主要软磁铁氧体材料厂商牌号对照表
铁氧体参数及国内外牌号对照表
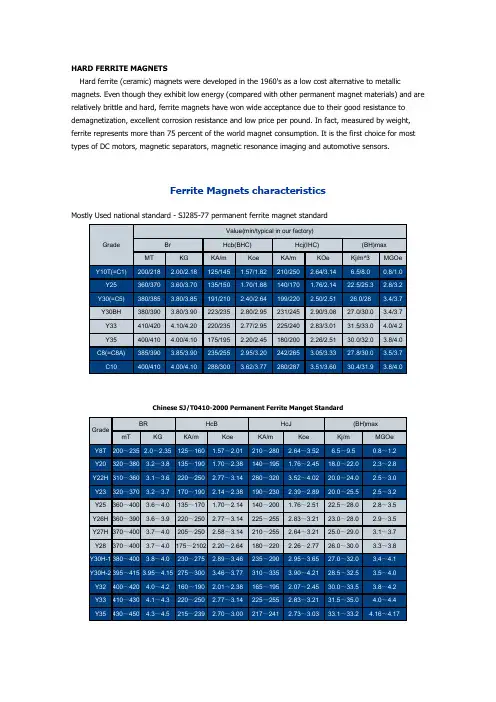
HARD FERRITE MAGNETSHard ferrite (ceramic) magnets were developed in the 1960's as a low cost alternative to metallic magnets. Even though they exhibit low energy (compared with other permanent magnet materials) and are relatively brittle and hard, ferrite magnets have won wide acceptance due to their good resistance to demagnetization, excellent corrosion resistance and low price per pound. In fact, measured by weight, ferrite represents more than 75 percent of the world magnet consumption. It is the first choice for most types of DC motors, magnetic separators, magnetic resonance imaging and automotive sensors.Ferrite Magnets characteristicsMostly Used national standard - SJ285-77 permanent ferrite magnet standardChinese SJ/T0410-2000 Permanent Ferrite Manget StandardIn MMPA(0100-87) standardRing shape size(mm) D×d×HФ115×45×5~23 Ф200×86×5~27 Ф70×32×3~17 Ф115×43×5~23 Ф200×83×5~27 Ф70×30.5×3~17 Ф115×45×5~23 Ф200×86×5~27 Ф70×32×3~17 Ф115×57×5~23 Ф200×95×5~27 Ф70×56×3~17 Ф115×58.7×3~23Ф200×100×5~27 Ф70×40×3~17 (elliptical)Ф115×60×5~23 Ф200×110×5~27 Ф71×40×3~17 Ф115×67×5~23 Ф200×120×5~27 Ф71×30.5×3~17 Ф115×80×5~23 Ф206×88.9×5~30 Ф71×32×3~17 Ф121×45×5~24 Ф206×89×5~30 Ф72×30.5×3~16 Ф121×57×5~24 Ф206×118×5~30 Ф72×32×3~16 Ф121×60×5~24 Ф210×86×5~30 Ф72×38×3~16 Ф121×65×5~24 Ф210×118×5~30 Ф72×40×3~16NdFeBKnown as third generation of Rare Earth magnets, Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnets are the most powerful and advanced commercialized permanent magnet today. Since they are made from Neodymium, one of the most plentiful rare earth elements, and inexpensive iron, NdFeB magnets offer the best value in cost and performance.NdFeB magnets are available in both sintered and bonded forms. Sintered NdFeB offers the highest magnetic properties (28 MGOe to 50 MGOe) while Bonded NdFeB offers lower energy properties. Although bonded magnets do not possess magnetic properties as advanced as those of sintered magnets, they can be made in shapes and sizes that are difficult to achieve with sintering.A variety of coatings can be applied to the magnets' surface to overcome the principle drawback of neodymium-based magnets, their tendency to corrode easily.Grade Max. EnergyProductRemanence Coercive Force Rev. Temp.Coeff.CurieTemp.WorkingTemp. (BH)max B r H c H ci B d H d T c T w MGOe kJ/m3kG mT kOe kA/m kOe kA/m%/°C%/°C°C°CN3331-33247-26311.30-11.701130-1170>10.5>836>12>955-0.12-0.6031080 N3533-36263-28711.70-12.101170-1210>10.9>868>12>955-0.12-0.60310801.Licensed Products by SSMC-MQ - ISO 9002 Quality Standard Certified2.The above-mentioned data of magnetic parameters and physical properties are given at room temperature.3.The maximum service temperature of magnet is changeable due to the ratio length and diameter and enviromental factors.4.Special properties can be achieved with custom method.Physical and Mechanical PropertiesMax Working Temperature。
永磁铁氧体牌号及性能

永磁铁氧体牌号及性能烧结永磁铁氧体材料的主要性能牌号Grade剩磁(Br) 磁感矫顽力(HcB) 内禀矫顽力(HcJ)最大磁能积(BH)max mT KGauss KA/m KOe KA/m KOe KJ/m3 MGOeY8T 200~235 2.0~2.35 125-160 1.57-2.01 210-280 2.64-3.51 6.5-9.5 0.8-1.2Y22H 310~360 3.10~3.60 220-250 2.76-3.14 280-320 3.51-4.02 20.0-24.0 2.5-3.0Y25 360~400 3.60~4.00 135-170 1.70-2.14 140-200 1.76-2.51 22.5-28.0 2.8-3.5Y26H-1 360~390 3.60~3.90 200-250 2.51-3.14 225-255 2.83-3.20 23.0-28.0 2.9-3.5Y26H-2 360~380 3.60~3.80 263-288 3.30-3.62 318-350 3.99-4.40 24.0-28.0 3.0-3.5Y27H 350~380 3.50~3.80 225-240 2.83-3.01 235-260 2.95-3.27 25.0-29.0 3.1-3.6Y28 370~400 3.70~4.00 175-210 2.20-3.64 180-220 2.26-2.76 26.0-30.0 3.3-3.8Y28H-1 380~400 3.80~4.00 240-260 3.01-3.27 250-280 3.14-3.52 27.0-30.0 3.4-3.8Y28H-2 360~380 3.60~3.80 271-295 3.40-3.70 382-405 4.80-5.08 26.0-30.0 3.3-3.8Y30H-1 380~400 3.80~4.00 230-275 2.89-3.46 235-290 2.95-3.64 27.0-32.5 3.4-4.1Y30H-2 395~415 3.95~4.15 275-300 3.45-3.77 310-335 3.89-4.20 27.0-32.0 3.4-4.0Y32 400~420 4.00~4.20 160-190 2.01-2.39 165-195 2.07-2.45 30.0-33.5 3.8-4.2Y32H-1 400~420 4.00~4.20 190-230 2.39-2.89 230-250 2.89-3.14 31.5-35.0 3.9-4.4Y32H-2 400~440 4.00~4.40 224-240 2.81-3.01 230-250 2.89-3.14 31.0-34.0 3.9-4.3Y33 410~430 4.10~4.30 220-250 2.76-3.14 225-255 2.83-3.20 31.5-35.0 3.9-4.4Y33H 410~430 4.10~4.30 250-270 3.14-3.39 250-275 3.14-3.45 31.5-35.0 3.9-4.4Y34 420~440 4.20~4.40 200-230 2.51-2.89 205-235 2.57-2.95 32.5-36.0 4.1-4.4Y35 430~450 4.30~4.50 215-239 2.70-3.00 217-241 2.73-3.03 33.1-38.2 4.1-4.8Y36 430~450 4.30~4.50 247-271 3.10-3.40 250-274 3.14-3.44 35.1-38.3 4.4-4.8Y38 440~460 4.40~4.60 285-305 3.58-3.83 294-310 3.69-3.89 36.6-40.6 4.6-5.1Y40 440~460 4.40~4.60 330-354 4.15-4.45 340-360 4.27-4.52 37.6-41.8 4.7-5.2 特点:* 采用粉末冶金方法生产、剩磁较低,回复磁导磁率小。
铁氧体材料特性及不同规格有效参数

i 铁氧体材料特性及不同规格有效参数10.3.1 国产铁氧体材料特性铁氧体的电阻率大约在106~1012μΩ·cm ,适用于几千到几百兆Hz 的频率之间。
对铁氧体软磁材料的主要要求是:初始磁导率μ 高,比损耗(单位体积或重量)小,磁导率随温度的变化要小等。
锰锌和镍锌铁氧体是常用的材料。
可用来制作滤波电感,高频功率变压器,谐振电感等。
铁氧体材料最高工作频率主要受损耗限制。
在一定的允许损耗下,频率提高,工作磁通密度相应减少,与提高频率来减少磁芯体积相矛盾。
一般建议的磁通密度是在工作频率下权衡损耗、体积、结构和效率的结果,不是绝对的。
例如PHILIPS 建议变压器磁芯:<100kHz 可用3C81、3C90、3C91、3C94 和3C96 等;<400kHz 可用3C90、3C94 和3C96 等;200kHz ~1MHz 可用3F3、3F4 和3F35;1~3MHz 可用3F4 和4F1;>3MHz 可用4F1 等。
电感磁芯:<500kHz 可用2P…、3C30 和3C90;<1MHz 可用3C90、3F3 和3F35 等等。
国产常用的牌号及主要磁性能见表10-7所示。
10.3.2 铁氧体尺寸规格铁氧体磁芯在通讯和开关电源中应用十分广泛,磁芯外形结构多种多样。
开关电源中主要应用的有E 型,ETD 型,EC 型,RM 型,PQ 型,EFD 型,EI 型,EFD 型,环形,LP 型.在模块电源中,主要应用扁平磁芯和集成磁元件。
例如FERROXCUBE-PHILIPS 的平面E 型磁芯,适于表面贴装的EP 、EQ 和ER 磁芯,以及集成电感元件(IIC -Integrated inductance component )等。
IIC 已将元件和磁芯合成一体,通过外部PCB 可自由组成电感和变压器。
各种磁芯结构往往是针对特定的应用设计的,有各自的优点和缺点,要根据应用场合,选择相应的磁芯结构。
磁芯材质对照表
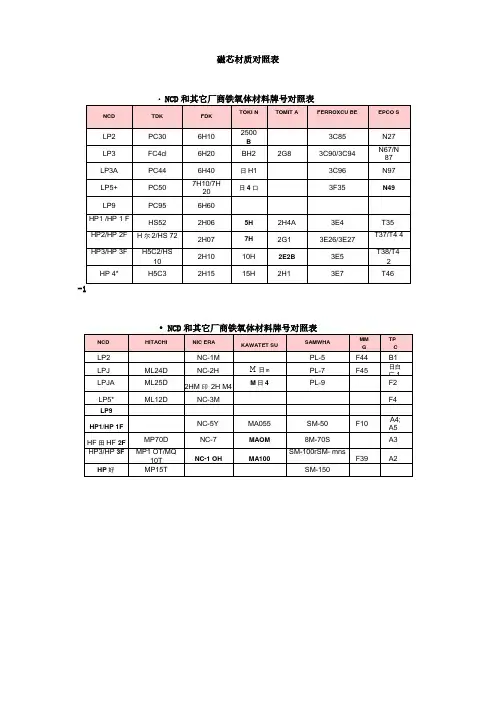
磁芯材质对照表・NCD和其它厂商铁氧体材料牌号对照表• NCD和其它厂商铁氧体材料牌号对照表・NCD和其它厂商铁氧体材料牌号对照表-3材料总览功率铁氧体材料LP2・导磁率Vs.频率特性・功率损耗Vs.温度特性FrequcmytkHEj功率铁氧体材料LP3特性 符号 单位LP3Characteristics SymbolUnit初始磁导率 Initial permeability □ i -2300±25% 相对损耗因数Relative loss factor tan6/uiX10-6 <4饱和磁通密度 Bs mT25℃ 500 Saturation flux density 1194A/m100℃ 390 剩磁 Remanence Br mT 130 矫顽力 Coercivity Hc A/m 13idDnnTJDtJ(teiiT12D・功率损耗Vs.频率特性'—I100mTSOmTLP2 1DOT二・导磁率Vs.温度特性・导磁率Vs.频率特性10・功率损耗Vs.温度特性1m・功率损耗Vs.频率特性F叫厕期1^|相对损耗因数Relative loss factor tan6/ui X10-6<3饱和磁通密度BsmT 25℃490Saturation flux density1194A/m100℃380剩磁 Remanence Br mT110矫顽力 Coercivity Hc A/m10功率损耗Pc kW/m325℃Power loss80℃60 (f=25kHz,B=200mT)100℃50功率损耗Pc kW/m325℃600Power loss80℃400 (f=100kHz,B=200mT)100℃350居里温度 Curie temperature Tc℃三200密度 Density d kg/m3X103 4.8・导磁率Vs.频率特性Ui Vs. Frequency・功率损耗Vs.温度特性1G-1t f10Frequency kHz)・功率损耗Vs.频率特性・高磁导率铁氧体材料・导磁率Vs.温度特性“峥1a•阻抗Vs.频率特性EE磁芯价格:¥面议Al:1kHz,0.5mA,100TsPc:100kHz,200mT,100°C100kHz,100mT,100°C(*)。
永磁铁氧体牌号及性能
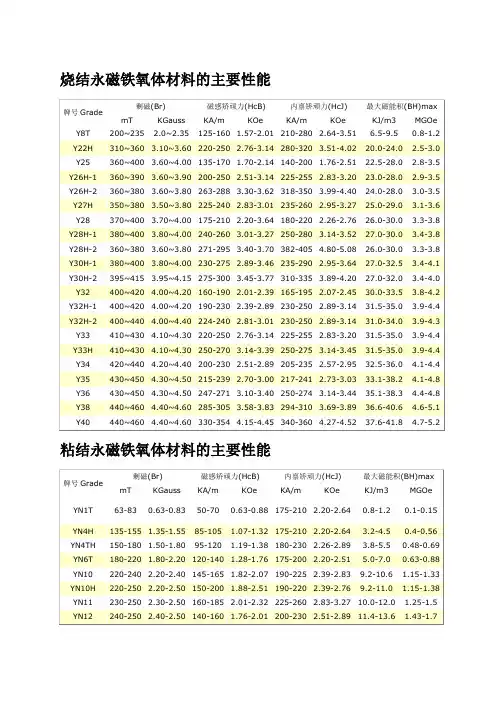
烧结永磁铁氧体材料的主要性能牌号Grade剩磁(Br) 磁感矫顽力(HcB) 内禀矫顽力(HcJ) 最大磁能积(BH)max mT KGauss KA/m KOe KA/m KOe KJ/m3 MGOeY8T 200~235 2.0~2.35 125-160 1.57-2.01 210-280 2.64-3.51 6.5-9.5 0.8-1.2 Y22H 310~360 3.10~3.60 220-250 2.76-3.14 280-320 3.51-4.02 20.0-24.0 2.5-3.0 Y25 360~400 3.60~4.00 135-170 1.70-2.14 140-200 1.76-2.51 22.5-28.0 2.8-3.5 Y26H-1 360~390 3.60~3.90 200-250 2.51-3.14 225-255 2.83-3.20 23.0-28.0 2.9-3.5 Y26H-2 360~380 3.60~3.80 263-288 3.30-3.62 318-350 3.99-4.40 24.0-28.0 3.0-3.5 Y27H 350~380 3.50~3.80 225-240 2.83-3.01 235-260 2.95-3.27 25.0-29.0 3.1-3.6 Y28 370~400 3.70~4.00 175-210 2.20-3.64 180-220 2.26-2.76 26.0-30.0 3.3-3.8 Y28H-1 380~400 3.80~4.00 240-260 3.01-3.27 250-280 3.14-3.52 27.0-30.0 3.4-3.8 Y28H-2 360~380 3.60~3.80 271-295 3.40-3.70 382-405 4.80-5.08 26.0-30.0 3.3-3.8 Y30H-1 380~400 3.80~4.00 230-275 2.89-3.46 235-290 2.95-3.64 27.0-32.5 3.4-4.1 Y30H-2 395~415 3.95~4.15 275-300 3.45-3.77 310-335 3.89-4.20 27.0-32.0 3.4-4.0 Y32 400~420 4.00~4.20 160-190 2.01-2.39 165-195 2.07-2.45 30.0-33.5 3.8-4.2 Y32H-1 400~420 4.00~4.20 190-230 2.39-2.89 230-250 2.89-3.14 31.5-35.0 3.9-4.4 Y32H-2 400~440 4.00~4.40 224-240 2.81-3.01 230-250 2.89-3.14 31.0-34.0 3.9-4.3 Y33 410~430 4.10~4.30 220-250 2.76-3.14 225-255 2.83-3.20 31.5-35.0 3.9-4.4 Y33H 410~430 4.10~4.30 250-270 3.14-3.39 250-275 3.14-3.45 31.5-35.0 3.9-4.4 Y34 420~440 4.20~4.40 200-230 2.51-2.89 205-235 2.57-2.95 32.5-36.0 4.1-4.4 Y35 430~450 4.30~4.50 215-239 2.70-3.00 217-241 2.73-3.03 33.1-38.2 4.1-4.8 Y36 430~450 4.30~4.50 247-271 3.10-3.40 250-274 3.14-3.44 35.1-38.3 4.4-4.8 Y38 440~460 4.40~4.60 285-305 3.58-3.83 294-310 3.69-3.89 36.6-40.6 4.6-5.1 Y40 440~460 4.40~4.60 330-354 4.15-4.45 340-360 4.27-4.52 37.6-41.8 4.7-5.2粘结永磁铁氧体材料的主要性能特点:* 采用粉末冶金方法生产、剩磁较低,回复磁导磁率小。
铁氧体参数及国内外牌号对照表

HARD FERRITE MAGNETSHard ferrite (ceramic) magnets were developed in the 1960's as a low cost alternative to metallic magnets. Even though they exhibit low energy (compared with other permanent magnet materials) and are relatively brittle and hard, ferrite magnets have won wide acceptance due to their good resistance to demagnetization, excellent corrosion resistance and low price per pound. In fact, measured by weight, ferrite represents more than 75 percent of the world magnet consumption. It is the first choice for most types of DC motors, magnetic separators, magnetic resonance imaging and automotive sensors.Ferrite Magnets characteristicsMostly Used national standard - SJ285-77 permanent ferrite magnet standardChinese SJ/T0410-2000 Permanent Ferrite Manget StandardIn MMPA(0100-87) standardRing shape size(mm) D×d×HФ115×45×5~23 Ф200×86×5~27 Ф70×32×3~17 Ф115×43×5~23 Ф200×83×5~27 Ф70×30.5×3~17 Ф115×45×5~23 Ф200×86×5~27 Ф70×32×3~17 Ф115×57×5~23 Ф200×95×5~27 Ф70×56×3~17 Ф115×58.7×3~23Ф200×100×5~27 Ф70×40×3~17 (elliptical)Ф115×60×5~23 Ф200×110×5~27 Ф71×40×3~17 Ф115×67×5~23 Ф200×120×5~27 Ф71×30.5×3~17 Ф115×80×5~23 Ф206×88.9×5~30 Ф71×32×3~17 Ф121×45×5~24 Ф206×89×5~30 Ф72×30.5×3~16 Ф121×57×5~24 Ф206×118×5~30 Ф72×32×3~16 Ф121×60×5~24 Ф210×86×5~30 Ф72×38×3~16 Ф121×65×5~24 Ф210×118×5~30 Ф72×40×3~16NdFeBKnown as third generation of Rare Earth magnets, Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnets are the most powerful and advanced commercialized permanent magnet today. Since they are made from Neodymium, one of the most plentiful rare earth elements, and inexpensive iron, NdFeB magnets offer the best value in cost and performance.NdFeB magnets are available in both sintered and bonded forms. Sintered NdFeB offers the highest magnetic properties (28 MGOe to 50 MGOe) while Bonded NdFeB offers lower energy properties. Although bonded magnets do not possess magnetic properties as advanced as those of sintered magnets, they can be made in shapes and sizes that are difficult to achieve with sintering.A variety of coatings can be applied to the magnets' surface to overcome the principle drawback of neodymium-based magnets, their tendency to corrode easily.Grade Max. EnergyProductRemanence Coercive Force Rev. Temp.Coeff.CurieTemp.WorkingTemp. (BH)max B r H c H ci B d H d T c T w MGOe kJ/m3kG mT kOe kA/m kOe kA/m%/°C%/°C°C°CN3331-33247-26311.30-11.701130-1170>10.5>836>12>955-0.12-0.6031080 N3533-36263-28711.70-12.101170-1210>10.9>868>12>955-0.12-0.60310801.Licensed Products by SSMC-MQ - ISO 9002 Quality Standard Certified2.The above-mentioned data of magnetic parameters and physical properties are given at room temperature.3.The maximum service temperature of magnet is changeable due to the ratio length and diameter and enviromental factors.4.Special properties can be achieved with custom method.Physical and Mechanical PropertiesMax Working Temperature。
软磁材料性能
上式说明:
a 工作频率f越大, Pth 越大
C、 μi –f特性
意义:
材料的磁导率随使用频率的变化关系即为μi –f特性,当μi 降低 时的频率为截止频
率 μi –f特性与使用的关系:
1
截止频率以上材料的μi值急剧下降,使材料的电感值急剧下降,会造成产品失效不能2 使
用。所谓宽频即为截止频率高。
影响μi –f特性的因素:
材料的制造工艺
材料的晶粒尺寸越小截止频率越高
3、我公司高导铁氧体材料的特性 命名方法 R 10K 磁导率大小 软磁
材料 名称 R4K R5K R7K R10K R12K R15K
μi
4300±25%
5000±25%
7000±25%
10000±30 % 12000±30 % 15000±30 %
tanδ/μi (×10-6)
<10
αμr ( ×106℃) (20—60℃)
μi高
1、功率铁氧体材料
主要用于高频小型化开关电源、电视机显示器的回扫变压器等。
①发展过程
70年代第一代
中国2KD TDK H35 PHILIPS 3C85 适于20KHZ
80年代初第二代 (DMR30)2KBD TDK PC30 EPCOS N27 适于100K以下
80年代后期第三代 (DMR40)2KB1 TDK PC40 PHILIPS 3C90 适于250K以下
