(完整版)英语状语从句汇总整理版
状语从句(完整版)

While there is life there is hope. (while = __a_s_l_o_n_g_a_s_ )
状语时用来修饰 动 词, 形容 词, 副 词或 句子 的一种句子成分。它可以表示时间、地点、 原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较、方式等。 当充当状语的部分是一个句子时,也就是状语从
句。分类如下:
状语从句
1. 时间状语从句 2. 地点状语从句 3. 原因状语从句 4. 条件状语从句 5. 让步状语从句 6. 目的状语从句 7. 结果状语从句 8. 方式状语从句 9. 比较状语从句
I had no sooner begun to talk than he rang off. No sooner had I begun to talk than he rang off. 我还未来得及讲话,他就挂断了电话。
1. I was so familiar with him that I recognized his voice
考点:名词短语引导时间状语从句
• 1. When every time I was in trouble, he would come to help me.
• 2. At next time you come, do remember bring your son here.
• 3. For the first time I met the girl. I felt in love with her.
c.f. He might be ill, for he didn’t come to
英语语法:状语从句归纳整理
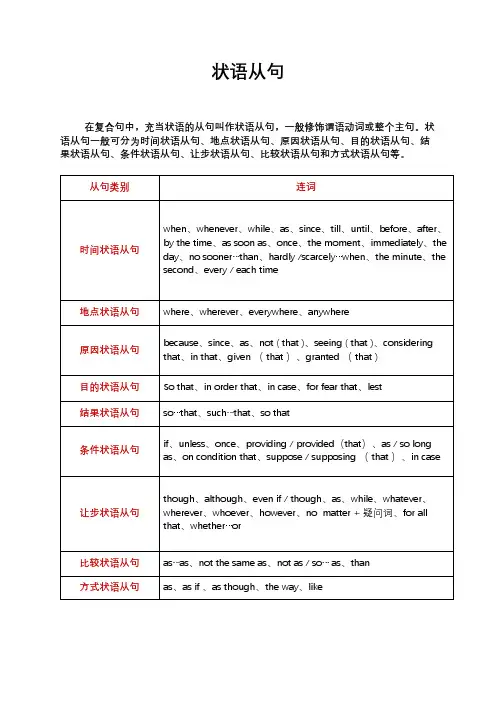
状语从句在复合句中,充当状语的从句叫作状语从句,一般修饰谓语动词或整个主句。
状语从句一般可分为时间状语从句、地点状语从句、原因状语从句、目的状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句、比较状语从句和方式状语从句等。
一、时间状语从句在复合句中起时间状语作用的从句称为时间状语从句,可放在句首、句中或句尾。
(二)until 和 till的用法1.肯定句:主句的谓语动词必须是延续性动词,主句、从句都为肯定式,意为“直到……为止”;2.否定句:主句的谓语动词必须是非延续性动词,从句为肯定式,表示“某动作直到某时才开始”;3.till 不可以置于句首,而until可以。
例:They waited till / until I returned.他们一直在等我回来。
You may stay here until / till the rain stops.你可以待在这里直到雨停。
He won’t go to bed until / till she returns.直到她回来,他才上床睡觉。
Until you told me I had no idea of it.直到你告诉我,我才知道这件事。
(三)since的用法(四)before的用法一般情况下before表示“在……之前”,有时根据上下文,还可表示“还未……就……” “不到……就……” “……才……” “趁……还未……”等例:Please write it down before you forget it.趁你还没忘,请把它记下来。
I must finish this letter before I go home.我必须在回家之前完成这封信。
Before I could get in a word, he had measured me.我还没来得及插话,他就给我量好了尺寸。
We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land.我们航行了四天四夜才看到陆地。
英语状语从句归纳总结

英语状语从句归纳总结英语状语从句是英语语法中的一个重要部分,它可以用来修饰句子中的主谓宾成分,提供更多的信息和细节。
在学习英语状语从句时,需要掌握从句的类型和用法,以下是一些常见的英语状语从句类型及其用法。
1. 时间状语从句时间状语从句用来表示某个动作发生的时间或顺序。
一些常用的时间状语从句包括:when, while, as, after, before, since, until 等。
例如:- When I was young, I used to play basketball with my friends.(当我年轻时,我曾经和我的朋友们一起打篮球。
)- While I was cooking dinner, the phone rang.(当我在做晚饭的时候,电话响了。
)- After I finish this project, I will take a break.(当我完成这个项目后,我会休息一下。
)2. 地点状语从句地点状语从句用来表示某个动作发生的地点。
一些常用的地点状语从句包括:where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere等。
例如:- She always knows where her keys are.(她总是知道她的钥匙在哪里。
)- Wherever he goes, he takes his laptop with him.(无论他去哪里,他都带着他的笔记本电脑。
)3. 原因状语从句原因状语从句用来表示某个动作发生的原因。
一些常用的原因状语从句包括:because, since, as, now that等。
例如:- Because it was raining, we decided to stay indoors.(因为下雨了,我们决定呆在室内。
)- Since you didn't like the movie, we can watch something else.(既然你不喜欢这部电影,我们可以看其他的。
状语从句归纳总结

状语从句归纳总结状语从句归纳总结:(as用法)一、时间状语从句:1、连接词when、while、as⑴when ①正当…时候be about to…ving…②从句动词先于或后于主语动作⑵while: 可表示对比(从句只用连续性动词)⑶as: “一边一边”“随着”省略句中: eg: As time goes on…随着时间的推移As a boy,hewao hopeless at English.2、before,afterbefore常用句型:It is/was/will be…beforeeg: It will be 5 years before we meet again.3、till,until①用于肯定句中“直到…为止”,主句谓语为持续性动词②用于否定句中“直到…才”,主句谓语为短暂性动词(until,till 可用before代替)③Not until位于句首倒装④强调句型只用until二、地点状语从句:where,wherever,everywhere也可引导定语从句:状语从句:We shall go where the condition are poor.定语从句:We shall go the place where the condition are poor.三、原因状语从句1、because\since\as⑴①用why提问②强调句中③关联词“not…but”④与“just”等副词连用eg:You shouldn’t any only because you had much.⑵since引导从句常放句首,往往表示对方已知的让步原因关系,主从时态一般相同⑶as从句放句首2、now(that) 既然3、considering that,seeing (that):与since,now that意相近: “鉴于…”“考虑到…”4、not that…,but that…“不是因为…而是因为…”四、目的状语从句1、that,so that,in order that“为了,以便”⑴从句中往往出现情态动词:can\could\may\might⑵当主从句的主语一致时,可转换为相应动词不定式结构:so as to\in order to2、in case,for fear that,lest“以防、以免、万一..”从句是肯定句五、结果状语从句1、so,that,so thatso that可以引导结果状语从句和目的状语从句,区别在于:目的状从中有情动(结果状从前有“,”号)2、so…thatsuch a\an +形+单名=so+形+a\an+单名“如此…以至于”3、such…thatsuch…that(状从)such…as(定从)4、such that (是这样…以致)六、条件状语从句:主句中用一般将来时,从句中用一般现在时或一般过去时1、if正面条件“如果”2、unless. 反面条件=if not 主句为否定意味,从句为肯定句(从句也可用否定结构)unless做介词“除非,如果不”3、so\as long as,on condition that “条件是…”“只要..”4、in case既可引导目的状,又可引导条件状=”if it happened that…”5、providing,provided that, suppsing,suppose (that),given (that) “如果,只要,假如”七、方式状语从句1、as,just as“如…”“正如…一样”Do just as you like2、as if, as though (虚拟语气)八、比较状语从句1、as…as,the same as. 否定句用not so\as…as,not the same as从句中常用省略句: eg:He runs as fast as he can.2、than3、the more…the more…“越…越…”4、more than九、让步状语从句1、although,though.句中不出现but,可出现still\yet(副词)though的位置较灵活,可倒装2、even if,even though“即使”even if表主观,时态往往用于将来even though通常表客观上的,往往表过去事实3、no matter wh…只用于让步状语从句wh..ever 让步状从/名词性从句4、as特殊倒状5、while,whereas突出对比6、if(=even if) 强调部分(n.\adj.\adv.\v.) +as+主+谓(可以是情动)。
(完整版)状语从句知识点大全

(完整版)状语从句知识点大全状语从句是一个句子做另一个句子的状语,用于描述、限制、补充或解释主句的动作或状态。
在英语语法中,状语从句非常常见且广泛应用。
以下是状语从句的一些常见知识点:1. 时间状语从句(Time Adverbial Clauses):用来表示时间,常用的引导词有when, while, as, before, after, until, since等。
例如:I will call you when I arrive home.翻译:我到家时会打电话给你。
2. 地点状语从句(Place Adverbial Clauses):用来表示地点,常用的引导词有where, wherever等。
例如:She can't find her keys anywhere.翻译:她无论到哪儿都找不到她的钥匙。
3. 原因状语从句(Cause Adverbial Clauses):用来表示原因,常用的引导词有because, since, as, for等。
例如:I didn't go to the party because I was tired.翻译:因为我累了,所以我没有去参加聚会。
4. 结果状语从句(Result Adverbial Clauses):用来表示结果,常用的引导词有so, therefore, thus等。
例如:He studied hard, so he passed the exam.翻译:他努力研究,所以他通过了考试。
5. 条件状语从句(Condition Adverbial Clauses):用来表示条件,常用的引导词有if, unless, provided that等。
例如:If it rains tomorrow, we won't go to the park.翻译:如果明天下雨,我们不会去公园。
6. 目的状语从句(Purpose Adverbial Clauses):用来表示目的,常用的引导词有so that, in order that等。
完整版英语语法状语从句的归纳总结

在复合句中修饰主句或主句中的某一成分的从句叫状语从句。
状语从句通常由从属连词或起连词作用的词组引导,有时甚至不需要连词直接和主句连接起来。
状语从句根据它表达的意思不同,可分为时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等九类。
一、时间状语从句时间状语从句是表示时间关系的从句。
可以引导时间状语从句的连词很多,根据意义和主从句之间的时间关系,通常可分为以下几种情况:A.when, while, as, wheneverwhen, while, as表示主句谓语作和从句的谓语动作同时发生或几乎同时发生。
1.when①when表示点时间时,从句中用短暂性动词;表示段时间时,用持续性动词。
When I got home, my family were already having dinner.我到家的时候,全家已在吃晚饭。
(when表示点时间)When they were still talking and laughing, the teacher came in.当他们还在说笑的时候,老师进来了。
(when表示段时间)He waved a hello when he saw her.当他看见她的时候,就挥手打了个招呼。
(when表示点时间)When you think you know nothing, you begin to know something.当你认为自己一无所知的时候,就开始知道一些事情了。
(when表示段时间)注意:当when意思是正当……时候(and at that moment)时,when只能跟在前一分句之后。
He was about to go to bed when the doorbel rang. 他正要上床,忽然门铃响了。
They were watching the World Cup when suddenly the lights went out.他们正看着世界杯比赛,突然灯灭了。
完整版)高中状语从句归纳
完整版)高中状语从句归纳状语从句是在句子中做状语的,包括时间、条件、让步、原因、目的、结果、比较、地点、方式状语从句。
时间状语从句可以由when、as、while、until、not…until、before、after、since、the minute、the moment、each (every。
next。
the first) time等引导。
在时间状语从句中,一般使用一般现在时或一般过去时来表达。
1.时间状语从句引导词当句子中有时间状语从句时,可以用when、as、while、until、not…until、before、after、since、the minute、the moment、each (every。
next。
the first) time等来引导。
这些引导词在句子中的使用有不同的侧重点和用法。
1.1 when当我们用when引导时间状语从句时,它的主语和主句的主语相同。
如果从句的谓语动词是be动词,那么从句的主语和be可以省略。
例如:When I arrived home。
I had a little rest.1.2 asas不仅可以表示“当。
的时候”,还可以表示“一面。
一面”和“随着”的意思。
例如:XXX(一面。
一面)You will XXX(随着)1.3 whileXXX表示“当。
的时候”,强调主句的动作和从句的动作同时发生。
从句一般使用进行时,动词必须是延续性动词。
例如:While we were working。
they were having a rest.While they were having a n。
they got very confused.注意:while也有对比的含义,可以解释为“然而”。
例如:XXX。
XXX.2.until和not。
untiluntil和not。
until都表示“直到。
才”。
在肯定句中,主句常用延续性动词;在否定句中,主句常用短暂性动词。
史上最全状语从句知识点总结,建议收藏!
史上最全状语从句知识点总结,建议收藏!状语从句在句中相当于副词,做状语,又叫副词性从句。
状语从句分为九类,包括时刻状语从句、条件状语从句、地点状语从句、缘故状语从句、目的状语从句、让步状语从句、结果状语从句、方式状语从句和比较状语从句。
1. 时刻状语从句⑴当......的时候:when, as, whileI fell asleep when/as/while he was doing his exercises .他正作练习时我睡着了。
When he arrived in Shanghai , his mother met him at the station .他到上海时,他妈妈到车站接他。
While John was watching TV, his wife was cooking.当约翰看电视的时候,他的妈妈在做饭。
She always sings as she walks .她总是一边走一边唱。
注意:when 引导的时刻状语从句中的谓语动词能够是连续的也能够是瞬时的;while和as引导的时刻状语从句中的谓语动词必须是连续的。
⑵一......就......:as soon as, the minute, the moment,the instant,im mediately , directly, instantly, no sooner …than..., hardly …when..., scarc ely…when...The children ran away from the orchard(果园) the moment they saw the guard.小孩们一看到守卫就从果园跑掉了。
No sooner had I arrived home than it began to rain.我一到家天就开始下雨。
⑶直到...... till,until, not...until...(直到......才......,not翻译成“才”)I didn’t realize how special my mother was until I became an adult.直到我长大成人,我才意识到我的妈妈是多么专门。
(完整版)状语从句(完整归纳)
状语从句分类:when (当 .. 的时候)before (在 .. 之前)as soon as (一.. 就.while (在... 期间)since (自从... 以来))after (在 .... 之后)as (当……的时候,一边……一边……)till/until (直到)hardly …when…(刚就)not …till/until (直至U 才)no sooner …than ••刚就no matter+what/which/where/who/when =whatever/whichever/wherever/whoever/whenever(不论什么/哪一个/哪里/谁/何时)比较状语从句:as (正如) as …as (和- ... 一样)not as/so…as (不如… …)than (比… …更)the+比较级 …+the+比较级 (越……越……)条件状语从句:if (假设) unless (如果不) so long as (只要)on condition that (如果)方式状语从句: as (像 ... 那样地) just as (正像)as if (好像)as though(好像)各种状语从句的简化方法:1.以after 和before 引导的状语从句的主语若与主句主语一致时,从句等于after/before+doing sth.作状语。
例 After she sang , she left the rich man's house . = After singing , she left the rich man's house .2.以as soon as 引导的状语从句的主语若与主句主语一致时,从句等于 on+doing sth.,作状语,此时的动词为 非延续性动词。
例: Mary began to operate on the wounded soldiers as soon as he arrived at the village .=Mary began to operate on the wounded soldiers on arriving at the village .3. 时间状语从句和条件状语从句的主语和主句主语一致时,有时可简化为不定式作状语。
初中英语中考常考状语从句整理汇总(共9类)
中考英语常考状语从句1.时间状语从句When/while/as, since, as soon as, until/till, before, after,once, by the time, the minute/ the moment(一...就...), every/each time, whenever,...(1) When & while &as①When:表示“当...时”,后面跟时间点、时间段均可,因而从句的动词可以是非延续性动词(又叫短暂性动词)或延续性动词。
例如:He was watching TV when his mom came back.当他妈妈回来时,他正在看电视。
When his mom was cooking, he was watching TV.当他妈妈做饭的时候,他正在看电视。
②While:表示“当..时”,后面只能跟时间段,因而从句的动词也只能是延续性动词,且常为进行时态(现在进行时或过去进行时)。
例如:While his mom was cooking, he was watching TV.当他妈妈做饭的时候,他正在看电视。
③as:表示“一边...一边...”【注意】与while区分:当一个人同时进行两个动作时(即主从句的主语是同一个人时),只能用as。
还可表示“随着...”。
例如:Tom sings as he works. Tom一边唱歌一边工作。
As time went by, I learned how to be strong.随着时间的流逝,我学会了如何变得坚强。
(2) until & till (介词/连词)until:表示“直到...”,表示某个动作或状态一直持续到...为止。
例如:They waited until/till their mom came back.他们一直等到妈妈回来。
(主句谓语动词为延续性动词)“not...until”表示“直到...才”。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
英语中的九大状语从句状语从句在主从复合句中修饰主句中的动词、形容词或副词等,按意义可以分为时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等状语从句。
一.时间状语从句。
通常由从属连词when, whenever, as, while, before, after, as soon as, till, until, since, once (一旦), hardly……when…, no sooner…….than…; 等引导。
例如:The cyclist started just as the lights changed to green.Whenever we met with difficulties , they cam to help us.He didn’t leave his office until he had finished the day’s work.应注意的问题1.在时间状语从句中,通常要用动词的一般现在时态表示一般将来时态,用一般过去时态表示过去将来时态。
但when 引导一般疑问句或名词性从句时不受上述语法规则的限制,因此,应该加以区分。
例如:When China will enter WTO depends on the bilateral (双边的)joint efforts.Once you understand the rules of the game, you’ll enjoy it.2.when , while, as 的不同用法。
一般说来,当主、从句的动作是同时发生的事,三者可以换用。
when 既可以引导一个持续动作,也可以引导一个短暂动作,可用于主句和从句动作同时发生或从句动作先于主句动作;while 引导的动作必须是持续性的,强调主句和从句的动作同时发生,往往侧重主句和从句动作的对比;as 用于引导“在某行为的继续中发生某事”的“继续之行为”,所以多与过去进行时连用,翻译成“一边……一边……”或者表示动作的变化,翻译成“随着……”。
例如:I hope you’ll think of my words as/when/while you drive on the busy roads.When he realized it, the chance had been lost.When he came home, I was cooking dinner.I was fat when I was a child.He took a bath while I was preparing dinner.As I was walking down the street, an American asked me for the directions to the nearest station.He sang songs as he was taking a bath.As he gets older he gets more optimistic.另外还必须注意 when和while 的特殊用法。
when 可以表示“就在这时,突然”之意;而while 则可以表示对比的含义,常可译作“而”。
例如:She thought I was talking about her daughter, __, in fact, I was talking about my daughter.(NMET95)A. whomB. whereC. whichD. while答案:D. 本句的意思是“她认为我在谈论她女儿,然而,实际上,我在谈论我女儿。
”再如:I was about to go to bed when the phone rang a second time.我正准备去睡觉,就在这时电话铃又响了。
3.since 和before 的用法区别。
两者都可用于“It + be + since/ before-从句”的句型,区别在于 since 表示“自从……以来”,所在主、从句的谓语动词的时态关系是:It is/has been some time since sb did something. 而before 的含义则是“(过了多久)才……”,主、从句的时态关系是:It was/ had been some time before sb did sth。
表示过去和将来时,两者相应的句型分别是:It was some time since sb had done something. 和It will be some time before sb does something. 例如:It was / had been years before I came back from abroad.It will be five years before we meet again.4.一些表示时间的名词词组如: the first time, the second time, last time,the moment, the minute,the year, every time, each time , next time, 或副词immediately, instantly, directly等也可以引导时间状语从句。
例如:I’ll tell you about it the moment you come.I recognized her the minute I saw her.I’m going to see him next time he comes to Shanghai.He left Europe the year World War II broke out.I got in touch with him immediately I received his letter.My sister came directly( = as soon as ) she got my message.5.till 和untiltill 和until 意义相同,多数情况下可以换用,但用以强调,句首多用until; 在强调结构或与not 连用时多用until. 例如:Nothing can be done till/until the boss returns.We waited till/until they came back.Until we know the facts, we can’t do anything about it.Not until midnight did the noise of the street stop.6.hardly……when和no sooner……than相当于as soon as 之意,也可引导时间状语从句。
从句谓语动词用一般过去时,主句谓语动词用过去完成时。
hardly 及no sooner 置于句首时,语气较强,主句的谓语要部分倒装。
例如:We had hardly begun when we were told to stop.= Hardly had we begun when we were told to stop.The spy had no sooner returned home than he was told to go to another country.= No sooner had the spy returned home than he was told to go to another country.二.地点状语从句。
地点状语从句由 where和wherever 引导,在主句前、后都可。
where 表示特指,wherever 则表示泛指。
但不少学生易将其和定语从句混淆,再者有的同学对地点状语从句不太注意,所以往往做错。
例如:You should make it a rule to leave things _you can find them again. (NMET99)A.whenB.whereC.thenD.there答案:B. 注意它引导的不是定语从句。
After living in Paris for fifty years he returned to the small town __he grew up as a child.(NMET 96)A.whichB. whereC. thatD. when答案:B. 这是一个由where 引导的定语从句,修饰先行词the small town.。
再如:Where there is a will, there’s a way.九大状语从句总复习(2)状语从句在主从复合句中修饰主句中的动词、形容词或副词等,按意义可以分为时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等状语从句。
三.原因状语从句。
1.原因状语从句多由because, since, as 引导。
because 引导的从句一般放在句末,表示直接的原因,语气最强,回答why提出的问题,重点在从句;since 引导的从句一般放在句首,表已知的原因,全句重在交代结果,比because 语气弱,常译作“既然”; as 引导的从句放在句首或句末,表示比较明显的原因,说明因果关系,语气较弱,重点在主句,译作“由于”。
例如:you have seen both fighters, will win ?(上海 95)A.Since; do you think whoB.As; who you thinkC.When; whoeverD.Since; who do you think答案:D. since 表示“既然”,所传达的信息是显而易见的。
再如:As all the seats are full, he had to stand waiting.—“Why aren’t you coming with us to the concert ?”—“Because I have got a bad headache.”此外,for 也可表示原因,但它是并列连词,引出并列分句,表示间接原因,用来补充说明内容,或据此而作出某种推断。
例如:She must have wept, for there are tear trails on her cheeks.2.now that也可引导原因状语从句,意思是“既然”,与since 同义,但更突出事实本身。
四.目的状语从句。
通常由so that, in order that, so, in case“以防、以免”等连词引导。
