摩托罗拉 Motorola 第二季度财务报告-2
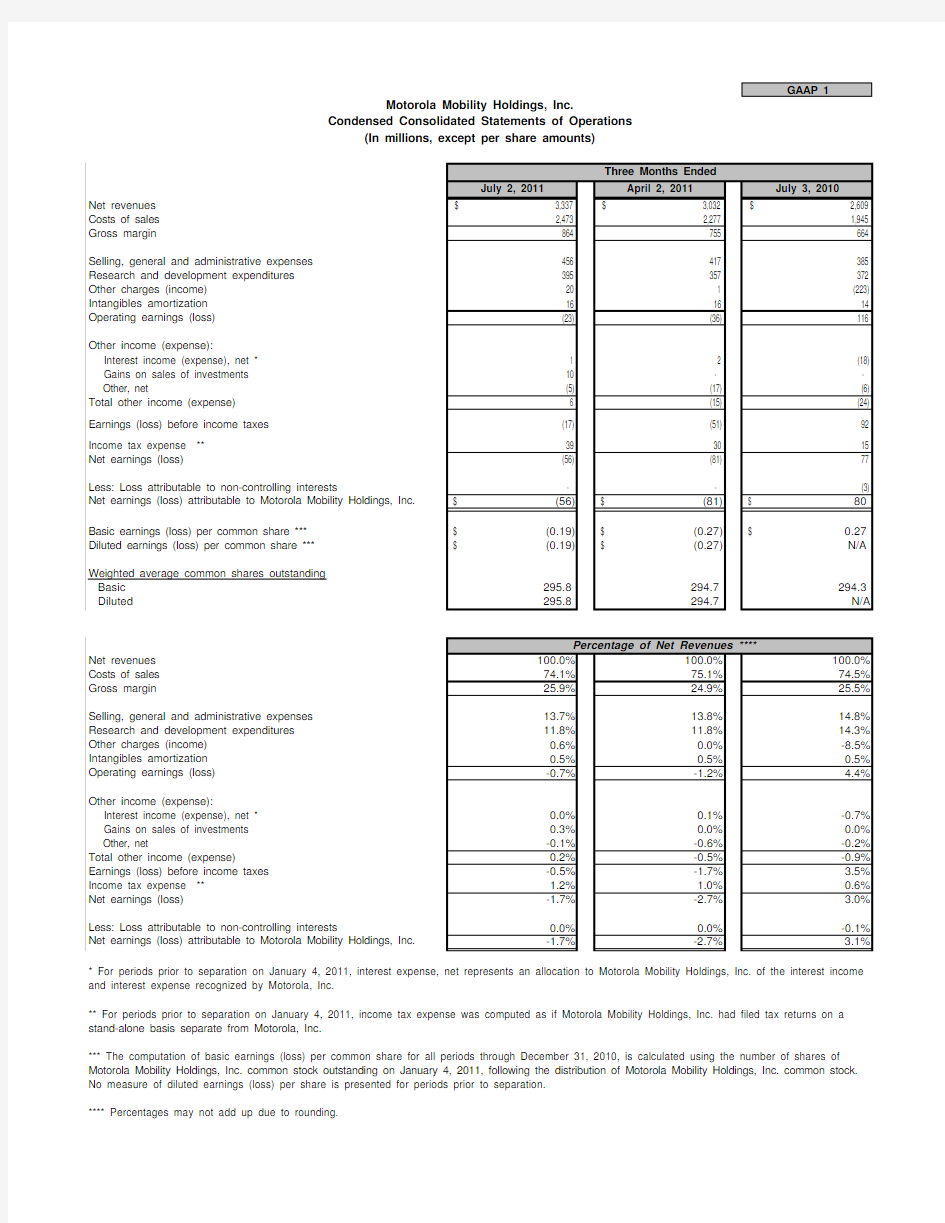
GAAP 1
July 2, 2011
April 2, 2011July 3, 2010Net revenues $ 3,337 $ 3,032 $ 2,609 Costs of sales 2,473 2,277 1,945 Gross margin
864 755 664 Selling, general and administrative expenses 456 417 385 Research and development expenditures 395 357 372 Other charges (income) 20 1 (223)Intangibles amortization 16 16 14 Operating earnings (loss) (23)
(36)
116
Other income (expense):
Interest income (expense), net * 1 2 (18) Gains on sales of investments 10 - - Other, net
(5) (17) (6)Total other income (expense) 6 (15) (24)Earnings (loss) before income taxes (17) (51) 92 Income tax expense ** 39 30 15 Net earnings (loss)
(56) (81) 77 Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests
- - (3)Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.(56)$ (81)$ 80$ Basic earnings (loss) per common share ***(0.19)$ (0.27)$ 0.27
$ Diluted earnings (loss) per common share ***(0.19)
$ (0.27)
$ N/A
Weighted average common shares outstanding Basic 295.8294.7294.3Diluted
295.8294.7N/A
Net revenues 100.0%100.0%100.0%Costs of sales 74.1%75.1%74.5%Gross margin
25.9%24.9%25.5%Selling, general and administrative expenses 13.7%13.8%14.8%Research and development expenditures 11.8%11.8%14.3%Other charges (income)0.6%0.0%-8.5%Intangibles amortization 0.5%0.5%0.5%Operating earnings (loss)
-0.7%
-1.2%
4.4%
Other income (expense):
Interest income (expense), net *0.0%0.1%-0.7% Gains on sales of investments 0.3%0.0%0.0% Other, net
-0.1%-0.6%-0.2%Total other income (expense)
0.2%-0.5%-0.9%Earnings (loss) before income taxes -0.5%-1.7% 3.5%Income tax expense ** 1.2% 1.0%0.6%Net earnings (loss)
-1.7%-2.7% 3.0%Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests
0.0%0.0%-0.1%Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
-1.7%
-2.7%
3.1%
** For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, income tax expense was computed as if Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. had filed tax returns on a stand-alone basis separate from Motorola, Inc.
*** The computation of basic earnings (loss) per common share for all periods through December 31, 2010, is calculated using the number of shares of
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock outstanding on January 4, 2011, following the distribution of Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock. No measure of diluted earnings (loss) per share is presented for periods prior to separation.**** Percentages may not add up due to rounding.
Percentage of Net Revenues ****
* For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, interest expense, net represents an allocation to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. of the interest income and interest expense recognized by Motorola, Inc.
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations
(In millions, except per share amounts)
Three Months Ended
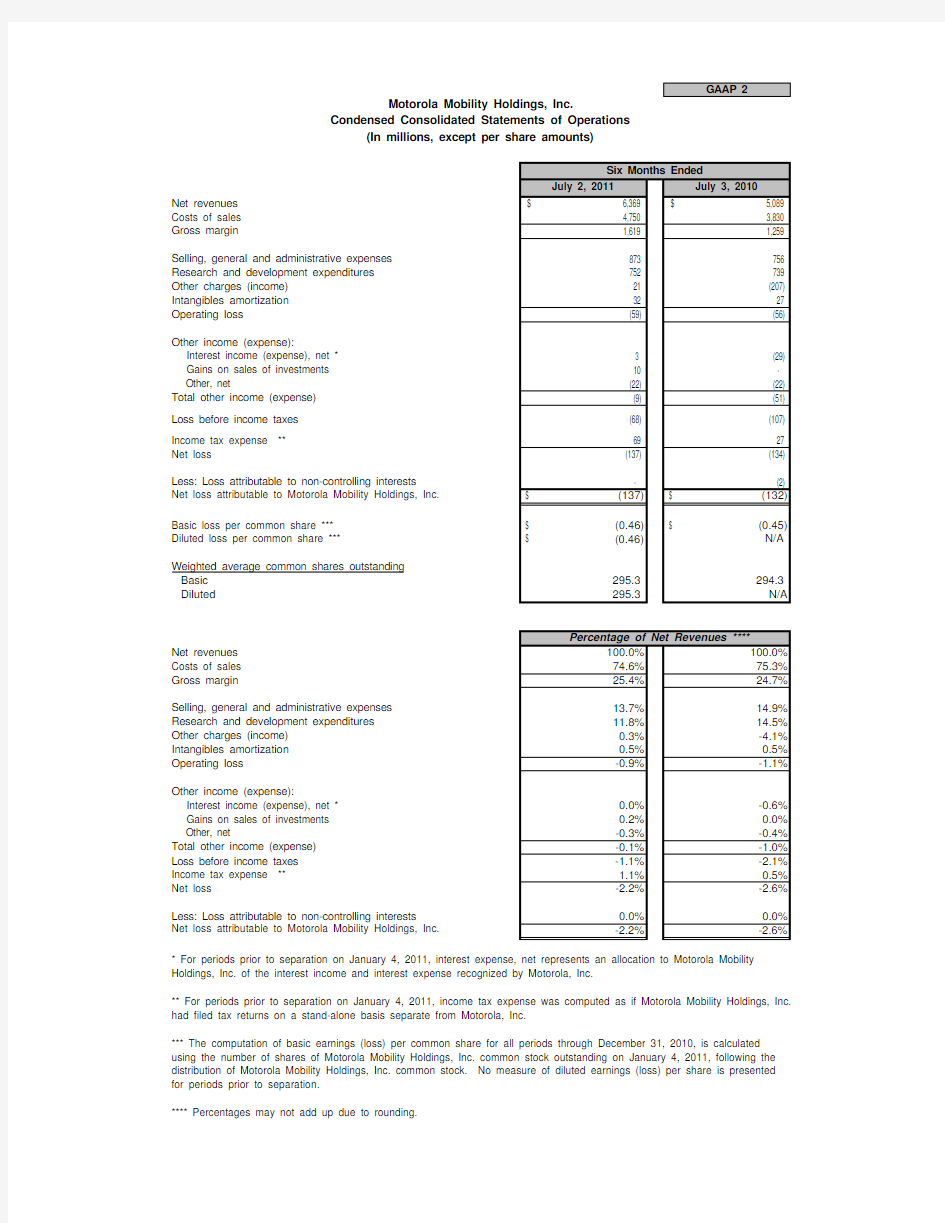
GAAP 2
July 2, 2011July 3, 2010Net revenues $ 6,369 $ 5,089 Costs of sales 4,750 3,830 Gross margin
1,619 1,259 Selling, general and administrative expenses 873 756 Research and development expenditures 752 739 Other charges (income) 21 (207)Intangibles amortization 32 27 Operating loss
(59)
(56)
Other income (expense):
Interest income (expense), net * 3 (29) Gains on sales of investments 10 - Other, net
(22) (22)Total other income (expense) (9) (51)Loss before income taxes (68) (107)Income tax expense ** 69 27 Net loss
(137) (134)Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests
- (2)Net loss attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.(137)$ (132)$ Basic loss per common share ***(0.46)$ (0.45)
$ Diluted loss per common share ***
(0.46)
$ N/A
Weighted average common shares outstanding Basic 295.3294.3Diluted
295.3N/A
Net revenues 100.0%100.0%Costs of sales 74.6%75.3%Gross margin
25.4%24.7%
Selling, general and administrative expenses 13.7%14.9%Research and development expenditures 11.8%14.5%Other charges (income)0.3%-4.1%Intangibles amortization 0.5%0.5%Operating loss
-0.9%
-1.1%
Other income (expense):
Interest income (expense), net *0.0%-0.6% Gains on sales of investments 0.2%0.0% Other, net
-0.3%-0.4%Total other income (expense)-0.1%-1.0%Loss before income taxes -1.1%-2.1%Income tax expense ** 1.1%0.5%Net loss
-2.2%-2.6%Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests
0.0%0.0%Net loss attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
-2.2%
-2.6%
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations
(In millions, except per share amounts)
Six Months Ended
** For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, income tax expense was computed as if Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.had filed tax returns on a stand-alone basis separate from Motorola, Inc.
**** Percentages may not add up due to rounding.
Percentage of Net Revenues ****
* For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, interest expense, net represents an allocation to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. of the interest income and interest expense recognized by Motorola, Inc.
*** The computation of basic earnings (loss) per common share for all periods through December 31, 2010, is calculated using the number of shares of Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock outstanding on January 4, 2011, following the distribution of Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock. No measure of diluted earnings (loss) per share is presented for periods prior to separation.
GAAP 3
July 2,April 2,July 3,2011
20112010Assets
Cash and cash equivalents *3,026$ 3,116$ -$ Accounts receivable, net 1,843 1,551 1,281 Inventories, net
744 859 629 Deferred income taxes **80 114 119 Other current assets 620 561 599 Total current assets
6,313 6,201 2,628 Cash deposits
180 168 - Property, plant and equipment, net 806 810 743 Investments
122 143 127 Deferred income taxes **98 58 50 Goodwill 1,423 1,397 1,292 Other assets 614 652 783 Total assets
9,556
$ 9,429
$ 5,623
$ Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable 1,728 1,580 1,323 Accrued liabilities 2,276 2,250 1,803 Total current liabilities 4,004 3,830 3,126 Other liabilities
648
670
495
Stockholders’ Equity:Common stock
3 3 - Additional paid-in capital
5,051 5,016 - Accumulated other comprehensive loss (13) (9) (328) Retained earnings (accumulated deficit)(137) (81) - Owner’s net investment, prior to Separation
- - 2,305 Total Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. stockholders’ equity 4,904 4,929 1,977 Non-controlling interests - - 25 Total stockholders’ equity
4,904 4,929 2,002 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity
9,556
$ 9,429
$ 5,623
$ ** For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, income taxes were computed as if Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. had filed tax returns on a stand-alone basis separate from Motorola, Inc.
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In millions)
* Until separation, the Company participated in Motorola, Inc.'s centralized cash management program. Accordingly, no cash and cash equivalents are presented on the Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet as of any reporting period prior to separation. On January 3, 2011, the Company received a cash contribution of $3.2 billion from Motorola, Inc., which included approximately $168 million of cash deposits.
July 2, 2011
April 2, 2011July 3, 2010Operating
Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.(56)$ (81)$ 80
$ Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests -
-
(3) Net earnings (loss)
(56) (81) 77 Adjustments to reconcile net earnings (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities:Depreciation and amortization
56 54 62 Share-based compensation expense 46 40 40 Non-cash other charges (income)18 (1) - Gains on sales of investments (10) -
- Deferred income taxes
(4) (11) 4 Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions and dispositions:Accounts receivable, net (284) 21 (97) Inventories
115 (16) (45) Other current assets
23 22 9 Accounts payable and accrued liabilities 94 1 112 Other assets and liabilities
2 78 (131) Net cash provided by operating activities - 107 31 Investing
Acquisitions and investments
(33) (11) - Proceeds from sales of investments 17 -
- Capital expenditures (46) (50) (23) Cash deposits (23) -
- Other, net
1 -
2 Net cash used for investing activities (84) (61) (21) Financing
Share-based compensation activity
(14) 16 - Capital contribution from Former Parent, net of cash deposits of $168-
3,032 - Other, net
-
15 - Net transfers to Former Parent
-
-
23 Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities
(14) 3,063 23 Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents 8 7 (33) Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents (90) 3,116 - Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period 3,116
-
- Cash and cash equivalents, end of period
3,026$
3,116$
-
$ * Until separation, the Company participated in Motorola, Inc.'s centralized cash management program. Accordingly, no cash and cash equivalents are presented on the
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet as of any reporting period prior to separation. On January 3, 2011, the Company received a cash contribution of $3.2 billion from Motorola, Inc., which included approximately $168 million of cash deposits.
(In millions)
Three Months Ended
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
July 2, 2011July 3, 2010Operating
Net loss attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.(137)$ (132)
$ Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests - (2) Net loss
(137) (134) Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities:Depreciation and amortization
110 111 Share-based compensation expense 86 78 Non-cash other charges
17 1 Gains on sales of investments (10) - Deferred income taxes
(15) (3) Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions and dispositions:Accounts receivable, net (263) 51 Inventories
99 60 Other current assets
45 79 Accounts payable and accrued liabilities 95 (89) Other assets and liabilities
80 (97) Net cash provided by operating activities 107 57 Investing
Acquisitions and investments
(44) (20) Proceeds from sales of investments 17 - Capital expenditures (96) (42) Cash deposits (23) - Other, net
1 6 Net cash used for investing activities (145) (56) Financing
Share-based compensation activity
2 - Capital contribution from Former Parent, net of cash deposits of $1683,032 - Other, net
15 - Net transfers to Former Parent
- (28) Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities
3,049 (28) Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents 15 27 Net increase in cash and cash equivalents
3,026 - Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period - - Cash and cash equivalents, end of period
3,026
$ -
$ * Until separation, the Company participated in Motorola, Inc.'s centralized cash management program. Accordingly, no cash and cash
equivalents are presented on the Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet as of any reporting period prior to
separation. On January 3, 2011, the Company received a cash contribution of $3.2 billion from Motorola, Inc., which included approximately $168 million of cash deposits.
(In millions)
Six Months Ended
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
GAAP 6
Three Months Ended
July 2, 2011
Three Months Ended
July 3, 2010% Change from
2010Mobile Devices 2,430$ 1,723$ 41% Home
907 886 2% Company Totals
3,337
$ 2,609
$ 28% Six Months Ended
July 2, 2011
Six Months Ended
July 3, 2010% Change from
2010Mobile Devices 4,558$ 3,365$ 35% Home
1,811 1,724 5% Company Totals
6,369
$ 5,089
$ 25%
Three Months Ended
July 2, 2011
Three Months Ended
July 3, 2010% Change from
2010Mobile Devices (85)$ 87$ (198)% Home
62 29 114% Company Totals
(23)
$ 116
$ (120)% Six Months Ended
July 2, 2011
Six Months Ended
July 3, 2010% Change from
2010Mobile Devices (174)$ (105)$ 66% Home
115 49 135% Company Totals
(59)
$ (56)
$ 5%
Net Revenues
Operating Earnings (Loss)
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Segment Information
(In millions)
Summarized below are the Company's Net revenues and Operating earnings (loss) by reportable segment for the three months and six months ended July 2, 2011 and July 3, 2010.
Net revenues $ 3,337 $ - $ 3,337 $ 3,032 $ - $ 3,032 Costs of sales 2,473 4 2,469 2,277 4 2,273 Gross margin
864 (4) 868 755 (4) 759 Selling, general and administrative expenses 456 28 428 417 21 396 Research and development expenditures 395 14 381 357 15 342 Other charges
20 20 - 1 - 1 Intangibles amortization 16 16 - 16 16 - Operating earnings (loss)
(23)
(82)
59
(36)
(56)
20
Other income (expense): Interest income, net
1 -
1
2 -
2
Gains on sales of investments 10 - 10 - - - Other, net
(5) - (5) (17) - (17)Total other income (expense)
6 - 6 (15) - (15)Earnings (loss) before income taxes (17) (82) 65 (51) (56) 5 Income tax expense 39 - 39 30 - 30 Net earnings (loss)
(56) (82) 26 (81) (56) (25)Less: Earnings attributable to non-controlling interests
- - - - - - Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.(56)$ (82)$ 26$ (81)$ (56)$ (25)$ Basic earnings (loss) per common share (0.19)$ (0.28)$ 0.09$ (0.27)$ (0.19)$ (0.08)$ Diluted earnings (loss) per common share (0.19)
$ (0.28)
$ 0.09
$ (0.27)
$ (0.19)
$ (0.08)
$ Weighted average common shares outstanding Basic 295.8
295.8295.8294.7294.7294.7Diluted
295.8295.8295.8294.7294.7294.7
Net revenues 100.0%100.0%100.0%100.0%Costs of sales 74.1%74.0%75.1%75.0%Gross margin
25.9%26.0%24.9%
25.0%Selling, general and administrative expenses 13.7%12.8%13.8%13.1%Research and development expenditures 11.8%11.4%11.8%11.3%Other charges
0.6%0.0%0.0%0.0%Intangibles amortization 0.5%0.0%0.5%0.0%Operating earnings (loss)
-0.7%
1.8%
-1.2%
0.7%
Other income (expense): Interest income, net
0.0%0.0%0.1%0.1% Gains on sales of investments 0.3%0.3%0.0%0.0% Other, net
-0.1%-0.1%-0.6%-0.6%Total other income (expense)
0.2%0.2%-0.5%-0.5%Earnings (loss) before income taxes -0.5% 1.9%-1.7%0.2%Income tax expense 1.2% 1.2% 1.0% 1.0%Net earnings (loss)
-1.7%0.8%-2.7%-0.8%Less: Earnings attributable to non-controlling interests
0.0%0.0%0.0%0.0%Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
-1.7%
0.8%
-2.7%
-0.8%
Percentage of Net Revenues *
* Percentages may not add up due to rounding.
Three Months Ended
Non-GAAP Results GAAP Results Non-GAAP Adjustments April 2, 2011
(In millions, except per share amounts)
Three Months Ended
July 2, 2011
GAAP Results
Non-GAAP Adjustments Non-GAAP Results
Net revenues $ 3,337 $ - $ 3,337 $ 2,609 $ - $ 2,609 Costs of sales 2,473 4 2,469 1,945 6 1,939 Gross margin
864 (4) 868 664 (6) 670 Selling, general and administrative expenses 456 28 428 385 22 363 Research and development expenditures 395 14 381 372 14 358 Other charges (income) 20 20 - (223) (223) - Intangibles amortization 16 16 - 14 14 - Operating earnings (loss)
(23) (82) 59 116 167 (51)Other income (expense):
- - - - - - Interest income (expense), net * 1 - 1 (18) - (18) Gains on sales of investments 10 - 10 - - - Other, net
(5) - (5) (6) - (6)Total other income (expense)
6 - 6 (24) - (24)Earnings (loss) before income taxes (17) (82) 65 92 16
7 (75)Income tax expense ** 39 - 39 15 15 Net earnings (loss)
(56) (82) 26 77 167 (90)Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests
- - - (3)- (3) Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.(56)$ (82)$ 26$ 80$ 167$ (87)$ Basic earnings (loss) per common share ***(0.19)$ (0.28)$ 0.09$ 0.27
$ 0.57
$ (0.30)
$ Diluted earnings (loss) per common share ***(0.19)
$ (0.28)
$ 0.09
$ N/A
N/A
N/A
Weighted average common shares outstanding***Basic 295.8295.8295.8294.3294.3294.3Diluted
295.8295.8295.8N/A N/A N/A
Net revenues 100.0%100.0%100.0%100.0%Costs of sales 74.1%74.0%74.5%74.3%Gross margin
25.9%26.0%25.5%
25.7%Selling, general and administrative expenses 13.7%12.8%14.8%13.9%Research and development expenditures 11.8%11.4%14.3%13.7%Other charges (income)0.6%0.0%-8.5%0.0%Intangibles amortization 0.5%0.0%0.5%0.0%Operating earnings (loss)
-0.7%
1.8%
4.4%
-2.0%
Other income (expense):
Interest income (expense), net *0.0%0.0%-0.7%-0.7% Gains on sales of investments 0.3%0.3%0.0%0.0% Other, net
-0.1%-0.1%-0.2%-0.2%Total other income (expense)
0.2%0.2%-0.9%-0.9%Earnings (loss) before income taxes -0.5% 1.9% 3.5%-2.9%Income tax expense ** 1.2% 1.2%0.6%0.6%Net earnings (loss)
-1.7%0.8% 3.0%-3.4%Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests
0.0%0.0%-0.1%-0.1%Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
-1.7%
0.8%
3.1%
-3.3%
Three Months Ended
** For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, income tax expense was computed as if Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. had filed tax returns on a stand-alone basis separate from Motorola, Inc.
July 2, 2011
GAAP Results
Non-GAAP
Adjustments Non-GAAP
Results * For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, interest expense, net represents an allocation to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. of the interest income and interest expense recognized by Motorola, Inc.
Percentage of Net Revenues ****
*** The computation of basic earnings (loss) per common share for all periods through December 31, 2010, is calculated using the number of shares of Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock outstanding on January 4, 2011, following the distribution of Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock. No measure of diluted earnings (loss) per share is presented for periods prior to separation.
**** Percentages may not add up due to rounding.
Three Months Ended
Non-GAAP Results GAAP Results Non-GAAP Adjustments July 3, 2010
(In millions, except per share amounts)
Non-GAAP 3
TOTAL
Mobile Devices Home
Net revenues
3,032$ 2,128$ 904$ Operating earnings (loss)
(36)
$ (89)$ 53$ Non-GAAP adjustments by P&L statement line:Statement Line Stock-based compensation expense Cost of sales 4 2 2 Stock-based compensation expense SG&A and R&D 36 23 13 Intangible assets amortization expense Intangibles amortization
16 3 13 Less: Total non-GAAP adjustments
56 28 28 Operating earnings (loss) after non-GAAP adjustments
20
$ (61)
$ 81
$ Operating earnings (loss) as a percentage of net revenues - GAAP
-1.2%-4.2% 5.9% Operating earnings (loss) as a percentage of net revenues - after non-GAAP adjustments
0.7%
-2.9%
9.0%
TOTAL
Mobile Devices Home
Net revenues
3,337$ 2,430$ 907$ Operating earnings (loss)
(23)
$ (85)$ 62$ Non-GAAP adjustments by P&L statement line:Statement Line Stock-based compensation expense Cost of sales 4 3 1 Stock-based compensation expense SG&A and R&D 42 29 13 Intangible assets amortization expense Intangibles amortization 16 2 14 Legal claim provision
Other charges (income)
20 20
- Less: Total non-GAAP adjustments
82 5428Operating earnings (loss) after non-GAAP adjustments
59
$ (31)
$ 90
$ Operating earnings (loss) as a percentage of net revenues - GAAP
-0.7%-3.5% 6.8% Operating earnings (loss) as a percentage of net revenues - after non-GAAP adjustments
1.8%
-1.3%
9.9%
Q2 2011
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Operating Earnings (Loss) after Non-GAAP Adjustments
Q1 2011
(In millions)
Non-GAAP Adjustments
Statement Line
Q1 2011 PBT (Inc)/Exp Q1 2011 Tax
Inc/(Exp)Q1 2011 PAT
(Inc)/Exp EPS Impact
(Incr)/Decr *GAAP Results
(51)$ 30$ (81)$ (0.27)$ Stock-based compensation expense Cost of sales, SG&A and R&D 40 - 40 (0.14) Intangible assets amortization expense Intangibles amortization
16 - 16 (0.05) Total Impact 56 - 56 (0.19) Non-GAAP Results
5
$ 30
$ (25)
$ (0.08)
$ Non-GAAP Adjustments
Statement Line
Q2 2011 PBT (Inc)/Exp Q2 2011 Tax
Inc/(Exp)Q2 2011 PAT
(Inc)/Exp EPS Impact
(Incr)/Decr *GAAP Results
(17)$ 39$ (56)$ (0.19)$ Stock-based compensation expense Cost of sales, SG&A and R&D 46 - 46 (0.16) Intangible assets amortization expense Intangibles amortization 16 - 16 (0.05) Legal claim provision Other charges (income)
20 - 20 (0.07) Total Impact 82 - 82 (0.28) Non-GAAP Results
65
$ 39
$ 26
$ 0.09
$ * EPS impact may not add up due to rounding.
Q2 2011
(In millions, except per share amounts)
Non-GAAP 4
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Non-GAAP Adjustments (Highlighted Items, Stock-Based Compensation Expense and Intangible Assets Amortization Expense)
Q1 2011
Non-GAAP 5
Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.
Revenue Mix by Region
(In millions)
Q1 2011
TOTAL Mobile Devices Home
North America62%56%77% Latin America17%20%11% Greater China11%15%2% EMEA6%5%8% Rest of Asia4%4%2% Total100%100%100%
Q2 2011
TOTAL Mobile Devices Home
North America51%43%73% Latin America21%24%13% Greater China11%14%2% EMEA9%9%9% Rest of Asia8%10%3% Total100%100%100%
《电工技术基础与技能》第二章电路的基础知识与基本测量习题(答案)
第二章电路的基础知识与基本测量 2.1电路与电路图 填空题 1.电路是指 所经过的路径。最简单的电路是由 、 、 和 组成。 2.画出以下各电气设备的图形符号(1)电灯 ,(2)接地 ,(3)电阻 3.电路通常有________、________和________三种状态。电路中不允许短路。 电流,电源、负载、导线、控制和保护装置 通路、断路、短路 选择题 1、电源在电路中的作用是( )。 A 、将电能转化为其它形式的能 B 、为电路提供保护 C 、形成电流的通路 D 、为电路提供能量 D 2、电路中安装熔断器,主要是为了( )。 A 、短路保护 B 、漏电保护 C 、过载保护 D 、以上都是 A 判断题 1、 电路在开路状态下,负载可能会损坏。( ) 2、 负载是提供电能的装置。( ) ×× 2.2电流及其测量 填空题 1.习惯上规定 电荷移动的方向为电流的方向。 的大小用电流强度来表示,其定义是单位时间内通过某一横截面的电荷量,电流强度的公式为I= 。电流的单位是 。 2.1min 内通过导体的电量是12c ,流过导体的电流是 A ,若导体两端电压是8v ,该导体的电阻为 Ω。 3. _____________是一种测量交流电流的专用仪表,其最大特点是可以在不断开线路的情况下测量电路的电流。 正,电流;t q ,A
0.2,40 钳形电流表 选择题 1、一般家用电器的工作电流为() A、100A B、0.3~0.6A C、2μA D、0.01 mA 2、以A作单位的物理量是() A、电量 B、电场强度 C、电流 D、电压 3、电流的基本单位是()。 A、安秒 B、安培 C、库仑 D、瓦特 4.如图所示,直流电流表接线图,正确的是()。 BCBC 判断题 1、电流是由电荷有规则的定向移动形成的。() 2、电流超过额定电流或低于额定电流,用电器具都不能正常工作。() 3、导体中电流的方向与电子流的方向一致。() √√× 2.3电压及其测量 填空题 1.单位换算:150Ω= KΩ 150mA= A , 0.008v= mV 2、电路中任意两点间的电压等于之差即UAB= 。 0.15,0.15,8 这两点电位,V A-V B 选择题 重点:电路中两点的电压高则() A、这两点的电位都高; B、这两点的电位差大; C 、这两点电位都大于零; D、以上说法都不对。 1、电路中两点的电压高,则() A、这两点的电位都高 B、这两点间的电位差大
摩托罗拉 MOTO
摩托罗拉MOTO 尽管摩托罗拉最近表现一直颇为沉寂,但其实也是暗流涌动,不少即将登场的新款机型已经悄然整装待发。日前,在网络上便泄露了摩托罗拉XT1053、XT1055、XT1056、XT1058、XT1080等五款新机的型号,预计在不久后将在北美市场推出。 代号Sasquatch和Yeti 此次泄露的摩托罗拉新机虽说有五款手机型号,但确切的说应该是仅有两款机型而已。包括摩托罗拉XT1053、XT1055、XT1056、XT1058等四款型号其实应该是一款新机的四个版本,隶属全新命名的摩托罗拉XT105X系列,主要针对不同的运营商推出或是类似MAXX此类的厚电版本而已。 尽管现在对这些机型的功能规格了解不多,但根据国外媒体披露的消息称,这两款新机的开发代号为“Sasquatch”和“Yeti”,其含义为大脚野人和大脚雪人,皆搭载的是Android4.2.2系统版本。 X Phone或在其中 值得一提的是,由于这些新机中的摩托罗拉XT1055此前曾经泄露了跑分成绩,所以不少人猜测该机很可能就是传说中的X Phone。而给出的理由便是该款手机搭载的是Android 4.2.2操作系统,拥有1.7GHz的高通骁龙600处理器。所以,该机前所未见的手机型号以及初步泄露的规格,使得摩托罗拉XT1055看上去似乎很有可能便是传说的X Phone。 而根据以往摩托罗拉手机型号的命名规则来看,摩托罗拉XT1055应该是一款支持HSPA+/WCDMA网络制式的机型;而摩托罗拉XT1056则可能是面向运营商Verizon的版本;摩托罗拉XT1058可能针对北美运营商AT&T推出;至于摩托罗拉XT1053则可能是面向欧洲或是全球市场推出的版本。 MOTO XT1080身世成谜 至于摩托罗拉XT1080则似乎显然更加神秘一些,目前所知道的部分是该机将搭载Andriod4.2.2系统,但没有任何其他有关功能规格方面的信息被泄露。不过,由于一款名为“Obake_verizon”的摩托罗拉神秘新机安兔兔跑分成绩的曝光,这使得该机的身份归属有了更多的猜测的空间。如果这款“Obake_verizon”是摩托罗拉XT1080的话,那么至少意味着该机不会是X Phone,原因在于该机将是一款面向运营商Verizon的机型。 而此前传闻X Phone将在8月的第一周上市, AT&T将成为首家销售X Phone的运营商,至于美国其他的运营商将在11月才能拿到这款手机。因此,综合以上信息来看,拥有多个版本的摩托罗拉XT150X系列有可能是传闻中的X Phone,其更多的信息预计将随着发布日期的临近而被不断披露。
摩托罗拉公司进入中国已经十多年
摩托罗拉公司进入中国已经十多年,取得了辉煌的业绩。其成功归功于许多因素,但很重要的一条是摩托罗拉把本土化列为公司在华发展四大战略之一,并且把它溶入所有业务之中。总结来看,主要有以下几个方面: 研发本土化 摩托罗拉在华取得成功的一个重要原因,是把世界上先进的技术带入了中国,并且积极推进技术研究与开发的本地化,加强与中国在研发上的合作。截止目前,摩托罗拉在华投资的8家合资企业,设在天津的生产基地和18家研发中心均引进了摩托罗拉公司的先进技术设备和一流产品,为在中国生产出世界一流的产品奠定了坚实的基础。 上海摩托罗拉寻呼机有限公司于1995年建立的时候,引进的是当时最新的FLEX 高速寻呼机技术。FLEX技术是摩托罗拉公司研究开发的。与传统制式寻呼机相比,这种制式的高速率寻呼机的用户容量增加了五倍,抗干扰能力增加10倍,电池寿命增加五倍,还能大大减少信号误差,改善接受信息的可靠性。经过三年时间的技术跟踪对比,FLEX技术已被国家有关部门正式确定为中国高速寻呼体制标准。 摩托罗拉于1996年成立杭州摩托罗拉移动电话用户机有限公司和杭州摩托罗拉移动电话系统有限公司,这两家企业均引进了摩托罗拉世界领先的技术,生产码多分址移动电话的系统设备和用户手机。这是中国最早的码多分址(CDMA)合资企业,也是摩托罗拉公司在美国境外第一家码多分址工厂。 此外,摩托罗拉公司在中国开展了一系列技术合作项目,其中主要的有:与清华大学合作建立"摩托罗拉北京亚洲制造研究中心",该中心是摩托罗拉在美国本土以外第一个生产技术研究实验室;与中国科学院下属的国家智能计算研究中心合作建立"高级计算机及通讯技术合作实验室",主要从事高级计算机技术的研究开发;与西安大唐电信公司合作,研究与开发CDMA系统;与联想集团合作建立"联想-摩托罗拉研究中心",从事个人计算机研究。 2000年,摩托罗拉还与东方通信和中国华大集成电路设计中心宣布联合开发中国的2。5G手机核心技术。据摩托罗拉(中国)电子有限公司总裁赖炳荣先生透露,摩托罗拉的半导体事业部准备与南开大学建立合作,共同开发半导体技术的研发,目前这方面的洽谈已有了良好的开端。
摩托罗拉发展史.
[]摩托罗拉在80后之前的几代人心里,几乎都占有相对重要的地位。在21世纪以前,摩托罗拉在中国乃至全球可以说都无愧于通讯终端领头人的这个称号,那个时期是摩托罗拉最为红火的时候。而到上世纪末,在手机制式由模拟制式向数字制式更替的关键时刻,摩托罗拉逐渐表现出了“廉颇老矣”的状态,由于转变速度和产品更新都没有跟上市场,其市场老大的地位逐渐被诺基亚替代,而且再也没有扳回。 进入21世纪之后,伴随着全球经济快速发展和各行业技术也飞速发展的同,无线通信行业也迎来了“百花齐放,百家争鸣”的第二春,在这个时期相比苹果 iPhone和谷歌Android后来者居上的状况,包括诺基亚在内的传统巨头都表现出了些许“力不从心”,而摩托罗拉借助谷歌Android之力大有“英雄末路,东山再起”之势头,下面我们就纵观一下摩托罗拉在近代的大致发展历程
摩托罗拉公司原名加尔文制造公司(Galvin Manufacturing Corp),创立于1928 年,由创始人之一的保罗.加尔文的名字命名。它最早是生产汽车里的收音机的,摩托罗拉则是这种收音机的品牌。在上世纪五六十年代,迫于日系厂商的竞争压力,摩托罗拉不得不放弃了汽车音响以及电视机业务,而当初正是摩托罗拉引发了这两个产品领域的技术变革。 1983年,摩托罗拉推出世界上第一部移动电话,并在随后的十几年里成为全球最大的移动电话厂商。其实早在1942年,摩托罗拉就研制出“手提式”的对讲机(Handy Talk ie)SCR-536 。这款手提式对讲机是为美国军方研制的。在当时美军的通信装备高出了其它国家一大截,因此在随后几年中,摩托罗拉一直都为美国军方提供服务。由此我们也可以从这一系列军用设备可以看出,摩托罗拉在无线电通信方面的实力有多强,它的调频技术和天线技术都是领先于世界的。
《电工技术基础》作业
本次作业是本门课程本学期的第1次作业,注释如下: 一、单项选择题(只有一个选项正确,共10道小题) 1. 电路如图1-67所示,流过电阻的电流I为( ). (B) -2A 2. 在图示1-71电感电路中,电压与电流的正确关系式应是( )。 (B) 3. 电路如图1-75所示,已知电源电压U= 9 V,电阻R= 3 Ω,R1= 6 Ω,R2= 3 Ω,则电流I值为 ( )。
(D) -3 A 4. 电路如图1-81所示,试计算电流源I S提供的功率为( )。 (D) 12W 5. 已知某电路的正弦电压 与正弦电流的相位差为,电路呈容性,则电压 与电流的相位关系为()。 (A) 滞后相位 6. 图3-63所示正弦交流电路中,已知,,V,则电压源有效值约为( )。 (A) 283 V
7. 电路如图5-49所示,换路前电路处于稳态,在 时开关S闭合,则电路的初始值电流为()。 (A) 0A 8. 电路如图5-53所示,换路前电路处于稳态,在 时开关S闭合,则电路的初始值电流为()。 (D) 4A 9. 电路如图5-55所示,在 时开关S闭合,则换路后电路的时间常数为()。
(D) 15C 10. 把图2-59 a 所示的电路用图2-59 b所示的等效电压源替代,则等效电压源的参数为 ( )。 (D) U S = -18V,R = 3 Ω 二、主观题(共10道小题) 11.试用电源的等效变换法求如图2-73所示电路中的电流I。 参考答案:
解题指南:电源等效变换法就是利用电压源串电阻与电流源并电阻之间对于外电路而言,可以进行等效替换。合理利用它们间的等效替换可以简化电路结构,有利于求解等效变换以外的电路部分的电压或电流(含待求参数部分电路不能参与变换)。本题中,根据待求电流I位置及电路结构,可将除电流I所在支路除外的电路进行等效变换化简电路。 解:根据电路结构,逐步进行电源的等效变换,如图所示 所以,电流 本题小结:电源等效变换法(变换公式及等效电源的方向),变换技巧(分析电路结构,使变换后的电路逐渐简化)。 12.试用电源的等效变换法求如图2-76所示电路中的电流I和电压U AB。 参考答案: 解题指南:本题可先采用电源等效变换法求出电流I,然后根据虚拟回路的电压方程求解电压U AB。
motorola协议解析
1、协议中Type是指Message Type,P是指Periodic message (注:The message is transmitted on a periodic basis only. The signals in the Periodic message do not have the ability to generate an event transmission of the message. All signals in a message may not have the same requirements on up-date time. Signals that have a lower requirement on the up-date time than the periodicity of the periodic message do not have to be up-dated every time the message is sent. However, the up-date time requirement has to be fulfilled for each signal, as defined by the Signal Age.) 2、协议中是motolora格式; 3、电池的总电流偏置-1600,是确定的格式,(当D=32000时,电流为0A。) 附: Position of signal in the CAN frame Each signal occupies a number of bit-positions in the Message Map, as indicated by the position range. The relation between the bit-positions used in the Message Map and the Byte/Bit position in the CAN frame is a static representation as illustrated in Table 1. Byte #0 in the table corresponds to the first data byte transmitted or received in the CAN frame, and Byte #n ( “n” is included between 0 and 7) is the last byte. Bit #7 is the most significant bit in the byte. Transmitting a message with 8 byte length on the bus, bit 7 (most significant bit of byte 0) will be transmitted first, followed by bit 6. Bit 56 (least significant bit of byte 7) will be transmitted at last. Bits row out: 7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,23, ………………,40,55,54,53,52,51,50,49,48,63,62,61,60 ,59,58,57,56 When a Module receives a message, the first bit received will be the bit located at position 7 in
中国联想并购摩托罗拉案例分析
中国联想并购摩托罗拉案例分析 2014年10月30日,联想集团(Lenovo)正式宣布完成并购摩托罗拉移动(Motorola),这起由国内IT届老大发起的海外并购行动终于落下帷幕。当年初联想作出从谷歌(Google)手中并购摩托罗拉的决定时,业界就有不同看法:有人认为谷歌是在抛售“鸡肋”,有人认为联想挖到了“璞玉”,众说纷纭,见仁见智。如今,联想已经完成并购审查和交易,并即将带领摩托罗拉重返中国市场。可以说,摩托罗拉已经为联想搭建了一座国际化的舞台,而盛装出镜的联想将为我们表演一台大戏。 一、案例简介 2014年1月30日,恰逢中国农历除夕,联想与谷歌同时宣布:前者将斥资29.1亿美元从后者手中收购摩托罗拉的智能手机业务(Motorola Smartphone)。2011年8月15日,摩托罗拉移动被谷歌以125亿美元收入麾下。这次收购,是联想自2005年并购IBM个人电脑业务后又一笔重大并购。 在并购消息正式公布之前,IT界人士就已经看出了联想的意图,不过几乎所有人都认为联想会收购黑莓(Blackberry)或台湾宏达(HTC),而摩托罗拉却成了最终的黑马。 杨元庆在接受媒体采访时说,“其实我们对摩托罗拉心
仪已久,但最后的结合可以说是‘闪婚’。”这位联想集团的掌舵人早在2010年就对摩托罗拉“动了心”,但后来被谷歌捷足先登。为此,杨元庆在自己家里专门宴请了谷歌董事长施密特,并明确表示,任何时候谷歌想放手这个业务,都可以找联想!两个多月前,杨元庆收到了施密特的E-mail,双方迅速展开谈判,并在短期内达成了共识。 据联想集团披露的消息,本次并购包括摩托罗拉旗下的诸多品牌,比如Moto X、Moto G以及Moto DROID等系列产品以及智能手机产品,包括产品规划与开发。至于专利,联想将只能获得摩托罗拉移动的2000项专利,而余下的15000项专利还是在谷歌手中。此外,联想还将收获摩托罗拉与50多家全球运营商的合作关系以及3500名员工。 联想为此付出多达29.1亿美元,在并购完成后随即支付14.1亿美元,其中现金支付6.6亿美元,联想普通股股份支付7.5亿美元,剩下的约15亿美元则以三年期本票支付。该价格至最终达成交易可能还会有所调整。 谷歌随后斥资7.5亿美元买入联想5.94%的股份,并于2月7日向HKEx提交了报告。 回顾联想近年来的发展可以发现,海外并购已成为联想拓展国际市场的一种强力手段:2005年并购IBM个人电脑,2011年并购日本NEC与德国Medion,2012年并购美国Stoneware及巴西CCE,这一系列的并购使得联想产品迅速
MOTO WLAN 摩托罗拉 AC快速配置指南
Motorola 摩托罗拉无线交换机 RFS7000/WS5100v3.x (以下配置以RFS7000为例) 快速配置
目录 快速配置指南 (3) 1 特别注意 (3) 2 AC配置前准备工作 (3) 3 AC基础配置 (4) 1.1 初次登录 (4) ***CLI 命令行指令概述 (7) 1.2 VLAN及IP地址配置 (9) 1.3 WLAN设置(含HOTSPOT配置) (12) 1.4 AP300设置及状态检查 (18) 1.5 接入终端状态检查 (22) 1.6 配置DHCP服务 (23) 1.7 配置静态路由 (25) 1.8 配置冗余热备 (27) 4 密码恢复 (29) 5 版本升级 (31) CLI命令行说明 (34) 参考拓扑 (38) 设备维护指南 (39) 1 日例行工作 (39) 1.1 机房温湿度检查。 (39) 1.2 电源设备检查。 (39) 1.3 设备供电情况检查(白班、夜班各一次)。 (39) 1.4 设备状态检查(白班、夜班各一次)。 (39) 1.5 设备告警信息(白班、夜班各一次) (42) 1.6 AP在线检查(白班、夜班各一次) (43) 1.7 检查各接入点登录网络的用户状态 (44) 1.8 检查DHCP SERVER服务器运行状态(3层部署时需要) (44) 2 周例行工作 (45) 2.1 故障统计汇总(每周一)。 (45) 2.2 备份电子版维护作业计划执行记录(每周五)。 (45) 3 月例行工作 (45) 3.1 WLAN MOTO设备配置文件备份。 (45) 3.2 传输资料的检查核对 (45) 3.3 AP终端运行情况检查 (45) 3.4 标签检查 (45) 3.5 进行系统设备巡检 (45)
摩托罗拉在中国手机市场竞争状况分析
摩托罗拉在中国手机市场竞争状况分析
摩托罗拉在中国手机市场竞争状况分析: (一)现有市场竞争格局发展 中国手机市场竞争格局的演变可以分为两个阶段:第一阶段是1987年至1995年。这一时期,摩托罗拉在中国手机市场上独领风骚。因为摩托罗拉是第一个进入中国移动通讯业的外国品牌。1987年,在广东省开通的移动通讯系统就是摩托罗拉的设备。由于缺乏竞争者,中国手机市场基本上由摩托罗拉独占。第二阶段是1996年至今。爱立信、诺基亚等后进者,抓住GSM数字网开通带来的机遇,市场份额急剧上升,直接挑战摩托罗拉,形成了摩托罗拉与爱立信、诺基亚三足鼎立的局面。除了这三大品牌外,飞力蒲、西门子、阿尔卡特、索尼等品牌也竞争激烈。近两年来,随着国内厂商实力的上升,出现了不少的国产手机品牌,如科键、东方通信、中兴、TCL等,也开始与国际品牌竞争。 (二)市场占有率 三大品牌(摩托罗拉、诺基亚、爱立信)在中国市场占有绝对优势,他们的市场占有率达到市场份额的80%以上。据慧聪国际咨询公司IT市场研究部的调查结果显示:目前,摩托罗拉手机在中国的市场占有率达到31.9%,居第一位;紧跟其后的是诺基亚,达到29.4%(考虑到有很多用户是几年前购买的手机,那么现有市场的实际销售量的品牌榜上,诺基亚应排前列)。排在第三位的是爱立信,达到21.4%,爱立信的用户群有相当部分分布在南方(如广州)等城市。摩托罗拉、诺基亚、爱立信市场占有率高达82.7%其余品牌的市场空间已非常狭窄。三大品牌之后的排名依次是:西门子、飞利蒲、松下及其他品牌。 (三)手机购买行为分析 90%的用户的手机是在1997年之后够买的。电视广告、他人介绍和报纸广告是购买手机的主要信息来源。有31.6%的手机用户购买手机是根据朋友、熟人的介绍。这表明在中国市场,亲情、友情等感情因素也相当会影响商业活动,也提醒手机商、经营商、网络运营商,每“善待三个老客户,将会
简单直流电路 练习题答案
电工技术基础与技能 第二章简单电路练习题 班别:高二()姓名:学号:成绩: 一、是非题 1、当外电路开路时,电源端电压等于零。() 2、短路状态下,电源内阻的压降为零。() 3、电阻值为R1=20Ω,R2=10Ω的两个电阻串联,因电阻小对电流的阻碍作用小,故R2中通过 的电流比R1中的电流大些。 () 4、一条马路上路灯总是同时亮,同时灭,因此这些灯都是串联接入电网的。() 5、通常照明电路中灯开得越多,总的负载电阻就越大。() 6、万用表的电压、电流及电阻档的刻度都是均匀的。() 7、通常万用表黑表笔所对应的是内电源的正极。() 8、改变万用表电阻挡倍率后,测量电阻之前必须进行电阻调零。() 9、电路中某两点的电位都很高,则这两点间的电压也一定很高。() 10、电路中选择的参考点改变了,各点的电位也将改变。() 二、选择题(2X20)请将正确的答案填在题后的答题卡中,否则无效。 1、在图2-29所示电路中,E=10V,R0=1Ω,要使Rp获得 最大功率,Rp应为( )Ω。 2、在闭合电路中,负载电阻增大,则端电压将( )。 A.减小 B.增大 C.不变 D.不能确定 3、将R1>R2>R3的三只电阻串联,然后接在电压为U的电源 上,获得功率最大的电阻是( )。 A. R1 B. R2 C. R3 D.不能确定 4、若将上题三只电阻并联后接在电压为U的电源上,获得功 率最大的电阻是( )。 A. R1 B. R2 C. R3 D.不能确定 5、一个额定值为220V、40W的白炽灯与一个额定值为220V、60W的白炽灯串联接在220V电源 上,则( )。 灯较亮较亮 C.两灯亮度相同 D.不能确定 6、两个电阻R1、R2并联,等效电阻值为( )。 A.两者的和除以两者的乘积 B. R1-R2 C.两者的乘积除以两者的和 D. 倒数和 7、两个阻值均为555Ω的电阻,作串联时的等效电阻 与作 并联时的等效电阻之比为( )。 :1 :2 :1:4 8、电路如图2-30所示,A点电位为( )V。 三、填充题 1、电动势为2V的电源,与9Ω的电阻接成闭合电 路,电源两级间的电压为,这时电路中 的电流为,电源内阻为___1__Ω。 2、在图2-31所示电路中,当开关S扳向2时,电压 表读数为;当开关S扳向1时,电流表读数 为3A,R = 2 Ω,则电源电动势为, 电源内阻为Ω。 3、有一个电流表,内阻为100Ω,满偏电流为3mA, 要把它改装成量程为6V的电压表,需Ω 的分压电阻;若要把它改装成量程为3A的电流表,则需Ω的分流电阻。 4、两个并联电阻,其中R1 = 200Ω,通过R1的电流I1 = ,通过整个并联电路的电流I = , 则R2 =Ω,R2中的电流I2 =。 5、用伏安法测电阻,如果待测电阻比电流表内阻__大得多__时,应采用__内接法__。这样测量 出的电阻值要比实际值___大_____。 6、用伏安法测电阻,如果待测电阻比电压表内阻__小得多__时,应采用__外接法__。这样测量 出的电阻值要比实际值___小_____。 7、在图2-32所示电路中,R1=2Ω,R2=3Ω,E=6V,内阻不计,I=,当电流从D流向A时, Uac=___5V__、Udc=;当电流从A流向D时,Uac=___7V__、Udc=。; 8、在图2-33所示电路中,E1=6V,E2=10V,内阻不计,R1=4Ω,R2=2Ω,R3 =10Ω,R4=9Ω, R5=1Ω,则V A=___2V__V,V B=___2V__V, V F=___1V___V。 四、计算题(5X6)
摩托罗拉MOTO602数字无绳电话说明书
摩托罗拉(MOTO)数字无绳电话操作说明 (提示:本机只能使用7号充电电池,首次充电需要充足24小时。)屏幕显示说明:
菜单功能介绍: 1.: PHONEBOOK (电话本). ADD ENTRY 储存电话号码 MODIFY ENTRY 修改已储存电话号码 DELETE ENTRY 删除已储存电话号码 2.: SETUP BASE VOLLIME 机座音量大小调节(0~5级大小调节)BASE MELODY 机座玲声选择(5种铃声选择) DEL HANDSET 删除手机 PIN CODE密码修改 DIAL MODE 音频与脉冲调节 RECALL 已注册手机查看 DEFAULT默认出厂设置 ECO MODE 节能模式
3.:HANDSET 手柄设置 BEEP 1. 按键声音开启/关闭低电量提醒开启/关闭超出范围提醒开启/关闭 INT RINGVOL 内部呼叫铃声音量调节 EXT RINGVOL 来电音量调节 INT MELODY 内部呼叫铃声选择 EXT MELODY 来电铃声选择 AUTO ANSWER (自动应答) 开启后会自动接听.无主人留言. NAME 手机名称编辑 LANGUAGE 语言设置 10种以上语言设置.(默认为英文) KEYLOCK?键盘锁 4.:DATE -- TIME 日期/时间调整 DATE SET 日期设置 CLOCK SET 时间设置 ALARM SET 报警开启/关闭 5.:REGISTER 注册 SELECT BASE 选择机座( 默认为BASE1 ) REG BASE 注册 (通话声音调节:按一下键.听到拨号音后按键调节.免提也一样) 一:接听/挂断来电/ 来电按和接听.按是听筒接听.按 是免提接听. 按接听后可以在按转换为免提. 但免提不可以转换为听筒接听的. 需要转接按后输入机器编号. 二:内部呼叫说明/待机状态下按后输入机器编号.接听按键. 三:储存电话号码/ ① : 储存新电话号码. 待机状态下.按键三下.然后输入姓名(编 辑为英文) 输入完成后按确认.然后在输入需要储存的电话号码.按 确认.然后您可以给此电话设置来电铃声.选择好后按确认.(不需要选择直接按确认) ② :修改已储存电话号码. 待机状态下.按键两下.在按键一 下. 按键两下确认修改.会显示您已储存的电话号码姓名.按键删 除然后重新编辑姓名. (如姓名不需要修改.则直接按确认到下一项.
摩托罗拉在中国手机市场竞争状况分析
摩托罗拉在中国手机市场竞争状况分析: (一)现有市场竞争格局发展 中国手机市场竞争格局的演变可以分为两个阶段:第一阶段是1987年至1995年。这一时期,摩托罗拉在中国手机市场上独领风骚。因为摩托罗拉是第一个进入中国移动通讯业的外国品牌。1987年,在广东省开通的移动通讯系统就是摩托罗拉的设备。由于缺乏竞争者,中国手机市场基本上由摩托罗拉独占。第二阶段是1996年至今。爱立信、诺基亚等后进者,抓住GSM数字网开通带来的机遇,市场份额急剧上升,直接挑战摩托罗拉,形成了摩托罗拉与爱立信、诺基亚三足鼎立的局面。除了这三大品牌外,飞力蒲、西门子、阿尔卡特、索尼等品牌也竞争激烈。近两年来,随着国内厂商实力的上升,出现了不少的国产手机品牌,如科键、东方通信、中兴、TCL等,也开始与国际品牌竞争。 (二)市场占有率 三大品牌(摩托罗拉、诺基亚、爱立信)在中国市场占有绝对优势,他们的市场占有率达到市场份额的80%以上。据慧聪国际咨询公司IT市场研究部的调查结果显示:目前,摩托罗拉手机在中国的市场占有率达到31.9%,居第一位;紧跟其后的是诺基亚,达到29.4%(考虑到有很多用户是几年前购买的手机,那么现有市场的实际销售量的品牌榜上,诺基亚应排前列)。排在第三位的是爱立信,达到21.4%,爱立信的用户群有相当部分分布在南方(如广州)等城市。摩托罗拉、诺基亚、爱立信市场占有率高达82.7%其余品牌的市场空间已非常狭窄。三大品牌之后的排名依次是:西门子、飞利蒲、松下及其他品牌。 (三)手机购买行为分析 90%的用户的手机是在1997年之后够买的。电视广告、他人介绍和报纸广告是购买手机的主要信息来源。有31.6%的手机用户购买手机是根据朋友、熟人的介绍。这表明在中国市场,亲情、友情等感情因素也相当会影响商业活动,也提醒手机商、经营商、网络运营商,每“善待三个老客户,将会有机会赢得一个新客户”。购买手机时,用户最关心的是通话质量,其次是性能、通话时间与待机时间。潜在用户最关心的是价格,然后才是性能、品牌。用户选择手
《电工技术基础》课程教学大纲
《电工技术基础》课程教学大纲 一、课程说明 适用专业:机械设备安装与维修、机械制造大类 前期课程:《普通物理》 二、教学性质和任务 《电工技术基础》是属于技术基础课。学生通过学习本课程应受到辩证唯物主义和爱国主义教育,获得电工技术必要的基础理论、基本知识和基本技能,了解电工技术的发展情况及在建设有中国特色的社会主义国家中的作用,为学习后续课程及从事有关的工程技术工作和科研工作打下一定的基础。 三、教学基本要求 (一)对基础部分的要求 1、基础部分包括:理解电路基本概念和定律;掌握电路分析方法;了解电工测量及安全 用电,掌握一阶线性电路暂态分析方法;对于正弦交流电路的基本概念要清楚;电路元件的特性、功率和能量转换关系要理解;电路的基本定律、定理、分析方法要掌握。 理解三相电路的基本概念,掌握对称三相电路的计算等内容。 2、非线性电阻电路的分析和周期性非正弦电路的分析由学生自学完成。 (二)对应用部分的要求 1、应用部分包括:铁心线圈和变压器,三相异步电动机,继电—接触器控制等内容。 2、本着加强基础,拓宽应用,压缩学时的原则,应用部分应确保电工技术发展的新领域, 使其体系和内容不断更新。又要对传统应用部分有基本的保证。应用部分的教学要求是对各种应用的基本情况进行介绍,掌握一些常规的概念和一些基本计算方法,为继续深造打下基础。 四、课程内容 (一)绪论 1、电能的利用与生产力的发展、工业革命、科学技术进步等的关系。 2、电气化对建设有中国特色的社会主义的关系及意义。 3、《电工技术》课程的性质、研究对象、任务、学习方法及与本专业的关系。 (二)电路的基本概念与定律 1、电路与电路模型的概念;电路变量的参考方向及理想电路元件R、L、C在一般激励
摩托罗拉在中国的投资战略
摩托罗拉在中国的投资是成功的。在全球所有的摩托罗拉子公 司中,中国的公司发展最快、效益最好、市场潜力最大。 ——摩托罗拉公司董事长 盖瑞·吐克(Gary Tooker) 以中国为家 ——摩托罗拉的本地化战略 摩托罗拉,一个中国家喻户晓的名字。1992年6月,摩托罗拉落户天津经济技术开发区,此后,它以惊人的速度向全国发展。据称,目前中国老百姓使用的寻呼机中,每10个就有8个是摩托罗拉产品,手机每3个就有一个是摩托罗拉生产的。到1998年底,摩托罗拉在中国的投资总额已达到12亿美元,是美国在华投资最多的企业,也是电子工业领域在华投资最多的外资企业。最近该公司又决定,在2000年前,将投资增加到25亿美元。 战略转移 摩托罗拉的前身是诞生于本世纪20年代的“高尔文制造公司”,该公司最初生产汽车用收音机和电池代用器。二战期间接受政府订货,生产无线电话机和FM 便携式无线电话收发机。1947年,公司更名为摩托罗拉公司,其通讯产品扩展到民用领域。 60年代,摩托罗拉产品开始大规模进入国际市场,并且在一些主要国家和地区建立起自己的生产基地。六七十年代,摩托罗拉的出口市场主要面向欧亚地区,生产基地主要建在亚洲特别是东南亚一带。1984年,摩托罗拉高层人士分析了亚太地区的形势,作出了一个具有战略性意义的决定,这就是进入中国市场。 摩托罗拉公司总裁罗伯特·高尔文于1986年秋访问了中国,他惊异地发现,中国到处都在蓬勃发展,而相比之下,通讯设备却是那样的落后。惊异过后,他有些喜不自禁,摩托罗拉施展拳脚的机会来了!次年,摩托罗拉在中国设立了代表处,接下来成立了摩托罗拉中国委员会。摩托罗拉将在中国的战略目标定义为:“整体投入,全公司参与;投资建立一个世界级的企业,使之在世界范围具有竞争力。”就这样,一期投资1.2亿美元的摩托罗拉(中国)电子有限公司在天津破土动工,这是一家独资的生产型企业,主要生产寻呼机、手机、半导体器件以及汽车电子配件等,以后又连续两次追加投资,使总投资达到了10亿美元。1996年,摩托罗拉在北京设立了一个投资性公司——摩托罗拉(中国)投资有限公司。与此同时,摩托罗拉与中国的其他合资合作项目也相继上马,到目前为止,摩托
激活老品牌之案例:摩托罗拉“MOTO”运动
激活老品牌之案例:摩托罗拉“MOTO”运动 ◆市场环境分析 从2001年7月开始,我国就超过美国成为世界上最大的移动通信市场,但我国的移动普及率只有近11%,与发达国家40%的普及率有很大差距,这说明中国手机市场潜力巨大。但同时,巨大的增长空间也令竞争变得空前激烈,每个品牌都有占据行业老大地位的机会。据统计,目前我国共有30多个品牌在争夺手机市场,国外品牌以摩托罗拉、诺基亚、爱立信、三星、西门子为主,国内品牌以TCL、波导、科健、联想为主。虽然目前国内品牌与国外品牌在销量上还存在很大差距,但不容怀疑的是,国产手机的市场份额正逐步上升,赛迪顾问在2002年11月发布的消息称,2002年三季度,中国手机市场正式排定新座次,摩托罗拉位居第一,国产手机商TCL杀入四强,并且与韩国三星的销量咬得很紧。 ◆社会环境分析 随着科技的发展,曾为奢侈品的手机已经变成非常大众化的消费品,并且各厂商生产的产品同质化程度非常高,如果单纯强调产品的功能性利益已完全不可能完全调动消费者的购买欲望,必须赋予产品更多的附加值,因此,各厂家纷纷开打心理战,依靠赋予产品的心理利益打动消费者。厂商之所以强调心理战,是因为现在的手机消费者追求个性化,不仅仅将手机作为沟通的工具,更把手机看作传达自己个性和情感的媒介。因此,消费者在选择手机时越来越重视产品的感性因素和符号意义,而不再是仅考虑产品的功能和价格。 ◆竞争对手分析 在中国手机市场第一位置拼得你死我活当属摩托罗拉和诺基亚,据零点调查对、XX、XX、成才等10个城市的实际用户和准备在2002年6月以前购买手机的潜在用户所做的调查显示,诺基亚无论在品牌提及率,还是品牌持有率,均与摩托罗拉难分伯仲。 与摩托罗拉相比,诺基亚进入中国市场的时间要晚许多,能在短时间内与摩托罗拉争锋,最大的原因是因为诺基亚准确地了解了消费者的需求,把握了手机的消费趋势。如在2000年,购买手机代表一种时尚,因此当时的年轻人不太在意手机有多大用处,而看重个性化的外观,于是诺基亚无外置天线的手机销势大为看涨。2001年,“拇指娱乐”市场显现。诺基亚联合运营商和IGP在互联网上推出更换手机显示图案、下载铃声的服务,顿时迎合了许多手机应用发烧友的喜好,把更换手机显示图案和铃声玩成一种时尚。由于不同品牌手机间的技术标准不同,同品牌手机才能互发手机显示图案,往往在一个朋友圈子里,大家都尽量买诺基亚手机,意外带动
摩托罗拉 Motorola 第二季度财务报告-2
GAAP 1 July 2, 2011 April 2, 2011July 3, 2010Net revenues $ 3,337 $ 3,032 $ 2,609 Costs of sales 2,473 2,277 1,945 Gross margin 864 755 664 Selling, general and administrative expenses 456 417 385 Research and development expenditures 395 357 372 Other charges (income) 20 1 (223)Intangibles amortization 16 16 14 Operating earnings (loss) (23) (36) 116 Other income (expense): Interest income (expense), net * 1 2 (18) Gains on sales of investments 10 - - Other, net (5) (17) (6)Total other income (expense) 6 (15) (24)Earnings (loss) before income taxes (17) (51) 92 Income tax expense ** 39 30 15 Net earnings (loss) (56) (81) 77 Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests - - (3)Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc.(56)$ (81)$ 80$ Basic earnings (loss) per common share ***(0.19)$ (0.27)$ 0.27 $ Diluted earnings (loss) per common share ***(0.19) $ (0.27) $ N/A Weighted average common shares outstanding Basic 295.8294.7294.3Diluted 295.8294.7N/A Net revenues 100.0%100.0%100.0%Costs of sales 74.1%75.1%74.5%Gross margin 25.9%24.9%25.5%Selling, general and administrative expenses 13.7%13.8%14.8%Research and development expenditures 11.8%11.8%14.3%Other charges (income)0.6%0.0%-8.5%Intangibles amortization 0.5%0.5%0.5%Operating earnings (loss) -0.7% -1.2% 4.4% Other income (expense): Interest income (expense), net *0.0%0.1%-0.7% Gains on sales of investments 0.3%0.0%0.0% Other, net -0.1%-0.6%-0.2%Total other income (expense) 0.2%-0.5%-0.9%Earnings (loss) before income taxes -0.5%-1.7% 3.5%Income tax expense ** 1.2% 1.0%0.6%Net earnings (loss) -1.7%-2.7% 3.0%Less: Loss attributable to non-controlling interests 0.0%0.0%-0.1%Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. -1.7% -2.7% 3.1% ** For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, income tax expense was computed as if Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. had filed tax returns on a stand-alone basis separate from Motorola, Inc. *** The computation of basic earnings (loss) per common share for all periods through December 31, 2010, is calculated using the number of shares of Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock outstanding on January 4, 2011, following the distribution of Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. common stock. No measure of diluted earnings (loss) per share is presented for periods prior to separation.**** Percentages may not add up due to rounding. Percentage of Net Revenues **** * For periods prior to separation on January 4, 2011, interest expense, net represents an allocation to Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. of the interest income and interest expense recognized by Motorola, Inc. Motorola Mobility Holdings, Inc. Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations (In millions, except per share amounts) Three Months Ended
第2章 建筑电气的电工技术基础
第2章建筑电气的电工技术基础 本章的前半部分介绍电路的基本概念和基本定律,然后着重阐述直流电路和交流电路的基本分析方法,这些电工的基本理论和基本知识贯穿于整个用电领域,所以通过对本章的学习,应该掌握好分析电路的基本方法,为后续内容的学习打下基础。 本章的后半部分介绍一些常用电气设备,如变压器、电动机、接触器、继电器等及其控制系统,这些设备都是在建筑施工及供配电中常用的电气设备,所以对这些设备的构造及其原理的了解,有助于施工过程中安全合理的使用。 2.1 电路的基本概念及基本定律 2.1.1 电路的基本概念 (1)电路的组成及作用 电流所流经的通路就称为电路。电路是为实现能量的传输和转换,或者为实现信号的传递和处理而将电气元件或设备组合而成的系统总称。 组成电路的系统可大可小,有的简单有的复杂,其形式多种多样,但通常都由电源、负载以及连接电源与负载的中间环节组成。 电源是将非电能量转换为电能的设备,如发电机、电池、整流电源等,它是电路运行的能量源泉。 负载是将电能转换为非电能的设备或元件,如电灯、电动机、电炉、扬声器等,它是电路中消耗能量的装置。 中间环节是传送、分配和控制电能的部分,它包括连接电源与负载的所有开关、导线、保护设备以及复杂的网络或系统。 如图2.1所示是一个最简单的照明电路,它由电源E、灯泡D、开关K及连接导线组成,当开关K闭合时,电路中就有电流流过,电灯D发光,将电能转换为光能和热能。 第3章建筑电气的电子技术基础 随着电子技术的飞速发展,通信系统、报警系统以及各种控制系统被越来越多地应用到各类建筑中,而且逐渐与建筑融为一体,因此,从事建筑工程的技术人员应对电子技术有一个基本的了解。本章首先介绍一些常用的半导体器件,井对其基本电路进行了分析计算,然后简单介绍一些基本的逻辑电路。 第4章电力系统 电能是能量的一种表现形式,在国民经济中占有十分重要的地位,不论是工农业生产中各种机械设备的运输、控制,还是日常生活中家用电器的使用和照明等都离不开电能。可以说,电力的发展与人们的生活密不可分,它直接影响着国民经济各部门的发展,影响着整个人类社会的进步。电能是如此的重要,它是如何产生并传输给用户的呢?众所周知,发电厂是把各种天然能源如煤炭、水能、核能、风力、太阳能、潮汐、地热等转化为电能的工厂,它分为火力发电厂、水
