国际经济学第二次作业解析

克鲁格曼《国际经济学》(第8版)笔记和课后习题详解 第2章~第4章【圣才出品】
第1篇国际贸易理论 第2章世界贸易概览 2.1复习笔记 1.经济规模与进出口总额之间的关系 (1)规模问题:引力模型 现实证明一国的经济规模与其进出口总额息息相关。把整个世界贸易看成整体,可利用引力模型(gravity model)来预测任意两国之间的贸易规模。引力模型方程式如下: 其中, T是i国与j国的贸易额,A为常量,i Y是i国的国内生产总值,j Y是j国的国 ij 内生产总值, D是两国的距离。引力模型方程式表明:其他条件不变的情况下,两国间的 ij 贸易规模与两国的GDP成正比,与两国间的距离成反比。 (2)引力模型的内在逻辑 引力模型之所以能较好地拟合两国之间的实际贸易现状,其原因在于:大的经济体收入高,因而大量进口产品;大的经济体能生产更多品种的系列产品,因而更能满足其他国家的需求,进而大量出口产品。在两国贸易中,任一方的经济规模越大,则双方的贸易量就越大。 (3)引力模型的应用:寻找反例 当两国之间的贸易量与依照引力模型计算得出的结果相差较大时,就需要从其他因素进行分析,如文化的亲和性、地理位置、运输成本等因素。事实上,这也是引力模型的重要用
途之一,即有助于明确国际贸易中的异常现象。 (4)贸易障碍:距离、壁垒和疆界 距离、壁垒和疆界对国际贸易有负面作用,会使得两国之间的贸易额大大小于根据引力模型所计算出的结果。另外,在各国GDP和距离给定的情况下,有效贸易协定(trade agreement)比无效的贸易协定更能显著增加成员国的贸易量,这也是美国与其邻国的贸易量明显大于其和相同大小的欧盟的贸易量的原因之一。 2.正在演变的世界贸易模式 (1)世界变小了吗? 人们认为,现代化的运输和通讯可以超越空间距离的束缚,世界因此成了小“村落”。事实的确如此。但是,有时候政治的力量可以超过技术进步的作用,两次世界大战、20世纪30年代的大萧条及战后全世界范围内的贸易保护主义等都严重制约着国际贸易的发展,使得国际贸易大幅萎缩,并且用了几十年才得以恢复。 (2)交易内容 从全世界范围来看,工业制成品是主要的交换产品,所占比重最大。矿产品特别是现代世界不可或缺的石油依旧是世界贸易的主要部分。引人注目的是发展中国家已经从初级产品出口国转变为主要的制成品出口国。另外,服务贸易在国际贸易中凸显重要,并且其重要性越来越突出。 (3)服务外包 随着现代信息技术的发展和应用,一种新的贸易形式——服务外包(service outsourcing)随之出现。服务外包也称之为离岸服务,是一种新兴的国际贸易现象,使得曾经必须在一国国内实现的服务现在可以在国外实现。 (4)旧规则依然可行吗?
国际经济学作业答案第一章
Chapter 1 Introduction Multiple Choice Questions Historians of economic thought often describe ___________ written by _______ and published in __________ as the first real exposition of an economic model. “Of the Balance of Trade,” David Hume, 1776 “Wealth of Nations,” David Hume, 1758 “Wealth of Nations,” Adam Smith, 1758 “Wealth of Nations,” Adam Smith, 1776 “Of the Balance of Trade,” David Hume, 1758 Answer: E From 1959 to 2000, the U.S. economy roughly tripled in size. U.S. imports roughly tripled in size. the share of US Trade in the economy roughly tripled in size. U.S. Imports roughly tripled as compared to U.S. exports. U.S. exports roughly tripled in size. Answer: C The United States is less dependent on trade than most other countries because the United States is a relatively large country. the United States is a “Superpower.” the military power of the United States makes it less dependent on anything. the United States invests in many other countries. many countries invest in the United States. Answer: A Ancient theories of international economics from the 18th and 19th Centuries are: not relevant to current policy analysis. are only of moderate relevance in today’s modern international economy. are highly relevant in today’s modern internationa l economy. are the only theories that actually relevant to modern international economy. are not well understood by modern mathematically oriented theorists. Answer: C
国际经济学克鲁格曼考试重点
绝对优势:是指以各国生产成本的绝对差异为基础进行的国际专业化分工,并通过自由贸易获得利益的一种国际贸易理论。 李嘉图模型:是一个单一要素模型,劳动是唯一的生产要素,劳动生产率的差异是不同国家各个产业部门之间唯一的不同之处,也是决定国际贸易的唯一因素。李嘉图模型的中心含义是如果每个国家都能够专门生产并出口本国劳动生产率较高的产品,那么他们之间的贸易就会给每个国家带来利益,他的两个核心含义:劳动生产率的差异在国际贸易中占据重要地位和贸易模式取决于比较优势而非绝对优势,至今仍能得到事实支持。 机会成本:是指因一种选择而放弃的最有替换物或失去最好机会的价值,即是指经济决策中影由中选的最优方案负担的,按所放弃的次优方案潜在收益计算的那部分资源损失。 要素比例理论/赫克歇尔俄林理论:是指从资源禀赋角度对国际贸易中的生产成本和价格的差异做出解释的国际贸易理论。其内容是:各国的贸易源于不同国家之间商品的价格存在差异,而价格差异的原因在于不同国家之间的生产成本有高有低,生产成本的高低是因为各国生产要素价格有差别,生产要素价格的差异又与各国生产要素丰裕程度密切相关。生产要素丰裕,其商品价格自认就相对低一些,生产要素稀缺,其价格相对高一些。生产要素丰裕度的差异是国际贸易产生的根本原因。 出口偏向性增长:是指一国的经济增长主要源于出口产品生产能力提高的经济增长方式,表现在生产可能性边界上就是使生产可能性边界扩张偏向出口产品。 福利恶化性增长:是指一国整体福利水平恶化的经济增长方式,是发展中国家的出口偏向型增长在严格假定下可能出现的一种极端情况。一国的出口偏向性增长可能导致该国的贸易条件恶化。因此,如果一国的经济增长方式表现为极强的出口偏向性,那么贸易条件恶化带来的负面影响就会抵消生产力提高带来的正面效应,使得该国整体的福利水平恶化。 出口补贴:是指国家为了降低出口商品的价格,提高其在国际上的竞争力,对出口商品给予的现金或财政上的补贴。 动态收益递增:成本随着累计产量下降而并非随着当前劳动生产率的上升而下降的情形就是动态收益递增 倾销:出口商以低于国内市场价格的价格,甚至以低于成本的价格在国际市场上销售商品的行为。 外部规模经济是指整个行业规模和产量的扩大而使单个企业平均成本下降或收益增加的经济现象。 边际收益:在生产的技术水平和其他投入要素的数量均保持不变情况下,新增加一个单位的某种投入要素所引起的产量的增加量。 幼稚工业论:认为新兴工业在发展初期需要国家提供保护以免在外国强大的竞争下夭折,并随着新兴工业的发展和竞争力的增强而逐步取消贸易保护,为自由贸易的实行创造条件。垄断竞争:介于完全竞争和完全垄断之间的一种市场结构,这种结构下既存在垄断,又存在竞争。 价格歧视:一家企业在销售同样的商品时,对不同的顾客索取不同价格的做法 完全垄断:完全排斥竞争的一种市场结构。 内部规模经济:单个企业生产规模不断扩大时,由其自身内部引起的平均成本不断下降,收益不断增加的经济现象。 相互倾销:不同国家生产同种或类似产品的厂商都对出口产品制定一个低于国内市场价的价格并进行双向贸易的现象。 行业内贸易:在国际贸易活动中,不同国家之间就同一产业的产品所进行的贸易。
国际经济学作业答案
C h a p t e r7I n t e r n a t i o n a l F a c t o r M o v e m e n t s Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following differs in its essential analytical framework (a) I nternational trade in goods (b) I nternational conflict resolution (c) I nternational trade in services (d) I nternational trade in factors of production (e) I nternational borrowing and lending Answer: B 2. The slope of the production function measures (a) t he physical increase in output as country grows. (b) t he dollar-value increase in output as a country grows. (c) t he increase in number of workers as immigration proceeds. (d) t he marginal product of labor. (e) t he marginal product of capital.
Answer: D 3. International free labor mobility will under all circumstances (a) i ncrease total world output. (b) i mprove the economic welfare of everyone. (c) i mprove the economic welfare of workers everywhere. (d) i mprove the economic welfare of landlords (or capital owners) everywhere. (e) N one of the above. Answer: E 4. If the world attained a perfect Heckscher-Ohlin model equilibrium with trade, then (a) w orkers in the labor abundant country would migrate to the capital abundant country. (b) w orkers in the labor abundant country would wish to migrate to the capital abundant country. (c) w orkers in the labor abundant country would have no desire to migrate to the capital abundant country.
国际经济学在线作业
国际经济学在线作业 1.第1题 比较优势理论认为国际贸易的驱动力是 ()。 A.劳动生产率的差异 B.技术水平的差异 C.产品品质的差异 D.价格的差异 您的答案: A 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 2.第2题 如果一个大国对进口商品征收关税()。 A.对贸易条件不产生影响 B.提高所有国家的贸易条件 C.提高本国的贸易条件 D.导致本国贸易条件恶化 您的答案: C 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 3.第3题 通常所说的“纸黄金”是()。 A.黄金 B.外汇 C.普通提款权 D.特别提款权 您的答案: D 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 4.第4题 甲乙两国货币的实际汇率由名义汇率以及
()共同决定。 A.甲国货币购买力 B.乙国货币购买力 C.两国利率水平 D.两国相对物价水平 您的答案: D 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 5.第5题 根据蒙代尔的“政策配合说”,用来实现外部均衡的 政策手段是()。 A.财政政策 B.货币政策 C.汇率政策 D.直接管制 您的答案: B 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 6.第6题 不能解释产业内贸易现象的理论有( )。 A.重叠需求理论 B.要素比例理论 C.规模经济理论 D.垄断竞争理论 您的答案: B 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 7.第7题 属于非关税壁垒的措施是( )。 A.反倾销税 B.反补贴税 C.进口附加税
D.国内最低限价 您的答案: D 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 8.第8题 下述哪一种不属于投机性外汇交易( )。 A.双边套汇 B.多边套汇 C.套利 D.套期保值 您的答案: D 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 9.第17题 IS-LM模型是宏观经济分析的一个重要工具,是描述____市场和____市场之间相互联系的理论结构。() A.货币资本 B.资本劳动力 C.资本商品 D.货币产品 您的答案: D 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0 10.第18题 国际经济一体化的形式不包括()。 A.关税同盟 B.自由贸易区 C.共同市场 D.自由市场 您的答案: D 题目分数: 2 此题得分: 2.0
国际经济学作业答案-第三章
Chapter 3 Labor Productivity and Comparative Advantage —The Ricardian Model Multiple Choice Questions 1. Countries trade with each other because they are _______ and because of ______. (a) different, costs (b) similar, scale economies (c) different, scale economies (d) similar, costs (e) None of the above. Answer: C 2. Trade between two countries can benefit both countries if (a) each country exports that good in which it has a comparative advantage. (b) each country enjoys superior terms of trade. (c) each country has a more elastic demand for the imported goods. (d) each country has a more elastic supply for the supplied goods. (e) Both (c) and (d). Answer: A 3. The Ricardian theory of comparative advantage states that a country has a comparative advantage in widgets if (a) output per worker of widgets is higher in that country. (b) that country’s exchange rate is low. (c) wage rates in that country are high. (d) the output per worker of widgets as compared to the output of some other product is higher in that country. (e) Both (b) and (c). Answer: D 4. In order to know whether a country has a comparative advantage in the production of one particular product we need information on at least ____unit labor requirements (a) one (b) two (c) three (d) four (e) five Answer: D
国际经济学作业答案-第八章
. Chapter 8 The Instruments of Trade Policy Multiple Choice Questions 1. Specific tariffs are (a) import taxes stated in specific legal statutes. (b) import taxes calculated as a fixed charge for each unit of imported goods. (c) import taxes calculated as a fraction of the value of the imported goods. (d) the same as import quotas. (e) None of the above. Answer: B 2. Ad valorem tariffs are (a) import taxes stated in ads in industry publications. (b) import taxes calculated as a fixed charge for each unit of imported goods. (c) import taxes calculated as a fraction of the value of the imported goods. (d) the same as import quotas (e) None of the above. Answer: C 3. The excess supply curve of a product we (H) import from foreign countries (F) increases as (a) excess demand of country H increases. (b) excess demand of country F increases. (c) excess supply of country H increases. (d) excess supply of country F increases. (e) None of the above. Answer: D 4. If a good is imported into (large) country H from country F, then the imposition of a tariff in country H (a) raises the price of the good in both countries (the “Law of One Price”). (b) raises the price in country H and cannot affect its price in country F. (c) lowers the price of the good in both countries. (d) lowers the price of the good in H and could raise it in F. 精品
克鲁格曼 国际经济学第9版教材答案
Chapter 1 Introduction ?Chapter Organization What Is International Economics About? The Gains from Trade The Pattern of Trade How Much Trade? Balance of Payments Exchange Rate Determination International Policy Coordination The International Capital Market International Economics: Trade and Money ?Chapter Overview The intent of this chapter is to provide both an overview of the subject matter of international economics and to provide a guide to the organization of the text. It is relatively easy for an instructor to motivate the study of international trade and finance. The front pages of newspapers, the covers of magazines, and the lead reports on television news broadcasts herald the interdependence of the U.S. economy with the rest of the world. This interdependence may also be recognized by students through their purchases of imports of all sorts of goods, their personal observations of the effects of dislocations due to international competition, and their experience through travel abroad. The study of the theory of international economics generates an understanding of many key events that shape our domestic and international environment. In recent history, these events include the causes and consequences of the large current account deficits of the United States; the dramatic appreciation of the dollar during the first half of the 1980s followed by its rapid depreciation in the second half of the 1980s; the Latin American debt crisis of the 1980s and the Mexican crisis in late 1994; and the increased pressures for industry protection against foreign competition broadly voiced in the late 1980s and more vocally espoused in the first half of the 1990s. The financial crisis that began in East Asia in 1997 and spread to many countries around the globe and the Economic and Monetary Union in Europe highlighted the way in which various national economies are linked and how important it is for us to understand these connections. These global linkages have been highlighted yet again with the rapid spread of the financial crisis in the United States to the rest of the world. At the same time, protests at global economic meetings and a rising wave of protectionist rhetoric have highlighted opposition to globalization. The text material will enable students to understand the economic context in which such events occur. ? 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Addison-Wesley
国际经济学作业复习资料第二章
Chapter 2 World Trade—An Overview Multiple Choice Questions 1. What percent of all world production of goods and services is exported to other countries? (a) 10% (b) 25% (c) 50% (d) 100% (e) None of the above Answer: B 2.What percent of all world imports of goods and services were exported? (a) 10% (b) 25% (c) 50% (d) 100% (e) None of the above. Answer: D 3. What percent of all world consumption (private and public, including real investment) was imported? (a) 10% (b) 25% (c) 50% (d) 100% (e) None of the above. Answer: B 4. The gravity model, that states that size matters,predicts that the weight of the traded good will ________ related to its likelihood to be exported (a) be directly (b) be inversely (c) not be (d) All of the above (e) None of the above Answer: E
克鲁格曼《国际经济学》计算题及答案
1. 在古典贸易模型中,假设A 国有120名劳动力,B 国有50名劳动力,如果生产棉花的话,A 国的人均产量是2吨,B 国也是2吨;要是生产大米的话,A 国的人均产量是10吨,B 国则是16吨。画出两国的生产可能性曲线并分析两国中哪一国拥有生产大米的绝对优势?哪一国拥有生产大米的比较优势? 思路:B 国由于每人能生产16吨大米,而A 国每人仅生产10吨大米,所以B 国具有生产大米的绝对优 势。 从两国生产可能性曲线看出A 国生产大米的机会成本为,而B 国为,所以B 国生产大米的机会成本或相对成 本低于A 国,B 国生产大米具有比较优势。 2.下表列出了加拿大和中国生产1单位计算机和1单位小麦所需的劳动时间。假定生产计算机和小麦都只用劳动,加拿大的总劳动为600小时,中国总劳动为800小时。 (1) 计算不发生贸易时各国生产计算机和小麦的产量。 (2) 哪个国家具有生产计算机的比较优势?哪个国家具有生产小麦的比较优势? (3) 如果给定世界价格是1单位计算机交换22单位的小麦,加拿大参与贸易可以从每单位的进 口中节省多少劳动时间?中国可以从每单位进口中节省多少劳动时间?如果给定世界价格是1 单位计算机交换24单位的小麦,加拿大和中国分别可以从进口每单位的货物中节省多少劳动 时间? (4) 在自由贸易的情况下,各国应生产什么产品,数量是多少?整个世界的福利水平是提高还是 降低了?试用图分析。(以效用水平来衡量福利水平) 思路: (1) 中国生产计算机的机会成本为100/4=25,加拿大为60/3=20 (2) 因为加拿大生产计算机的机会成本比中国低,所以加拿大具有生产者计算机的比较优势,中国就具有生 产小麦的比较优势。 (3) 如果各国按照比较优势生产和出口,加拿大进口小麦出口计算机,中国进口计算机出口小麦。 加拿大进口一单位小麦需要出口1/22单位计算机,折合成劳动时间来算,生产一单位小麦本国要用3小 时,但生产1/22单位计算机本国要用60/22小时劳动,所以加拿大进口一单位小麦相当于用60/22小时 的劳动换回本国3小时生产的产品,节省了3-60/22=3/11小时的劳动时间。中国进口一单位计算机需要 出口22单位小麦,相当于用22*4=88小时的劳动换回本国需用100小时生产的产品,节省了100-88=12 小时的劳动时间。 如果世界价格是1单位计算机交换24单位的小麦,则相当于用60/24小时的劳动换回本国3小时生产的 产品,节省了3-60/24=1/2小时的劳动时间。中国进口一单位计算机需要出口24单位小麦,相当于用 24*4=96小时的劳动换回本国需用100小时生产的产品,节省了100-96=4小时的劳动时间。 (4) 在自由贸易的情况下,加拿大应专业生产计算机,数量为600/60=10单位;中国应专业生产小麦,数量 为800/4=200单位。 中国的福利水平从U 01上升到U 11,加拿大的福利水平从U 02上升到U 12,整个世界的福利水平上升了。 3. 假定中国总劳动为600小时,生产每单位钢铁Y 需要4小时,而生产每单位大米X 需要2小时,用图画出:
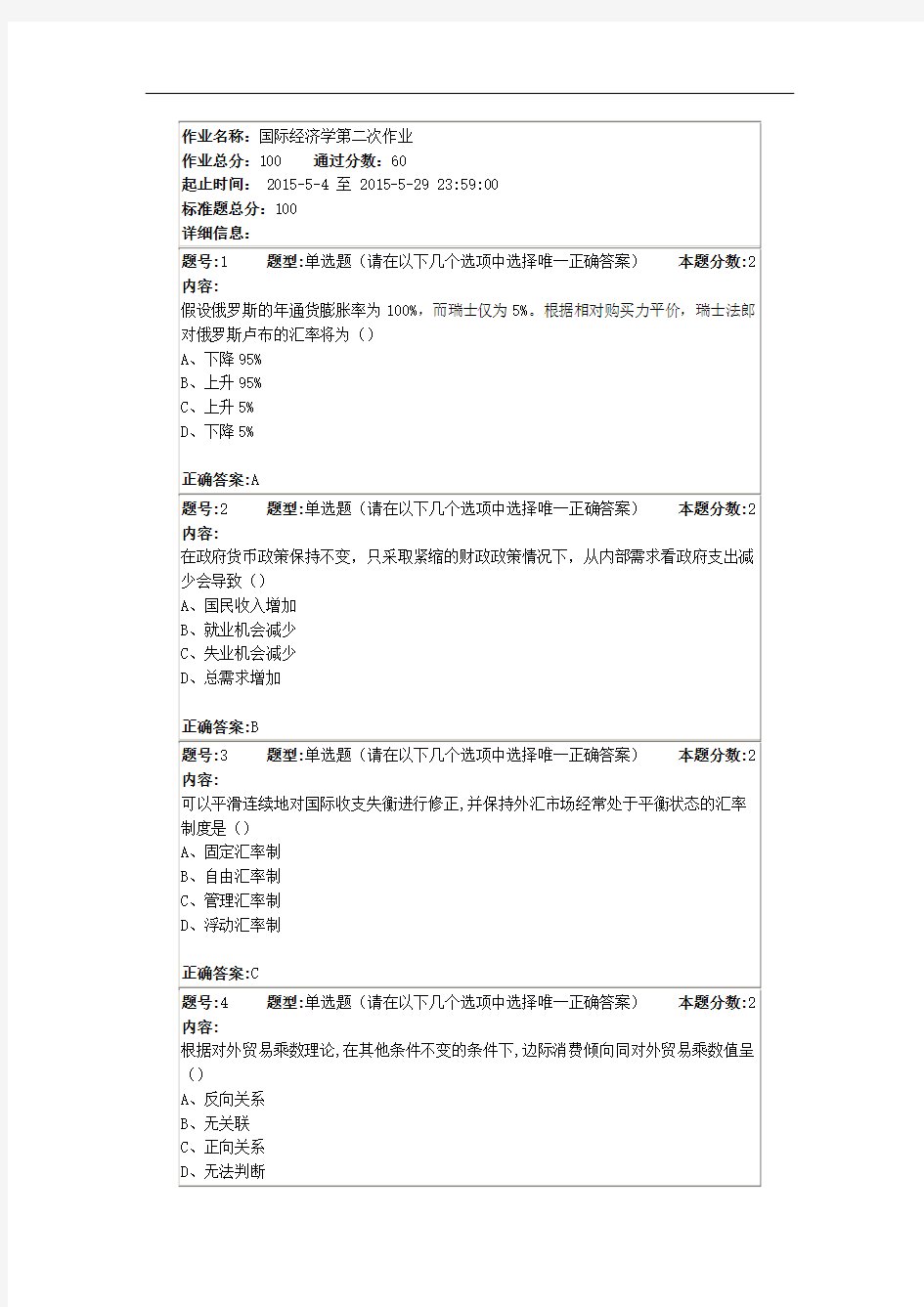
国际经济学第二次作业
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 作业名称:国际经济学第二次作业 作业总分:100 通过分数:60 起止时间: 2015-5-4 至 2015-5-29 23:59:00 标准题总分:100 详细信息: 题号:1 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:2 内容: 一般来说,对于来自外部的冲击,如出口需求冲击、进口供给冲击和资本流动等,要想更有效减轻冲击,必须采取() A、浮动汇率 B、固定汇率 C、盯住制度 D、管理汇率 正确答案:A 题号:2 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:2 内容: 在其他条件不变时,国外居民将需求从其本国产品转向该国的出口商品,一国货币对外币的实际汇率将()
B、不变 C、上升 正确答案:C 题号:3 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:2 内容: 在本国货币贬值后,一国的贸易状况在得到改善之前,反而可能先恶化,这种现象被称为() A、需求时滞 B、反应时滞 C、J曲线效应 D、特里芬难题 正确答案:C 题号:4 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:2 内容: 使用购买力平价法估算发达国家的经济数量时会()实际数量,而估算发展中国家时会() A、高估,低估 B、低估,高估 C、高估,高估 D、低估,低估
题号:5 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:2 内容: 给定对未来汇率的预期,国内实际GNP的增加对汇率的短期影响是() A、本币升值 B、本币贬值 C、国内货币需求减少 D、利率降低 正确答案:A 题号:6 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:2 内容: 马歇尔-勒纳条件分析汇率变动能否改善国际收支的切入点是() A、收入变化 B、汇率变化 C、供求弹性 D、经济周期 正确答案:C 题号:7 题型:单选题(请在以下几个选项中选择唯一正确答案)本题分数:2 内容: 如果客户向银行购买外汇,应该使用银行所报出的()
国际经济学(克鲁格曼)教材答案
Chapter 3 1.Home has 1200 units of labor available. It can produce two goods, apples and bananas. The unit labor requirement in apple production is 3, while in banana production it is 2. a .Graph out the production possibilities frontier: b .What is the opportunity cost of apples in terms of bananas? 5.1=Lb La a a c .In the absence of trade, what would the price of apples in terms of bananas be? In the absence of trade, since labor is the only factor of production and supply decisions are determined by the attempts of individuals to maximize their earnings in a competitive economy, only when Lb La b a /a a /P P =will both goods be produced. So 1.5 /P P b a = 2.Home is as described in problem 1. There is now also another country, Foreign, with a labor force of 800. Foreign ’s unit labor requirement in apple production is 5, while in banana production it is 1. a .Graph Foreign ’s production possibilities frontier: b .Construct the world relative supply curve. Home's PPF 0200400600800 200400600800Q apple Q banana Foreign's PPF 02004006008001000 80160240320400Q*apple Q*banana
《国际经济法》第二次作业
《国际经济法》第二次作业49 《国际公法》第二次作业;02—0001;一、单项选择题(共10道试题,共30分; 1.保险公司承担保险责任的期间通常是(C);A.钩至钩期间;B.舷至舷期间; C.仓至仓期间; D.水面责任期间;2.下列各种关于提单的类型中,(B)是与对货物记;A.直运提单B.清洁提单C.指示提单D.记名提单;3.下列表述中,不正确的是哪项?(D);A.委付一经保险人接受,不得撤 《国际公法》第二次作业 02—0001 一、单项选择题(共 10 道试题,共 30 分。) 1. 保险公司承担保险责任的期间通常是( C ) A. 钩至钩期间 B. 舷至舷期间 C. 仓至仓期间 D. 水面责任期间 2. 下列各种关于提单的类型中,( B )是与对货物记载有关的提单。
A. 直运提单 B. 清洁提单 C. 指示提单 D. 记名提单 3. 下列表述中,不正确的是哪项?(D ) A. 委付一经保险人接受,不得撤回 B. 保险标的全损后,保险人支付了保险赔偿金后,即取得了代位求偿权 C. 保险标的发生推定全损后,保险人支付了保险赔偿金后,可以取得代位求偿权和残存标的物的所有权 D. 保险标的发生推定全损后,被保险人有权将保险标的物的权利义务转让给保险人,保险人必须接受并支付全额赔偿 4. 《海牙规则》规定的承运人使船舶适航的责任,限于( A ) A. 在开航前和开航时 B. 开航前 C. 航行中 D. 开航后至到达目的地时 5. 将海上班轮运输承运人的不完全过失责任制改为承运人的推定完全过失责任制的国际公约是:( B ) A. 海牙规则 B. 汉堡规则 C. 维斯比规则 D. 华沙公约 6. 被保险人把残存被保险货物的所有权转让给保险公司,并请求赔付全额保险金的条件是货物发生:( D ) A. 实际全损 B. 部分损失 C. 共同海损 D. 推定全损 7. 中国人民保险公司海洋运输货物保险条款规定的基本险别不包括( B )
国际经济学作业
Quiz for Ch5 1) In the 2-factor, 2-good Heckscher-Ohlin model, an influx of workers from across the border w ould A) move the point of production along the production possibility curve. B) shift the production possibility curve outward, and increase the production of both goods. C) shift the production possibility curve outward and decrease the production of the labor-inten sive product. D) shift the production possibility curve outward and decrease the production of the capital-inte nsive product. E) shift the possibility curve outward and displace preexisting labor. 2) In the 2-factor, 2-good Heckscher-Ohlin model, the two countries differ in A) tastes and preferences. B) military capabilities. C) the size of their economies. D) relative abundance of factors of production. E) labor productivities. 3) One way in which the Heckscher-Ohlin model differs from the Ricardo model of comparative a dvantage is by assuming that ________ is (are) identical in all countries. A) factor endowments B) scale of production C) factor intensities D) technology E) opportunity costs 4) If a country produces good Y (measured on the vertical axis) and good X (measured on the hor izontal axis), then the absolute value of the slope of its production possibility frontier is equal to A) the opportunity cost of good X. B) the price of good X divided by the price of good Y. C) the price of good X divided by the price of good Y. D) the opportunity cost of good Y. E) the cost of capital (assuming that good Y is capital intensive) divided by the cost of labor. 5) The Heckscher-Ohlin model differs from the Ricardian model of Comparative Advantage in tha t the former A) has only two countries. B) has only two products. C) has two factors of production. D) has two production possibility frontiers (one for each country). E) has varying wage rates.
