四种时态总结

一般现在时总结
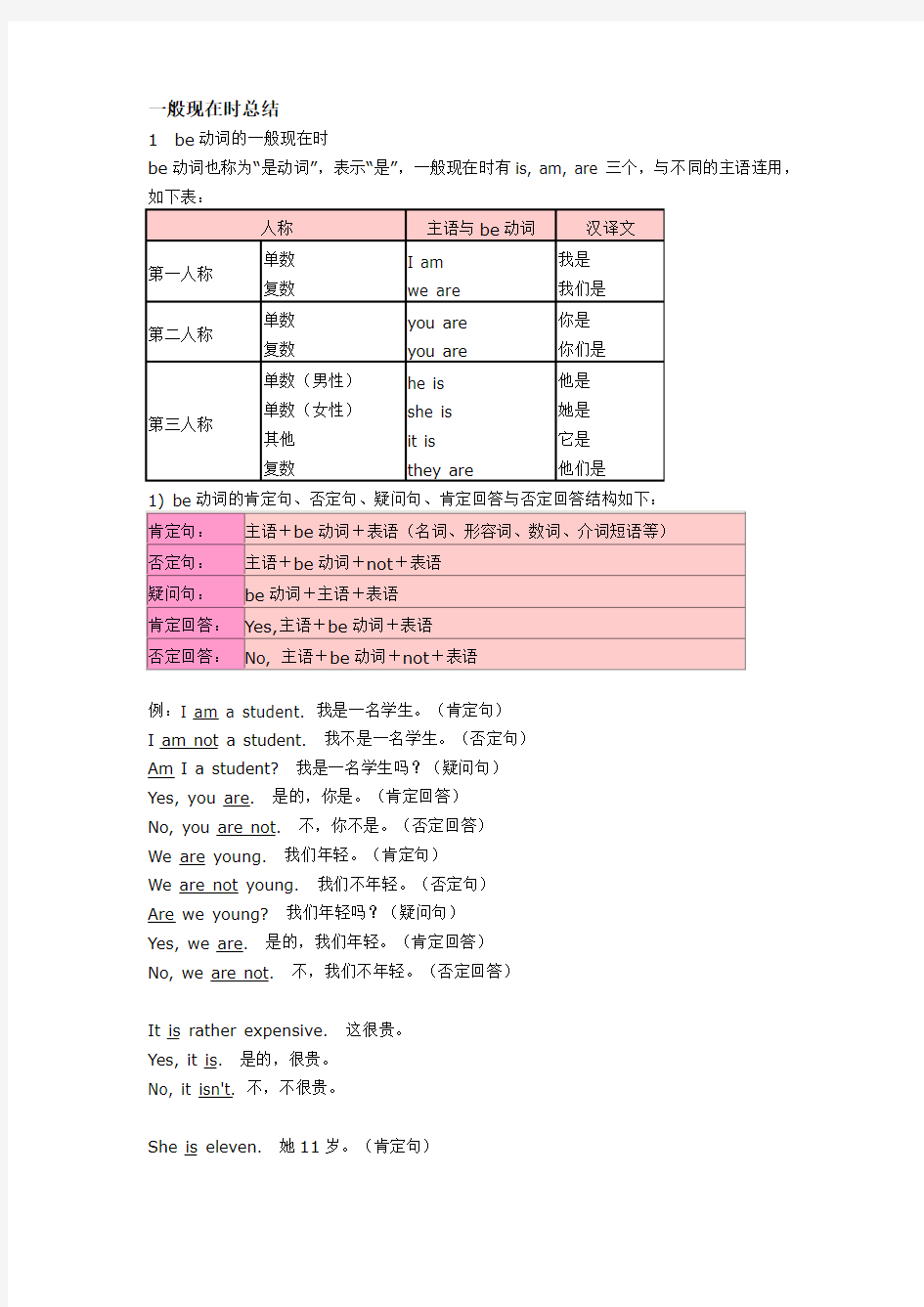
1be动词的一般现在时
be动词也称为“是动词”,表示“是”,一般现在时有is, am, are三个,与不同的主语连用,如下表:
人称主语与be动词汉译文
第一人称单数
复数
I am
we are
我是
我们是
第二人称单数
复数
you are
you are
你是
你们是
第三人称单数(男性)
单数(女性)
其他
复数
he is
she is
it is
they are
他是
她是
它是
他们是
1) be动词的肯定句、否定句、疑问句、肯定回答与否定回答结构如下:肯定句:主语+be动词+表语(名词、形容词、数词、介词短语等)否定句:主语+be动词+not+表语
疑问句:be动词+主语+表语
肯定回答:Yes,主语+be动词+表语
否定回答:No, 主语+be动词+not+表语
例:I am a student. 我是一名学生。(肯定句)
I am not a student.我不是一名学生。(否定句)
Am I a student?我是一名学生吗?(疑问句)
Yes, you are.是的,你是。(肯定回答)
No, you are not.不,你不是。(否定回答)
We are young.我们年轻。(肯定句)
We are not young.我们不年轻。(否定句)
Are we young?我们年轻吗?(疑问句)
Yes, we are.是的,我们年轻。(肯定回答)
No, we are not.不,我们不年轻。(否定回答)
It is rather expensive.这很贵。
Yes, it is.是的,很贵。
No, it isn't. 不,不很贵。
She is eleven.她11岁。(肯定句)
She is not eleven.她不是11岁。(否定句)
Is she eleven?她11岁吗?(疑问句)
Yes, she is.是的,她11岁。(肯定回答)
No, she is not.不,她不是11岁。(否定回答)
You are right.你是对的。
You are not right.你不对。
Are you right?你对吗?
Yes, I am.是的,我对。
No, I am not.不,我不对。
It is a clock.这是一口钟。
It is not a clock.这不是一口钟。
Is it a clock?这是一口钟吗?
Yes, it is.是的,它是。
No, it isn't.不,它不是。
The children are in the park.孩子们在公园里。
The children are not in the park.孩子们不在公园里。Are the children in the park?孩子们在公园里吗?Yes, they are.是的,他们在公园里。
No, they aren't.不,他们不在公园里。
提示
a.代词I (我)永远要大写。
b.问句中的主语you,回答时要改用I.
c.在答语中,主诃要用代词。
例:Is your father a doctor? 你父亲是医生吗?
Yes, he is.(正)是的,他是。
Yes, my father is.(误)
Is your pen in the box?你的钢笔在盒子里吗?Yes, it is.(正)是的,它在盒子里。
No, my pen is.(误)
2) be动词常用缩写式。
方式如下:
is not
isn't [5iznt] are not
aren't [5B:nt]
I am
I'm
we are wr're you are
you're
he is
he's
she is she's it is
it's
they are
they're
I am not=I'm not(但am not不可缩写在一起)
例:I'm not a singer. I'm a painter. 我不是歌手,我是画家。
We aren't hungry, but we're very tried.我们不饿,但很累。
It's an egg. It isn't an orange.这是一个鸡蛋,不是一只橘子。
2行为动词的一般现在时
这里所说的行为动词,指的是除be动词、情态动词和助动词之外的全部动词。行为动词为数众多,主语为第三人称单数he, she, it时,词形有变化。
行为动词的肯定句、否定句、疑问句、肯定回答和否定回答结构如下:
肯定句:I
We
You
They
+动词原形......
He
She
it
+动词原形......(动词要加-s, -es或
变y为i加-es)
否定句:I
We
You
They
+do not (don't) +动词原形......
He
She
it
+do not(don't) +动词原形......
疑问句:Do
I
we
you
they
+动词原形...... Does
he
she
it
+动词原形......
肯定回答:Yes,
I
we
you
they do. Yes,
he
she
it
does.
否定回答:No,
I
we
you
they
do not (don't). No,
he
she
it
does not (doesn't)
例:I like sports. 我喜欢运动。(肯定句)
I do not(/don't) like sports.我不喜欢运动。(否定句)
Do I like sports?你喜欢运动吗?(疑问句)
Yes, I do.是的,我喜欢。(肯定回答)
No, I do not(don't)不,我不喜欢。(否定回答)
She teaches English in a middle school.她在一所中学教英语。(肯定句)
She does not(/doesn't) teach English in a middle school.她不在一所中学教英语。(否定句)
Does she teach English in a middle school?她在一所中学教英语吗?(疑问句)Yes, she does.是的,她在一所中学教英语。(肯定回答)
No, she does not(doesn't).不,她不在一所中学教英语。(否定回答)
His brother swims well.他弟弟游泳游得好。(肯定句)
His brother does not swim well.他弟弟游泳游得不好。
Does his brother swim well?他弟弟游泳游得好吗?(疑问句)
Yes, he does. 是的,游得好。(肯定回答)
No, he does not(doesn't)不,游得不好。(否定回答)
The flight goes direct to New York.航班直飞纽约。(肯定句)
The flight does not go direct to New York.航班不直飞纽约。(否定句)
Does the flight go direct to New York?航班直飞纽约吗?(疑问句)
3动词have (has) 的一般现在时
1.当have(has)表示“有,所有”时,可以把have (has)提到主语前变为疑问句,在have(has)后加not变为否定句。主语为第三人称单数时,要用has.
例:We have five English dictionaries. 我们有5本英语词典。(肯定句)
We have not (haven't) five English dictionaries.我们没有5本英语词典。(否定句)
=We don't have five English dictionaries.
Have we five English dictionaries?我们有5本英语词典吗?
=Do we have five English dictionaries?
She has a car.她有一部车。(肯定句)
She has not (hasn't) a car.她没有一部车。(否定句)
=She doesn't have a car.
Has she a car?她有一部车吗?(疑问句)
=Does she have a car?
2.当have(has) 表示“吃,开会,举行……”等时,要用助动词do, does构成否定句和疑问句。
例:I have fish for lunch.我午餐吃鱼。(肯定句)
I do not(don't) have fish for lunch.我午餐不吃鱼。(否定句)
Do I have fish for lunch?我午餐吃鱼吗?(疑问句)
She has a meeting every week.她每星期开一次会。(肯定句)
She doesn't have a meeting every week.她并不是每个星期都开会。(否定句)Does she have a meeting every week?她每个星期都开会吗?
我不吃早餐。
I have not breakfast.(误)
I don't have breakfast.(正)
4 一般现在时的基本用法
1) 表示经常性、反复发生的动作,常同一些时间状语连用
常用的这类时间状语有:
always(总是), often(经常), usually(通常),
sometimes(有时候), seldom(很少), every day(每天),
every week(每周), every year(每年), once a week(每周一次),
twice a month(每月两次), from time to time(不时地),
on Sundays(每星期天)
例:We often play football in the afternoon. 我们经常在下午踢足球。
I usually have breakfast at the past six.我通常6点半吃早饭。
He spends his holiday in the north every summer.他每年夏天在北方度假。
I seldom go to the movies.我很少去看电影。
Sometimes he goes to work by car.他有时候坐汽车去上班。
We have a party once a week.我们每周聚会一次。
2) 表示现在的状态或主语的特征、职业
例:She is ill. 她病了。
He looks tired.他看上去累了。
She sings well.她唱得好。
John likes collecting stamps.约翰喜欢集邮。
My mother teaches maths.我母亲教数学。
My father does not smoke.我父亲不抽烟。
Mary has two brothers.玛丽有两个弟弟。
3) 表示客观真理,也用于格言、谚语中
例:Light goes faster than sound. 光比声音传得快。
Water boils at 100℃.水在摄氏100度沸腾。
Spring follows winter.冬去春来。
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.太阳从东方升起,在西方落下。An apple a day keeps the doctor away.天天一苹果,医生远离我。
Where there is a will, there is a way.有志者事竟成。
A good medicine tastes bitter.良药苦口利于病。
主句为过去时,表示客观真理的宾语从句也用一般现在时
例:The teacher said that the sun is bigger than the moon.
老师说,太阳比月亮大。
4) 用在由when, until, as soon as, if等引导的时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,表示将来的动作
例:He will tell you the news when he gets back. 他回来后将把消息告诉你。
We'll wait here until the rain stops.我们将在这里等到雨停。
I'll ring you up as soon as I finish my homework this evening.今天晚上我一做完功课就给你打电话。
If he is free tomorrow, he will go with us.如果他明天有空,他将同我们一起去。
5) 表示预先安排、计划将要发生或预定要发生的事
主要用于begin, start, leave, stop, come, go, return等动词,句中常有表示将来的时间状语。
例:The train starts at nine o'clock tonight. 火车今晚9点钟开出。
I leave for Nanjing next Friday.我下星期五要去南京。
The plane arrives at five o'clock this afternoon.飞机将在今天下午5点钟到达。The new semester starts on September 1st.新学期9月1日开始。
Tomorrow is Sunday.明天是星期天。
6) 某些表示情感或心理状态的动词,常用一般现在时表示现在的行为状态,如:love, know, want, think, feel, remember, need, understand等
例:I think he is right. 我认为他是对的。
I feel pain in my left leg.我左腿痛。
I wish you all a happy new year.我祝你们大家新年愉快。
I don't know what you mean.我不知道你什么意思。
I want a cup of coffee.我想喝杯咖啡。
7) 表示瞬间发生的事,常用在某些习惯说法中
例:There goes the bell! 铃响了!
Here he comes.哈,他来了。
Here comes Tom!汤姆来了!
Here comes the bus!公交车来了!
There she is!她在那儿呢!
三、现在进行时
1 构成方式
肯定句:is
am
are
+现在分词
否定句:is
am
are
+ not+现在分词
疑问句:Is
Am
Are
+主语+现在分词
特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+
is
am
are
+主语+现在分词who(主语)+
is
are
+现在分词
2 基本用法
1) 表示现在说话时正在进行的动作
例:I am listening to the radio now. 我正在听广播。
Some birds are flying in the sky. 一些鸟正在天空中飞翔。
Look! The monkey is climbing the tree. 瞧,猴子在爬树。
Listen! Someone is singing in the park. 听,有人在公园里唱歌。What are you doing? 你在干什么?
Who is cleaning the window? 谁在擦窗户?
She is not watching TV now. 她现在不在看电视。
2) 表示现阶段正在进行的动作(但说话时不一定在进行),常同these days(这几天), this week(本周), at present(目前)等连用
例:She is reviewing her lessons these days. 这些天她在复习功课。
I am writing a paper on city planning this week. 本周我在写一篇关于城市规则的论文。
They are living in an old house at present. 他们目前住在一所旧房子里。He is studying English at the university. 他正在大学里学习英语。(现阶段)
3) 表示一个在最近按计划或安排要进行的动作,常有一个表示将来的时间状语这种用法仅限于少数动词,如:go, come, leave, start, arrive, return, stay, visit等
例:We are leaving for Beijing on Saturday. 我们星期六动身去北京。Many people are coming to the concert tomorrow. 明天许多人要来听音乐会。
I'm staying at home this afternoon. 今天下午我将呆在家里。
They are visiting the factory next week. 他们下周将参观那个工厂。
My father is arriving tomorrow afternoon on the 15:20 train. 明天下午我父亲将乘15时20分的火车到达。
4) 现在进行时有时同always, forever, continually连用,表示某种感情色彩,如赞扬、不满等
例:He is always thinking of others. 他总是为别人着想。(赞扬)
The man is always making trouble. 那人总是找麻烦。(责备)
Jack is always coming late. 杰克总是迟到。(不满)
He is always forgetting people's names. 他老是把人家的名字忘了。(责备)
比:He always helps others. 他总是帮助别人。(陈述一个事实)
He's always helping others. 他总是帮助别人。(赞扬)
5) be going to+动词原形
这种句型表示“打算,准备”做某事或即将发生某事
例:They are going to have a get-together at the weekend. 他们打算在周末举行一次聚会。
She isn't going to attend the meeting. 她不打算参加会议。
I'm afraid it is going to rain. 恐怕要下雨了。
比:Where are you going tomorrow? 你明天准备去哪里?(打算、计划)Where are you going? 你到哪里去?(此刻、现在)
6) 某些表示感官的动词表示说话时的感觉要用一般现在时,不用现在进行时
这类动词有:
see(看见,明白), hear(听见), smell(闻到,闻起来),
taste(尝起来), sound(听起来), feel(摸起来)等
例:我听见有人在那边喊。
I am hearing someone shouting over there. (误)
I hear someone shouting over there. (正)
我闻到有东西燃烧的味道。
I am smelling something burning. (误)
I smell something burning. (正)
这橘子很好吃。
The orange is tasting nice. (误)
The orange tastes nice. (正)
我看见树上有一只鸟。
I am seeing a bird in the tree. (误)
I see a bird in the tree. (正)
a. feel表示“摸起来”时,只能用一般现在时,表示说话时的感觉。但feel 表示“感觉”时,可用一般现在时或现在进行时表示说话时的感觉。
例:这条床单摸起来潮湿。
This sheet is feeling wet. (误)
This sheet feels wet. (正)
How are you feeling now? 你现在感觉如何?
I'm feeling a little cold. 我感觉有点冷。
I feel tired. Let's have a rest. 我感到有点累了,我们休息一下吧。
b. 有些感官动词表示动作时,可用进行时。
例:I hear someone knocking. 我听见有人敲门。
I am hearing a talk on the present situation. 我在听有关当前形势的报告。
I see a plane in the sky. 我看见天空中有一架飞机。
Mr. Smith is not here. He's seeing some foreign friends off at the airport. 史密斯先生不在这里,他正在机场为一些外国朋友送行。
I'm seeing the manager this afternoon. 我今天下午要会见经理。
7) 某些表示心理感觉、认识、看法或状态的动词,一般不用于现在进行时,要
用一般现在时表示说话时的感觉或状态
这类动词有:
think(认为), feel(认为), find(认为), know(知道), wish(希望),
want(想), hate(不喜欢), like(喜欢), love(热爱), believe(相信), guess(认为), remember(记得), show(表明), dislike(不喜欢), understand(理解), mean(意味着), fit(适合), lie(位于), seem(似乎), belong(属于), own(拥有), need(需要), matter(有关系), agree(同意), need(需要), prefer(较喜欢)
例:I wish you a happy journey. 我祝你旅途愉快。
I hope you will enjoy the music. 我希望你喜欢这首曲子。
She likes singing, but hates dancing. 她喜欢唱歌,但不喜欢跳舞。
I don't understand the sentence. Can you explain it again? 我不理解这
个句子,你再解释一下好吗?
I can't remember where she lives. 我不记得她住在哪里了。
提示
有些感觉、状态动词,词义发生变化,表示动作时,也可以用于进行时。
例:I have a lot of friends here. 我在这里有许多朋友。(状态)
We are having a meeting. 我们正在开会。(动作)
I think he can repair the radio. 我认为他能修这部收音机。(状态)
What are you thinking about? 你在想些什么?(动作)
His pale face shows that he is ill. 他面色苍白,表明他病了。
She is showing the guests around the office. 她正在带领客人参观办公室。
Shanghai lies in the southeast of China. 上海位于中国的东南部。(状态)
He is lying under the tree. 他在一棵树下躺着。
8) 现在进行时和一般现在时的比较
现在进行时加强此刻或现阶段正在进行的动作,而一般现在时表示经常或反复发
生的动作,或表示主语的特征。
比:He plays computer games every day. 他每天都玩电脑游戏。(经常性)
He is playing computer games. 他在玩电脑游戏。(此刻)
Linda often does her homework in the evening. 琳达经常在晚上做作业。
Linda is doing her homework now. 琳达现在正在做作业。
It snows a lot here in winter. 这儿冬天多雪。
It is snowing outside. 外面在下雪。
四、一般过去时
1 构成方式
be动词: was were
have动词:had
行为动词:肯定句:主语+动词过去式
否定句:主语+did not+动词原形疑问句:Did +主语+动词原形
2 基本用法
1) 表示过去某时发生的动作或存在的状态,常同确定的过去时间状语连用
这类时间状语有:
yesterday(昨天), last night(昨晚), three days ago(3天前),
last week(上周), the other day(前几天), just now(刚才),
once upon a time(从前), in the past(过去), in 2003(在2003年), when I was seven years old(我7岁时)
例:She was busy yesterday. 她昨天很忙。
He was a bus driver years ago. 几天前他是个公交车驾驶员。
They had a meeting last night. 他们昨晚开了一个会。
He left an hour ago. 他一小时前离开的。
We played tennis yesterday afternoon. 我们昨天下午打网球了。
I didn't see her last Monday. 我上星期一没有见她。
He did not have breakfast at seven this morning. 他今天早上不是在7
点钟吃的早饭。
Did you go to see the film the day before yesterday? 你前天看电影了吗?What did you say to him just now? 你(刚才)对他说了什么?
My uncle smoked a lot when he was young. 我叔叔年轻时抽烟很多。
2) 有时虽没有表示过去时间的状语,但上下文表示的是过去的动作,也要用一般过去时
例:I forgot to post the letter. 我忘了寄信了。
I thought you would not come. 我本以为你不来了。
I didn't know you were ill. 我不知道你病了。
提示
描写已故人的行为或状态,要用一般过去时。
例:Columbus discovered America. 哥伦布发现了美洲。
3) 表示过去经常、反复发生的动作
例:She usually took a walk along the river in the morning when she lived here. 她住在这里时,早上通常沿着河边散步。
Same often played chess with John in those days. 在那些日子里,山姆经常同约翰下棋。
Father took me to the park once a week when I was young. 我小时候,父亲每周带我去一次公园。
4)在时间和条件状语从句中,用一般过去时代替过去将来时
例:Mr. Wang said that he would give us a report when he returned from England. 王老师说他从英国回来后将给我们作一个报告。
He told me that they would go on a picnic if it didn't rain the next day. 他告诉我说,如果第二天不下雨,他们将会野餐。
5) used to +动词原形,表示过去的习惯,该习惯现在已终止
例:She used to work in a bookstore. 她从前在一家书店工作。(现在已不在那里工作)
He used to read English for half an hour in the morning. 他过去早上读半个小时英语。
He used to be very strong. 他以前身体很强壮。(暗示现在身体状况很差)There used to be a flowerbed here. 这里从前有一个花坛。
My parents used to live a quiet life in the country. 我父母以前在乡村过着平静的生活。
比:He used to walk to the office. 他以前步行去办公室。(现在不步行去了)
He walked to the office. 他步行去了办公室。(只说明过去一个动作,或强调不是坐车去的)
初中考英语八大时态总结
巧用英语时态表,掌握英语谓语形式 一、英语时态名称的记忆 二、英语时态形式的记忆:(以动词work为例) 可以分两个步骤记忆: 1、一般现在时: work(当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词也要用第三人称单数形式。) 现在进行时: be + working (be随主语人称和数的变化而变化。) 现在完成时: have + worked (have随主语人称和数的变化而变化,worked 是work的过去分词。) 这三种基本时态形式位于时态表的中心位置,是必须首先记住的。其它形式可推导而出。
2、记住了上面三种时态的形式后,可以设想把时间提前至过去,这三种时态的形式就相应地左移一格成为一般过去时:worked (worked是work的过去式);过去进行时was / were + working;过去完成时had + worked (worked是work 的过去分词)。 把时间错后至将来,这三种时态的形式也就相应地右移一格成为 一般将来时: shall / will + work; 将来进行时: shall / will + be working; 将来完成时: shall / will + have worked。(shall仅用于主语是第一人称时,will可用于主语是任何人称时。)当然,根据shall / will 的用法要求,紧随其后的动词或助动词要用原形形式。 简而言之,把这三种现在时态形式左移变成三种过去时态形式,只需把第一个动词变成过去式即可(一般现在时谓语只有一个动词,也可把它看成为第一个动词)。与此类似,过去将来时的变化是在一般将来时的基础上把第一个动词变成过去式。把这三种现在时态形式右移变成三种将来时态形式,只需在前面加一助动词shall / will (紧随其后的动词或助动词用原形形式)即可。 三、英语被动语态形式的记忆(以动词ask为例)
小学英语四大时态总结及练习题
你知道时态是什么意思吗?时态代表什么吗? 小学英语就四个时态,你掌握了吗? 时态动词变形名称动词变形规则各举一例 一般现在时动词变 第三人称单数形 式 1.一般情况下 2.动词结尾是ch, sh, s, x 3.动词结尾是o 4.结尾是辅音字母加y 1.不规则动词 一般过去时动词变过去式 2.一般情况下 3.动词结尾是e 4.重读闭音节辅元辅结构 5.结尾是辅音字母加y 6.不规则动词 一般将来时Be going to + Will+ 现在进行时动词变动名词 1.一般情况下 2.以不发音字母e结尾的动词 7.重读闭音节辅元辅结构 3.以y结尾的动词 4.以ie结尾的动词 你能发现它们之间的共同点和不同点吗? 勤加练习,百战不殆 I.把下列动词变为第三人称单数形式。 1. clean-- 2. go-- 3. have-- 4. do- 5.play-- 6. fly-- 7. come-- brush- 9. watch-- 10. study-- 11. ask-- 12.answer-- 13. swim-- 14. catch-- 15. write-- 16. eat-- 17. make-- 18. paint— 19. learn-- 20. phone-- 21. run— 22. hop-- 23. sing-- 24. pick— II.把下列动词变成过去式 is\am________ fly______ plant_____ are________ drink_________ play_______ go________ make ______ do_________ dance________ worry_____ask _____ taste_________ eat________ draw________ put ______ throw________ kick_________ pass_______ do ________ III.把下列动词变成动名词形式。 wake________ make__________ come____________ have____________take_________ leave__________ rid_________, regret__________,begin________ cut________, get_________, hit_________, run_________, set_________, sit__________, spit__________, stop_________, swim________, beg_________, drop__________, fit_________, nod_________, dig___________, forget_________, travel_________ visit_________ carry_________ enjoy___________ play ___________ study _____die_________ lie_________
英语十六时态表格完整总结
英语十六时态表格总结(很全面) 目录 一般现在时、一般过去时 ........................................................................................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。一般将来时、过去将来时?错误!未定义书签。 现在进行时、过去进行时 ........................................................................................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。现在完成时、过去完成时?错误!未定义书签。 英语时态表—英语时态举例!?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-一般现在时?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-现在进行时、一般过去时 ....................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 现在进行时?错误!未定义书签。 一般过去时?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-过去进行时、过去完成时、 ................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 过去进行时?错误!未定义书签。 过去完成时?错误!未定义书签。 详细讲解-过去完成进行时、一般将来时 ............................................................................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。 过去完成进行时............................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 一般将来时....................................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。详细讲解-将来进行时?错误!未定义书签。 将来进行时....................................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。详细讲解-过去将来时、将来完成时 ....................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。 过去将来时?错误!未定义书签。 将来完成时....................................................................................................................................................................... 错误!未定义书签。
(完整版)初中英语语法八大时态总结,推荐文档
初中英语语法八大时态 一.一般现在时 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有:always、often、usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将 来要发生的动作。 例如:I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 二.一般过去时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Did+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+did (否)No,主语+did not 基本结构否定句一般疑问句
四大时态总结
四大时态总结 般现在时 标志词:always (总是)usually (通常)often (经常)sometimes (有时)never (从不)every (每一) 行为动词词型变化形式 一般现在时动词只有第三人称有词形变化, 其他人称(第一人称:I, we ;第二人称:you ;第三人称复数:they 、my friends )动词均用原 形 当主语是第三人称单数时,一般动词在一般现在时句子中的变化规律: 1、多数在动词后加 s P lay — plays like — likes 2、以 s , x , sh , ch , o 结尾的动词力口 es wash -vashes catch -catches do -does 3、以辅音字母加 y 结尾,把y 改i 再加es fly — flies study — studies 5、不规则变化 have — has 般现在时基本用法 功能 1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。 如:The sky is blue. 天空是蓝色的。 女口: I get up at six every day. 我每天六点起床。 女口: The earth goes around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。 The earth is round. 构成 1. be 动词:主语+be (am,is,are )+ 其它。 女口: I am a boy.我是一个男孩。 2.行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。 女口: We study English.我们学习英语。 句型 4、以元音字母加y 结尾,直接加 s buy -buys 2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。 3.表示客观现实。
初中英语语法八大时态总结
初中英语语法八大时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有:always、often、usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。 例如:I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Did+主语+动词原形+其他
四种时态总结
四种时态总结 一、一般现在时 标志词:always(总是) usually(通常) often(经常) sometimes(有时) never(从不) every(每一) 行为动词词型变化形式 一般现在时动词只有第三人称有词形变化, 其他人称(第一人称:I, we;第二人称:you;第三人称复数:they、my friends)动词均用原形 当主语是第三人称单数时,一般动词在一般现在时句子中的变化规律: 1、多数在动词后加s play—plays like—likes , 2、以s,x,sh,ch,o结尾的动词加es wash–washes catch–catches do–does 3、以辅音字母加y结尾,把y改i再加es fly—flies study—studies 4、以元音字母加y结尾,直接加s buy – buys 5、不规则变化 have—has 一般现在时基本用法 功能 1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。 2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。 3.表示客观现实。如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
构成 1. be动词:主语+be(am,is,are)+其它。如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。 2.行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。如:We study English.我们学习 英语句型 肯定句:A.be动词:主语+ be + 其它成分 He is a worker. B.行为动词:主语+动词(注意人称变化) +其它成分 We like the little cat. 否定句:A.be动词:主语+ be + not +其它成分 They are not students. B.行为动词:主语+助动词(do/does) + not +动词原形+其它成分 We don’t like the little cat. 一般疑问句:A.be动词:Am / Is /Are +主语 + 其它成分 Are you a teacher? Yes, I am. / No, I am not. Are they students of your school.Yes they are / No they aren,t. B.行为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形 + 其它成分 Do you like it? Yes, I do. / No. I don’t . Does he(she) like it? Yes, he( she )does. / No, he ( she )doesn’t. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+ 一般疑问句 A.be动词: How many students are there in your school? B.行为动词:What do you usually do on Sunday?
小学英语四种时态总结
小学英语四种时态总结 1、一般现在时。主要描述经常会发生的动作、状态或不变的 真理。句末常出现every day/week/year/Monday , in the morning, 句中常有always, usually, often, sometimes组成: 主语+be+名词(形容词) I am a student、 He is tall、否定句:在be 后加not I am not a student、 He is not tall、疑 问句:be 动词提前到第一位。A re you a student? Is he tall? Yes, I am、 / No, I am not、Yes, he is、 / No, he isn’t、主语+动词+地点+时间 We go to school on Monday、 He goes to the park on Sunday、否定句:主语 +don’t/doesn’t’t+动词原形+地点+时间We don’t go to school on Monday、He doesn’t’t go to the park on Sunday、疑问句:在句首加do或does Do you go to school on Monday? Yes, we do、/ No, we don’t、 Does he go to the park on Sunday? Yes, he does、/ No, he doesn’t’t、动词 单三变化: 1、在原单词末尾加s , 如:like – likes 2、单词以o, sh, ch, s, x 结尾加es, 如:go – goes 3、单词末尾为辅音+y结尾去y加ies 如:study- studies 2、现在进行时:主要叙述正在发生的事情。句末常出现now, 句首常出现look, listen组成:主语+be +动词ing形式 I am
高中16种英语时态总结归纳
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。) 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法: A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging
英语八大时态归纳总结
英语八大时态归纳总结文件编码(TTU-UITID-GGBKT-POIU-WUUI-0089)
1、一般现在时 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语: always,usually,often,sometimes,everyweek(day,year, month…),onceaweek,onSundays,etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 2、一般过去时 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语: ago,yesterday,thedaybeforeyesterday,lastweek(year,n
ight,month…),in1989,justnow,attheageof5,oneday,lo nglongago,onceuponatime,etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词。 3、现在进行时 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 时间状语:now,atthistime,thesedays,etc. 基本结构:am/is/are+doing 否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing. 一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。 4、过去进行时 概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
最新小学英语四种时态总结
小学英语四种时态总结 1.一般现在时。主要描述经常会发生的动作、状态或不变的真理。句末常出现every day/week/year/Monday , in the morning, 句中常有always, usually, often, sometimes 组成:主语+be+名词(形容词) I am a student. He is tall. 否定句:在be 后加not I am not a student. He is not tall. 疑问句:be 动词提前到第一位。 Are you a student? Is he tall? Yes, I am. / No, I am not.Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t. 主语+动词+地点+时间 We go to school on Monday. He goes to the park on Sunday. 否定句:主语+don’t/doesn’t’t+动词原形+地点+时间 We don’t go to school on Monday. He doesn’t’t go to the park on Sunday. 疑问句:在句首加do或does Do you go to school on Monday? Yes, we do./ No, we don’t. Does he go to the park on Sunday? Yes, he does./ No, he doesn’t’t. 动词单三变化:1. 在原单词末尾加s , 如:like –likes
2. 单词以o, sh, ch, s, x 结尾加es, 如:go –goes 3. 单词末尾为辅音+y结尾去y加ies 如:study- studies 2. 现在进行时:主要叙述正在发生的事情。句末常出现now, 句首常出现look, listen 组成:主语+be +动词ing形式 I am reading English. They are swimming. He is playing football. 否定句:在be后加not I am not reading English. They are not swimming. He is not playing football. 疑问句:将be 放到第一位。 Are you reading English? Yes, I am./ No, I am not. Are they swimming? Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t. Is he playing football? Yes, he i s. / No, he isn’t. 动词变ing形式:1.在动词末尾加ing. 如:play- playing 2. 末尾有e 要去e加ing. 如:ride –riding 3. 末尾以辅音元音辅音结尾双写末尾一个辅音如:swim-swimming 3.一般将来时。主要描述将来要发生的事情。 句末常出现next Monday/week/ year, tomorrow
(完整版)各种时态结构的总结
各种时态结构的总结 各种时态的主动结构: 一般现在时(表习惯性,经常性,反复性): 1.主语+am/is/are+其他 2.三单主语+动词-s/-es形式+其他 3.非三单主语+实义动词原形+其他 一般过去时(表动作发生在过去): 1.主语+was/were+其他 2.主语+实义动词过去式+其他 一般将来时(表动作发生在将来): 1.am/is/are going to+动词原形 2.will/shall+动词原形 过去将来时(表动作发生在过去的将来): 1.was/were going to +动词原形 2.Would+动词原形 现在进行时(表动作现在或目前正在发生):am/is/are +动词-ing 过去进行时(表动作过去某一时间正在发生):was/were+动词-ing 现在完成时(表动作发生在过去,对现在造成的影响或结果;或者动作持续到现在或将来): has/have+动词过去分词(have/has done)(三单主语用has,其他人称用have) 过去完成时:(表过去某个动作之前的那个动作,即过去的过去)had+
动词过去分词(had done) 各种时态的被动结构:(done指过去分词)一般现在时:am/is/are done 一般过去时:was/were done 一般将来时:1,shall/will be done 2, am/is/are going to be done 过去将来时:1,would be done 2, was/were going to be done 现在进行时:am/is/are being done 过去进行时:was/were being done 现在完成时:have/has been done 过去完成时:had been done 含情态动词的被动结构:情态动词+be done 不定式的被动结构:“to be done”。
中考初中英语语法八大时态总结(附答案)
中考初中英语语法八大时态总结(附答案) 初中英语语法八大时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词) don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有: always、often、 usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。 例如: I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他
pep小学英语四种时态总结
pep小学英语时态总结 一.一般现在时 表示一般情况下按照某种频度发生的事,或者存在的某种状态。 特征:句子中一般有usually often 等表示频度的词。 1.陈述句句子结构。 a、主语(非第三人称单数)+动词原形+ 时间、地点等 例: Usually I play football on the weekend. b、主语(第三人称单数)+动词(单三形式)+时间、地点 例:Usually he plays football on the weekend. 2.特殊疑问句结构。 疑问代词(what等)+do/does+ 主语+时间等其他? 例:What do you do on the weekend? 3.一般疑问句机构。 Do/Does +陈述句+? 回答: Y es, 主语+do/does. No, 主语+don't/doesn't. 例:Do you play football on the weekend? Y es, I do.No, I don't. 二.现在进行时。 表示现在正在进行的动作。 1.陈述句。 主语+be(is,am,are)+动词ing形式+ 地点。 例:I am playing football on the playground. 2.特殊疑问句。 疑问代词(what等)+be+主语+doing+? 例:What are you doing? 3.一般疑问句。 Be+主语+动词ing形式+? Y es,主语+be。No,主语+be的否定形式 例:Are you playing football? Y es,I am. No,I am not. 三、一般将来时。 表示将要或者准备发生的事,句子中一般有表示将来的时间词(如:next weekend等) 1.陈述句。 主语+be(is,am,are) going to +动词原形+ 时间、地点等例:I am going to play football next weekend. 2.特殊疑问句。 疑问代词(what等)+be + 主语+going to do+时间、地点等? 例:What are you going to do next weekend? 3.一般疑问句。 Be+主语+ going to + 动词原形+ 时间地点等? Y es,主语+be。No,主语+be否定形式。 例:Are you going to play football next weekend? Y es,I am. No,I am not. 四.一般过去时。 表示过去已经发生过的事,句子中一般有表示过去的词(如:last
小学英语 六年级四种时态总结
小学英语四种时态总结 1.一般现在时。主要描述经常会发生的动作、状态或不变的真理。句末常出 现every day/week/year/Monday , in the morning, 句中常有always, usually, often, sometimes 口诀:―经常有每没(美眉^^)总星周‖ 经常:often 有:sometimes (记住,―有‖不是have,而是―有时‖) 每:every week/month/year 等 没:never 总:always,usually等 星周:on Mondays,on Tuesdays等 组成:主语+be+名词(形容词) I am a student. He is tall. 1. He isin New York with his cousin.他和他的堂兄在纽约。 2. These postcardsare great.这些明信片真棒! 3. It‘s a picture of the Great Wall.这是一张关于长城的明信片。 4.It‘s more than twenty thousand kil ometers long.它超过两万公里长 5.It‘s in the eastof China.它在中国的东部。 6.There isa Chinatown in New York.纽约有一个唐人街。
7.There arelots of Chinese shops and restaurants there.那里有许多中国商店和餐馆。 8.There are lots of beautiful lakes in China.在中国有许多偏凉漂亮的湖泊。 9.It‘s a big fa mily dinner.它是一次大的家庭晚餐。 否定句:在be 后加not I am not a student. He is not tall. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 疑问句:be 动词提前到第一位。
八大时态语法总结
八大时态语法总结 一、时态 一般现在时,现在进行时,一般过去时,现在完成时,一般将来时,过去进行时,过去完成时,过去将来时 1. 一般现在时 表示一般性,经常性的动作或一般性事实。 (1)含有be动词的句子 ★一般肯定句 He is a teacher. The girl is very beautiful. Tim and Jack are students. ★变疑问句将be动词移到句首 Is he a teacher? Is the girl very beautiful? Are Tim and Jack students? ★变否定句在be动词后面加not He is not a teacher. The girl is not very beautiful. Tim and Jack are not students. ★肯定回答及否定回答 Yes, he is. No, he is not. Yes, she is. No, she is not. Yes, they are. No, they are not.
(2)不含有be动词的句子,即含有一般动词的句子 A、第三人称he she it单数及单数名词apple apples(复数名词=they) ★一般肯定句 He likes books. She likes him. The dog likes bones. ★变疑问句在句首加does, 动词变为原型 Does he like books? Does she like him? Does the dog like bones? ★变否定句在主语及动词之间加doesn’t, 动词变为原型,原句中的动词不再有第三人称变化。 He doesn’t like books. She doesn’t like him. The dog doesn’t like bones. ★肯定回答及否定回答: Yes, he does. No, he doesn’t. Yes, she does. No, she doesn’t Yes, it does. No, it doesn’t. 注意:第三人称单数形式一般在动词后面加S,不要和名词复数混淆,变否定句或疑问句时名词复数没有任何变化。
最新小学六年级英语四种时态总结
小学六年级英语四种时态总结 一、一般现在时 标志词:always(总是) usually(通常) often(经常) sometimes(有时) never(从不) every(每一) 行为动词词型变化形式 一般现在时动词只有第三人称有词形变化, 其他人称(第一人称:I, we;第二人称:you;第三人称复数:they、my friends)动词均用原形当主语是第三人称单数时,一般动词在一般现在时句子中的变化规律: 1、多数在动词后加s play—plays like—likes , 2、以s,x,sh,ch,o结尾的动词加es wash–washes catch–catches do–does 3、以辅音字母加y结尾,把y改i再加es fly—flies study—studies 4、以元音字母加y结尾,直接加s buy – buys 5、不规则变化have—has 一般现在时基本用法 功能 1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。 2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。 3.表示客观现实。如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。 The earth is round. 构成 1. be动词:主语+be(am,is,are)+其它。如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。 2.行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。如:We study English.我们学习英语。 句型 肯定句:A.be动词:主语+ be + 其它成分He is a worker. B.行为动词:主语+动词(注意人称变化) +其它成分We like the little cat. 否定句:A.be动词:主语+ be + not +其它成分They are not students. B.行为动词:主语+助动词(do/does) + not +动词原形+其它成分 We don’t like the little cat. 一般疑问句:A.be动词:Am / Is /Are +主语+ 其它成分 Are you a teacher? Yes, I am. / No, I am not. Are they students of your school.Yes they are / No they aren,t. B.行为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形+ 其它成分 Do you like it? Yes, I do. / No. I don’t . Does he(she) like it? Yes, he( she )does. / No, he ( she )doesn’t.特殊疑问句:疑问词+ 一般疑问句 A.be动词:How many students are there in your school? B.行为动词:What do you usually do on Sunday? 一般现在时动词be和have的变化形式 1.动词Be 叫连系动词, 用法:第一人称单数用am,第三人称单数用is,其它人称用are。
