一般过去时和现在完成时的区别

区分一般过去时和现在完成时
一.相同点:
1. 这两中时态中的动作都发生在过去
2. 倘若这个动词的过去时是加ed构成,那么这个动词的过去分词和过去时相同
例如:I cleaned(过去时) the room yesterday.
I have already cleaned(过去分词)the room.
二.不同点
1. 一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的事、存在的状态或经常发生的动作,说话的侧重点在于陈述一件过去的事情,与现在没有关系。如果你只是要陈述你做了什么,陈述的东西和目前状况没有太大影响,就用一般过去时;现在完成时表示与现在有关系的发生在过去的动作,到现在为止这个动作可能结束也可能继续下去。它不与表示过去的时间状语连用. 例如:
(1.) I washed the plate. “我洗盘子了”(那么洗盘子这个话题基本到此打住,基本没有下文)
(1.) I have washed the plate. “我已经洗好盘子了。”(强调做过,完成了。还有可能意思是,既然我已经
洗好盘子了,我就该干什么什么了,或者你就应该履行什么承诺之类的。)
(2.)I saw the film yesterday. 强调看电影的时间是昨天。
(2.) I have seen the flim.我已经看过这部电影了(我现在知道电影的内容/ 我不想在看这电影了,我们选其
他的吧。)
(3.) I taught here for eight years我在这教过八年书(只陈述过去的事实,现在可能不在这教书了)
(3.) I have taught here for eight years 我在这教书八年了(现在还在教,还可能继续教下去)
(4.) I leanrt English for six years 我学过六年英语(以前学过,现在可能不学了)
(4.) I have learnt English for six years我学英语已经学了六年了(现在还在学,可能还要学下去)
2. 常连用的时间状语不同
(1)常与一般过去时连用的时间状语
yesterday (morning, afternoon, evening):昨天(早上,下午,晚上)
the day before yesterday前天
last+时间名词:上一个…如:last night (week,Sunday,weekend,month,winter,year,century 世纪)
时间段+ ago:在…之前如:three days ago:三天前 a moment ago刚才
this morning/afternoon今天早上/ 今天下午
when+ 过去时的句子:当…的时候when I got up
just now 刚刚
before 以前或before+时间点
at the age of 10 (过去年龄段):在10岁的时候
in the old days 在古时候
at that time/ moment在那时候
(2)常与现在完成时连用的时间状语
for + 时间段: 持续了一段时间
I have lived here for 8 years.
He has done his homework for two hours.
since + 过去时间点/ 过去时句子:自从…开始
since + 时间段+ ago:自从…开始
I have lived here since 2008
He has done his homework since 8:00 p.m. / He has done his homework since two hours ago.
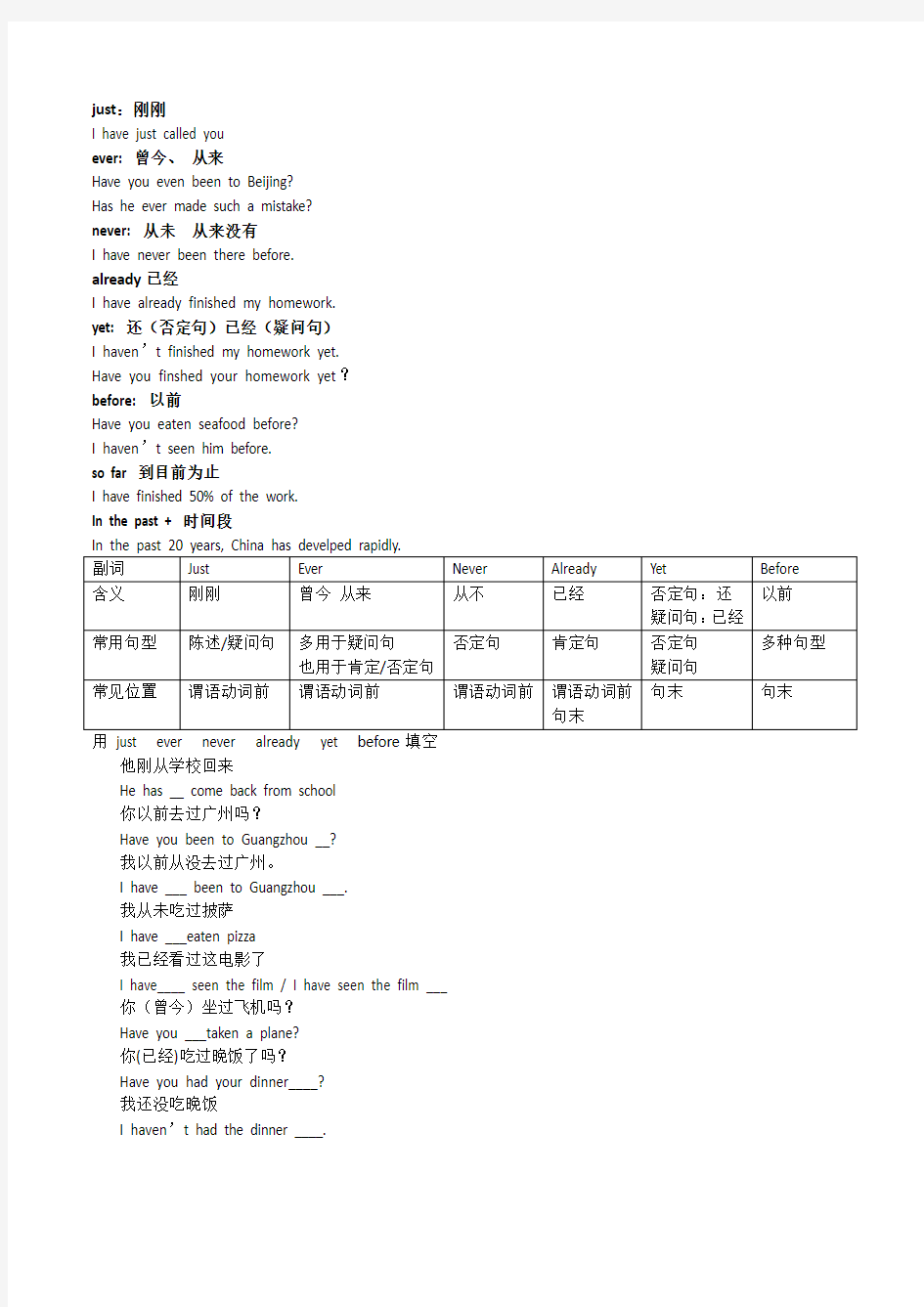
just:刚刚
I have just called you
ever: 曾今、从来
Have you even been to Beijing?
Has he ever made such a mistake?
never: 从未从来没有
I have never been there before.
already已经
I have already finished my homework.
yet: 还(否定句)已经(疑问句)
I haven’t finished my homework yet.
Have you finshed your homework yet?
before: 以前
Have you eaten seafood before?
I haven’t seen him before.
so far 到目前为止
I have finished 50% of the work.
In the past + 时间段
用just ever never already yet before填空他刚从学校回来
He has __ come back from school
你以前去过广州吗?
Have you been to Guangzhou __?
我以前从没去过广州。
I have ___ been to Guangzhou ___.
我从未吃过披萨
I have ___eaten pizza
我已经看过这电影了
I have____ seen the film / I have seen the film ___
你(曾今)坐过飞机吗?
Have you ___taken a plane?
你(已经)吃过晚饭了吗?
Have you had your dinner____?
我还没吃晚饭
I haven’t had the dinner ____.
3. 短暂性动词与持续性动词在一般过去时和现在完成时中应用:
短暂性动词可以用于一般过去时和现在完成时,但若在现在完成时中,动词跟since和for连用表示持续一段时间,那么要用持续性动词,短暂性动词不能用。
例如:
1.His grandpa died in 1990
His grandpa has already died.
Hies grandpa has been dead for over 20 years.
2.He left school at 5:00 p.m.
He has just left school.
He has been away from school for two hour / since 5:00p.m. / since two hours ago.
3.I came to Saming in 2008
I have been in Sanming for 8 years
4.He joined the basketball team last year
He has already joined the basketball team.
He has been in / has been a member of the basketball for one year.
5.My dad bought a car last month.
My dad has had a car for one month
6.I borrowed a book from the library three days ago
I have just borrowed a book from the library.
I have kept the book for three days / since three days ago.
总结:从以上例句可以归纳出,短暂性动词可以用于一般过去时和现在完成时,但是用于有时间段的现在完成时中,这些短暂性动词要变形。
用for+时间段,since+过去时间点/ 时间段+ago / 过去时句子表示时间段
died— have/ has been dead
left---have/ has been away (from+地点)
came --- have/ has been in
arrived--- have/ has been here
joined--- have / has been in
began / started --- have / have been on
bought--- have/ has had
borrowed—have/ has kept
came back --- have/ has been back
feel ill – have/ has been ill
go out – have/ has been out
got up – have/ has been up
练习:
改错题
1.My sister has been away yesterday
2.He has waited for you for two hours ago
3.I have got up for one hour ago
4.We have lived in Sanming when we were born.
翻译题:
1.我已经到这2个小时了
2.电影已经开始15分钟了
3.他已经买这房子3年了
4.(自从)两个小时之前我就已经回来了
5.(自从)我离开他就生病了
6.他已经起床一个小时了
一般过去时与现在完成时的用法区别
一般过去时与现在完成时区别专题 一、前言: 初一下学期同学们学习了一般过去时态的相关知识,即将到来的初二上学期英语学习中,现在完成时是重要的学习内容。本文通过对比一般过去时和现在完成时,对现在完成时进行初步讲解,希望使同学们读新学期的学习有所准备。 二、现在完成时 1. 现在完成时的构成 现在完成时是由助动词have (has)+动词的过去分词构成。助动词说明该谓语是属于现在时范围。它和主语的人称、数要保持一致。过去分词是主要的谓语动词,说明句子的意义。 2. 现在完成时的用法 现在完成时表示过去某时发生的行为对主语目前产生的影响。即用过去发生的某个行为来说明现在的某种情况。 We are good friends.(现在的情况) I knew him in 1997.(过去的动作) We have known each other since 1997. (现在完成时把过去的动作和现在联系起来并着眼于现在) (1)表示动作发生在过去某个不确定的时间,但对现在留下了某种影响和结果。常被just、already、yet 等副词修饰。如: -Have you had lunch yet? -Yes, I have. I've just had it. 你(已经)吃午饭了吗?我刚刚吃过。(现在我不饿了) (2)表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。这个动作可能刚停止,可能仍然在进行。常带有for和since等表示一段时间的状语。 如:He has taught here since 1981 他自1981年就在这儿教书。(可能还要继续教) I haven't seen her for four years. 我有四年没见到她了。 (3)表示说话前发生过一次或多次的动作,现在成为一种经验,一般译为汉语“过”,常带有twice,ever, never,three times等时间状语。 如:I have been to Beijing twice.我去过北京二次。 3.现在完成时的时间状语 (1)现在完成时属于现在时范围,故不能和过去的时间状语连用。如:yesterday,last Sunday,in1990,three years ago等。但是,在强调动作产生的后果和影响时,可以和一些表示不确定的时间状语连用。 a. 用副词already和yet。already一般用于肯定句中,yet一般用于否定句和疑问句中。 如:We have already finished our homework.我们已完成作业了。 They haven't finished their homework yet.他们还没有完成作业。 b.用ever 和never。多用于否定或疑问句中,表示“曾经”或“从未“等。 如:-Have you ever been to the Great Wall? 你曾经去过长城吗? -I have never been to the Great Wall.我从未去过长城。 c.用表示到说话为止的过去时间状语,如just, before, up to now, the past few years等。 例如:I have seen her before, but I can not remember where. 我以前见过她,但记不起在哪里见过。
一般过去时-现在完成时和过去完成时
一般过去时,现在完成时和过去完成时 一般过去时态表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用,也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和表示频度的时间状语连用,试看下列例句: 1. I was in the classroom yesterday morning 2. My father was at work last week. 3. I visited the Palace Museum three weeks ago. 4. He always went to work by bus last year. 5. I wrote home once a week at college. 1. yesterday或以其构成的短语:yesterday morning(afternoon, evening)等; 2. 由"last+一时间名词"构成的短语:last night, last year (winter, month, week)等; 3. 由"时间段+ago"构成的短语:a moment ago, a short time ago, an hour ago等; 4. 其它:just now或者由句子本身的时态所反映出来的。 现在完成时表示:(1)过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果, 常与already,just,yet,before,ever,never 等副词连用;(2)发生在过去某一时刻的,持续到现在的动作(用行为动词表示)或状态(be动词表示),常与for(+时间段),since(+时间点或过去时的句子)连用。试看下列例句: 1.My father has brought many books for me , so I can do some reading now. 2.I have already finished my homework, so I can give it to my teacher now. 3.Kevin hasn't seen the film yet, so he has nothing to say about the film. 4.This is the best film I have ever seen. 5.Mary has been ill for three days. 6.I have lived here since 1998. 现在完成时不能和表示过去的时间状语连用,如yesterday, last year, two days ago, just now 等等,但可以和already, yet, sometimes, always, before, recently,ever, never等连用。
现在完成时和过去时的区别及练习
现在完成时和过去时的区别及练习 一、现在完成时的用法。 1.现在完成时强调过去动作对现在的影响 I have lost my wallet now. I can’t find it now. 我的钱包掉了,我现在找不到。 2.现在完成时强调过去动作一直持续到现在。 I have had this book for a year. 我拥有这本书1年了。 3.现在完成时表示动作尚未完成。 I have lived here for 5 years. 我在这里住了5年(现在也还在这里住) 4.现在完成时可以与不确切的过去时间连用。 She has entered speaking competition before. 她曾经参加过演讲比赛。 5.现在完成时可以用来描述活着的人的经历。 He has been to America four times. 他去过美国4次。(他现在还活着) 6.现在完成时可以与未完成的时间状语连用。 She has finished her homework today. 今天他已经完成了家庭作业。(today, this week, this year 是未完成的时间状语) 二、过去时的用法 1.
1.表示过去完成的动作,现在已不是这样。 —What do you think of her? 你认为她怎样? —She was cute. 她曾经很可爱(表示她现在已不可爱了。) 2.与过去某一具体的时间状语连用,表示过去完成的动作。 She lost her wallet yesterday. (她昨天弄丢了她的钱包。) 3.表示去世的人过去的经历。 He went to America four times.一生中, 他去过美国4次(表示他已去世)练习 1.Ronaldo ______________( win) 29 major trophies in his career. 2.I ____________(have)him for three months and I really feel healthy. 3.She_______________(be) ill for three days. 4.They ________________ (not do) much exercise since they got their computer. 5.Kobe Byrant _______________(win) five championships with The Los Angeles Lakers. 6.Fans___________________(buy)about 200 million copies of Tintin’s stories in more than 50 languages. 7.When I was young, I ___________(not like) green vegetables. 8.After he graduated from university, he _________(work) in a big company.
现在完成时和一般过去时专项练习
现在完成时和一般过去时专项练习 一、用所给单词的正确形式填空。 1.--_____ you _____ (have) lunch yet? ---Yes,I . --- When____ you _____ (have) it? ---I______ (have) it at 12:00. 2._____ she _____(write) a letter to her aunt yet? Yes, she_____ . She__________ (write)it the day before yesterday 3. --______ you____ (find) your knife yet? ---Not yet. 4. I _________(sing) the English song before. 5. I ____ never _____(see) him before. 6.. She_____ just _____(ride) a horse? 7. Tom with his mother _________(shop)just now. . 8. Sam ________ (go) to school by bike last year. 9.My brother _______(join) the army in 1999. 10.My brother _______(be)in the army since1999. 11.John_________( not watch ) TV last night. 12.She ______ (do) her homework already. 13.Where is Jack? He______(go) the park. 14. I _________ (read) the magazine yesterday. 15.What was she doing when she __ (come) here. 16.We_______ (play) football five hours ago. 17..Mike ______ already ______(finish) the work. 18. We ___________(run) out of money. What shall we do? 19. I _____ just ______ (lose) my math book. 20. I ___ _ (be) to Beijing twice 21.My father _____ never____(eat)ice cream. 22.I __________(work) here since 1995. 23.The_______(teach) English since they (come) to this school. 24.We __________(learn) 1000 words so far. 25. Tom ____________( be) away for three days. He will come back tomorrow. 26.The teacher _________(leave) two days ago. 27.The teacher______(be) here since two days ago. 28.--- _____ you ______ (clean) the room yet? --Yes, we __________ (do) that already. --When _______ you ______ (do) it? ---We _______ (do) it an hour ago. 29. ---______ he ______ (see) this film yet? --Yes,he _____. --When _____ he _____ (see) it? --He ____ it last week. 30. I _________ (read) the book twice. It’s interesting. 31—Where’s she? .-- She ________ (go) to Pairs. -- How ______she ______(go) there? --She _______ (go) there by air. 32. So far, many countries ___ _ (improve) their environment. 33. Mr Chen _____ (give)up smoking last year. 34. Mr Chen ______ (give) up smoking since last year. 35.It’s ten years since I ________(meet) her. 36.This is the most interesting book that I_________(read). 37.She _________(work) in this hospital in 2005. 38. She _________(work) in this hospital since 2005. 39.I __________ (clean) my room two hours ago. 40. I ________(clean) my room since two hours ago. 41 The old men ____________ (live)in the house for ten years. 42. Mum is not at home now. She _______ (go) the shop. 43.The sun ________(rise) since five o’clock. 44.I’m sorry I’ve already_______(forget) your name. 45.My leg _______(hurt) a lot last night. 46.They ________(eat) a lot of chichen already. 47.--- he ______ (give) the book back to the library? --Not yet. 48.My uncle _______(teach) English for ten years. He loves his job. 49.I ________(spend) five hours watching TV last weekend. 50.He’s just _______(tell) us a story. 二、按要求变换句型。 1.I have already eaten the food.(否定句) 2..We have ever read this book. .(否定句) 3.The plane has arrived. (否定句) 4. She’s lent some money to others. (否定句) 5. She has already visited her aunt.(一般疑问句并肯定回答) 6..My father has already hadlunch. (一般问句并否
现在完成时和过去完成时的区别
I have cleaned the classroom .(强调扫地所产生的结果:地干净了!) We have lived here for ten years.(“住”从过去持续到现在的动作用现在完成时) We have lived here since we came here.(“住”是从过去持续到现在的动作用现在完成时) Mr Green had lived in New York for ten years before he came to China.("来”中国已过去,而先前“住”在纽约更过去!)(另外注意:“住”在纽约可没有持续到现在!) We had learned 1000 words by the end of last term. (“上期期末”已过去,而是在其前“学”的就更过去了!) 一、从结构上区别 现在完成时: 主语 + have / has(not) + 过去分词 过去完成时: 主语 + had (not) + 过去分词 (二)从时间状语区别 现在完成时: 常用的时间状语包括“now, today, tonight, this week, this year, already, yet, just, recently…etc”。 过去完成时: 常用的时间状语包括“by, at, before等构成的短语”。 注意:当表示一段时间,现在完成时和过去完成时都可以用for 或since引导的状语。 例如: The meeting had begun when we got there. 我们到那儿时,会议已经开始了。 We had learned about 500English words when we were 6 years old. 我们六岁时就已经学了500个英语单词。
一般过去时和现在完成时用法区别(详细点)
一般过去时和现在完成时用法区别(详细点) 1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频腮度的时间状语连用。时间状语:every…, sometimes, at…, on Sunday I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。 The earth moves around the sun. 不受时间限制的 Shanghai lies in the east of China. 客观存在 表示格言或警句中。 Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。 例:Columbus proved that the earth is round.. 3) 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性、特征。 I don't want so much. Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well. 比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup. I am doing my homework now. ※4)由连词if unless before as soon as when once however 等引起的时间(条件、让步)状语从句,需要用一般现在时,表示将来时. 第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。再如:Now watch me, I switch on the current and stand back. 第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。 现在完成时用法解析 1.构成 现在完成时是由助动词have(has)+动词的过去分词构成。助动词说明该谓语是属于现在时范围。它和主语的人称、数要保持一致。过去分词是主要的谓语动词,说明句子的意义。 2.用法 (1)表示动作发生在过去某个不确定的时间,但对现在留下了某种影响和结果。常被just、already、yet 等副词修饰。如: -Have you had lunch yet? -Yes,I have. I've just had it. 你(已经)吃午饭了吗?我刚刚吃过。(现在我不饿了) (2)表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。这个动作可能刚停止,可能仍然在进行。常带有for和since等表
一般过去时与现在完成时和过去完成时的比较
①一般过去时的基本用法 a)表示过去某个特定时间发生的动作或存在的状态。常与过去时间连用. a moment ago(刚才),yesterday morning,last night/ week,the day before yesterday(前天),just now(刚才)等。 He suddenly fell ill yesterday. 昨天他突然生病了。 b)表示过去经常发生的动作或存在的状态。 I wrote home once a week at college. 我上大学时每周给家里写一封信. c)表示过去连续发生的一系列动作。 She entered the room, picked up a magazine and looked through it carefully. 她走进房间,拿起一本杂志,认真地翻阅了起来。 d)在时间、条件状语从句中用一般过去时代替过去将来时. We would not leave until the teacher came back. 老师回来我们才会离开。 ②一般过去时的特殊用法 a)在虚拟语气中表示现在或将来时间的动作或状态。 I wish I were twenty years younger. 但愿我年轻20岁。 b)在口语中,一般过去时往往显示委婉客气 Might I come and see you tonight? 我想今晚来看你,好吗? 现在完成时的用法: 1) 表示过去发生或已完成的某个动作对现在产生的影响或结果,强调的是这个影响或结果,一般不与过去时间连用,常同already, just, yet等状语连用例:I have just turned off the light. 我刚刚把灯关上。(结果是灯已经关上了) She has lost her bike. 她把自行车丢了。(影响是他现在没有自行车骑了) 2) 表示开始于过去、持续到现在的动作或状态,并可能继续下去(也可能不继续下去),常同包括现在在内的时间状语连,也同“for+时间段”或“since+时间点”的状语连用 She has taught in the school for ten years. 她在这所学校教书已经10年了。 I haven’t eaten anything since breakfast. 我从早饭起就一直没有吃东西。
现在完成时和一般过去时
现在完成时专项练习 一、用since和for填空 1______ two years 2_______ two years ago 3_______lastmonth 4______1999 5 _______ yesterday 6 _______ 4 o’clock 7 ______ 4 hours 8_______ an hour ago 9_______ we were children 10 _____ lunch time 11 ______ she left here 12. He has lived in Nanjing ________ the year before last. 13. I’ve known him __________ we were children. 14. Our teacher has studied Japanese _________ three years. 15. She has been away from the city ___________ about ten years. 16 It’s about ten years __________ she left the city. 17 How long have you been here?-______ half past three. 18How long has that car been here?-______ yesterday. 19 How long have you been in this school?-______ four years. 20 How long has that boy been in your class?-______ six weeks. 21 How long have you lived here?-______ 1996 二、用have(has) been、have(has) gone 、have/has been to/in, have gone to填空。 1、A: Where ____________ Li Fei ___________? B: He ____________ to Hainan Island. A: How long ___________ he ___________ there? B: He _____________ there for three days. A: When will he come back , do you know? B: I’m afraid he won’t come back recently. A: Could you tell me the way to Hainan Island? B: Sorry, I _________ never ___________ there. A: How many times ___________ Li Fei __________ to that place? B: He _____________ there only once. 2、Where is Jack? He __________ his country. John _______ England since he came back. How long _____ he _____ this village? The Smiths ______ Beijing for years. _____ you ever ____ America? -- Yes, I _____ there many times. I _____ this school since three years ago. 三、选择填空
现在完成时与一般过去时专项练习
现在完成时与一般过去时专项练习 每日一句 God helps those who help themselves. Review 单项选择题 1.Mother _____ me a new coat yesterday. I _______ it on. It fits me well. A. had made…have tried B. made…have tried C. has made…tried D. made…tried 2 “He ____to draw horses already”. “When ______ he ?” “ Last year “ A. learned...has B. learned (i) C. has learned...has D. has learned (i) 3.Tom _____up into the tree. Look, he ____ high up there ! A. has got…is B. has climbed…was C. got …was D. climbed…is 4.____ you _____ the text yet ? Yes, we ____ it two hours ago. A. Did…copy…did B. Have…copied…have C. Have…copied…did D. Did …copy…had 5. “Why ______ she _______ angry ?” “Because he _____ at her just now .” A. did…get…shouted B. has…got…shouted C. di d…get…has shouted D. has…got…has shouted 6. ______you __________ the film before ? Where _____ you ____ it ? A. Have …seen…did…see B. Did …see…did…watch C. Have…seen…have…seen D. Did …see…have…seen 7.You ____ me waiting for two hours. I ____ for you since five. A. kept…waited B. have kept…waited C. kept…have waited D. have kept…have waited 8.Where ______ John _______ ? To the library. He _________ there for an hour. A.has…been…has gone B. has…gone…has been C. did…go…went D. did…be…went 9.______ the baby still _____ ? No, it _______ crying. A. Has…cried…has stopped B. Is…crying…stopped C. Did …cry…stopped D. Is…crying…has stopped 10. I _______ the way. I ________ here for quite many years. A. knew...have lived B. kne w (iv) C. know...have lived D. know (iv) Summary 现在完成时与一般过去时的比较 (一)一般过去时态和现在完成时态的概念 一般过去时表示在过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作常与yesterday, yesterday afternoon, last year, in 1965, a moment ago等表示过去的时间状语连用, 例如: He came here yesterday. 现在完成时表示过去的动作(或状态)对现在产生的_________, 例如: He has broken his bottle.
一般过去时与现在完成时
一般过去时 1.一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。一般过去时也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。 2.Be动词在一般过去时中的变化: ⑴am 和is在一般过去时中变为was。(was not=wasn’t) ⑵are在一般过去时中变为were。(were not=weren’t) ⑶带有was或were的句子,其否定、疑问的变化和is, am, are一样,即否定句在was或were 后加not,一般疑问句把was或were调到句首。 3.句中没有be动词的一般过去时的句子 否定句:didn’t +动词原形,如:Jim didn’t go home yesterday. 一般疑问句:在句首加did,句子中的动词过去式变回原形。如:Did Jim go home yesterday? 特殊疑问句:⑴疑问词+did+主语+动词原形?如:What did Jim do yesterday? ⑵疑问词当主语时:疑问词+动词过去式?如:Who went to home yesterday? 动词过去式变化规则: 1.一般在动词末尾加-ed,如:pull-pulled, cook-cooked 2.结尾是e加d,如:taste-tasted 3.末尾只有一个元音字母和一个辅音字母的重读闭音节,应双写末尾的辅音字母,再加-ed,如:stop-stopped 4.以“辅音字母+y”结尾的,变y为i,再加-ed,如:study-studied 5.不规则动词过去式:am,is-was, are-were, do-did, see-saw, say-said, give-gave, get-got, go-went, come-came, have-had, eat-ate, take-took, run-ran, sing-sang, put-put, make-made, read-read, write-wrote, draw-drew, drink-drank, fly-flew, ride-rode, speak-spoke, sweep-swept, swim-swam, sit-sat 现在完成时: 基本结构:主语+have/has+过去分词(done) ①肯定句:主语+have/has+过去分词+其他 ②否定句:主语+have/has+not+过去分词+其他 ③一般疑问句:Have/Has+主语+过去分词+其他 ④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句(have/has+主语+过去分词+其他) (1)现在完成时用来表示现在之前已发生过或完成的动作或状态,但其结果却和现在有联系,也就是说,动作或状态发生在过去但它的影响现在还存在. I have spent all of my money.(含义是:现在我没有钱花了.) Jane has laid the table.(含义是:现在桌子已经摆好了.) Michael has been ill.(含义是:现在仍然很虚弱) He has returned from abroad. (含义是:现在已在此地) (2)现在完成时可以用来表示发生在过去某一时刻的,持续到现在的动作(用行为动词表示)或状态(be动词表示)常与for(+时间段),since(+时间点或过去时的句子)连用. Mary has been ill for three days. I have lived here since 1998. 注:瞬间动词(buy,die,join,lose……)不能直接与for since 连用。要改变动词 come-be go out-be out finish-be over open-be open die-be dead …… a)1.have代替buy
过去完成时与现在完成时的区别及用法
现在完成时和过去完成时这两个时态的相似之处是动作都发生在过去,差别是两个时态所对应的时间参照点不一样。 现在完成时的动作发生在过去,但是时间参照点是现在 过去完成时的动作发生在过去,但是时间参照点是过去的某一时间。请看下面两个例句 -I have lived in Thailand for five years. (我目前在泰国已经住了五年了) live(居住)是上面例句的谓语,那么这个动作显然是发生在过去(五年前),但是一直持续到现在,我们的时间参照点是“现在、当下”。我们再看下面一个例句: I had lived in Thailand for five years before I went to China. (在我来中国之前,我已经在泰国住了五年了) live这个动作发生在过去,是前面句子的谓语,但是整句话的时间参照点变成了before I went to China,这个动作也是过去的一个时间点,所以我们要把go 变成went。所以从上面两个例句中大家可以看出,其实这两个时态的不同之处就在于时间参照点的不同。总结一下,现在完成时用来表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响,通常我们可以用现在完成时态表达三类情况: 第一、经验 -I have seen that movie before. (我之前看过那部电影) 凡是我们谈论之前的经验,看过、听过、吃过、去过、读过等等的经验都可以用现在完成是来表达,那么上面例句的意思是我不仅看过那部电影,而且我对电影的情节还有印象。 第二、持续 -I have known John since we were kids. (当我们还是小孩的时候我就认识John了) Know(认识)这个动作发生在过去,而参照点是现在,说明我们现在还是朋友,而且友谊还可能继续持续下去 第三、改变 -I have bought a new car. (我买了一辆新车) buy这个动作发生在过去,但是时间参照点是现在,其实言下之意是我不仅买了一辆新车,而且这辆新车我现就在我家,我随时都能用。之前没有车,现在有车了,这就是改变。 那么过去完成是则是谈论过去的两个动作谁先谁后的问题,请看下例:-The plane left at 5 pm. (飞机下午五点起飞的) -We arrived at the airport at 6 pm. (我们六点到的机场) 上面两个句子都是一般过去时,表示两件完整的发生在过去的事情,这个时候我们可以用过去完成时态把这两个句子串起来,就变成了下面的句子:-The plane had left when we arrived at the airport.
一般过去时、过去进行时和现在完成时-区别
过去进行时与一般过去时 一、时间状语不同 一般过去时的时间状语主要有:yesterday (morning, afternoon, evening), last night (week, month, year), ago, the day before yesterday, in 2003, just now, long long ago, one day等; 过去进行时的时间状语有:at this / that time yesterday, the whole evening, all day yesterday等。试比较: He introduced Tom to us just now. 刚才他向我们介绍了汤姆。 She was doing some washing all day yesterday. 昨天她洗了一整天的衣服。 二、强调动作的角度不同 一般过去时强调动作的发生或状态的存在;而过去进行时强调动作正在进行的延续性。试比较: I got up at five the day before yesterday. 前天我是五点起床的。 He was painting the lab the whole day yesterday. 昨天他一整天都在粉刷实验室。 三、动词的特点不同 1. 行为动词在这两种时态中均可使用。例如: We planted trees two days ago. 两天前我们植树了。 We were planting trees this time last Friday. 上周五这时候我们在植树。 2. 有些动词只用于一般过去时,而不能用于过去进行时。例如: 1) 表示感观的动词:feel, hear, know, see, smell, taste等。 2) 表示状态、感情的动词:be, dislike, have, hate, love, like, want, wish等。 3) 表示心理活动的动词:forget, realize, recognize, remember, understand等。 4) 表示所属关系的动词:own, belong 等。 3. 一般过去时的谓语动词既可是延续性的也可是终止性的;过去进行时的谓语动词只能是延续性的。例如: Li Jian joined the army in 1998. 李健于1998年参军。( join为终止性动词) She was cooking at that time. 那时她在做饭。(cook为延续性动词) 四、情感不同 一般过去时是对过去事实的客观描述,语气比较客观、肯定;过去进行时有时也可表示埋怨、厌烦等情绪,带有描绘性和感情色彩。试比较: The plane took off late this morning. 这架飞机今天早上起飞晚了。(说明客观事实) The plane was always taking off late. 这架飞机总是起飞晚。(带有埋怨情绪,指责某事的发生) 现在完成时与一般过去时的区别 1. 一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的事、存在的状态或经常发生的动作。说话的侧重点只在于陈述一件过去的事情,不强调对“现在”产生的影响。如: He visited Guilin in 1998.他1998年参观过桂林。(只说明去桂林的时间) 时间状语: ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, once upon a time, etc. 2. 现在完成时表示动作发生在过去,对现在造成了影响或产生了结果。不与确定的过去时间状语连用。如: Jill has bought a new computer.吉尔买了一台新电脑。(着重点是现在有了一台新电脑)
一般过去时态和现在完成时态的区别练习题资料讲解
一般过去时态和现在完成时态的区别练习 题
一般过去时态和现在完成时态的区别练习题 1)一般过去时态表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;现在完成时态中动作为过去发生的,强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。如:I saw this film yesterday. (强调看的动作发生过了) I have already seen this film.(强调对现在的影响,电影的内容已经知了)I haven’t finished my work yet. (强调对现在的影响,还有工作要做,不能去玩) When did you finish your homework? (询问过去的动作所发生的时间,与现在无关) 2)一般过去时态表示动作在过去已经停止;现在完成时态表示过去开始的动作一直延续到现在。 如:Ann visited her uncle last weekend.(visit这个动作在过去已经停止) They have lived here since 1983. (live here 这个动作从1983年开始,一直延续到现在) 3)一般过去时态常用非延续性动词,如borrow, buy, come, go, leave, start, die, finish, become等。现在完成时态可表示持续到现在的动作或状态,与时间段连用时动词一般是延续性的,如keep, have, live, teach, learn, work, study, know, be等。如:He joined the League three years ago .(join是短暂动词)
