核酸BLAST
BLAST种类及使用方法

BLAST种类及使用方法BLAST(Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)是一种常用的生物信息学工具,用于在数据库中和比对生物序列。
BLAST工具有多种不同的变体,每种都有不同的用途和适用范围。
下面将介绍几种常见的BLAST工具及其使用方法。
1.BLASTN:BLASTN用于比对核酸序列(DNA或RNA)。
它可以识别相似的核酸序列,并计算相似度和比对长度。
通过对两个序列之间的匹配和错配进行比较,BLASTN可以找到最佳的比对结果。
BLASTN对于找到相似的基因和寻找保守序列非常有用。
使用方法:a.输入待比对的核酸序列。
b.选择合适的数据库(如NCBI的NR数据库)。
c.选择期望的输出格式。
d.运行BLASTN比对。
e.分析比对结果,并根据需要进行相关的进一步分析。
2.BLASTP:BLASTP用于比对蛋白质序列。
它可以找到相似的蛋白质序列,并计算相似度和比对长度。
BLASTP通过比较两个蛋白质序列之间的氨基酸匹配和错配来找到最佳的比对结果。
BLASTP对于找到相似的蛋白质序列、预测蛋白质结构和功能非常有用。
使用方法:a.输入待比对的蛋白质序列。
b. 选择合适的数据库(如NCBI的RefSeq数据库)。
c.选择期望的输出格式。
d.运行BLASTP比对。
e.分析比对结果,并根据需要进行相关的进一步分析。
3.BLASTX:使用方法:a.输入待比对的核酸序列。
b. 选择合适的数据库(如NCBI的RefSeq数据库)。
c.选择期望的输出格式。
d.运行BLASTX比对。
e.分析比对结果,并根据需要进行相关的进一步分析。
4. BLAST2Seq:使用方法:a.输入两个待比对的生物序列。
b.选择合适的数据库(如NCBI的NR数据库)。
c.选择期望的输出格式。
d. 运行BLAST2Seq比对。
e.分析比对结果,并根据需要进行相关的进一步分析。
5.tBLASTn:tBLASTn用于比对核酸序列,并将其翻译成六个阅读框的蛋白质序列,然后与蛋白质序列进行比对。
核酸BLAST
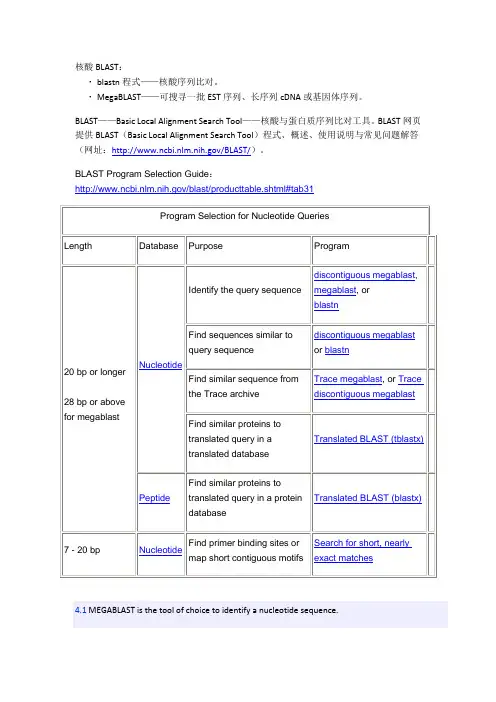
核酸BLAST:‧blastn程式——核酸序列比对。
‧MegaBLAST——可搜寻一批EST序列、长序列cDNA或基因体序列。
BLAST——Basic Local Alignment Search Tool——核酸与蛋白质序列比对工具。
BLAST网页提供BLAST(Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)程式、概述、使用说明与常见问题解答(网址:/BLAST/)。
BLAST Program Selection Guide:/blast/producttable.shtml#tab31在做BLASTn的时候,系统会给出三个程序选项,分别是Highly similar sequences (megablast), More dissimilar sequences (discontiguous megablast),Somewhat similar sequences (blastn) 。
第一个选项megablast是对高度相似DNA序列间的比较。
鉴别一段未知DNA序列的最好办法就是看看在公共数据库中这段序列是否存在。
Megablast就是对那些具有高度相似(相似性95%以上)的长序列片断所特别设计的一种序列比较工具。
Megablast除了提供序列联配的显著性期望值域之外,还提供了一种百分值域。
在进行序列比较时,用户可以同时调整这两个参数以优化搜索结果。
第二个选项discontiguous megablast,当序列之间的差异比megablast大时,一般选用这个程序。
其算法的基本原理是将查询序列分为一个一个的小片断,我们把它叫做字,通过字与数据库序列相比较,如果能够精确匹配,则以这个字为种子向两边延伸,从而获得符合我们要求的相似性序列。
discontiguous megablast所应用的字是不连续的,这使得他的搜索精确性在三种搜索程序中是最高的。
其模板类型选项分为三种编码(0),非编码(1),两者都有(2)。
Blast软件及常用数据库介绍

blastall:通用检索命令 -p(program name):为需要使用的程序名 blastn:为核酸序列对比搜索程序 -d(database name):指定所使用的数据库 的名称 -i (input file):待搜索的序列文件 -o(output file):指定保存结果的文件
2011-12-22
对比对结果分析比对结果登入ncbi主页点击进入对核酸进行blast点击进入直接输入fasta格式的未知核酸序或者本地上传一个fasta格式的核酸序列文件选择一个合适的数据库进行比对点击运行图形结果匹配序列列表输入的序列在库里比对到的序列genebank库包含了所有已知的核酸序列和蛋白质序列以及与它们相关的文献著作和生物学注释它是由美国国立生物技术信息中心ncbi建立和维护的
12
2011-12-22
blast软件及常用数据库介绍
如何在windows操作系统下安装使用本 操作系统下安装使用本 如何在 软件? 地BLAST软件? 软件
STEP3
执行Blast比对
2011-12-22
blast软件及常用数据库介绍
13
具体步骤 1.将所需比对的序列转化为fasta格式
2.执行比对命令
BLAST软件及常用数据库介绍 软件及常用数据库介绍
制作人:faneds
BLAST的概述:
Blast,全称Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, 即“基于局部比对算法的搜索工具” ,能够实现 比较两段核酸或者蛋白序列之间的同源性的功能, 具有较快的比对速度和较高的比对精度,适用于 多种序列比对的情况,在常规双序列比对分析中 应用最为广泛。
3.对比对结果分析
2011-12-22
blast软件及常用数据库介绍
blast分类及特点

blast分类及特点Blast分类及特点Blast(Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)是一种常用的生物信息学工具,用于在数据库中搜索相似序列。
它通过比较待查询的序列与数据库中已知的序列进行比对,从而找到最相似的序列。
Blast分类及特点主要分为以下几个方面:1. BlastP:BlastP用于比对蛋白质序列。
它通过比较待查询的蛋白质序列与数据库中已知的蛋白质序列进行比对,从而找到最相似的序列。
BlastP常用于寻找蛋白质的同源序列,以及预测蛋白质的功能。
2. BlastN:BlastN用于比对核酸序列。
它通过比较待查询的核酸序列与数据库中已知的核酸序列进行比对,从而找到最相似的序列。
BlastN常用于寻找DNA序列的同源序列,以及寻找同源基因。
3. BlastX:BlastX用于比对核酸序列与蛋白质序列的比对。
它通过将待查询的核酸序列翻译成蛋白质序列,然后与数据库中已知的蛋白质序列进行比对,从而找到最相似的序列。
BlastX常用于寻找未知的核酸序列的蛋白质编码区域。
4. TblastN:TblastN用于比对蛋白质序列与核酸序列的比对。
它通过将待查询的核酸序列翻译成蛋白质序列,然后与数据库中已知的蛋白质序列进行比对,从而找到最相似的序列。
TblastN常用于寻找未知的核酸序列中的蛋白质编码区域。
Blast具有以下特点:1. 快速:Blast是一种高效的序列比对工具,它利用了一系列的优化算法,如索引技术和快速查找算法,以提高比对速度。
2. 灵敏:Blast能够在大规模数据库中快速搜索相似序列,它采用了一种基于局部比对的策略,即先找到局部相似的片段,然后通过扩展这些片段来找到最终的比对结果。
3. 准确:Blast通过计算比对序列的得分来评估序列的相似性,得分越高代表相似性越高。
Blast使用了一种统计方法来计算得分,并通过设定一个阈值来判断比对结果的可靠性。
4. 可定制性:Blast提供了丰富的参数选项,用户可以根据自己的需求进行定制。
Blast使用入门

在过去的十年中,Altschul博士在发展评估序列相似 性更有效的统计方法方面起到了重要作用,无论是提高
搜索速度,还是加大相似序列间的敏感性上,这些贡献 对 于 BLAST 的 发 展 是 至 关 重 要 的 , 随 着 1997 年 PSIBLAST的采用,Altschul博士和他的合作伙伴再一次展示 了聪明地使用统计学是如何使得序列搜索变成了一个真 实地、令人生畏的科学工具。
Smith-Waterman算法 局部比对
Fasta算法
Blast算法
建立评分矩阵
Pam250 blosum62
执行比对
Needleman-Wunsch
(动态规划算法) Smith-Waterman
确定最佳途径
当面向数据之海的时候,该怎么办?
生物信息学:努力在数据的海洋里畅游
BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) is a set of similarity search programs that explore all of the available sequence databases for protein or DNA.
在速度上比完全只使用动态规划大约快上50倍左右
引用次数:36501 引用次数:35799
常用生物信息学软件BLAST

Blast的主程序是blastall。程序的输入文件是query序列(-i 参数)和库文件(-d 参数),比对类型的 选择(-p 参数)和输出文件(-o 参数)由用户指定。其中“-p”参数有 5 种取值: -p blastp:蛋白序列与蛋白库做比对。 -p blastx:核酸序列对蛋白库的比对。 -p blastn:核酸序列对核酸库的比对。 -p tblastn:蛋白序列对核酸库的比对。 -p tblastx:核酸序列对核酸库在蛋白级别的比对。 这些元素就构成了blast的基本运行命令(以blastn为例): blastall -i query.fasta -d database_prefix -o blast.out -p blastn 其中如果"-o"参数缺省,则结果输出方式为屏幕输出。下面以一个blastn比对为例,来说明比对全过程: Query序列(query.fasta): >gi|45593933|gb|AY551259.1| Oryza sativa precursor microRNA 319c gene AGGAAGAGGAGCTCCTTTCGATCCAATTCAGGAGAGGAAGTGGTAGGATGCAGCTGCCGATTCATGGATA CCTCTGGAGTGCATGGCAGCAATGCTGTAGGCCTGCACTTGCATGGGTTTGCATGACCCGGGAGATGAAC CCACCATTGTCTTCCTCTATTGATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCCACATCTCT >gi|45593932|gb|AY551258.1| Oryza sativa precursor microRNA 319b gene CATATTCTTTTAATTTGATGGAAGAAGCGATCGATGGATGGAAGAGAGCGTCCTTCAGTCCACTCATGGG CGGTGCTAGGGTCGAATTAGCTGCCGACTCATTCACCCACATGCCAAGCAAGAAACGCTTGAGATAGCGA AGCTTAGCAGATGAGTGAATGAAGCGGGAGGTAACGTTCCGATCTCGCGCCGTCTTTGCTTGGACTGAAG GGTGCTCCCTCCTCCTCGATCTCTTCGATCTAATTAAGCTACCTTGACAT 库文件Database(db.seq,已经运行formatdb -i db.seq -p F -o T建库): >fake_seq AGGAAGAGGAGCTCCTTTCGTTCCAATTCAGGAGAGGAAGTGGTAGGATGCAGCTGCCGATTCATGGATA CCTCTGGAGTGCATGCAGCAATGCTGTAGGCCTGCACTTGCATGGGTTTGCATGACCCGGCGAGATGAAC CCACCATTGTCTTCCTCTATTGATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCCACATCTCT 运行命令: blastall -i query.fasta -d db.seq -o blast.out -p blastn 运行结果: BLASTN 2.2.8 [Jan-05-2004] Reference: Altschul, Stephen F., Thomas L. Madden, Alejandro A. Schaffer, Jinghui Zhang, Zheng Zhang, Webb Miller, and David J. Lipman (1997), "Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs", Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3389-3402. Query= gi|45593933|gb|AY551259.1| Oryza sativa precursor microRNA 319c gene, complete sequence
NCBI中Blast种类简介
NCBI中Blast种类简介NCBI中Blast种类简介NCBI中Blast种类简介1. Blast Assembled Genomes在一个选择的物种基因组序列中去搜索。
2.Basic Blast2.1 nucleotide blast--- 用核酸序列到核酸数据库中进行搜索,包括3个程序2.1.1 Blastn----核酸序列(n)到核酸序列数据库中搜索,是一种标准的搜索。
2.1.2 megablast----该程序使用“模糊算法”加快了比较速度,可以用于快速比较两大系列序列。
可以用来搜索一匹ESTs序列和大的cDNA或基因组序列, 适用于由于测序或者其他原因形成的轻微的差别的序列之间的比较2.1.3 discontiguous megablast----与megablast不同的是主要用来比较来自不同物种之间的相似性较低的分歧序列。
2.2 Protein Blast2.2.1 Blastp ---蛋白质序列到蛋白质序列数据库中搜索,是一种标准的搜索。
2.2.2 psi-blast---位点特异迭代BLAST —用蛋白查询来搜索蛋白资料库的一个程式。
所有被BLAST发现的统计有效的对齐被总和起来形成一个多次对齐,从这个对齐,一个位置特异的分值矩阵建立起来。
这个矩阵被用来搜索资料库,以找到额外的显著对齐,这个过程可能被反复迭代一直到没有新的对齐可以被发现。
2.2.3 PHI-BLAST---以常规的表达模型为特别位置进行PSI - BLAST检索,找出和待查询序列具有一样的表达模型且具有同源性的蛋白质序列。
2.3 Translating BLAST2.3.1 blastx----先将待查询的核酸序列按6 种读框翻译成蛋白质序列,然后将翻译出的蛋白质序列与NCBI 蛋白质序列数据库比较。
2.3.2 tblastn-----先将核酸序列数据库中的核酸序列按6 种读框翻译成蛋白质序列,然后将待查询的蛋白质序列与翻译结果进行比较。
blast 用法
BLAST的使用方法与参数选项调整
BLAST(Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)是一种在生物信息学中广泛使用的序列比对工具,可以用于搜索数据库中的序列,并找到与之相似的序列。
以下是BLAST的基本用法:
1.选择BLAST软件:BLAST包括多种算法,如BLASTN、BLASTP、BLASTX、
TBLASTN和TBLASTX等。
根据需要搜索的序列类型,选择相应的BLAST 算法。
2.准备查询序列:将要搜索的序列准备妥当,可以是DNA、蛋白质或RNA
序列。
3.选择数据库:选择将要搜索的数据库,可以是核酸数据库或蛋白质数据库
等。
4.运行BLAST:在相应的BLAST软件中输入查询序列和选择数据库,运行
BLAST程序。
5.结果解析:解析BLAST结果,包括匹配的序列、匹配的位置、匹配的得分
和E值等。
需要根据E值和得分来判断匹配的可靠性和相似性。
在BLAST的使用过程中,还有一些参数和选项可以调整,例如设置期望值阈值、最大目标序列数目等。
这些参数和选项可以通过查阅BLAST的官方文档或相关教程来了解和使用。
在线blast的用法总结
在线b l a s t的用法总结-标准化文件发布号:(9556-EUATWK-MWUB-WUNN-INNUL-DDQTY-KIIBlast(Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)是一套在蛋白质数据库或DNA数据库中进行相似性比较的分析工具。
BLAST程序能迅速与公开数据库进行相似性序列比较。
BLAST结果中的得分是对一种对相似性的统计说明。
BLAST 采用一种局部的算法获得两个序列中具有相似性的序列NCBI的在线blast:/Blast.cgi本文详细出处参考:/475/举例一:核酸序列的比对1,进入在线blast界面,可以选择blast特定的物种(如人,小鼠,水稻等),也可以选择blast所有的核酸或蛋白序列。
不同的blast程序上面已经有了介绍。
这里以常用的核酸库作为例子。
(补充介绍下:1、BLASTN【 nucleotide blast】是核酸序列到核酸库中的一种查询。
库中存在的每条已知序列都将同所查序列作一对一地核酸序列比对。
2、BLASTP【protein blast】是蛋白序列到蛋白库中的一种查询。
库中存在的每条已知序列将逐一地同每条所查序列作一对一的序列比对。
3、BLASTX是核酸序列到蛋白库中的一种查询。
先将核酸序列翻译成蛋白序列(一条核酸序列会被翻译成可能的六条蛋白),再对每一条作一对一的蛋白序列比对。
4、TBLASTN是蛋白序列到核酸库中的一种查询。
与BLASTX相反,它是将库中的核酸序列翻译成蛋白序列,再同所查序列作蛋白与蛋白的比对。
5、TBLASTX是核酸序列到核酸库中的一种查询。
此种查询将库中的核酸序列和所查的核酸序列都翻译成蛋白(每条核酸序列会产生6条可能的蛋白序列),这样每次比对会产生36种比对阵列。
)2,粘贴fasta格式的序列。
选择一个要比对的数据库。
关于数据库的说明请看NCBI在线blast数据库的简要说明。
一般的话参数默认。
3,blast参数的设置。
Blast使用技巧解析
两个蛋白是否有共同的模体或信号序列. 两个蛋白质是不是一个合理的多序列比对的
一局部 两个蛋白质是否共有一个相像的生物学功能. 两个蛋白质是否具有相像的三维构造. PSI-BLAST搜寻
30
BLAST搜寻策略调整
搜寻结果过多状况 加Entrez限制条件 利用序列的一局部进展搜寻 调整记分矩阵 调整期望值 搜寻结果过少状况 去掉Entrez限制 提高期望值 使用更高PAM值或更低BLOSUM值的记分矩阵 高级BLAST搜寻
选择需要显示的选项 以及显示的文件格式
显示数目
Alignment的显
筛选结果
示方式
点击开头搜寻
其他一些显示格式参数
15
提交任务
返回查询号〔request id〕 修改完显示格式后点 击进入结果界面
可以修改显示结果格式
16
结果页面〔一〕
图形示意结果
17
结果页面〔二〕
目标序列描述局部
带有genbank的链接,点击可以进入 相应的genbank序列
34
PSI-blast
Position specific iterative BLAST (PSI-BLAST) 位 点特异的迭代blast搜寻,主要针对蛋白序列。第 一次blast搜寻后,结果中最相像的序列重新构建 PSSM (位点特异性打分矩阵),然后再使用该矩 阵进展其次轮blast搜寻,再调整矩阵,搜寻,如 此迭代。
最终高度保守的区域就会得到比较高的分值, 而不保守的区域则分数降低,趋近0。 这样可以提高blast搜寻的灵敏度,有助于查找 远源相关的蛋白。
35
PHI-BLAST
模式识别BLAST〔Pattern hit intiated BLAST〕
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
核酸BLAST:‧blastn程式——核酸序列比对。
‧MegaBLAST——可搜寻一批EST序列、长序列cDNA或基因体序列。
BLAST——Basic Local Alignment Search Tool——核酸与蛋白质序列比对工具。
BLAST网页提供BLAST(Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)程式、概述、使用说明与常见问题解答(网址:/BLAST/)。
BLAST Program Selection Guide:/blast/producttable.shtml#tab31在做BLASTn的时候,系统会给出三个程序选项,分别是Highly similar sequences (megablast), More dissimilar sequences (discontiguous megablast),Somewhat similar sequences (blastn) 。
第一个选项megablast是对高度相似DNA序列间的比较。
鉴别一段未知DNA序列的最好办法就是看看在公共数据库中这段序列是否存在。
Megablast就是对那些具有高度相似(相似性95%以上)的长序列片断所特别设计的一种序列比较工具。
Megablast除了提供序列联配的显著性期望值域之外,还提供了一种百分值域。
在进行序列比较时,用户可以同时调整这两个参数以优化搜索结果。
第二个选项discontiguous megablast,当序列之间的差异比megablast大时,一般选用这个程序。
其算法的基本原理是将查询序列分为一个一个的小片断,我们把它叫做字,通过字与数据库序列相比较,如果能够精确匹配,则以这个字为种子向两边延伸,从而获得符合我们要求的相似性序列。
discontiguous megablast所应用的字是不连续的,这使得他的搜索精确性在三种搜索程序中是最高的。
其模板类型选项分为三种编码(0),非编码(1),两者都有(2)。
在编码模式中,根据第三位碱基的摆动原理,只要第一个和第二个碱基能够精确匹配,那么第三个碱基可以忽略,不做比较。
在字的长度相同的情况下,discontiguous megablast的精确度要高于blastn。
第三个选项Somewhat similar sequences (blastn),这个程序比较的序列其相似程度可以非常低。
它采用的算法与discontiguous megablast相同,只不过它的字是连续的。
Blastn的字要比megablast短,所以其精确度要高于megablast,但是运算速度要慢一些。
注:字是影响blast灵敏度的一个主要参数,其取值要根据具体情况具体而定。
NCBI BLASTn:/public_documents/vibe/details/NcbiBlastn.htmlStandard nucleotide-nucleotide BLASTTakes nucleotides sequences and compares them against the NCBI nucleotide databases. It is better at finding sequences similar, but not identical, to your query.The BLAST nucleotide algorithm finds similar sequences by generating an indexed table or dictionary of short subsequences called words for both the query and the database. The program can then rapidly find initial exact matches to the query words by simply looking up a particular word in the database dictionary. These initial matches serve as starting points for longer alignments that are generated in several steps, ending with a final gapped alignment.One of the important parameters governing the sensitivity of BLAST searches is the length of the initial words (word size). The most important reason that blastn is more sensitive than MEGABLAST is that it uses a shorter default word size. Because of this, blastn is better than MEGABLAST at finding alignments to related nucleotide sequences from other organisms since the initial exact match can be shorter. The word size is adjustable in blastn and can be reduced from the default value of 11 to a minimum of 7 to increase sensitivity. This word size can also be increased to increase the search speed and limit the number of database hits.Search for short and near exact matchesIt is useful for primer or short nucleotide motif searches.Short sequences (less than 20 bases) will often not find any significant matches to the database entries under the standard nucleotide-nucleotide BLAST settings. The usual reasons for this are that the significance threshold governed by the expect value parameter is set too stringently and the default word size parameter is set too high. You can adjust both the word size and the expect value on parameter table to work with short sequences.A common use of this is to check the specificity of primers used in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or hybridization. A useful way to check a pair of PCR primers is to concatenate them and search them as one sequence. The forward primer and thereverse primer can simply be pasted together with a string of ten or more N's between the two sequences. Since BLAST looks for local alignments and searches both strands, there is no need to reverse complement one of the primers before doing the concatenation or the search.NotesNucleotide-nucleotide searches are not the recommended way to find homologous protein coding regions in other organisms. It is better to perform searches at the protein level, either with translations of the nucleotide sequences or by direct protein-protein BLAST. This is because of the degeneracy of the genetic code, the greater information available in amino acid sequence, and the more sophisticated algorithm in protein-protein BLAST.The query sequence should contain no ambiguous bases. Consensus motifs with degenerate bases will not work for this type of search.Parameters Setting[COMPOSITION BASED STATISTICS] Do search with tweak parameter set to true, learn more. This will automatically perform a gapped alignment, so using UNGAPPED_ALIGNMENT also is unnecessary and will trigger a warning message from NCBI rather than generating results.∙Value : yes, no∙Default : no[DATABASE] Valid database name,∙Value : see nucleotide databases∙Default : nr[EXPECT] The statistically significant expectation value. If the statistical significance ascribed to a match is greater than the E value, the match will not be reported. Lower E values are more stringent, leading to a fewer chance matches being reported. Learn more∙Value : double type value∙Default : 10.0[ENTREZ_QUERY] Entrez query to limit Blast search∙Value :Entrez query format∙Default : Empty[FILTER]Sequence filter identifier∙L for Low Complexity∙R for Human Repeats∙m for Mask for Lookup[GAP_OPEN_COSTS] Gap open costs∙Value : integer values∙Default : 5 for nuc-nuc, 11 for proteins, non-affine for megablast[GAP_EXTEND_COSTS] Gap extend costs∙Value : space separated float values∙Default : 2 for nuc-nuc, 1 for proteins, non-affine for megablast [HITLIST_SIZE] Number of hits to keep∙Value : integer value∙Default : 20[LCASE_MASK] Enable masking of lower case in query∙Value : yes, no∙Default : no[NUCL_PENALTY] Penalty for a nucleotide mismatch (blastn only)∙Value : negative integer value∙Default : -3[NUCL_REWARD] Reward for a nucleotide match (blastn only)∙Value : integer value∙Default : 1OTHER_ADVANCED*[DROPOFF] Blast extensions in bits (default if Zero), not applicable for megablast∙Value : integer value∙Default :20 for nuc-nuc, 7 for other programs*[FIANL_X_DROPOFF]Final X dropoff value for gapped alignment (in bits), not applicable for megablast∙Value : integer value∙Default :50 for nuc-nuc (blastn), 25 for other programs*[DB_LENGTH] Effective length of the database (use Zero for real size)∙Value :real value∙Default :0[PROGRAM] Blast program name∙Value : blastn, blastp, blastx, tblastn, tblastx∙Default : blastn[QUERY_BELIEVE_DEFLINE] Whether to believe defline in FASTA query∙Value : yes, no∙Default : no[QUERY_FROM] Start of subsequence (one offset)∙Value : integer value∙Default : 0[QUERY_TO] End of subsequence (one offset)∙Value : integer value∙Default : 0, that means not to use subsequence[SEARCHSP_EFF] Effective length of the search space∙Value : integer value∙Default : 0[SERVICE] Blast service which needs to be performed∙Value : plain, psi, phi, rpsblast, megablast∙Default : plain[THRESHOLD] Threshold for extending hits∙Value : integer value∙Default : ???[UNGAPPED_ALIGNMENT] Should the ungapped alignment be performed? Note that this parameter should not be set to TRUE or YES when usingCOMPOSITION_BASED_STATISTICS since that will automatically perform a gappedalignment; if this parameter is on, it will trigger a warning message from NCBI rather than generating results.∙Value : yes, no∙Default : no[WORD SIZE] The search word size∙Value : integer value; 2 or 3 for proteins, 7 or greater for nuc∙Default : 3 for proteins, 11 for nuc-nuc, 28 for megablast/blast/megablast.shtmlMEGABLAST SearchMega BLAST uses a greedy algorithm [1] for the nucleotide sequence alignment search. This program is optimized for aligning sequences that differ slightly as a result of sequencing or other similar "errors". When larger word size is used (see explanation below), it is up to 10 times faster than more common sequence similarity programs. Mega BLAST is also able to efficiently handle much longer DNA sequences than the blastn program of traditional BLAST algorithm.Default parametersWord size.Word size is roughly the minimal length of an identical match an alignment must contain if it is to be found by the algorithm. Mega BLAST is most efficient with word sizes 16 and larger, although word size as low as 8 can be used.If the value W of the word size is divisible by 4, it guarantees that all perfect matches of length W + 3 will be found and extended by Mega BLAST search, however perfect matches of length as low as W might also be found, although the latter is not guaranteed. Any value of W not divisible by 4 is equivalent to the nearest value divisible by 4 (with 4i+2 equivalent to 4i).Gapping parametersBy default, non-affine gapping parameters are assumed. This means that the gap opening penalty is 0, and gap extension penalty E can be computed from match reward r and mismatch penalty q by the formula: E = r/2 - q. The non-affine version of Mega BLAST requires significantly less memory and is also significantly faster, however affine gapping parameters can also be used, preferrably with larger word sizes. Non-affine gapping parameters tend to yield alignments with more gaps, but the gap lengths are shorter.X-dropoff valueAs in BLAST, this value provides a cutoff threshold for the extension algorithm tree exploration. When the score of a given branch drops below the current best score minus the X-dropoff, the exploration of this branch stops. However the actual values of the X-dropoff for Mega BLAST and for traditional nucleotide BLAST algorithms are not necessarily compatible, i.e. with the same word size, match, mismatch and gapping penalties and with the same X-dropoff, the two algorithms might produce different results, which can be remedied by changing the X-dropoff value for one of the algorithms.。
