Dicom文件中图像参数详解

DICOM文件可以大致分为两部分:
一部分:与图像相关的元信息,包括患者信息,检查信息,序列信息,图像信息等等。
另一部分:图像的像素数据。
在解析DICOM文件中的像素数据的时候,我们先需要读取以下图像相关信息:
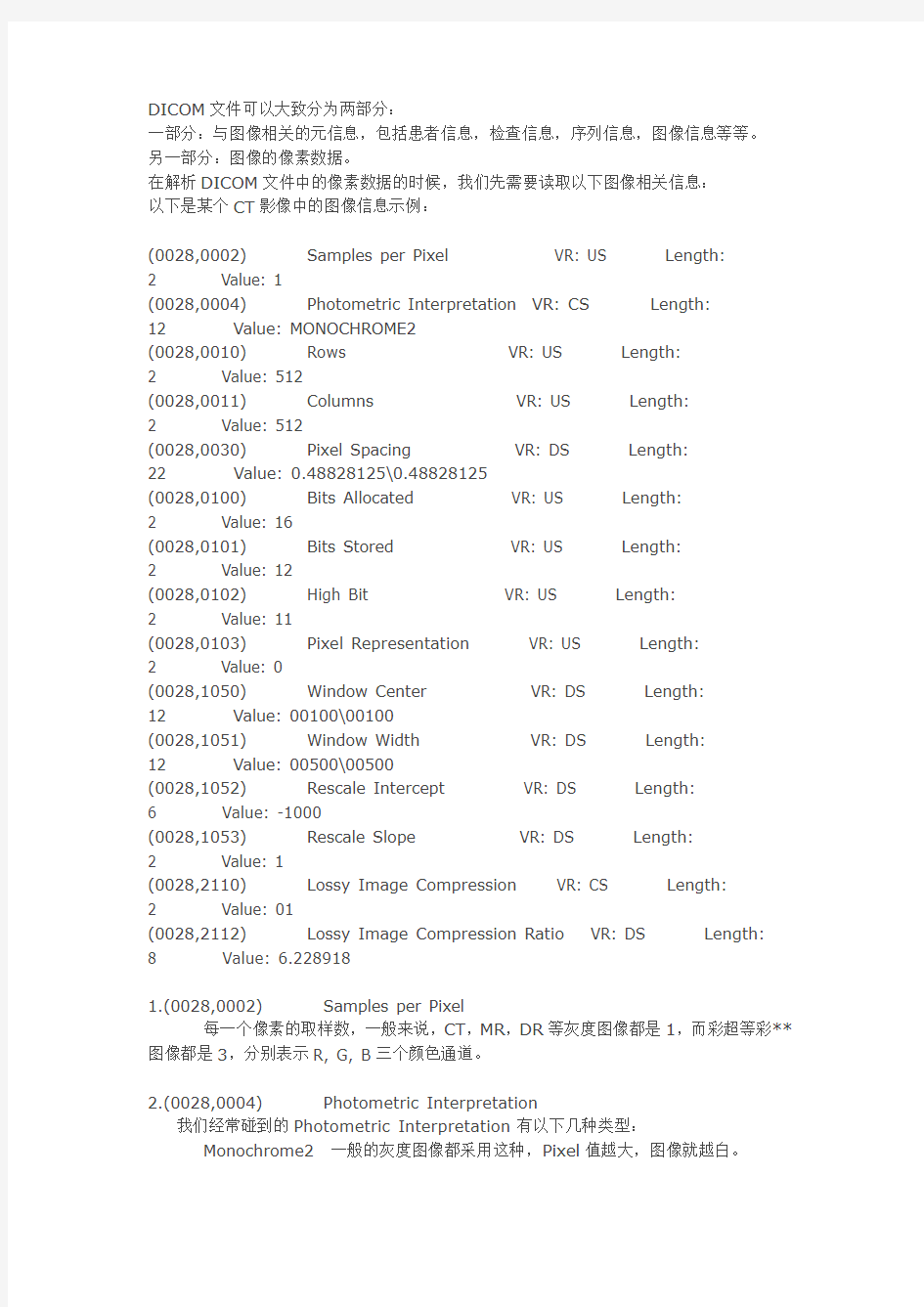
以下是某个CT影像中的图像信息示例:
(0028,0002) Samples per Pixel VR: US Length:
2 Value: 1
(0028,0004) Photometric Interpretation VR: CS Length:
12 Value: MONOCHROME2
(0028,0010) Rows VR: US Length:
2 Value: 512
(0028,0011) Columns VR: US Length:
2 Value: 512
(0028,0030) Pixel Spacing VR: DS Length:
22 Value: 0.48828125\0.48828125
(0028,0100) Bits Allocated VR: US Length:
2 Value: 16
(0028,0101) Bits Stored VR: US Length:
2 Value: 12
(0028,0102) High Bit VR: US Length:
2 Value: 11
(0028,0103) Pixel Representation VR: US Length:
2 Value: 0
(0028,1050) Window Center VR: DS Length:
12 Value: 00100\00100
(0028,1051) Window Width VR: DS Length:
12 Value: 00500\00500
(0028,1052) Rescale Intercept VR: DS Length:
6 Value: -1000
(0028,1053) Rescale Slope VR: DS Length:
2 Value: 1
(0028,2110) Lossy Image Compression VR: CS Length:
2 Value: 01
(0028,2112) Lossy Image Compression Ratio VR: DS Length: 8 Value: 6.228918
1.(0028,0002) Samples per Pixel
每一个像素的取样数,一般来说,CT,MR,DR等灰度图像都是1,而彩超等彩**图像都是3,分别表示R, G, B三个颜色通道。
2.(0028,0004) Photometric Interpretation
我们经常碰到的Photometric Interpretation有以下几种类型:
Monochrome2 一般的灰度图像都采用这种,Pixel值越大,图像就越白。
Monochrome1 只有部分CR, DR图像使用,Pixel值越大,图像就越黑。
Palette Colour 一般用于彩超图像,每个像素占用8位或者16位,调色板保存在[0028,1201]RedPaletteColorLookupTableData,
[0028,1202]GreenPaletteColorLookupTableData,
[0028,1203]BluePaletteColorLookupTableData的属性中。
RGB 这是最常用的彩**图像格式。
YBR_FULL 另外一种彩**图像格式,存储格式为Y(Luminance 亮度),
B(Blueness 蓝色),R(Redness, 红色)
YBR_FULL_422 一般用于JPG有损压缩格式的彩**图像,每两个像素共同使用32位,每一个像素都有自己的Y(Luminance 亮度),但是共享相同的B(Blueness 蓝色),R(Redness, 红色)。所以,它的像素值存储方式是:YYBR,YYBT,YYBR YBR_RCT 用于JPEG 2000无损压缩彩**图*像,Reversible Color Transformation, 可逆色彩变换。
Y = (R+2G+B)/4, CB = B-G ,CR = R - G
G = Y - (CR+CB)/4 , R = CR + G, B = CB + G
YBR_ICT 用于JPEG 2000有损压缩彩**图像Irreversible Color Transformation, 不可逆色彩变换。
Y = + .29900R + .58700G + .11400B
CB = - .16875R - .33126G + .50000B
CR = + .50000R - .41869G - .08131B
3. (0028,0010)Rows
图像的高度
4. (0028,0011)Columns
图像的宽度
5. (0028,0030)Pixel Spacing
图像像素间距,读取Pixel Data的时候不需要,主要用于长度测量。
6. (0028,0100)Bits Allocated
一个像素取样点存储时分配到的位数,一般RGB的图像,每一个颜色通道都使用8位,所以一般取值为8。对于灰度图像,如果是256级灰阶,一般就是8位。如果高于256级灰阶,一般就采用16位。
7. (0028,0101)Bits Stored
一个像素取样点存储时使用到的位数。比方说示例中CT影像,采用的是4K灰阶,像素值取值范围为0~4095,所以使用到的位数为12位。
8. (0028,0102)High Bit
最高位序号,它定义了存储点在分配的内存中的排列方式,它的值是最后一个bit的序号。如果第一个bit放在0位,那么最后一个bit为Bits Stored -1。
9. (0028,0103)Pixel Representation
如果这个值为0,这表明是无符号类型,其VR类型应该为US,Unsigned Short. 如果这个值为1,这表明为有符号类型,其VR类型应该为SS,Signed Short.
10. (0028,1050)Window Center 和(0028,1051) Window Width
窗宽窗位,不解释
11. (0028,1052)Rescale Intercept 和(0028,1053)Rescale Slope
用于根据像素值计算原始值,比方说,CT可以用于计算HU值。
比方说:HU = Rescale Slope * X + Rescale Intercept.
12. (0028,2110)Lossy Image Compression
当该值为1时,表明该图像曾经经过有损压缩处理。即使后来解压缩后,再用非压缩格式存储和传输,该值也需要保持为1.
13. (0028,2112)Lossy Image Compression Ratio
有损压缩压缩率。
对于多帧图像,我们还需要读取Number of Frames (0028,0008)来获取帧数,然后,逐帧读取Pixel Data。
对于彩*图像,我们还需要读取Planar configuration (0028,0006),它定义了各个彩色通道值在Pixel Data中排列的排列方式。
当此值为0的时候,它这样排列的RGBRGBRGBRGBRGB。
当此值为1的时候,它是这样排列的:RRRRR......GGGGG.......BBBBB。对于多帧图像,它是这样排列的:第一帧的RRR..,第一帧的GGG...,第一帧的BBB...,第二帧的RRR..,第二帧的GGG...,第二帧的BBB...
Dicom文件中图像参数详解
DICOM文件可以大致分为两部分: 一部分:与图像相关的元信息,包括患者信息,检查信息,序列信息,图像信息等等。 另一部分:图像的像素数据。 在解析DICOM文件中的像素数据的时候,我们先需要读取以下图像相关信息: 以下是某个CT影像中的图像信息示例: (0028,0002) Samples per Pixel VR: US Length: 2 Value: 1 (0028,0004) Photometric Interpretation VR: CS Length: 12 Value: MONOCHROME2 (0028,0010) Rows VR: US Length: 2 Value: 512 (0028,0011) Columns VR: US Length: 2 Value: 512 (0028,0030) Pixel Spacing VR: DS Length: 22 Value: 0.48828125\0.48828125 (0028,0100) Bits Allocated VR: US Length: 2 Value: 16 (0028,0101) Bits Stored VR: US Length: 2 Value: 12 (0028,0102) High Bit VR: US Length: 2 Value: 11 (0028,0103) Pixel Representation VR: US Length: 2 Value: 0 (0028,1050) Window Center VR: DS Length: 12 Value: 00100\00100 (0028,1051) Window Width VR: DS Length: 12 Value: 00500\00500 (0028,1052) Rescale Intercept VR: DS Length: 6 Value: -1000 (0028,1053) Rescale Slope VR: DS Length: 2 Value: 1 (0028,2110) Lossy Image Compression VR: CS Length: 2 Value: 01 (0028,2112) Lossy Image Compression Ratio VR: DS Length: 8 Value: 6.228918 1.(0028,0002) Samples per Pixel 每一个像素的取样数,一般来说,CT,MR,DR等灰度图像都是1,而彩超等彩**图像都是3,分别表示R, G, B三个颜色通道。 2.(0028,0004) Photometric Interpretation 我们经常碰到的Photometric Interpretation有以下几种类型: Monochrome2 一般的灰度图像都采用这种,Pixel值越大,图像就越白。
dicom读取方法
Dicom格式文件解析器 学数字图像与通讯,这里讲的暂不涉及通讯那方面的问题只讲*.dcm 也就是diocm格式文件的读取,读取本身是没啥难度的无非就是字节码数据流处理。只不过确实比较繁琐。 分析 整体结构先是128字节所谓的导言部分,说俗点就是没啥意义的破数据跳过就是了,然后是dataElement依次排列的方式就是一个dataElement接一个dataElement的方式排到文件结尾通俗的讲dataElement就是指tag 就是破Dicom标准里定义的数据字典。tag是4个字节表示的前两字节是组号后两字节是偏移号比如0008,0018。所有dataElement在文件中都是按tag排序的 比如0002,0001 0002,0002 0003,0011 文件整体结构如下: 又把论文里的这图贴上来总结的很好。单个dataElement的结构如下: 显示VR:VR为OB OW OF UT SQ UN的元素结构 显示VR:VR为普通类型时元素结构(少了预留那一行) 隐式VR 时元素结构
要问VR是啥东东,值表示法啥叫值表示法啊俺不懂 int string short ushort 懂不就是这个意思,Dicom标准真坑爹非要整个怪怪的概念。 VR总共27个跟c#值类型对应关系我都写好了: 1string getVF(string VR, byte[] VF) 2 { 3string VFStr = string.Empty; 4switch (VR) 5 { 6case"SS": 7 VFStr = BitConverter.ToInt16(VF, 0).ToString(); 8break; 9case"US": 10 VFStr = BitConverter.ToUInt16(VF, 0).ToString(); 11 12break; 13case"SL": 14 VFStr = BitConverter.ToInt32(VF, 0).ToString(); 15 16break; 17case"UL": 18 VFStr = BitConverter.ToUInt32(VF, 0).ToString(); 19 20break; 21case"AT": 22 VFStr = BitConverter.ToUInt16(VF, 0).ToString(); 23 24break; 25case"FL": 26 VFStr = BitConverter.ToSingle(VF, 0).ToString(); 27 28break; 29case"FD": 30 VFStr = BitConverter.ToDouble(VF, 0).ToString(); 31 32break; 33case"OB": 34 VFStr = BitConverter.ToString(VF, 0); 35break; 36case"OW": 37 VFStr = BitConverter.ToString(VF, 0);
DICOM标准及医学影像设备
DICOM标准 1.定义 DICOM(Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine)即医学数字成像和通信,是医学图像和相关信息的国际标准(ISO 12052)。它定义了质量能满足临床需要的可用于数据交换的医学图像格式。 2.历史 在1970年代,随着以CT为代表的数字成像诊断设备在临床得到广泛应用,美 国放射学院(ACR)和国家电气制造协会(NEMA)在1983年成立了一个联合委员会,以制定相应规范。 ACR-NEMA联合委员会于1985年发布了最初的1.0版本(ACR-NEMA Standards Publications No.300-1985),又分别于1986年10月和和1988年1月发布了校订No.1和校订No.2。1988年该委员会推出2.0版本(ACR-NEMA Standards Publications NO.300-1988),到1993年发布的DICOM标准3.0,已发展成为医学影像信息学领域的国际通用标准。 3.目的 (1)推动不同制造商的设备间数字图像信息通信标准的建立。 (2)促进和扩展图片归档及通讯系统(PACS),使它可以与其它医院信息系统进行交互。 (3)允许广泛分布于不同地理位置的诊断设备创建统一的诊断信息数据库。 4.意义 DICOM标准中涵盖了医学数字图像的采集、归档、通信、显示及查询等几乎所有信息交换的协议;以开放互联的架构和面向对象的方法定义了一套包含各种类 型的医学诊断图像及其相关的分析、报告等信息的对象集;定义了用于信息传递、交换的服务类与命令集,以及消息的标准响应;详述了唯一标识各类信息对象的 技术;提供了应用于网络环境(OSI或TCP/IP)的服务支持;结构化地定义了制造厂 商的兼容性声明。 DICOM标准的推出与实现,大大简化了医学影像信息交换的实现,推动了远程放射学系统、图像管理与通信系统(PACS)的研究与发展,并且由于DICOM的开放性与互联性,使得与其它医学应用系统(HIS、RIS等)的集成成为可能。
DICOM图像最大密度投影
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Share Information %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Tag:Matlab, Medical Imaging, DICOM %%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %% 标题:DICOM图像最大密度投影 %% 内容:对DICOM图像最大密度投影 %% 作者:Destiny %% 日期:2012-10-05 %% 是否转载:否 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%% MIP %%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %For initial P = zeros(249,512); %To store the final result CP = zeros(1,512); %To store the line-image after projection % for each image on coronal plane %For read all images automaticly filename = dir('*.dcm'); [r c]=size(filename); %Maximum Intensity Projection for a = 1:r %For each image, read it by using dicominfo() an dicomread() %str = sprintf(filename(a).name); info=dicominfo(filename(a).name); Y = dicomread(info); %Get the image size [m,n] = size(Y); %For each DICOM image, find its maximum value in coronal plane CP = max(Y,[],1); %For final result, add line-images into the matrix P with the size %249*512 P(r-a+1,:) = CP; end figure,imshow(P,[])%Here use [] to show P, % make P's minumum values into 0, % while Maximum values into 255.
DICOM图像读取
Windows平台下多层DICOM图像读取与显示的方法 【摘要】目的实现Windows环境下读取与显示多层DICOM格式图像,为医学图像三维配准与重建等后处理提供数据。方法针对DICOM文件格式,在Visual C++6.0下设计了简化的图像类结构,将多层DICOM图像的相关数据读入到动态数组中,并转换成BMP位图实现在Windows环境下不同层图像间的切换显示。结果选取CT、MR、PET等不同模态的DICOM图像进行实验,均可正确读取。结论通过解析DICOM图像文件存储格式,实现了多层DICOM图像文件的读取与不同层间的切换显示。本程序运行于Windows环境,不依赖于具体DICOM工作站,便于科研教学使用。 【关键词】多层DICOM图像读取;图像显示;医学图像后处理;数据元素;窗宽窗位 A method of reading and displaying multi-slice DICOM images under Windows ZHU Zhi-liang,YANG Ye,WANG Bei-lei,et al.Biomedical and Multimedia Information Technology Group,Northeastern University,Shenyang110004,China [Abstract]Objective To implement reading and displaying multi-slice DICOM images under Windows environment.Methods According to the format of DICOM file,we designed the simplified DICOM class under Visual C++6.0.We read the information of multi-slices DICOM images into dynamic array and translated the DICOM file into BMP file to realize switched displaying of DICOM image under Windows environment.Results We tested with several DICOM images from different modalities,all images could be properly read and displayed.Conclusion The software of this article realizes the reading and switched displaying of multi-slice DICOM images.It runs under Windows that was independent on DICOM image work station and can provide data for medical image of3-dimensional registration and reconstruction. [Key words]read of multi-slice DICOM images;image display;medical image postprocess;data element;window center-window width 医学数字成像和传输(Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine,DICOM)[1]是用于医学图像存储和通信的国际标准,规范了医学图像及各种数字信息在异构系统和设备之间存储、传送时的文件格式和语义描述,为不同的医学影像设备提供了一个一致性的接口,以实现数字影像在各种医学影像设备间的交换传输。随着DICOM标准的不断发展,现在生产的各种医疗设备(如CT、PET、MRI等)都已采用DICOM30标准的数字接口。 目前,多数DICOM图像浏览软件都基于UNIX平台且仅能读取与显示一幅图像,而在科研和教学中常需要在Windows环境下显示处理DICOM图像。另外,对医学图像进行后处理如三维配准及重建之前,首先要得到多层DICOM图像的信息,故本文对在Windows 环境下读取与显示多层DICOM图像的方法进行了初步研究,现将结果阐述如下。 1资料与方法 11DICOM文件格式DICOM文件是采用面向对象的方法来设计和编码的,每个文件有一个信息对象(IOD)与之相关联,信息对象的属性由数据元素来表示,而且对象的属性只能编码一次,用UID标识符来唯一标识[2]。DICOM文件一般可分为文件头和数据集两部分。文件头又有两部分:开头有128个字节的同步码,通常以十六进制的00填充;紧随其后4个字节的ASCII码“DICM”是所有DICOM数据文件的标识符。数据集是一些数据元的有序集合,其中包含诸如受检者信息、成像的技术参数、医生诊断信息、图像数据等资料。数据元一般由标签(TAG)、值表示(value representation,VR)、值长度(value
DICOM图像浏览器
Image Viewer using Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) Trupti N. Baraskar Department of Information Technology, Maharashtra Institute of Technology, Pune University, Maharashtra, India Email: trupti_001@https://www.360docs.net/doc/112527909.html,, baraskartn@https://www.360docs.net/doc/112527909.html, Mobile No. +91-9922789956, +91-20-25462867 Abstract- Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine is a standard for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting information in medical imaging. The National Electrical Manufacturers Association holds the copyright to this standard. It was developed by the DICOM Standards committee. The other image viewers cannot collectively store the image details as well as the patient's information. So the image may get separated from the details, but DICOM file format stores the patient's information and the image details. Main objective is to develop a DICOM image viewer. The image viewer will open .dcm i.e. DICOM image file and also will have additional features such as zoom in, zoom out, black and white inverter, magnifier, blur, B/W inverter, horizontal and vertical flipping, sharpening, contrast, brightness and .gif converter are incorporated. Keyword - Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine (DICOM), National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), Information Object Definitions (IOD), Value Representation (VR). I.Introduction DICOM stands for Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine. The DICOM standard addresses the basic connectivity between different imaging devices and also the workflow in a medical imaging department. The DICOM standard was created by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and it also addresses distribution and viewing of medical images. The standard comprises of 16 parts [1] and it is freely available at the NEMA website: https://www.360docs.net/doc/112527909.html,./dicom.html[2] .Within the innards of the standard are also contained a detailed specification of the file format for images. The latest version of the document is as of 2008[3]. In this article present a viewer for DICOM images DICOM Image File Format This present a brief description of the DICOM image file format. Like other image file formats, a DICOM file consists of a header, followed by pixel data. The header comprises of the patient name and other patient particulars and image details. Important in the image details are the image dimensions - width, height and image bits per pixel. All these details are hidden inside the DICOM file in the form of tags and their values. Before it gets into tags and values, a brief about DICOM itself and related terminology is in place. In what follows, this explains only those terms and concepts related to a DICOM file. In particular, this does not discuss the communication and network aspects of the DICOM standard. Everything in DICOM is an object - medical device, patient, etc. An object, as in object oriented programming is characterized by attributes. DICOM objects are standardized according to IODs (Information Object Definitions). An IOD is a collection of attributes describing a data object. In other words, an IOD is a data abstraction of a class of similar real world objects which defines the nature and attributes relevant to that class [4]. DICOM has also standardized on the most commonly used attributes and these are listed in the DICOM data dictionary [6]. An application which does not find a needed attribute name in this standardized list may add its own private entry, termed as a private tag; proprietary attributes are therefore possible in DICOM. Examples of attributes are study date, patient name, modality, transfer syntax UID, etc. As it can be seen, the attributes require different data types for correct representation. This “data type” is termed as Value Representation (VR) in DICOM. There are 27 such VRs defined[5], and these are AE, AS, AT, CS, DA, DS, DT, FL, FD, IS, LO, LT, OB, OF, OW, PN, SH, SL, SQ, SS, ST, TM, UI, UL, UN, US, and UT. For example, DT represents Date Time, a concatenated date time character string in the format YYYYMMDDHHMMSS.FFFFFF&ZZXX. An important characteristic of VR is its length, which should always be even. Characterizing an attribute are its tag, VR, VM (Value Multiplicity) and value. A tag is a 4 byte value which uniquely identifies that attribute. A tag is divided into two parts, the Group Tag and the Element Tag, each of which is of length 2 bytes. For example, the tag 0010 0020 (in hexadecimal) represents Patient ID, with a VR of LO (Long String). In this example, 0010 (hex) is the group tag, and 0020 (hex) is the element tag. The DICOM data dictionary gives a list of all the standardized group and element tags. Also important is to know whether a tag is mandatory or not. For data element type, five categories are defined - Type 1, Type 1C, Type 2, Type 2C, and Type 3. One more important concept is transfer syntax. In simple terms, it tells whether a device can accept the data sent by another device. Each CP1324,I nt e r nat i onal Conf e r e nc e on M e t hods and M ode l s i n Sc i e nc e and Te c hnol ogy (I CM 2ST-10) e di t e d by R. B. Pa t e l a nd B. P. Si ngh ? 2010 A m e r i c a n I ns t i t ut e of Phys i c s 978-0-7354-0879-1/10/$30.00
DICOM医学图像文件格式
DICOM医学图像文件格式 何斌金永杰 何斌先生,清华大学硕士研究生; 金永杰先生,清华大学教授,博士生导师,中国电子学会核医学电子学专业委员会副主任委员。 关键词: DICOM PACS 数字医学影像系统 为了提升医疗服务水准,跟随医学影像技术和网络技术的发展,我国众多医院都在大量配备各种数字影像设备,并开始建立医院管理信息系统(HIS),开展远程医学试验。他们对于图像存档和传输系统(PACS)的需求越来越紧迫,PACS的应用前景十分诱人。然而,我国PACS的研究开发尚处于起步阶段,尽快自主开发适合我国国情的基于In-tranet的PACS是当务之急。 PACS必需解决的技术问题之一是统一各种数字化影像设备的图像数据格式和数据传输标准。为此,诞生了新的医学数字成像及通信标准,即DICOM 3.0。只要遵照这个标准就可以通过PACS沟通不同厂家生产的、不同种类的数字成像设备。DICOM 3.0已经得到了世界上主要厂商的支持,新一代医学影像设备均以支持该标准作为基本特征,我国的医疗器械开发、生产部门都十分重视这个发展趋势。 DICOM 3.0标准极为庞大、复杂,本文将根据我们的开发经验,介绍如何制定符合DICOM 3.0标准的医学图像文件格式。 一 DICOM概述 DICOM是Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine的缩写,其字面含义很清楚,包括了医学的数字成像和通信两个方面。DICOM标准是由美国放射学院(Ameri-can College of Radiology,ACR)和国家电气制造商协会(National Electrical Manufacturers Association,NEMA)共同制定的。 1. DICOM的发展过程 20世纪70年代以来,计算机断层成像技术(CT)和其它数字成像技术飞速发展,很多厂商都研制了具有计算机的成像设备,制定了各自不同的图像格式。随着计算机网络的普及及其在医学上的广泛应用,在不同厂商生产的设备之间交换图像和相关信息的需求日趋迫切,而缺乏统一的标准成为图像交换的主要障碍。因此,ACR和NEMA在1983年组成一个联合委员会发起制定一个公共的标准,它的目的是: (1) 促进数字图像设备的网络化,而不论设备的开发商是谁。
dicom格式图片怎样转换
Dicom图片转换大师是一个将医学CT图片、MRI图片(dicom/dcm)转换成普通jpg bmp png tif等多达24种图片格式的处理工具,该工具支持批量处理,一次处理多张图片。 dicom转bmp dicom convert to bmp dicom转jpg dicom convert to jpg dicom转jpeg dicom convert to jpeg dicom转jpe dicom convert to jpe dicom转png dicom convert to png dicom转tiff dicom convert to tiff dicom转tga dicom convert to tga dicom转pcx dicom convert to pcx dicom转wbmp dicom convert to wbmp dicom转wmf dicom convert to wmf dicom转emf dicom convert to emf dicom转jp2 dicom convert to jp2 dicom转j2c dicom convert to j2c dicom转jpc dicom convert to jpc dicom转pgx dicom convert to pgx dicom转pnm dicom convert to pnm dicom转pgm dicom convert to pgm dicom转ppm dicom convert to ppm dicom转ras dicom convert to ras dicom转mng dicom convert to mng dicom转jng dicom convert to jng dicom转ska dicom convert to ska dicom转raw dicom convert to raw
dicom图像显示
DICOM(Digital Imaging Communications in Medicine)标准是医学数字成像和通信的国际标准。DICOM虽然是在美国产生、发展的,但已被欧洲各国、日本等发达国家和地区接受,并被列入国家标准。在我国,DICOM是唯一被接受的医疗影像国际规范。DICOM 已经成为国际医疗影像设备的图像通信/交流的唯一规范。DICOM标准逐渐得到国内外的高度重视,一些科研机构和高等院校纷纷展开了对标准的研究和基于标准的开发。因此对DICOM标准文件的正确解读是医学数字图像处理和建设的关键技术之一。 1 DICOM文件的数据结构和编码规定 DICOM格式文件包括了数字成像和通信两个方面内容。该文件格式基于面向对象的思想,制定了一系列信息对象定义和服务对象定义,文件的数据结构和编码规则包含了数字成像和通信的真实信息[1]。 1.1 DCM文件的结构DCM是比较常用的DICOM文件名后缀,其他PACS软件也使用到了IMG,或是完全不使用后缀,直接就是一连串的数字或字符串命名的。DCM文件从本质上说是一个关于信息体实例的数据集,主要包括患者、检查、序列和图像等信息。文件的结构主要由文件头和文件结构像素数据两大部分组成,文件头又分为文件引言和数据集两部分,其中文件引言是由128个全部置为00的字节序列和一个长度为4个字节的字符串组成[2]。数据集是整个文件中信息量最大的部分,囊括了所有信息实体(患者、图像、检查等)的信息,结构也最为复杂,文件最后的图像数据表示像素,数据结构单一,因此解读文件实际上就是解读数据集。 1.2 DICOM数据集结构数据集由多个数据元素串连组成,每个数据元素具有类似的结构,都是由标签、值描述、值长度和值域组成。标签表示该数据元素的特定含义。每个标签在整个数据集中只能出现1次(嵌套除外),共4个字节,分为组号(高位两字节)和元素号(低位两字节)。如00100010表示该数据元素里的信息为患者姓名。标签含义的详细规定在标准的3.62004(数据字典)中。描述了该数据元素中值域的数据种类,大多数情况下是一个长度为2字节的字符串。值得注意的是标签是可选的,取决于商定的传输语法。值域表示该数据元素所保存的实际信息,必须为偶数个字节,不足补0或空格。 2 DCM文件的读取 理解了文件的结构和数据集的结构,解读文件就不是一件很难的事情,但有些关键性的问题如数据嵌套、高位截取等在读取时需要注意。 2.1 数据嵌套当数据元素的值为0时,则该数据元素的值域又是由1个或多个数据元素组成的,即数据元素中包含了子数据集。如果子数据集中又有值为0的数据元素时,就构成了递归嵌套。嵌套的存在要求解读算法能遍历树型数据结构的所有元素。 2.2 图像数据的高位截取通常文件采取2个字节表示1个像素,但是一般情况下,真实像素值的动态范围不足以完全填满这2个字节。因此,高字节的高位可能因为被用于存储其他信息。解读图像数据时应该截取高位,把低位的信息读取出来。标准规定标签为00280101的数据元素储存像素数据的最高位数,标签为00280102的数据元素储存实际存储像素数据的位数。对于某些图像,图像数据中储存的像素值没有实际意义,需要采用斜率和截距来修正,而斜率和截距则储存在标签为00281053和00281052的数据元素中。因
