particular插件教程

Trapcode公司是很有名的视频软件公司,开发了Shine、SoundKeys、Lux、3Dstroke、StarGlow、Particular整套插件(在https://www.360docs.net/doc/3815224735.html,下载),这里学习Trapcode
Particular粒子插件( 3d粒子系统)。
本文是Trapcode Particular(最新版本为v1.5)的基础知识篇,主要介绍Particular 的组成、基本功能、效果的实时预览、主要参数的设置与调整。笔者列出了参数不同设置值
时的效果图,帮助读者提高动画创建效率。
一、启动
运行AfterEffect6.5。
1、建立新合成文件,Composition->New Composition,名字自取,比如Trapcode。
2、建立新层,Layer->New->Solid,取名Particular。
3、引入特效:Effect->Trapcode->Particular。
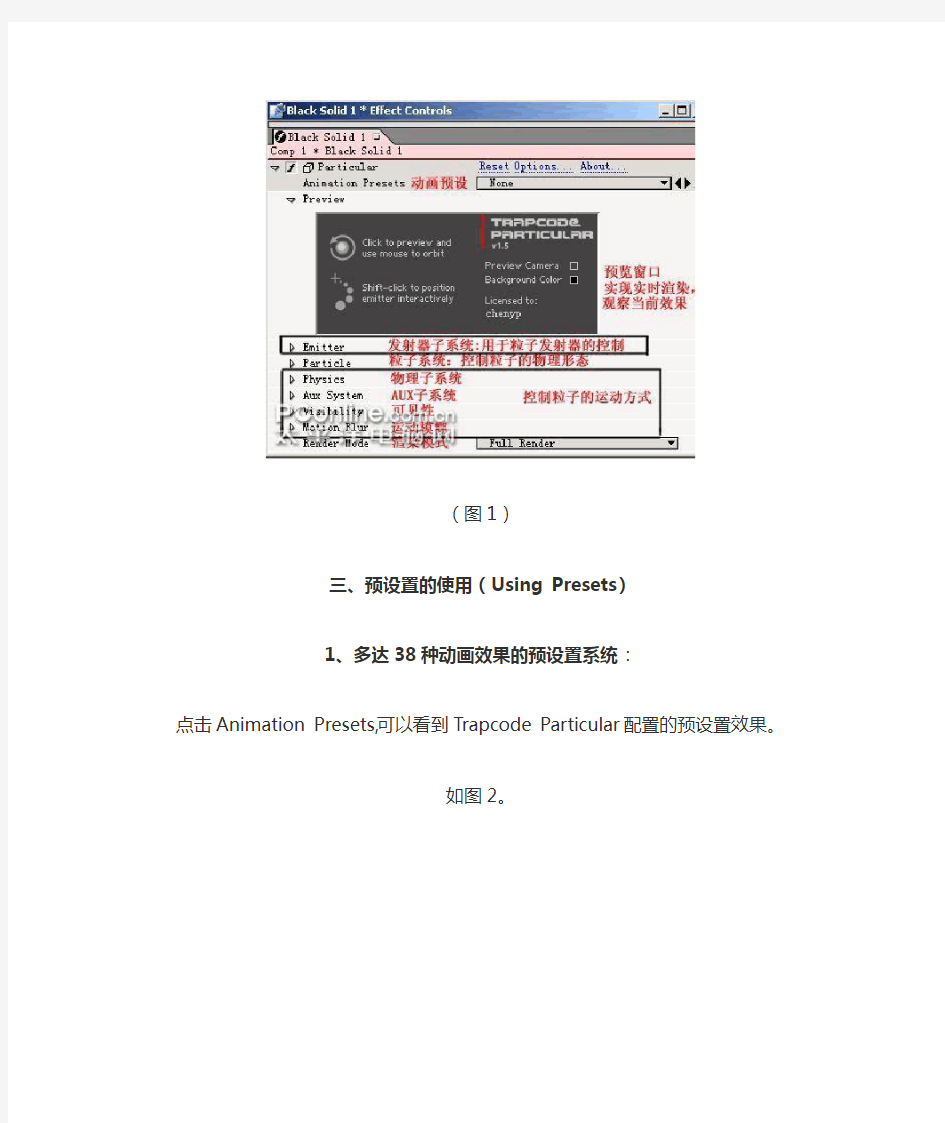
二、Particular系统的组成
如图1
(图1)
三、预设置的使用(Using Presets)
1、多达38种动画效果的预设置系统:
点击Animation Presets,可以看到Trapcode Particular配置的预设置效果。
如图2。
(图2)
这些预设置的帧大小在640*480到PALD1之间,帧速率在20-40fps。当然你完全可以根据你的喜好和需要调整参数,比如粒子的大小、速率和运动快门角度等。可以选择"Save Selection as Animation Preset"保存你自己建立的特效效果,为了避免和系统中内置的效果发生混乱,保存自定义的效果时注意不要再使用前缀名"t_"。同时还得注意在选择预设置之前,必须确保引入特效的当前时间点在时间线控制窗口工作区的开始端。也就是0秒处。
如图3。
(图3)
选择了预设置,可以在如图1的预览窗口中预览。
2、实现预览的两种方法:
一是在预览窗口中点击并按住鼠标左键不放,拖移鼠标,动画随着鼠标移动的路径而运
动;
二是按住shift,在预览窗口中点击,当前的鼠标位置点位置作为发射器的发射点,动画效果就会播放出来,松开鼠标,发射器停止发射,再按住鼠标,又继续发射粒子。
通过预览可以实时观察当前的设置效果,不需要用渲染的方式,节省了时间和系统资源,
大大提高工作效率。
四、系统主要参数的设置
该部分是本基础教程的重点。
(一)、Emitter
既然是粒子系统,那首先就要设计好粒子的发射器。没有发射器,任何粒子也无处谈起。第一步是设计好发射器,在这个子系统中可以控制每秒钟可以发射的粒子数量、发射器的形状,粒子的初始化方向和速度等。界面如图4。
(图4)
1、EmitterType
(1)、Point(点形):所有的粒子都从同一个点发出,如图5。
(图5)
(2)、Box(方形):粒子在一个矩形范围内生成,如图6。
(图6)
(3)、Sphere(球形):粒子在一个球形范围内生成,如图7。
(图7)
(4)、Grid(网格):粒子2D或3D网格里面生成,如图8。
(图8)
注意Velocity(速率)的调整,在图8中,我们设置Velocity为20,默认值为100。
(5)、Light(光):
必须先建立名字为Emitter1的点光源(Layer->New->Light),设置Emitter->Direction
为"Directional",调整Emitter1点光源的X和Y轴的旋转角度为45度。效果如图9。
(图9)
(6)、Layer(层):如图10。
(图10)
(7)、LayerGrid(层的网格),如图11。
(图11)
2、Direction Spread(扩散):
控制粒子的扩散,该值越大,向四周扩散出来的粒子就越多;反之,该值越小,向四周扩散出来的粒子就越少。比较图12和图13的效果吧。
在如图12中,设置Direction Spread为20%(默认值),
图12
在如图13中,设置Direction Spread为60%
图13
3、EmitterSizeX,Y和Z(发射器在X、Y、Z轴的大小):
只有当EmitterType(发射类型)设置为Box、Sphere、Grid和Light时,才能设置发射器在X轴、Y轴、Z轴的大小;而对于Layer和LayerGrid发射器,只能调节Z方向发射
器的大小。
比如,EmitterType(发射类型)为Box,我们把EmitterSizeX设置为300,EmitterSizeY、
EmitterSizeZ都设置为50,效果如图14。
图14
(二)、Particle(粒子参数子系统)如图15。
1、如图15
(图15)
2、ParticleType:
(1)、Sphere(球形粒子),这是基本粒子类型。
通过SphereFeather(球的羽化)控制粒子的羽化强度。
Sphere Feather(球体的羽化):设置为100;
Size(粒子的大小):66.5;
SizeRandom[%](大小的随机性):66.5%;
Opacity(不透明度):7.4%
效果如图16。
(图16)
(2)、GlowSphere(炽热的发光球体),如图17。
(图17)
通过羽化功能来调整球体中心的羽化状态,球体的发光状态在TrapcodeParticular的Options(高级设置)中的Glow窗口进行设置。
注意:图17中的粒子羽化、大小、不透明度设置与图16中的参数设置完全一致,这样读者就可以直观地比较出GlowSphere(发光球体)和Sphere(球形)的区别了。
(3)、Star(星形粒子):
设置ParticleType为Star(NoDOF),Rotation(旋转角度)为0 ,效果如图18。
图18
设置Rotation(旋转角度)为45,发现星形粒子旋转了45度。效果如图20。
图19
(4)、Cloudlet(云块):如图20。
图20
可以通过Rotation(旋转)/Cloudlet Feather(云块的羽化)来控制云块效果。
Cloudlet Feather(云块粒子的羽化):设置为79.1;
Rotation(旋转):120
Size(云块粒子的大小):35;
SizeRandom[%](大小的随机性):30%;
Opacity(不透明度):10%
(5)、Smokelet(阴影):如图21。
(图21)
通过Rotation/SmokeletFeather来控制云块阴影变化。该阴影粒子效果的设置和云块粒子的设置一致,读者可以比较这两种粒子的效果。
(6)、Custom(自定义):创建个性化粒子。
CustomColorize:(自定义颜色):通过光的作用来给粒子添加颜色。
CustomFill(自定义填充):通过填充Alpha通道来给粒子添加颜色。
我们可以在图22中看到个性化粒子的一例效果。
(图22)
3、Set Color:
设置粒子的颜色有三种方法:
AtBirth:设置粒子刚生成时的颜色,并在整个生命期内有效。
OverLife:利用"Color over Life"项,使粒子的颜色在生命期内变化。
Random from Gradient:选择随机颜色。
4、TransferMode:(合成模式)、Transfer Mode over Life
(1)、Normal:正常模式
(2)、Add(增加):粒子效果添加在一起。用于光效和火焰效果。
(3)、Screen(屏幕):用于光效和火焰效果。
(4)、Lighten(加亮):先比较通道颜色中的数值,然后再将亮的部分调整得比原来
更亮。
(5)Normal/Add Over Life(在生命期内的正常/增加):在Normal模式和Add模式
之间切换。
(6)、Normal/Screen Over Life(在生命期内的正常/屏幕):在Normal模式和Screen
模式之间切换。
当粒子是火焰时,TransferMode应当是Add或Screen模式。而当粒子为烟雾效果时,Transfer Mode(合成模式)应当是Normal。
(三)、Physics(物理子系统)
控制粒子发射后的运动方式。
图23
1、Physics Model:
Air(空气):该模式用于创建粒子穿过空气时的运动效果,主要设置空气的阻力、扰
动等参数。
Bounce(弹跳):该模式实现粒子的弹跳。
2、Bounce:
该项只有当"Physics Model"设置为Bounce时有效,如图24。
图24
(四)、Aux System(Aux子系统)
该系统是粒子系统中的粒子系统,通过Aux System可以实现更生动的粒子效果,比如
火焰礼花的拖尾效果。如图25。
图25
当Emit选择为off时,Aux System中的参数无效。只有选择"From Main Particles"
或"At collission Event"时,AuxSystem中的参数才有效,也就是才能发射Aux粒子。AUX
粒子的类型选择如图26所示。
图26
在这里说明一下"Same as Main",表示AUX粒子的类型和主系统的粒子类型一样。
(五)、Visibility(可见性)
控制粒子在哪些地方可见。例如,远处的粒子可以设置为淡出,模拟烟雾效果。界面如
图27。
图27
AE插件大全以及部分汉化插件
Red Giant系列官网https://www.360docs.net/doc/3815224735.html,/红巨星系列插件注册码 0、Trapcode_Suite_Win_Full_11_原版+注册机(Form更新至2.0) 1、Red.Giant.Trapcode.合集.V4.0中英文安装版32位Particular_预置(英汉双语) Form_预置(英汉双语) 2、Red.Giant.Trapcode.合集.For.AECS5中英文安装版64位也适用于AECS5.5 3、魔法子弹调色系列Red Giant Magic Bullet Suite 11 英文原版+注册机+汉化+安装教程下载 Magic Bullet Suite 11破解版安装图解 Magic Bullet Suite 11调色系列包括以下九个插件(其中Grinder用于MAC):
4、调色插件Magic_Bullet_Looks_AE_1.4.3_32bit英文版+汉化(baxianhua) MBLooks.预置(安装时直接复制粘贴即可) Magic_Bullet_Looks_PPro_1.4.3_64bit英文版+汉化(baxianhua) 5、调色师Magic.Bullet.Colorista.II.注册版+汉化(32位+64位)详细说明 6、调色插件MBMojo.32位(1.1).64位(1.2)+汉化(AE.PR.VEGAS) 7、AE降噪极品.Magic.Bullet.Denoiser.1.0.1.32bit64bit原版加汉化 8、AE视频转换Magic.Bullet.InstantHD.3264bit 9、AEPR场插件MB.Frames.(32位1.02版).(64位1.1版) 10、Red_Giant_Keying_Suite_11包括:Primatte Keyer 5.0 、Key Correct 1.2.1 和Warp 1.1.1 Keying_Suite_11.0_安装注册图文教程 11、Red.Giant.KeyCorrectWinFull.ChsPackV2.0.(32.64bit)AE抠像校正原版加汉化汉化说明 12、极品抠像插件_Primatte_Keyer_Pro_4.0_中英文安装版32位 13、Red.giant.Warp.1.1.3264bit.AEPR(三维变形反射投影) Red_Giant_Warp_1.0_中英文版(三维变形反射投影)32位 14、灯光工厂Red.Giant.Knoll.Light.Factory.2.52.英文原版(带汉化)新增100组预设ffx后缀lfp后缀 灯光工厂Knoll.Light.Factory.Win.Full.(2.5版+2.7版) 2.5版本用于32位,2.7版本用于64位 15、3D助手Red.Giant.PlaneSpace.v1.4.3264bit+汉化(曹润)汉化说明 16、天空大海滤镜.Red.Giant.Psunami.v1.4(3264bit)+32bit汉化 17、AE烟雾水火.RedGiant.Image.Lounge.1.4.5.(3264bit) 18、卡通.水墨.油画Red.Giant.ToonIt.v2.1.3264bit.注册版 AE卡通、水墨、油画Red_Giant_Toon_It_AE(带汉化1.1.1版)32位 19、极品文字特效插件.Red.Giant.Text.Anarchy.2.4.(32.64bit)(AEPR) 极品文字特效插件_Red_Giant_Text_Anarchy_V2.35中英文版32位 20、AE屏幕视觉Red.Giant.Holomatrix.1.2.(3264bit) 21、Reflector.1.5.0.PC反射倒影(32位) 22、Magic.Bullet.Steady.for.AE.1.1.1(稳定降噪) 23、Red.Giant.Film.Fix.v1.0.for.AE【修复老旧影片插件】 DigiEffects系列官网https://www.360docs.net/doc/3815224735.html,/DE系列注册破解方法 1、DE.Delirium.1.8(原版加汉化)32位 DE-DeliriumV2-64bit原版
正确使用DSC基线
Thermal Analysis Information for Users User Com 25 Introduction In thermal analysis, baselines are mostly used in connection with the integration of peaks. The peak area is determined by integrating the area between the measurement curve and a virtual or true baseline. In the same way, the peak temperature is defined as the point on the curve where the distance to the baseline is greatest. Extrapolated baselines are important for the determination of glass transition temperatures Choosing the correct baseline is crucial for the determination of the enthalpy of a transi- tion or a reaction. The baseline represents the DSC curve that would be measured if no transition or reaction occurred. The examples described in this article illustrate how to choose the right baseline for a particular evaluation. Dear Customer, We are very pleased to receive more and more articles from you for publication in UserCom. Thanks to new techniques and better performance, thermal analysis is being used in an ever-increasing number of scien- tific fields. Hyphenated techniques such as evolved gas analysis, microscopy and chemiluminescence yield much more information about samples and very often greatly simplify the interpretation of measurement results. We think this issue of UserCom will once again give you ideas for applications in new and interesting areas using the multitude of techniques now available. Choosing the right baseline Dr. Rudolf Riesen Contents 1/2007 TA Tip - Choosing the right baseline 1 Applications - Determination of the Noack evaporation loss of lubricants by TGA 7 - The characterization of poly- morphs by thermal analysis 9 - Analysis of melting processes using TOP EM? 13 - Characterization of delivery systems by thermogravimetry 18 Tips and hints - Detection and evaluation of weak sample effects in DSC 21 Dates - Exhibitions 23 - Courses and Seminars 23
SAP系统配置参数详解
SAP系统配置参数详解 SAP 系统参数设置 path: /usr/sap/PRD/SYS/profile profile: PRD_DVEBMGS00_sapapp 如果您想查看所有的参数及当前设定,可使用SA38 执行程序 RSPARAM 修改附加配置 T-CODE:RZ10 进行SAP系统参数的设置,设置后需激活参数并重启SAP实例,配置参数才会生效login/system_client 登录时默认的Client号 login/password_expiration_time 密码有效期 login/fails_to_user_lock 密码输错多少次后锁定 login/failed_user_auto_unlock 用户失效后多长时间解锁 rdisp/mshost 状态栏中显示的系统名称 rdisp/rfc_use_quotas 是否激活配额资源分配,0是关闭,1是启用.以下相关限制必须这个为1时才生效. rdisp/gui_auto_logout 表示如果客户在指定时间内没有进行任何操作,则会自动退出SAP系统。时间为秒 rdisp/max_wprun_time 程序运行的最长时间限制 rdisp/rfc_max_login 最大SAP用户登录数 login/disable_multi_gui_login 限制用户多次登录,该参数可以设置同个client 同个用户ID可以允许同时登录几个,当设为1时,系统将提示用户选择: 'Terminate the Current Sessions' or 'Terminate this Login.' ,以达到保证只允许一个登录. rdisp/tm_max_no 这个参数是限制每个实例最大的用户数,默认是200个. rdisp/rfc_max_own_login 一个程序在一个服务器上允许分配的RFC资源个数,也就是同时能运行多少个.默认值25. rdisp/rfc_min_wait_dia_wp 设置RFC保留的会话设置, rdisp/wp_no_dia 在一个实例中处理的会话数目,如果设置为10,rdisp/rfc_min_wait_dia_wp=3则可用的会话处理是7,3个被保留 rdisp/rfc_max_own_used_wp rdisp/rfc_max_comm_entries rdisp/rfc_max_wait_time rdisp/btctime
AE插件particular面板中文翻译
Particular面板参数设置 Emitter 发射器 Emitter Type 发射类型Poin 线 Box 盒子 Sphere 球型 Grid 网格 Direction 发射方向uniform 统一 Directional 单向 Bi- Directional 双向 Dics 圆盘 Outwards 向外的 Velocity 速度 Velocity distribution 速度分布 Velocity from motion 速度运动 Emission extras 发射附加 Pre run 紊乱 Periodicity rud 周期 Random seed 随机种子 Particle 粒子 Life sec 生命值 Life random 生命值随机值 Particle type 粒子种类sphere 球型 Glow sphere(no dof)发光球型(无景深) Star(no dof)星星无景深 Cloudlet 云彩 Streaklet 小团图案 Sprite 子画面妖精 Sprite colorize 子画面彩色替换 Sprite fill 子画面填充 Textured polygon 多边形机理贴图 Textured polygon colorize 多边形贴图颜色替换 Textured polygon fill 多边形贴图填充
Rotation 旋转 Size 大小 Size random 大小随机值 Size over life 发射的大小和生命变化控制Opacity 透明度 Opacity random 透明度随机值 Opacity over life 发射的透明度与生命值变化控制 Set color 设置颜色 At birth 出生时 Over life 发射过程 Random from gradient 随机梯度 From light emitter 灯的反射 Color random 颜色随机 Color over life 发射的颜色与生命值控制
AE常用particular粒子中英文对照表教学文稿
A E常用p a r t i c u l a r 粒子中英文对照表
10xLinear(10x线性) 10x Smooth(10x平滑) Exact(slow)精确(慢) Direction(方向) Uniform(统一)——任一粒子发射类型发射粒子时,会向各个方向移动。 Directional(方向)——(如枪口喷射)通过调节X、Y、Z Rotation来实现。 Bi-Directional(双向)——和Directional(方向)十分相似,但是向着两个完全相反的方向发射。通常为180度。 Disc(圆形)——通常只在两个维度上,形成一个盘形。 Outwards(向外)——粒子会始终向远离发射点的方向移动。而Uniform(统一)是随机的。Direction Spread(方向伸展)—20—可以控制粒子发射方向的区域。 粒子会向整个区域的百分之几运动。(即粒子发射方向有多宽) X Rotation(X旋转) 0x0 X Rotation (Y旋转) 0x0 X Rotation (Z旋转) 0x0 Velocity(速率)—100—粒子每秒钟运动的像素数。 Velocity Random[%](随机运动【%】)20 ——每个粒子Velocity的随机性会随机增加或者减小每个粒子的Velocity。 Velocity Distribution(速度分布)—0.5— Velocity from Motion[%](继承运动速度【%】)20 ——粒子在向外运动的同时也会跟随发射器的运动方向运动。 Emitter Size X(发射器尺寸X ) 50
Emitter Size Y (发射器尺寸Y ) 50 Emitter Size Z (发射器尺寸Z) 50 Particles/sec modifier粒子数/秒修改器--- Light(灯光)下有效 Light Intensity光照强度 Shadow Darkness阴影暗部 Shadow Diffusion阴影漫射 None无 Layer Emitter(发射图层)----Layer(图层)、Layer Grid(图层网格)下有效; Layer(图层)—None无—选用哪一个图层作为发射器; Layer Sampling(图层采样)—— Current Time(当前时间) Particular Birth Time(粒子产生时间) Layer RGB Usage(图层RGB用法)—— Lightness-Size(发光-尺寸)——随着图像的明暗变化,粒子的大小也跟着变化 Lightness-Velocity(发光-速率)——随着图像的明暗变化,粒子的速度也跟着变化 Lightness-Rotation(发光-旋转)——随着图像的明暗变化,粒子的旋转也跟着变化 RGB-Size,Vel,Rot(RGB-大小、速率、旋转)——随着图像的颜色变化,粒子的大小,速度,旋转同时变化 RGB-Particle Color(RGB-粒子颜色)——随着图像的颜色变化,粒子的颜色也跟着变化 None无 Grid Emitter(网格发射)----在(网格、图层网格下有效) Particular in X(粒子在X方向上的数量)5 Particular in Y(粒子在Y方向上的数量)5 Particular in Z(粒子在Z方向上的数量)1 Type(类型)
加速度传感器参数讲解(AD)
加速度传感器参数讲解(AD)Accelerometer Specifications - Quick Definitions Measurement range is the level of acceleration supported by the sensor’s output signal specifications, typically specified in ±g. This is the greatest amount of acceleration the part can measure and accurately represent as an output. For example, the output of a ±3g accelerometer is linear with acceleration up to ±3g. If it is accelerated at 4g, the output may rail. Note that the breaking point is specified by the Absolute Maximum Acceleration, NOT by the measurement range. A 4g acceleration will not break a ±3g accelerometer. Sensitivity is the ratio of change in acceleration (input) to change in the output signal. This defines the ideal, straight-line relationship between acceleration and output (Figure 1, gray line). Sensitivity is specified at a particular supply voltage and is typically expressed in units of mV/g for analog-output accelerometers, LSB/g, or mg/LSB for digital-output accelerometers. It is usually specified in a range (min, typ, max) or as a typical figure and % deviation. For analog-output sensors, sensitivity is ratiometric to supply voltage; doubling the supply, for example, doubles the sensitivity. Sensitivity change due to Temperature is generally specified as a % change per °C. Temperature effects are caused by a combination of mechanical stresses and circuit temperature coefficients.
AE中particular插件中英文对照
AE中particular插件中英文对照(一) Emitter(发射器) Particular/sec (粒子/秒)——每秒钟发射粒子得数量。 Emitter Type(发射器类型)——它决定发射粒子得区域与位置。 Point(点)——从一点发射出粒子 Box(盒子)——粒子会从立体盒子中发射出来, (Emitter Size中XYZ就是指发射器大小) Sphere(球形)——与Box很像,只不过发射区域就是球形 Grid(网格)——(在图层中虚拟网格)从网格得交叉点发射粒子 Light(灯光)——(要先新建一个Light Layer)几个Light Layer可以共用一个Particular。Layer——使用合成中得3D图层生成粒子, Layer Grid——同上,发射器从图层网格发射粒子,像Grid一样。 Direction(方向) Uniform(统一)——任一粒子发射类型发射粒子时,会向各个方向移动。 Directional(特定方向)——(如枪口喷射)通过调节X、Y、Z Rotation来实现。 Bi-Directional(相反特定方向)——与Directional十分相似,但就是向着两个完全相反得方向发射。通常为180度。 Disc(盘状)——通常只在两个维度上,形成一个盘形。 Outwards (远离中心) ——粒子会始终向远离发射点得方向移动。而Uniform就是随机得。Direction Spread(方向拓展)——可以控制粒子发射方向得区域。粒子会向整个区域得百分之几运动。 (即粒子发射方向有多宽) Velocity(速度)——粒子每秒钟运动得像素数。Velocity Random——每个粒子Velocity得随机性会随机增加或者减小每个粒子得Velocity。 Velocity Distribution()—— Velocity from Motion(速度跟随运动)——粒子在向外运动得同时也会跟随发射器得运动方向运动。 Layer Emitter(图层发射器) Layer(选用哪一个图层作为发射器) Layer Sampling()—— 2 Current Time(当前时间) Particular Birth Time(粒子生成时间) Layer RGB Usage(图层颜色使用方式) Lightness-Size——随着图像得明暗变化,粒子得大小也跟着变化
ABAP Number Ranges设置及使用
ABAP:ABAP--How to use Number Ranges' Function? 2007-08-16 14:29:20| 分类:SAP ABAP | 标签:|字号大中小订阅 在SAP系统中,号码范围用于给数据记录提供惟一标识. 1 号码范围对象分类 ?无子对象的号码范围对象 无分组 (1) one, two or several number ranges 有分组 (2) one number range, external or internal, per group (3) two number ranges, external and internal, per group ?有子对象的号码范围对象 无分组 (4) one, two or several number ranges 有不依赖子对象的分组 (5) one number range, external or internal, per group (6) two number ranges, external and internal, per group 有依赖子对象的分组 (7) one number range, external or internal, per group (8) two number ranges, external and internal, pergroup 二、如何使用号码范围 2.1 确定号码范围的类型并创建新的号码范围对象(SNRO) 需要多少个号码范围: 1, 2 或者更多? 号码范围是否需要子范围对象(如:company code, plant, controlling area等等)? 号码范围是否需要分组(如:物料类型)? 如果需要分组,那分组的是否需要子范围对象? 号码范围是否需要区分财务年度? 2.2 维护号码范围对象的间隔; 3.3 在程序中使用号码范围的函数进行记录编号或检查可用号码;
amber动力学常用参数说明
amber动力学常用参数说明 个人日记2009-05-08 19:32:18 阅读130 评论1 字号:大中小订阅 IMIN Flag to run minimization =0 No minimization (only do molecular dynamics;default) = 1 Perform minimization (and no molecular dynamics) =5 Read in a trajectory for analysis. NTX Option to read the initial coordinates, velocities and box size from the "inpcrd" file. The options 1-2 must be used when one is starting from minimized or model-built coordinates. If an MD restrt file is used as inpcrd, then options 4-7 may be used. = 1 X is read formatted with no initial velocity information (default) = 2 X is read unformatted with no initial velocity information = 4 X and V are read unformatted. = 5 X and V are read formatted; box information will be read if ntb>0. The velocity information will only be used if irest=1. = 6 X, V and BOX(1..3) are read unformatted; in other respects, this is the same as option "5". =7 Same as option "5"; only included for backward compatibility with earlier versions of Amber. IREST Flag to restart the run. = 0 Noeffect (default) = 1 restart calculation. Requires velocities in coordinate input file, so you also may need to reset NTX if restarting MD. NTRX Format of the Cartesian coordinates for restraint from file "refc". Note: the program expects file "refc" to contain coordinates for all the atoms in the system. A subset for the actual restraints is selected by restraintmask in the control namelist. = 0 Unformatted (binary) form = 1 Formatted (ascii, default) form NTPR Every NTPR steps energy information will be printed in human-readable form to files "mdout" and "mdinfo". "mdinfo" is closed and reopened each time, so it always contains the most recent energy and temperature. Default 50. NTWR Every NTWR steps during dynamics, the "restrt" file will be written, ensuring that recovery from a crash will not be so painful. In any case, restrt is written ev ery NSTLIM steps for both dynamics and minimization calculations. If NTWR<0, a unique copy of the file, restrt_nstep, is written every abs(NTWR) steps. This option is useful if for example one wants to run free energy perturbations from multiple starting points or save a series of restrt files for minimization. Default 500. NTF Force evaluation. Note: If SHAKE is used (see NTC), it is not necessary to calculate forces for the constrained bonds. = 1 complete interaction is calculated (default) = 2 bond interactions involving H-atoms omitted (use with NTC=2) = 3 all the bond interactions are omitted (use with NTC=3) = 4 angle involving H-atoms and all bonds are omitted = 5 all bond and angle interactions are omitted = 6 dihedrals involving H-atoms and all bonds and all angle interactions are omitted
AE--particular插件实用讲解(一定用得到)
AE particular插件实用讲解(一定用得到) 一.Emitter:用于产生粒子 1.Particles/sec控制每秒钟产生的粒子数量 2. Emitter Type设定粒子的类型。有point、box、sphere、grid、 light、layer、layer grid等七种类型。 3 .Position XY 和 Position Z设定粒子的位置 4 .Direction用于控制粒子的运动方向。 5 .Direction Spread控制粒子束的发散程度 6 .X,Y and Z Rotation用于控制粒子发生器的方向。 7 Velocity用于设定新产生粒子的初始速度。 8. Velocity Random为粒子设定随机的初始速度。 9. Velocity from Motion粒子继承粒子发生器的速度。 10. Emitter Size X,Y and Z设定粒子发生器的大小 二.Particle设定粒子的所有外在属性 1 .Life 以秒为单位控制粒子的生命周期 2 .Life Random 为粒子的生命周期随机值 3 .Particle Type粒子类型:球形、发光球形、星形、云团(cloudlet)、烟雾、自定义形对于custom类型的粒子,如果用户选择一个动态的层作为粒子时,还有一个重要的概念: time sampling mode时间采样方式,选择自定义类型时能用。4中方式 (1)Start at Birth – Play Once 从头开始播放custom层粒子一次。(2)Start
at Birth – Loop 循环播放custom层粒子。 (3)Start at Birth – Stretch延伸播放,匹配粒子的生命周期。 (4)Random – Still Frame 随机抓取custom层中的一帧作为粒子(5)Random – Play Once随机抓取custom层中的一帧作为播放起始点,然后按照正常的速度进行播放custom层。 (6)Random – Loop随机抓取custom层中的一帧作为播放起始点,然后循环播放custom层。 (7)Split Clip – Play Once随机抽取custom层中的一个片断(clip)作为粒子,并且只播放一次。 (8)Split Clip – Loop 随机抽取custom层中的一个片断(clip)作为粒子,并进行循环播放。(9)Split Clip – Stretch 随机抽取custom层中的一个片断,并进行时间延伸,以匹配粒子的生命周期。 4.Sphere/Cloudlet/Smokelet Feather控制球形、云团和烟雾状粒子的柔和程度 5. Custom该参数组在粒子类型为custom时才起作用。 6. Rotation用来控制粒子的旋转属性 7 .Rotation Speed用来控制粒子的旋转速度。 8. Size用来控制粒子的大小。
可视化的PLC程序使用XML
Visualization of PLC Programs using XML M. Bani Younis and G. Frey Juniorprofessorship Agentenbased Automation University of Kaiserslautem P. 0. Box 3049, D-67653 Kaiserslautem, Germany Abstract - Due to the growing complexity of PLC programs there is an increasing interest in the application of formal methods in this area. Formal methods allow rigid proving of system properties in verification and validation. One way to apply formal methods is to utilize a formal design approach in PLC programming. However, for existing software that has to be optimized, changed, or ported to new systems .There is the need for an approach that can start from a given PLC program. Therefore, formalization of PLC programs is a topic of current research. The paper outlines a re-engineering approach based on the formalization of PLC programs. The transformation into a vendor independent format and the visualization of the structure of PLC programs is identified as an important intermediate step in this process. It is shown how XML and corresponding technologies can be used for the formalization and visualization of an existing PLC program. I. INTRODUCTION Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are a special type of computers that are used in industrial and safety critical applications. The purpose of a PLC is to control a particular process, or a collection of processes, by producing electrical control signals in response to electrical process- related inputs signals. The systems controlled by PLCs vary tremendously, with applications in manufacturing, chemical process control, machining, transportation, power distribution, and many other fields. Automation applications can range in complexity from a simple panel to operate the lights and motorized window shades in a conference room to completely automated manufacturing lines. With the widening of their application horizon,PLC programs are being subject to increased complexity and high quality demands especially for safety-critical applications. The growing complexity of the applications within the compliance of limited development time as well as the reusability of existing software or PLC modules requires a formal approach to be developed [I]. Ensuring the high quality demands requires verification and validation procedures as well as analysis and simulation of existing systems to be carried out [2]. One of the important fields for the formalization of PLC programs that have been growing up in recent time is Reverse-engineering [3]. Reverse Engineering is a process of evaluating something to understand how it works in order to duplicate or enhance it. While the reuse of PLC codes is being established as a tool for combating the complexity of PLC programs, Reverse Engineering is supposed to receive increased importance in the coming years
Trapcode的3D粒子系统 参数详解
Trapcode的3D粒子系统参数详解 1.Emitter面板 粒子发生器:用于产生粒子,并设定粒子的大小、形状、类型、初始速度与方向等属性。 1.1 Particles/sec 控制每秒钟产生的粒子数量,该选项可以通过设定关键帧设定来实现在不同的时间内产生的粒子数量。 1.2 Emitter Type 设定粒子的类型。粒子类型主要有point、box、sphere、grid、light、layer、layer grid等七种类型。 1.3 Position XY & Position Z 设定产生粒子的三维空间坐标。(可以设定关键帧) 1.4 Direction 用于控制粒子的运动方向。 1.5 Direction Spread 控制粒子束的发散程度,适用于当粒子束的方向设定为Directional、Bi-directional、Disc和Outwards等四种类型。对于粒子束方向设定为Uniform和以灯光作为粒子发生器等情况时不起作用。 1.6 X,Y and Z Rotation 用于控制粒子发生器的方向。 1.7 Velocity 用于设定新产生粒子的初始速度。 1.8 Velocity Random 默认情况下,新产生的粒子的初速度是相等的,我们可以通过该选项为新产生的粒子设定随机的初始速度。 1.9 Velocity from Motion
让粒子继承粒子发生器的速度。此参数只有在粒子发生器是运动的情况下才会起作用。该参数设定为负值时能产生粒子从粒子发生器时喷射出来一样的效果。设定为正值时,会出现粒子发生器好象被粒子带着运动一样的效果。当该参数值为0时,没有任何效果。 1.10 Emitter Size X,Y and Z 当粒子发生器选择Box, Sphere, Grid and Light时,设定粒子发生器的大小。对于Layer and Layer Grid粒子发生器,只能设定Z参数。 2.Particle面板 在particle参数组可以设定粒子的所有外在属性,如大小、透明度、颜色,以及在整个生命周期内这些属性的变化。 2.1 Life [sec] 控制粒子的生命周期,它的值是以秒为单位的,该参数可以设定关键帧。 2.2 Life Random [%] 为粒子的生命周期赋予一个随机值,这样就不会出现“同生共死”的情况。 2.3 Particle Type 在该粒子系统中共有八种粒子类型:球形(sphere)、发光球形(glow sphere)、星形(star)、云团(cloudlet)、烟雾(smokelet)、自定义形(custom、custom colorize、custom fill)等。自定义类型(custom)是指用特定的层(可以是任何层)作为粒子,custom colorize类型在custom类型的基础上又增加了可以为粒子(层)根据其亮度信息来着色的能力,custom fill 类型在custom类型的基础上又增加了为粒子(层)根据其Alpha通道来着色的能力。 对于custom类型的粒子,如果用户选择一个动态的层作为粒子时,还有一个重要的概念:时间采样方式(time sampling mode)。系统主要提供了以下几种方式: (1)Start at Birth –Play Once 从头开始播放custom层粒子一次。粒子可能在custom层结束之前死亡(die),也可能是custom 层在粒子死亡之前就结束了。 (2)Start at Birth –Loop 循环播放custom层粒子。 (3)Start at Birth –Stretch 从头开始或者是对custom层进行时间延伸的方式播放custom层粒子,以匹配粒子的生命周
