中英文翻译

Fuzzy Logic Based Autonomous Skid Steering Vehicle Navigation
L.Doitsidis,K.P.Valavanis,N.C.Tsourveloudis
Technical University of Crete
Department of Production Engineering and Management
Chania,Crete,Greece GR-73100
{Idoitsidis ,kimonv,nikost}@dpem.tuc.gr
Abstract-A two-layer fuzzy logic controller has been designed for 2-D autonomous Navigation of a skid steering vehicle in an obstacle filled environment. The first layer of the Fuzzy controller provides a model for multiple sonar sensor input fusion and it is composed of four individual controllers, each calculating a collision possibility in front, back, left and right directions of movement. The second layer consists of the main controller that performs real-time collision avoidance while calculating the updated course to be applicability and implementation is demonstrated through experimental results and case studies performed o a real mobile robot.
Keywords - Skid steering, mobile robots, fuzzy navigation.
Ⅰ.INTRODUCTION
The exist several proposed solutions to the problem of autonomous mobile robot navigation in 2-D uncertain environments that are based on fuzzy logic[1],[2],evolutionary algorithms [3],as well as methods combining fuzzy logic with genetic algorithms[4] and fuzzy logic with electrostatic potential fields[5].
The paper is the outgrowth of recently published results [9],[10],but it studies 2-D environments navigation and collision avoidance of a skid steering vehicle. Skid steering vehicles are compact, light, require few parts to assemble and exhibit agility from point turning to line driving using only the motions, components, and swept volume needed for straight line driving.
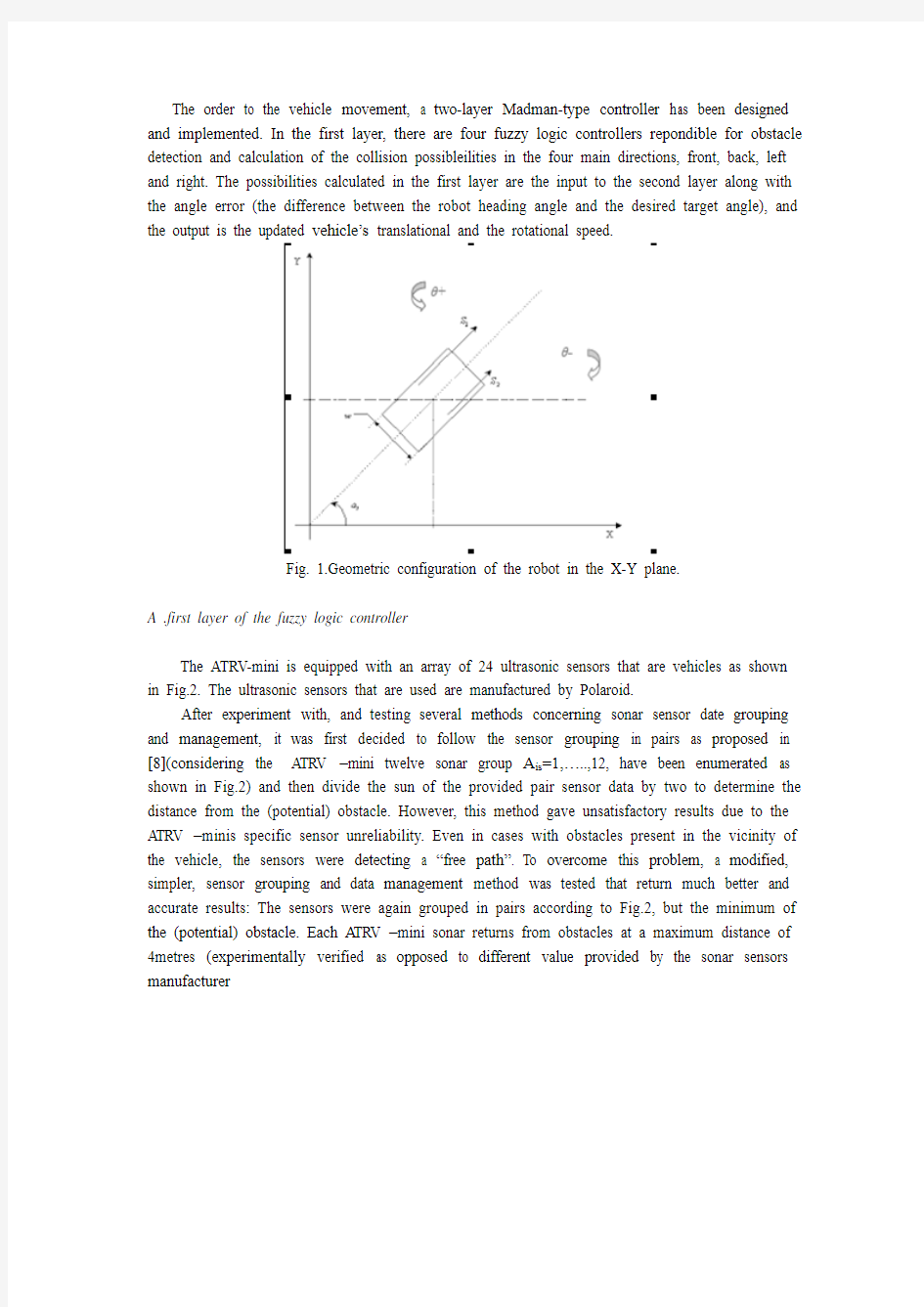
Skid steering vehicle motion differs from explicit steering vehicle motion in the way the skid steering vehicle turns. The wheels rotation is limited around one axis and the back of steering wheel results in navigation determined by the speed change in either side of the skid steering vehicle. Same speed in either side results in a straight-line motion. Explicit steering vehicles turn differently since the wheels are moving around two axes. The geometric configuration of a skid steering vehicle in the X-Y plane is shown in Fig1,while a t is the heading angle, W is the robot width, θthe sense of rotation and S1, S2 are the speeds in the either side of the robot.
The derived and implemented planner a two-layer fuzzy logic based controller that provides purely” reactive behavior” of the vehicle moving in a 2-D obstacle filled environment, with inputs readings from a ring of 24 sonar sensors and angle errors, and outputs the updated rotational and translational velocities of the vehicle.
Ⅱ.DESIGN OF THE FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The order to the vehicle movement, a two-layer Madman-type controller has been designed and implemented. In the first layer, there are four fuzzy logic controllers repondible for obstacle detection and calculation of the collision possibleilities in the four main directions, front, back, left and right. The possibilities calculated in the first layer are the input to the second layer along with the angle error (the difference between the robot heading angle and the desired target angle), and the output is the updated vehicle’s translational and the rotational speed.
Fig. 1.Geometric configuration of the robot in the X-Y plane.
A .first layer of the fuzzy logic controller
The ATRV-mini is equipped with an array of 24 ultrasonic sensors that are vehicles as shown in Fig.2. The ultrasonic sensors that are used are manufactured by Polaroid.
After experiment with, and testing several methods concerning sonar sensor date grouping and management, it was first decided to follow the sensor grouping in pairs as proposed in [8](considering the ATRV –mini twelve sonar group A is=1,…..,12, have been enumerated as shown in Fig.2) and then divide the sun of the provided pair sensor data by two to determine the distance from the (potential) obstacle. However, this method gave unsatisfactory results due to the ATRV –minis specific sensor unreliability. Even in cases with obstacles present in the vicinity of the vehicle, the sensors were detecting a “free path”. To overcome this problem, a modified, simpler, sensor grouping and data management method was tested that return much better and accurate results: The sensors were again grouped in pairs according to Fig.2, but the minimum of the (potential) obstacle. Each A TRV –mini sonar returns from obstacles at a maximum distance of 4metres (experimentally verified as opposed to different value provided by the sonar sensors manufacturer
Fig.2. Grouping of the Sensors.
The form of each first layer individual fuzzy controller, including the obstacle detection module, is shown in Fig.3.Observing Fig.3, data from group sensors A1, A2, ….,A5(5 inputs) and group sensors A7, A8 , …,A11(5 inputs) serve as inputs to the individual controllers responsible for the calculation of the front and back collision possibilities, respectively. Data from group sensors A5, A6, A7 (3 inputs) serve as input to calculate the left and right possibilities, respectively. The individual fuzzy controllers utilize the same membership functions to calculate the collision possibilities. The linguistic values of the variable distance_from_obstance are defined to be three, near, meium_distance, away with membership functions as shown in Fig.4 reflecting the maximum distance of 4 meters a sonar returns accurate information about potential obstacles.
Fig.3.Obstacle detection module.
Fig.4.Input Variable Distance_ From _ Obstacle.
The first layer output is a collision possibility in each direction taking values from 0 to 1.The linguistic variables describing each direction output variable collision possibility (with empirically Derived for best performance) membership functions as shown In Fig.5.A part of the rules base for left collision is presented in TableⅠ.
An example of the rules used to extract front collision possibilities is: IF A1 is near AND A2 is near AND A3 is Near AND A4 is medium_distance AND A5is near THEN collision_possibility is high. Similar for the back collision possibility.For left (equivalently for right collision)possibilities the rule is of the form: If A5 is near And A6 is nearAnd A7 is near THEN collision_possibility is high.
Fig.5.Output Variable collision_possibility
TABLE Ⅰ
PART OF THE RULES BASE FOR LEFT COLLISION
B. Second layer of the fuzzy logic controller
The second layer fuzzy controller recives as inputs the four collision possibilities in the four directions and the angle error, and outputs the translational velocity, which is responsible for moving the vehicle backward or forward and the rotational speed, which is responsible for the vehicle rotation as shown in Fig.6.
The angle error represents the difference between the robot-heading angle and the desired angle the robot should have in order to reach its target. The angle error takes values ranging from-1800to 1800. The linguistic variables that represent the angle error are: Backwards_1, Hard_Left, Left, right, Hard_right, Backwards_2 with (empirically derived from tests) membership functions as shown in Fig.7.
The translational velocity (m/sec) , which is one of the outputs of the second layer controller, is described with the following linguistic variables: back_full, back, back_solw, stop, front_slow, front, frontfull, with membership functions as in Fig.8.
Fig 6.Block diagram of the 2nd layer of the fuzzy logic controller
Fig 7.Input Variable Angle Error.
Fig 8.Output Variable Translational_Velocity.
The rotational_speed (rad/sc) is described with the following linguistic variables: Right_full, right, no_ratation, left, let_full with membership functions as in Fig.9.
An example of the rules that control the vehicle is demonstrated: If front_collision is Not_Possible AND Back_Collision is Not_possible And Left_Collision is Not_possible And Right_Collision is Not_possible And Angle Error is Ahead THEN Translational_velocity is Front_Full AND Rotational_Velocity is No_Ratation.
Fig. 9. Output Variable Rotational_velocity.
Ⅲ. RUSULTS
The fuzzy logic controller has been designed and implemented using C++ in an ATRV-mini manufactured by Real World Interface(RWI). In all experiments the robot is considered to have reached its target when stopping inside a circle with radius of 30 cm. This assumption has been dictated because all calculations have been made relative to the center of the robot. So if the robot stops inside that circle it is assumed that it has reached its target.
Several scenarios in an indoor 2-D obstacle filled environment have been tested to study the robot behavior and the controller’s applicability.
The arrow in Fig.10, Fig.15, Fig.20 is showing the initial direction of the vehicle.
In test case 1 we examine the behavior of the vehicle in an environment with three obstacles. The test case 1 is presented in Fig.10. Fig.11 shows the translational velocity, while the rotational velocity is given in Fig.12.Fig.13 presents the front collision possibility. In Fig.14, the solid line indicates the left collision possibility while the doted the right collision possibility. The behavior of the vehicle is defined from the surrounding obstacles.
In the beginning the left collision possibility is high due to the obstacle in the left. The robot moves forwards and it’s steering right in order to avoid the obstacle. Then it steers left and moves towards its target.
In the second test case presented in Fig.15, a more complicated environment with three obstacles has been tested. Fig.16 shows the translational velocity, while the rotational velocity is given in Fig.17. Fig.18 presents the front collision possibility while in Fig.19 the solid line indicates the left collision possibility while the doted the right collision possibility. In Fig.15 we can see that the path in front of the robot is blocked. The robot uses only the rotational velocity in order to steer and avoid the obstacle. Then it moves in a curve towards its target.
The third test case considers an environment with many small obstacles. The path the vehicle is following is presented in Fig.20. Due to the obstacles that are around the vehicle, the vehicle is forced to make a small right turn an then it escapes from the closed area. Fig.21 shows the translational velocity, while the rotational velocity is given in Fig.22.Fig.23 presents the front collision possibility while in Fig.24 the solid line indicates the left collision possibility while the
doted the right collision possibility.
The behavior of the vehicle in each case can verified by observing the relative figures concerning the collision possibility in each direction.
Fig. 10.Test Case 1. Environment with three obstacles and remote target point.
Fig.11. Translational Velocity in Test Case Fig. 14. Left and right Collision Possibilities in Test Case 1.
Fig.12. Rotational Velocity in Test Case 1. Fig. 15. Test Case 2. Environment with three obstacles.
Fig.13. Front Collision Possibility in Test Case 1. Fig.16. Translational Velocity in Test Case 2.
Fig.17.Rotational Velocity in Test Case 2. Fig.20. Test Case . Environment with many small obstacles.
Fig.18. Front Collision Possibility in Test Case 2. Fig.16. Translational Velocity in Test Case 3.
Fig.19. Left and right Collision Possibilities in Test Case 2 Fig.22.Rotational Velocity in Test Case 3.
Fig.23. Front Collision Possibility in Test Case 3.
Fig.24. Left and right Collision Possibilities in Test Case 3
Ⅳ.DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
We have presented a navigation system for a skid steering vehicle with the use of a two-layer fuzzy logic controller. The first layer of the fuzzy logic controller is composed of four fuzzy logic controllers. The rule base of the controllers responsible for front and back collision contains 60 rules and the rule base of the controllers responsible for front and back collision contains 57 rules. The rule base of the second layer fuzzy logic controller responsible for real-time navigation and collision avoidance contains 238 rules.
The fuzzy logic controller has performed satisfactorily. The results show that the vehicle has the ability to move in complicated environments. The controller, which is proposed in this paper, is based in the controller proposed in [9] but it is implemented in a skid steering vehicle.
Future directions of the research include the testing of dynamic environments, and the use of other sources of information.. The goal is to create an autonomous vehicle that will use for navigation and the collision avoidance combined information from visual inputs, sonars and outdoors GPS data that will guide the vehicle in remote target points.
中译文
模糊控制理论在自动引导车智能导航中的应用
L. Doitsidis, K. P. Valavanis, N. C. Tsourveloudis
(克利特科技大学生产过程和管理工程系,克利特岛,希腊,希腊GR-73100,
电子邮箱:{ldoitsidis, kimonv, nikost}@dpem .tuc .gr)
摘要:本文设计了一种双层的基于模糊控制理论的控制器,用来在一个充满障碍物的环境下为自动引导车提供自主领航。控制器的第一层建立了一个复合的声纳传感器的输入端模型,它是由四个独立的控制器组成,这四个控制器分别用来计算自动引导车向前、后、左、右四个方向移动时碰撞可能性。第二层是由一个主控制器构成,它能计算自动引导车的行驶路线,因此能执行相应的程序以避免碰撞。通过对一个移动机器人进行研究证明了这个双层控制器的适用性。
关键词:自动引导,移动机器人,智能导航
1.引言
自主移动的机器人在2维不确定环境下的导航的问题,现存有很多方法,这些建议有的是以模糊控制理论的算法为基础的,还有的是把把模糊控制理论和调优算法结合起来的,以及把模糊控制理论和静电学领域结合起来的方法。
这篇文章是结合最近的一些研究成果而提出的。本文主要研究自动引导车的2维环境下的导航问题。自动引导车是坚实而轻巧的,只要求很少的装配部件,并且它可以很迅速的从点运动转变到线运动时, 本文导论的就是自动引导车的直线驾驶问题[6].
自动引导车和明确指点车的运动的不同在于自动引导车的转弯方式. 轮子的转动被限于绕一条轴, 方向盘的缺陷导致导航由每边的速度变化决定。只要任一方向有相同速度就将导致自动引导车沿直线运动。而明确指点车的轮子绕着两条轴转动。自动引导车在X-Y 平面里的几何结构如图1所示,在这张图里,α表示的是航向角度,w表示的是机器人的宽度,θ自转角和S1、S2时该车在每个方向的速度。.
2.模糊逻辑控制系统的设计
为了控制车的移动,一个双层的Mamdani型的控制器已经设计出来并完成。在第一层,四个模糊控制器负责对障碍物的探测和对前后左右四个方向的碰撞可能性进行计算。这四个控制器接收来自声纳传感器的数据,同时输出前后左右四个方向的碰撞的可能性。这些可能性在第一层中计算出来并和角度误差一起被输入到第二层中,输出量是车的最新的平移和旋转速度。
图1. 自动引导车在X-Y平面上的模型
A.模糊逻辑控制器的第一层
在自动引导车周围装有24个超声波传感器,如图2所示。这里所用到的这些超声波传感器由Polaroid制造。
在测试一些关于声纳传感器数据编组和管理之后,最初决定按照文献[8]的方法对传感器编组(把小测距系统中的十二台生波探侧器的传感器编组为Ai, i=1,4a.., 12,如图2),然后再把来自两组传感器的一对数据分开来讨论,可以得到潜在障碍物的距离。然而,由于小型测距系统特有的声纳传感器的不可靠性, 这个方法得到的结果不尽如人意,当车附近有障碍时,传感器却探测到一条“自由道路”。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了一个改进的,更简单的传感器编组和数据管理方法,并得到了更好更准确的结果:对图2的传感器再编组,它们的读数的最小数是到障碍物的距离的一个衡量值。每个A TRV生波探侧器传感器以4米作为最大距离,从这个距离处的障碍物返回数据。(这由生波探侧器传感器制造商进行了实验性地核实).
图2. 传感器组
第一层的每个独立的模糊控制器的模型,即障碍物探测模块,如图3所示。从图3可知,对前、后方向的碰撞可能性的测定由传感器A1,A2,…A5(5个输入数据)和传感器A7,A8,…A11(5个输入数据)完成,而对左、右方向的碰撞可能性的测定由传感器A5,A6,A7(3个输入数据)和传感器A11,A12,A13(3个输入数据)完成,每个独立的模糊控制器利用隶属度函数来计算碰撞的可能性。距离障碍物的距离按照隶属度函数分为三个标准:近、中等距离、远,如图4,反映了关于潜在障碍物在4 米内的准确信息。
图3.障碍物探测模块。
图4.输入变量:距离障碍物的距离
第一层的输出结果是各个方向的碰撞可能性,取从0 到1的值来表示,.描述各个方向撞击可能性按照隶属度函数的标准有:不可能、可能、非常可能性,如图5。基于左碰撞可能性的输出结果如表1。
图5. 输出变量:碰撞可能性。
以前碰为类: 如果A1、A2、A3、A5是近的、A4 是中等距离,那麽碰撞可能性高的。后面碰撞与此相似。为左边(等效为右碰)碰撞可能性是: 如果A5 、A6、A7
都是近的,那碰撞的可能性是高的。
表1.
一部分的规则基地为左碰撞。
B.模糊逻辑控制器的第二层
模糊控制器的第二层输入的是四个方向的碰撞可能性和角度误差,输出的是使车子前后移动的移动速度和转动速度,如图6所示。角度误差描述的是机器人航向角度和机器人要达到它的目的地的目标角度之间的差距。角度误差的范围是-180度到180度之间。按照隶属度函数描述角度误差的词有:偏后1、正左方、左边、前面、正右面、偏后2,如图7.
可平移速度(m/sec), 作为第二层的输出结果,按照隶属度函数用以下词描述: 向后加速, 向后、向后减速、停止, 向前减速、向前、向前加速,如图8.
按照隶属度函数转动速度(rad/sec)用以下词汇描述:向右加速,、向右、不转、向左、向左加速,如图9.
图6. 模糊控制器的第2 层模型
图7. 输入变量:角度误差
图8. 输出变量:平移速度
控制车运动的例子: 如果前面碰撞、后面碰撞、左面碰撞、右面碰撞都是不可能的,则角度误差是前面,平移速度是向前加速、加速度是不旋转
图9. 输出变量:旋转速度。
3.结论
模糊控制器已经被设计出来,并在一个由R W I制造的小型测距系统中运用,而且利用C++语言进行了设计并执行。在所有的实验中,当机器人能在一个半径为30厘米的圆圈中停下来的时候,就可以认为它达到了它的目标。这个假设是成立的,因为所有的计算都已经被验证。所以,如果机器人在假定的圆圈内停下来,它的目标就实现了。
通过研究该机器在有障碍的2维环境中的一些情况,来测定它的运行情况和控制器的适用性。
图10、图15、图20的箭头显示的是车的初始方向。
在测试情形1中,我们检查了车在一个有三个障碍物的环境下的运行情况,具体如图10所示。图11显示了平移速度以及图12显示的是转速。图13介绍的是前撞的可能性。在图14中,实线表示的是左撞的可能性,而虚线表示右撞的可能性。车的运行情况是由周围的障碍所决定的。
一开始,左撞的可能性是由左边的障碍物决定的。机器向前移动,然后向右行驶避开障碍,然后再向左驶向其目标运动。
图15所示的测试情形2,显示的是一个更加复杂的三个障碍物的测试环境。图16 显示了平移速度,图17显示了转动速度。图18表示的是前撞的可能性,图19 中的实线代表的是左撞的可能性,而虚线代表的是右撞的可能性。在图15中,我们可以发现机器人前面的路是被封锁的。机器仅仅利用转动速度来行驶并避开障碍物。然后它以曲线行驶向着目标前进。车
的行使路线如图20所示。由于周围的障碍物,车不得不稍稍向右转了一个弯,然后逃离了
这个封闭的区域。
图21显示了平移速度,图22显示了转动速度。图23表示的是前撞的可能性,图24 中的
实线代表的是左撞的可能性,而虚线代表的是右撞的可能性。每种情形中的车的运行情况可
以通过各个方向的碰撞可能性的相关数据得到检验。
图10. 判例1 :三个障碍并且目标点较远
图11. 判例1中平移速度。图14. 判例1中左右碰撞可能性
图12. 判例1中旋转速度图15 判例2:较复杂的三个障碍
图13. 判例1中前面碰撞可能性图16. 判例2中平移速度
【精选】翻译服务合同英文
翻译服务合同英文 合同翻译一般是指对国际贸易中的合同、章程、条款的翻译。以下是整理的翻译服务合同英文模板,欢迎参考阅读。 翻译服务合同英文模板一 Technical Cooperation Agreement 甲方:XX油脂化学有限公司 Party A: XX Grease Chemical Co. , Ltd. 地址: XX高新技术工业园 Address: XXHigh-tech Industrial Park 法定代表人:XXX Legal Representative: XXX 乙方: Party B: 地址: Address: 本协议合作双方就组建技术研发团队事项,经过平等协商,在真实、充分地表达各自意愿互惠互利的基础上,根据《中华人民共和国合同法》的规定,达成如下协议,并由合作各方共同恪守。 This Agreement, concerning the setting up of a technical research and development team, is made according to the Contract Law of PRC regulations and entered into through equal negotiation by both
Parties as the free and full expression of their own wishes to mutual benefits, and to this end both Parties shall abide by this Agreement as following. 第一条、甲方同意雇用乙方为新产品研发技术顾问。乙方同意为甲方提供技术 顾问服务。 Article 1: Party A hereby agrees to employ party B as the technical consultant for the new product research and development. Party B hereby agrees to offer technical consultation service to Part A. 第二条、甲方同意每月支付乙方的研究费用,包括:薪资、办公费、检测费、 差旅费以及其他相关费用。 Article 2: Party A hereby agrees to pay Party B for the research each month, including salaries, administrative expenses, detection cost, traveling expenses and other cost associated. 第三条、乙方有责任为甲方提供相关国内外技术及市场信息,并及时答复甲方 技术上所遇到的问题。 Article 3:Party B is responsible to provide relevant technical and market information home and abroad and is ready to answer any technical problem frequently asked by Party A. 第四条、乙方有义务向甲方提供有关个人简历和相关证明材料,甲方要尊重乙
spss软件的菜单及所有单词中英文翻译大全
SPSS 统计软件的主菜单及子菜单
spss软件的中英文翻译 Absolute deviation, 绝对离差 Absolute number, 绝对数 Absolute residuals, 绝对残差 Acceleration array, 加速度立体阵 Acceleration in an arbitrary direction, 任意方向上的加速度Acceleration normal, 法向加速度 Acceleration space dimension, 加速度空间的维数Acceleration tangential, 切向加速度 Acceleration vector, 加速度向量 Acceptable hypothesis, 可接受假设 Accumulation, 累积 Accuracy, 准确度 Actual frequency, 实际频数 Adaptive estimator, 自适应估计量 Addition, 相加 Addition theorem, 加法定理 Additivity, 可加性 Adjusted rate, 调整率 Adjusted value, 校正值 Admissible error, 容许误差 Aggregation, 聚集性 Alternative hypothesis, 备择假设 Among groups, 组间 Amounts, 总量 Analysis of correlation, 相关分析 Analysis of covariance, 协方差分析 Analysis of regression, 回归分析 Analysis of time series, 时间序列分析 Analysis of variance, 方差分析 Angular transformation, 角转换 ANOVA (analysis of variance), 方差分析 ANOVA Models, 方差分析模型 Arcing, 弧/弧旋 Arcsine transformation, 反正弦变换 Area under the curve, 曲线面积 AREG , 评估从一个时间点到下一个时间点回归相关时的误差ARIMA, 季节和非季节性单变量模型的极大似然估计 Arithmetic grid paper, 算术格纸 Arithmetic mean, 算术平均数
中英文翻译(修改)
建筑结构在冲击负载作用下连续倒塌分析方法 摘要:建筑物在冲击负载作用下的连续倒塌已经引起了全世界的极大关注。对于一个经济的,安全的,能够抵抗冲击负载作用下连续倒塌的建筑结构设计,连续倒塌分析是必不可少的。因为连续倒塌的灾难性特点,和为了抵抗它而潜在的建造和改造建筑物的高额费用,所以连续倒塌分析方法是绝对必要且可信的。对于工程师们而言,他们估算连续倒塌的方法不仅仅要求精确和简要,而且容易上手,立竿见影。因而,最近许多研究者都在发展可靠有效和直接的连续倒塌分析方法上花费了很多的精力。在最近的干物上,当前在文献资料中找得到的关于连续倒塌的分析方法被重新审阅。人们广泛讨论它们的适宜性、适用性和可靠性。我们也提出了最近刚刚完成的关于钢筋混凝土框架在爆破荷载下的连续倒塌新分析方法。 关键词:连续倒塌分析;建筑结构;爆炸荷载;冲击荷载 连续倒塌被定义为“由于一个基本的局部构件失效在构件之间扩散最终造成整个结构或者是不成比例的一大部分倒塌”。其含义为一个或者一组关键承重构件的失效造成周围构件的失效和部分或者是整个结构的倒塌。建筑结构的连续倒塌可能由一系列的意外和人为的因素造成,比如:错误的建造顺序,偶然过载造成的局部失效,爆炸和地震造成的关键组件的损坏。这篇论文仅仅研究了特殊荷载(如:爆炸和冲击),造成的建筑结构连续倒塌的分析。 随着最近Alfred P.Murrah联邦大楼和世界贸易中心(WTC)的倒塌,许多的研究更多的关注如何建造抵抗由于爆炸和冲击荷载造成连续倒塌的建筑。对于一个经济的,安全的,能够抵抗冲击负载作用下连续倒塌的建筑结构设计,连续倒塌分析是必不可少的。因为连续倒塌的灾难性特点,和为了抵抗它而潜在的建造和改造建筑物的高额费用,所以连续倒塌分析方法是绝对必要且可信的。对于工程师们而言,他们估算连续倒塌的方法不仅仅要求精确和简要,而且容易上手,立竿见影。因而,最近许多研究者都在发展可靠有效和直接的连续倒塌分析方法上花费了很多的精力。
专业英文合同翻译服务收费标准
专业英文合同翻译服务收费标准拨--打【4000-537-407】 精诚翻译提前您,找翻译服务时,请勿在收到翻译稿件之前进行银行转账,根据我们的经验,要求未做事之前银行卡付款的,很多是骗子,请你切记切记!精诚翻译五折优惠中六年经验!先翻译后付费学生客户送50元优惠券,可以搜索精诚翻译找到我们 英语中,比较结构的句型复杂,表现形式多样。在翻译的时候,需要仔细分析,在准确理解的基础上,才能进行贴切的表达。所以,从理解与表达的角度来看,比较的形式是次要的,真正重要的是意义上的比较。只要意义上表示比较,就属于比较句式。常见的比较结构的意义很容易理解,所以也比较容易翻译,如:I am taller than he.(我比他高)。因此,这里不再叙述基本比较结构的翻译方法,而主要介绍在意义上容易混淆的比较结构的翻译。 一、as…as…句型 (一)as…as…句型 as…as…句型是同级比较,表示两者比较程度一样。所以在翻译的时候,通常翻译为“…和….一样”。 My parcel is as heavy as yours. 我的包裹和你的包裹一样重。 She is as much interested in music as ever. 她和以前一样对音乐感兴趣。 The economic development in our country is as stable recently as formerly. 最近,我国的经济发展和以前一样稳定。 (二)not as (or so)…as…句型 跟as…as…句型相反的结构not as (or so)…as…表示两者的程度不一样,前者不如后者,所以,通常翻译为“…不如…”。 My uncle is not as (or so) tall as your father. 我叔叔不如你父亲高。 People are not so honest as they once were. 人们现在不如过去那样诚实了。 (三)not so much …as…句型 not so much …as…这个结构表示的基本意义和not as (or so)…as…一样,但是通常翻译为“与其说…不如说…”。 He was not so much angry as disappointed. 他与其说是生气,还不如说是失望了。(可以理解为:“他的生气不如失望多”,就是说“他
中英文翻译
多危害公路桥梁设计标准 George C. Lee1 , Mai Tong2 and Phillip Yen3 摘要: 根据AASHTO标准LRFD在哲学的研究方法,一项具有比例的作为危险比较的标准被作为联邦公路管理局和土木工程硕士研究的课题。本文介绍的一般做法是由MCEER进行建立各种灾害事件及其影响,预计公路桥梁适当比较的平台。 1.0介绍: 除了正常的功能要求外,多重危害(如:如地震、风的风味,洪水、船舶碰撞,交通超载事故,和恐怖主义袭击等)必须适当考虑在公路桥梁设计内,。当前的AASHTO桥梁设计规范提供了每个载荷危害的详细危险识别。为进一步研究抗多种灾害的桥梁,有必要建立桥梁对接的测量标准。例如在返回期间或在某一时间内发生的概率超出标准的各种危害就可以用一个简单的标准来考虑解决。然而,它并不完全合理运用这种标准来校准,因为许多其他有影响的因素,如危害持续时间的不确定性,桥梁设计荷载的危险,关键部件的脆弱性,风险危害引起的后果,影响潜力的地区和损伤的桥梁可能会有所不同。事实上,在目前的AASHTO 标准规范,设计地震灾害定为475的回报期,其中已经有50年超出标准10%的历史。从NEHRP(NEHRP 2000)最近建议的基础上,还打算增加对重大桥梁的回报期至2000-2500年。正确的设计地震重现期仍在研究和专业的社会讨论。根据ASCE的07-95,风危害的回报期定于50年,根据FHWA HEC 18 冲刷的回报期定为100年。相比之下,根据设计的生命桥跨度(戈恩等2003),活负载的最高年限定为75年,目前尚没有统一的对跨板灾害发生频率的设计要求。 2.0AASHTO标准LRFD致多灾害大桥设计改进 美国公路桥梁设计的主旨是在于将标准规格的AASHTO标准过渡到AASHTO标准的LRFD上。在认识到LRFD设计方法的优势基础上,又因为设计上主要的不确定性来自需求装载危险。所以适当的对公路桥梁设计的多重危险的比较是非常重要的。 从AASHTO标准LRFD设计方法论的角度看,每一个桥梁的设计应为指定的极限状态。低强度的危害桥梁的经验,定期和极端灾害事件这两个的设计标准是极限状态的设计代表。这意味着,桥梁结构系统,包括其部分和连接的设计必须首先达到失效机制。因此,过度意外的构件要尽量避免,因为它可能会在对结构产生不利影响,不良的位置 导致损坏(如塑料合页)。 AASHTO标准LRFD不同于AASHTO是因为LRFD的设计不同于传统的ASD,.应力设计方法。建筑署设计的一个主要弱点是,没有考虑到既高于预期负荷概率和低于预期的实力在同一时间和地点发生,而把所有载荷和载荷组合一视同仁的看待。因此,它具有很少或根本没有设计标准之间的假设,以及许多实际性成分的桥梁,或实际发生的事件的概率(Kulicki 1999年)有直接关系。 为了克服ASD方法的不足,LRFD在标准偏差或者变异系数的随机变量- 破坏指数β(这是一个失败的概率测量给定的负载设置,该元件的标称电阻正在设计。)的规范基础上建立。 β值直接关系到失败的概率大小。依据以往对剪力和弯矩规格模拟和实际的桥梁的设计, 可靠性指标对其进行了评价模拟。可靠性指标的范围涵盖了从小于2广泛高于4。正如(诺瓦克1999)编制的数据表明,过去的做法是由β= 3.5表示,该值被选中作为对LRFD规范校准目标。β= 3.5对应的安全统一的概率(1 - 对失败的概率),这是等于或大于99.98%。 AASHTO标准LRFD的优点是,它提供了一个统一的概率为基础的标准来衡量一个桥梁设计的安全水平。最好是,如果有相类似的统一标准能为多种灾害对桥梁的影响进行比较,那么它将加强AASHTO标准LRFD,并提供一个危险因子校正负载坚实的基础。可惜的是,似乎没有一个可以给予灾害事件和上述原因很好的解释。继LRFD和比较缺乏统一的危害的标准在目前的多个危险桥梁设计视图的基本方法后,FHWA的研究任务是探索和建立一些可能的和合理的非均匀commeasurable标准。 3.0COMMEASURABLE准则的多种危害公路桥梁设计 单词“commeasurable”是指根据“平等”的基础上比较。从多种灾害影响或危害桥梁载荷校准比较方面说,“平等”是相当复杂的。例如,危害分类上,commeasurable回收期基础确定是建立对个人发生危害的基础上设计荷载的。在这方面,commeasurable 标准只考虑了灾害发生的不确定性; 而没有考虑造成危害的电阻结构。船只的大小和重量在特定河流的物理限制到导致了船舶碰撞是一种不能得到妥善的风险投资。因此,碰撞的影响不会随着时间显著变化。据测定,每一年的总碰撞事故与事故位置无关。 commeasurable标准的目标是不是要审判桥梁设计本身,而是提供一个“平等”的基础来评估桥梁上的一个潜在危险的事件可能造成的影响。上文指出了“平等”的基础,可以解释“发生”,“安全”,“维修费用”,“中断服务”等的不同之处。
英文翻译工具
五分钟搞定5000字-外文文献翻译【你想要的工具都在这里】 五分钟搞定5000字-外文文献翻译 工具大全https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/node/2151 在科研过程中阅读翻译外文文献是一个非常重要的环节,许多领域高水平的文献都是外文文献,借鉴一些外文文献翻译的经验是非常必要的。由于特殊原因我翻译外文文献的机会比较多,慢慢地就发现了外文文献翻译过程中的三大利器:G oogle“翻译”频道、金山词霸(完整版本)和CNKI“翻译助手"。 具体操作过程如下: 1.先打开金山词霸自动取词功能,然后阅读文献; 2.遇到无法理解的长句时,可以交给Google处理,处理后的结果猛一看,不堪入目,可是经过大脑的再处理后句子的意思基本就明了了; 3.如果通过Google仍然无法理解,感觉就是不同,那肯定是对其中某个“常用单词”理解有误,因为某些单词看似很简单,但是在文献中有特殊的意思,这时就可以通过CNKI的“翻译助手”来查询相关单词的意思,由于CNKI的单词意思都是来源与大量的文献,所以它的吻合率很高。
另外,在翻译过程中最好以“段落”或者“长句”作为翻译的基本单位,这样才不会造成“只见树木,不见森林”的误导。 注: 1、Google翻译:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/language_tools google,众所周知,谷歌里面的英文文献和资料还算是比较详实的。我利用它是这样的。一方面可以用它查询英文论文,当然这方面的帖子很多,大家可以搜索,在此不赘述。回到我自己说的翻译上来。下面给大家举个例子来说明如何用吧 比如说“电磁感应透明效应”这个词汇你不知道他怎么翻译, 首先你可以在CNKI里查中文的,根据它们的关键词中英文对照来做,一般比较准确。 在此主要是说在google里怎么知道这个翻译意思。大家应该都有词典吧,按中国人的办法,把一个一个词分着查出来,敲到google里,你的这种翻译一般不太准,当然你需要验证是否准确了,这下看着吧,把你的那支离破碎的翻译在google里搜索,你能看到许多相关的文献或资料,大家都不是笨蛋,看看,也就能找到最精确的翻译了,纯西式的!我就是这么用的。 2、CNKI翻译:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html, CNKI翻译助手,这个网站不需要介绍太多,可能有些人也知道的。主要说说它的有点,你进去看看就能发现:搜索的肯定是专业词汇,而且它翻译结果下面有文章与之对应(因为它是CNKI检索提供的,它的翻译是从文献里抽出来的),很实用的一个网站。估计别的写文章的人不是傻子吧,它们的东西我们可以直接
十个最流行的在线英汉翻译网站准确性评测对比
Facebook、Digg、Twitter、美味书签(https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,)……很多名声大噪且已逐渐步入主流的网络服务都是从国外开始引爆的,而即便是抛却技术上的前瞻性,仅从资源上来看“外域”的也更丰富.当网友们浏览国外网站时,即使有些英文基础,也大都或多或少要使用到翻译工具.在线翻译显然是最便捷的方式,目前提供此类服务的网站有不少,但机器智能翻译尤其考验真功夫,翻译质量的优劣直接影响着用户的阅读效果.在这里我们将全面网罗十个颇有些关注度的在线翻译服务,试炼其翻译质量、速度等各方面的表现. 参评在线翻译 1、Google翻译 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/language_tools?hl=zh-CN 2、Windows Live在线翻译 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/Default.aspx 3、雅虎翻译 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/ 4、爱词霸 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/trans.php
5、百度词典 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/ 6、海词在线翻译 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/ 7、金桥翻译 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/ 8、谷词在线词典 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/ 9、木头鱼在线翻译 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/translation/ 10、nciku在线词典 网址:https://www.360docs.net/doc/d618407246.html,/ 一、翻译质量比拼 单词翻译 测试项1:日常用语 翻译单词:boil 参考释义:煮沸 测试结果: 1、Google翻译:沸腾、煮沸等 2、Windows Live在线翻译:煮沸
翻译服务合同(含英文译本)
翻译服务合同(含英文译本) 甲方:_________ 地址:_________ 乙方:_________ 地址:_________ 甲乙双方本着友好协商、共同发展的原则签订本翻译服务合同,其条款如下: 一、甲方委托乙方为其提供翻译服务,及时向乙方提交清晰、易于辨认的待译资料,提出明确要求,并对乙方的翻译质量进行监督。 二、乙方按时完成翻译任务(如发生不可抗力的因素除外),向甲方提供已翻译好的打印件及电子文件各一份。具体交稿日期由双方商定。对于加急稿件,交稿期限由双方临时商议。 三、乙方对甲方提供的任何资料必须严格保密,不得透露给第三方。 四、翻译工作量统计:电子译稿:按电脑统计的中文版字符数计算(中文版word2000中"不计空格的字符数");打印译稿:按中文原稿行数×列数统计计算(行×列)。 五、乙方按优惠价格向甲方收取翻译费用:英译汉为_________元/千字符(_________字以上)。
六、乙方可以在翻译开始前为甲方预估翻译费,甲方付款时则按实际发生的工作量支付给乙方翻译费用(工作量统计方法见本合同第四条)。 七、乙方承诺,交稿后,免费对翻译稿进行必要修改,不另行收取费用。 八、付款方式:甲方在收到乙方译稿的当日按实际费用先支付乙方翻译总费用的50%,余款应在交稿后的_________日内付清,如第_________日余款还未付清,则甲方每延误一天需要向乙方交纳翻译总费用_________‰的滞纳金。 九、乙方应当保证译文的翻译质量和翻译服务达到行业公允的水平,如对译文的翻译水平发生争议,应由双方共同认可的第三方评判,或者直接申请仲裁。 十、本合同一式两份,双方各执一份,经甲乙双方签章后生效。 甲方(盖章):_________ 乙方(盖章):_________ 代表(签字):_________ 代表(签字):_________ 签订地点:_________ 签订地点:_________ _________年____月____日_________年____月____日 附件: translation agreement
翻译(笔译)合同 (中英文)
合同编号:Contract No. 甲方: Party A: 乙方:Party B: 乙方为甲方提供翻译服务,甲乙双方确认提供的联系方式准确无误。经双方协商一致,特签订本合同,以资恪守。 Party B shall provide Party A with translation service and both parties confirm that the contact information provided hereunder is accurate. The parties, on the basis of consensus, have entered into the Agreement as follows: 一、翻译项目名称:Translation Project: 二、合作价格: Price: 字数计算办法及译件规格要求:WORD文档以字符数不计空格为准,书写稿以含标点 符号与阿拉伯字数的手工点数为准;文本框或图片中的文字另行计算。 Word count measures and source text specifications: Word count shall be subject to "Number of characters excluding spaces" for a WORD document; manual count of characters including punctuation and Arabic numbers for a manuscript; characters in text boxes and pictures shall be counted separately. 三、付款方式: 合同签订之日甲方预付50%定金,交稿三天内按实际翻译费用向乙方 支付余款 Payment Term: Party A shall pay Party B 50% of the contract amount as a deposit within three days from the date of signature, and pay the balance according to the actual translation fees within one week after delivery of the translation.
云技术和服务中英文对照外文翻译文献
中英文对照外文翻译文献 (文档含英文原文和中文翻译) 译文: 利用云技术和服务的新兴前沿:资产优化利用 摘要 投资回报最大化是一个主要的焦点对所有公司。信息被视为手段这样做。此信息是用来跟踪性能和提高财务业绩主要通过优化利用公司资产。能力和速度,这是可能的收集信息并将其分发到当前的技术该组织正在不断增加,事实上,有超过了行业的能力,接受和利用它。今天,生产运营商被淹没在数据的结果一种改进的监控资产的能力。智能电机保护和智能仪器和条件监控系统经常提供32多块每个设备的信息都与相关的报警。通常运营商没有装备来理解或行动在这个信息。生产企业需要充分利用标的物专门为这个目的,通过定位他们的工程人员区域中心。这些工程师需要配备足够的知识能够理解和接受适当的行动来处理警报和警报通过这些智能设备。可用的信息可以是有用的,在寻找方法增加生产,减少计划外的维护和最终减少停机时间。然而,寻找信息在实时,或在实时获得有用的信息,而不花了显着的非生产时间,使数据有用的是一个巨大的挑战。本文将介绍云技术作为一种获取可视化和报告的经济方法条件为基础的数据。然
后,它将讨论使用云技术,使工程资源与现场数据可通过网络浏览器访问的安全格式技术。我们将覆盖资产的方法多个云服务的优化和效益飞行员和项目。 当重工业公司在全球范围看,世界级运营实现整体设备效率(OEE)得分百分之91。从历史上看,石油和天然气行业的滞后,这得分十分以上(Aberdeen 集团“操作风险管理”十月2011)。OEE是质量的商,可用性和效率得分。这些,可用性似乎影响了石油和天然气行业的最大程度。在石油和天然气的可用性得分的根源更深的研究导致旋转资产作为故障的根本原因,在70%的情况下,失去的生产或计划外停机。鉴于这一行业的关键资产失败的斗争,但有方法,以帮助推动有效性得分较高,以实现经营效率的目标。. 在未来十年中,海上石油储量的追求将涉及复杂的提取方法和海底提取技术的广泛使用。提取下一波的储量将需要复杂的设施,在海底,以及更传统的表面生产设施的形式。面对日益复杂的生产系统,石油和天然气经营公司正在努力成功地经营这些复杂的设施与一个退休池的主题专业知识。 该行业的答复,这一现象是显着的使用智能设备组织的斗争,把数据转换成过程控制系统,成本很高,然后向工程师提出所有的数据,每一次发生的事件。工程师然后花时间挖掘数据,建立数据表和创建有用的信息,从桩。由此他们可以开始工作的问题或问题。不幸的是,这项工作需要的经验,资产和数据。 更换行业和组织的知识是一个挑战,推动生产企业探索定位主题的专业知识,在资源的枢纽,跨多个资产。挑战来自于2个方面。首先,生产系统,无论是在表面上,在海底,需要复杂的生产系统和子系统的许多组件。其结果是,操作这些设施的自动化系统是非常复杂的,往往需要运营商与200000多个标签的数据和由此产生的报警接口。 其次,将标的物专家在区域枢纽创建的安全风险,必须解决的设计自动化系统。启用24小时的实时数据访问远程定位的主题的专业知识,需要建立在互联网技术的隧道,使监控从远程办公室,平板电脑和移动设备。一个健全的安全策略是需要这种支持的一部分。 传统的方法继续影响停机时间。简而言之,如果工程或维护需要建立一个电子表格,查找数据,操纵它,然后通过它来查找真相,在采取行动时损失的时间会导致停机时间的增加。基于角色的可视化和报告,与非生产性工作的自动化配
软件工程中英文翻译
Internet of electronic information resources development and utilization The development and utilization of Internet richness of the electronic information resource, which can be directly consider E-mail, file transfer, Telnet approach, also can indirectly consider using several common information retrieval tool, the paper made a detailed introduction and analysis, aims to help help user well using the Internet. For information institutions or library is concerned, to learn and use well, not only can enlarge Internet information resources development and utilization of the scope, but also able to enhance the level of service to users. Keywords Internet electronic information resources development and utilization Exploitation andUtilization of Electronic Information Resources on Internet - The Internet can be extensive communication in the world every person, connect all the computer and provides a wealth of information resources, and provide A variety of service tool to obtain these resources. Information institutions or libraries in the Internet for information resources, retrieval electricity The son journals and newspapers, orders and electronic publications, retrieval online catalogue and union catalog, a searchable database system, access journals to discuss, through the file transfer (FTP) receiving documents. So we can use Internet richness of the information resources to expand its collection, still can use directly these information resources to carry on the information retrieval consulting services. In searching available in the email, database retrieval, file transfer, remote login, and information query tools etc. In order to enrich the exploitation and utilization of Internet information resources, the author thinks that should through the following ways. 1 directly use the Internet E-mail (hereinafter Email) Electronicmail, E-mail is a based on computer network to store, forward form various data, images, and exchange information in words of exchange System, sending and receiving and managementare in computer Internet E-mail systems management software. Email software generally provide teleport, browse, storage, transfer, delete, restore E-mail and the reply, and other functions, can match a communication, also can spread, each user has a particular coding mailbox, can with any users online information transmission, spontaneous since the received or forwardingletters. User simply equipped with a modem, a telephone lines and thcorresponding communication software, can in any part of the microcomputer with communication phase even on sending and receiving information, to realize communication. Email take storage, forwarding way, open E-mail program is adopted, the web server machine online way 24 hours working around-the-clock, always receive emails from all of the world, no matter what, when and where will the computer connected server only, can scoop out your E-mail. Need to send electronic information, users first the arbitrary length of letters for its input computer plus addressee address, and send button, the information being sent to the information high male road. On the other side of the addressee open
英译汉翻译服务合同(一)范本
甲方:_________ 地址:_________ 乙方:_________ 地址:_________ 甲乙双方本着友好协商、共同发展的原则签订本翻译服务合同,其条款如下: 一、甲方委托乙方为其提供翻译服务,及时向乙方提交清晰、易于辨认的待译资料,提出明确要求,并对乙方的翻译质量进行监督。 二、乙方按时完成翻译任务(如发生不可抗力的因素除外),向甲方提供已翻译好的打印件及电子文件各一份。具体交稿日期由双方商定。对于加急稿件,交稿期限由双方临时商议。 三、乙方对甲方提供的任何资料必须严格保密,不得透露给第三方。 四、翻译工作量统计:电子译稿:按电脑统计的中文版字符数计算(中文版Word2000中“不计空格的字符数”);打印译稿:按中文原稿行数×列数统计计算(行×列)。 五、乙方按优惠价格向甲方收取翻译费用:英译汉为_________元/千字符(_________字以上)。 六、乙方可以在翻译开始前为甲方预估翻译费,甲方付款时则按实际发生的工作量支付给乙方翻译费用(工作量统计方法见本合同第四条)。 七、乙方承诺,交稿后,免费对翻译稿进行必要修改,不另行收取费用。 八、付款方式:甲方在收到乙方译稿的当日按实际费用先支付乙方翻译总费用的50%,余款应在交稿后的______日内付清,如第___日余款还未付清,则甲方每延误一天需要向乙方交纳翻译总费用_________‰的滞纳金。 九、乙方应当保证译文的翻译质量和翻译服务达到行业公允的水平,如对译文的翻译水平发生争议,应由双方共同认可的第三方评判,或者直接申请仲裁。 十、本合同一式两份,双方各执一份,经甲乙双方签章后生效。 甲方(盖章):_________ 乙方(盖章):_________ 代表(签字):_________ 代表(签字):_________ 签订地点:_____________ 签订地点:_____________ _________年____月____日_________年____月____日
中英文在线翻译
英文翻译中文在线翻译 英文翻译中文在线翻译 (一)促进经济平稳较快发展 1. Promoting steady and robust economic development 扩大内需特别是消费需求是我国经济长期平稳较快发展的根本立足点,是今年工作的重点。 Expanding domestic demand, particularly consumer demand, which is essential to ensuring China’s long -term, steady, and robust economic development, is the focus of our economic work this year. 着力扩大消费需求。加快构建扩大消费的长效机制。大力调整收入分配格局,增加中低收入者收入,提高居民消费能力。完善鼓励居民消费政策。大力发展社会化养老、家政、物业、医疗保健等服务业。鼓励文化、旅游、健身等消费,落实好带薪休假制度。积极发展网络购物等新型消费业态。支持引导环保建材、节水洁具、节能汽车等绿色消费。
扩大消费信贷。加强城乡流通体系和道路、停车场等基础设 施建设。加强产品质量安全监管。改善消费环境,维护消费 者合法权益。 We will work hard to expand consumer demand. We will move faster to set up a permanent mechanism for boosting consumption. Wewill vigorously adjust income distribution, increase the incomes of low-and middle- income groups, and enhance people ’s ability to consume. We will improve policies that encourage consumption. We will vigorously develop elderly care, domestic, property management, medical and healthcare services. We will encourage consumer spending on cultural activities, tourism, and fitness; and implement the system of paid vacations. We will actively develop new forms of consumption such as online shopping; support and guide the consumption of green goods such as environmentally friendly building materials, water-saving sanitation products, and energy-efficient vehicles; and expand consumer credit. We will improve the urban-rural logistics system and infrastructural facilities, such as roads and parking lots, strengthen supervision over product quality and
售后服务相关中英文翻译
九、设备制作周期:Manufacture cycle: 设备制作周期:收到定金之日起150个天完工(制作时间100天、安装调试时间50天)。 Complete in 150 working days after receive down payment (manufacture time: 100 days, installation and commissioning time: 50 days) 十、售后服务及质量保证:After Sales Service & Warranty: 1、售后服务保证:After Sales Service & Warranty: A、设计图纸:Design Drawing 乙方在设备验收前,向甲方交付:文字版或电子版技术资料一套,包括: 设备主要性能、技术参数、主要机械结构图、网管图、电器原理图及接 线图。 Before acceptance of the equipment, HEKEDA will supply the following documents to the customer: 1 set English text version and Chinese version or an electronic version of the technical information, including: major equipment performance data, technical parameters, the main mechanical structure drawings, piping diagrams, electrical schematics and wiring diagram B、使用说明书Operation instruction 乙方在设备验收前,向甲方交付:设备使用手册及维护保养手册各一套。 Before acceptance of the equipment, HEKEDA will supply 1 set of equipment operation manual and maintenance manual in English version to the customer. C、易损件、关键部件Consumable Parts and main parts: 乙方在设备验收前,向甲方交付一套易损件、关键部件的清单。 Before the acceptance of the equipment, HEKEDA will supply the consumable and main parts list to the customer D、技术培训Technical Training 技术培训人员为机电工程师和现场操作工人,培训内容为机械及电气维 修、保养和生产线操作。 Provided technical training for the operators, training content is including mechanical and electrical repair, maintenance and plating line operation. E、质保期及服务方法Warranty Period & Service 乙方所提供的设备保修期为一年。保修期内,凡该生产线所出现的非人
