
2.1.5 过热和过烧
2.1.6 钢的晶粒度对性能影响
2.1.7 奥氏体晶粒度的显示和测定
2.2 加热介质和加热计算
2.2.1 加热介质分类
2.2.2 金属在各种介质中加热时行为
2.2.3 加热计算公式及常用图表
2.2.4 加热节能措施
2.3 可控气氛
2.3.1 分类及用途
2.3.2 制备方法
2.3.3 炉气控制原理
2.3.4 炉气检测方法
2.4 加热熔盐和流态床
2.4.1 加热熔盐的成分及用途
2.4.2 盐浴的脱氧及脱剂
2.4.3 长效盐
2.4.4 流态床加热的特点
2.5 真空中的加热
2.5.1 金属在真空中加热时的行为
2.5.2 金属在真空中加热时速度
参考文献
第3章金属热处理的冷却
3.1 钢的过冷奥氏体转变
3.1.1 过冷奥氏体的高温分解
3.1.2 马氏体转变与马氏体
3.1.3 贝氏体转变与贝氏体
3.1.4 过冷奥氏体等温分解转变动力学
3.2 钢件热处理的冷却过程
3.2.1 热处理的各种冷却方式
3.2.2 钢冷却时的内应力
3.2.3 淬火裂纹
3.2.4 淬火畸变
3.3 淬火冷却介质
3.3.1 淬火冷却介质就具备的特性及其分类3.3.2 淬火冷却介质特性评价方法
3.3.3 常用淬火介质及冷却方式
3.4 淬火冷却过程的计算机模拟
3.4.1 导热计算
3.4.2 相变量的计算
3.4.3 应力场分析
3.4.4 复杂淬火操作的模拟以及非线性处理3.4.5 借助于计算机模拟进行热处理虚拟生产参考文献
第4章钢铁件的整体热处理
4.1.1 钢的退火与正火
4.1.2 钢的淬火
4.1.3 钢的回火
4.1.4 钢的感应穿透加热调质
4.2 铸铁的热处理
4.2.1 铸铁的热处理
4.2.2 铸铁热处理基础
4.2.3 白石铸铁热处理
4.2.4 灰铸铁的热处理
4.2.5 球墨铸铁的热处理
4.2.6 可锻铸铁的热处理
参考文献
第5章表面加热热处理
5.1 感应加热热处理
5.1.1 感应加热原理
5.1.2 钢件感应加热时的相变特点
5.1.3 感应器
5.1.4 感应淬火工艺
5.1.5 超高频脉冲和大功率脉冲感应淬火5.1.6 感应淬火件的回火
5.2 火焰加热表面淬火
5.2.1 火焰加热方法
5.2.2 为焰喷嘴和燃料气
5.2.3 火焰加热表面淬火工艺规范
5.3 激光\电子束处理
5.3.1 激光处理的特点
5.3.2 电子束热处理的特点
5.3.3 表面相变硬化
5.3.4 表面熔化快速凝固硬化
5.3.5 表面合金化的熔覆
5.3.6 激光热处理设备
5.4 其他表面热处理方式
5.4.1 电接触加热表面淬火
5.4.2 电解液加热表面淬火
5.4.3 浴炉加热表面淬火
参考文献
第6章化学热处理
6.1 钢的渗碳
6.1.1 渗碳原理
6.1.2 渗碳方法
6.1.3 渗碳用钢及渗碳后的热处理
6.1.4 渗碳层的组织和性能
6.1.5 参碳件质量检查\常见缺陷及防止措施
6.2.1 概述
6.2.2 气体碳氮共渗
6.2.3 其他碳氮共渗方法
6.2.4 碳氮共渗用钢及共渗后的热处理
6.2.5 碳氮共渗层的组织和性能
6.2.6 碳氮共渗工件质量检查与常见缺陷及防止措施6.3 渗氮及氮为主的共渗
6.3.1 渗氮
6.3.2 氮碳共渗
6.3.3 氧氮共渗
6.3.4 硫氮共渗
6.3.5 硫氮碳共渗
6.4 渗金属及碳氮之外的非金属
6.4.1 渗硼
6.4.2 渗铝
6.4.3 渗锌
6.4.4 渗铬
6.4.5 熔盐碳化物覆层工艺
6.4.6 渗硫
6.4.7 渗硅、钛、铌、钒、锰
6.4.8 我元共渗与复合渗
6.5 离子化学热处理
6.5.1 离子化学热心处理基础
6.5.2 离子渗氮
6.5.3 离子氮碳共渗
6.5.4 离子渗碳及碳氮共渗
6.5.5 离子硫氮(碳)共渗
6.5.6 离子渗硼
6.5.7 离子渗金属
6.5.8 气相沉积技术
6.5.9 离子注入技术
参考文献
第7章形变热处理
7.1 概述
7.2 低温变形热处理
7.2.1 低温形变热处理工艺
7.2.2 钢低温形变热处理的组织变化
7.2.3 钢低温形变热处理后的力学性能
7.2.4 其他低温形变热处理
7.3 高温形变热处理
7.3.1 高温形变热处理工艺
7.3.2 钢高温形变淬火的组织变化
7.3.3 钢高温形变热处理后的力学性能
7.3.4 钢的锻热淬火
7.3.5 控制轧制
7.3.6 非调质钢
7.4 表面形变热处理
7.4.1 表面高温形变淬火
7.4.2 预冷形变表面形变热处理
7.4.3 表面形变时效
7.5 形变化学热处理
7.5.1 形变对扩散过程的影响
7.5.2 网件化学热处理后冷形变
7.5.3 钢件化学热处理后的表高温形变淬火7.5.4 钢件晶粒多边化处理后的化学热处理参考文献
第8章非铁金属的热处理
8.1 铜及铜合金的热处理
8.1.1 铜及铜合金
8.1.2 铜及铜合金的热处理
8.1.3 工业纯铜的热处理
8.1.4 黄铜的热处理
8.1.5 青铜的热处理
8.1.6 白铜的热处理
8.2 铝及铝合金的热处理
8.2.1 铝及铝合金
8.2.2 变形铝合金退火
8.2.3 变形铝合金的固熔处理与时效
8.2.4 其他热处理
8.2.5 变形铝合金加工及热处理状态标记8.2.6 铸造铝合金的热处理
8.2.7 铝合金的热处理缺陷
8.3 镁合金的热处理
8.3.1 镁及镁合金
8.3.2 镁合金热处理的主要类型
8.3.3 热处理设备和操作
8.3.4 热处理缺陷及防止方法
8.3.5 镁合金热处理安全技术
8.4 钛及钛合金的热处理
8.4.1 钛合金中的合金元素
8.4.2 钛及钛合金的分类
8.4.3 钛合金中不平衡相变
8.4.4 钛合金的热处理工艺
8.4.5 影响钛合金热处理质量的因素
参考因素
第9章铁基粉末冶金件及硬质合金的热处理9.1 概论
9.1.1 粉末冶金的应用范围
9.1.2 粉末冶金方法
9.1.3 粉末冶金材料的分类
9.2 铁基粉末冶金件及其热处理
9.2.1 铁基粉末冶金材料的分类
9.2.2 铁基粉末冶金材料的标记方法
9.2.3 铁基粉末冶金件制造工艺流程
9.2.4 粉末冶金用铁和铁合金粉末
9.2.5 烧结、钢、不锈钢粉末冶金件的性能
9.2.6 提高铁基粉末冶金件性能的方法
9.2.7 铁基粉末冶金的应用
9.2.8 铁基粉末冶金件的热处理
9.2.9 国外铁基粉末冶金件的牌号、成分和性能9.3 钢结硬质合金及其热处理
9.3.1 钢结硬质合金的特点、牌号、性能和用途9.3.2 钢结硬质合金的热处理
9.3.3 钢结硬质合金的组织与性能
9.4 粉末高速钢及其热处理
9.4.1 粉末高速钢类别和性能
9.4.2 热等静压和热压粉末高速钢
9.5 硬质合金及其热处理
9.5.1 硬质合金的分类和用途
9.5.2 影响硬质合金性能因素
9.5.3 硬质合金的牌号、性能和用途
9.5.4 硬质合的热处理
9.5.5 国外硬持合金牌号、性能及用途
参考文献
第10章功能合金的热处理
10.1 磁性合金的热处理
10.1.1 软磁合金的热处理
10.1.2 永磁合金的热处理
10.2 膨胀合金的热处理
10.2.1 低膨胀合金的热处理
10.2.2 铁磁性定膨胀合金的热处理
10.2.3 无磁性定膨胀合金的热处理
10.2.4 高膨胀合金的热处理
10.3 弹性合金的热处理
10.3.1 高弹性合金的热处理
10.3.2 恒弹性合金的热处理
10.4 形状记忆合金及其成形处理
10.4.1 超弹性和形状记忆效应
10.4.2 钛镍形状合金
10.4.3 铜基形状记忆合金
10.4.4 形状记忆合金的应用
参考文献
第2卷典型零件热处理
第1章零件热处理工艺制订原则与程序
第2章零件热处理工艺性
第3章齿轮的热处理
第4章滚动轴承零件的热处理
第5章弹簧的热处理
第6章紧固件的热处理
第7章大型锻铸件的热处理
第8章工具的热处理
第9章模具的热处理
第10章量具热处理
第11章汽车、拖拉机及柴油机零件的热处理
第12章金属切削机床零件的热处理
第13章气动工具及钻探机械零件的热处理
第14章农机具零件的热处理
第15章发电设备零件的热处理
第16章石油化工机械零件的热处理
第17章液压元件的零件热处理
第18章手表、自行车、缝纫机和纺织机械零件的热处理第19章飞机零件的热处理
参考文献
第3卷热处理设备和工辅材料
第1章绪论
第2章热处理设备常用材料及基础构件
第3章热处理电阻炉
第4章热处理浴炉及流态粒子炉
第5章真空与等离子热处理炉
第6章热处理燃料炉
第7章热处理感应加热及火焰加热装置
第8章表面改性热处理设备
第9章热处理冷却设备
第10章热处理辅助设备
第11章热处理生产过程控制
第12章热处理工艺材料
第13章热处理节能与环境保护
第14章热处理车间设计
第15章热处理炉设计基础资料表
第4卷热处理质量控制和检验
第1章热处理质量管理
1.1概论
1.1.1质量管理和质量保证基本术语1.1.2现代质量管理特点
1.1.3热处理质量管理和质量体系
1.1.4热处理技术标准化与质量管理
1.2产品设计中的热处理质量控制
1.2.1材料选择
1.2.2热处理技术要求的确定
1.3热处理工艺设计中的质量控制
1.3.1热处理工艺流程及规范的优化设计1.3.2热处理技术文件的制订
1.3.3热处理工艺设计中的经济分析1.3.4设计中的评审与更改
1.4采购质量
1.4.1制订采购与委托服务文件
1.4.2选择合格的供货或委托单位
1.4.3签订质量保证协议
1.4.4采购品或委托热处理零件的质量验收1.5原材料质量管理
1.6热处理工艺过程中的质量管理
1.6.1待处理工件的核查
1.6.2建立工序管理点,进行工序控制1.6.3数理统计法在工序质量控制中的应用1.6.4车间环境条件管理
1.6.5车间设备管理
1.6.6车间节能管理
1.6.7工艺材料的管理
1.7热处理质量检验
1.7.1质量检验工作的职能
1.7.2质量检验方式
1.7.3常用热处理质量检验方法
1.7.4热处理检测设备的检定和管理
1.8不合格品的控制与纠正措施
1.9热处理后的质量服务
1.10热处理质量改进
1.11质量成本
1.11.1核算质量成本的必要性
1.11.2质量成本构成
1.11.3质量成本构成比例及质量成本分析1.12人员培训
1.12.1人员培训形式
1.12.2培训内容
1.12.3资格
1.13计算机在质量管理中的应用
1.13.1热处理工艺过程的控制
1.13.2质量检验
1.13.3质量档案及质量信息检索1.13.4工序质量分析
1.13.5数据库的应用
参考文献
第2章热处理过程中的质量控制
2.1待热处理工件的核查或验收
2.1.1原始资料
2.1.2待热处理件的外观、形状及尺寸要求2.2加热质量控制
2.2.1热处理的炉温控制
2.2.2热处理加热介质控制
2.2.3正确选择加热参数
2.2.4加热缺陷及其控制
2.3正火与退火质量控制
2.3.1加热设备
2.3.2工件装炉
2.3.3冷却速度控制
2.3.1质量检验
2.3.2正火退火缺陷及其控制
2.4淬火与回火质量控制
2.4.1加热设备
2.4.2淬火介质及淬火槽
2.4.3淬火操作
2.4.4回火操作
2.5淬火、回火后的附属工序
2.4.6质量检验
2.4.7淬火回火质量缺陷及其控制
2.5感应加热与火焰加热表面淬火质量控制2.5.1感应加热表面淬火质量控制
2.5.2火焰加热表面淬火质量控制
2.6化学热处理质量控制
2.6.1渗碳和碳氮共修质量控制
2.6.2渗氮质量控制
2.6.3渗硼质量控制
2.7铝合金及钛合金热处理质量控制2.7.1变形铝合金热处理质量控制
2.7.2钛合金热处理的质量控制
参考文献
第3章材料化学成分的检验
3.1钢的火花检验
3.1.1火花的形成及结构
3.1.2检验设备与操作
3.1.3钢的成分与火花特征
3.2光谱分析
3.2.1发射光谱分析
3.2.2X射线荧光光谱分析
3.2.3激光显微光谱分析
3.2.4原子吸收和原子荧光光谱分析
3.3微区化学成分分析
3.3.1概述
3.3.2电子探针X射线显微分析
3.3.3俄歇电子能谱技术
3.3.4离子探针显微分析仪
参考文献
第4章宏观组织检验及断口分析
4.1宏观检验
4.1.1钢的酸蚀检验
4.1.2印痕法检验
4.1.3液体渗透着色法
4.2断口分析
4.2.1断口试样的选择
4.2.2断口试样的清洗
4.2.3断口试样的保存
4.3宏观断口分析
4.3.1断裂分类
4.3.2各类断口形貌特征
4.3.3裂纹源位置及裂纹扩展方向的判别
4.4显微断口分析
4.4.1显微断口分析方法
4.4.2断口显微形貌特征
4.4.3断口显微形貌与显微组织的关系
4.4.4断口的典型显微形貌特征举例
4.5失效分析
4.5.1失效
4.5.2失效分析的目的
4.5.3失效分析方法
参考文献
第5章显微组织分析与检验
5.1金相试样的制备
5.1.1取样
5.1.2制样
5.l.3显微组织的显示
5.2光学显微镜及电子显微镜在显微分析中的应用5.2.1光学显微镜
5.2.2电子显微镜
5.3定量金相方法
5.3.1定量金相的标准符号及基本公式
5.3.2测量方法
5.3.3定量金相数据的统计分析
5.3.4常用显微组织参数测定举例
5.3.5图像分析仪
5.4彩色金相技术
5.4.1彩色成像的基本原理
5.4.2乾涉膜形成方法
5.4.3彩色显微摄影的特点与要求
5.4.4彩色金相在显微检验中的应用
5.5典型工程合金的显微组织检验技术
5.5.1结构钢与工具钢
5.5.2钢中非金属夹杂物的显微检验
5.5.3铸铁
5.5.4不锈钢和奥氏体锰钢
5.5.5非铁合金
5.5.6粉末冶金材料与硬质合金
5.6热处理质量及缺陷组织检验
5.6.1偏析与带状组织
5.6.2过热与过烧
5.6.3脱碳
5.6.4表面硬化层深度的测定
5.6.5表面渗金属(或涂覆处理)的显微检验
参考文献
第6章力学性能试验
6.1硬度试验
6.1.1硬度试验的意义及分类
6.1.2布氏硬度试验法
6.1.3洛氏硬度试验法
6.1.4维氏硬度、显微硬度和努氏硬度试验6.1.5肖氏硬度试验
6.1.6莫氏硬度试验
6.1.7理氏硬度试验
6.1.8硬度与强度及各种硬度之间的换算关系6.2静拉伸试验
6.2.1静拉伸试验的特点与意义
6.2.2试样
6.2.3拉伸试验机
6.2.4应力-应变曲线及其力学性能指标
6.2.5真实应力-应变曲线(σ-l或σ-ψ曲线)6.2.6缺口拉伸与缺口偏斜拉伸试验
6.2.7低温拉伸试验
6.2.8拉伸试样断口分析
6.2.9几种常用钢材的静拉伸数据
6.2.10影响拉伸试验性能数据的主要因素6.2.11拉伸试验中的计算机控制
6.3压缩、弯曲及扭转试验
6.3.1压缩试验
6.3.2弯曲试验
6.3.3静扭转试验
6.3.4剪切试验
6.4冲击试验
6.4.1冲击试验的意义
6.4.2冲击试验与冲击试验机
6.4.3冲击试验的应用
6.4.4几种接近实际服役条件的冲击试验
6.5断裂韧度试验
6.5.1断裂过程和断裂力学的一般概念
6.5.2应力强度因子K和平面应变断裂韧度KIC 6.5.3裂纹尖端张开位移CTOD和J积分
6.5.4断裂韧度测试技术
6.6疲劳试验
6.6.1疲劳失效特点
6.6.2疲劳性能指标
6.6.3常用结构钢、球墨铸铁及热处理后的疲劳特性6.6.4多次冲击抗力试验
6.6.5疲劳裂纹萌生与扩展的性能
6.6.6疲劳试验技术
6.6.7疲劳试验机
6.7磨损试验
6.7.1磨损分类
6.7.2磨损试验机
6.7.3磨损量的测量及表示方法
6.8高温力学性能试验
6.8.1高温蠕变
6.8.2松弛稳定性
6.8.3其他高温力学性能
参考文献
第7章无损检测
7.1内部缺陷检测
7.1.1射线检测
7.1.2超声波检测
7.1.3声发射检测
7.2表层缺陷检测
7.2.1磁力检测
7.2.2渗透检测
7.2.3涡流检测
7.3材质与热处理质量的无损检测
7.3.1硬度的无损检测
7.3.2表面硬化层深度的无损检测
7.3.3力学性能、显微组织的无损检测
7.3.4混料分选
7.4红外检测与微波检测
7.4.1红外检测
7.4.2微波检测
参考文献
第8章残余应力的测定
8.1概述
8.1.1残余应力的分类
8.1.2残余应力与质量控制的关系
8.2残余应力的产生
8.2.1残余应力产生的根本原因
8.2.2热处理淬火时的残余应力
8.2.3表面淬火的残余应力
8.2.4表面化学热处理的残余应力
8.2.5表面强化的残余应力
8.3残余应力的测定
8.3.1残余应力的特点及测试方法
8.3.2常用残余应力测试方法
8.3.3X射线应力测定法(GB7704一1987)
参考文献
第9章合金相分析及相交过程测试
9.1合金相分析方法
9.1.1X射线衍射分析
9.1.2电子衍射法
9.1.3中子衍射法
9.1.4低能电子衍射
9.1.5场离子显微分析
9.2相变过程测量
9.2.1相变点测定
9.2.2等温转变图(TTT曲线)与连续冷却转变图(CCT曲线)的建立方法9.3钢中残留奥氏体测定
9.3.1金相法测定残留奥氏体
9.3.2磁性法测定残留奥氏体
9.3.3X射线衍射法测定残留奥氏体
9.4其他物理方法简介
9.4.1内耗法
9.4.2正电子湮没技术
9.4.3穆斯堡尔谱仪
9.4.4核磁共振法
参考文献
第10章金属腐蚀与防护试验
10.1概述
10.1.1金属腐蚀定义
10.1.2金属腐蚀分类
10.1.3金属的氧化
10.1.4电化学腐蚀
10.l.5金属腐蚀评定方法
10.1.6影响腐蚀的因素
10.2局部腐蚀
10.2.1点蚀
10.2.2缝隙腐蚀
10.2.3电偶腐蚀
10.2.4晶间腐蚀
10.3金属在不同环境、介质中的腐蚀10.3.1大气腐蚀
10.3.2淡水中的腐蚀
10.3.3熔盐腐蚀
10.4应力作用下的腐蚀破坏
10.4.1应力腐蚀断裂
10.4.2腐蚀疲劳
10.4.3氢致损伤
10.5高温氧化
10.5.1高温氧化特点
10.5.2钢铁材料的高温氧化
10.5.3高温氧化试验
10.6防腐蚀技术
10.6.1合理选择与使用材料
10.6.2表面防护
10.6.3缓蚀剂
10.6.4电化学防腐蚀
参考文献
第11章热处理常用数据
11.1常用物理量单位换算
11.2常用物理化学数据
11.2.1元素周期表
11.2.2常见碳化物和金属间化合物点阵结构11.2.3元素的物理和化学性质
11.2.4常用无机化合物的物理化学性质11.2.5常用有机化合物的物理化学性质11.2.6常用金属材料的物理性能
11.2.7元素饱和蒸气压对应的温度11.2.8氧化物饱和蒸气压对应的温度11.2.9钢的温度色
11.2.10回火温度色
11.3常用金属材料牌号、化学成分和力学性能11.3.1钢
11.3.2铸钢
11.3.3合金材料
11.4常用金属材料热处理工艺参考数据
11.4.1钢
11.4.2高温合金
11.5常用钢热处理工艺参考曲线
11.5.1常用钢奥氏体等温转变曲线
11.5.2常用钢奥氏作连续冷却转变曲线
11.5.3常用钢改型连续冷却曲线
11.5.4常用钢的淬透性曲线
11.6常用钢的回火曲线和方程
11.6.1常用钢的回火曲线
11.6.2常用钢回火方程
11.7常用标准名称、代号及分类
11.7.1常用国外标准组织、行业名称及代号11.7.2热处理专业现行标准名称、级别代号11.7.3金属热处理工艺分类标准、代号
11.7.4国产标准型热处理电(热)炉系列代号、名称11.7.5钢铁产品分类标记、名称代号
11.7.6变形铝及铝合金状态代号
11.8近代材料分析方法概要
参考文献
附录法定计量单位及常用物理量的法定计量单位
版权所有,如果你喜欢本书,请至各大新华书店购买。
高级英语第三版第一册课后英译汉答案
高级英语第三版第一册课后英译汉答案 Unit1Paraphrase: 1.We’re23feet above sea level. 2.The house has been here since1915,andno hurricane has ever caused any damag e to it. 3.We can make the necessary preparations and survive the hurricane without much damage. 4.Water got into the generator and put it out.It stopped producing electricity,so the lights also went out. 5.Everybody goes out through the back door and runs to the cars! 6.The electrical systems in the car(the battery for the starter)had been put out by w ater. 7.As John watched the water inch its way up the steps,he felt a strong sense of guilt because he blamed himself for endangering the whole family by deciding not to flee i nland. 8.Oh God,please help us to get through this storm safely 9.Grandmother Koshak sang a few words alone and then her voice gradually grew di mmer and finally stopped. 10.Janis displayed the fear caused by the hurricanerather late. 1.每架飞机起飞之前必须经过严格的检查。(check out) Each and every airplane must be checked out thoroughly before taking off. 2.居民坚决反对在附近建立垃圾焚烧厂,因为他们担心工厂排放的气体会污染周围的空气。(waste incineration plant,concerned about) The residents were firmly against the construction of a waste incineration plant in th eir neighborhood because they were deeply concerned about the air pollution emitt ed by the plant. 3.在这个地区,生态工程的投资额高达数十亿。(mount to) In this area,investment in ecological projects mounted up to billions of yuan. 4.干枯的河道里布满了大大小小的石块。(strewn with) The dry riverbed was strewn with rocks of all sizes. 5.虽然战争给这个国家造成巨大的损失,但当地的文化传统并没有消亡。(perish)Although war caused great losses to this country,its local cultural traditi ons did not perish. 6.为了建筑现代化的高楼大厦,许多古老的、具有民族特色的建筑都被拆毁了。(demolish) To make space for modern high rises,a lot of ancient buildings with ethnic cultural fe atures had to be demolished. 7.在地震中多数质量差的房子的主体结构都散架了。(disintegrate) The main structures of most of the poor-quality houses disintegrated in the earthqua ke. 8.他为实现自己的目标付出了最大的努力,但最后美好的梦想还是化为了泡影。
高级英语第三版第一册课后答案
高英课内考点:第一课:Paraphrase 1、we’re elevated 23 feet. Our house is 23 feet above sea level. 2、The place has been here since 1915,and no hurricane has ever bothered it. The house was built in 1915,and since then no hurricane has done any damage to it. 3、We can batten down and ride it out. We can make the necessary preparation and survive the hurricane without much damage. 4、The generator was doused,and the lights went out. Water got into the generator,it stopped working.As a result all lights were put out. 5、Everybody out the back door to the cars! Everyone go out through the back door and get into the cars! 6、The electrical systems had been killed by water.
The electrical systems in the cars had been destroyed by water. 7、John watched the water lap at the steps,and felt a crushing guilt. As John watched the water inch its way up the steps,he felt a strong sense of guilt because he blamed himself for endangering the family by making the wrong decision not to flee inland. 8、Get us through this mess,will You? Oh,God,please help us to get through this dangerous situation. 9、She carried on alone for a few bars;then her voice trailed away. She sang a few words alone and then her voice gradually grew dimmer and stopped. 10、Janis had just one delayed reaction. Janis didn’t show any fear on the spot during the storm,but she revealed her feelings caused by the storm a few nights after the hurricane by getting up in the middle of the night and crying softly. 英译汉: 1、But,like thousands of others in the coastal communities,John was reluctant to abandon his home unless the family----his wife,Janis,and their seven children,aged 3 to 11---was clearly endangered.
高级英语(第三版)的说明Word版
《高级英语》第三版是什么样的书? 《高级英语》第一版由张汉熙主编,于1980年由商务印书馆出版,已经走过了三十年的历程,对于一本教科书来说,寿命可算是长的,但至今仍有旺盛的生命力,因为它经过了两次修订,即两次吐故纳新:1995年由外研社出版修订版;2011年外研社出版了第三版。 张汉熙教授在主编《高级英语》中做出了特别重要的贡献。张汉熙于1921年出生印度,母亲为印度人,父亲是中国人。1942年毕业于印度加尔各答大学(注:加尔各答大学创建于1857年,是印度3所历史最悠久、规模最大的综合性大学之一。被NAAC评价为五星级大学。2005年,加尔各答大学在Times评出的全球最佳人文大学中排名第39位)。1948年回国执教。曾在辅仁大学任教,解放后分到华北革大研究院,后调到北京外国语学院任教。70年代末,系里决定把多年选用的高年级精读教材编辑成书,这个任务交给张汉熙老师。他的确是最佳人选,不仅因为他一直教授此课,积累了丰富宝贵的教学经验,而且他精通英语,有外国专家的优势。他是编写这样一本教材的最佳人选,他具备独特的资格:精通英语,母语为英语;数十年的教育生涯全部贡献给高年级阅读和写作的教学,积累了丰富宝贵的教学经验。也就是说,他既具备一位中国教师长期从事第一线教学经验,又具备一位母语为外语的外国专家的英语水准。此外,他的聪明才智、准确的判断力和惊人的记忆力在编写此书中发挥了至关重要的作用。《高级英语》以及修订版是他一生教学的结晶。当我阅读周燕主编的《用精神行走的人》时,我注意到比我年长、我尊重的许多老师在谈到他们如何学习英语时提到了张汉熙教授,他们无一例外地对他的英语水平赞叹佩服,连加拿大专家伊莎白都说,张汉熙是真正的学者。 1995年由外研社出版的修订版(张汉熙主编,王立礼编)继续发扬了第一版的优点,更加强调贯彻文化教学与人文关怀的宗旨。所新增的课文比较新,题材方面更加重视体现当代人们所关注的重大问题,如环境保护,这在当时的精读课文是极少的,说明新课文的选择有前瞻性。修订版的最重大的变化是增加了教师用书,提供了补充背景资料,课文难点详解,练习答案,使得此套教科书更加user-friendly. 由于张汉熙教师已于1999年去世,此次修订《高级英语》的重任落在了我的肩上,令我诚惶诚恐,压力很大,但我决心尽自己最大的努力,不辱使命,本着对主编负责,对出版社负责,尤其是对读者负责的态度修订了此书。2011年夏第三版出版,受到了出版社和读者的肯定。 《高级英语》第三版有什么特点呢? 坚持语言训练与能力发展相结合的理念,突出思辨能力培养
(完整版)高级英语第三版第二册张汉熙1-4单元课后题及答案
Lesson One 1. And it is an activity only of humans. And conversation is an activity found only among human beings. 2. Conversation is not for making a point. Conversation is not for persuading others to accept our ideas or points of views. 3. In fact, the best conversationalists are those who are prepared to lose. In fact , people who are good at conversation will not argue to win or force others to accept his ideas. 4. Bar friends are not deeply involved in each other’s lives. People who meet each other for a drink in the bar of a pub are not close friends for they are not deeply absorbed in each other’s private lives. 5. ....it could still go ignorantly on ... The conversation could go on without anybody knowing who was right or wrong. 6. There are cattle in the fields ,but we sit down to beef. These animals are called cattle when they are alive and feed in the fields , but when we sit down at the table to eat, we call their meet beef. 7. The new ruling class had built a cultural barrier against him by building their French against his own language. The new ruling class by using French instead of English made it hard for the English to accept or absorb the culture of the rulers. 8. English had come royally into its own. English received proper recognition and was used by the King once more. 9. The phrase has always been used a little pejoratively and even facetiously by the lower classes. The phrase , the King’s English ,has always been used disrespectfully and jokingly by the lower classes.(The working people often mock the proper and formal language of the educated people.) 10. The rebellion against a cultural dominance is still there. As the early Saxon peasants , the working people still have a spirit of opposition to the cultural authority of the ruling class. 11. There is always a great danger that “ words will harden into things for us. “ There is always a great danger , as Carlyle put it , that we might forget that words are only symbols and take them for things they are supposed to represent. Translation
(完整word版)高级英语第1册1234614课修辞练习含答案(第三版),推荐文档
高级英语第1册修辞练习第3版 Point the rhetorical devices used in the following sentences Lesson 1 1.We can batten down and ride it out. (Metaphor ) 2.Wind and rain now whipped the house. ( Metaphor ) 3.Stay away from the windows. (Elliptical sentence ) 4.--- the rain seemingly driven right through the walls. ( Simile) 5.At 8:30, power failed. (Metaphor ) 6.Everybody out the back door to the cars. (Elliptical sentence ) 7.The children went from adult to adult like buckets in a fire brigade. ( Simile ) 8…the electrical systems had been killed by water.( metaphor ) 9.Everybody on the stairs. ( elliptical sentence) 10.The wind sounded like the roar of a train passing a few yards away. ( simile ) 11. A moment later, the hurricane, in one mighty swipe, lifted the entire roof off the house and skimmed it 40 feet though the air. ( personification ) 12…it seized a 600,000-gallon Gulfport oil tank and dumped it 3.5 miles away. ( personification ) 13.Telephone poles and 20-inch-thick pines cracked like guns as the winds snapped them.( simile ) 14.Several vacationers at the luxurious Richelieu Apartments there held a hurricane party to watch the storm from their spectacular vantage point. ( Transferred epithet ) 15. Up the stairs --- into our bedroom. ( Elliptical sentence ) 16.The world seemed to be breaking apart. ( Simile ) 17. Water inched its way up the steps as first floor outside walls collapsed. (Metaphor ) 18.Strips of clothing festooned the standing trees.. (Metaphor ) 19…and blown-down power lines coiled like black spaghetti over the road.( simile ) 20…household and medical supplies streamed in by plane, train, truck and car. (metaphor ) 21.Camille, meanwhile, had raked its way northward across Mississippi, dropped more than 28 inches of rain into West.( metaphor ) Lesson2 1 Hiroshima—the”Liveliest”City in Japan.—irovy 2 That must be what the man in the Japanese stationmaster’s uniform shouted,as the fastest train in the world slipped to a stop in Hiroshima Station.—alliteration 3 And secondly.because I had a lump in my throat and a lot of sad thoughts on my mind that had little to do with anything in Nippon railways official might say.—metaphor 4 Was I not at the scene of crime?—rhetorical question 5 The rather arresting spectacle of little old Japan adrift amid beige concrete skyscrapers is the very symbol of the incessant struggle between the kimono and the miniskirt.—synecdoche,metonymy
高级英语第三版课后答案整理
Lesson 1 Question: 1. Why did John Koshak decide to stay although he knew the hurricane would be bad? For the following reasons: For one thing, the house was 23 feet above sea level; for another,he was unwilling to abandon his home. 2. How did the man prepare for the hurricane? Why was a generator necessary? They filled bathtubs and pails. Besides, they checked out batteries for portable radio and flashlights, and fuel for the lantern. A generator was necessary because John's father wired several light bulbs to it and prepared a connection to the refrigerator. 3. What made it impossible for the Koshak to escape? It was impossible for the Koshers to escape both by car and on foot. The car's electrical system had been killed by water. Meanwhile, the water became too deep for them to escape on foot. 4. Why did John Koshak feel a crushing guilt? Because he blamed himself for underestimating the power of the hurricane and then endangering the whole family by his wrong decision not to flee safer inland. 5. Why did Grandma Koshak ask children to be sing? A: Because she knew how frightened the children were and wanted to boost their spirit. 6. What was a hurricane party? What happened to the party gores? A hurricane party was the one that was held by several vacationers to enjoy the spectacle of the hurricane with a clear and broad view in the fancy Richelieu Apartments from where they believed they would be safe. Richelieu Apartments were smashed apart by the hurricane and 26 people perished. 7. What did Grandma Koshak mean when she said," We lost practically all our possessions, but the family came through it. When I think of that, I realize we lost nothing important?" She meant that human lives are more important than material possessions. 8. How did the community of Gulfport act after Hurricane Camille was over? They managed to make their lives return to normal and began rebuilding their community without any delay. Paraphrase: 1. We're elevated 23 feet. Our house is 23 feet above sea level. 2. The place has been here since 1915, and no hurricane has ever bothered it. The house was built in 1915 and since then no hurricane has done any damage to it. 3. We can batten down and ride it out. We can prepare ourselves for the hurricane and manage to survive it without much damage. 4. The generator was doused, and the lights went out. Water got into the generator, and it didn't work. As a result, the lights were put out. 5. Everybody out the back door to the cars! Everybody go out though the back door and get into the cars. 6. The electrical system had been killed by water. The electrical system in the cars had been destroyed by water. 7. John watched the water lap at the steps, and felt a crushing guilt. When John watched the water inch its way up the steps, he felt a strong sense of guilt because he b
高级英语-1-答案-(外研社;第三版;张汉熙主编)
第一课Face to face with Hurricane Camille Translation (C-E) 1. Each and every plane must be checked out thoroughly before taking off. 每架飞机起飞之前必须经过严格的检查。 2. The residents were firmly opposed to the construction of a waste incineration plant in their neighborhood because they were deeply concerned about the plant’s emissions polluting the air.居民坚决反对在附近建立垃圾焚烧厂,因为他们担心工厂排放的气体会污染周围的空气。 3. Investment in ecological projects in this area mounted up to billions of Yuan. 在这个地区,生态工程的投资额高达数十亿元。 4. The dry riverbed was strewn with rocks of all sizes.干枯的河道里布满了大大小小的石块。 5. Although war caused great losses to this country, its cultural traditions did not perish.虽然战争给这个国家造成巨大的损失,但当地的文化传统并没有消亡。 6. To make space for modern high rises, many ancient buildings with ethnic cultural features had to be demolished.为了建筑现代化的高楼大厦,许多古老的,具有民族特色的建筑物都被拆毁了。 7. In the earthquake the main structures of most of the
高级英语第三版,张汉熙主编,paraphrase
U n i t2M a r r a k e c h 1. The burying-ground is merely a huge waste of hummocky earth, like a derelict building-lot. The burying-ground is just a huge piece of wasteland full of mounds of earth looking like a deserted and abandoned construction site. 2. All colonial empires are in reality founded upon that fact. All the imperialists build up their empires by treating the people in the colonies like animals. 3. They rise out of the earth, they sweat and starve for a few years, and then they sink back into the nameless mounds of the graveyard. They are born. Then for a few years they work, toil and starve. Finally they die and are buried in graves without a name, and nobody notices that they are dead. 4. A carpenter sits cross-legged at a prehistoric lathe, turning chair-legs at lightning speed. Sitting with his legs crossed and using a very old-fashioned lathe, a carpenter quickly gives a round shape to the chair-legs he is making.
高级英语(1)第三版 Lesson 6 Mark Twain Paraphrase&Translation 答案
1) Most Americans remember Mark Twain as the father of Huck Finn's idyllic cruise through eternal boyhood and Tom Sawyer's endless summer of freedom and adventure 2) The cast of characters set before him in his new profession was rich and varied-- a cosmos. 3) All would resurface in his books, together with the colorful language that he soaked up with a memory that seemed phonographic 4) Steamboat decks teemed not only with the main current of pioneering humanity, but its flotsam of hustlers, gamblers, and thugs as well. 5) He went west by stagecoach and succumbed to the epidemic of gold and silver fever in Nevada's Washoe region. 6) Mark Twain began digging his way to regional fame as a newspaper reporter and humorist. 7) "It was a splendid population – for all the slow, sleepy, sluggish-brained sloths stayed at home... 8) 'Well, that is California all over’'" 9) "What a robust people, what a nation of thinkers we might be, if we would only lay ourselves on the shelf occasionally and renew our edges." 10) The last of his own illusions seemed to have crumbled near the end. 参考答案 1) Mark Twain is known to most Americans as the author of The Adventures of Tom Sawyer and its sequel Huckleberry Finn, which are generally acknowledged to be his greatest works. Huck Finn is noted for his simple and pleasant journey through his boyhood which seems eternal and Tom Sawyer is famous for his free roam of the country and his adventure in one summer which seems never to end. The youth and summer are eternal because this is the only age and time we knew them. They are frozen in that age or season for all readers. 2) In his new profession he could meet people of all kinds. His work on the boat made it possible for him to meet a large variety of people. It is a world of all types of characters. 3) All would reappear in his books, written in the colorful language that he seemed to be able to remember and record as accurately as a phonograph. 4) Steamboat decks were filled with people of pioneering spirit (people who explored and prepared the way for others) and also lawless people or social outcasts such as hustlers, gamblers and thugs. 5) He took a horse-drawn public vehicle and went west to Nevada, following the flow of people in the Gold Rush. 6) Mark Twain began working hard to became well known locally as a newspaper reporter and humorist. 7) Those who came pioneering out west were energetic, courageous and reckless people, because those who stayed at home were slow, dull and lazy people. 8) That's typical of California. 9) If we relaxed, rested or stayed away from all this crazy struggle for success occasionally and kept the daring and enterprising spirit, we would be able to remain strong and healthy and continue to produce great thinkers. 10) At the end of his life, he lost the last bit of his positive view of man and the world.
高级英语第三版第一册 paraphrase 和translation
Words and expressions(P16) 1.Main: a principal pipe or line in a distributing system for water, electricity, gas, etc. 2.Sit out: to stay until the end of… 3.Report: a loud, resounding noise, especially one made by an explosion or shot 4.Douse: to put out (a fire, light, generator, etc.) quickly by pouring water on it 5.Kill: (AmE) to cause (an engine, a car, etc.) to stop 6.Litter: the young animals borne at one time by a dog, cat, or other animals 7.Swath: a broad strip, originally the area covered with one cut of a scythe or other mowing device 8.Bar: a measure in music; a group of notes between two vertical lines on a music sheet 9.Lean-to: a shed or other small building which is attached to one wall of a larger building, and which usually has a slopping roof. 10.Break up: be brought to an end; to disperse 11.Pitch in: to join in and help with an activity 12.The blues: depressed and sad feelings Paraphrase(P15) 1.We’re 23 feet above sea level. 2.The house has been here since 1915, and no hurricane has ever caused any damage to it. 3.We can make the necessary preparations and survive the hurricane without much damage. 4.Water got into the generator and put it out. It stopped producing electricity, so the lights also went out. 5.Everybody goes out through the back door and runs to the cars. 6.The electrical systems in the car had been put out by water. 7.As John watched the water inch its way up the steps, he felt a strong sense of guilt because he blamed himself for endangering the whole family by deciding not to flee inland. 8.Oh God, please help us to get through this storm safely. 9.Grandmother Koshak sang a few words alone and then her voice gradually grew dimmer and finally stopped. 10.Janis displayed the fear caused by the hurricane rather late. Translation(P17) A. 1. Each and every airplane must be checked out thoroughly before taking off. 2. The residents were firmly against the construction of a waste incineration plant in their neighborhood because they were deeply concerned about the air pollution emitted by the plant. 3. In this area, investment in ecological projects mounted up billions of yuan. 4. The dry riverbed was strewn with rocks of all sizes. 5. Although war caused great losses to this country, its local cultural traditions did not perish. 6. To make space for modern high rises, a lot of ancient buildings with ethnic cultural features
