(完整版)高中英语时态一表全
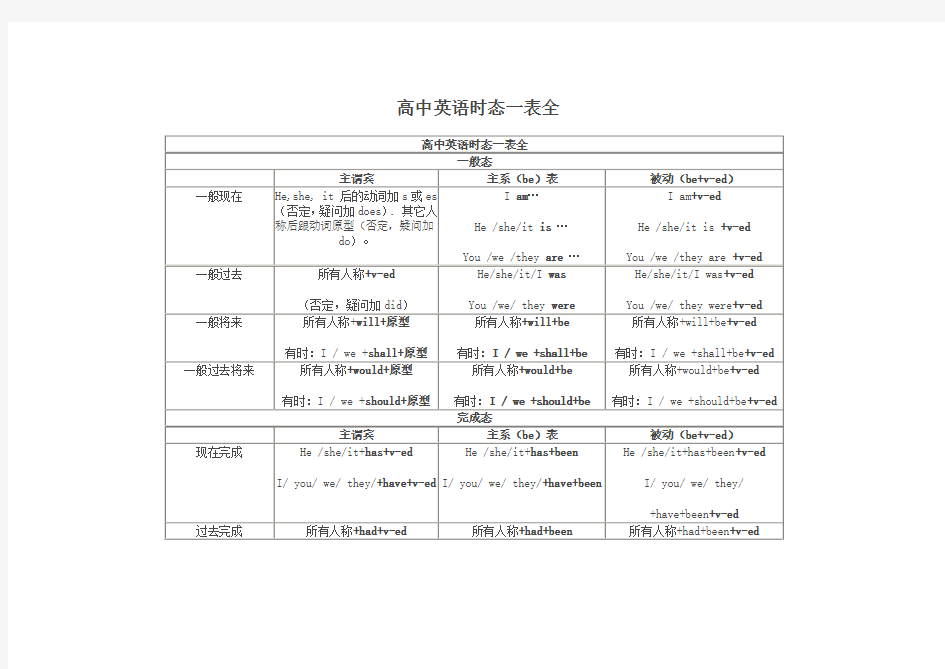
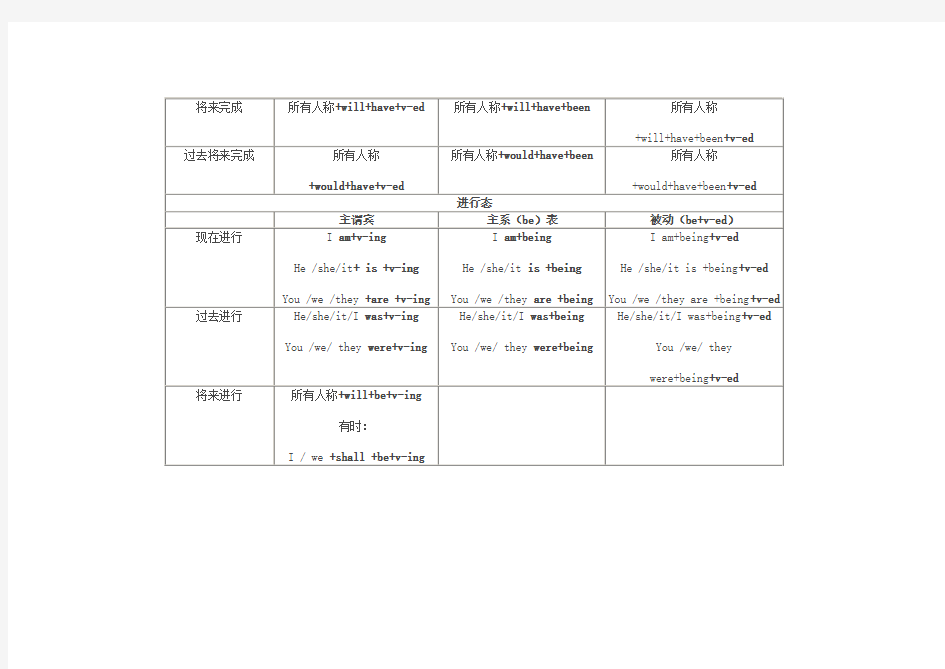
高中英语时态一表全
高中16种英语时态总结归纳
时态 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。) 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法: A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging C) 表示发生在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常用点动词,如:arrive, begin, find, give, lose 等。 例:John has broken his left leg.(约翰摔断了左腿。) 注意事项 A) 现在完成时是联系过去和现在的纽带。现在完成时和过去时的区别在于:现在完成时强调动作的动态,或受动态的影响,是动态的结果,对现在有影响;过去时只表示过去的某个具体时间里发生的动作,与现在没有联系。 例:He worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他曾经在那家医院工作了8年。这只是讲述一个过去的事实,他现在已经不在那家医院了。) He has worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他已经在那家医院里工作了8年。表示他从过去开始工作,一直工作到现在,现在仍在那家医院工作。) B) 因为含有for加一段时间或since加一个时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有动态和延续性的特点,所以
高中英语各种时态讲义
一、一般现在时的用法 1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。时间状语:every…, sometimes, at…, on Sunday I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。 The earth moves around the sun. 3) 表示格言或警句中。 Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。例如:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 4) 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。 Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well. 比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup. I am doing my homework now. 第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。再如:Now watch me, I switch on the current and stand back. 第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况。 知识扩展:一般现在时表将来 1)下列动词:come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时表将来。这主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。 The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. 2)倒装句,表示动作正在进行,如: Here comes the bus. = The bus is coming. 3)在时间或条件句中。 When Bill comes (不是will come), ask him to wait for me. 4)在动词hope, take care that, make sure that等后。 I hope they have a nice time next week. 二、一般过去时的用法 1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。时间状语有:yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982等。 I saw Tom in the street yesterday. 2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。 When I was a child, I often played football in the street. 3)用过去时表示现在,表示语气委婉礼貌。 (1)动词want, hope, wonder, think, intend 等。例如: Did you want anything else? I wondered if you could help me. (2)情态动词could, would,例如: Could you lend me your bike? 4)用在条件句中表示与现在或将来事实不符的虚拟语气。 If he were here now, we could turn to him for help. 注意比较下列句型: ◎It is time for sb. to do sth“到……时间了;该……了”,例如: It is time for you to go to bed.你该睡觉了。 ◎It is time sb. did sth. “时间已迟了;早该……了”,例如:
(完整版)高中英语时态语态练习及答案
1. I can guess you were in a hurry. You your sweater inside out. A. had worn B. wore C. were wearing D. are wearing 2. —We that you would fix the TV set this week. —I’m sorry. I to, bu t I’ve been too busy. A. had expected;had intended B. are expecting;had intended C. expect;intend D. expected;intend 3. He will stop showing off, if no notice of him. A. is taken B. will be taken C. takes D. has taken 4. —It is said that another new car factory now. —Yeah. It one and a half years. A. is building;takes B. is being built;will take C. is built;will take D. is being built;takes 5. —I’m sorry, but I shouldn’t have been so rude to you. —You your temper but that’s OK. A. have lost B. had lost C. did lose D. were losing 6. — Why? Tom, your shirt is so dirty! —Mum, I my storeroom downstairs。 A. cleaned B. have worked C. was cleaning D. have been cleaning 7. They won’t buy new clothes because they money to buy a color TV set. A. save B. are saving C. has saved D. were saving 8. Good heavens! There you are! We anxious about you, and we you back throughout the night. A. are;expect B. were;had expected C. have been;were expecting D. are;were expecting 9. I’ve finally finished my paper and it me an entire month. A. takes B. took C. was taken D. had taken 10. The traffic in our city is already good and it even better. A. gets B. got C. has got D. is getting 11. — Has Jack finished his homework yet? —I have no idea;he it this morning. A. was doing B. had been doing C. has done D. did 12. — I will come to attend your lecture at 10:00 tomorrow. —I’m sorry, by then my lecture will have ended and I my guests in my office. A. is being met B. will meet C. will be meeting D. will have met 13. — Alice came back home the day before yesterday. —Really ? Where ? A. has she been B. had she been C. has she gone D. had she gone 14. John and I friends for eight years. We first got to know each other at a Christmas party. But we each other a couple of times before that. A. had been;have met B. have been;have met C. had been;had met D. have been;had met 15. I ping-pong quite well, but I haven’t had time to play since the new year. A. will play B. have played C. played D. play 16. I’ve won a holiday for two to Florida. I my mum. A. take B. am taking C. have taken D. will have taken 17. —You haven’t said a word about my new coat, Brenda. Do you like it? —I’ m sorry I anything about it sooner. I certainly think it’s pretty on you. A. wasn’t saying B. don’t say
高中16种英语时态总结归纳
16种英语时态总结归纳 时态(Tense )是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相 应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A)表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B)习惯用语。 C)经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D)客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E)表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续 等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点 运行的交通方式。 例: The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F)在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例: When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours. (等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。) 2. 现在进行时(be doing)用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法: A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例: I bought a new house, but I _________ m y old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold 。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动 词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例: Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged
(完整)高中英语语法(时态和语态)
高中英语语法(时态和语态) 一.动词的时态 时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。 (一)一般现在时(do / does) 1.具体用法 1) 表示经常性或习惯性动作 We always care for each other and help each other. 我们总是互相关心互相帮助。 He goes to school every day. 2)表示现在的特征或状态 He is very happy. Do you sing? ----A little. 3)表示普遍真理 Light travels faster than sound. 光速比声速快。 Actions speak louder than words. 行动胜过言语。 * 常与一般现在时态连用的词或短语主要有:often, usually, sometimes, every day, every morning/afternoon, on Sundays/weekends等等。 I often go to the cinema on Sundays. 我经常星期天去看电影。 He goes to work early every day. 他每天上班很早。 (二)一般过去时( did ) (1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。例如: We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film. (2)表示过去习惯性动作。例如: He always went to class last. I used to do my homework in the library. (三)一般将来时( will / shall do) 1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。例如: I shall graduate next year. 2)一般将来时有时可以表示一种倾向或习惯性动作。如 Crops will die without water. You won’t succeed with out their support. 3) 几种替代形式: *be going to +v在口语中广泛使用,表示准备做或将发生的事情。例如: I'm going to buy a house when we've saved enough money. *be to +v表示计划安排要做的事,具有"必要"的强制性意义。例如: I am to play tennis this afternoon. *be about to +v表示即将发生的事情。例如: He was about to start. *be due to +v表示预先确定了的事,必定发生的事。例如: The train is due to depart in ten minutes. 5)少数动词如:begin, come, leave, go, arrive, start, stop, return, open, close等的一般现在时可用来表示将来的动作。(多用来表示按计划事先安排好即将发生的动作,句中通常还有一个表示将来的时间状语)。例如: The meeting begins at seven.
(完整版)高中16种英语时态总结归纳
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。) 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法: A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging
(完整版)高中英语动词时态和语态专项练习题及答案
高中英语动词时态和语态专项练习题 语境中的时态和语态具有灵活多变的特点,因此找出隐含于上下文中的时间信息,正确认定动作行为所发生的时间是解题的关键。做动词时态和语态填空题时,常常按以下几个步骤: (1)注意题干所提供的信息,如语境、情景以及说话人的情感; (2)根据句中的时间状语以及一些副词判断时态; (3)考虑语态; (4)考虑时态的一致性。另外,复习时,还要涉及到短暂性动词与延续性动词,这两个概念一定要搞清。短暂性动词用于进行时态和完成时态都要受到限制。 1.(2002全国高考题)-You haven't said a word about my new coat,Brenda.Do you like it? -I'm sorry I ________ anything about it sooner.I certainly think it's pretty on you. A.wasn't saying B.don't say C.won't say D.didn't say 2.(2002全国高考题)I wonder why Jenny ________us recently.We should have heard from her by now. A.hasn't written B.doesn't write C.won't write D.hadn't written 3.(2003北京春季高考题)-When will you come to see me,Dad? -I will go to see you when you ________ the training course. A.will have finished B.will finish C.are finishing D.finish 4.(2003北京春季高考题)-How long ________ at this job? -Since 1990. A.were you employed B.have you been employed C.had you been employed D.will you be employed 5.(2003上海春季高考题)By the end of last year,another new gymnasium ________ in Beijing. A.would be completed B.was being completed
(word完整版)高中英语时态语态讲解及习题
时态与语态 一.一般现在时,表示现在经常性、习惯性的动作和状态,常见的时间状语包括sometimes, often, usually, always,occasionally, now and then,on weekends,on Sundays,every week/month/year等 She always takes a walk in the evening. He often does his homework in his study. 1.一般现在时表示客观真理、科学事实及自然现象和谚语格言中,此用法即使出现在 过去语境中,也用一般现在时。 The moon goes around the earth. Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败 He said the earth is round. 2.主句是一般将来时,由when,after, before, as soon as, the minute,whenever等 引导的时间状语和由if, unless, so long as, once等引导的条件状语和however,even if等引导的让步状语从句中一般用一般现在时表示将来。如: l’ll go there after I finish my work. If it rains tomorrow,I won’t go there. I will tell her when she comes tomorrow. Even if it rains tomorrow, the sports meeting will take place. 3.在以here,there开头的句子里,go,come等少数动词的一般在时表示正在发生的动 作。例如: There goes the bell.铃响了。 There comes the bus.汽车来了。 Here she comes.她来了。 4. But for the fact that…从句中,that 从句的谓语动词时态要根据句子谓语所表示 的时间而定。 But for the fact that he is busy now, he would be here. But for the fact that you were ill, I would have had you print the papers. 二、一般过去时 表示过去的经常性、习惯性的动作或状态或者某个人过去的经历,与现在无关,常用的时间状语有yesterday, the day before yesterday, an hour ago, the other day, last month/year, just now, in 1982, in the old days, in the past, when I was young, when I was in London,when I was a child等 I received two letters last week. The Olympic Games were held in Beijing in 2008. When I was in Beijing, I often went to Beijing university. 1.表示某人过去的经历 1) ---- Have you graduated from the university? ----- Yes, I learned English for 4 years in the university.
高中英语中10种动词时态
英语中的动词有时态(Tense)要求。所谓“时”,即动作发生的时间;“态”, 即动作的方式状态。“时”有四种:现在时,过去时,将来时,过去将来时; “态”也有四种:一般式,进行式,完成式,完成进行式。因此,英语中一共有 二.新课讲解 1.一般过去时(the Past Simple) (1)用法(uses) 表示过去某时发生的动作或存在的情况。如: He worked in a bank all his life. He discovered a desert island in the Pcific. The safari was exciting but dangerous. I knew what he meant. They always interviewed new employees on Fridays. (2)形式(form) 即动词的过去式,分两种情况,一种是在动词结尾加ed或ied,这种动词 称为规则动词,另一种不能加,形式多样,称为不规则动词。 规则动词: a.一般情况下,动词词尾加 -ed ,如: work-worked play-played want-wanted act-acted b.以不发音的 -e 结尾动词,动词词尾加 -d,如: live-lived move-moved decide-decided decline-declined hope-hoped judge-judged raise-raised wipe-wiped c.以辅音字母 + y结尾的动词,把-y变为-i 再加-ed,如: study-studied try-tried copy-copied justify-justified cry-cried carry-carried embody-embodied empty-emptied d.以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,双写词尾辅音字母,再加 -ed,如: stop-stopped beg-begged drag-dragged drop-dropped plan-planned drip-dripped
英语时态总结表格
定义时间状语(标志)主动结构被动结构备注 一般现在时 经常、反复发生 的动作或行为及 现在的某种状况。 科学真理,客观 规律 often, usually, always, sometimes, every day(week,month), once a week, on Mondays, etc. 动词原形/第三人称 单数+s/es eg. do/does Be+过去分词 Eg.be +done 感观动词、 在时间,让步, 条件状语从句中, 一般现在时表将 来(主将从现) 一般过去时 过去某个时间里 发生的动作或状 态;过去习惯性、 经常性的动作、行 为。 ago, yesterday, last week(month, year…), in +年份, just now, one day,once, long long ago,in the past, etc. 动词过去时 eg. did Was/were+过去 分词 Eg.Was/were +done 过去经常发生用 used to do 一般将来时 表示将要发生的 动作或存在的状 态及打算、计划或 准备做某事。 Tomorrow,tomorrow morning/afternoon, the day after tomorrow ,next Sunday/week/year/mont h,soon, in a few days/ minutes(in+时间段)、时间 段+later,in(the)future, before long,etc 1.will/shall+动词原形 3.be going to do 2.be about to do Eg. will do Will /shall+be+ 过去分词 Eg.Will /shall be done 现在进行时 表示现阶段或说 话时正在进行的 动作或状态。 now, at this time, these days,look!listen! etc. am/ is/ are +现在分 词 eg.am/ is/ are+doing Is/am/are+being +过去分词 Eg.Is/am/are being done 感官动词无进行 时、 表位置移动的词 进行时表将来。 过去进行时表示过去某时刻 (时段)正在发生 或进行的动作或 行为。 过去将要发生 at this time yesterday when+一般过去时从句 Was/were+现在分词 Eg.was/ were+ doing Was/were +being+过去分 词 Eg.Was/were being done 现在完成时 过去发生或已经 完成的动作对现 在造成的影响或 结果,或从过去已 经开始,持续到现 在的动作或状态。 already, yet, just, ever, never, before, recently,in the past few years,由 for/since引导的时间状 语。 Have/has+过去分词 Eg.have/ has +done Has /have +been +过去分词 Eg.Has /have been done 动词必须用持续 性动词,不用短 暂性动词。 不和明确表示时 间的状语连用,只 和不确定时间连 用。 过去完成时 表示在过去某一 时间或动作之前 已经发生或完成 的动作或情况。表 示“过去的过 去” by, before等构成的过去 时间短语连用或用于 when, before, until等引导 的从句中。 Had +过去分词 Eg.had+ done Had+been+过去 分词 Eg.had been done Hardly/scarcely …when,no sooner…than “一…就…”,前 句用完成,后句用 过去 过去将来时 表示在过去的某 个时候看来将要 发生的动作或者 存在的状态。 The next day(morning, year), the following month (week),etc. 1.would+动词原形 2.was/ were going to +do Eg.would do 常用于转述某人 的话(间接引语 中) 规则V: 过去分词=过去式:V+ed 现在分词:V+ing 不规则V:P147
高中英语时态总结精选
一、一般现在时 1.结构:主语为第三人称单数,谓动要变化,其余人称用原形. 2.用法: ①表示现在经常性或习惯性的动作。描述当前时间内经常出现、反复发生的动作或存在的状态。在这种情景中,句子常带有表示频率的时间状语:always,everyday,often,onceaweek(month,year,etc.),sometimes,seld om,usually等等,以表示句中的动作或状态是习惯性的、经常性的。 ②表示现在的能力、特征、职业等。 ③陈述客观事实和普遍真理。即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时 ④表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式 ⑤主句是将来时态或表示将来意义,时间状语从句和条件状语从句须用一般现在时表将来。常用的引导词有:时间: when,until,after,before,assoonas,once,themoment/theminute,thed ay;条件:if,unless,provided. ⑥用于“the+比较级?,the+比较级?”(越……越……)句型中,若主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现在时。 二、现在进行时(bedoing) 1.结构:be(am,are,is)+doing 2.时间状语:now,atthemoment,thesedays,nowadays,atpresent 3.用法:主要用来描述正在发生的动作,或是"现阶段"一直在进行的动作。 ①表示现在(指说话时)正在发生的事情。
②表示目前这段时间内正在进行的动作,但说话时动作未必正在进行 ③现在进行时表示将来,主要表示在近期按计划或安排要发生的动作 ④现在进行时与always/forever/constantly/continuously/allthetime 等副词连用表示反复或习惯性的动作,表示说话人的情感,如:赞许、批评;喜欢、厌恶等。这时的动作并不是正在发生或进行,而是表示经常性,相当于"一般现在时"所描述的情况。 ⑤动词be的现在进行时,表示一时的表现或暂时的状态 能这样用的形容词多为 angry,careful,clever,stupid,kind,brave,friendly,rude,polite等动态形容词。 ⑥表示思维、心理状态,感觉、情感的动词 love,hate,please,want,hope,need,prefer,believe,think?表存在状态的动词appear,exist,lie,be,have,include,contain,belongto,datefrom?表感官的动词feel,see,hear,notice,smell,taste,look?不宜用进行时 三、一般将来时 1.时间状语:tomorrow,nextweek,fromnowon,inthefuture,in+时间段 2.表示将来时的常见形式:beto/begoingto/beaboutto/be+ v-ing/bedueto/will/shall+动原 3.用法:主要用来描述将要发生的动作或存在于未来的情况。 ①动作在现在或目前还未发生,要在将来的某个时间内发生;它没有主观性,是"纯粹的将来动作"。 ②表示某个意图没有经过事先考虑,而是在说话的时候才决定做某事用will。
英语十六时态表格完整总结
英语十六时态表格总结(很全面) 目录 一般现在时、一般过去时 (1) 一般将来时、过去将来时 (2) 现在进行时、过去进行时 (2) 现在完成时、过去完成时 (3) 英语时态表—英语时态举例! (3) 详细讲解-一般现在时 (5) 详细讲解-现在进行时、一般过去时 (6) 现在进行时 (6) 一般过去时 (6) 详细讲解-过去进行时、过去完成时、 (7) 过去进行时 (7) 过去完成时 (7) 详细讲解-过去完成进行时、一般将来时 (8) 过去完成进行时 (8) 一般将来时 (9) 详细讲解-将来进行时 (10) 将来进行时 (10) 详细讲解-过去将来时、将来完成时 (11) 过去将来时 (11) 将来完成时 (11)
英语共有16种时态! 常用的有12个:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、过去将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、将来完成时、现在完成进行时和过去完成进行时。 其他时态很少单独使用!下面发部分英语时态表吧!希望能对你们有帮助! 一般现在时、一般过去时 时态 名称 结构常连用的词主要用法例句 一般现在时1 be动词用am/is/are表 示,之后接名词,形容 词或介词。 often; usually; every…; sometimes; always; never; once/twice/… a week/month/year; on Sundays/Mondays /….; 一般现在时表示没 有时限的持久存在 的习惯性的动作或 状态,或现阶段反 复发生的动作或状 态 陈述句:I am an office worker. He is so lazy.They are at home now. 否定句:I am not Tim. She is not very beautiful. They are not in the office. 一般疑问句:Are you an officeassistant? Is she beautiful? 2行为动词用V原形或 V-s/es,引导疑问句和否 定句,用do或don’t; 第三人称时用does或 doesn’t,有does出现动 词用原形;第三人称陈 述句V后加s或es. 陈述句:I work in Shanghai. He works at home. Davy never watches TV at home. 否定句: I don’t like the food in KFC. Davy doesn’t like the food in KFC either. 一般疑问句: Do you want a cup of coffee? Does she live near thesubway station? 一般过去时1.be动词用过去式was 或were表示。 yesterday; the day before yesterday; last week/month/year/ ….; … ago; a moment ago; just now; on/in+过去的时 间; 在过去时间里所发 生的动作或存在的 状态。 陈述句:I was a big boss.He was beautiful. We were in Beijing last year. 否定句: I was not at home at that moment. We were not at work yesterday. 一般疑问句: Were you a teacher? Was she in the office last week? 2行为动词用V-ed,陈 述句,疑问句和否定句 借助于did,有did出现动 词用原形。 陈述句:I worked in Sunmoon. We studied English there. He lived inHongKong. 否定句: I didn’t work here. They didn’t see me. She liked English a lot. 一般疑问句: Did you go to America? Did he work in Sunmoon?
(完整版)高中英语时态和语态专项练习题
高中英语动词时态和语态专项练习题 1 (2002全国高考题)—You haven’t said a word about my new coat,Brenda.Do you like it? —I’m sorry I ________ anything about it sooner.I certainly think it’s pretty on you. A.wasn’t saying B.don’t say C.won’t say D.didn’t say 2.(2002全国高考题)I wonder why Jenny ________us recently.We should have heard from her by now. A.hasn’t written B.doesn’t write C.won’t write D.hadn’t written 3.(2003北京春季高考题)—When will you come to see me,Dad? —I will go to see you when you ________ the training course. A.will have finished B.will finish C.are finishing D.finish 4.(2003北京春季高考题)—How long ________ at this job? —Since 1990. A.were you employed B.have you been employed C.had you been employed D.will you be employed 5.(2003上海春季高考题)By the end of last year,another new gymnasium ________ in Beijing. A.would be completed B.was being completed C.has been completed D.had been completed 6.(2002北京高考题)The little girl ________her heart out because she ________ her toy bear and believed she wasn’t ever going to find it. A.had cried; lost B.cried; had lost C.has cried; has lost D.cries; has lost 7.(2002北京高考题)—Excuse me,sir.Would you do me a favor? —Of course.What is it? —I ________ if you could tell me how to fill out this form. A.had wondered B.was wondering C.would wonder D.did wonder 8.(2002上海高考题)He will have learned English for eight years by the time he ________ from the university next year. A.will graduate B.will have graduated C.graduates D.is to graduate 9.(2002上海高考题)I feel it is your husband who ________for the spoiled child. A.is to blame B.is going to blame C.is to be blame D.should blame 10.He has been writing the composition the whole morning and he still ________. A.has been B.does C.has D.is 11.If city noises ________ from increasing,people ________ shout to be heard even at the dinner table 20 years from now.
