光合作用 (英文)
光合作用化学方程式及其场所

光合作用化学方程式及其场所英文回答:Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds. The overall chemical equation for photosynthesis is:6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2。
This equation shows that six molecules of carbon dioxide, six molecules of water, and light energy are used to produce one molecule of glucose (C6H12O6) and six molecules of oxygen (O2).Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, while the Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts.The light-dependent reactions use light energy to produce ATP and NADPH. ATP and NADPH are energy-carrier molecules that are used in the Calvin cycle to drive the synthesis of glucose. The light-dependent reactions also produce oxygen as a byproduct.The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. The Calvin cycle is a cyclic process that occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts.Photosynthesis is an essential process for life on Earth. It provides food for plants, animals, and other organisms. Photosynthesis also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is necessary for respiration.中文回答:光合作用是植物和其他生物利用阳光将二氧化碳和水转化为氧气和富含能量的有机化合物的一个过程。
初二年级学生如何在日常生活中运用英文单词

初二年级学生如何在日常生活中运用英文单词在初二年级学生的日常生活中,英文单词的运用是一项至关重要的技能。
正如一位贴心的导师,我将带领你们探索如何在各种情境中使用这些单词,从而提升你们的语言能力和交流技能。
首先,让我们来到学校的校园。
在这里,英文单词无处不在。
当你走进教室,你会看到门上贴着标签,上面写着“Classroom”和“Teacher's Desk”。
在黑板上,老师可能会写上“Mathematics”或者“Science”。
这些词汇不仅帮助你理解周围的环境,还能够让你更好地参与到课堂活动中去。
在课堂上,老师会用英文来解释新的概念和知识点。
比如,当老师讲解“Photosynthesis”(光合作用)时,理解这个单词可以帮助你更深入地了解植物如何生长。
而当你需要在小组讨论中表达你的观点时,“I agree”(我同意)或者“I disagree”(我不同意)等简单的表达方式会让你的思想更加清晰地传达给其他同学。
此外,在日常生活中,英文单词也贯穿着我们的社交互动。
在学校的午餐时间,你可能会在餐厅看到标有“Menu”(菜单)的牌子。
当你想要点一份“Sandwich”(三明治)或者“Salad”(沙拉)时,正确地使用这些单词可以确保你得到想要的食物。
而在体育课上,当你和队友一起玩篮球或者足球时,“Pass”(传球)、“Shoot”(射门)等指令不仅能够帮助你们更好地协作,还能增强你们之间的沟通和理解能力。
总的来说,学会在日常生活中运用英文单词不仅是提升语言能力的一种方式,更是一种融入国际社会的重要技能。
通过熟练掌握这些单词,你们可以更自信地与世界各地的人们交流和互动,拓展自己的视野和理解力。
因此,让我们一起努力,每天都充满着对新单词的好奇和学习,使英语学习成为你们生活的一部分,为未来的学习和职业生涯奠定坚实的基础。
生物学专业英语常用词汇

~SINICOO BIO WORDS~1, lipid ['lipid, 'laipid]n. 油脂;脂质2, photosynthetic [,fəutəsin'θetik]adj. 光合的;光合作用的3, enzyme ['enzaim]n. 酶4, extracellular [,ekstrə'seljulə]adj. [生](位于或发生于)细胞外的(副词extracellularly) 5, cytosol ['saitəsɔl]n. [生]胞液,细胞溶质6, detergent [di'tə:dʒənt]n. 清洁剂;去垢剂7, myristic [mi'ristik, mai-]adj. 肉豆蔻的8, myristic acid肉豆蔻酸;十四酸9, fluorescence [fluə'resns]n. 荧光;荧光性fluorescence: 荧光|萤光|光度Inherent fluorescence: 固有荧光delayed fluorescence: 延迟荧光|迟滞荧光|迟延荧光10, raftsn. 救生艇(raft的复数形式);皮筏;竹排v. 乘筏;划筏(raft的三单形式)Rafts: 皮筏|木筏Life Rafts: 救生艇Lipid Rafts: 脂筏|脂质筏|脂质浮排11, numerical [nju:'merikəl]adj. 数字的;数值的;用数字表示的(等于numeric)12, trypsin ['tripsin]n. [生化]胰蛋白酶;胰岛素Trypsin: 胰蛋白酶|胰朊酶|胰蛋白insulin trypsin: 胰岛素Trypsin Crystallized: 释义:结晶胰蛋白酶[蛋白水解酶13, celiac disease[医]乳糜泻;脂泻病Celiac Disease: 乳糜泻|严重慢性腹泻症|麸质过敏症adult celiac disease: 释义:成人腹腔疾病|成人腹腔疾病 refractory celiac disease: 难治性乳糜泻14, yeast [ji:st]n. 酵母;酵母片;泡沫;引起骚动因素15, detect [di'tekt]vt. 发现;察觉;探测16, halt [hɔ:lt]vi. 停止;踌躇,犹豫;立定n. 停止;立定;休息vt. 使停止;使立定17, convert [kən'və:t]vt. 使转变;转换…;使…改变信仰vi. 转变,变换;皈依;改变信仰n. 皈依者;改变宗教信仰者18, whereby [hwεə'bai]adv. 凭什么;靠那个19, amino [ə'mi:nəu]adj. 氨基的n. 氨基20, peptidesn. 多肽类;缩氨酸21, dissolved gas溶解气体22, dissolvedadj. 溶解的;溶化的v. 使溶解;使溶化(dissolve的过去分词) 23, sap [sæp]n. 树液;活力;坑道;精力,元气vt. 使衰竭,使伤元气;挖掘以破坏基础 vi. 挖坑道24, endocrine ['endəukrain, -krin]n. 激素;内分泌;内分泌物adj. 内分泌的;激素的25, pancreas ['pænkriəs]n. 胰腺26, gland [ɡlænd]n. [解]腺27, glucouseglucouse: 葡萄糖28, insulin ['insjulin, 'insə-]n. 胰岛素29, regulate ['reɡjuleit]vt. 调节,规定;有系统的管理;控制;校准 30, paracrine [,pærə'krain]n. 旁分泌;副分泌;旁泌性31, diffuse [di'fju:s]adj. 散开的;弥漫的vt. 传播;扩散;漫射vi. 传播;四散32, mediator ['mi:dieitə]n. 调停者;传递者;中介物33, autocrine [ɔ:təukrain]n. 自分泌,自泌34, proliferation [prəu-,lifə'reiʃən]n. [生]增殖,扩散;分芽繁殖35, neuronaladj. 神经元的36, axon ['æksɔn,-səun]n. 轴索,轴突(神经细胞)37, synapse ['sainæps, 'si-, si'næps]n. 突触38, spinal ['spainəl]adj. 脊骨的;脊髓的;脊柱的;尖刺的;针的n. 脊椎麻醉39, cord [kɔ:d]n. 束缚;绳索vt. 用绳子捆绑40, toe [təu]n. 脚趾;足尖vt. 用脚尖走;以趾踏触vi. 动脚尖;用足尖跳舞41, neurotransmitter [,njuərəutrænz'mitə, -træns-] n. [生]神经递质;神经传递素42, intimate ['intimət]adj. 亲密的;私人的;精通的;[婉]有性关系的n. 至交;知己vt. 暗示;通知;宣布43, lodge [lɔdʒ]n. 旅馆;门房;集会处;山林小屋vt. 提出;寄存;借住;嵌入vi. 寄宿;临时住宿44, plasma membrane质膜;浆膜(等于cell membrane)45, embryonic [,embri'ɔnik]adj. 胚胎的;似胚胎的46, adjacent [ə'dʒeisənt]adj. 邻近的,毗连的47, akin [ə'kin]adj. 同族的;同类的;类似的48, epithelial [,epi'θi:liəl]adj. [生]上皮的;皮膜的49, bind [baind]vi. 结合;装订;有约束力;过紧vt. 绑;约束;装订;包扎;凝固n. 捆绑;困境;讨厌的事情;植物的藤蔓50, mediate ['mi:dieit]vi. 调解;斡旋;居中vt. 调停;传达adj. 间接的;居间的51, fatty acid[化]脂肪酸52, disorder [dis'ɔ:də]n. 混乱;骚乱vt. 扰乱;使失调53, kinase ['kaineiz, 'ki-]n. 激酶;致活酶Kinase: 激酶|激酶??|致活酶thymidine kinase: 胸腺嘧啶核苷漱酶|胸苷激酶|胸[腺嘧啶脱氧核]苷激酶 Glucose kinase: 葡萄糖激酶54, trimeric [trai'merik]adj. 三聚物的55, circuit ['sə:kit]n. 电路,回路;环道;一圈;巡回vi. 环行vt. 绕回…环行56, ligand ['liɡənd, 'lai-]n. [化]配合基(向心配合价体)57, physiology [,fizi'ɔlədʒi]n. 生理学;生理机能58, hijacking ['haidʒækiŋ]n. 劫持(hijack的现在分词)59, cholera ['kɔlərə]n. [医]霍乱60, ion ['aiən]n. 离子ion: 离子|智能光网络|翼扬ion plating: 离子电镀|离子镀|离子镀敷descript ion: 品名61, stretch [[stretʃ]]n. 伸展,延伸adj. 可伸缩的vt. 伸展,张开vi. 伸展stretch: 伸展|拉伸|缩放reel stretch: 卷圆压平|卷...stretch receptor: 牵张感受器|伸展感受器|(肌肉的)牵张感受器62, hypertonic [,haipə'tɔnik]adj. [化]高渗的;[医]张力亢进的hypertonic: 张力亢进的|高渗的|高张的,高渗的Hypertonic incoordinate: 高张性、不协调和延长的子宫收缩hypertonic gallbladder: 胆囊张力过强63, hypotonic [,haipəu'tɔnik]adj. [医]低渗的;张力减退的hypotonic: 低张的|低渗的|低渗hypotonic hypoxia: 低张性缺氧hypotonic duodenography: 低张力十二指肠造影术|低张十二指肠造影64, isotonic [,aisəu'tɔnik]adj. 等张的,等压的isotonic: 等渗的|等张的,等渗的|等分的isotonic contraction: 等张力性收缩|等张收缩: 张力维持不变而使肌肉缩短或加长的肌肉收缩。
光合作用过程英文作文初一

光合作用过程英文作文初一对于光合作用这个过程,我觉得非常有趣和重要。
光合作用是植物利用太阳能将二氧化碳和水转化为能量的过程。
这个过程发生在叶绿体内,利用叶绿素这种绿色色素来吸收光能。
这个过程对于地球上的生物来说至关重要,因为它提供了氧气和能量。
英文:When it comes to the process of photosynthesis, I findit very interesting and important. Photosynthesis is the process where plants use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into energy. This process takes place within the chloroplasts, using chlorophyll, a green pigment, to absorb light energy. It is crucial for living organisms on Earth as it provides oxygen and energy.中文:光合作用是植物利用太阳能将二氧化碳和水转化为能量的过程。
这个过程发生在叶绿体内,利用叶绿素这种绿色色素来吸收光能。
这个过程对于地球上的生物来说至关重要,因为它提供了氧气和能量。
As a matter of fact, photosynthesis is the foundationof the food chain. Let me give you an example. When a cow eats grass, it is actually consuming the energy that the grass obtained through photosynthesis. And when we eat beef, we are indirectly benefiting from the process of photosynthesis. It's amazing how everything is interconnected in nature.英文:事实上,光合作用是食物链的基础。
新东方200个一定要学的英文词根词缀photo

新东方200个一定要学的英文词根词缀photo■词根考古学词根photo来自拉丁语,意为light,表示“光的,光电的”。
■单词拆拆看photograph = photo + graph释[ˈfoʊtəɡræf] v. 拍照n. 照片解photo表示“光”,graph表示“书写”,用光写,即“拍照”。
例He wants to take some photographs of the beautiful scene. 他想给这美丽的景色拍一些照片。
photosynthesis = photo + syn + thes释[ˌfoʊtoʊˈsɪnθəsɪs] n. 光合作用解photo表示“光”,syn-表示“一起”,thes表示“放置”,把光放在一起,即“光合作用”。
例Sunlight is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis. 植物吸收太阳光进行光合作用。
photon = phot + on释[ˈfoʊtɑːn] n. [物] 光子解phot表示“光”,-on表示“…的物”,光的东西,即“光子”。
例When a photon collides with a molecule, several things can happen. 当光子与分子碰撞时,会有几种情况发生。
■词汇拓展营photography [fəˈtɑːɡrəfi ] n. 摄影phototropism [ˌfoʊtoʊˈtroʊpɪzəm] n. [生物]向光性photographer [fəˈtɑːɡrəfər] n. 摄影师photographic [ˌfoʊtəˈɡræfɪk] a. 摄影的;逼真的■词缀一家亲1. syn-(一起)synthesis n. 综合,合成;综合体2. -on (…的物)electron n. 电子。
生物学 生命科学概论中英文对照专有名词
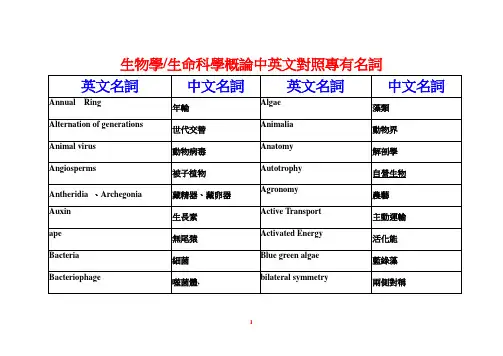
Eukarytic Cell
真核細胞
Ethylene
乙烯
Family
科名
Fern
蕨類
Fibrous root
鬚根
Ecology
生態學
Fermentation
發酵
Food Sciences
食品科學
Forestry
森林
Fungi
真菌界
Gibberellin
激勃素
Germination
萌芽
Gametophyte
周鞘
Physiological unit
生理單位
Primary Roots
主根
Protective Tissue
保護組織
Prokaryotes
原核生物
Phylum Porifera
海綿動物門
PhylumCnidaria
腔腸動物門
PhylumPlatyhelminthes
扁形動物門
Phylumannelids
植物學、動物學、微生物學、微生物學、細胞學生理學、遺傳學、生物化學、生物物理學、分子生物學、分子生物學、解剖學、免疫學、生統、分類學、生態學
DNA=DeoxyribonucleicAcid(double helix)
去氧核糖核酸
(雙螺旋狀)
Amino acid
氨基酸
Adenosine(A)、Thymine,(T)、(A=T)
環節動物門
PhylumArthropoda
節肢動物門
PhylumEchinodermata
棘皮動物門
PhylumAmphibia、Reptilia、
Aves、Mammalia
兩棲動物門、爬蟲類、鳥類、哺乳類動物門
关于光合作用的功能英文作文
关于光合作用的功能英文作文Photosynthesis is a vital biological process that occurs in plants, algae, and some species of bacteria. It is the means by which these organisms convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organism's activities. This essay will explore the functions of photosynthesis, its importance to life on Earth, and the process itself.Firstly, photosynthesis plays a critical role in the global carbon cycle. It is the primary process through which carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, is removed from the atmosphere and converted into organic compounds. This not only helps to mitigate climate change but also sustains the oxygen levels in the atmosphere, which are essential for the survival of aerobic organisms, including humans.Secondly, the process of photosynthesis is fundamental to the food chain. The organic compounds produced by photosynthetic organisms, such as glucose, are used as an energy source by these organisms themselves and by othersthat consume them. This makes photosynthesis the basis of energy transfer throughout ecosystems, supporting life from the smallest bacteria to the largest mammals.The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle. Duringthe light-dependent reactions, which occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts, light energy is captured by chlorophyll and other pigments. This energy is used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are energy-rich molecules.The ATP and NADPH produced are then used in the Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. Here, carbon dioxide is fixed into an organic molecule through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, ultimately producing glucose and other sugars that can be used by the plant for growth and energy.In addition to its ecological and physiological importance, photosynthesis has also been a subject of scientific fascination due to its efficiency and thepotential for harnessing its mechanisms in renewable energy technologies. Researchers are exploring ways to mimic photosynthesis to create sustainable fuels and increase crop yields to address food security challenges.In conclusion, photosynthesis is a complex and essential process that underpins life on Earth. It is responsible for the production of oxygen, the foundation of the food chain, and the sequestration of carbon dioxide. Understanding the functions of photosynthesis not only deepens our appreciation for the natural world but also opens up possibilities for innovative solutions to global challenges.。
关于光合作用的功能英文作文
关于光合作用的功能英文作文The Importance of Photosynthesis.Photosynthesis is a vital process that occurs in plants, algae, and certain bacteria, allowing them to convert light energy into chemical energy. This process is essential for life on Earth as it produces oxygen and glucose, which are necessary for the survival of both plants and animals. In this article, we will explore the function and importanceof photosynthesis in detail.The process of photosynthesis begins with theabsorption of light energy by a green pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is found in the chloroplasts of plant cells, which are specialized organelles responsiblefor photosynthesis. When chlorophyll absorbs light, it becomes excited and releases electrons. These electrons are then passed through a series of electron transport chains, ultimately resulting in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotidephosphate (NADPH).ATP is a high-energy molecule that is used by cells for various metabolic processes, including the synthesis of proteins and carbohydrates. NADPH, on the other hand, is used in the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide and water. This process, known as the Calvin cycle, occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast and involves the fixation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules.The production of oxygen is another crucial aspect of photosynthesis. During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, water is split into oxygen, electrons, and protons. The oxygen is then released into the atmosphere, while the electrons and protons are used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP and NADPH.The importance of photosynthesis cannot be overstated. Firstly, it is the primary source of oxygen for the atmosphere, which is essential for animal respiration. Without photosynthesis, there would be no oxygen for animals to breathe, and life on Earth would not exist as itdoes today.Secondly, photosynthesis is the basis of the food chain. Plants and algae produce glucose during photosynthesis, which is then used by herbivores as a source of energy. These herbivores, in turn, are eaten by carnivores, and so on, creating a complex web of interdependencies known asthe food chain. Without photosynthesis, this food chain would collapse, and the survival of many species would be jeopardized.In addition to its role in oxygen production and food production, photosynthesis also plays a crucial role in climate regulation. Plants and algae absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, which helps to reduce the concentration of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. Without this carbon dioxide absorption, the Earth's climate would be significantly warmer, leading to extreme weather events and changes in ecosystems.Finally, photosynthesis also has applications in biotechnology and renewable energy production. Biofuelssuch as bioethanol and biodiesel can be produced from plants that have been genetically engineered to have improved photosynthetic efficiency. Additionally, photosynthetic bacteria can be used in biophotovoltaics, a type of solar cell that converts light into electricity using photosynthetic pigments.In conclusion, photosynthesis is a remarkable process that is essential for life on Earth. It produces oxygen, glucose, and other organic molecules that are crucial for the survival of both plants and animals. It also plays a key role in climate regulation and has applications in biotechnology and renewable energy production. As we continue to explore the wonders of photosynthesis, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of all life on our planet.。
酿酒有关的化学过程中英文翻译对照
酿酒有关的化学过程中英文翻译对照Transpiration:蒸腾作用Evaporation:蒸发Photosynthesis:光合作用Maillard Reaction :麦拉德反应Veraison:转色期Thermovinification:热浸渍酿造法Malolactic fermentation(MLF) :苹果酸-乳酸发酵Malo-Alcohol Fermentation(MAF):苹果酸-酒精发酵Methode Charantaise:夏朗德壶式蒸馏法Maceration Carbonique :CO2浸渍发酵Whole bunch fermentation :CO2浸渍发酵Ageing:陈酿Sur lies:带酒脚陈酿Esterify:酯化Saccharify:糖化Liquefy:溶解、液化Bottle aging:瓶内陈酿Chaptalization:加糖Distillation:蒸馏Fractional Distillation:分馏Rectification:精馏Clarification:澄清Amelioration:原料改良Chaptalization:加糖Beaujolasis method:宝祖利酿造法Unareobic fermentation:厌氧发酵法Heterofermentation:异型发酵Malolactic fermentation(MLF) :苹果酸-乳酸发酵CO2浸渍发酵Transpiration:蒸腾作用Evaporation:蒸发Photosynthesis:光合作用Maillard Reaction :麦拉德反应Veraison:转色期Thermovinification:热浸渍酿造法Malolactic fermentation(MLF) :苹果酸-乳酸发酵Malo-Alcohol Fermentation(MAF):苹果酸-酒精发酵Methode Charantaise:夏朗德壶式蒸馏法Maceration Carbonique :CO2浸渍发酵Whole bunch fermentation :CO2浸渍发酵Whole bunch fermentation :CO2浸渍发酵Maillard Reaction :麦拉德反应Veraison:转色期Enzymatic browning:酶促褐变Acetification:酸败CO2浸渍发酵Beaujolasis method:宝祖利酿造法Unareobic fermentation:厌氧发酵法Heterofermentation:异型发酵Malolactic fermentation(MLF) :苹果酸-乳酸发酵CO2浸渍发酵Transpiration:蒸腾作用Evaporation:蒸发Photosynthesis:光合作用Maillard Reaction :麦拉德反应Veraison:转色期Thermovinification:热浸渍酿造法Malolactic fermentation(MLF) :苹果酸-乳酸发酵Malo-Alcohol Fermentation(MAF):苹果酸-酒精发酵Methode Charantaise:夏朗德壶式蒸馏法Maceration Carbonique :CO2浸渍发酵Whole bunch fermentation :CO2浸渍发酵Whole bunch fermentation :CO2浸渍发酵Maillard Reaction :麦拉德反应Veraison:转色期Enzymatic browning:酶促褐变Acetification:酸败CO2浸渍发酵Distillation:蒸馏Fractional Distillation:分馏Rectification:精馏Clarification:澄清。
光合作用
②区别:(见下表)
项目 光反应 暗反应
实质 光能→ 化学能,释放O2 同化CO2形成(CH2O)(酶促反应)
1.2 英文描述
Photosynthesis is the conversion of energy from the Sun to chemical energy (sugars) by green plants. The "fuel" for ecosystems is energy from the Sun. Sunlight is captured by green plants during photosynthesis and stored as chemical energy in carbohydrate molecules. The energy then passes through the ecosystem from species to species when herbivores eat plants and carnivores eat the herbivores. And these interactions form food chains.
4.1.4 细胞色素b6/f复合体(cyt b6/f complex)
可能以二聚体形成存在,每个单体含有四个不同的亚基。细胞色素b6(b563)、细胞色素f、铁硫蛋白、以及亚基Ⅳ(被认为是质体醌的结合蛋白)。
4.1.5 光系统Ⅰ(PSI)
能被波长700nm的光激发,又称P700。包含多条肽链,位于基粒与基质接触区和基质类囊体膜中。由集光复合体Ⅰ和作用中心构成。结合100个左右叶绿素分子、除了几个特殊的叶绿素为中心色素外外,其它叶绿素都是天线色素。三种电子载体分别为A0(一个chla分子)、A1(为维生素K1)及3个不同的4Fe-4S。
