TL_528_2008_06

Chrome-Plated Plastic Parts Material Requirements
Previous issues
TL 528: 1965-01, 1973-09, 1979-01, 1985-01, 1986-06, 1988-06, 1993-06, 2000-07, 2006-04Changes
The following changes have been made as compared to TL 528: 2006-04:–Sections 3 and 4 revised
–Referenced documents updated Scope
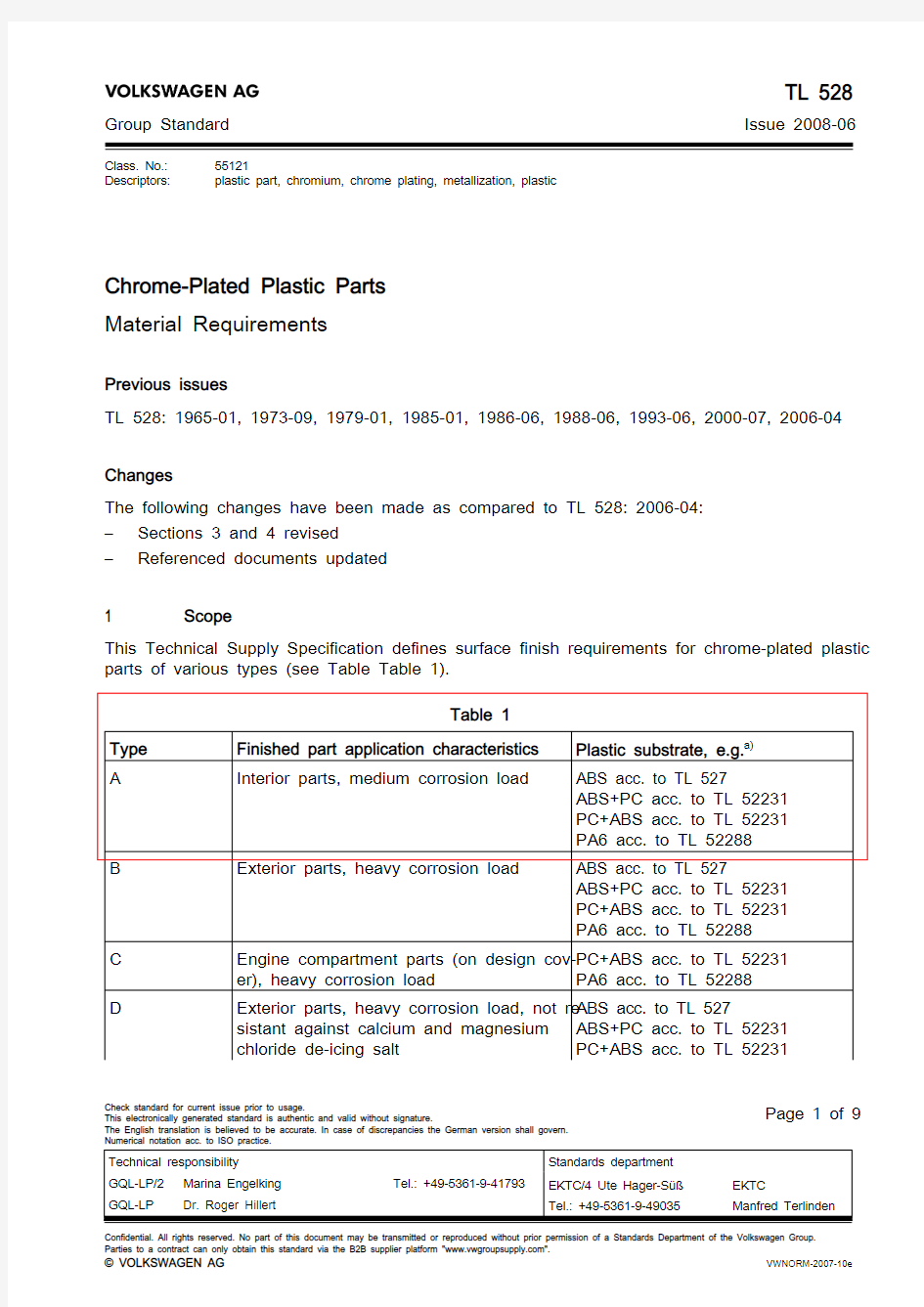
This Technical Supply Specification defines surface finish requirements for chrome-plated plastic parts of various types (see Table Table 1).
Table 1
Type Finished part application characteristics Plastic substrate, e.g. a)A
Interior parts, medium corrosion load
ABS acc. to TL 527
ABS+PC acc. to TL 52231PC+ABS acc. to TL 52231PA6 acc. to TL 52288B Exterior parts, heavy corrosion load
ABS acc. to TL 527
ABS+PC acc. to TL 52231PC+ABS acc. to TL 52231PA6 acc. to TL 52288C Engine compartment parts (on design cov‐er), heavy corrosion load
PC+ABS acc. to TL 52231PA6 acc. to TL 52288
D
Exterior parts, heavy corrosion load, not re‐sistant against calcium and magnesium chloride de-icing salt ABS acc. to TL 527ABS+PC acc. to TL 52231PC+ABS acc. to TL 52231
1
Group Standard
TL 528
Issue 2008-06
Class. No.:55121
Descriptors:
plastic part, chromium, chrome plating, metallization, plastic
Check standard for current issue prior to usage.
This electronically generated standard is authentic and valid without signature.
The English translation is believed to be accurate. In case of discrepancies the German version shall govern.Numerical notation acc. to ISO practice.
Page 1 of 9
Technical responsibility Standards department GQL-LP/2Marina Engelking Tel.: +49-5361-9-41793
GQL-LP
Dr. Roger Hillert
EKTC/4 Ute Hager-Sü?EKTC
Tel.: +49-5361-9-49035
Manfred Terlinden
Confidential. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be transmitted or reproduced without prior permission of a Standards Department of the Volkswagen Group.Parties to a contract can only obtain this standard via the B2B supplier platform "https://www.360docs.net/doc/7610310556.html,".
? VOLKSWAGEN AG
VWNORM-2007-10e
Type Finished part application characteristics Plastic substrate, e.g. a)
D
Exterior parts, heavy corrosion load, not re‐sistant against calcium and magnesium chloride de-icing salt
PA6 acc. to TL 52288Type D must not be used any more for new designs of the brands Volkswagen, Volkswagen Com‐mercial vehicles and Skoda; when drawings are changed, the respective entries related to this type must be deleted!
a) tried and tested plastics previously used in these areas
Description
Description example for a finished part made of ABS used as interior part and chrome-electroplated:
ABS according to TL 527, chrome-plated according to TL 528-A
Requirements General requirements
Approval of first supply and changes according to Volkswagen standard VW 01155.Avoidance of hazardous substances according to VW 91101.
10 finished parts (depending on the size) are required for complete testing.
The following information shall additionally be provided by the supplier for all parts under test (see table in Appendix B):1.Part number
2.Plastic part manufacturer, location
3.Substrate material (type of plastic, manufacturer, manufacturer's designation)
4.Electroplating plant and system, location
5.Electroplating date
6.Type of plastic activation/metallizing method (e.g. standard colloidal chrome-plating method,ionogenic method, direct metallizing, bright chrome, microporous, with micro-cracks)
7.Position/arrangement on the rack
8.
Color
Molded part Base material
Plastics designated by the substrate manufacturer as material suitable for electroplating according to Table 1. Plastic types deviating from this require basic tests with additional tests to be determined individually, if necessary.Appearance
The parts shall be free of flaws such as voids or cracks. They shall be free of internal stresses which might influence the adhesion and appearance of the electroplated coatings. The person responsible
2 3 3.1
3.2 3.2.1
3.2.2
Page 2
TL 528: 2008-06
for injection molding and the person responsible for electroplating shall ensure that the parts are free of stress.
The sprues shall be placed in such a way that the danger of sink marks under thermal load is mini‐mized and there is no impairment to the visible surface when removing the sprues either before or after electroplating.
Burrs shall be avoided. Sharp edges shall be rounded off in the design with radii.Surface appearance of uncoated molded part
The surface shall be smooth and free of flow lines, cracks, sink marks, craters or bursting which might impair the appearance of the finished parts. Furthermore, the surface shall be absolutely clean and free of grease and sweat. Do not use mold parting agents. The parts shall not be mechanically pol‐ished prior to coating; deburring prior to electroplating shall be avoided. Deviations shall be agreed with the relevant engineering department responsible for the release.Finished part
The supplier is responsible for the quality of the finished part. An agreement with respect to the design and manufacture should be made at the earliest possible opportunity between the Design Engineer‐ing, the supplier, mold-maker, injection molder and those responsible for electroplating. In the case of defects of the type described under No. 3 in Table 2, the cause shall be sought in all process steps (mold design, injection molding and electroplating) in cooperation with everyone involved in the supply chain.
The chrome electroplating date shall be specified on the parts according to TL 528 in order to ensure traceability of the parts.Surface finish
In the visible area, the appearance of the parts shall comply with the original sample. The contact points for electroplating shall be positioned in a way that flaws cannot be recognized in the installed condition. The coating shall be free from pores, coarse cracks, flaws or other damage that impairing the corrosion protection or the specified appearance. The compliance of the component with the released original sample chart or the original sample part in terms of gloss and color shall be ensured and verifiable using measuring instruments and/or shall be visually verifiable. If necessary, maximum deviation samples shall be specified by the Quality Assurance department of the vehicle manufac‐turing https://www.360docs.net/doc/7610310556.html,posite quality
The individual layers layers shall tightly adhere to the substrate material and to each other and shall be free of bubbles.
Prior to testing, the parts shall be aged at room temperature for 24 hours.Coating process
Provided the requirements of these supply specifications are met, the manufacturer may choose the coating procedure. The standard-production parts shall correspond to the released first-sample parts regarding the coating procedure and coating thickness. In the case of major process changes, e. g.a change of the coating company, new sampling is required.
3.2.3
3.3
3.3.1
3.3.2
3.3.3
Page 3
TL 528: 2008-06
Technological requirements for the coated part
See Table 2.
Measuring points and deviations of coating thickness, extent of micro-cracks, micropores and po‐tential differences are defined by the engineering department responsible for the release.
The positions on the electroplating racks representing the items to be provided for the release tests are also specified. To this end, the supplier provides a photograph or a draft of the equipped rack including a numbering of the rack positions. The rack positions (parts) to be provided will be defined on this basis together with the engineering department issuing the release. The parts shall preferably be checked transversely over the rack, e. g. right top, center, left bottom of the rack.
Table 2
No.Property Requirement
TL 528-A TL 528-B
TL 528-C
TL 528-D 1
Coating
Coating systems acc. to DIN 50960-1,
DIN EN 1403, DIN EN 12540and Section 4.1
PL/Cu20/Ni10b (or d or s)/Crr (or mp or mc)PL/Cu25/Ni16,5d (or s)/
Crmc
PL/Cu25/Ni16,5d (or s)/Crmp
1.1Copper coating thickness acc. to DIN EN ISO 2177
≥ 20 μm
≥ 25 μm 1.2
Semi-bright nickel coating thick‐ness acc. to DIN EN ISO 2177and PV 1065
-≥ 7,5 μm
1.3Bright nickel coating thickness (also matt nickel coating thick‐ness for matt surfaces) acc. to DIN EN ISO 2177 and PV 1065≥ 10 μm ≥ 7,5 μm
1.4Coating thickness of microdis‐continuous nickel acc. to PV 1065
-microcracks: ≥ 1,5 μm
micropores:≥ 1,5 μm
1.5
Chrome coating thickness acc.to DIN EN ISO 2177
(0,3 to 1,0)μm deposited from hexava‐lent Cr elec‐trolytes Crmc: ≥ 0,8 μm deposited from hexavalent Cr electrolytes Crmp: (0,3 to 0,5) μm deposited from hexava‐lent Cr elec‐trolytes
1.6
Potential step between micro‐porous nickel/bright nickel (or satin nickel) acc. to PV 1065
--≥ 20 mV
The micro‐porous nickel must be no‐bler than the bright nickel.
1.7
Potential step between bright nickel (or satin nickel)/semi-bright nickel acc. to PV 1065
-
≥ 100 mV
The semi-bright nickel must be nobler than the bright nickel. -
3.3.4 Page 4
TL 528: 2008-06
No.Property Requirement
TL 528-A TL 528-B TL 528-C TL 528-D
1.8Crack density acc. to PV 1058,
pore density and for unclear pat‐
terns acc. to PV 1063-Crmc: (250 to 800) cracks/
cm
Crmp: ≥ 8000
pores/cm2
2Adhesive strength of the total structure
2.1Crosscut test
see Section 4.2
With removal of adhesive tape, no stripping of coating
2.2relative peel strength acc. to
DIN EN 1464
test rate: 50 mm/min, specimen
width: where possible 10 mm to
20 mm; the edges must be
ground smooth The test shall be performed in arbitration cases. The lo‐cations of the measuring strips shall be defined by the engineering department responsible for the release when measuring the arbitration samples.
Mean value of maximum peak forces ABS/PC: ≥ 3,5 N/cm ABS: ≥ 7 N/cm
3Temperature and climatic resistance
3.1Dimensional stability under heat
in ASSY and as individual part
ABS: 6 h at +100 °C
ABS/PC: 6 h at +110 °C
PA6: 6 h at +110 °C
(or acc. to drawing)
No change in appearance. The requirements on adhesion according to Table 2, No. 2 must be complied with.
3.2Temperature resistance after
aging in mechanical circulation
oven with forced air circulation 500 h at +90 °C (only if spec‐
ified in the drawing)
240 h at
+110 °C (or
acc. to draw‐
ing)
500 h at
+90 °C (only
if specified in
the drawing) No change in appearance. The requirements on adhesion according to Table 2, No. 2 must be complied with.
3.3Environmental cycle test
3.3.1acc. to PV 1200 (short term) in
ASSY and as individual part 8 cycles
No change in appearance (e.g. cracks, bubbles, pores, folds, sink marks). The requirements on adhesion accord‐ing to Table 2, No. 2 must be complied with.
3.3.2acc. to PV 2005 (long term) in
ASSY and as individual part only
for function parts in mechanically
loaded areas (e.g. door operat‐
ing mechanism, brake lever re‐
lease button, anchor plates for
selector, radio buttons, switches
etc.)50 cycles
No change in appearance (e.g. cracks, bubbles, pores, folds, sink marks). The requirements on adhesion accord‐ing to Table 2, No. 2 must be complied with.
4Corrosion resistance
4.1CASS test acc. to
DIN EN ISO 922724 h48 h
Page 5
TL 528: 2008-06
No.Property Requirement TL 528-A
TL 528-B
TL 528-C
TL 528-D
Test in as-installed position or in consultation with the re‐sponsible department
No change in appearance, no visually discernible corro‐sion when assessed from a distance of 60 cm under optimal lighting. Prior to the assessment, adhering salt residue must be removed.
4.2
Environmental cycle aging acc.to PV 1200, then salt spray test NSS acc. to DIN EN ISO 9227.96 h environ‐mental cycle aging, fol‐
lowed by 240 h NSS 96 h environmental cycle aging, followed by 480 h NSS
No change in appearance, no corrosion when assessing visually from a distance of 60 cm. Prior to the assessment,adhering salt residue must be removed.
Notes on testing Coating system
Definition of abbreviated terms:b =bright nickel
d =doubl
e or triple nickel s =matt/satin nickel
mp =chrome surface with micropores mc =chrome surface with microcracks
Crosscut test (St. Andrew’s cross),
The test shall be carried out using a cutter knife (e. g. Edding Cutter M9). A Saint-Andrews cross (Figure 1) shall be applied, a sharp blade shall be used for the cut. The cut shall penetrate the coating and reach the substrate. The blade shall be drawn at an angle of 90° to the sample surface. It shall be ensured that the surface is free of substances impairing the tape adhesion, isopropyl alcohol shall be used for cleaning if required. Then, an adhesive tape (Tesa 4657 by Tesa AG) shall be affixed to the cut area and pressed on until the outline of the cut is clearly discernible through the tape (see Figure 2). The adhesive tape shall then be removed in a jerk-like motion in the direction of the acute angle (see Figure 3).
Figure 1 – St. Andrew's
cross Figure 2 – Application of the
tape
Figure 3 – Removal of the tape
4 4.1
4.2
Page 6
TL 528: 2008-06
Referenced documents
The following documents cited in this standard are necessary for application.
In this Section terminological inconsistencies may occur as the original titles are used.PV 1058Chrome-Plated Surfaces; Determination of the Microcracked Chrome De‐posit
PV 1063Chrome-Plated Surfaces; Determination of Micropore Density
PV 1065Chrome-Plated Surfaces; Determination of Potential Differences and Nick‐el Coating Thicknesses
PV 1200Vehicle Parts; Testing of Resistance to Environmental Cycle Test (+80/-40) °C
PV 2005Fahrzeugteile; Prüfung der Klimawechselfestigkeit (only available in Ger‐man)
TL 52231ABC and PC Polymer Blends; Material Requirements
TL 52288Polyamide, Mineral-Reinforced, Finished Parts; Material Requirements TL 527ABS Graft Polymer, Finished Parts; Material Requirements VW 01155Vehicle Supply Parts; Approval of First Supply and Changes
VW 91101Environmental Standard for Vehicles; Vehicle Parts, Materials, Operating Fluids; Avoidance of Hazardous Substances
DIN 50960-1
Electroplated coatings - Designation in technical documents / Note: Ap‐plies in conjunction with DIN EN 1403 (1998-10).*To be replaced by DIN 50960-1 (2005-10).
DIN EN 12540
Corrosion protection of metals - Electrodeposited coatings of nickel, nickel plus chromium, copper plus nickel and copper plus nickel plus chromium;German version EN 12540:2000 / Note: Applies in conjunction with DIN EN 1403 (1998-10).*To be replace...
DIN EN 1403Corrosion protection of metals - Electrodeposited coatings - Method of specifying general requirements; German version EN 1403:1998DIN EN 1464
Adhesives - Determination of peel resistance of high-strength adhesive bonds - Floating roller method (ISO 4578:1990, modified); German version EN 1464:1994
DIN EN ISO 2177
Metallic coatings - Measurement of coating thickness - Coulometric
method by anodic dissolution (ISO 2177:2003); German version EN ISO 2177:2004
DIN EN ISO 9227
Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres - Salt spray tests (ISO 9227:2006);German version EN ISO 9227:2006
5 Page 7
TL 528: 2008-06
Page 8
TL 528: 2008-06
Appendix A (informative)
Suggestion for standard-production monitoring methods for electroplated plastic parts:
Standard-production monitoring of the required features also serves the purpose of monitoring the electroplating process itself, in addition to ensuring product-specific properties. As prompt monitoring of all individual articles is generally not possible for large quantities of products manufactured daily, identical versions (e.g. nameplates, strips etc.) can be combined to form product groups. Continuous monitoring of these product groups is the responsibility of the supplier. The supplier shall check an adequate number of random samples at regular intervals. The results shall be documented.
In addition to the tests required for first samples, the following product properties are subject to con‐tinuous standard-production monitoring:
1.(Minimum) coating thicknesses according to DIN EN ISO 2177
2.Potential differences and nickel coating thicknesses according to PV 1065
3.Number of micropores acc. to PV 1058 or number of micropores for microporous coating acc. to
PV 1063.
4.Corrosion resistance acc. to DIN EN ISO 9227-CASS
5.Environmental cycle test according to PV 1200
or as quick test
Coating adhesion (thermal shock test)
Heating of components to +110 °C (for ABS 1 h at +100 °C) until temperature equalization, then quenching in water (+18 ± 3) °C (no adhesion loss of coatings).
S u p p l i e r d e t a i l s o n t h e s p e c i m e n p a r t :
T a b l e B .1
S u p p l i e r
P a r t n u m b e r
P a r t d e s i g n a t i o n
P l a s t i c p a r t m a n u f a c t u r e r
S u b s t r a t e m a t e r i a l (t y p e o f p l a s t i c , m a n u f a c t u r e r , m a n u f a c t u r e r 's d e s i g n a ‐t i o n )
N u m b e r o f c a v i t i e s i n m o l d
I n j e c t i o n t e m p e r a t u r e
M o l d t e m p e r a t u r e
E l e c t r o p l a t i n g p l a n t a n d s y s t e m , l o c a t i o n
E l e c t r o p l a t i n g d a t e
L a y e r s t r u c t u r e
T y p e o f p l a s t i c a c t i v a t i o n /m e t a l l i z i n g m e t h o d (e .g . c h r o m e p l a t i n g m e t h o d ,s t a n d a r d c o l l o i d a l , i o n o g e n i c m e t h o d , d i r e c t m e t a l l i z i n g ; v e r s i o n w i t h m i ‐c r o c r a c k s , m i c r o p o r e s )
S i m p l e d r a f t s h o w i n g t h e s e t u p o f p a r t s i n t h e r a c k (i n c l u d i n g d i s t a n c e s p e c i f i c a t i o n s )
F o r d e v e l o p m e n t p a r t s : s t a t u s o f b l a n k (i n j e c t i o n d a t e , i m p r o v e m e n t s m a d e )
F o r d e v e l o p m e n t p a r t s : s t a t u s o f c h r o m e -p l a t i n g p r o c e s s (i m p r o v e m e n t s m a d e )
A p p e n d i x
B (i n f o r m a t i v e ) P a g e 9T L 528: 2008-06
