语言学课后习题树形图
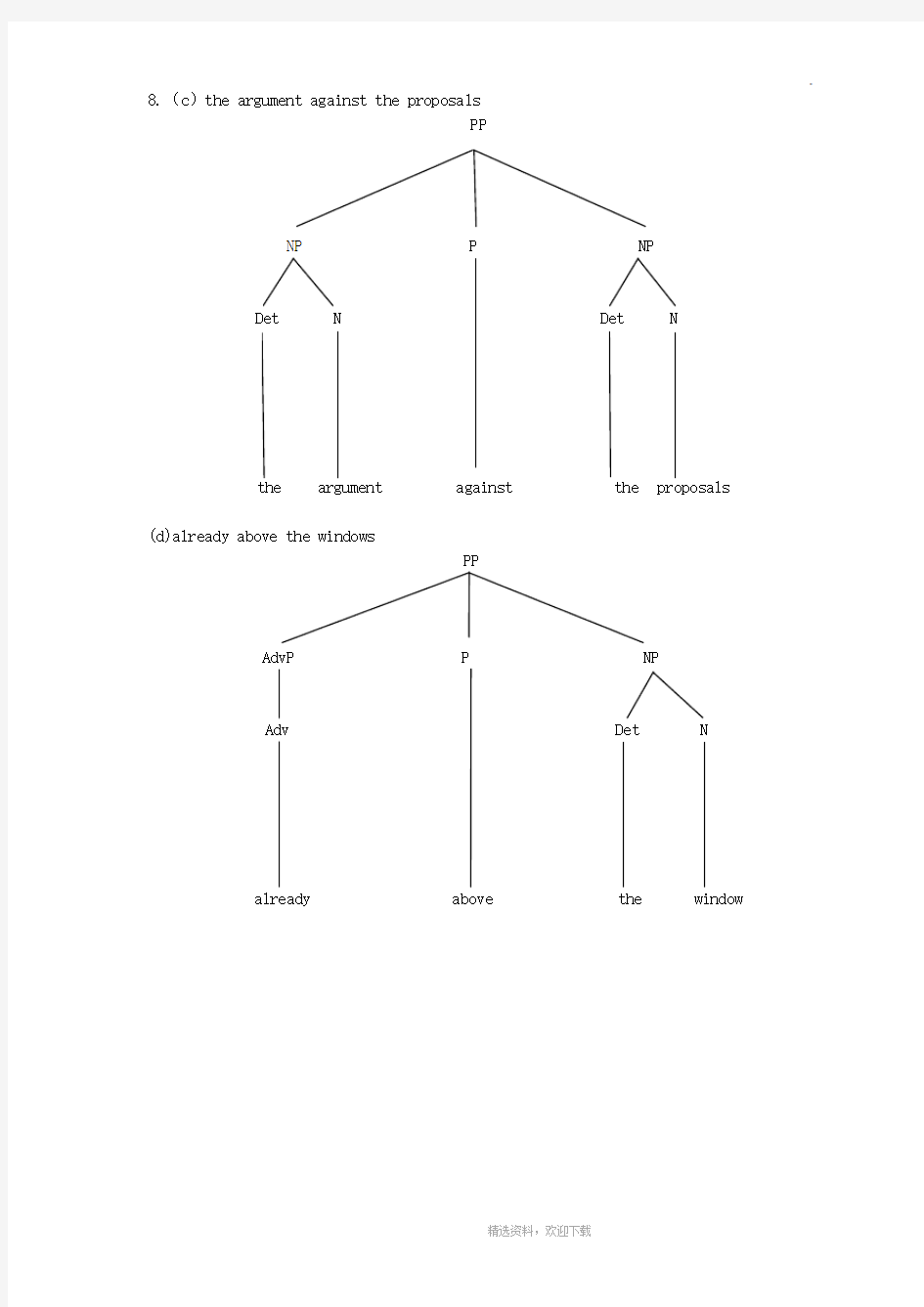
8.(c)the argument against the proposals
PP
NP P NP
Det N Det N
against the
(d)already above the windows
PP
AdvP P NP
Adv Det N already above the window
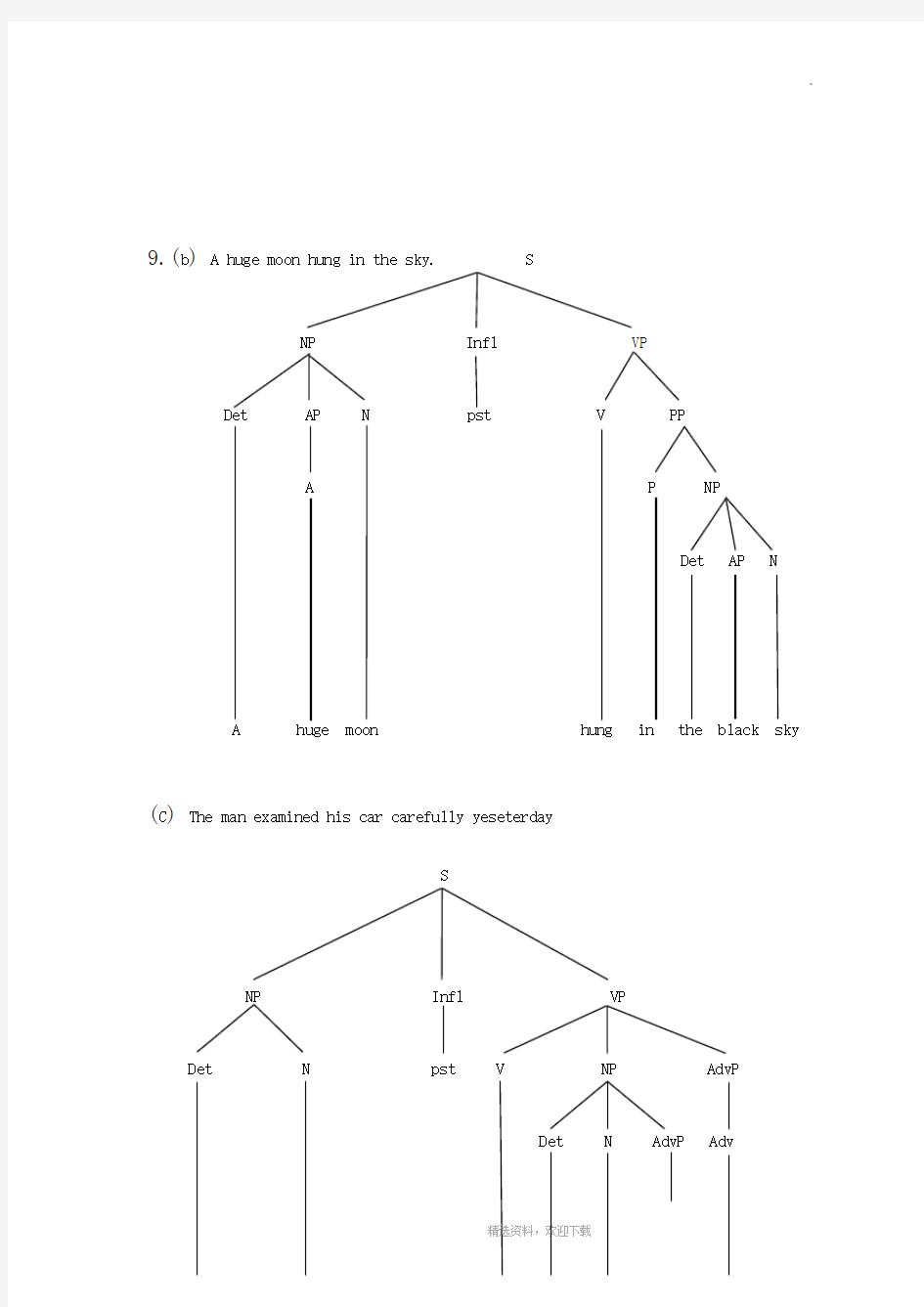
9.(b) A huge moon hung in the sky.S
NP Infl VP
Det AP N pst V PP
A P NP
Det AP N
(C) The man examined his car carefully yeseterday
S
NP Infl VP
Det N pst V NP AdvP
Det N AdvP Adv
。
Adv
A man examined his car carefully yesterday
10.(b)Helen put on her clothes and went out
S
NP Infl VP
N pst V PP Con V PP
P NP P
Det N
Helen put on her clothes and went out
c)Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.
S
NP Infl VP
N Pre V AP Con AP
A PP A PP
P NP P NP N
Mary is fond of literature but tired of
statistics
11.(b) Gerry belives the fact that Anna fluncked the English exam.
S
NP Infl VP
N Pre V NP
Det N CP
C S
NP Infl VP
NP N Pst V NP
Det AP N
A
Gerry believes the fact that Anna fluncked the English exam
(c) Chiris was happy that his father bought him a Roll-Royce.
S
NP Infl VP
N Pst V AP
A CP
C S
NP NP Infl VP
Det N Pst V NP
N Det N
Chris was happy that his father bought him a Roll-Royce
(d) The children argued over whether bats had wings.
S
Det N Pst V PP
P CP
C S
NP Infl VP
N V NP
N
The children argued over whether bats had wings 12.(a) Herbert bought a house that she loved .
S
NP Infl VP
Det N CP
C S
NP Infl VP
N Pst V NP
Herbert bought a house that she loved e
(c) The girl whom he adores majors in linguistics.
S
NP Infl VP
Det N CP Pre V PP
C S P NP
NP Infl VP N
N Pre V NP
The girl whom he adores e majors in linguistics
13.(a) Would you come tomorrow?
CP
C S
Aux NP Infl VP
N Aux V Advp
Adv Would you e come tomorrow
(b)What did Helen bring to the party?
CP
Spec C S
N Infl NP Infl VP
Pst N Pst V NP
N PP
P Det NP N
最新英语语言学树型图详细讲解
树形图详细讲解 1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a) The old lady suddenly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. a) full of people AP A P N full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det N P NP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP A N often read detective stories
d) the argument against the proposals NP NP PP Det N P NP Det N the argument against the proposals e) move towards the window VP V PP P Det N move towards the window 3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences. a) The jet landed. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP Det N Pst V The jet landed b) Mary became very ill. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP N Pst V AP Deg A Mary became very ill
语言学树形图课后答案.
树形图详细讲解 网上的相对理想的树形图答案,注意正两 点: 1. 短语和中心词在一竖线上 2. 含有形容词修饰语的名词短语的画法 NP Det N A N a little boy 1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a) The old lady suddenly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. a) full of people AP A P N
full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det N P NP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP A N often read detective stories
《新编简明英语语言学教程》第二版课后练习题答案
《新编简明英语语言学教程》第二版练习题参考答案 Chapter 1 Introduction 1. How do you interpret the following definition of linguistics: Linguistics is the scientific study of language. 答:Linguistics is based on the systematic investigation of linguistic data, conducted with reference to some general theory of language structure. In order to discover the nature and rules of the underlying language system, the linguists has to collect and observe language facts first, which are found to display some similarities, and generalizations are made about them; then he formulates some hypotheses about the language structure. The hypotheses thus formed have to be checked repeatedly against the observed facts to fully prove their validity. In linguistics, as in any other discipline, data and theory stand in a dialectical complementation, that is, a theory without the support of data can hardly claim validity, and data without being explained by some theory remain a muddled mass of things. 2. What are the major branches of linguistics? What does each of them study? 答:The major branches of linguistics are: (1) phonetics: it studies the sounds used in linguistic communication; (2) phonology: it studies how sounds are put together and used to convey meaning in communication; (3) morphology: it studies the way in which linguistic symbols representing sounds are arranged and combined to form words; (4) syntax: it studies the rules which govern how words are combined to form grammatically permissible sentences in languages;
语言学练习Chapter2 习题
Chapter 2:Phonology I. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False: 1. Voicing is a phonological feature that distinguishes meaning in both Chinese and English. F 2. If two phonetically similar sounds occur in the same environments and they distinguish meaning, they are said to be in complementary distribution. T 3. A phone is a phonetic unit that distinguishes meaning. 4. English is a tone language while Chinese is not. 5. In linguistic evolution, speech is prior to writing. 6. In everyday communication, speech plays a greater role than writing in terms of the amount of information conveyed. 7. Articulatory phonetics tries to describe the physical properties of the stream of sounds which a speaker issues with the help of a machine called spectrograph. 8. The articulatory apparatus of a human being are contained in three important areas: the throat, the mouth and the chest. 9. Vibration of the vocal cords results in a quality of speech sounds called voicing. 10. English consonants can be classified in terms of place of articulation and the part of the tongue that is raised the highest. 11. According to the manner of articulation, some of the types into which the consonants can be classified are stops, fricatives, bilabial and alveolar. 12. Vowel sounds can be differentiated by a number of factors: the position of tongue in the mouth, the openness of the mouth, the shape of the lips, and the length of the vowels. 13. According to the shape of the lips, vowels can be classified into close vowels, semi-close vowels, semi-open vowels and open vowels. 14. Any sound produced by a human being is a phoneme. 15. Phones are the sounds that can distinguish meaning. 16. Phonology is concerned with how the sounds can be classified into different categories.
英语语言学树形图举例word精品
树形图详细讲解 1. In dicate the category of each word in the follow ing senten ces. a) The old lady sudde nly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He n ever appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. b) a story about a sen time ntal girl NP Det A N a story about a sen time ntal girl c) ofte n read detective stories Qual V NP ofte n read detective stories d) the argume nt aga inst the proposals NP NP a) full of people AP full of people NP PP VP Det N
八 Det N the argume nt aga inst the proposals
语言学第四单元课后答案 synta 树状图 the s rule
syntax 1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a) The old lady suddenly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. a) full of people AP A P N full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP
A N often read detective stories d) the argument against the proposals NP NP PP Det N the argument against the proposals e) move towards the window VP V PP P Det N move towards the window 3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences. a) The jet landed. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP Det N Pst V The jet landed b) Mary became very ill. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP N Pst V AP
教你如何画语言学树型图
树形图详细讲解 1、 Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences、 a) The old lady suddenly left、 Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road、 Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road、 Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature、 N Qual V Deg A 2、 The following phrases include a head, a plement, and a specifier、 Draw the appropriate tree structure for each、 a) full of people AP A P N full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det N P NP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP A N often read detective stories d) the argument against the proposals NP NP PP Det N P NP Det N the argument against the proposals e) move towards the window VP
新编简明英语语言学教程戴炜栋第1-3章课后练习题答案
《新编简明英语语言学教程》第二版第1-3章练习题参考答案 Chapter 1 Introduction P13 1. How do you interpret the following definition of linguistics: Linguistics is the scientific study of language? 答:Linguistics is based on the systematic investigation of linguistic data, conducted with reference to some general theory of language structure. In order to discover the nature and rules of the underlying language system, the linguists has to collect and observe language facts first, which are found to display some similarities, and generalizations are made about them; then he formulates some hypotheses about the language structure. The hypotheses thus formed have to be checked repeatedly against the observed facts to fully prove their validity. In linguistics, as in any other discipline, data and theory stand in a dialectical complementation, that is, a theory without the support of data can hardly claim validity, and data without being explained by some theory remain a muddled mass of things. 2. What are the major branches of linguistics? What does each of them study? 答:The major branches of linguistics are: (1) phonetics: it studies the sounds used in linguistic communication; (2) phonology: it studies how sounds are put together and used to convey meaning in communication; (3) morphology: it studies the way in which linguistic symbols representing sounds are arranged and combined to form words; (4) syntax: it studies the rules which govern how words are combined to form grammatically permissible sentences in languages; (5) semantics: it studies meaning conveyed by language; (6) pragmatics: it studies the meaning in the context of language use. 3. In what basic ways does modern linguistics differ from traditional grammar? 答:The general approach thus traditionally formed to the study of language over the years is roughly referred to as “t raditional gramma r.” Modern linguistics differs from traditional g rammar in several basic ways. Firstly, linguistics is descriptive while traditional grammar is prescriptive. Second, modem linguistics regards the spoken language as primary, not the written. Traditional grammarians, on the other hand, tended to emphasize, maybe over-emphasize, the importance of the written word, partly because of its permanence. Then, modem linguistics differs from traditional grammar also in that it does not force languages into a Latin-based framework. 4. Is modern linguistics mainly synchronic or diachronic? Why? 答:In modem linguistics, a synchronic approach seems to enjoy priority over a diachronic one. Because people believed that unless the various states of a language in different historical periods are successfully studied, it would be difficult to describe the changes that have taken place in its historical development. 5. For what reasons does modern linguistics give priority to speech rather than to writing? 答:Speech and writing are the two major media of linguistic communication. Modem linguistics regards the spoken language as the natural or the primary medium of human language for some obvious reasons. From the point of view of linguistic evolution, speech is prior to writing. The writing system of any langu age is always “invented” by its users to reco rd speech when the need arises. Even in today's world there are still many languages that can only be spoken but not written. Then in everyday communication, speech plays a greater role than writing in terms of the amount of information conveyed. And also, speech is always the way in which every native speaker acquires his mother tongue, and writing is learned and taught later when he goes to school. For modern linguists, spoken language reveals many true features of human speech while written language is only the “revised” record of spe ech. Thus their data for investigation and analysis are mostly drawn from everyday speech, which they regard as authentic.
语言学课后习题树形图
8.(c)the argument against the proposals PP NP P NP Det N Det N against the (d)already above the windows PP AdvP P NP Adv Det N already above the window
NP Infl VP Det AP N pst V PP A P NP Det AP N A huge moon hung in the black sky (C) The man examined his car carefully yeseterday S NP Infl VP Det N pst V NP AdvP Det N AdvP Adv Adv A man examined his car carefully yesterday 10.(b)Helen put on her clothes and went out S
N pst V PP Con V PP P NP P Det N Helen put on her clothes and went out c)Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics. S NP Infl VP N Pre V AP Con AP A PP A PP P NP P NP N Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics 11.(b) Gerry belives the fact that Anna fluncked the English exam. S NP Infl VP
语言学教程课后习题答案第一章资料(最新整理)
Chapter 1 Invitations to Linguistics 1. Define the following terms: design feature: the distinctive features of human language that essentially make human language distinguishable from languages of animals. function: the role language plays in communication (e.g. to express ideas, attitudes) or in particular social situations (e.g. religious, legal). synchronic: said of an approach that studies language at a theoretical ‘point’ in time. diachronic: said of the study of development of language and languages over time. prescriptive: to make authoritarian statement about the correctness of a particular use of language. descriptive: to make an objective and systematic account of the patterns and use of a language or variety. arbitrariness: the absence of any physical correspondence between linguistic signals and the entities to which they refer. duality: the structural organization of language into two abstract levels: meaningful units (e.g. words) and meaningless segments (e.g. sounds, letters). displacement: the ability of language to refer to contexts removed from the speaker’s immediate situation. phatic communion: said of talk used to establish atmosphere or maintain social contact. metalanguage: a language used for talking about language. macrolinguistics: a broad conception of linguistic enquiry, including psychological, cultural, etc. competence: unconscious knowledge of the system of grammatical rules in a language. performance: the language actually used by people in speaking or writing.
语言学教程第三版___练习及答案
胡壮麟语言学教程第三版练习及答案 Chapter I Introduction I. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False: 1. Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language. 2. Linguistics studies particular language, not languages in general. 3. A scientific study of language is based on what the linguist thinks. 4. In the study of linguistics, hypotheses formed should be based on language facts and checked against the observed facts. 5. General linguistics is generally the study of language as a whole. 6. General linguistics, which relates itself to the research of other areas, studies the basic concepts, theories, descriptions, models and methods applicable in any linguistic study. 7. Phonetics is different from phonology in that the latter studies the combinations of the sounds to convey meaning in communication. 8. Morphology studies how words can be formed to produce meaningful sentences. 9. The study of the ways in which morphemes can be combined to form words is called morphology. 10. Syntax is different from morphology in that the former not only studies the morphemes, but also the combination of morphemes into words and words into sentences. 11. The study of meaning in language is known as semantics. 12. Both semantics and pragmatics study meanings. 13. Pragmatics is different from semantics in that pragmatics studies meaning not in isolation, but in context. 14. Social changes can often bring about language changes. 15. Sociolinguistics is the study of language in relation to society. 16. Modern linguistics is mostly prescriptive, but sometimes descriptive. 17. Modern linguistics is different from traditional grammar. 18. A diachronic study of language is the description of language at some point in time. 19 Modern linguistics regards the written language as primary, not the written language. 20. The distinction between competence and performance was proposed by F. de Saussure.
语言学教程复习题与答案
语言学教程复习题与答案(胡壮麟版第一章) Chapter I In troduct ion I. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False: 1. Lin guistics is gen erally defi ned as the scie ntific study of Ian guage. 2. Lin guistics studies particular Ian guage, not Ian guages in gen eral. 3. A scientific study of Ianguage is based on what the linguist thinks. 4. In the study of linguistics, hypotheses formed should be based on Ianguage facts and checked aga inst the observed facts. 5. Gen eral lin guistics is gen erally the study of Ian guage as a whole. 6. General linguistics, which relates itself to the research of other areas, studies the basic concepts, theories, descriptions, models and methods applicable in any lin guistic study. 7. 7. Phon etics is differe nt from phono logy in that the latter studies the comb in ati ons of the sounds to convey meaning in com muni cati on. 8. Morphology studies how words can be formed to produce meanin gful senten ces. 9. The study of the ways in which morphemes can be combined to form words is called morphology. 10. Syntax is different from morphology in that the former not only studies the morphemes, but also the comb in ati on of morphemes into words and words into senten ces. 11. The study of meaning in Ianguage is known as semantics. 12. Both semantics and pragmatics study meanings. 13. Pragmatics is different from semantics in that pragmatics studies meaning not in isolatio n, but in con text. 14. Social changes can often bring about Ianguage changes. 15. Sociolinguistics is the study of Ianguage in relation to society. 16. Modern linguistics is mostly prescriptive, but sometimes descriptive. 17. Modern linguistics is different from traditional grammar. 18. A diachronic study of Ianguage is the description of Ianguage at some point in time. 19. Modern linguistics regards the written Ianguage as primary, not the written Ian guage. 20. The disti nction betwee n compete nee and performa nee was proposed by F.de Saussure. II. Fill in each of the following blanks with one word which begins with the letter give n: 21. Chomsky defi nes “ compete nee ” as the ideal user ' s k ___________ of the rules of his Ian guage. 22. La ngue refers to the a _______ lin guistic system shared by all the members of a speech com munity while the parole is the con crete use of the conven ti ons and applicati on of the rules. 23. D _______ is one of the desig n features of huma n Ian guage which refers to the
