国际结算 英文版5.1-5.5 Letters of credit(1)

Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
1
5. Letters of credit
5.1-5.5 General introduction
5.1 Definition 5.2 Procedures 5.3 Characteristics
5.4 Parties’ liabilities and rights
5.5 contents
5.6 Examination of a documentary credit
5.7 Types of credit
5.8 Financing provided by banks
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
2
About UCP
The formal maturation of the letter of credit was in the 1920’s;
ICC Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credit (UCP)
Versions of 1933,1951,1962, 1974,1983 and 1993(UCP500);
The latest version is UCP600
ISBP subject to UCP 600 (ICC Publication No. 681)
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 35.1 What is a letter of credit
According to UCP600 Article 2:
Credit means any arrangement, however named or described, that is irrevocable and thereby constitutes a definite undertaking of the issuing bank to honour a complying presentation .
信用证指一项不可撤销的安排,无论其名称或描述如何,该项安排构成开证行对相符交单予以承付的确定承诺。
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 4
“Provided that the stipulated documents are presented to the nominated bank or to the issuing bank and that they constitute a complying presentation, the issuing bank must honour...”
In simple terms, a credit is a conditional bank undertaking of payment.
In UCP600 Article 7 a.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
5
Irrevocable:
“A credit is irrevocable even if there is no indication to that effect.”
In 500, the Art 2 gave the meaning of credit and four types of L/C, and in Art 6 the
irrevocable and revocable L/C were listed at the same time,
The revocable L/C has been deleted and all L/Cs are irrevocable under UCP600.
In UCP600 Article 3 Interpretations
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 6
Undertakeing:
to put oneself under obligation to perform; also to accept as a charge or responsibility
该词在英美法中具有特定含义,专指行为人单方自行承担的一种义务,无须对价支持即具有可执行性,一般具有无因性、独立性,不受其可能基于的其他交易下的抗辩影响。
UCP600中译为“承诺”、“责任”、“承担……责任”
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 7
Issuing bank (开证行,opening bank) “means the bank that issues a credit at the request of an applicant or on its own behalf.”
It is usually the bank located in the importer ’s place.
In UCP600 Article 2 Definition
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 8
Honour (承付)means:
a. to pay at sight if the credit is available by sight payment. (即期付款信用证)
b. to incur a deferred payment undertaking and pay at maturity if the credit is available by deferred payment. (延期付款信用证)
c. to accept a bill of exchange (“draft ”) drawn by the beneficiary and pay at maturity if the credit is available by acceptance. (承兑信用证)
In UCP600 Article 2 Definition
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
9
Complying presentation (相符交单)
means a presentation that is in accordance
with the terms and conditions of the credit, the applicable provisions of these rules,and international standard banking practice.
Compared with UCP500: “…against stipulated document(s), provided that the terms and
conditions of the credit are complied with ”(单证相符)
In UCP600 Article 2 Definition
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
10
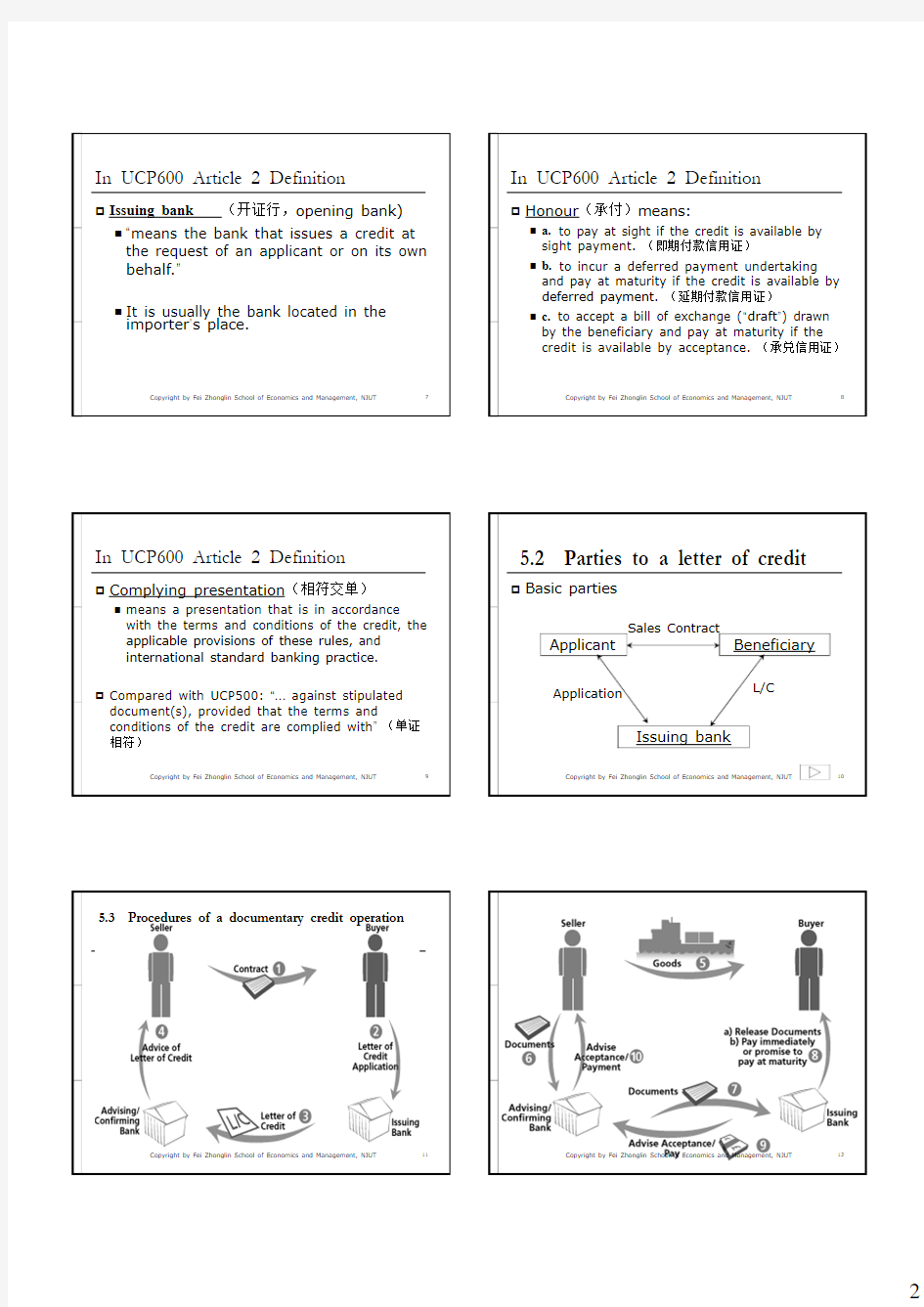
5.2 Parties to a letter of credit
Basic parties
Applicant
Beneficiary
Issuing bank
Application
Sales Contract
L/C
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 115.3 Procedures of a documentary credit operation
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 12
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 13
5.4 Characteristics of a credit
A written undertaking on the part of the issuing bank
Art. 7 b.An issuing bank is irrevocably
bound to honour as of the time it issues the credit.
Art. 6 c. A credit must not be issued available by a draft drawn on the applicant.
Bank credit
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
14
Independent of the sales contract
Art 4 a.A credit by its nature is a separate transaction from the sale or other contract on which it may be based. Banks are in no way concerned with or bound by such contract, even if any reference whatsoever to it is included in the credit.
The parties to a letter of credit are only bound by the terms and conditions of the credit itself.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 15
Exclusively dealing with documents
Art 5 :Banks deal with documents and not with goods, services or performance to which the documents may relate.
Under UCP500:The documents comply with the terms and conditions of the credit and
documents are consistent with one another. (单单一致,单证相符)
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 16
Applicant (开证申请人)
“means the party on whose request the credit is issued.”
It is
the buyer under the sales contract account party (US)
consignee (收货人)on the Bill of Lading
In UCP600 Article 2 Definition
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 17Applicant ’s liability and rights
Submit application for issuing a credit in
accordance with the stipulation of sales contract and pay a certain percentage of cash deposits;
Make payment to the issuing bank if there ’s complying presentation;
Examine the documents received from issuing bank and has the right to refuse payment if discrepancies (不符点)are found.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 18
Beneficiary (受益人)
“means the party in whose favour a credit is issued.”
It is
the seller under the sales contract
consignor (发货人)on the Bill of Lading
In UCP600 Article 2 Definition
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
19
Beneficiary ’s liabilities and rights
Carry out the contract and complete the export documents;
Examine the L/C to see whether the terms and conditions on the credit comply with those in the sales contract;
Obtain the payment if no discrepancy among above documents;
Refuse the L/C and ask for amendment if there ’s any discrepancy.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
20
UCP600 Article 7 Issuing Bank undertaking
a . Provided that the stipulated documents are presented to the nominated bank or to the
issuing bank and that they constitute a complying presentation, the issuing bank must honour, if the credit is available by ……
b. An issuing bank is irrevocably bound to honour as of the time it issues the credit.
c. An issuing bank undertakes to reimburse a nominated bank that has honoured or negotiated a complying presentation and forwarded the documents to the issuing bank ……
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 21
Open L/C according to the instruction of the application and get the deposits from the applicant;
Refuse to pay if there ’s any discrepancy with the documents submitted.
Issuing bank ’s liability and right
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 22
In UCP600 Article 2 Definition
Nominated bank (指定银行)
means the bank with which the credit is available or any bank in the case of a credit available with any bank.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 23In UCP600 Article 2 Definition
Negotiation 议付
means the purchase by the nominated bank of drafts (drawn on a bank other than the
nominated bank ) and/or documents under a complying presentation , by advancing or agreeing to advance funds to the beneficiary on or before the banking day on which
reimbursement is due to the nominated bank.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 24
Other parties
Advising bank/ Transmitting bank 通知行/转递行 Confirming bank 保兑行
Paying bank/ Accepting bank 付款行/承兑行
Negotiating bank 议付行
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
25
Advising bank/ Transmitting bank
A bank in the seller ’s country that receives the credit from the issuing bank.
To check the apparent authenticity of the credit; to inform or advise the seller (beneficiary) that the credit is available.
“An advising bank …advises the credit and any amendment without any undertaking to honour or negotiate .”(Art. 9 a)
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 26
Usually selected by the issuing bank.
An advising bank may utilize the services of
another bank (“second advising bank ”), the latter has the same right with the former.
Note that unless the credit specifies otherwise, the beneficiary is not required to present documents to or through the advising bank.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
27
Confirming bank (UCP600 Art.2)
Confirming bank means the bank that adds its confirmation to a credit upon the issuing bank ’s authorization or request.
Confirmation means a definite undertaking of the confirming bank, in addition to that of the issuing bank, to honour or negotiate a complying presentation.
a Confirming Bank acts the role of second Issuing Bank, therefore it should undertake the same responsibility as the Issuing Bank.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
28
The Paying Bank/Accepting Bank
The bank nominated by the issuing bank, to which the beneficiary is directed to present documents for payment, acceptance, or a deferred payment.
To claim reimbursement from the Issuing Bank after payment.
Lose its right of recourse to the beneficiary after payment.
The Paying Bank is the drawee bank of the draft drawn by the Beneficiary, and the payment of the drawee will discharge the draft.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT 29
The Negotiating Bank
Difference from the paying bank:
Has the right of recourse to the beneficiary.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT
30
Benefits for the exporter
Bank credit is better than trade credit.
The payment commitment is made by a third party —a bank.
Most banks, in most countries, are responsible and reliable, and generally believed to adhere to ethical business practices and to exercise prudence in their commercial dealings.
The precondition for obtaining payment is to provide the correct documents to the issuing bank at the right place on time.
Benefits for the importer
The Issuing Bank provides credit to him once issuing the credit.
The ability to obtain a letter of credit expands the buyers purchasing power.
Only creditworthy buyers can obtain an L/C
from the issuing bank.
Cash deposits will be required for those who
are not creditworthy.
Copyright by Fei Zhonglin School of Economics and Management, NJUT31
《国际结算》补充习题与答案(第6讲)范文
第6部分补充习题 一、填空题 1.信用证支付方式的特点为:信用证是____________、是____________、是____________。 2.在信用证业务中,开证行是以____________的名义向受益人作出有条件付款保证的。 3.____________是信用证的开立基础,是进口人凭以____________、出口人凭以审核信用证的依据。 4.信用证的开证形式有____________和____________两种。 5.信用证中所要求的单据一般包括____________、____________、____________及____________。 6.SWIFT是____________________________________的英文缩写。 7.信用证是____________银行应进口商要求向出口商开立的,在一定条件下保证付款的一个书面承诺文件。 8.信用证的当事人有____________、____________、____________、____________、____________、____________、____________、____________等。 9.分析信用证业务下的契约,受益人与开证申请人之间存在一份____________,开证申请人与开证行之间有一份____________,而开证行与受益人之间则是由____________来联结的。 10.信用证的开证申请人一般是____________。 11.信用证结算的基本当事人有____________、____________、____________等。 12.跟单信用证应贯彻____________和____________的原则。 13.跟单信用证业务有____________、____________、____________特点。 二、单选题 1.信用证要求_________开立汇票,作为支取信用证款项下的凭证 A.通知行 B.议付行 C.受益人 D.开证行 2.在L/C、D/P和D/A三种支付方式下,就卖方风险而言,按由大到小顺序排列,哪个正确_________ A.L/C>D/A>D/P B.L/C>D/P>D/A C.D/A>D/P>L/C D.D/P>D/A>L/C 3.如果获悉贸易合同所规定的货物在运输途中灭失了,开证申请人_________要求开证行停止审单付款。 A.有权 B.无权 C.经开证行同意才有权 D.经保兑行同意才有权 4.跟单信用证业务中,三角契约安排规定了开证银行与受益人之间权责义务受_________约束。 A.销售合同 B.开证申请书 C.担保文件 D.跟单信用证 5.国际贸易中贸易额特别大时,一般采取_________方式结算。 A.国际汇兑结算 B.信用证结算 C.托收结算 D.预付货款 6.下列提法中不正确的是_________。
国际结算英文版课后练习答案.doc
Chapter One 1.Fill in the blanks to complete each sentence. (1)local legal system, political, exchange risks (2)open account, advance payment, remittance and collection (3)letter of credit, bank guarantee (4)price terms, delivery terms (5)least/minimum, most/maximum (6)advance payment (7)open account (8)clean collection, documentary collection 2.略 3.Translate the following terms into English. (1)settlement on bank credit (2)the potential for currency fluctuation (3)to dear the goods for export (4)to pay the insurance premium (5)to carry out export formalities (6)the major participants in international trade (7)the commodity inspection clause (8)to fulfill the obligation to deliver the goods (9)the goods have passed over the ship's rail (10)International contract is concluded in a completely different context than domestic ones 4.Decide whether the following statements are true or false. ⑴ F (2)F (3)T (4)T (5) T (6)T (7)F (8)T (9)T (10) F 5.Choose the best answer to each of the following statements ⑴?(5) BCCBD (6)-(10) DACCC (11)-(15) BDDCD (16)-(20) DCACD Chapter Two 1. Fill in the blanks to complete each sentence. (1)barter (2)medium of exchange (3)expensive, risky (4)our ⑸ Vostro (6)vostro ⑺ nostro (8) specimen of authorized signatures, telegraphic test keys, terms and conditions, Swift authentic keys 2. Define the following terms (1)Correspondent relationship KA bank having direct connection or friendly service relations with another bank.』 (2)International settlements [[International settlements are financial activities conducted among different countries in which payments are effected or funds are transferred from one country to another in order to settle accounts, debts, claims, etc. emerged in the course of political, economic or cultural contracts among them. 3 (3)Visible trade [[The exchange of goods and commodities between the buyer and the seller across borders.2 (4)Financial transaction [[International financial transaction covers foreign exchange market transactions^ government
国际结算英文术语
国际结算英文术语
国际结算(International settlement) 贸易(Trade Settlement) 非贸易(Non-Trade Settlement) EDI(Electronic Data Intercharge)电子数据交换, 控制文件(Control Documents) 有权签字人的印鉴(Specimen Signatures) 密押(Test Key) 费率表(Terms and Condition) 货物单据化,履约证书化,( cargo documentation , guarantee certification) 权利单据(document of title) 流通转让性(Negotiability) 让与(Assignment) 转让(Transfer) 流通转让(Negotiation) 汇票的定义是:A bill of exchange is an unconditional order in writing, addressed by one person to another, signed by the person giving it, requiring the person to whom it is addressed to pay on demand or at a fixed or determinable future time a sum
payable at days/ months after stated date) ④板期付款(bills payable on a fixed future date) ⑤延期付款(bills payable at days/months after shipment/ the date of B/L) 收款人名称(payee) 同样金额期限的第二张不付款”〔pay this first bill of exchange(second of the same tenor and dated being unpaid) 需要时的受托处理人(referee in case of need)出票人(drawer) 收款人(payee) 背书人(endorser) 被背书人(endorsee) 出票(issue) (1)制成汇票并签字(to draw a draft and to sign it); (2)将制成的汇票交付给收款人(to deliver the draft
国际结算英语翻译
1.汇票的制作10个项目 汇票的内容又分为绝对必要项目和相对必要项目。绝对必要项目:1.有“汇票”的字样。2.无条件支付命令。3.确定金额4.收款人名称5.付款人名称6出票日期7出票人签章 相对必要项目:1.出票地2.付款地3.付款日期 2.支票的种类 按抬头不同分类:1.记名支票2.不记名支票 对付款闲置不同分类:1.普通支票:可取现金。2.划线支票:不可取现金,只能转账。划线支票好处在于可以延缓交易时间,可以便于追踪资金轨迹。划线支票又分为特别划线支票和一般划线支票。特别划线支票平行线会加注付款账号行名称。一般划线无须固定账户。 按是否可以流通分为可流通支票和不可流通支票。 3.提单的总类 按提单收货人的抬头划分:1.记名提单,不记名提单,指示提单。 按货物是否已装船划分:1.已装船提单,收妥备运提单。 按提单上有无批注划分:1.清洁提单2不清洁提单。 按照运输方式的不同划分为:1.直达提单2转船提单3.联运提单4.多式联运提单 按签发提单的时间划分为:1.正常提单2过期提单3.预借提单4.倒签提单 4.信用证的种类 1.不可撤销信用证 2.保兑信用证 3.即期付款信用证,迟期信用证,议付信用证,承兑信用证。 4.假远期信用证 5.红条款信用证 6.循环信用证 7.可转让信用证8背靠背信用证9对开信用证 5.托收的种类 托收根据金融单据是否伴随商业单据分为光票托收和跟单托收。跟单托收又根据票据的期限分为付款交单(D/P)(即期)和承兑交单(D/A)(远期)。付款交单是指付款人对即期汇票付款然后交单。而承兑交单是指付款人对远期汇票承兑而进行交单。 汇票 BILL OF EXCHANGE No. 汇票编号Date: 出票日期 For: 汇票金额 At 付款期限sight of this second of exchange (first of the same tenor and date unpaid) pay to the order of 受款人 the sum of金额 Drawn under 出票条款 L/C No. 信用证号Dated 信用证开征时间 To. 付款人 出票人签章
国际结算(1)剖析
国际结算 第一章国际结算概述 1、国际结算:两个不同国家的当事人,不论是个人、单位、企业或政府间因 为商品买卖、服务供应、资金调拨、国际借贷而需要通过银行办理的两国间的外汇收付业务,叫做国际结算。 2、国际结算业务的分类(了解一下) 按照使用结算支付手段的不同,国际结算业务大体可以分为以下四类: (1)现金/货币结算:如果国际结算业务使用现金或货币结算,则其必须是可自由兑换的货币 (2)票据结算: 贸易结算中使用的汇票是逆汇形式,即债权人或其代理人作为出票人,命令受票行/付款行将票款付给出票人自己或其代理人。汇票和本票均为可流通票据,可以背书转让。 (3)凭单结算:海运提单具有货物收据、运输合约和物权单据三种作用 (4)电讯结算: 汇出行发出电讯汇款指示给汇入行,委托汇入行解付汇款给收款人。 第二章国际结算中的票据 1、票据流通的形式(大概知道对应的有哪些类型) (一)过户转让或通知转让:采用过户转让的票据有股票、人寿保险单、政府证券、债券等,它们不是完全可流通的证券。 (二)交付转让:采用交付转让的票据有提单(B/L)、仓单(Warehouse Receipt)、栈单(Dock Warrants)、写明“不可流通”字样的划线支票或即期银行汇票(Not Negotiable Crossed Cheque or Demand Draft)等,它们是准流通证券(Quasi-negotiable Instruments)或半流通证券(Semi-negotiable Instruments)。(三)流通转让:采用流通转让的票据有汇票、本票、支票、国库券、大额定期存单(Certificate of Deposit)、不记名债券(Bearer Securities)等,它们是完全可流通证券(Negotiable Instruments)。 2、票据的特性 (一)流通性:除非票据上写出“禁止转让”字样,或是表示它是不可转让的意旨以外,一切票据不论它是采用任何形式支付票款给持票人,该持票人都有权把它流通转让给别人。
国际结算1-5章选择判断
国际结算习题第四章托收结算方式。 二、是非题 1.托收是一种付款人主动向收款人支付货款的方式。() 【答案】× 2.在托收业务中,银行的一切行为是按照托收委托书来进行的。() 【答案】√ 3.光票托收和跟单托收一样,都是用于贸易款项的收取。() 【答案】× 4.托收因是借助银行才能实现货款的收付,所以托收是属于银行信用。() 【答案】× 5.从理论上讲,承兑交单相比于付款交单对于买方更为便利,因为承兑交单中买方承兑后即可提货,往往可以不必自备资金而待转售所得的货款到期时付款。() 【答案】√ 6.托收业务中,代收行对于汇票上的承兑形式,只负责表面上完整和正确之责,不负签字的正确性,或签字人是否有权限签署之责。() 【答案】√ 7.委托人在出口托收申请书上可指定代收行,如不指定,委托行可自行选择它认为合适的银行作为代收行。委托行由于使用其他银行的服务而发生的费用和风险,在前种情况下由委托人承担,在后种情况下由委托行承担。() 【答案】× 8.托收业务中,只要选择合适的委托行和代收行,委托人收回货款就不成问题。() 【答案】× 9.相比于付款交单,承兑交单一定是远期付款,对买方比较有利。() 【答案】√ 10.无论何种情况下,代收行同意进口商凭信托收据借货后产生的风险和后果都由出口商承担。() 【答案】× 国际结算习题 第一章国际结算概述 单项选择题: 1. 商品进出口款项的结算属于( C ) A . 双边结算 B . 多边结算 C . 贸易结算 D . 非贸易结算 2. “汇款方式”是基于( B )进行的国际结算 A . 国家信用 B . 商业信用 C . 公司信用 D . 银行信用 3. 实行多边结算需使用( D ) A . 记账外汇 B . 外国货币 C . 黄金白银 D . 可兑换货币 4. 以下( C )反映了商业汇票结算的局限性 A . 进、出口商之间业务联系密切, 相互信任; B . 进、出口商一方有垫付资金的能力;
国际结算(英文版)清华大学出版社-答案
国际结算(英文版)清华大学出版社-答案
KEY OF INTERNATIONAL SETTLEMENT Chapter 1 I.Put the following phrases into English 2.Put the following sentences into English (1)国际结算涉及有形贸易和无形贸易,外国投资, 从其他国家借贷资金,等等。
The international settlement involves tangible trades, intangible trades, foreign investments, funds borrowed from or lent to other countries and so on. (2)许多银行注重发展国际结算和贸易融资的业 务。 Many banks have focused on their business of international settlement and trade finance. (3)大多数国际间的支付来自于世界贸易。 Most of the international payments originate from transactions in the world trade. (4)一般来说,国际结算的方式分为三类:汇款、 托收和信用证。 Usually the international settlement is divided into three broad categories: remittance, collection and letter of credit. 3.True or False 1)I nternational payments and settlements are finan cial activities con ducted in the domestic coun try. (F)
国际结算 英文名词翻译 按章整理
英文名词翻译 第一章 国际结算导论 international settlement 美国CHIPS 系统:纽约清算银行同业支付系统 英国CHAPS 系统: 清算所自动支付体系 布鲁塞尔SWIFT 系统: 环球银行金融电讯协会 (Critical Point for Delivery) 交货临界点 (Critical Point for Risk) 风险临界点 (Critical Point for Cost)费用临界点 《国际贸易术语解释通则》 Incoterms2000 visible trade :有(无)形贸易 (representative office) 代表处 ( agency office)代理处 (overseas sister bank /branch,subbranch )海外分/支行 (correspondent bank ) 代理银行 (subsidiary bank )附属银行(子银行) (affiliated banks ) 联营银行 (consortium bank )银团银行 甲行以乙国货币在乙行设立帐户: 甲行是往帐(Nostro a/c),即我行在你行设帐(Our a/c with you ) 乙行以甲国货币在甲行设立帐户 甲行是来帐(V ostro a/c),即你行在我行设帐(Your a/c with us ) 在银行实际业务中,增加使用“贷记”(To Credit ),减少使用“借记”(To Debit ) 第二章 票据Instrument drawer 出票人 drawee/payer 付款人 payee 收款人 endorser 背书人 endorsee 被背书人 holder in due course 善意持票人 acceptor 承兑人 guarantor 保证人 bill of exchange 汇票 mandatory elements issue 出票 endorsement 背书 presentation 提示 acceptance 承兑 payment 付款 dishonor 拒付 recourse 追索 guarantee 保证 限制性抬头 restrictive order (pay E company only)(pay E company not transferable) 指示性抬头 demonstrative order (pay to the order of B company)(pay to B company or order) 持票来人抬头 payable to bearer (pay to bearer)(pay to A company or bearer) UCP600:《跟单信用证统一惯例》 URC 522 ;《托收统一规则》 URDG458:《见索即付保函统一规则》 URR 525:《跟单信用证项下银行间偿付统一规则》 URCB524:《合同保函统一规则》
(完整word版)第一章国际结算概述练习题
第一章国际结算概述 名词解释 国际结算、国际贸易结算、国际非贸易结算、双边结算制度、国际结算信用管理 单项选择题: 1. 商品进出口款项的结算属于( ) A . 双边结算 B . 多边结算 C . 贸易结算 D . 非贸易结算 2. “汇款方式”是基于( )进行的国际结算 A . 国家信用 B . 商业信用 C . 公司信用 D . 银行信用 3. 实行多边结算需使用( ) A . 记账外汇 B . 外国货币 C . 黄金白银 D . 可兑换货币 4. 以下( )反映了商业汇票结算的局限性 A . 进、出口商之间业务联系密切, 相互信任; B . 进、出口商一方有垫付资金的能力; C . 进、出口货物的金额和付款时间不一致; D . 出口商的账户行不在进口国 5. 当代国际结算信用管理的新内容涉及到( ) A . 系统信用和司法信用 B . 员工信用和银行信用 C . 公司信用和商业信用 D . 银行信用和商业信用 6. 以下 ( )引起的货币收付,属于“非贸易结算”. A. 服务供应 B . 资金调拨 C . 设备出口 D. 国际借贷 7. ( )不是纸币本位制度下使用多边结算方式必备的条件. A . 结算货币具有可兑换性 B . 不实行资本流动管制 C . 有关国家的商业银行间开立各种清算货币的账户 D . 清算账户之间资金可以自由调拨 8. 建国初我国对苏联和东欧国家的贸易使用( )的方式 A . 单边结算 B . 多边结算 C . 双边结算 D .集团性多边结算 9. 传统的国际贸易和结算中的信用主要是( )两类。 A .系统信用和银行信用 B . 系统信用和司法信用 C .商业信用和司法信用 D . 商业信用和银行信用 10. 国际结算制度的核心即是( )。
国际结算双语课程标准--英文版
International settlement(bilingualism) course standard First, summary of course It is the core course of international economic and trade major, based on the operating skills’cultivation about methods of international settlement, combining theory with reality, emphasising on positional operation, paying attention to the cultivation of comprehensive ability about finding, analyzing and solving problems, etc. Second, before and after courses International settlement(before courses are International trade practice (bilingualism)、International business documents) , after courses are international trade business comprehensive trading and Foreign trade correspondence. Third, the course content
国际结算(英文版)清华大学出版社-答案
KEY OF INTERNATIONAL SETTLEMENT Chapter 1 1.Put the following phrases into English 2.Put the following sentences into English (1)国际结算涉及有形贸易和无形贸易,外国投资,从其他国家借贷资金,等等。 The international settlement involves tangible trades, intangible trades, foreign investments, funds borrowed from or lent to other countries and so on. (2)许多银行注重发展国际结算和贸易融资的业务。 Many banks have focused on their business of international settlement and trade finance. (3)大多数国际间的支付来自于世界贸易。 Most of the international payments originate from transactions in the world trade. (4)一般来说,国际结算的方式分为三类:汇款、托收和信用证。 Usually the international settlement is divided into three broad categories: remittance, collection and letter of credit.
3. True or False 1)International payments and settlements are financial activities conducted in the domestic country. (F) 2)Fund transfers are processed and settled through certain clearing systems.(T) 3)Using the SWIFT network, banks can communicate with both customers and colleagues in a structured, secure, and timely manner.(T) 4)SWIFT can achieve same day transfer.(T) 4.Multiple Choice 1)SWIFT is __B__ A.in the united states B. a kind of communications belonging to TT system for interbank’s fund transfer C.an institution of the United Nations D. a governmental organization 2)SWIFT is an organization based in __A___ A.Brussels B.New York C.London D.Hong Kong 3) A facility in fund arrangement for buyers or sellers is referred to __A___ A.trade finance B.sale contract C.letter of credit D.bill of exchange 4)Fund transfers are processed and settled through __C___
《国际结算》补充习题与答案(第5讲)教学文稿
《国际结算》补充习题与答案(第5讲)
第5部分补充习题 一、填空题 1.在托收结算方式下,银行对出口商、进口商可以采取以下几种方式进行资金融通,____________,____________,____________,____________。 2.托收按交单条件不同,可分为____________和____________两种。其中就卖方风险而言,____________风险小些。 3.托收的基本当事人有____________、____________、____________、____________和____________。 4.托收的种类,按照委托托收时是否附带货运单据来划分,一般可分为两种:____________和____________。 5.托收业务中“需要时的代理人”是指发生____________时,受委托人指定代为____________的代理人。 6.托收的交单条件有____________、____________、____________和____________等。 7.卖方仅开立汇票而不附任何货运单据委托银行收取款项的托收结算方式称为____________。 8.跟单托收的交单条件可分为____________和____________。 9.付款交单指代收行必须在进口商付清票款后,才将____________交给进口商的交单条件。 10.托收和汇款方式是____________信用。 二、单选题 1.D/P·T/R意指_________ A.付款交单 B.承兑交单 C.付款交单凭信托收据借单 D.承兑交单凭信托收据借单 2.某出口公司有一笔托收业务,为了安全收汇就擅自采取将提单收货人作成代收行名称,要求代收行在付款人付清货款后才能放货。这样若付款人不付款,货权仍掌握在代收行手中,付款人无法提货。这种办法_________。 A.不可行 B.可行 C.国际惯例中并未涉及 D.不一定 3.以下关于托收指示说法错误的是:_________。 A.是根据托收申请书缮制的 B.是代收行进行托收业务的依据 C.是托收行制作的 D.是托收行进行托收业务的依据 4.D/P和D/A做法步骤不同主要发生在_________之间。 A.委托人与托收行 B.委托人与代收行 C.托收行与代收行 D.代收行与付款人 5.国际货物买卖使用托收方式,委托并通过银行收取货款,使用的汇票是_________。 A.商业汇票,属于商业信用 B.银行汇票,属于银行信用 C.商业汇票,属于银行信用 D.银行汇票,属于商业信用 6.承兑交单的简称是________. A.D/P B.D/A C.O/A D.B/L 7.合同中规定采用D/P30天的托收方式付款,托收日为8月l日,如寄单邮程为7
国际结算英文术语
国际结算(International settlement) 贸易(Trade Settlement) 非贸易(Non-Trade Settlement) EDI(Electronic Data Intercharge)电子数据交换, 控制文件(Control Documents) 有权签字人的印鉴(Specimen Signatures) 密押(Test Key) 费率表(Terms and Condition) 货物单据化,履约证书化,( cargo documentation , guarantee certification) 权利单据(document of title) 流通转让性(Negotiability) 让与(Assignment) 转让(Transfer) 流通转让(Negotiation) 汇票的定义是:A bill of exchange is an unconditional order in writing, addressed by one person to another, signed by the person giving it, requiring the person to whom it is addressed to pay on demand or at a fixed or determinable future time a sum certain in money to the order or specified person or to bearer. “汇票” (bill of exchange,exchange或draft) 无条件支付命令(unconditional order to pay) 出票条款(drawn clause) 利息条款(with interest) 分期付款(by stated instalment) 支付等值其它货币( pay the other currency according to an indicated rate of exchange) 付款人(payer)受票人(drawee) 付款期限(time of payment)或(tenor) 即期(at sight, on demand, on presentation)付款。 远期(at a determinable future time , time/ usance / term bill)付款。 期限远期付款的表现形式: ①见票后若干天(月)付款(bills payable at days/ months after sight) ②出票后若干天(月)付款(bills payable at days/ months after date) ③预定日期后若干天(月)付款(bills payable at days/ months after stated date) ④板期付款(bills payable on a fixed future date) ⑤延期付款(bills payable at days/months after shipment/ the date of B/L) 收款人名称(payee) 同样金额期限的第二张不付款”〔pay this first bill of exchange(second of the same tenor and dated being unpaid) 需要时的受托处理人(referee in case of need) 出票人(drawer) 收款人(payee) 背书人(endorser) 被背书人(endorsee) 出票(issue)
第一章 国际结算导论 习题及答案
第一章国际结算导论 复习思考题 一、填空题 1.国际结算是指世界各个国家或地区相互之间,为了清算债权、债务关系而发生的()。 2.现代国际结算的主要工具是( )。 3.记账贸易结算,也称为( ) 。它是在两国政府所签订的贸易协定项下的商品进出口贸易结算。 4.推定交货原理的实质就是 ( ) ,以货物单据代表货物所有权,常称为以单代物。 5.国际结算一般使用可兑换货币进行结算,但不是所有的可兑换货币均可用于国际支付和国际结算。国际贸易及经济活动集中使用的货币称为()货币,主要指美元、欧元和日元等。 6.非现金结算是指使用各种( ),通过银行间的划账冲抵来结清国际间债权债务关系。 7.支付系统是由提供()的中介机构和实现支付指令传送及资金清算的专业技术手段共同组成,用以实现债权债务清偿及资金转移的一种金融安排,有时亦称清算系统。 8.全额实时结算是对每一笔支付业务的发生额立即单独全部进行交割,是()进行结算。 9.为保证国际结算的顺利进行,不同国家的银行之间通常建立()关系以便于国际业务的顺利进行。 10.两家分处不同国家的商业银行,因发生货币收付业务的需要,或者一方在对方设账,或者相互设账,就建立了()关系。 二、单选 1.现代国际结算就是指通过银行办理的国与国之间的()收付业务。 A、信用证 B、支票 C、货币 D、汇票 2.下列哪项不属于国际结算得范围:() A 、有形贸易类B、物物交换类C、无形贸易类D、金融交易类 3.结算工具包括货币现金、()以及电报、邮寄支付凭证等。 A 、票据B、黄金C、信用卡D、代金券 4.现金结算已越来越不符合实际的需要,于是出现了()等非现金结算方式。 A、黄金 B、铸币 C、商业汇票 D、股票 5.一般而言经营银团贷款业务的是()。 A、银团银行 B、办事处 C、代理银行 D、联营银行 6.在对海外银行的选择上,银行最先选择()协助办理国际结算业务。 A、账户行 B、办事处 C、代理行 D、联行 7.下列属于国际银行间非营利性组织的是()。 A、FEDWIRE B、CHIPS C、TARGET D、SWIFT 8.A行在B行设立B行所在国货币的账户,下列说法正确的是( )。 A、从A行的角度看,这个账户是往账 B、从B行的角度看,这个账户是往账 C、从A行的角度看,这个账户是来账 D、上述说法均不正确。
金陵科技学院《国际结算》(英文版)习题集
《国际结算》(英文版)习题集 Chapter 1: International Settlement under Globalization 5. Please decide whether the following statements are true or false. (1) Greater imports offer consumers a wider variety of goods at higher prices, while providing strong incentives for domestic industries to remain competitive. ( ) (2) Information technology makes the international trade more efficient than ever. ( ) (3) International lending is often accompanied by international payments. ( ) (4) Under the term CFR, it is the seller’s responsibility to insure the goods transported. (5) Cash in advance, open account, collection and documentary credit are the usual methods of payment to settle international trade transactions. ( ) (6)To the exporter of goods, the most satisfactory arrangement as far as payment is concerned is to receive it in advance. ( ) (7) Trade on open account arrangement usually satisfies the seller’s desire for cash and the import’s desire for credit. ( ) 6. Please choose the answers to each of the following questions. (1) international payments and settlements may arise from( ). A. commercial payments B. payments for the services rendered C. payments between governments D. transfer of funds among countries. (2) An additional risk borne by the seller when granting a credit to the buyer is that the latter will not_______. A. accept the bill B. take up the documents C. take delivery D. make payment at maturity (3) To the exporter, the fastest and safest method of settlement is_____. A. letter of credit B. advance payment C. collection D. banker’s draft (4) To the importer, the fastest and safest method of settlement is_____. A. letter of credit B. cash in advance C. open account D. banker’s draft 7. Please answer the following questions. (1) Explain the definition of international settlement. (2) How many main types of international settlement methods are used in the internatinal trade? (3) What are the liabilities of a exporter in the international settlement?
参考资料:《国际结算》相关术语中英文对照与中文名词解释
参考资料:《国际结算》相关术语中英文对照 国际结算 International Settlement 有形贸易 Visible Trade 无形贸易 Invisible Trade 洗钱 Money Laundering 支付协定 Payment Agreement 国际结算制度 System of International Settlement 支付系统 Payment System 代表处 Representative Office 代理处 Agency Office 海外分、支行(境外联行) Overseas Sister Bank/Branch,Subbranch 代理银行 Correspondent Banks 附属银行(子银行) Subsidiary Banks 联营银行 Affiliated Banks 银团银行 Consortium Bank 票据 Instrument 设权性 Right to Be Paid 无因性 Non causative Nature 要式性 Requisite in Form 流通性 Negotiability 可追索性 Recoursement 基本当事人 Immediate Parties 附属当事人 Remote Parties 出票人 Drawer 付款人 Payer,Drawee 收款人 Payee 背书人 Endorser 被背书人 Endorsee 持票人 Holder 承兑人 Acceptor 保证人 Guarantor 汇票 Bill of Exchange 限制性抬头 Restrictive Order 指示性抬头 Demonstrative Order 持票来人抬头 Payable to Bearer 出票日期 Date of Issue 出票人签字 Signature of the Drawer 出票地点 Place of Payment 付款地点 Place of Payment 付款日期 Tenor
