第一篇 实验室认可相关的术语和定义(原创,含解读)

第一篇实验室认可相关的术语和定义1.合格评定与实验室认可
合格评定:Conformity Assessment (ISO 17000:2004)
对关于产品、过程、体系、人员或机构的规定要求已被满足的证明。
注1 合格评定范畴包括本标准其它地方所描述的活动,如检测、检查和认证,以及对合格评定机构的认可;
注2 本标准所称的“合格评定对象”或“对象”包含合格评定所针对的特定材料、产品、安装、过程、体系、人员或机构,产品的定义中包含服务。
合格评定机构:Conformity Assessment Body(ISO 17000:2004)
从事合格评定服务的机构。
注认可机构不是合格评定机构。
认证:Certification (ISO 17000:2004)
与产品、过程、体系或人员有关的第三方证明。
注1 管理体系认证有时也被称为注册;
注2 认证适用于除合格评定机构自身以外的所有合格评定对象,对合格评定机构适用认可。
认可:A ccreditation (ISO 17000:2004)
正式表明合格评定机构具备实施特定合格评定工作的能力的第三方证明。
认可机构:A ccreditation Body (ISO 17000:2004)
实施认可(5.6)的权威机构。
注认可机构的权利通常源自政府。
检测:Testing(ISO 17000:2004)
按照程序确定合格评定对象的一个或多个特性的活动。
注“检测”主要应用于材料、产品或过程。
校准:Calibration (VIM)
在规定的条件下,为确定测量仪器或测量系统所指示的量值,或实物量具或标准物质所代表的量值,与对应的由测量标准所复现的量值之间关系的一组操作。
注1 校准结果既可赋予被测量以示值,也可确定示值的修正值;
注2 校准也可以确定其它计量特性,如影响量的作用;
注3 校准结果可以记录在“校准证书”或“校准报告”中。
2.理解
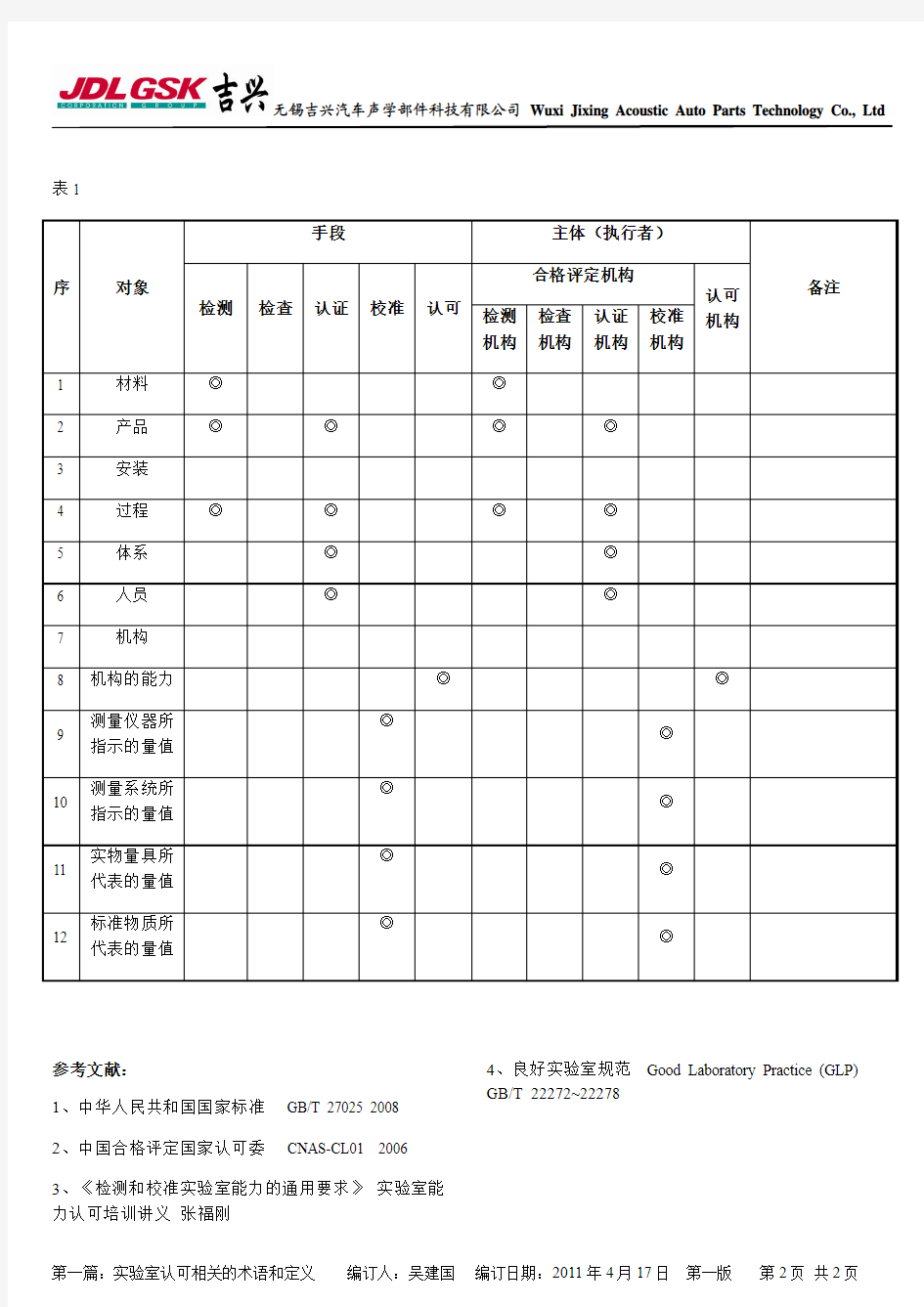
检测是合格评定的手段之一,适用于合格评定的部分对象,如材料、产品或过程;
校准是确保检测准确性的手段之一,适用于检测活动中使用的测量仪器或测量系统所指示的量值,多实物量具或标准物质所代表的量值等对象;
表1
参考文献:
1、中华人民共和国国家标准 GB/T 27025 2008
2、中国合格评定国家认可委 CNAS-CL01 2006
3、《检测和校准实验室能力的通用要求》实验室能力认可培训讲义张福刚
4、良好实验室规范 Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) GB/T 22272~22278
建筑工程专业术语及名词解释
建筑工程专业名词及解释 1、基坑:基坑是指为进行建筑物(包括构筑物)基础与地下室的施工所开挖的地面以下 空间。>5米的基坑叫做深基坑,基坑分为三个等级:一级:开挖深度大于10米。三级: 开挖深度小于或等于7米。二级:介于一、三级以外的基坑。 2、建筑工程意外伤害保险:《建设工程安全生产管理条例》第38条规定:“施工单位 应当为施工现场从事危险作业的人员办理意外伤害保险。意外伤害保险费由施工单位支付。 实行施工总承包的,由总承包单位支付意外伤害保险费。意外伤害保险期限自建设工程开 工之日起至竣工验收合格止。”根据这个条款,分包单位的从事危险作业人员的意外伤害保险的保险费是由总承包单位支付的。 3、工程质量保证金:建设单位全部或者部分使用政府投资的建设项目按工程价款结 算总额5% 左右的比例预留保证金,社会投资项目采用预留保证金方式的,预留保证金的比 例可以参照执行发包人与承包人应该在合同中约定保证金的预留方式及预留比例。 4、墙裙:墙裙,又称护壁,很直观、通俗的说就是立面墙上像围了裙子。这种装饰方法是在四周的墙上距地一定高度(例如1米5)范围之内全部用装饰面板、木线条等材料包住,常用于卧室和客厅。 5、勒脚:勒脚是建筑物外墙的墙脚,即建筑物的外墙与室外地面或散水部分的接触墙体部位的加厚部分。勒脚的高度不低于700mm。勒脚部位外抹水泥砂浆或外贴石材等防水耐久的材料,应与散水、墙身水平防潮层形成闭合的防潮系统 6、普通烧结砖泛霜:原材料黏土中含有的硫酸镁或硫酸钙等可溶性硫酸盐受潮吸水溶 解,随着砖内的水分的蒸发而在砖的表面产生盐析现象,一般为白霜。呈晶体析出时, 使砖面剥落,抗冻性减小,影响工程质量。 7、水泥凝结时间:初凝时间(不得小于45分钟);终凝时间:硅酸盐水泥不得大于390 分钟/普通硅酸盐水泥不得大于600分钟。(混凝土凝结时间:初凝时间不小于45分钟;终凝时间不大于10h) 8、堆积密度:疏松状(小块、颗粒纤维)材料在堆积状态下单位体积的质量。砂的松散堆积密度:> 1350kg/m 3;碎石的堆积密度:1480kg/m 3。 9、表观密度:在自然状态下,单位体积材料质量。砂的表观密度:> 2500kg/m 3;碎石的表观密度:2700kg/m 3。 10、和易性:砼拌合物易于施工操作(工作性)包括流动性、粘聚性和保水性三方面的含义。 11、砂率:指混凝土中砂的质量占砂、石总质量的百分率。 12、砼抗压强度:150mm的立方体试件,标养室(20± 2C ,相对湿度95%以上),养护28天龄期,测得抗压强度,feu表示,单位N/m怦或MPa。普通砼强度范围C15—C80。 13、砼表观密度:普通砼的表观密度2000-2800kg/m 3,一般工程中设计的砼密度为 2350-2450 之间,可以取2400kg/m 3。 14、砖的单位(经验)用量:标准砖512块/m3 (529块)。每块砖的实际体积是(240*115*53) =0.00146 立方米加口砂浆的体积是(0.24)*{(0.05灰缝0.01)}*{(0.11灰缝0.01)}=0.0018立方米那么每立方米墙体用砖是1/0.00189=52块砂浆用量是1/0.00146=68块.684-529=1块*0.00146=0.2立方米(计算没考虑损耗) 15、钢筋的单位理论质量:0.00617d2kg/m。 16、砼抗渗性:用抗渗等级表示:P4、P6、P8、P10、P12五个等级。 17、砂浆的强度等级:边长70.7cm的立方体试件;M2.5、M5、M7.5、M10、M15、M20六个等级。 18、基坑边缘堆置土方和材料:距基坑上部边缘不少于2m ,堆置高度不应超过1.5m。
语料库术语中英对照
Aboutness 所言之事 Absolute frequency 绝对频数 Alignment (of parallel texts) (平行或对应)语料的对齐 Alphanumeric 字母数字类的 Annotate 标注(动词) Annotation 标注(名词) Annotation scheme 标注方案 ANSI/American National Standards Institute 美国国家标准学会 ASCII/American Standard Code for Information Exchange 美国信息交换标准码Associate (of keywords) (主题词的)联想词 AWL/Academic word list 学术词表 Balanced corpus 平衡语料库 Base list 底表、基础词表 Bigram 二元组、二元序列、二元结构 Bi-hapax 两次词 Bilingual corpus 双语语料库 CA/Contrastive Analysis 对比分析 Case-sensitive 大小写敏感、区分大小写 Chi-square (χ2) test 卡方检验 Chunk 词块 CIA/Contrastive Interlanguage Analysis 中介语对比分析 CLAWS/Constituent Likelihood Automatic Word-tagging System CLAWS词性赋码系统Clean text policy 干净文本原则 Cluster 词簇、词丛 Colligation 类联接、类连接、类联结 Collocate n./v. 搭配词;搭配 Collocability 搭配强度、搭配力 Collocation 搭配、词语搭配 Collocational strength 搭配强度 Collocational framework/frame 搭配框架 Comparable corpora 类比语料库、可比语料库 ConcGram 同现词列、框合结构 Concordance (line) 索引(行) Concordance plot (索引)词图 Concordancer 索引工具 Concordancing 索引生成、索引分析 Context 语境、上下文 Context word 语境词 Contingency table 连列表、联列表、列连表、列联表 Co-occurrence/Co-occurring 共现 Corpora 语料库(复数) Corpus Linguistics 语料库语言学 Corpus 语料库 Corpus-based 基于语料库的
GMP术语名词解释
GMP术语名词解释 1、药品:是指用于预防、治疗、诊断人的疾病,有目的地调节人的生理机能并规定有适应症或者功能主治、用法用量的物质,包括中药材、中药饮片、中成药、化学原料药及其制剂、抗生素、生化药品、放射性药品、血清、疫苗、血液制品和诊断药品等。 2、GMP: GMP是在药品生产全过程中,用科学、合理规范的条件和方法来保证生产优质药品的一整套系统的、科学的管理规范,是药品生产和质量管理的基础准则。 3、物料:用于生产药品的原料、辅料、包装材料等。 4、批号:用于识别“批”的一组数字或字母加数字。用以追溯和审查批药品的生产历史(,表示2010年5月第8批生产的药品。) 5、待验:物料在进厂入库前或成品出厂前所处的搁置等待检验结果的状态。 6、批生产记录:一个批次的待包装品或成品的所有生产记录。 批生产记录能提供该批产品的生产历史以及与质量有关的情况。 7、物料平衡:产品或物料的理论产量或理论用量与实际产量或用量之间的比较,并适当考虑可允许的正常偏差。 8、标准操作规程:经批准用以指示操作的通用性文件或管理办法。 9、生产工艺规程:规定为生产一定数量成品所需起始原料和包装材料的数量,以及工艺、加工说明、注意事项,包括生产过程中的控制等一个或一套文件。 10、工艺用水:药品生产工艺中使用的水,包括饮用水、纯化水、注射用水。 11、纯化水:为饮用水经蒸馏法、离子交换法、反渗透法或其它适宜方法制得供药用的水,不含任何附加剂。 12、注射用水:为纯化水经蒸馏所得的水。 13、饮用水:达到饮用标准,可供人饮用的水。 14、洁净室(区):空气悬浮粒子浓度受控的房间。它的建造和使用应减少
词汇学 名词解释(部分)
Types of meaning Types of lexical changes 1.Elevation:词义升格 Definition: words rise from humble beginnings to positions of importance Some words early in their history signify something quite low or humble, but change as time goes by to designate something agreeable or pleasant. For example: nice: ignorant---foolish---delightful, pleasant Marshal: a keeper of horses---a high ranking army officer So elevation refers that the meaning of word changes from the neutral/negative to positive. 2.Old English:It refers to the English starting from 450 to 1100 AD. The old English is made up of different sources of languages spoken then –that of Anglo-Saxons, that of Celts, and that of Jutes, with a lot of Latin elements used for common peopl e’s life. 3.Bound morpheme: It is the smallest unit of grammar, a unit which cannot occur as separate words. They have no independent semantic meaning; instead, they have: Attached meaning E.g. un-kind, hope-ful Grammatical meaning E.g. cat-s, slow-ly, walk-ing, call-ed For an exact example, in the word “careful”, care is free morpheme, “-ful” is a bound morpheme. 4.Hyponymy: Hyponymy deals with the relationship of semantic inclusion, or to say, the relationship between general lexical items and specific lexical items. That is to say, when X is a kind of Y, the lower term X is the“hyponym”, and the upper term Y is the “superordinate”. For example, “fiction”is the superordinate of “novel”, “novelette”and “short story”, which are the hyponyms of “fiction”. Knowing the semantic features of the hyponyms and their superordinates can help us achieve vividness, exactness, and concreteness in expression.
建筑工程专业术语及名词解释教学文稿
建筑工程专业术语及 名词解释
建筑工程专业名词及解释 1、基坑:基坑是指为进行建筑物(包括构筑物)基础与地下室的施工所开挖的地面以下空间。≥5米的基坑叫做深基坑,基坑分为三个等级:一级:开挖深度大于10米。三级:开挖深度小于或等于7米。二级:介于一、三级以外的基坑。 2、建筑工程意外伤害保险:《建设工程安全生产管理条例》第38条规定:“施工单位应当为施工现场从事危险作业的人员办理意外伤害保险。意外伤害保险费由施工单位支付。实行施工总承包的,由总承包单位支付意外伤害保险费。意外伤害保险期限自建设工程开工之日起至竣工验收合格止。”根据这个条款,分包单位的从事危险作业人员的意外伤害保险的保险费是由总承包单位支付的。 3、工程质量保证金:建设单位全部或者部分使用政府投资的建设项目,按工程价款结算总额5%左右的比例预留保证金,社会投资项目采用预留保证金方式的,预留保证金的比例可以参照执行发包人与承包人应该在合同中约定保证金的预留方式及预留比例。 4、墙裙:墙裙,又称护壁,很直观、通俗的说就是立面墙上像围了裙子。这种装饰方法是在四周的墙上距地一定高度(例如1米5)范围之内全部用装饰面板、木线条等材料包住,常用于卧室和客厅。 5、勒脚:勒脚是建筑物外墙的墙脚,即建筑物的外墙与室外地面或散水部分的接触墙体部位的加厚部分。勒脚的高度不低于700mm。勒脚部位外抹水泥砂浆或外贴石材等防水耐久的材料,应与散水、墙身水平防潮层形成闭合的防潮系统
6、普通烧结砖泛霜:原材料黏土中含有的硫酸镁或硫酸钙等可溶性硫酸盐受潮吸水溶解,随着砖内的水分的蒸发而在砖的表面产生盐析现象,一般为白霜。呈晶体析出时,使砖面剥落,抗冻性减小,影响工程质量。 7、水泥凝结时间:初凝时间(不得小于45分钟);终凝时间:硅酸盐水泥不得大于390分钟/普通硅酸盐水泥不得大于600分钟。(混凝土凝结时间:初凝时间不小于45分钟;终凝时间不大于10h) 8、堆积密度:疏松状(小块、颗粒纤维)材料在堆积状态下单位体积的质量。砂的松散堆积密度:>1350kg/m3;碎石的堆积密度:1480kg/m3。 9、表观密度:在自然状态下,单位体积材料质量。砂的表观密度:> 2500kg/m3;碎石的表观密度:2700kg/m3。 10、和易性:砼拌合物易于施工操作(工作性)包括流动性、粘聚性和保水性三方面的含义。 11、砂率:指混凝土中砂的质量占砂、石总质量的百分率。 12、砼抗压强度:150mm的立方体试件,标养室(20±2℃,相对湿度95%以上),养护28天龄期,测得抗压强度,fcu表示,单位N/m㎡或MPa。普通砼强度范围C15—C80。 13、砼表观密度:普通砼的表观密度2000-2800kg/m3,一般工程中设计的砼密度为2350-2450之间,可以取2400kg/m3。 14、砖的单位(经验)用量:标准砖512块/m3(529块)。每块砖的实际体积是(240*115*53)=0.00146立方米,加砂浆的体积是(0.24)*{(0.053+灰缝0.01)}*{(0.115+灰缝 0.01)}=0.00189立方米.那么每立方米墙体用砖是1/0.00189=529块.砂浆用量是 1/0.00146=684块.684-529=155块*0.00146=0.226立方米(计算没考虑损耗)
《词汇学》名词解释总汇
《词汇学》名词解释总汇 1.Conversion(转换)is a word-formation whereby a word of a certain word-class is shifted into a word of another without the addition of an affix. It is also called zero derivation. 2.Neologisms(新词用法)are newly coined words or words that are given new meaning to fit new situation because of social, economic, political, cultural, scientific and technological changes in human society. 3.Lexicology(词汇学)is a branch of linguistics concerned with the study of the vocabulary of a given language. It deals with words, their origin, development, structure, formation, meaning and usage. 4.the elevation of meaning(词义的升格)refers to the process by which words rise from humble beginnings to positions of importance. 5.Acronyms(首字母拼音词)words formed from the initial letters of words and pronounced as words. They differ from initialisms in that they are pronounced as words rather than as sequences of letters. 6.Hyponymy(上下义关系)deals with the relationship of semantic inclusion. It refers to the relationship which obtains between the genus (general lexical item)and the species(specific lexical items). 7.Analogy(类比)is a process by which words or phrases are created or re-formed according to the existing patterns in the language. 8.Motivation(理据)deals with the connection between name (word-symbol) and its sense (meaning). It is the relationship between the word structure and its meaning. 9.Metaphor(隐喻)is a figure of speech containing an implied comparison. It is a simile without like or as. 10.Antonymy(反义关系)is concerned with semantic opposition. It can be defined as words which are opposite in meaning. 11.Suffix(后缀): an affix attached to the end of a base (root or stem) 12. synecdoche(提喻)means using a part for a whole, an individual for a class, a material for a thing, or vice versa, the whole for a part. 13. prefix(前缀): an affix attached to the beginning of a base (root or stem) 14. initialism(首字母连写词): a type of shortening, using the first letters of words to form a proper name, a technical term, or a phrase; it is pronounced letter by letter. 15.morpheme(词素): the smallest meaningful linguistic unit of language, not dividable or analyzable into smaller forms. 16.the degradation of meaning(词义的降格): is the opposite of semantic elevation. It is a process whereby words of good origin fall into ill reputation or non-affective words come to be used in derogatory sense. 17.Derivational affixes (派生词缀)Affixes added to other morphemes to create new words. They can be further divided into prefixes and suffixes。 18. back-formation(逆成法): is a process of word-formation by which a word is created by the deletion of a supposed suffix. It is also known as a reverse derivation. 19. derivation(派生): the process by which noninfectional affixes are added to roots to form words. 20. compounding(复合): the process of joining together two linguistic forms which can function independently.
建筑专业术语名词解释
建筑专业术语名词及解释 1、房地产专业术语 1.房地产:房产与地产的合称,是不动产。 2.五证二书:《建设用地规划许可证》、《国土使用证》、《建设工程规划许可证》、《施工许可证》、《预售许可证》、《商品房质量保证书》、《商品房使用说明书》 3.商品房:专门用以买卖的房屋。有产权保障,可自由出租抵押。 4.商住房:即可用于住家使用,也可以用于办公的商品房。 5.集资房:由单位统一筹集各需要住房的客户资金,而建造之房屋,通常仅有一整栋的一张产权证,客户没有单独的产权证。 6.安居房:﹙经济实用房=安居房﹚是指以中低收入家庭住房困难户为供应对象,并按国家住宅建设标准﹙不含别墅、高级公寓、外销住宅﹚建设的普通住宅。﹙其实行的是土地无偿划拔,住户只拥有该土地的使用权,如需办理国土证,则要另外出资,并享受政府扶持税费减半征收。其房价由政府部门核定,利润只能在3%以下。﹚ 7.跃层:是一套住宅占两个楼层,有内部楼梯联系上下层。﹙一般在首层安排起居室、厨房、餐厅、卫生间,二层安排卧室、书房、卫生间。﹚ 8.复式:概念上是一层,并不具备完整的两层空间,但层高比普通住宅高,可在局部分出夹层,安排卧室或书房等,用楼梯联系上下。﹙夹层在底层的投影面积只占底层面积的一部分,夹层和底层之间有视线上的交流和空间上的流通。﹚9.错层:纵向或横向剖面中,楼层的几部分之间楼地面高低错开。
10.标准层:平面布置相同的住宅楼层。 11.高层:8层以上,带有电梯,钢筋混凝土结构 12.多层:7层以下,一般不带电梯,砖混结构 13.骑楼:有雨遮之一楼直道部分 14.裙楼:指建筑体底部较庞大之建筑体,常用于商业、办公 15.承重墙:承受房屋重力的墙,不可任意拆改、破坏 16.非承重墙:一般情况下仅承受自重的墙。 17.剪力墙:承受地震力的钢筋混凝土墙 18.隔墙:用以隔断空间的墙,一般不承重 19.结构墙:主要承受侧向力或地震作用,并保持结构整体稳定的承重墙,又称剪力墙、抗震墙等。 20.框架结构:由梁和柱以刚接和铰接相连接成承重体系的房屋建筑结构。 21.消防电梯:专门用以消防灭火电梯,有抽烟排风功能 22.客梯:住户人流用梯有相配套安全配置保障 23.货梯:用以运送货物电梯 24.管道井:用以布置各类管道的空间井道 25.井筒:指大楼电梯、步梯、管道、公共厕所、茶水间集中的地方 26.空气流动:空内通风对流通畅,自然对流的换气能力 27.采光:获得光亮,直接接受自然光线和亮度 28.通风:风(空气)之来源、去路。
词汇学概念整理
1、区别Lexeme Word Morphemes A lexeme is the smallest unit in the meaning system of a language. The lexeme “give” includes as members “give”, “gives”, “given”, “giving”, “gave”, but excludes “giver” and “givers”. A lexeme is an abstract unit. It can occur in many different forms in actual spoken and written sentences. A word is a minimal meaningful unit of a language that can function independently. Morphemes are known as minimal meaningful units of a language. 2、组合形式 A combining form is a bound root that can form a new word by combining with another combining form, a word, or sometimes an affix, for example techno- and -phobe in technophobe. 3、区别Root base sterm ?A root is the basic form of a word which cannot the further analyzed without total loss of identity. e.g. international ?A base is a form to which affixes of any kind (both derivational and inflectional) can be added. e.g. grace ---- graceful ---- ungraceful ?The stem is used only when we deal with inflectional affixes, so any form to which an inflectional affix is attached is a stem. e.g. works, workers, workshops 4、转化法定义 Conversion is the formation of new words by converting words of one class to another class. Since words that are made do not change in morphological structure but in function, this process is also known as functional shift. Words produced by conversion are primarily nouns, adjectives, and verbs. N---V bottle to bottle Adj----V dry to dry V------N look have a look 5、截短法定义及分类 Clipping/shortening(截短法)is the formation of new words by cutting a part off the original and using what remains instead. Words formed in this way are called “clipped words”. There are four common types of clipping: apocope/back clipping, aphaeresis/front clipping, front and back clipping, syncope.例子exam---examination phone---telephone tec----detective pacifist----pacificist 6、关联意义的定义与分类 Associative meaning is the secondary meaning supplemented to the conceptual meaning. It differs from the conceptual meaning in that it is open-ended and indeterminate. 1.Connotative meaning refers to the overtones(弦外之音) or associations suggested by the conceptual meaning.woman--frail,cowardly,emotional 2.Affective meaning expresses the speaker’s attitude towards the person or thing in question.dear hello 3.Collocative meaning is that part of the word meaning suggested by the words with which it co-occurs. pretty handsome 4.Stylistic meaning: daddy male parent 7、同形异义词的定义及分类 ?Concretely speaking, homonyms are words different in meaning, but either identical both in sound and spelling or identical only in sound or spelling. ?Homonyms fall into three types: absolute homonyms, which are words identical both in sound and spelling; date base . homophones, which are words identical only in sound but different in spelling and meaning; night/knight leak/leek homographs, which are words identical only in spelling but different in sound and meaning.tear sow 8、区分歧义与含混 Ambiguity refers to the phenomenon that a word, phrase or sentence has more than one meaning. Are you engaged?Vagueness is caused by the indistinction and unclearness of language. A vague word is one that has an indefinite denotation(外延概念).forest wood city town 9、同义词及其分类 A synonym is a word or expression that has the same or nearly the same meaning as another in the same language. Synonyms can be classified into two groups: perfect synonyms, which are words identical in grammatical meaning and lexical meaning including conceeptual and associative meaning, compounding/composition and partial synonyms, which are similar in essential meaning, but embrace different shades of meaning or different degrees of a give quality.couple/pair 10、上义词和下义词 The relationship in which the meaning of a more specific word is included in that of another more general word is called hyponymy. For example, the words animal and dog are related in this way. The specific term dog is called a hyponym, and the general term animal is called a superordinate term. 11、词义变化 Extension of meaning, also known as generalization, is a process by which a word which originally had a specialized meaning has now become generalized or has extended to cover a broader and often less definite concept. Narrowing of meaning, also called specialization, is a process by which a word of wide meaning acquires a narrower or specialized sense. Elevation or amelioration refers to the process by which words rise from humble beginnings to positions of importance. Degadation or pejoration of meaning is a process by which words of good origin or affective neutrality fall into ill reputation or come to be used in a derogatory sense. 12、为什么英语谚语具有结构固定性 Characteristics of idioms: 1) Semantic unity : Each idiom is a semantic unity. The meaning of an idiom is very often not the total sum of the meanings of the constituent parts. In other words, an idiom
语料库简单dye 第二讲
2008/7/31 语料库简单DIY 第二讲语料库软件初探-- 语料库软件初探--MonoConcPro 2.2 本软件是Athelstan开发小组https://www.360docs.net/doc/3213699476.html,/ ,于1996年开发的语料库比较检索工具。目前,我的服务器上提供学术性下载,下载地址: http://vu.flare.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/whistle/corpus/MoconcPro2. 2.rar (本软件为学术交流使用,所有权归本软件开发小组所有,一切商务性盈利目的的违法使用,所带来的连带责任关系与本人及本论坛无关。请慎重下载,小心使用!!!) 功能介绍: 软件主界 面 基本功能: MonoConc Pro 2.2 的软件界面比较简单。适合语料库初学者和初级研究人员使用。 本软件据作者的研究,其内部主核使用UTF-8编码,基本支持欧洲几种主要语言。当然,其主要的应用领域还是针对英语。本软件主要处理的文本素材是以TXT结尾的记事本文件,当然,本软件还可以导入RTF文档和其他格式的操作系统默认文档格式。不过,从DIY的角度来说,我们自己收集到的语料,为了免除格式,字体,行距等等文本要求,最好全部使用TXT文档,方便,省
事!用了都说好!(谁用谁知道) 我们按照自己的研究目的,研究方向,收集我们所需要的语料素材,具体的收集方法因人而异。可以从报纸杂志的电子文文档上直接下载,也可以从网站上直接下载整理好的TXT版本的小说,资料素材等,还可以直接从各大语料库中检索需要的语用素材,然后拷贝粘贴到TXT文本中。由于MonoConc Pro 强大的跨文档处理系统,一次可以同时导入多个TXT文档进行比较处理,所以我们可以把文章或者资料按照自己喜好的分类标准进行分类,然后存成不同的TXT文件名。检索的时候,只需要同时导入这些文件就可以了。(异常强大~)下载好软件,解压缩,然后打开MP22.EXE文件,你就可以看到上图那个简单的主界面了。 之后,选择File→Lord Corpus File(s),找到你需要导入处理的TXT文档,一个或者多个都可以,然后选择[打开]。指定的TXT文件就被全部导入进MonoConc Pro中了。 如果导入了过多的TXT文档,比如您导入了莎士比亚全集+马克思选+恩格斯选+列宁选+毛泽东选+邓小平选.....(不能否认,真的有这样的朋友存在)。那么,为了方便您查询检索结果所出现的文章,你可以选择File→View Corpus File/URL,这样就能看到查询结果所在的文章,还可以删除不需要的文章,或者添加新的文章,非常简单。 *这里的URL,指的是在HTTP或者FTP上,可以直接打开的文字页面的链接。一般朋友们DIY的语料库都是存在本地硬盘上的,所以基本上可以无视这个选项。不过,将来我们的个人语料库要实现点对点,点对多的平台连接。连接后,我们就可以相互查询对方个人语料库中的资料,此时在导入对方语料库中的文档的时候,就要用这个了。(这个目前还很遥远,大家还是踏踏实实做自己的DIY语料库吧!) 当我们要删除所有的文章的时候,这个时候仅仅关闭文章的窗口,是不能实
完全版英语词汇学名词解释
第一章word 1.Word --- A word is a minimal free form of a language that has a given sound and meaning and syntactic funtion. 第三章formation 1 1. Morpheme --- A morpheme is the smallest functioning unit in the composition of words. 2. Allomorph --- Some morphemes are realized by more than one morph according to their position in a word. Such alternative morphs are know as allomorphs. 3. Free morphemes (Free root) --- They are morphemes which are independent of other morphemes. 4. Bound Morphemes--- They are morphemes which cannot occur as separate words. 5. Bound root --- A bound root is that part of the word that carries the fundamental meaning just like a free root. Unlike a free root, it is a bound form and has to combine with other morphemes to make words. 6. Affixes --- Affixes are forms that are attached to words or word elements to modify meaning or function. 7. Inflectional affixes --- Affixes attaches to the end of words to indicate grammatical relationships are known as inflectional morphemes. 8. Derivational affixes --- Derivational affixes are affixes added to other morphemes to create new words. 9. Prefixes --- Prefixes are affixes that come before the word. 10. Suffixes --- suffixes are affixes that come after the word. 11. Roo t --- A root is the basic form of a word which cannot be further analysed without total loss of identity. 12. Stem--- a stem can be defined as a form to which affixes of any kind can be added. 第四章formation 2 1. Affixation --- affixation is generally defined as the formation of words by adding word-forming or derivational affixes to stems. 2. Prefixation --- is the formation of new words by adding prefixes to stems. Suffixation--- is the formation of new words by adding suffixes to stems. 3. Compounding(Compositon)-- is the formation of new words by joining two or more stems. 4. Conversion-- is the formation of new words by converting words of one class to another class. 5. Blending-- is the formation of new words by combined by parts of two words or a word plus a plus a part of another word. 6. Clipping- is the formation of new words by shortening a longer word by cutting a
