一气呵成学语音(一)测试题

一气呵成学语音(一)测试题
Name mark
试题一:勾选出所听到的音标 (每题1分,共20分)
1.A. [?] B.[e] 2.A. [d] B.[t] 3.A. [b] B.[p] 4.A. [i:] B. [I]
5.A [k] B[g] 6.A [?:] B[?] 7.A [?:] B[D]8.A [j] B [w]
9.A [tS] B[dz] 10.A [h] B[r] 11.A [S] B[?] 12.A
[e?] B [aI]
13.A [r?:] B [r?] 14.A [??] B [e?]
15.A [m a?] B [n a?] 16.A [n??] B [naI]
17.A [laI] B [leI] 18.A [ru:d] B [r U d]
19.A [tI] B [dI] 20.A [si:] B [zi:]
试题二:听录音补充所缺音标(每题2分,共20分)
1.[p___]
2.[___?d]
3.[___?p]
4.[___?t]
5.[p___t]
6.[___pi:k]
7.[dI___k]
8.[eg___]
9.[___?st] 10.[m___k]
试题三:分解拼读如下单词(每题5四分,共20分)
1.passenger[`p?sIn??] n.乘客
2.chicken [`?Ik?n] n.鸡
Step1_______________________ Step1_______________________
Step2________________________ Step2________________________
Step3________________________ Step3________________________
Step4________________________ Step4________________________
https://www.360docs.net/doc/623003715.html,test[`leItIst]adj.最新的
4.assistant[?`sIst?nt]n. 助手Step1________________________ Step1________________________
Step2________________________ Step2________________________
Step3________________________ Step3________________________
Step4________________________ Step4________________________
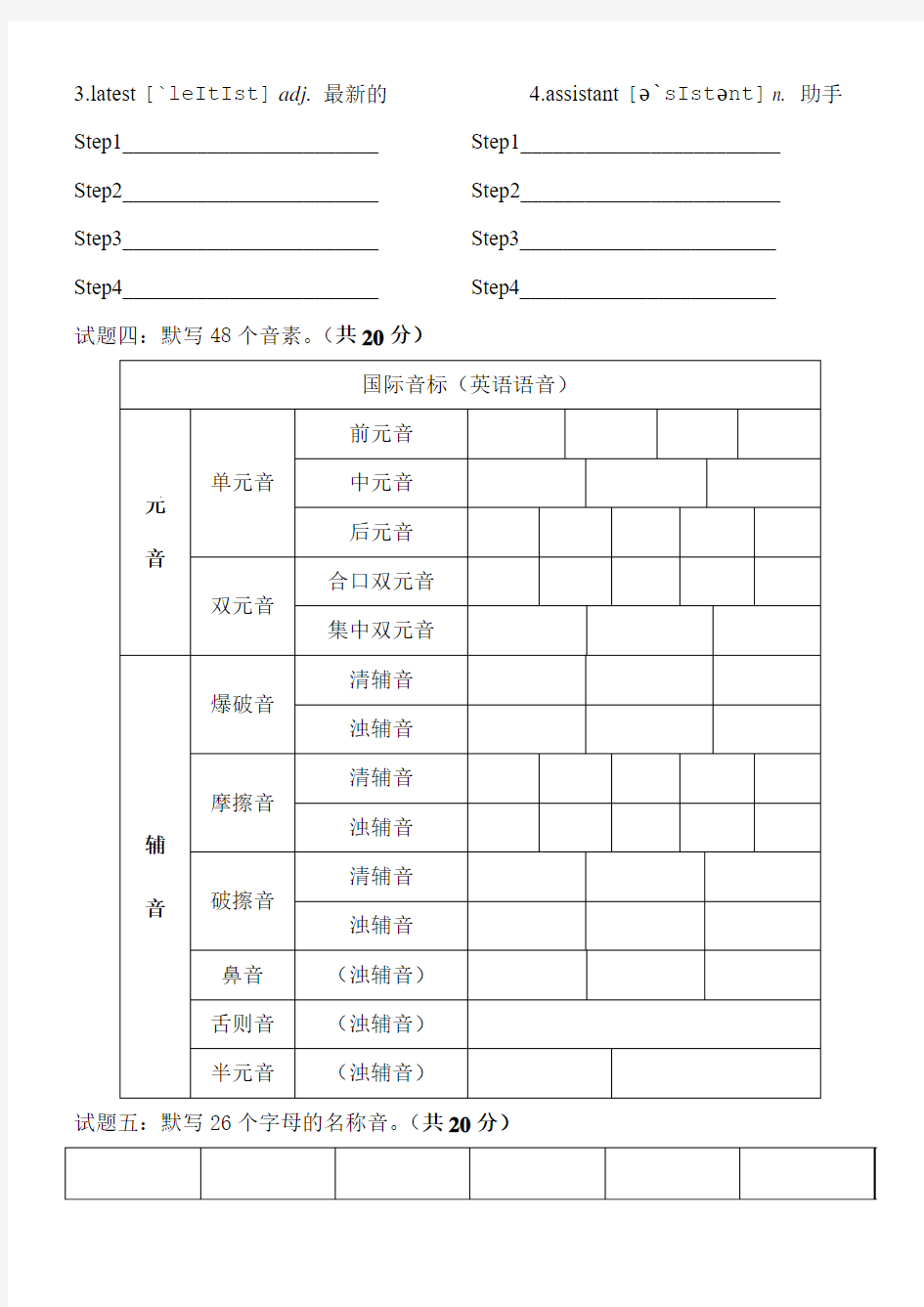
试题四:默写48个音素。(共20分)
试题五:默写26个字母的名称音。(共20分)
汉语作为第二语言的要素教学语音1
汉语作为第二语言的要素教学 课程简介 ◇教学对象 对外汉语专业本科高年级必修课程,汉语作为第二语言教学相关专业研究生专业课程,也适用于对外汉语教师培训的有关课程 ◇教学目的 ?全面了解对外汉语语音、语法、词汇和汉字教学的特点、内容、教学目标、教 学原则与方法 ?把握对外汉语教学中的重点、难点以及应对策略 ?具备一定的分析和解决教学实际问题的能力 ◇教学内容 ?汉语作为第二语言的要素教学,包括语音教学、语法教学、词汇教学、汉字教 学四个组成部分 ?系统介绍语言要素教学的基本概念、特点、内容、理论基础、教学目标、教学 原则、方法和技巧 ?通过教学实例,使学生把握对外汉语教学中的重点、难点以及应对策略,并具 备一定的分析和解决教学实际问题的能力,为多种类型的汉语教学实践做准备,并为今后从事汉语作为第二语言的教学和研究工作打下专业基础。 第一章汉语作为第二语言的语音教学 内容—— ?介绍汉语语音系统的理论知识(体系)——教什么 ?介绍汉语作为第二语言的语音教学的内容和教学方法——怎么教 要求—— ?掌握必要的理论,熟悉基础知识 ?掌握汉语语音学习的难点、问题和纠音正调的方法 参考书目 ?林焘、王理嘉(1992)《语音学教程》,北京大学出版社 ?吴宗济主编(1991)《现代汉语语音概要》,华语教学出版社
?赵金铭主编(1997)《语音研究与对外汉语教学》,北京语言文化大学出版社?朱川主编(1997)《外国学生汉语语音学习对策》,语文出版社 ?李明、石佩雯(1986)《汉语普通话语音辨正》,北京语言文化大学出版社?刘广徽编著(2002)《汉语普通话语音教程》,北京语言文化大学出版社 ?金晓达、刘广徽编著(2006)《汉语普通话语音图解课本(教师用书)》,北 京语言大学出版社 第一节汉语语音教学的原则、内容与教学方法 一、语音教学的原则 1 科学性原则 ?讲授知识和概念要准确, ?遵循和掌握教学规律, ?研究和采用有效的教学方法 2 实践性原则 ?理论指导下大量练习,实践 ?精讲多练,提高开口率 3 对比性原则 ?普通话和学生母语的比较 ?正确发音与错误发音的比较 ?普通话相近音的对比 4 直观性原则 ?对某些基本规则和理论的讲解,需采取必要的辅助手段,用图示方法形象化 5 趣味性原则 6 语音教学必须贯穿始终 二、语音教学的内容 现代汉语普通话的语音 1、语音概况 2、语音教学的具体内容 (1)语音部分 ①汉语拼音字母与音节②声母③韵母④拼写规则⑤声调 ⑥变调⑦语气助词“啊”音变⑧轻声⑨儿化韵
《新编简明英语语言学教程》第二版课后练习题答案
《新编简明英语语言学教程》第二版练习题参考答案 Chapter 1 Introduction 1. How do you interpret the following definition of linguistics: Linguistics is the scientific study of language. 答:Linguistics is based on the systematic investigation of linguistic data, conducted with reference to some general theory of language structure. In order to discover the nature and rules of the underlying language system, the linguists has to collect and observe language facts first, which are found to display some similarities, and generalizations are made about them; then he formulates some hypotheses about the language structure. The hypotheses thus formed have to be checked repeatedly against the observed facts to fully prove their validity. In linguistics, as in any other discipline, data and theory stand in a dialectical complementation, that is, a theory without the support of data can hardly claim validity, and data without being explained by some theory remain a muddled mass of things. 2. What are the major branches of linguistics? What does each of them study? 答:The major branches of linguistics are: (1) phonetics: it studies the sounds used in linguistic communication; (2) phonology: it studies how sounds are put together and used to convey meaning in communication; (3) morphology: it studies the way in which linguistic symbols representing sounds are arranged and combined to form words; (4) syntax: it studies the rules which govern how words are combined to form grammatically permissible sentences in languages;
一气呵成学语音一测试题
一气呵成学语音(一)测试题 Name mark 试题一:勾选出所听到的音标(每题1分,共20分) 1.A. [?] B. [e] 2.A. [d] B. [t] 3.A. [b] B. [p] 4.A. [i:] B. [I] 5.A [k] B [g] 6.A [?:] B [?] 7.A [?:] B [D] 8.A [j] B [w] 9.A [tS] B [dz] 10.A [h] B [r] 11.A [S] B [?] 12.A [e?] B [aI] 13.A [r?:] B [r?] 14.A [??] B [e?] 15.A [m a?] B [n a?] 16.A [n??] B [naI] 17.A [laI] B [leI] 18.A [ru:d] B [r U d] 19.A [tI] B [dI] 20.A [si:] B [zi:] 试题二:听录音补充所缺音标(每题2分,共20分) 1.[p___] 2.[___ ?d] 3.[___ ?p] 4.[___ ?t] 5.[p___t] 6.[___pi:k] 7.[dI___k] 8.[eg___] 9.[___?st] 10.[m___k] 试题三:分解拼读如下单词(每题5四分,共20分) 1.passenger[`p?sIn??] n.乘客 2.chicken [`?Ik?n] n.鸡 Step1_______________________ Step1_______________________ Step2________________________ Step2________________________ Step3________________________ Step3________________________ Step4________________________ Step4________________________ https://www.360docs.net/doc/623003715.html,test[`leItIst]adj.最新的 4.assistant[?`sIst?nt]n. 助手 Step1________________________ Step1________________________ Step2________________________ Step2________________________ Step3________________________ Step3________________________
(完整版)胡壮麟《语言学教程》测试题及答案
胡壮麟《语言学教程》(修订版)测试题 第一章:语言学导论 I. Choose the best answer. (20%) 1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human A. contact C. relation B. communication D. community 2. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary? A. tree C. crash B. typewriter D. bang 3. The function of the sentence “ Waterboils at 100 degrees Centigrade. i”s A. interrogative C. informative B. directive D. performative 4. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say “碎碎(岁岁)平安”asa means of controlling the forces which they believes feel might affect their lives. Which functions does it perform? A. Interpersonal C. Performative B. Emotive D. Recreational 5. Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place, due to this feature of language, speakers of a language are free to talk about anything in any situation? A. Transferability C. Displacement B. Duality D. Arbitrariness 6. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language? —A nice day, isn 't it? Right! I really enjoy the sunlight. A. Emotive C. Performative B. Phatic D. Interpersonal 7. __________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language usesr knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances. A. Performance C. Langue B. Competence D. Parole 8. When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone that exists hear and now.
《现代汉语》北大汉语教研室 北大版(语音部分详解)
现代汉语语音部分笔记 现代汉语语音部分主要参考书目 北京大学中文系现代汉语教研室编,《现代汉语》,商务印书馆,1993年 黄伯荣、廖序东主编,《现代汉语》(第二版增订本),高等教育出版社,1997年 胡裕树主编,《现代汉语》(重订本),上海教育出版社,1995年 林焘、王理嘉,《语音学教程》,北京大学出版社,1992年 现代汉语界定·汉语共同语发展简况 现代汉语广义上指“五四”以来汉民族的交际语言,包括共同语和各种方言;狭义则专指现代汉民族的共同语——普通话。普通话是在汉族内部通过长期的互相交往在方言的基础上逐渐自然形成的。汉语的书面形式和口头形式形成共同语的历史过程不同,分述如下: 我国很早就有共同书面语,汉代所谓“通语”(见扬雄《方言》)就是全国通行的语言。古代正统书面语文言文最初基于口语产生,但这种书面语传统一旦形成,就逐渐与口语脱节,最终成为大众难以读懂的语言。唐末(公元九世纪)以后,民间逐渐产生一种与口语直接联系的新的书面语言,后来称作“白话文”,是今天普通话书面形式的源头。白话文到了宋元之际(公元十二三世纪)已经相当成熟,明清以来又涌现了大量白话文学作品。这种书面语是在北方话的基础上形成的,它通行于全国,在相当大的程度上带有民族共同语的性质。书面语中向来是文言文占统治地位,直到“五四”运动以后“白话文运动”的兴起,才使白话文取得正式书面语言的地位。 汉语共同语的口语形式出现得比书面形式晚。至迟在十四世纪,一种后来被称为“官话”的共同口语已经在北方话的基础上形成,而这种口语至少到清代就已经相当通行。
因为北京长久以来的政治、经济、文化中心的地位,北京话在官话的形成过程中成为最有影响的方言。到了“五四”时期,“国语运动”与“白话文运动”同时兴起,“国语”这一名称取代了“官话”的提法。两种运动互相推动,互相影响,使民族共同语的书面形式和口头形式得到前所未有的发展。新中国成立后,开始用“普通话”称呼现代汉民族共同语。 煜按:北大版《现代汉语》未提“雅言”一说,大概是不认可它的共同语地位;把“通语”处理成书面形式的共同语,而非共同口语形式。并且“通语”只是就文言 文的发展而言,并非“现代汉语”所着重追溯的源头,现代汉语书面语的源头是早 期白话文。所以那种“雅言-通语-官话-国语-普通话”的发展脉络不为所用, 是因为雅言的共同语特征不明显,通语不是完全的口语形式;雅言和通语不是现代 汉语的直接源头。所以要注意两点:一、着重的是现代汉语的直接来源;二、分为 口语(官话…)和书面语(白话文)两种形式。 汉语方言分歧很大,非常复杂,根据方言的主要特点,大致可以分为七大方言:一、北方方言:以北京话为代表使用人口:约占汉族总人口百分之七十 分布区域:长江以北汉族居住区,长江以南镇江以上、九江以下的沿江地带,湖北(东南一带除外)、四川、云南、贵州四省、湖南省西北一带 说明:北方方言是普通话的基础方言,分布地域最广,使用人口最多,内部一致性较强。包括四个次方言区:
语言学教程测试题及答案
Chapter 1 Introductions to Linguistics I. Choose the best answer. (20%) 1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human __________ A. contact B. communication C. relation D. community 2. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary? A. tree B. typewriter C. crash D. bang 3. The function of the sentence “Water boils at 100 degrees Centigrade.” is __________. A. interrogative(疑问) B. directive C. informative D. performative 4. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say“碎碎(岁岁)平安”as a means of controlling the forces which they believes feel might affect their lives. Which functions does it perform? A. Interpersonal B. Emotive C. Performative√ D. Recreational 5. Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place, due to this feature of language, speakers of a language are free to talk about anything in any situation? A. Transferability B. Duality C. Displacement D. Arbitrariness 6. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language? —A nice day, isn’t it? — Right! I really enjoy the sunlight. A. Emotive B. Phatic C. Performative D. Interpersonal 7. __________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances. A. Performance B. Competence C. Langue D. Parole 8. When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone that exists hear and now. It couldn’t be sorrowful for some lost love or lost bone. This indicates the design feature of __________. A. cultural transmission B. productivity C. displacement D. duality 9. __________ answers such questions as how we as infants acquire our first language. A. Psycholinguistics linguistics C. Sociolinguistics D. Applied linguistics 10. __________ deals with language application to other fields, particularly education. A. Linguistic theory B. Practical linguistics C. Applied linguistics D. Comparative linguistics II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%) 11. Language is a means of verbal communication. Therefore, the communication way used by the deaf-mute is not 12. Language change is universal, ongoing and ? 13. Speaking is the quickest and most efficient way of the human communication ? 14. Language is written because writing is the primary medium for all
一气呵成学语音 音标二随堂册
睿思英语 音标二册 Teacher: Grade: Name:
L1-L2 一、填出单词中每个字母的功能音。 / /←cat→/ / / /←dog→ / / / / / / / /←met→/ / / / ←dip →/ / / / / / 二、将26个字母按类别填入表格中。 三、写出下列单词的发音。 1. bat 2. dad 3. fan 4. hat / / / / / / / / 5.jet 6. lip 7. run 8. kid / / / / / / / / 9. zip 10. wet 11. am 12. sheep / / / / / / / / one
13. pack 14. high 15. coat 16. pig / / / / / / / / 17. from 18. man 19. ten 20. not / / / / / / / / L3 一、写出相对应发音。 ar _______ er_______ ir _______ or_______ ur_______ are_______ ere_______ ire_______ore_______ure_______ 二、根据音标排序 ① arkb /ba:k/ ______ ② nrbu /b?:n/ _______ ③ rhbe /h?:b/ _______ ④dcra /ka:d/ ______ ⑤ hton /n?:θ/ ______⑥ tidr /d?:t/ _____ ⑦ rtide /taI?d/ _______ ⑧ hsoer /??:/ _________ ⑨ rehe /hI?/ _______ ⑩ ramf /fa:m/ _______ 三、写出下列单词划线的音标 1 harm / / 2 turn / / 3.jar / / 4 herb / / 5 nor / / 6 bored / / 7 dare/ / 8 more / / 9 farm / / 10 jet / / L4 一、根据音标写单词。 /red/ ______ /bed/ ______ /wet/ ______ /net/ ______ /kId/ ______ /hIt/ ______ /top/______ /p?t/______ two
语言学教程(胡壮麟版)综合测试题含标准答案
语言学教程(胡壮麟版)综合测试题含标准答案 英语语言学试卷 (一) 第一部分选择题 I. Directions: Read each of the following statements carefully. Decide which one of the four choices best completes the statement and put the letter A, B, C or D in the brackets. (2%X10=20%) 1.Saussure’s distinction and Chomsky’s are very similar, but they differ in that ____________. A. Saussure took a sociological view of language while Chomsky took a psychological point of view B. Saussure took a psychological view of language while Chomsky took a sociological point of view C. Saussure took a pragmatic view of language while Chomsky took a semantic point of view D. Saussure took a structural view of language while Chomsky took a pragmatic point of view 2. Language is a system of ____________ vocal symbols used for human communication. A.
北京大学中文系的课程
北京大学中文系的课程
我本身就是学中文的.所谓中文就是汉语言文学,顾名思义汉语言文学包括语言和文学两大部分,只不过大学不象研究生分方向分的那么详细,语言和文学是都要学的. 语言这块主要学习古代汉语现代汉语语言学应用语言学,文学这块主要学习中国古代文学中国现当代文学外国文学其他辅助理论还有文学概论(主要是初级阶段的文艺理论,很枯燥的) 美学写作等,要是师范类的中文系还要设置教法. 至于共同课无非是外语政治计算机还有现在需要选课(一般为本专业以外的课程是自己自由选择) 这个是北京大学中文系的课程 现代汉语 古代汉语 中国古代文学史 中国当代文学 语言学概论 中国古代文化 中文工具书 语言工程与中文信息处理 文学原理 高级汉语 汉语修辞 现代汉语 中国古代文化 语法研究 中文工具书使用中国古代文学 中国现代文学 中国民间文学 中国当代文学作品 中国古代文学 中国古代史 中国文学理论批评史 汉语方言学 理论语言学 文字学 版本学 古文献学史
散曲研究 实验语音学基础 索绪尔语言学理论 说文解字概论 诗经 汉语史 西方文论经典研究 西方文学理论史 文言小说研究专题中国现代散文研究《论语》《孟子》选读 中国古代文化 中文工具书及古代典籍概要 汉语和汉语研究 《论语》《孟子》导读 古代汉语 文学概论 民俗研究 大学语文 沈从文研究 专书选读 现代汉语词汇词义研究 近代汉语研究 古音学 语言学前沿问题讲座 当代语言学 <说文解字>研读 <马氏文通>研读 现代文学批评史 汉学师承记研究 汉书艺文志研究 欧美汉学文本导读 宋诗史料学 清代考据学 现代学术史研究 中国古代画论研究 系统功能语法
语言学教程Chapter 3练习题
Chapter 3:Lexicon I. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False: 1. Morphology studies the internal structure of words and the rules by which words are formed. 2.Words are the smallest meaningful units of language. 3. Just as a phoneme is the basic unit in the study of phonology, so is a morpheme the basic unit in the study of morphology. 4. The smallest meaningful units that can be used freely all by themselves are free morphemes. 5. Bound morphemes include two types: roots and affixes. 6. Inflectional morphemes manifest various grammatical relations or grammatical categories such as number, tense, degree, and case. 7. The existing form to which a derivational affix can be added is called a stem, which can be a bound root, a free morpheme, or a derived form itself. 8. Prefixes usually modify the part of speech of the original word, not the meaning of it. 9. There are rules that govern which affix can be added to what type of stem to form a new word. Therefore, words formed according to the morphological rules are acceptable words. 10. Phonetically, the stress of a compound always falls on the first element, while the second element receives secondary stress. II. Fill in each blank below with one word which begins with the letter given: 11. M ____ is the smallest meaningful unit of language. 12. The affix “-ish” in the word boyish conveys a g____ meaning. 13. B___________ morphemes are those that cannot be used independently but have to be combined with other morphemes, either free or bound, to form a word. 14. Affixes are of two types: inflectional affixes and d__________ affixes. 15. D________ affixes are added to an existing form to create words. 16. A s______ is added to the end of stems to modify the meaning of the original word and it may case change its part of speech.
《语言学教程》(修订版)复习测试题(1-12章,含答案)
胡壮麟《语言学教程》(修订版)测试题(1-12章,含答案) Chapter 1 Introductions to Linguistics I. Choose the best answer. (20%) 1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human ___ B_______ A. contact B. communication C. relation D. community 2. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary? A A. tree B. typewriter C. crash D. bang 3. The function of the sentence ―Water boils at 100 degrees Centigrade.‖ is _____C____. A. interrogative B. directive C. informative D. performative 4. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say―碎碎(岁岁)平安‖as a means of controlling the forces which they believes feel might affect their lives. Which functions does it perform? C_ A. Interpersonal B. Emotive C. Performative D. Recreational 5. Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place, due to this feature of language, speakers of a language are free to talk about anything in any situation? C A. Transferability B. Duality C. Displacement D. Arbitrariness 6. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language?B —A nice day, isn’t it? — Right! I really enjoy the sunlight. A. Emotive B. Phatic C. Performative D. Interpersonal 7. _______A___ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances. A. Performance B. Competence C. Langue D. Parole 8. When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone that exists hear and now. It couldn’t be sorrowful for some lost love or lost bone. This indicates the design feature of ______C____. A. cultural transmission B. productivity C. displacement D. duality 9. ____A______ answers such questions as how we as infants acquire our first language. A. Psycholinguistics B.Anthropological linguistics C. Sociolinguistics D. Applied linguistics 10. _______C___ deals with language application to other fields, particularly education. A. Linguistic theory B. Practical linguistics C. Applied linguistics D. Comparative linguistics I. Choose the best answer. (20%) 1. Pitch variation is known as ______A____ when its patterns are imposed on sentences. A. intonation B. tone C. pronunciation D. voice 2. Conventionally a _____C_____ is put in slashes (/ /).
语音教程课后练习答案
语音教程课后练习答案 Le?on 1 1.略 2.略 3.略 4.翻译下列句子。 这是谁 Qui est-ce 这是利娜。 C’est Lina. 她在哪儿 Où est-elle 她在里尔。 Elle est à Lille. 5.略 Le?on 2 1.略 2.略 3.略 4.就下列句子提问。 (1)Est-ce que c’est Pascal Oui,c’est Pascal. Que fait-il Il est journaliste. (2)Est-ce que c’est Nathalie Oui,c’est Nathalie. Que fait-elle Elle est actrice. (3)Qui est-ce C’est phillippe. Où est-il Il est à Lille. (4)Qui est-ce C’est Fanny. Où est-il Elle est à Sète. 5.翻译下列句子。 这是夏尔吗 Est-ce que c’est Charles 对,这是夏尔。 Oui,c’est Charles. 他是干什么的 Que fait-il 他是邮递员。 Il est facteur. 利娜是研究员。 Lina est chercheur. 帕斯卡尔是服装设计师。 Psacal est styliste. 6.略
Le?on 3 1.略 2.略 3.略 4.回答下列问句。 (1)Est-ce que c’est Phillippe (2)Est-ce que Thomas est pilote Oui,c’est Phillippe. Oui,il est pilote. Que fait-il Où est-ce qu’il habite Il est facteur. Il habite à Berne. (3)Qui est-ce (4)Est-ce que Nathalie est journaliste C’est Sabine. Oui,elle est journaliste. Est-ce que Sabine habite à Grenoble. Où est-ce qu’elle habite Oui, elle habite à Grenoble. Elle habite à Nice. 5.略 6.翻译下列句子。 (1)雅克是邮递员。他住在巴黎。 (2)韦罗尼克是电影编导。她住在日内瓦。 Jacque est facteur. Il habite à Paris. Véronique est ciné habite àGenève. (3)雅克琳是演员。她住在北京。 (4)菲利普是研究员。他住在伯尔尼。 Jacqueline est actrice. Elle habite à Beijing. Phillippe est habite àBerne. 7.略。 Le?on 4-Révision 1.略 2.略 3.略 4.就下列句子提问。 (1)Philiippe habite à Nice. (2)Oui,Phillippe habite à Nice. Où Habite Phillippe Est-ce que Phillippe habite à Nice. (3)Marie est secrétaire. (4)Oui,le camarade Li est avocat.
一气呵成学语音一测试题
一气呵成学语音一测试 题 Document number【980KGB-6898YT-769T8CB-246UT-18GG08】
一气呵成学语音(一)测试题 Name mark 试题一:勾选出所听到的音标 (每题1分,共20分) 1.A. [] B. [e] 2.A. [d] B. [t] 3.A. [b] B. [p] 4.A. [i:] B. [I] 5.A [k] B [g] 6.A [:] B [] 7.A [:] B [D] 8.A [j] B [w] 9.A [tS] B [dz] 10.A [h] B [r] 11.A [S] B [] 12.A [e] B [aI] [r:] B [r] 14.A [] B [e] 15.A [ma] B [na] 16.A [n] B [naI] [laI] B [leI] [ru:d] B [r U d] [tI] B [dI] [si:] B [zi:] 试题二:听录音补充所缺音标(每题2分,共20分) 1.[p___] 2.[___ d] 3.[___ p] 4.[___ t] 5.[p___t] 6.[___pi:k] 7.[dI___k] 8.[eg___] 9.[___st] 10.[m___k] 试题三:分解拼读如下单词(每题5四分,共20分) [`psIn] n.乘客 [`Ikn] n.鸡 Step1_______________________ Step1_______________________ Step2________________________ Step2________________________ Step3________________________ Step3________________________
(完整版)教师口语课程教学大纲
《教师口语》课程教学大纲 课程编号:00000002 课程类别:公共选修课程 授课对象:全院各专业学生 开课学期:春/秋季 学分:2学分 主讲教师:陈晓红等 指定教材:国家教育委员会师范教育司组编,《教师口语》、《教师口语训练手册》,北京师范大学出版社,1996年 教学目的: “教师口语”是根据发展基础教育的需要和强化教师职业技能的需要而为全校师范生开设的一门公共必修课,同时也是积极贯彻国家语言文字工作的方针政策、深化教育改革、实施素质教育的一项重要举措。该课程以训练为手段,在理论指导下,以特定的训练目标和训练内容,培养师范生在教育、教学过程中的口语运用技能、言语识别能力、言语判断力和应变力,为将来从事的教育、教学工作打下扎实的基础。 第一章语音常识与发声技能 课时:2周,共4课时 教学内容 第一节语音的产生 一、发音器官 二、发音原理 思考与练习: 1、在发音器官图上指出发音器官的名称、部位及各种活动方式。 第二节发声技能 一、用气发声训练 二、共鸣控制训练 三、吐字归音训练 思考与练习: 1、共鸣控制有何作用?按要领训练中、低、高三腔共鸣的方式。 2、慢速吟诵《雨巷》,要求把每一音节的出字、立字、归音按要领读好。 第三节语音的基本概念与训练步骤 一、语音的基本概念(重点掌握语音的四要素) 二、语音训练的一般步骤 第二章普通话语音训练 课时:3周,共6课时 第一节普通话声调训练
一、四声基本训练 二、声调辩正 三、声调发音检测 思考与练习: 1、对照方言与普通话的声调差异,找出对应的规律。 2、进一步体会声调的区分词义的作用——训练《施氏食狮史》。 第二节普通话声母训练 一、声母基本训练(掌握辅音发音要领) 二、声母辩正(重点辨正平翘舌音、边鼻音、舌面音和舌尖音、唇齿音和舌根音等方言难点音,提供记忆的规律) 三、声母发音检测 思考与练习: 1、对照方言与普通话存在的声母差异,找出对应的规律。 2、针对性训练——根据“声母处方”制定训练计划。 第三节普通话韵母训练 一、韵母基本训练(掌握元音发音部位及韵母发音要领) 二、韵母辩正 三、韵母发音检测 思考与练习: 1、对照方言与普通话存在的韵母差异,找出对应的规律。 2、针对性训练——根据“韵母处方”制定训练计划。 3、加强前后鼻音的训练。 第四节普通话语流音变训练 一、声调音变训练 二、轻声的发音训练 三、儿化的发音训练 四、语气词“啊”的音变训练 五、语流音变检测 思考与练习: 1、什么叫语流音变?举例说明轻声和儿化的作用。 3、朗读训练《老朋友相遇》 第三章普通话词汇和语法的规范运用 课时:1周,共2课时 第一节词语的规范运用 一、词语规范运用应注意的问题 二、方言词汇与普通话词汇的主要差异 三、如何面对层出不穷的新词 思考与练习: 1、收集整理本地的方言词语,与相对应的普通话词语进行比较。
