Photodegradation Performance of g-C3N4 Fabricated by Directly Heating Melamine

https://www.360docs.net/doc/6e1430933.html,/Langmuir ?2009American Chemical Society
Photodegradation Performance of g-C 3N 4Fabricated by Directly Heating
Melamine
S.C.Yan,?,§Z.S.Li,*,?,?,§and Z.G.Zou ?,?,§
?
Eco-Materials and Renewable Energy Research Center (ERERC ),Department of Physics and ?Department of Materials Science and Engineering and §National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures,Nanjing
University,Nanjing 210093,P.R.China
Received March 17,2009.Revised Manuscript Received July 3,2009
The g-C 3N 4photocatalyst was synthesized by directly heating the low-cost melamine.The methyl orange dye (MO)was selected as a photodegrading goal to evaluate the photocatalytic activity of as-prepared g-C 3N 4.The comparison experiments indicate that the photocatalytic activity of g-C 3N 4can be largely improved by the Ag loading.The strong acid radical ion (SO 42-or NO 3-)can promote the degrading rate of MO for g-C 3N 4photocatalysis system.The MO degradation over the g-C 3N 4is mainly attributed to the photoreduction process induced by the photogenerated electrons.Our results clearly indicate that the metal-free g-C 3N 4has good performance in photodegradation of organic pollutant.
Introduction
In recent years,there has been increasing interest in the study of photocatalysis technology application in water/air purification,1hydrogen production from splitting water,2self-cleaning coat-ings,3and high-efficiency solar cells.4This is related to serious environmental pollution and the global energy shortage.So far,various oxide,sulfide,and oxynitride semiconductor photocata-lysts have been developed to drive the photocatalytic reaction.5However,one of the main goals in materials science fields is to find photocatalytic materials with high quantum efficiency.For water purification,an optical material is needed that has a band gap that absorbs visible light,strong oxidative ability,and high stability in a complex water solution system.Recently,Wang et al.6reported that a metal-free photocatalyst,graphite-like carbon nitride (g-C 3N 4),has the photocatalytic performance for hydro-gen or oxygen production from water splitting under visible light irradiation.Very recently,they developed the g-C 3N 4metal-including compounds to degrade organic dyes.7The functional organic -metal hybrid material exhibited modified electronic properties.However,the authors did not report the comparison results for degrading organic dyes over the bare and metal-ion-modified g-C 3N 4.The g-C 3N 4semiconductor is recognized to be the most stable allotrope at ambient conditions.Unlike the photocatalysts of sulfide and oxynitride semiconductor,the g-C 3N 4photocatalyst is stable under light irradiation in water solution as well as in acid (HCl,pH=0)or base (NaOH,pH=14)solutions due to the strong covalent bonds between carbon and
nitride atoms.The high stability and moderate band gap imply that the metal-free g-C 3N 4has numerous potential applications in the photocatalysis fields.
Several precursors,such as cyanamide,dicyandiamide,and melamine,have been used to obtain the g-C 3N 4solids.8The former two kinds of precursors are virulent and expensive in comparison to the latter one.So far,several research groups have reported that the g-C 3N 4can be fabricated by heat treatment of melamine in the low-vacuum system 9,10or under high pressure.11Depending on reaction conditions,g-C 3N 4with different degrees of condensation and properties was obtained.However,from an industrial applications viewpoint,the g-C 3N 4material obtained under ambient pressure was expected due to the low cost and facile operation.
In the present paper,the g-C 3N 4photocatalyst powder was obtained by directly heating the melamine in a semiclosed system with two-step heat treatment.The melamine was first heated at 500°C (heating rate:20°C /min)for 2h,and the further deammonation treatment was set at 520,550,and 580°C for 2h,respectively.For comparison,a reference sample was prepared by polymerization of cyanamide at 550°C for 4h.6The photode-gradation behavior of methyl orange (MO)over the as-prepared photocatalyst was studied.The sample of treated melamine at 520°C for 2h exhibits high photodegradation activity.Our studies probably imply that the g-C 3N 4has the potential to treat industrial wastewater due to its good photodegradation perfor-mance and environmental adaptability.On the basis of our comparison experiments,a possible MO photodegradation me-chanism for the g-C 3N 4photocatalysis system was proposed.
Experimental Section
The photocatalyst of g-C 3N 4was prepared by directly heating melamine in the semiclosed system to prevent sublimation of
*Corresponding author.E-mail:zsli@https://www.360docs.net/doc/6e1430933.html, (Z.S.Li).Postal address:NO.22,Hankou Road,Nanjing,Jiangsu 210093,P.R.China.Phone number:86-25-83686630.Fax number:86-25-83686632.
(1)Fujishima,A.;Rao,T.N.;Tryk,D.A.J.Photochem.Photobiol.C 20001,1–21.
(2)Yamasita,D.;Takata,T.;Hara,M.;Kondo,J.N.;Domen,K.Solid State Ionics 2004,172,591–595.
(3)Zhang,X.T.;Sato,O.;Taguchi,M.;Einaga,Y.;Murakami,T.;Fujishima,A.
Chem.Mater.2005,17,696–700.(4)O 0Regan,B.;Gr €a tzel,M.Nature 1991,353,737–740.(5)Osterloh,F.E.Chem.Mater.2008,20(1),35–54.
(6)Wang,X.C.;Maeda,K.;Thomas,A.;Takanabe,K.;Xin,G.;Carlsson J.M.;Domen,K.;Antonietti,M.Nat.Mater.2009,8,76–80.
(7)Wang,X.C.;Chen,X.F.;Thomas,A.;Fu,X.Z.;Antonietti,M.Adv.Mater.2009,21,1–4.
(8)Thomas,A.;Fischer,A.;Goettmann,F.;Antonietti,M.;M €u
ller,J.;Schl €o gl,R.;Carlsson,J.M.J.Mater.Chem.2008,18,4893–4908.(9)Komatsu,T.J.Mater.Chem.2001,11,799–801.
(10)Zhao,Y.C.;Yu,D.L.;Yanagisawa,O.;Matsugi,K.;Tian,Y.J.Diamond Relat.Mater.2005,14,1700–1704.
(11)Ma,H.A.;Jia,X.P.;Chen,L.X.;Zhu,P.W.;Guo,W.L.;Guo,X.B.;Wang,Y.D.;Li,S.Q.;Zou,G.T.;Zhang,G.;Bex,P.J.Phys.:Condens.Matter 2002,14,11269–11273.
Article Yan et al.
melamine.10g of melamine powder was put into an alumina crucible with a cover,then heated to 500°C in a muffle furnace for 2h at a heating rate of 20°C/min;the further deammonation treatment was performed at 500,520,550,and 580°C for 2h,respectively.The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD)for phase identification on the Rigaku RINT2000dif-fractometer.The specific surface area was determined with the Brunauer -Emmett -Teller (BET)equation at 77K by using an adsorption apparatus (Micromeritics TriStar,USA).UV -vis diffuse reflection spectra were measured using a UV -vis spectro-photometer (Varian CARY 100,USA)and converted from reflection to absorbance by the Kubelka -Munk method.Photo-catalytic activity of g-C 3N 4for methyl orange (MO)photode-gradation was evaluated in a Pyrex reactor.0.3g of g-C 3N 4was dispersed in MO aqueous solution (100mL,0.4mg L -1).The light irradiation system contains a 300W Xe lamp with cutoff filter L42for visible light and a water filter to eliminate the temperature effect.Measurement of apparent quantum efficiency for degrad-ing MO over g-C 3N 4was performed by using a monochromatic filter (420nm).The intensity of the corresponding incident light is 9.764μW/cm 2.
Results and Discussion
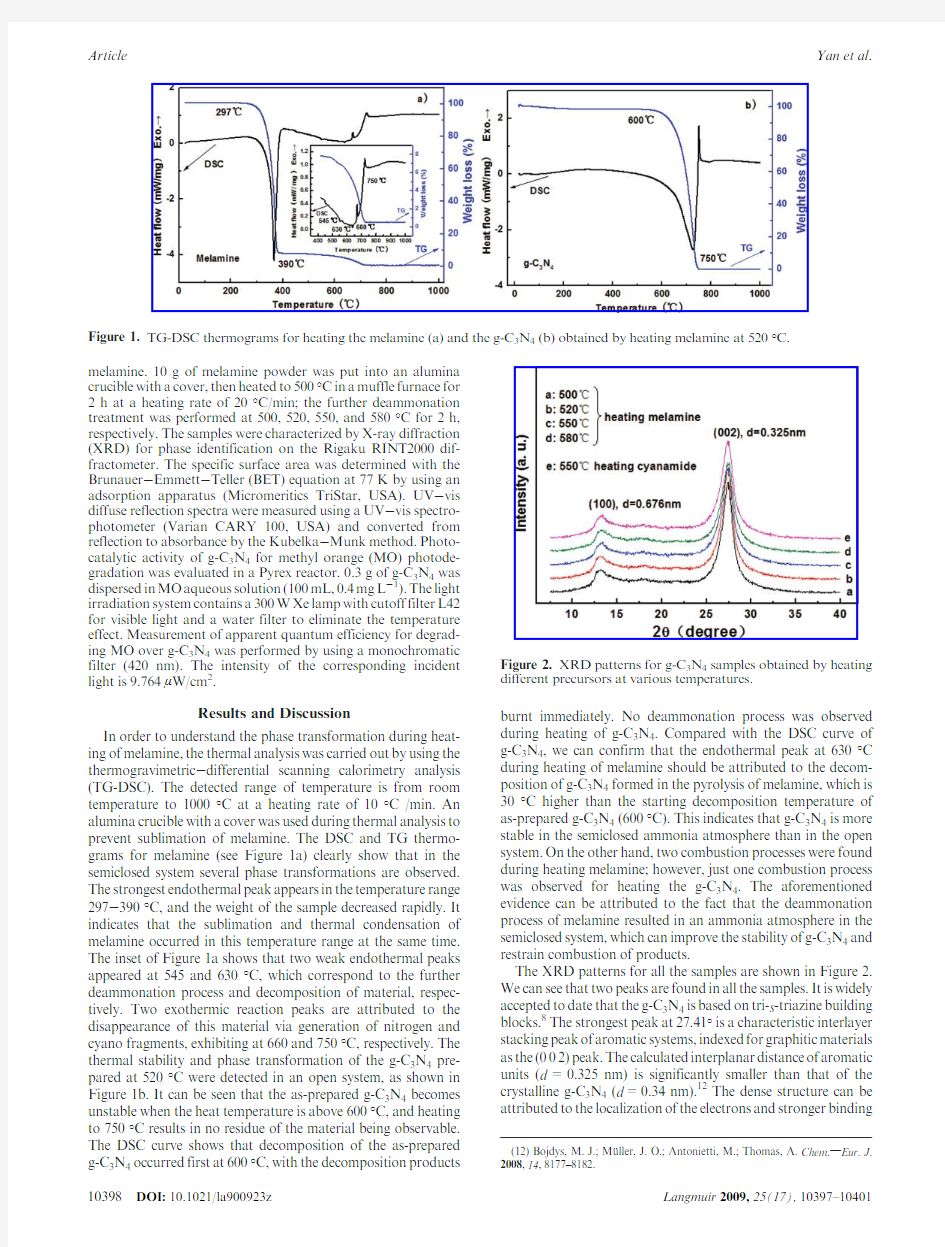
In order to understand the phase transformation during heat-ing of melamine,the thermal analysis was carried out by using the thermogravimetric -differential scanning calorimetry analysis (TG-DSC).The detected range of temperature is from room temperature to 1000°C at a heating rate of 10°C /min.An alumina crucible with a cover was used during thermal analysis to prevent sublimation of melamine.The DSC and TG thermo-grams for melamine (see Figure 1a)clearly show that in the semiclosed system several phase transformations are observed.The strongest endothermal peak appears in the temperature range 297-390°C,and the weight of the sample decreased rapidly.It indicates that the sublimation and thermal condensation of melamine occurred in this temperature range at the same time.The inset of Figure 1a shows that two weak endothermal peaks appeared at 545and 630°C,which correspond to the further deammonation process and decomposition of material,respec-tively.Two exothermic reaction peaks are attributed to the disappearance of this material via generation of nitrogen and cyano fragments,exhibiting at 660and 750°C,respectively.The thermal stability and phase transformation of the g-C 3N 4pre-pared at 520°C were detected in an open system,as shown in Figure 1b.It can be seen that the as-prepared g-C 3N 4becomes unstable when the heat temperature is above 600°C,and heating to 750°C results in no residue of the material being observable.The DSC curve shows that decomposition of the as-prepared g-C 3N 4occurred first at 600°C,with the decomposition products
burnt immediately.No deammonation process was observed during heating of g-C 3N https://www.360docs.net/doc/6e1430933.html,pared with the DSC curve of g-C 3N 4,we can confirm that the endothermal peak at 630°C during heating of melamine should be attributed to the decom-position of g-C 3N 4formed in the pyrolysis of melamine,which is 30°C higher than the starting decomposition temperature of as-prepared g-C 3N 4(600°C).This indicates that g-C 3N 4is more stable in the semiclosed ammonia atmosphere than in the open system.On the other hand,two combustion processes were found during heating melamine;however,just one combustion process was observed for heating the g-C 3N 4.The aforementioned evidence can be attributed to the fact that the deammonation process of melamine resulted in an ammonia atmosphere in the semiclosed system,which can improve the stability of g-C 3N 4and restrain combustion of products.
The XRD patterns for all the samples are shown in Figure 2.We can see that two peaks are found in all the samples.It is widely accepted to date that the g-C 3N 4is based on tri-s -triazine building blocks.8The strongest peak at 27.41°is a characteristic interlayer stacking peak of aromatic systems,indexed for graphitic materials as the (002)peak.The calculated interplanar distance of aromatic units (d =0.325nm)is significantly smaller than that of the crystalline g-C 3N 4(d =0.34nm).12The dense structure can be attributed to the localization of the electrons and stronger
binding
Figure 1.TG-DSC thermograms for heating the melamine (a)and the g-C 3N 4(b)obtained by heating melamine at 520°
C.Figure 2.XRD patterns for g-C 3N 4samples obtained by heating
different precursors at various temperatures.
(12)Bojdys,M.J.;M €u
ller,J.O.;Antonietti,M.;Thomas,A.Chem.;Eur.J.2008,14,8177–
8182.
Yan et al.Article
between the layers.The small angle peak at 13.08°,corresponding to interplanar distance of 0.676nm,is indexed as (100),which is associated with interlayer stacking.The distance is slightly below the size of one tris-s -triazine unit (ca.0.73nm),which presumably is attributed to the presence of small tilt angularity in the structure.
The Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR)spectra of two kinds of samples are shown in Figure 3.Several strong bands in the 1200-1650cm -1region were found,which correspond to the typical stretching modes of CN heterocycles.13Additionally,the characteristic breathing mode of the triazine units at 801cm -1was observed.It should be noted that the broad bands at around 3000cm -1are indicative of NH stretching vibration modes.12This indicates that the amino functions still existed in the products by directly heating the melamine or cyanamide.The C/N ratios for all samples were determined by elemental analysis on the elemental analyzer (vario EL II,Elementar,Germany).The experimental error in weighing was (0.001mg.For heating melamine at 500,520,550,and 580°C,the C/N ratio of the product is 0.721,0.735,0.737,and 0.742,respectively.It indicates that the C/N ratios increase with increasing condensation tem-perature.However,the C/N ratios for all cases of heating melamine are lower than 0.75for the ideal crystal g-C 3N 4.The results are in agreement with the FT-IR,implying that the amino groups originated from the incomplete condensation of the as-prepared g-C 3N 4.Indeed,as reported,the residual hydrogen atoms bind to the edges of the graphene-like C -N sheet in the form of C-NH 2and 2C-NH bonds.14On the other hand,as we know from DSC observation,the as-prepared g-C 3N 4is unstable above 600°C.The existence of amino groups and the low thermal stability of g-C 3N 4indicate that it is very difficult to lower the hydrogen content by directly heating melamine at ambient pressure.
The optical properties of the samples by heating melamine were investigated by UV -vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy,and the results are shown in Figure 4.The spectrum of the sample of cyanamide treated at 550°C for 4h is also shown for comparison.We can see that absorption edges of the samples obtained from heating melamine shift remarkably to longer wavelengths with increasing heating temperature.The decrease in band gaps of the samples is from 2.8to 2.75eV when the heat treatment tempera-ture is increased from 500to 580°C.It is worth noting that the
main absorption of the sample heated at 520°C,which exhibits a band gap of ca.2.75eV,is close to that of the samples heated at 550and 580°C.The spectra of the samples heated at higher temperature,520°C,show a weak absorption tail,especially for the sample of cyanamide heated at 550°C,for which the absorption tail may reach 550nm.This probably is attributed to the structure defects formed in samples treated at the high temperatures,which improve the optical absorption of materials.The photocatalytic activities of all the samples obtained by pyrolysis of melamine were evaluated for methyl orange (MO)photodegradation under visible light (λ>420nm)irradiation,as shown in Figure 5a.The photodegradation of MO over the commercial nitrogen-doped-TiO 2(TPS201,Sumitomo Corp.Japan)(denoted as N-TiO 2)and the sample obtained by heating cyanamide was also given here for comparison.It is well-known that,as a typical organic contaminant,MO is stable under UV -vis irradiation if there is no photocatalyst involved.15,16The absorption spectrum of the homogeneous MO solution without catalyst submitted to illumination with UV -vis light irradiation from a 300W xenon lamp for 5h exhibits almost no difference from the original absorption.We can know that the MO is stable in our experimental conditions.The N-TiO 2possesses a specific surface area (64.8m 2/g)more than eight times higher than that (an average value,ca.8m 2/g)of g-C 3N 4samples;however,it is obvious that photocatalytic activities for all the g-C 3N 4samples are much higher than those of the N-TiO 2.The optical absorption spectrum of N-TiO 2was shown in Figure 4.We can know that the main absorption edge of N-TiO 2is at 390nm,corresponding to the essential light absorption of TiO 2.17The weak absorption tail in the wavelength range 390-480nm originated from the substitutional doping of N,because its p states contribute to narrowing of the band gap by mixing with O 2p states.18The weak light absorption of N-TiO 2means poor visible light response.As a result,N-TiO 2has a low activity for photodegrading MO dye.The g-C 3N 4sample obtained from heating melamine at 520°C (denoted as M520)shows the highest activity,which is the same as that of the sample obtained
from
Figure 3.FT-IR spectra for g-C 3N 4fabricated from different
precursors.
Figure 4.UV -vis absorption spectra for commercial N-doped-TiO 2and g-C 3N 4samples obtained by heating the different pre-cursors at different temperatures.
(13)Li,X.F.;Zhang,J.;Shen,L.H.;Ma,Y.M.;Lei,W.W.;Cui,Q.L.;Zou G.T.Appl.Phys.
A:Mater.Sci.Proc.2009,94,387–392.
(14)Zhao,Y.C.;Liu,Z.;Chu,W.G.;Song,L.;Zhang,Z.X.;Yu,D.L.;Tian,Y.J.;Xie,S.S.;Sun,L.F.Adv.Mater.2008,20,1777–1781.
(15)Wang,Y.Y.;Zhou,G.W.;Li,T.D.;Qiao,W.T.;Li,https://www.360docs.net/doc/6e1430933.html,mun.2009,10,412–415.
(16)Gao,F.;Chen,X.Y.;Yin,K.B.;Dong,S.;Ren,Z.F.;Yuan,F.;Yu,T.;Zou,Z.G.;Liu,J.M.Adv.Mater.2007,19,2889–2892.
(17)Rajeshwar,K.;de Tacconi,N.R.;Chenthamarakshan,C.R.Chem.Mater.2001,13(9),2765–2782.
(18)Asahi,R.;Morikawa,T.;Ohwaki,T.;Aoki,K.;Taga,Y.Science 2001,293,269–271.
Article Yan et al.
heating cyanamide at 550°C (denoted as C550);the dye of MO is completely degraded after 5h visible light irradiation.However,the pathway of MO photodegradation is different for the M520and C550samples (see Figure S1in the Supporting Information).No light absorption peak shift was observed during degradation of MO over M520sample,indicating that the M520sample can directly mineralize MO without intermediate products.For the C550sample,the main absorption peak of MO gradually shifted to the shorter wavelengths with increasing light irradiation times,implying that the intermediate products were formed during the photodegradation reaction process.In other words,this means that the photooxidation ability of M520is better than that of C550sample.In the UV -visible absorption spectrum of C550,the obvious absorption tail,which resulted from poor thermal stability of g-C 3N 4,suggests that the high-temperature heat treatment at 550°C leads to the decreased photooxidation ability for C550.For the samples of melamine heated at 500,550,and 580°C,only 89%,78%,and 69%MO,respectively,was photo-degraded in the same irradiation time.Indeed,compared with the M520sample,the sample treated at 500°C has a low C/N ratio of 0.721;this means that the slightly decreased photocatalytic activity is attributed to the uncompleted condensation.However,there is a big drop in photocatalytic activity for the samples treated at temperatures above 520°C.Apparently,increasing the heat temperature will decrease the photooxidation ability of g-C 3N 4.The C/N ratio,i.e.,the degree of condensation,is
inconsistent with the structural integrality.To obtain a sample with high C/N ratio,a high heat treatment temperature is needed to lower the content of hydrogen in products,which leads to decreased structural integrality for the final product.Indeed,in combination with the elemental analysis and thermal analysis results discussed above,it is obvious that in the case of g-C 3N 4preparation by pyrolysis of melamine the degrees of condensation for the final product increase with increasing heat temperature,but the thermal stability of g-C 3N 4decreases.This probably implies that,in our case of g-C 3N 4preparation,520°C is an appropriate temperature for obtaining the g-C 3N 4with good crystal structure and moderate degree of condensation,and therefore,the M520sample exhibits high activity in degrading MO.Furthermore,it is worth pointing out that a one-time increase in the rate of MO photodegradation was achieved over the M520sample under full arc light irradiation;the dye of MO can be degraded completely after 2.5h UV -vis light irradiation.Some active species,such as the hydroxyl radicals (3OH),the superoxide (O 23or HOO 3),and the holes,are formed during the photodegradation reaction induced by light irradiation.The 3OH in aqueous solutions,as the primary oxidant,is generated via the direct hole oxidation 19or photogenerated electron induced multi-step reduction of O 2(O 2te f O 23,O 23te t2H tf H 2O 2,H 2O 2te f 3OH tOH -).20Generally,it is confirmed that the generation of superoxide is associated with the photogenerated electron induced direct reduction of O 2(O 2te f O 23).In addition,the photogenerated hole can directly react with organic compounds if the semiconductor photocatalyst has moderate redox potential.For these active species,hydroxyl radical reac-tions are nonselective and will virtually react with almost all the organic compounds by either H-atom abstraction,direct electron transfer,or insertion.
In order to investigate the possible photodegradation mechan-ism of MO over g-C 3N 4semiconductor,several comparison experiments were performed,and the results were shown in Figure https://www.360docs.net/doc/6e1430933.html,pared with photodegradation of the pure MO /g-C 3N 4solution,we can know that no change in the rate of MO photodegradation is observed when methanol (10vol %)was added as a sacrificial hole acceptor.This implies that the photo-generated hole is not an effective active species during degrading MO over g-C 3N 4;this reaction is not attributed to the direct hole oxidation.Indeed,as reported by Wang et al.,6the oxidation level for water splitting is located slightly above the top of the valence band of g-C 3N 4,which would permit transfer of holes,but with a low driving force.This suggests that the low driving force is not beneficial for the hole reactions in aqueous solution system.However,there is a big increase in rate of MO photodegradation when Ag particles (5wt %)were loaded onto the g-C 3N 4surface using the photodeposition method;21the MO can be degraded completely after 1h visible light irradiation,which is 5times faster than that over the bare g-C 3N 4.A further investigation,the effect of O 2on photodegradation of MO,was preformed in argon atmosphere.The reaction setup was vacuum-treated several times in order to eliminate O 2,and then,high-purity argon gas (purity,99.999%)was followed into the reaction setup for obtaining ambient pressure.After 5h visible light irradiation,only 43%MO was photodegraded in the absence of O 2(see Figure S2in Supporting Information).It means that O 2is a main factor for MO photodegradation over the g-C 3N 4photocatalyst,which affects the formation of superoxide via direct reduction of O 2
Figure 5.Photodegradation of methyl orange:(a)over the com-mercial N-doped-TiO 2and the g-C 3N 4obtained by heating the different precursors at different temperatures;(b)in the different catalytic systems based on the g-C 3N 4prepared by heating mela-mine at 520°C.
(19)Yoon,S.H.;
Lee,J.Environ.Sci.Technol.2005,39,9695–9701.
(20)Liu,G.G.;Li,X.Z.;Zhao,J.C.;Horikoshi,S.;Hidaka,H.J.Mol.Catal.A:Chem.2000,153,221–229.
(21)Tada,H.;Ishida,T.;Takao,A.;Ito,https://www.360docs.net/doc/6e1430933.html,ngmuir 2004,20,7898–7900.
Yan et al.Article
and hydroxyl radicals via multistep reduction of O2.A valuable
fact is that,if the strong acid radical ion,such as SO42-(0.01M)
or NO3-(0.01M),was introduced into the aqueous MO/g-C3N4
solutions,the MO degradation is significantly accelerated,and
the reaction was completed after80min visible light irradiation.
Clearly,the improved reaction activity is due to the introduction
of a strong acid radical ion,which increases the Htconcentration
and therefore accelerates the reaction of O23tet2Htf H2O2, further accelerating the formation of hydroxyl radicals via multi-
step reduction of O2.The experimental fact suggests that g-C3N4
photocatalyst possesses good environmental adaptability,which
can directly apply to industrial wastewater treatment to degrade
organic pollutants.On the basis of the aforementioned evidence,
we are inclined to believe that for the MO photodegradation over
g-C3N4the photocatalytic activity has mainly resulted from active
species which originated from photogenerated electron induced
reduction of O2.For practical application of the photocatalyst,
the stability during photoreaction was a crucial factor.Our
stability test indicates that no decrease in photocatalytic activity
was observed in the MO photodegradation reaction that was
repeated three times(see Figure S5in Supporting Information).
The XRD pattern of the as-prepared g-C3N4is similar to that
of the sample after reaction(see Figure S6,in Supporting
Information),meaning that the g-C3N4is stable in the photo-
reaction.The apparent quantum efficiency is a criterion to
evaluate photocatalytic activity of a given material.For MO
degradation,taking into account a single electron process,22the
apparent quantum efficiency(denoted as E Q)for degrading MO
was defined by E Q=N nup/N nip,where N nup and N nip represent
the number of used photons and the number of incident photons,
respectively.It is assumed that all incident photons are absorbed
by the photocatalyst.The calculated value of E Q at420nm is 1.5%,implying that the low-cost g-C3N4has potential in water purification due to its good photodegradation performance and environmental applicability.
Summary
In summary,we have successfully fabricated the g-C3N4 photocatalyst by directly heating melamine.The stable MO dye was selected as a degrading goal to evaluate the photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4.Our results clearly indicate that the metal-free g-C3N4has good performance in the photooxidation of organic pollutant.For the typical MO dye photodegradation,the photo-catalytic avtivity of g-C3N4can be improved significantly when Ag is used as a cocatalyst.This means that g-C3N4is a promising material possessing a good potential in photocatalytic application fields if some techniques,such as loading cocatalyst and doping, are used to improve its photocatalytic activity.Our comparison studies showed that the photodegradation activity of MO over g-C3N4is mainly attributed to the generation of active species induced by photogenerated electrons.Moreover,the g-C3N4 photocatalyst showed good photocatalytic activity in the presence of a strong acid radical ion;this further indicates that it is feasible to apply the g-C3N4with low cost and facile synthesis to treat industrial wastewater containing organic pollutants. Acknowledgment.This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(no.20528302),the Na-tional Basic Research Program of China(973program, 2007CB613301and2007CB613305).
Supporting Information Available:UV-visible spectro-scopic changes for MO degradation,XRD and SEM for Ag-modified g-C3N4,and the stability test for g-C3N4.This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http:// https://www.360docs.net/doc/6e1430933.html,.
(22)Bandara,J.;Morrison,C.;Kiwi,j.;Pulgarin,C.;Peringer,P.J.Photochem. Photobiol.A1996,99,57–66.
(完整版)北师大版小学六年级数学毕业考试题及答案
小学六年级数学毕业测试题 一、填空。(28分。) 1、据统计,我国汉族人口是十一亿三千七百三十九万人,写作( ),省略“亿”后面的尾数约是( )人。 2、 5时24分=( )时 8050平方米=( )公顷 3456立方厘米=( )升 3千克50克=( )千克 3、填上合适的单位名称: 一个水桶高约4( ) 数学书的封面面积约为360( ) 一袋大米约重25( ) 喝水杯的的容积250( ) 4、( )/10=( ):45=6÷( )=2/5 5、一个三角形三个内角的度数比是5:3:1,这个三角形最大的角是( )度,这个三角形是( )三角形 6、一台收音机原价100元,先提价10%,又降价10%,现在售价是( )元。 7、经过两点可以画出( )条直线,两条直线相交有( )个交点。 8、找规律: (1)4、 9、16、( )、36、49。 (2)1/2、2/4、( )4/8、( )。 9、把3米长的绳子平均分成5段,每段占全长的( ),是( )米。 10、等底等高的圆柱和圆锥体积之差是4.6立方分米,圆柱的体积是( )立方分米。 11、鸡兔同笼,共有30个头,88只脚。求笼中鸡( )只,兔有( )只。 12、在一个口袋里有2个红球和8个黄球,从中任意摸出1个球,摸出红球的可能性是( ),如果摸10000次,摸出红球的可能性是( )次。 二、选择。(10分。) 1、长方体体积一定,底面积和高( ) ①成正比例;②成反比例;③不成比例;④既可能成批比例,又可能成正比例。 2、下列图形中对称轴最多的是( ) ① 长方形; ② 正方形; ③ 三角形; ④ 圆。 3、一个长方形框架拉成平行四边形后,面积( )。 ①不变; ②减小; ③增大; ④既可能减小又可能增大。 4、一个长方形、一个正方形和一个圆的周长相等,那么面积最大的是( ) ① 长方形 ② 正方形 ③ 圆 5、要反映小红六年级数学成绩变化情况,应选择( ) ①条形统计图 ②折线统计图 ③扇形统计图 三、计算。(28分) 1、直接写出得数(8分) 24.06+0.4= ( 5165-)×30= =+5 3 73 12.5×32×2.5= 121÷6= 5-(9792+)= 5 4×25= 2.8×25+12×2.5= 2、脱式计算,能简算的要写出简算过程。(18分) 85.87-(5.87+2.9) 1.25×7×0.8 54.2-2/9+4.8- 19 7 125)731(35÷-? 1387131287÷+? 11 8 )26134156(?-? 3.求未知数x 6/7x +4.8=5 χ-3/5 χ= 6/5 0.8x+1.2x =25 四、操作题 (6分) 1、把三角形向右移动5格; 2、把三角形绕B 点逆时针旋转900 , 3、把三角形按2:1的比放大。 (3分) 2、在下图上完成下列问题。(3分) (1)科技馆在学校北偏东30°方向2000米处。请在图中标出科技馆的位置,并标出数据。 (2)南京路经过电影院,与上海路平行。请用直线标出南京路的位置。
北师大版小学数学六年级知识点
北师大版小学数学六年级(上册)知识点 第一单元圆 1、使学生认识圆的特征:圆的半径、直径、圆心。认识在同圆内半径和直径的关系。知道圆是轴对称图形,有无数条对称轴,而这些对称轴都过圆心。知道生活中有了圆才使我们的生活更美好。 2、认识同心圆、等圆。知道圆的位置由圆心决定,圆的大小由半径或直径决定。等圆的半径相等,位置不同;而同心圆的半径不同,位置相同。 3、使学生知道圆的周长和圆周率的含义,掌握圆的周长的计算公式,能够正确地计算圆的周长.介绍祖冲之在圆周率研究上的成就,渗透爱国主义教育。在运用上,要能根据圆的周长算直径或半径,会算半圆的周长:圆的周长×1/2+直径。会求组合图形的周长。 4、了解圆的面积的含义,经历圆面积计算公式的推导过程,掌握圆面积计算公式。 5、能正确运用圆的面积公式计算圆的面积,并能运用圆面积知识解决一些简单实际的问题。会灵活运用圆的面积公式。已知圆的周长会算圆的面积,会求组合图形的面积。会算圆环的面积,并且知道在周长相等的情况下,正方形、长方形、圆三种图形中,圆的面积最大。 6、在估一估和探究圆面积公式的活动中,体会“化曲为直”的思想,初步感受极限思想。 第二单元百分数的应用 本单元重点讲解百分数在生活中的应用,知识点为: 1、知道百分数的意义:表示一个数是另一个数的百分之几的数,叫做百分数。百分数也叫做百分率或百分比。百分数通常不写成分数形式,而用百分号“%”
表示;百分数有时也定义为分母是100的分数,但百分数与分数是有区别的:分数既可表示具体的量,又可表示两个数量间的倍比关系;然而百分数只能表示两个数量间的倍比关系;所以是不名数,也就是不能带单位的数。 2、在具体情景中理解“增加百分之几”或“减少百分之几”的意义,加深对百分数意义的理解。 3、能解决有关“增加百分之几”或“减少百分之几”的实际问题,提高运用数学解决实际问题的能力,体会百分数与现实生活的密切联系。 4、知道出勤率、出粉率、成活率等百分数的意义及在实际生活中的应用,会计算这种百分数。 5、知道成数、打折的含义。表示一个数是另一个数十分之几、百分之几的数,叫做成数。打折就是按原价的百分之几十、十分之几出售。八五折就是按原价的85%出售。成数和折扣数不能用小数表示。 6、能解决“比一个数增加百分之几的数是多少”或“比一个数减少百分之几的数是多少”的实际问题。 7、进一步加强对百分数的意义的理解,并能根据百分数的意义列方程解决实际问题,会解含有百分数的方程。 8、能利用百分数的有关知识,解决一些与储蓄有关的实际问题,提高解决实际问题的能力。知道利息是本金存入银行过一段时间取出后多出来的钱;本金是存入银行的钱;利率就是某段时间中利息占本金的百分比;利息税是国家银行规定的针对利息收入的税收。会计算利息。利息=本金×利率×时间 9、结合储蓄等活动,学习合理理财,逐步养成不乱花钱的好习惯。 第三单元图形的变换 1、通过观察、操作、想象,知道一个简单图形是怎样经过平移或旋转制作复杂图形的过程,体验图形的变换,发展空间观念。并能借助方格纸上的操作和分析,有条理地表达图形的平移或旋转的变换过程。
2018年北师大版小学六年级数学毕业试题共10套
六年级数学下册(北师大版)总复习综合练习题 班别:姓名:评分:等级: 一、填空题。(每空1分,共24分) 1、由3个十万,4个千组成的数写作(),改写成“万”为单位是 ()。 2、3时45分=()时 3.08升()毫升 3、1 2 千米:8米化成最简整数比是(),比值是()。 4、某地早晨气温-5℃,中午气温6℃,从早晨到中午气温上升了()℃。 5、60千克是40千克的()%,1米的3 5 和()米的20%一样长。 6、把4米长的铁丝平均截成8段,每段是这根铁丝的() () ,每段长()米。 7、36和48的最大公因数是(),最小公倍数是()。 8、在一张长是8分米,宽6分米的长方形卡纸中,剪一个面积最大的圆,这个圆的面积 是()平方分米。 9、一幅地图的比例尺是1:500000,表示实际距离是图上距离的()倍,在这幅地 图上量得甲、乙两地相距8.8厘米,甲、乙两地间的实际距离是()千米。 10、在24、22、20、26、26、26、这组数据中,中位数是(),众数是(), 平均数是()。 11、等底等高的圆柱与圆锥的体积总和是60立方米,那么圆柱的体积是()立方米, 圆锥的体积是()立方米。 12、4根小棒长分别是2厘米,3厘米、5厘米,7厘米,选其中的三根,围成一个三角形, 三角形的周长是()厘米。 13、摆一个三角形需要3根小棒,摆两个三角形需要5根,摆3个三角形需要() 根小棒,摆m个三角形需要()根小棒。 二、判断题(正确的在括号里打“√”,错的打“×”)。(5分) 1、0.8和0.80的大小相等,计数单位也一样。() 2、圆的面积和它的半径成正比例。() 3、师徒两人共同生产一批零件,徒弟生产的零件合格率是90%,那么师傅生产的零件合 格率是110%。()
最新北师大版小学六年级数学毕业试卷及答案
最新北师大版小学六年级数学毕业试卷 姓名____________ 得分____________ 一、填空。(22分) l.一个数的亿位上是5、万级和个级的最高位上也是5,其余数位上都是0,这个数写作(),省略万位后面的尾数是() 2、2小时15分=()小时 4.2吨=()千克 3、篮球个数是足球的125%,篮球比足球多()%。 4、6÷15=( )/45=()%=24÷()=____(填小数)。 5、一个圆锥的体积是76立方厘米,底面积是19平方厘米。这个圆锥的高是()厘米。 6、把化成最简整数比是( ),比值是( )。 7、一个直角三角形中,两个锐角度数的比是3 : 2 ,这两个锐角分别是()度、()度。 8、12的因数中可以选出4个数组成一个比例,请你写出比值不同的两组:()。 9、甲乙的比为5:4,甲数比乙数多()%,乙数又比甲数少()%。 10、比a的3倍多1.8的数,用含有字母的式子表示是(),当a=2.4时,这个式子的值是()。 11、投掷100次硬币,有48次正面向上,那么投掷第101次硬币正面向上的可能性是() 12、一根长2米的直圆柱木料,横着截去2分米,和原来比,剩下的圆柱体木料的表面积减少12.56平方分米,原来圆柱体木料的底面积是()平方分米,体积是()立方分米。 二、判断( 7分)
1、圆锥体的底面半径扩大3倍,高不变,体积也扩大3倍。() 2、在比例里,如果两个内项的乘积是1,那么,组成比例外项的两个数一定互为倒数。() 3、有10张卡片,上面分别写着1——10这些数。任意摸出一张,摸到偶数的可能性是1/5。() 4、如果4a=3b,那么a :b = 4 :3。() 5、从学校走到电影院,甲用了10分钟,乙用了12分钟。甲和乙每分钟所走的路程的最简整数比是5∶6。 ( ) 6、两个相邻的非零自然数一定是互质数。( ) 7、生产的90个零件中,有10个是废品,合格率是90%。() 三、选择。( 7分 ) 1、某班女生人数的4/7 等于男生人数的2/3,那么男生人数()女生人数. A.小于B.大于C.等于 2、某产品降价前售价是150元,降价后售价是120元,降低了( )。 A. 20% B. 25% C. 80% D. 75%] 3、下列三句话中,正确的是() A.一种商品打八折出售正好保本,则不打折时该商品只获20%的利润 B.三角形中最大的角不少于60度 C.分母能被2和5整除的分数一定能化成有限小数 4、两根2米长的铁丝,第一根截去它的3/4,第二根截去3/4 米。余下部分( )。 A、长度相等 B、第一根长 C、第二根长 5、用三根同样长的绳子,分别围成一个长方形、正方形和圆形,面积最大的是()。
新北师大版小学六年级数学下册总
新北师大版小学六年级数学下册总复习教案
20、图形的认识(一)线与角 学习目标: 1、系统整理学过的图形,沟通各种图形之间的联系。 2、可以结合具体情境认识各种角。 学习重点:建立知识之间的网络图,结合具体情境理解线与角。 学习难点:根据平面的基本特征,能够理解平面图形相互之间的联系。 学习准备:多媒体。 教学过程: 一、自主尝试: 1、我们学过哪些图形? 2、学过哪些角? 二、合作探究: 1、用自己喜欢的方式展示你学过的图形,并对它们进行分类。介绍整理的方法,培养学生整理知识的能力。 2、直线、射线、线段的特征各是什么?学生可以动手操作。 3、平行线和垂线的特征是什么? 4、角的概念,角的分类,角的大小与什么有关?让学生画一画,进行交流。 三、汇报点评: 1、直线没有端点,射线有一个端点,线段有两个端点。 2、在同一个平面内,两条直线的相互位置是平行或相交。两条直线相交成直角这两条直线叫做垂直;在同一平面内不相交的两条直线叫平行。 四、巩固练习:
下面图形中,有几组平行线?有几条互相垂直的线? 板书设计 线与角 直线没有端点,射线有一个端点,线段有两个端点。 在同一个平面内,两条直线的相互位置是平行或相交。两条直线相交成直角这两条直线叫做垂直;在同一平面内不相交的两条直线叫平行。 教学反思: 21、平面图形 学习目标 1、能够按照一定的标准对平面图形进行分类。 2、掌握各种平面图形的特征。 3、通过观察、操作、了解三角形两边之和大于第三边。 学习重点寻找复习平面图形的角度和方法。 学习难点在观察、操作中体会平面图形的特征及应用。 学习准备多媒体,直尺,三角尺。 教学过程: 一、自主尝试: 1、我们学过哪些平面图形? 2、我们可以从哪些角度去梳理平面图形? 二、合作探究: 根据哪些特征可以把平面图形分成哪些类? 学生讨论,使学生知道,从边的角度,角的角度。
最新北师大版小学六年级数学毕业试卷(附答案)
小学六年级数学毕业试卷 学校班级姓名 一、填空。(每空1分,共15分。) 1、5时24分=( 5.4 )时 8平方米6平方分米=( 806 )平方米 2、由3个亿、8个千万、9个万、6个千和5个百组成的数写作( 380096500 ),四舍五入到亿位约是( 4亿)。 3、在1∶2000的地图上量得甲、乙两地距离是36厘米,甲、乙两地的实际距离是( 720 )米。 4、如果在1:5的前项加上2,要使它的比值不变,后项应增加(10 ) 5、a×4=5×b,(a≠b),那么b和a成(正)比例。 6、m、n是非零自然数,m÷n=1……1,那么m和n的最大公因数是( 1 )最小公倍数是( mn ) 7、一个三角形三个内角的度数比是1∶1∶2,这个三角形是(等腰直角)三角形。 8、一个圆形花坛直径为8米,绕花坛有一条小路,宽3米,这条小路的面积是(103.62)平方米。 9、一台收音机原价100元,先提价10%,又降价10%,现在售价是( 99 )元。 10、等底等高的圆柱和圆锥体积之差是4.6立方分米,圆柱的体积是( 6.9 )立方分米 11、小东、小明和小军三人同在一张球桌上练习打乒乓球,他们轮流上场共打了一小时,平均每人打球( 40 )分钟。 12、32名同学正在10张乒乓球桌前进行单打或双打比赛,正在进行双打比赛的乒乓球桌有 ( 6 )张。 二、选择。(每题1分,共8分。) 1、三角形的面积一定,底和高( B ) A.成正比例; B.成反比例; C.不成比例; 2、a、b是两个不为0的自然数,a÷6=b,a、b的最小公倍数是( A )
A.a ; B. b ; C.6 ; D. 6a 。 3、一种盐水,盐占盐水的10%,盐和水的重量比是( C ) A 、1∶11 B 、1∶10 C 、1∶9 4、4、甲数的512 等于乙数的50%,则甲数是乙数的( A )。 A 、56 B 、65 C 、245 D 、4 25 5、把一根木头锯成7段,若每次锯的时间都相等,那么锯完每段的时间是总时间的( B )。 A 、15 B 、16 C 、17 D 、18 6、有5个数的平均数是20,如果把其中的一个数改成4,这时候5个数的平均数是18,改动的 数原来是( B )。 A.10 B.14; C.20; D.24 7、甲数是a ,它比乙数的3倍少b ,表示乙数的式子是( B )。 A.3a -b B.(a +b )÷3 C.a ÷3-b D. 3a +b 8、一个圆柱的侧面展开图是一个正方形,这个圆柱的底面直径与高的比是( A )。 A.1:π B. 1:2π C.2:π 三、判断(5分) 1、把甲队人数的 51调入乙队后两队人数相等,原来甲队人数比乙队多32。( √ ) 2、一瓶油5 4千克,先倒出它的51,再往瓶里加51千克。现在瓶内的油不变。 ( × ) 3、一个三角形中最小的一个内角是600,这个三角形一定是锐角三角形。 ( √ ) 4、一个数四舍五入后是8万,那么这个数最大可能是84999。 ( √ ) 5、如果3a =4b(a≠0,b≠0),那么 a∶b= 3∶4。 ( × ) 四、计算。(34分) 1、直接写出得数(8分) 3500-700=2800 0.4×0.2= 0.08 9-0.9= 8.1 24÷11 2=132
北师大版小学六年级下册数学期末试卷及答案
2012年北师大版六年级数学下册期末试卷(100分) 班级 ________ 姓名 ________ 考号 ________ 成绩 _______ 一、填空(每空1分,共25分) 1.3 8 = ()% = 12 ÷()= 9:()= () 315 8 + + 2.二亿七千零九写作(),省略亿位后面的尾数约是()。 3.1时45分=()时=()分;3050升=()立方米。 4.3个 1 10 与()个0.01的和是1。 5.妈妈买一件上衣花200元,比裤子贵3 5 ,裤子花了()元。 6.a和b都是自然数,a÷b=6,a和b的最大公约数是()。 7.4个苹果平均分给8个人,每人分得苹果总数的(),2人分到()个。 8.A C B =(B不为0),当A一定时,B和C成()比例。 9.小明带X元钱,买每千克b元的桃子,买了3千克,还剩()元;如果X=30, b=4时,小明剩下()元。 10.爸爸给汽车加了20升93#汽油,花了92元。总价与数量的比是():(),比值(),这个比值表示的是()。 11.小明用圆规画一个圆,圆规两脚张开的大小是1厘米,画出圆的周长是(),面积是()。 12.在比例尺是20:1的图纸上量得一个零件的直径是4厘米,这个零件直径的实际长度是()毫米。 13.一个直角三角形的两条直角边长分别是3厘米和4厘米,斜边长5厘米,如果以4厘米长的直角边为轴把三角形旋转一周,得到一个圆锥体,这个圆锥体的高是()厘米,底面半径是()厘米,体积是()立方厘米 二、判断(对的打“√”,错的打“×”并改正)(每小题1分,共5分) ()1.圆和半圆都有无数条对称轴。 ()2.如果3X=1 8 Y,(X、Y均不为0),那么X和Y成反比例关系。 ()3.分母是8的所有真分数的和是2。 ()4.淘气做12道题,对了12道,他的正确率是100%。。()
(完整)最新北师大版小学六年级(上册
最新北师大版小学六年级上册数学书中的应用题 1 .汽车车轮的半径为0.3m,它滚动1圈前进多少米?1000圈呢? 2.笑笑绕着花坛边缘走了一周,走了62.8m这个花坛的直径是多少米? 3.一个一面靠墙,另一面用篱笆围城的半圆形养鸡场,这个半圆的直径为6m,篱笆多长? 4.在一个边长是10m的正方形内放置一个最大的圆。这个圆的周长是多少? 5.一个边长为2cm的正方形和一个直径为2cm的圆,两只蚂蚁分别沿着正方形和圆走一圈,谁走的长?为什么? 6.一个圆形杯垫的半径是4cm,这个杯垫的面积是多少平方厘米? 7.有一个圆形蓄水池。它的周长是31.4m,它的占地面积是多少? 8.北京天坛公园的回音壁是闻名世界的声学奇迹,它是一道圆形围墙。圆的直径约为61.5m,周长与面积分别是多少?(结果保留一位小数) 9.一个运动场两边是半圆,中间是长方形,长方形的长是50m,宽式 20m,这个运动场的占地面积是多少? 10.某钟表的分针长10cm. (1)从1时到2时,分针针尖走过了多少厘米?(2)从1时到2时,分针扫过的面积是多少平方厘米? 11.一个水缸的直径是1m。要为这个水缸做一个盖子,这个盖子的面积至少是多少平方米 12.长12.25m的绳子,正好绕树干10圈。树干横截面的直径是多少呢? 13.一个圆形和一个长方形的面积相等。圆的直径和长方形的长都是16cm。长 方形的宽是多少厘米?
14.淘气用两根长度都是62.8cm的铁丝分别围城正方形和圆。它们围城的面积一样大吗? 15.某汽车车轮的直径为0.5cm,汽车行驶到1km时,车轮大约转了多少圈? 16.一只羊栓到木桩上,绳子长6m,羊能吃到草的面积有多大? 17.我国约有660个城市。其中约2/3的城市供水不足。在这些供水不足的城市中,又有的城市严重缺水。全国严重缺水的城市大约有多少个? 18.一本故事书有820页,第一周看了全书的,第二周看的是第一周的,第二周看了多少页? 19.有两只船,大船一次可以运载5吨货物,小船一次运载的货物是大船的大船6次运完的货物,如果改用小船运,几次运完? 20.有3瓶饮料。每瓶如果每杯装。能装9杯吗? 21.十一黄金周,游乐场第一天的门票收入为960元,第二天比第一天增加了第二天的门票收入是多少?画出图形,在运算。 22.水结成冰后,体积大约增加现有20L的水,能竭诚多少立方分米的冰? 23.一本故事书有140页,奇思已经看了这本书的,还剩多少没有看? 24.笑笑的体重是40KG,淘气的体重比笑笑重,淘气的体重是多少? 25.淘气的体重是45KG,笑笑比淘气轻笑笑的体重是多少? 26.公园的园丁新种植了480盆花,其中杜鹃花占,月季花占,新种植的这两种花共有多少盆? 27.越野赛跑全程12KM。其中环山路占,海滨路占,其余的是公路。(1)环山路段比海滨路长多少千米? (2)如果明年把赛跑全程延长,将是多少米?
北师大版小学六年级数学(上下)答案
一圆 1 圆的认识(一) 1.对称轴,无数2.圆心,位置,半径,大小,直径,半径3.C4.5 5.46.都相等7.C8.无数,以A为圆心2.5cm为半径的圆上 9.(1)5,10;(2)a,2a10.411.宽是4cm12.略 聚沙成塔 2 圆的认识(二) 1.(1)半径,r,无数,相等;(2)直径,d,无数,相等2.2,1 2 3.(1)14;(2)8;(3) 2a4.10 5.2.5 6.(1)对;(2)错;(3)对;(4)错;7.(1)4.4cm,2.2cm;(2)1.5cm,1cm;(3)4.5cm,2.25 cm;(4)4cm,4cm,2cm8.略9.8,410.轴对称,对称轴11.2,4,1,1,1,无数,312.长24cm,宽9cm 3 圆的周长 1.(1)7π;(2)4π;(3)500,10002.(10π+20)米3.6厘米4.周长 5.10,20π6.3,6π7.0.71×3.14=2.2294(米)≈2.2(米)8.(8+4π)cm 9.C1=4×4+4π=16+4π(cm);C2=4×4+4π×4×1 4 =16+4π(cm);C3=4×4+2π×4=16+8π(cm) ∴第三个图的阴影部分周长最长10.(15.7×4)÷3.14=20cm 11.设直径为x米,则4×3.14x+1.72=8,解得x=0.5,答:略 12.6π+2×6+4=6π+16(cm)13.1 4 ×2π×5= 5 2 π(cm) 聚沙成塔:红、黑蚂蚁一起到达终点. 4 圆的面积 1.长方形,半径或周长一半,周长一半或半径,πr22.半径4米,周长8π米,面积16π平方米3.半径1.5,面积7.065 4. 5.(1 7.半径为2.5分米;面积为6.25π平方分米;剩余面积为(60-6.25π)平方分米 8.增加13π平方米9.B10.A11.6个圆的阴影部分面积相等,都为(4-π)cm212.设半 圆半径为r,则2r+πr=15.42,解得r=3(分米),所以面积:3.14×9×1 2 =3.14×4.5=14.13(平 方米)13.(1)(2500+625π)平方米;(2)230×(2500+625π)=575000+143750π(元)14.面积:4π2平方分米15.半径为300米,面积:282600平方米
北师大版小学数学六年级上册知识点整理
第一单元圆 圆概念总结 1.圆的定义:平面上的一种曲线图形。 2.将一张圆形纸片对折两次,折痕相交于圆中心的一点,这一点叫做圆心。圆心一般用字母O表示。它到圆上任意一点的距离都相等. 3.半径:连接圆心到圆上任意一点的线段叫做半径。半径一般用字母r表示。把圆规两脚分开,两脚之间的距离就是圆的半径。 4.圆心确定圆的位置,半径确定圆的大小。 5.直径:通过圆心并且两端都在圆上的线段叫做直径。直径一般用字母d表示。6.在同一个圆内,所有的半径都相等,所有的直径都相等。 7.在同一个圆内,有无数条半径,有无数条直径。 8.在同一个圆内,直径的长度是半径的2倍,半径的长度是直径的一半。 用字母表示为:d=2r r =1 d 2 用文字表示为:半径=直径÷2 直径=半径×2 9.圆的周长:围成圆的曲线的长度叫做圆的周长。 10.圆的周长总是直径的3倍多一些,这个比值是一个固定的数。我们把圆的周长和直径的比值叫做圆周率,用字母π表示。圆周率是一个无限不循环小数。在计算时,取π≈3.14。世界上第一个把圆周率算出来的人是我国的数学家祖冲之。 11.圆的周长公式:C=πd 或C=2πr 圆周长=π×直径圆周长=π×半径×2 12、圆的面积:圆所占面积的大小叫圆的面积。 13.把一个圆割成一个近似的长方形,割拼成的长方形的长相当于圆周长的一半,用字母(πr)表示,宽相当于圆的半径,用字母(r)表示,因为长方形的面积=长×宽,所以圆的面积= πr×r。圆的面积公式:S=πr2。 14.圆的面积公式:S=πr2或者S=π(d÷2)2或者S=π(C÷π÷2)215.在一个正方形里画一个最大的圆,圆的直径等于正方形的边长。 16.在一个长方形里画一个最大的圆,圆的直径等于长方形的宽。 17.一个环形,外圆的半径是R,内圆的半径是r,它的面积是S=πR2-πr2或S=π(R2-r2)。 (其中R=r+环的宽度.)
北师大版小学六年级
北师大版小学六年级语文上册期末试题 班级姓名分数 一、拼音( 12 分) 1.加点字完全正确的一项是()(4分) A、袅袅 ..(niǎo)磨.练(mó)掠.过(lua)倔.强(jua) B、憨.直(hān)颤.动(zhàn)似.的(shì)喧.闹(xuān) C、澎湃.(bài)勉强.(qiǎng)填.饱(tiān)仍.然(r?ng) D、宫殿.(diàn)喃喃 ..(xù) ..(nán)悔.改(huǔ)絮絮 2、给加点的字选择正确的读音用“√”画出来。(8分) 捕.捉(pǔ bǔ)荆.州(jìng jīng)咀嚼.(jiáo ju?勉强.(qiǎng qiáng) 内疚.(jiù jiū)野雉.(zhì zì)脊.背(jí jǐ)潜.伏(qiǎn qián)二、字、词(32分) 1.解释加点词语(12分) 谒见()东施效颦()好士细腰() 学弈()故人知君()擎挈妻子() 2.比一比,在组成词语。(12分) 捂()脆()辨()俏() 悟()诡()辩()峭() 梧()跪()瓣()悄() 3.把下面词语补充完整(8分) 低()浅唱倾诉()肠难以()信挥()自如 惊()动()()耳()聋()牙()爪 全()()注 三、句子。(26分)
1. 选词填空。(4分) 如果……就……不但……而且……不管……总…… ①桑娜()关心自己的丈夫和孩子,()对西蒙一家的悲 惨遭遇十分同情。 2. 把下面句子中有毛病的地方修改过来。(8分) ①战士们击落了敌人的三架飞机和四辆坦克。 ②参加比赛的同学基本上都到齐了。 ③我的家乡是齐齐哈尔市人。 ④我国有世界没有的万里长城。 3.缩写句子。(4分) ①魁梧,黝黑的渔夫拖着湿淋淋的撕破的渔网。 4.扩写句子。(2分) 玫瑰花红啊! 5.把陈述句改成反问句。(2分) 四周黑洞洞的,很容易碰壁。 6.把陈述句改成“把”字句和“被”字句。(4分) 桑娜收养了西蒙的孩子。 7.改成比喻句。(2分) 天上的云形态各异,什么样子的都有。 四、常识填空。(32分) (1)鲁迅,原名,是伟大的、、,现代文学的奠 基人,著有、、。 (2)列夫?托尔斯泰,国伟大的。代表作品有、 、。 (3)《墨梅图题诗》的作者是,朝的诗人,诗中哪句交待 了梅花生长的位
(完整版)北师大版小学六年级数学总复习资料
2013小学六年级毕业班数学总复习资料 常用的数量关系式 1、每份数×份数=总数总数÷每份数=份数总数÷份数=每份数 2、1倍数×倍数=几倍数几倍数÷1倍数=倍数几倍数÷倍数=1倍数 3、速度×时间=路程路程÷速度=时间路程÷时间=速度 4、单价×数量=总价总价÷单价=数量总价÷数量=单价 5、工作效率×工作时间=工作总量工作总量÷工作效率=工作时间 工作总量÷工作时间=工作效率 6、加数+加数=和和-一个加数=另一个加数 7、被减数-减数=差被减数-差=减数差+减数=被减数 8、因数×因数=积积÷一个因数=另一个因数 9、被除数÷除数=商被除数÷商=除数商×除数=被除数 小学数学图形计算公式 1、正方形(C:周长 S:面积 a:边长) 周长=边长×4 C=4a 面积=边长×边长S=a×a 2、正方体(V:体积 S:表面积 a:棱长) 表面积=棱长×棱长×6 S=a×a×6体积=棱长×棱长×棱长V=a×a×a 3、长方形( C:周长 S:面积 a:边长) 周长=(长+宽)×2 C=2(a+b) 面积=长×宽 S=ab 4、长方体(V:体积 S:表面积 a:长 b: 宽 h:高) (1)表面积(长×宽+长×高+宽×高)×2 S=2(ab+ah+bh) (2)体积=长×宽×高 V=abh 5、三角形(s:面积 a:底 h:高) 面积=底×高÷2 s=ah÷2 三角形高=面积×2÷底三角形底=面积×2÷高 6、平行四边形(s:面积 a:底 h:高) 面积=底×高 s=ah 7、梯形(s:面积 a:上底 b:下底 h:高) 面积=(上底+下底)×高÷2 s=(a+b)× h÷2 8、圆形(S:面积 C:周长л d=直径 r=半径) (1)周长=直径×л=2×л×半径 C=лd=2лr (2)面积=半径×半径×л S= πr2 9、圆柱体(v:体积 h:高 s:底面积 r:底面半径 c:底面周长) (1)侧面积=底面周长×高=ch(2лr或лd) (2)表面积=侧面积+底面积×2 (3)体积=底面积×高(4)体积=侧面积÷2×半径 10、圆锥体(v:体积 h:高 s:底面积 r:底面半径) 体积=底面积×高× 3 1 11、总数÷总份数=平均数 12、相遇问题 相遇路程=速度和×相遇时间 相遇时间=相遇路程÷速度和 速度和=相遇路程÷相遇时间 13、浓度问题 溶质的重量+溶剂的重量=溶液的重量 溶质的重量÷溶液的重量×100%=浓度 溶液的重量×浓度=溶质的重量 溶质的重量÷浓度=溶液的重量 14、利润与折扣问题 利润=售出价-成本 利润率=利润÷成本×100%=(售出价÷成本-1)×100% 涨跌金额=本金×涨跌百分比 利息=本金×利率×时间 税后利息=本金×利率×时间×(1-20%) 常用单位换算 长度单位换算 1千米=1000米1米=10分米1分米=10厘米1米=100厘米1厘米=10毫米 面积单位换算 1平方千米=100公顷1公顷=10000平方米1平方米=100平方分米 1平方分米=100平方厘米1平方厘米=100平方毫米 体(容)积单位换算 1立方米=1000立方分米1立方分米=1000立方厘米1立方分米=1升 1立方厘米=1毫升1立方米=1000升1升=1000毫升 重量单位换算 1吨=1000 千克1千克=1000克1千克=1公斤 人民币单位换算 1元=10角1角=10分1元=100分 时间单位换算 1世纪=100年1年=12月大月(31天)有:1\3\5\7\8\10\12月小月(30天)的有:4\6\9\11月平年2月28天, 闰年2月29天平年全年365天, 闰年全年366天1日=24小时 1时=60分1分=60秒1时=3600秒 1
【最新】北师大版小学六年级数学小学毕业测试题
(北师大版)小学数学毕业测试题 班级 姓名 分数 一、填空题。(每空1分,共20分) l 、一个数的亿位上是5、万级和个级的最高位上也是5,其余数位上都是0,这个数写作( ),省略万位后面的尾数是( )。 2、0.375的小数单位是( ),它有( )个这样的单位。 3、6.596596……是( )循环小数,用简便方法记作( ),把它保留两位小数是( )。 4、61<()5<3 2,( )里可以填写的最大整数是( )。 5、在l ——20的自然数中,( )既是偶数又是质数;( )既是奇数又是合数。 6、甲数=2×3×5,乙数=2×3×3,甲数和乙数的最大公约数是( )。最小公倍数是( )。 7、被减数、减数、差相加得1,差是减数的3倍,这个减法算式是( )。 8、已知4x +8=10,那么2x +8=( )。 9、在括号里填入>、<或=。 1小时30分( )1.3小时 1千米的8 7( )7千米81。 10、一个直角三角形,有一个锐角是35°,另一个锐角是( )。 11、一根长2米的直圆柱木料,横着截去2分米,和原来比,剩下的圆柱体木料的表面积减少12.56平方分米,原来圆柱体木料的底面积是( )平方分米,体积是( )立方分米。 12、在含盐率30%的盐水中,加入3克盐和7克水,这时盐水中盐和水的比是( )。 二、判断题。对的在括号内打“√”,错的打“×”。(每题1分,共5分) 1、分数单位大的分数一定大于分数单位小的分数。( ) 2、36和48的最大公约数是12,公约数是1、2、 3、 4、6、12。( ) 3、一个乒乓球的重量约是3千克。( ) 4、一个圆有无数条半径,它们都相等。( ) 5、比的前项乘以2 1,比的后项除以2,比值缩小4倍。( ) 三、选择题。把正确答案的序号填入括号内。(每题2分,共10分) 1、两个数相除,商50余30,如果被除数和除数同时缩小10倍,所得的商和余数是( )。 (l )商5余3 (2)商50余3 (3)商5余30 (4)商50余30 2、4x +8错写成4(x +8),结果比原来( )。 (1)多4 (2)少4 (3)多24 (4)少24 3、在一幅地图上,用2厘米表示实际距离90千米,这幅地图的比例尺是( )。 (1)451 (2)45001 (3)450001 (4)4500000 1 4、一个长方体,长6厘米,宽3厘米,高2厘米,它的最小面的面积与表面积的比是( )。
新北师大版小学六年级数学[上册]单元测试题_(全册)
北师大版六年级数学上册第一单元测试题 卷面(3分),我能做到书写端正,卷面整洁(时间:40分钟满分:100分) (74分) 一、积极思考,认真填写。(每空2分,共30分) 1.看图填空。 圆的直径=() cm 长方形的宽=() cm 2.一个圆的半径是5 cm,直径是() cm,周长是() cm, 面积是() cm2。 3.一个圆的面积是28.26 cm2,用圆规画圆时,圆规两脚之间的距离是 () cm。这个圆的直径是() cm,周长是() cm。 4.一位老奶奶沿着街心公园的一个圆形花坛走了一圈,走了18.84 m, 花坛占地() m2。 5.将一个圆沿半径剪开,得到若干个小扇形,然后拼成一个近似的长 方形,这个长方形的长是圆的(),宽是圆的()。如果这 个长方形的宽是2 cm,那么这个长方形的长是() cm,圆的 周长是() cm,圆的面积是() cm2。如果拼成的长方 形的长是9.42 dm,那么原来圆的面积是() dm2。 二、仔细推敲,正确判断。(8分)
1.若一个圆的周长是1 2.56 cm,则面积是12.56 cm2。() 2.一个圆的面积和一个正方形的面积相等,它们的周长也一定相等。() 3.(2015·安徽省安庆市怀宁县小升初试题)1500多年前,我国南北 。()朝时期著名的数学家祖冲之就得到了圆周率的约率22 7 4.半圆的面积等于这个圆面积的一半。() 三、反复比较,谨慎选择。(12分) 1.下面各图形中,对称轴最多的是() A.正方形 B.圆 C.等腰三角形 D.平行四边形 2.圆周率π的值() 3.14。 A.大于 B. 等于 C.小于 D.无法比较 3.圆的半径由3 cm增加到4 cm,圆的面积增加了() cm2。 A.3.14 B.12.56 C.21.98 D.6.28 4.一个圆环,内圆半径是4 cm,外圆半径是5 cm,计算这个圆环面 积的算式是() A.3.14×(52-42) B.3.14×(5-4)2 C.3.14×(52+42) D.3.14×(5-4)×2 四、求下面图形中阴影部分的面积。(单位:cm)(8分)
北师大版小学六年级数学知识点总结(全)
北师大版小学数学六年级知识点 第一单元圆 1、使学生认识圆的特征:圆的半径、直径、圆心。认识在同圆内半径和直径的关系。知道圆是轴对称图形,有无数条对称轴,而这些对称轴都过圆心。知道生活中有了圆才使我们的生活更美好。 2、认识同心圆、等圆。知道圆的位置由圆心决定,圆的大小由半径或直径决定。等圆的半径相等,位置不同;而同心圆的半径不同,位置相同。 3、使学生知道圆的周长和圆周率的含义,掌握圆的周长的计算公式,能够正确地计算 圆的周长?介绍祖冲之在圆周率研究上的成就,渗透爱国主义教育。在运用上,要能根据圆的周长算直径或半径,会算半圆的周长:圆的周长X1/2+直径。会求组合图形的周长。 4、了解圆的面积的含义,经历圆面积计算公式的推导过程,掌握圆面积计算公式。 5、能正确运用圆的面积公式计算圆的面积,并能运用圆面积知识解决一些简单实际的问题。会灵活运用圆的面积公式。已知圆的周长会算圆的面积,会求组合图形的面积。 会算圆环的面积,并且知道在周长相等的情况下,正方形、长方形、圆三种图形中,圆的面积最大。 6、在估一估和探究圆面积公式的活动中,体会化曲为直”的思想,初步感受极限思想。 第二单元百分数的应用 本单元重点讲解百分数在生活中的应用,知识点为: 1、知道百分数的意义:表示一个数是另一个数的百分之几的数,叫做百分数。百分数也叫做百分率或百分比。百分数通常不写成分数形式,而用百分号“%表示;百分数 有时也定义为分母是100的分数,但百分数与分数是有区别的:分数既可表示具体的量, 又
可表示两个数量间的倍比关系;然而百分数只能表示两个数量间的倍比关系;所以是不名数,也就是不能带单位的数。 2、在具体情景中理解增加百分之几”或减少百分之几”的意义,加深对百分数意义的理解。 3、能解决有关增加百分之几”或减少百分之几”的实际问题,提高运用数学解决实际问题的能力,体会百分数与现实生活的密切联系。 4、知道出勤率、出粉率、成活率等百分数的意义及在实际生活中的应用,会计算这种 百分数。 5、知道成数、打折的含义。表示一个数是另一个数十分之几、百分之几的数,叫做成 数。打折就是按原价的百分之几十、十分之几出售。八五折就是按原价的85%出售。成数和折扣数不能用小数表示。 6、能解决比一个数增加百分之几的数是多少”或比一个数减少百分之几的数是多少” 的实际问题。 7、进一步加强对百分数的意义的理解,并能根据百分数的意义列方程解决实际问题, 会解含有百分数的方程。 &能利用百分数的有关知识,解决一些与储蓄有关的实际问题,提高解决实际问题的能力。知道利息是本金存入银行过一段时间取出后多出来的钱;本金是存入银行的钱;利率就是某段时间中利息占本金的百分比;禾U息税是国家银行规定的针对利息收入的税收。会计算利息。利息=本金>利」率刈寸间 9、结合储蓄等活动,学习合理理财,逐步养成不乱花钱的好习惯。 第三单元图形的变换 1、通过观察、操作、想象,知道一个简单图形是怎样经过平移或旋转制作复杂图形的过程,体验图形的变换,发展空间观念。并能借助方格纸上的操作和分析,有条理地表达图形的平移或旋转的变换过程。 2、能利用七巧板在方格纸上变换各种图形。能运用图形的变换在方格纸上设计美丽的图
新北师大版小学六年级数学上册单元测试题-全册
北师大版六年级数学上册第一单元测试题 一、积极思考,认真填写。(每空2分,共30分) 1.看图填空。 圆的直径=()cm 长方形的宽=()cm 2.一个圆的半径是5 cm,直径是()cm,周长是()cm, 面积是()cm2。 3.一个圆的面积是28.26 cm2,用圆规画圆时,圆规两脚之间的距离是()cm。这个圆的直径是()cm,周长是()cm。 4.一位老奶奶沿着街心公园的一个圆形花坛走了一圈,走了18.84 m, 花坛占地()m2。 5.将一个圆沿半径剪开,得到若干个小扇形,然后拼成一个近似的长 方形,这个长方形的长是圆的(),宽是圆的()。如果这个长方形的宽是2 cm,那么这个长方形的长是()cm,圆的周长是()cm,圆的面积是()cm2。如果拼成的长方形的长是9.42 dm,那么原来圆的面积是()dm2。 二、仔细推敲,正确判断。(8分) 1.若一个圆的周长是1 2.56 cm,则面积是12.56 cm2。()
2.一个圆的面积和一个正方形的面积相等,它们的周长也一定相等。() 3.(2015·安徽省安庆市怀宁县小升初试题)1500多年前,我国南北 。()朝时期著名的数学家祖冲之就得到了圆周率的约率22 7 4.半圆的面积等于这个圆面积的一半。() 三、反复比较,谨慎选择。(12分) 1.下面各图形中,对称轴最多的是() A.正方形B.圆 C.等腰三角形 D.平行四边形 2.圆周率π的值() 3.14。 A.大于 B. 等于 C.小于 D.无法比较 3.圆的半径由3 cm增加到4 cm,圆的面积增加了()cm2。 A.3.14 B.12.56 C.21.98 D.6.28 4.一个圆环,内圆半径是4 cm,外圆半径是5 cm,计算这个圆环面 积的算式是() A.3.14×(52-42) B.3.14×(5-4)2 C.3.14×(52+42) D.3.14×(5-4)×2 四、求下面图形中阴影部分的面积。(单位:cm)(8分)
北师大版小学六年级
北师大版小学六年级(下)数学第二次月考 一、填一填.(每空1分,共16分) 1.地球上海洋面积大约是三亿六千一百万平方米,这个数写作(),省略亿后面的尾数约是()。 2 3.如果3a=b(a、b是非0的数),那么a,b的最大公因数是()。 4.一个摩天轮转动起来,最高点和最低点之间的距离是10米,坐这个摩天轮转一圈是()米。 5.照样子,填一填。 6.在日常生活中,我们经常用一些成语来形容事件发生的可能性大小。 ①平分秋色②百发百中③希望渺茫④十拿九稳 成语按可能性由小到大排列的顺序是()。 7.原价每袋1元的某种牛奶,正在搞促销活动,甲商店每袋降价15%,乙商店“买四送一”,丙商店打八八折出售,妈妈买5袋牛奶,从()商店买最便宜,从()商店买最贵。 8. 8个外观相同的球中有一个次品(次品比正品略轻),至少要用天平秤()次,才能保证找出次品。 9.按糖与水的质量比是2:23配制一种糖水,这种糖水的含糖率是()%,现有糖68克,可配制糖水()克。 10.10.用8个棱长1厘米的立方体拼成一个长方体,其中表面积最大的与最小的相差()平方厘米. 二、我是公正小法官.(每题2分,共10分) 2.把一圆心角是270°的扇形按1:10的比例尺画在纸上,纸上的圆心角是27°。() 3. 某市20XX年冬天某地气温是-2℃到5℃,这天的温差是6℃。()
4. 在掷骰子游戏中,要想掷出的点数一定有两个相同,至少要掷7次。() 5. 一个长13cm,宽7cm的长方形纸片,最多可以剪出多少个半径1cm的圆片,小明列式为:13×7÷(3.14×12)。() 三、选一选. (每题2分,共10分) 四、计算题.(3+3+3+3+4=16分) 1.列式计算. (1)3 的 2 比 7 少多少?
