大学英语三级-语法结构

大学英语三级(CET3)考试应试技巧全解:语法结构
(二)全真试题命题特点及应试策略
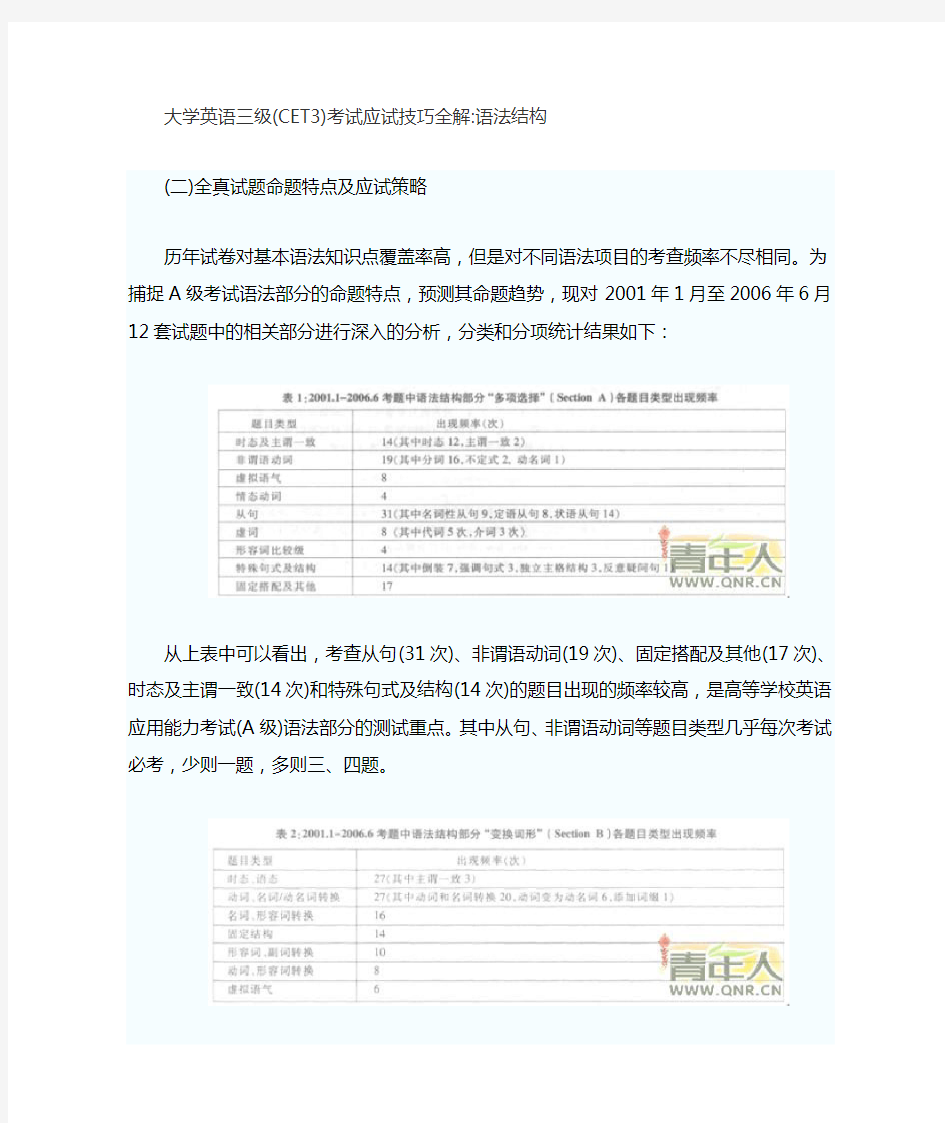
历年试卷对基本语法知识点覆盖率高,但是对不同语法项目的考查频率不尽相同。为捕捉A级考试语法部分的命题特点,预测其命题趋势,现对2001年1月至2006年6月12套试题中的相关部分进行深入的分析,分类和分项统计结果如下:
从上表中可以看出,考查从句(31次)、非谓语动词(19次)、固定搭配及其他(17次)、时态及主谓一致(14次)和特殊句式及结构(14次)的题目出现的频率较高,是高等学校英语应用能力考试(A级)语法部分的测试重点。其中从句、非谓语动词等题目类型几乎每次考试必考,少则一题,多则三、四题。
语法结构的第二部分要求考生用单词的适当形式填空,所考查的主要语法项目与第一部分基本相同。从频率上看,考查次数最多的是时态、语态和动词、名词(包括动名词)之间的转换,各为27次。其次,名词、形容词转换和固定结构两个语法点的考查都超过了年均一次的频率。从历年真题的出题角度来看,考生不仅需要掌握相应的语法点,还必须掌握同一单词的各种词性的词形变化,以及同根词的各种变化。在考试过程中,除须重点确定需要填入的单词外,还需要考虑填入单词的单复数、主谓一致等因素。
以下我们将以选择题为例,对语法部分的重要考点作一归纳总结,并在此基础上提出相应的应试策略:
1.从句在语法部分的考试中所占比重最大。从句主要有三种:名词性从句(含主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句),形容词性从句(含定语从句),副词性从句(含状语从句)。
但从近6年的考试来看,主语从句和表语从句尚未涉及,因此在以后的考试中有可能出现相关题目。从句在复合句中一定与其他部分有联系,所以起连接作用的关联词就尤为重要,因此这部分试题也经常同时考查从句关联词的用法。例如:
【例l】Li Lei didn’t meet the famo us American professor ____he was on holiday in America last year.(2004.6/T24)
A.unlessB.untilC.if D.whether
【译文】直到去年李雷在美国度假时,才见到了这位著名的美国教授。
【题解】在选项的四个关联词中,只有until可以和not构成not…until,表示“直到……才……”,据此判断正确答案为选项B。
对于考查状语从句的试题,大家应该先搞清楚主句和从句的逻辑关系并结合平时掌握的表示各种关系的关联词的用法,就能做出正确的选择。对于考查定语从句的试题,应先确定空格部分缺少的语法成分,再依据先行词,判断出合适的关联词。另外应注意的是在试题中曾重复考查同位语从句的关联词that的用法。当引导同位语从句时,that只起引导词的作用,在从句中不作任何语法成分;而当that引导定语从句时,它在起引导词作用的同时也作从句的
语法成分。例如:
【例2】He got a message from Miss Zhang_____ Professor Wang couldn’t see hi m the following day.(2003.6/T25)
A.whichB.whomC.that D.what
【译文】他从张小姐那里得到消息说王教授第二天不能见他。
【题解】题中的句子意义完整,不缺少任何语法成分,且有先行词“message”,因此可以确定为同位语从句,选择C项。
2.非谓语动词的考查主要集中在考查分词作定语和状语的情况。分词可以放在名词或代词之前或之后作定语,分别被称为前置定语和后置定语,而尤以后者为测试的重点。现在分词(-ing)和过去分词(-ed)都可以被用作后置定语,现在分词多以短语的形式出现,表示进行或瞬间的动作和状态,其一般式跟其修饰的名词或代词间是主动关系。过去分词常表示完成意义,即谓语动词的动作之前的动作,过去分词作后置定语与其修饰的中心词之间为被动关系。以真题为例:
【例3】we were shocked to find that the man(come)_____towards US was carrying a gun.(2002.1/T32)
【译文】我们吃惊地发现朝我们走过来的那个人带着枪。
【题解】答案为comin9。该句中“man”和“come”之间是主动关系,所以应该用现在分词“coming"的形式。现在分词和过去分词作状语时用法上主要的区别是:现在分词与句子主语为主动关系,而过去分词与句子主语为被动关系。
3.固定搭配考查一些常用的固定结构的运用,如表示比较的“as…as…”,常用的“Compared to/with”等。这些固定结构的考查点都相当分散,还是需要在平时的学习过程中一点一滴地积累。现以真题为例:
【例4】My boss said that he was badly___need of my assistance.(2006.6/T16)
A.atB.inC.for D.with
【译文】老板说他急需我的帮助。
【题解】“be in need of”是英语中的固定结构,需要在平时的学习中掌握。同类由介词in加上名词构成的词组还有in order,in other words,in peace,in time等等。
4.在特殊句式和结构的考查中考查倒装结构的试题数量最多,共为7次,而且多集中在第一部分,且考查的主要是表否定意义的词或短语出现在句首时的倒装结构或so…that…/such…that…中so…/such…放在句首时的倒装结构。如下列真题所示:【例5】__got in the wheat than it began to rain heavily.(2001.1/T20)
A.No sooner have they B.No sooner had they
C.No sooner they have D.No sooner they had
【译文】他们刚收割完小麦就开始下大雨。
【题解】“No sooner”是否定词,常与“than”搭配,意为“刚……就……”,当其位于句首时,句子要用部分倒装,因此正确答案为选项B。
常见的表示否定意义的词或结构有:little,few,neither,nor, seldom,rarely,seldom,hardly,by no means,under no circumstances,no sooner…than,not…until,hardly/scarcely…when等。做此类题目时,大家应该对上述表示否定意义的词或短语格外敏感,以便在宝贵的考试时间里做出快速的反应和判断。
5.对于时态的考查以过去完成时态、将来完成时态、完成进行时态、将来进行时、过去将来时等为主;从多项选择题的考查内容来看,将来进行时出现次数最多,10次中出现了3次。
考生遇到时态题目时,应首先判断是简单句还是复合句或并列句。如果是简单句,通常可以由句首或句尾的时
间副词决定时态。例如:将来完成时常见的时间标志有by the end of…,next month, this term等;如果是复合句或并列句,往往需比较两个从句中动词动作的时间关系从而确定时态。例如:
【例6】Though he____well prepared before the job interview,he failed to answer some important questions.(2005.6/T23)
A.will beB.would beC.has been D.had been
【译文】虽然在面试之前他已经做了充分的准备,但对于一些重要的问题他还是未能回答好。
【题解】“before”这个单词说明“prepare”应该发生在“interview”之前,当然也就在“fail”之前,因为主句的谓语动词“failed”是一般过去时,从句中的动作就该是“过去的过去”,所以空白处应该为过去完成日寸,答案是选项D(had been)。
6.虚拟语气考查的次数虽然不多,但由于在语法考查中是较为复杂的一部分,考生比较容易丢分。不过A级语法部分所涉及的虚拟语气的考查内容以虚拟语气的基本用法为主,因此在备考时必须把这些基本形式牢记在心(见表3).考试时才可能灵活运用,而且在做多项选择题时不爱错误选项的干扰。
此外,常常被考查的虚拟语气的知识点是“be”型虚拟语气的用法(即用动词原形),在第一部分和第二部分均出现多次,且多为宾语从句和主语从句的形式。
【例7】It is required that every employee(come)____in their uniform before 8:00 a.m.(2003.6/T31)
【译文】根据要求,每个员工都应在上午8:00之前穿制服来上班。
【题解】答案为(should)come。该句为主语从句,“required”之后的宾语从句中要求用虚拟语气“(should)+动词原形”结构。同类表示建议、命令、要求、愿望等的动词还有:suggest,propose,recommend,demand,order,desire,require,request,insist,advise,decide等。大家应特别注意在这些表示建议、命令、要求、愿望等的动词派生或转化而来的名词的同位语或表语从句中,谓语动词也要使用虚拟语气,对这种形式的考查可能会出现在以后的考试中,因此需要大家加以注意。
(三)复习提示
结合语法部分的命题特点,建议广大考生在复习备考的过程中遵循以下原则:
1.把握重点,建立框架意识
重点复习时态、分词、从句、虚拟语气和倒装等语法项目,了解英汉结构的差异,注意减少母语(汉语)对英语学习的影响。另外应该清楚各个语法项目之间并不是孤立的,而是相互联系的一个有机的整体,因此同一个句子中必然涉及多个语法项目。这就要求在学习语法时不仅要掌握每一个语法项目的内容,同时也要在各个语法项目之间建立有效的联系,从而在解答语法题目时,可以顺藤摸瓜,找到相关语法细节考点,通过理论来解决具体的问题。
2.培养语感,注重实际应用
语法项目不是孤立的理论,语法只有在具体的语境中才更突现它的意义。考生可以通过阅读英语语篇,培养良好的语感,加深对所学语法知识的理解,培养运用语法知识的能力。
3.适当练习,熟悉出题形式
为了更好地适应考试,考生应该适时适量地做一些真题和模拟题,在巩固所学习或复习的语法知识的同时熟悉出题形式,培养良好的应考能力。更为重要的是,应该格外注意对做错的题目做总结和分析。结合答案和分析,彻底搞清出错原因,找到自己的弱点,以便在以后的学习和考试中做到有的放矢,举一反三。
一、定语从句引导定语从句的关系代词有that,which,who(宾格whom),所有格whose)
和关系副词where when why 等,关系代词或关系副词在定语从句中充当一个成分,关系代词that,which,who,whom 等在从句中分别作主语或宾语,whose 在从句中作定语,而关系副词when,where,why 等在从句中作状语。如:①I will never forget the days when/in which we worked together. ②I will never forget the days which/that we spent together. 解析:在句①中,表示时间的名词the days 在从句中充当的是状语,所以用解析关系副词when 来代指,引导定语从句修饰先行词the days;而在句②中,表示时间的名词the days 在从句中充当的是动词spent 的宾语,所以用关系代词that 或which 来代指。同样,表示地点或原因的名词如果在从句中作状语,则用关系副词where 或w hy 来代指;如果在从句中作动词的宾语,则用which 或that 来代替。如:①This is the factory where/in which I worked.(作状语)②This is the factory that/which I visited years ago.(作宾语)注:当先行词为time,reason, place 时,引导词可以省略。如:①This was the first (when/what) I had serious trouble with my boss. ②That is the reason (why) I did it. ③This is the place (where) we met yesterday. 另外,定语从句中谓语动词
的数应与先行词的数相一致。如:①Mr. Jackson is the only foreigner that is present at the party. 0 ②He is one of the students who were praised by the teacher. 解析:在句①中,先行词foreigner 被only 修饰,强调只有一个,所以从句中谓解析语动词用单数形式,而在句②中,who 引导的定语从句修饰先行词the students,为复数,所以从句谓语动词应为复数。感悟:学生之所以在这一点上经常出错,主要是对定语从句的理解不够深刻,分辨不出主句和从句,对句子成分的把握也不到位,搞不清关系代词或关系副词在从句中充当何种句子成分。所以要做好这一类题,要首先弄清关系代词和关系副词的用法,而且应善于分辨和分析句子结构及其相应成分,这样才能对症下药,快速准确地找到瓿之所在。二名词性从句中的易错点(一)that 引导的定语从句与同位语从句定语从句与前面的的名词是修饰与被修饰的关系,“……的名词”,而同位语从句是用来说明前面名词的内容。与that 从句同位的名词必须是一些表示事实或概念的抽象名词,如fact,news,belief,truth,reply 等。That 在定语从句中必须作成分,可用which 或who/whom 代替,而that 在同位语从句中不充当任何句子成分,只起连接作用。如:①Along with the letter was his promise that he would visit me this com ing Christmas.
②Do you still remember the chicken farm that we visited three months ago. 解析:在句①中,that 引导同位语从句解释说明promise 的内容,that 不充当任何句子成分,只起连接作用,而在句②中,that 在其引导的定语从句中作动词visited 的宾语,对先行词the chicken farm 起修饰作用。感悟:学生之所以在这一点上容易出错,主要还是因为对定语从句的理解不够深刻,分辨不出that 在从句中是否充当了句子成分,因此,还需在句子分析上下功夫,并且搞清何谓同位语从句。(二)名词性从句中,关于it 作形式主语和形式宾语的易错点 1. 名词性从句作主语或宾语时,为保持句子平衡,常用it 作形式主语或形式宾语。如:It’s a pity that he don’t come to give a speech.(形式主语)We think it possible that you can finish the job today.(形式宾语)2)谓语动词appreciate, dislike, hate, like, love, make 等接由if 或when 引导的宾语从句时往往在从句前加上形式宾语it. 例如:I would appreciate it if you could come to my birthday party. 3)动词hare, take, hide, punish, put 等,后接由that 引导的病因从句式,往往在从句前加形式宾语it. 例如:①I take it that you will be leaving Shanghai soon.
②we punished it that we had finished the project ahead of time. 4)短语动词answer for, count on depend on, insist on, see to 等后接有th at 引导的宾语从句时,必须冠以形式宾语it. 例如:①I’m counting on it that you will come. ②She’ll see to it that he goes ahead. 注:作形式主语和形式宾语时只能用it. 三、代词it、one、that 的用法与区别. One 泛指,指代前面提到的那类人或物,用于指代可数名词,相当于a+名词单数,其复数形式ones 前一般要有定语,否则就要用some. That(those 复数)即可指代不可数名词,表特指,相当于the+名词,后面经常与介词修饰语连用。It 指代上文出现的名词,表示同类同物,另外还可表示时间、距离、天气、还可指代人称代词,表示性别身份不明,可作形式主语,形式宾语,引导强调句式以及一些固定搭配,如:get it, catch it, make it. 例如:①I have lost my watch. I think I must buy one.我丢了只表,我想我必须再买一只。(代指上文指到的同类事物,但不指同一个)②Where is my pen? Have you seen it? 我的钢笔不知弄到哪去了,你见了吗?(代指上文提到的同一事物)③The land of China is larger than that of America. ④Tome has a red pen and a blue one (或two blue ones)⑤He has no child, and he wants to adopt one (或some)四、虚拟语气I 虚拟语气在if 引导的条件句中的易错点。①if my lawyer had been here last Saturday, he would have prevented me from going. ②if you had studied hard at school, you would be a college student no w. 句子①②都是虚拟语气在条件句中的使用,从句中都是假设过去的
情况,所以用过去完成时,但在主句中,句①依然指代过去的情况,谓语动词是would have done,而②中含有一个表示现在的时间状语now, 这样就必须将其理解为假设现在的情况,所以谓语动词必须为would/should/might+动词原形,学生在这一点上经常会忽略now 的存在,从而按句①的形式填写答案。Ⅱ虚拟语气在名词性从句中的用法 1.在it is important (strange, natural, necessary……)+that 句子或者It i s decided (ordered, suggested, demanded, advised……)+that 句子中,主语从句中的谓语动词常用(should)+动词原形结构,表示某事“重要”、“必要”、“被决定”等例如:①it is important that everyone (should ) obey the rules all day and all night. ②it is decided that the meeting (should) be held tomorrow afternoon. 2. suggest, insist 后面指宾语从句时需注意的地方1)①suggest 当“建议”“提出”讲时,其后宾语从句的谓语动词常用“should+ 动词原形” 例如:He suggested that the work (should) be started at once 他建议立即动工。类似的动词还有insist 坚持,demand 要求,desire 要求、请求,request 请求,require 要求、需要,order 命令,propose 建议,command 命令,ask 要求,advi se 建议,prefer 宁愿等。这些动词变被动语态(如:It is suggested + that 主语从句)形式后,主语从句谓语动词仍用“(should)+动词原形” 这些动词变名词(如suggestion)后,其后的表语从句和同位语从句中的谓语部分仍用“(should)+动词原形” ②suggest 当“提出(某看法),暗示,启发”讲时,其后宾语从句的动词不用虚拟语气。例如:(1)The police suggested that the thief might be one of the famil y member 警察局提出窃贼可能是一名家庭成员。(2)Her yawns suggests that she is sleepy. 她打哈欠表明她困了。(3)Although he didn’t suggest that we __ the decision to swim across the river, but his look suggested that our decision __wrong.虽然他没提出我们应该终止游过这条河的决定,但他的表情表明我们的决定是错误的。A:stop; was B: should stop; be C: stopped ;was D: stopped; should be 在这个句子中,前一个suggest 当“建议”“提出”讲,而后一个作“表明”讲,所以答案为“A” 2)①insist 作“坚决要求…该…;坚持认为…定要…”讲时,其后宾语从句的谓语动词用“(should)+动词原形” 例如:I insisted that you (should) be there on time.我坚持认为你应该准时到那里去②insist 作“坚持(意见,看法);坚持说,确信”讲时,其后从句不用虚拟语气。例如:He suggested (that) he heard someone in the next room. 他坚持说他听到隔壁屋子里有人。五.反意疑问句中的易错点 1.在一般疑问句中,无论肯定的问或是否定的问,如果回答为肯定则用yes,反之则用no.特别注意如果出现省略则看下文所暗示的意义。①—Are you a new comer? —Yes, I came here only yesterday.
②—Isn’t Tom a good student? —Yes, he is excellent. ③—Don’t you think the composition good? —No, It can’t be any worse. 注意:在②③句中,当回答的意思与问句相一致时,则用No,译为“是的”,当回答的意思与问句相反时,则用Yes,译为“不” 2.情态动词must ①I must leave now, mustn’t I ? ②He must be in the classroom, isn’t ?(表推测)③He must have finished his homework, hasn’t he ? (表现在的结果)④He must have finished his homework yesterday afternoon,didn’ he? t (表过去)当句子中有表示猜测的情态动词时,其反意疑问句的构成不能再用原句中的情态动词,而应根据原句在去掉情态动词的情况下的主谓关系来确定其反问形式。六、非谓语动词中的易错点非谓语与其逻辑主语(即动作的执行者或承受者)之间有三种关系,如为主谓关系,则用现在分词或不定式的主动式;如为被动关系则用过去分词、现在分词的被动(强调动作正在进行)或不定式的被动式(动作将进行);如既无主动也无被动关系则只能用状语从句或独立主格结构(即非谓语加上自己的逻辑主语)。Judging/considering/genrally speaking/supposing 指说话者的动作,故只用主动式。如:Having been ill in bed for nearly a month , he had a hard time passin g the exam. 解析:从这个句子可以看出,句词
的逻辑主语与句子的主语he 一致,并且是主谓关系,所以用了现在的分词作状语,同时,分词的动作明显地发生在句子的谓语动词动作之前,故采用了现代分词的完成式。In order to improve English , ________. A. Jenny’s father bought her a lot of tapes. B.
Jenny’s father bought a lot of tapes for herself. C. A lot of tapes were bought by Jenny. D. A lot of tapes were bought by Jenny father. 解析:根据不定式短语我们可以推知,句子的逻辑主语应该是人而不是物,所以,应该排除CD,再就是应该是Jenny 提高自己的英语,而不是她爸爸,故答案先B. ———,we decided to go out for a walk. A. It is fine B. It fine C. Being fine D.It being fine 解析:主句主语we 与动词短语be fine 之间既无主动关系与无被动关系,所以要加上自己的逻辑主语It,由于不存在主、被动关系,故不能选C 项,而应该选D 项。————more attention, the trees could have grown better. A. Given B.To give C.Giving D. Having giving 解析:give 与主句的主语之间是被动关系,故选A.如为主动关系则选 C. 易出错的问题一般都是学生在学习中对知识理解不深刻或能力欠缺的地方,应及时纠错和建立“错题档案”,还应“借题发挥”,有意地把一些易错题予以归类,找出错误根源,总结规律。
大学英语三级语法知识总结汇总
三级语法考点归纳一.虚拟语气 1. if 句中虚拟形式句中虚拟形式if 引导的非真实条件句(纯粹假设或发生的可能性不大):条件从句主句与现在相反did (be were) would/ should/ might/ could do 与将来相反did (be were) would/ should/ might/ could do 与过去相反had done would/ should/ might/ could have done 例句If we left (leave) now, we should arrive in time. If they hadn’t gone on vacation, their house wouldn’t have been broken (break) into. 2. 原形虚拟:原形虚拟:a. 表命令、决定、要求、建议等词语之后的that-分句中,用动词原形。suggest, demand, advise, propose, order, arrange, insist, command, require, request, de sire …… that +(should) do 例如He suggested that we should leave early. My suggestion is that we should tell him. b. It is (was) 形容词/名词that …… (should) do/ 例如It is absolutely essential that all the facts be examined first. 3. 一些句型中的虚拟形式:一些句型中的虚拟形式:1. It’s (high, about, the first, etc.) time (that) …动词过去时… 例如It’s time we left. 例如It is time we went to bed. 2 would rather/sooner 宁愿as if/ though 好像would rather/sooner 谓语用过去时与现在或者将来相反as if/ though 谓语用过去完成时与过去相反4.练习.1.
I _______ try it again if I_______you. A. will;am B. should;am C. would;were D. would;had been 2. If it _______ not for the water,the plants _______live. A. were;would not B. is;could not C. were;could D. did;could not 3. If I _______ that chance to show my ability, I _______the president of this school. A. have not had;could not become B. had not had;would not have become C. did not have;could not become D. doesn’t have;will not become 4. He _______ by that burglar if you _______ to save him. A. might have been killed;hadn’t com e B. will be killed;didn’t come C. may be killed;did’t come D. could be killed;haven’t come 5. If it _______for your help,I _______that hard time with so little money. A. were not;would not spend B. is not;can not spend C. had not been;would not have spent D. have not been;will not spend 6. Where _______ you go if war _______? A. will;breaks out B. do;will break out C. would;were to break out D. will;is to break out 7. She wishes she _______ that humiliating thing. A. doesn’t do B. didn’t do C. haven’t done D. hadn’t done 8. The chairman suggested that the meeting _______ put off. A. can be B. be C. is D. will be 9. It is vital that he _______ immediately. A. should go B. must go C. goes D. went 10. It is time we _______do our homework.
A. begin to
B. can begin to
C. began to
D. will begin to 答案:1.选C。表示与现在事实相反
的假设(指现在的假设) (译文; 如果我是你,我会再试一次) 2 选A。表示与现在事实相反的假设(指现在的假设)。(译文:要是没有水,植物就不能存活。) 3. 选B。表示与过去事实相反的假设。4 A。表示与过去事实相反的假设。(译文:要不是你来救他,他早就被那个窃贼杀了。) 5. C。与过去事实相反的假设。(译:要没有你帮忙,我那点儿钱是无法度过那段艰苦岁月的。) 6.选C。表示与将来事实相反的假设。(译文:要是战争爆发了,你会上哪儿去?) 7.选D。虚拟语气用于宾语从句。(译文:她真希望自己没有做过那件丢脸的事情。) 8. 选B。虚拟语气用于表示“建议”等意义的动词后。(译文:主席建议会议延期举行。) 9. 选A。虚拟语气用于主语从句(It is /was + 形容词+ that 引导的分句)。10. 选C。虚拟语气用于定语从句It is time (that)...句型。(译文:我们该开始做作业了。) 二.动词的时态 1. 各个时态动词基本变形一般现在时be( be(is,am,are) do/does 一般过去时was/were did 一般将来时will do 一般过去将来时would do 现在完成时现在完成时现在进行时(is/am/are) am/are)+ be (is/am/are)+ doing have/has done 过去进行时was/were doing 将来进行时will do 过去将来进行时would be doing 过去完成时had done 将来完成will have done 过去将来完成时would have done 现在完成进行时have/has been doing 过去完成进行时had been doing 将来完成进行时will have been doing 过去将来完成进行时would have been doing 2. 时间状语与动词时态的搭配一定的时态往往和一定的时间状语连用。一定的时态往往和一定的时间状语连用。always ,usually, sometimes, 一般现在时do/does last week, yesterday, a few days ago 一般过去时did next week, tomorrow, in a week, this year 一般将来时will do now, at present, at this moment 现在进行时be +doing so far, up to now, by the time, since 的主句现在完成时has/have done 3. 练习,用动词的适当形式填空练习,1. He _______ (be) eighteen next year. 2. It _______ (rain) every day so far this month. 3. Mozart _______ (write) more than 600 pieces of music. 4. If it _______ (rain) tomorrow,we’ll have to stay at home. 5. How fast _______ he _______ (drive) when the accident happened? am is are was/ were 6. By the time Mr. Smith left school,he _______ (teach) that course for twenty-five years. 7. Perhaps he _______ (finish) reading the book by this time tomorrow. 1. 填will be。next year 为表示将来时态的时间状语2. 填has rained。so far 是“到目前为止”的意思,常和现在完成时搭配使用。3. 填wrote。Mozart (莫扎特)是已去世的音乐家,故应使用过去时。 4. 填rains。在条件状语从句中,要用一般现在时表示将来发生的事情。 5. 填was...driving。表示过去某一时刻发生的动作要用过去进行时。6. 填had taught。句中有by the time Mr. Smith left school,主语的谓语应用过去完成时。7. 填will have finished。句中有by this time tomorrow,主语的谓语应用将来完成时。三动词的被动语态 1. 各个时态的被动语态时态一般现在现在进一般过过去进一般将过去将现在完过去完现在完将来完成时时行时去时行时来时来时成时成时成进行时主动do am/is/are did doing was/ were doing will do would has/ do have done has/ have been done had done has/ will have done have been doing will have been done 被动am/is/are am/is/are was/ was/ done being were were done done being done will be would done be done had been done 1. The construction of the library_______ before the end of next month. A. must have completed B. must have been completed C. must be completed D. must complete 2. The subject of these lectures _______ by the lecture committee. A. announces B. have been announced C. announced D. has been announced 3. My pictures _______ until next week. A. won’t develop B. aren’t developing C. don’t develop D.won’t be developed 4. They _______ so that we wouldn’t recognize them. A. costumed B. disguised C. were disguising D.were disguised 5. All the apparatus (器械) _______ before the experiment began. A. had been prepared B. were prepared C. had been prepared D. had prepared 6. The world’s supplies of copper _______ . A. have been
gradually being exhausted B. has gradually exhausted C. are gradually exhausted D. are being gradually exhausted 7. The goods _______ when we arrived at the airport. A. were just unloading B. were just being unloaded C. had just unloaded D. were just been unloaded 8. Tom _______ the best student in his class. A. regards B. regards as C. has regarded as D. is regarded as 9. The sports meeting _______ because of the bad weather. A. put off B. was put off C. was putted off D. has put off 1. C。情态动词的被动语态为:情态动词+be+done。(译:到下月底图书馆的修建必须完工) 2.D 现在完成时的被动语态为:have been+done (译:讲座的课题已由讲座委员会宣布了。) 3. D。一般将来时的被动语态为:will be+done,其否定形式为:will not be +done 4.D 一般过去时的被动语态为was/were+过去分词(译:为了不让我们认出来,他们伪装了起来) 5. C。过去完成时的被动语态的构成为:had been+过去分词。 6. D 现在进行时的被动语态为:are/is/am being+过去分词。(译:世界的铜资源正逐渐被耗尽) 7.B。过去进行时的被动语态为:was/were being+过去分词。(译:我们到机场时正在卸货物。) 8. D。(译文:汤姆被认为是班里最好的学生。) 9. B。(译文:运动会因天气不好被取消了。) 四定语从句 1.定语从句(Attributive Clauses)在句中做定语,修饰一个名词或代词,被修饰的名词,词组或代词即先行词。定语从句通常紧跟在先行词后,由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引出。关系代词有:who, whom, whose, that, which等。关系副词有:when, where, why等。例题:The Social Security Retirement Program is made up of two trust funds,_______ could go penniless by next year. A. the large one B. the larger of which C. the largest one D. the largest of which 选B。因为前面有two,所以不能选D,A 没有连接手段,也不能选。三级试题中定语从句的考题:1、I tried to get of the business _____ I found impossible to carry on. A) why B)which C)what D)where 2、Once more I have to leave Beijing , _____ I have been living for eight years. A) that B)where C)which D)as 3、This book is designed for the leaners_____native languages are not English. A)whose B)which C)who D)what 4、She got to know the young man very well_____she had worked for so long. A)to whom B)in whom C)whom D)with whom 5、The hotel_____during the vacation was rather poorly managed. A)as I stayed B)where I stayed C)which I stayed D)what I stayed 6、There are so many dresses there that I really don’t know____to choose. A)whether B)when C)which D)why 7、I think that Anna is_____far the most active member in our group. A)with B)at C)as D)by 五.倒装1. 当only 放在句首,表示强调时,要用倒装只有用这种方法,你才可以解决这个问题。例:Only in this way can you solve this problem. Only yesterday did I finish the book. 到昨天我才读完那本书。2. 具有否定意义的副词或词组用于句首,要用倒装。常见的否定词有:never, seldom, rarely, little, hardly, not until, by no means, not only, neither, no sooner, hardly 等。例句:Never shall I forget the days when you were with us. 1、Olny when we had finished all the work_____that it was too late to take a bus home. A)did we realize B)informing C)informed D)to inform 2、Not until the day before yesterday_____to give a speech at the meeting. A)he agreed B)does he agree C)he agrees D)did he agree 3、Young_____he is, he has proved to be an able sale sman. A)that B)who C)as D)which 4、Not until yesterday_____anything about the project that will be completed soon. A)did I learn B)have I learnt C)I learnt D)that I learnt 5、He is used to flying by air and on no occasion_____frightened. A)he has ever felt B)he ever feels C)ever does he feel D)has he ever felt 6、So_____after she learned the good news that she could hardly fall asleep that night. A)excited the mother was B)was the mother excited C)the mother was excited D)excited was the mother 7、So loudly_____that people could hear it out in the street. A)did the students play the music B)the students playing the music C)the students played the music D)have the students played the music 六.it 的用法1.it 作形式主语或者形式宾语It is necessary for us to learn English. it 这里指
代to learn English It was not very clear what she meant. it 这里指代what she meant 2. it 在强调句型强调句型的结构为:It is/was +被强调部分+ that(who) +句子的其余部分练习 1. It was only when I read his poems recently _______ I began to appreciate their beauty. A. until B. that C. then D. so 选B。强调句型强调when 引导的时间状语从句。2.It was about 600 years ago _______the first clock with a face and an hour hand was made. A. that B. until C. before D. when 选A。强调句型强调时间状语。七.形容词比较级1.不规则变法比较级better worse more less 最高级best worst most least good/well bad many/much little 2. 形容词比较级结构(1) 形容词+than 例句:Real friendship is more valuable than money. (2) the +形容词比较级,the + 形容词比较级例句:The more medicine I take, the worse I feel.
大学英语三级语法大全 II 倒装:倒装句之全部倒装 全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用于一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有: 1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首,谓语动词常用be, come,go, lie, run等表示来去或状态的动词。例如: Then came the chairman. 那时总裁来了。 Here is your letter. 你的信。 2)表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。例如: Out rushed a missile from under the bomber. 轰炸机肚底下窜出一枚导弹。 Ahead sat an old woman. 前面坐着一个老妪。 注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。例如: Here he comes. 他来了。 Away they went. 他们走开了。 倒装:以否定词开头作部分倒装 否定词如 Not only…but also, Hardly/Scarcely…when, No sooner… than等放在句首,后面要用倒装。例如: Not only did he refuse the gift, he also severely criticized the sender. 他没有收下礼物,还狠狠批评了送礼的人。 Hardly had she gone out when a student came to visit her. 她刚出门,就有个学生来访。 No sooner had she gone out than a student came to visit her. 她刚出门,就有个学生来访。 典型例题 No sooner___ than it began to rain heavily. A. the game began B. has the game begun C. did the game begin D. had the game begun 答案 D. 以具有否定意义的副词放在句首时,一般采用倒装句(谓语前置)。这类表示否定意义的词有never, seldom, scarcely, little, few, not, hardly,以及not only…but (also), no sooner…than, hardly… when scarcely… when 等等。 注意:只有当Not only… but also连接两个分句时,才在第一个分句用倒装结构。如果置于句首的Not only… but also仅连接两个并列词语,不可用倒装结构,如Not only you but also I am fond of music. 倒装:倒装句之部分倒装
2002年6月浙江省大学英语三级考试试卷 Part I Listening Comprehension Section A Directions: In this section, you will hear 10 short conversations. At the end of each conversation, a question will be asked about what was said. You will hear the conversation and the question only once. After each question there will be a pause. During the pause, you will read the four choices marked A, B, C and D. You should choose the best answer. 1. A) Warm B) Hot. C) Mild. D) Cold. 2. A) In an office B) In a library C) In a classroom D) In a bookstore 3. A) By sea. B) By train. C) By bus. D) By air. 4. A) He is doubtful about the one-bedroom apartment. B) He’s prepared to pay more for the bigger apartment. 、 C) There is a big difference between the apartments. D) The one-bedroom apartment is better as it is cheaper. 5. A) The train may arrive but the woman is not sure. B) The train will probably arrive at 10:45. C) The train broke down and will not arrive. D) The will probably arrive at 9:45 6. A) She will help him next week. B) She has finished her work quickly. C) She had her work done a week ago. D) She did her work carelessly. 7. A) She likes it as well as the man. B) She takes her vacations in autumn. C) She prefers summer. D) She doesn’t like it. 8. A) He’ll play the game. # B) He won’t watch the game standing. C) He’ll watch the game on TV. D) He has little knowledge of the game. 9. A) To learn another language. B) To practice the dialogues. C) To give up French. D) To give up practicing. 10. A) The woman should take her time. B) They are supposed to leave in twenty minutes. C) Alice is arriving in twenty minutes D) They are already late for the appointment. Section B Directions: In this section, you will hear 3 short passages. The passages will be read 】 twice. At the end of each passage, you will hear some questions, which will be read only once. After you hear a question, you must choose the
1.Noun Identify the uncountable nouns ? 1. Nouns that have no distinct, separate parts, we look as the whole (气、液、固体) ? 2. Nouns that have parts that are too small or insignificant to count (sand grass hair) ? 3. Nouns that are classes or categories of things (food, clothing, money) P49 ? 4. Nouns that are abstraction (life, work, music) ? 5. Subjects of study (history, math) 不可数变可数三大规律 ? 1. 物质名词(总称名词)若表示不同的种类,或者表示特定的意思,或者是液体名词表示“几杯”或“几瓶”这样的数量时。 ? 2. 抽象名词若是具体化,则可数。与此相反,可数转化为不可数。 ? 3. 当一个名词表示抽象、总称的概念,则为不可数,当一个名词表示具体、特定的事物,则为可数。 物质名词/总称名词变可数 ? 1. 总称名词具体化 ?A: Would you like a cake? ?B: No. I don’t like cake. ? 2. 物质名词变意思 ?I need some paper. / I bought a paper. ? 3. 液体物质名词表数量 ?Two beers and three coffees, please. 抽象名词变可数 ?Art (an art) / beauty (a beauty) / youth (a youth) ?Eg. 1. Youth is not a time of life. It is a state of mind. ? 2. When as a child I laughed and wept– time crept. ?When as a youth I dreamed and talked-time walked. 2Articles Specific reference--the ? 1. 特指是针对交际双方来说的 ? 2. 特指就是根据说话者和听话者共有的知识,或根据上下文,可以识别的事物。 ? 3. 说话者用the是想要听话者找到双方心中都知道的所知,而听话者一方“断定”或“还原”所指对象的方法有多种。 ? 1. Situational/cultural reference ?Eg. Albert Einstein, the famous physicist. ? 2. textual co-reference— ?anaphoric reference (前指)& ?cataphoric reference (后指 ? 1. general knowledge (the sun, the moon, the North Pole, the Equator, the universe, the Renaissance, the Pope 罗马教皇) ? 2. specific knowledge/ local use (let’s go to the library) ? 3. immediate situation (The roses are very beautiful. Can you find the page?)
大学英语三级-6 (总分:85.00 ,做题时间:90 分钟) 一、Part I Vocabulary and Structure (总题数:20,分数:20.00) 1.In this battle, about one thousand soldiers were killed and one thousand more _____ . (分数: 1.00 ) A. injured B. hurt C. wounded V D. damaged 解析:动词辨析。wound指外来强力引起的身体损伤,尤其是在战斗中受伤。 2.I believe that our teacher will take your illness into _____ , for she is very considerable. (分数: 1.00 ) A. account V B. regard C. observation D. respect 解析:take sth. into account 意为"把......... 考虑在内",为固定搭配。 3.Its five years since I was ______ with them, so I don know how they are getting along. (分数: 1.00 ) A. out of control B. out of the question C. out of touch V D. out of sight 解析:out of touch with sb 与某人失去联系。 4. The committee ____ the suggestions the experts made. (分数: 1.00 ) A. acted as B. acted for C. acted on V D. acted up 解析:act on “遵照.... 行事"。 5. Enquiries (询问,打听)__ the condition of patients may be made personally or by telephone. (分数: 1.00 ) A. revealing B. concerning V C. affecting D. containing 解析:动词辨析。concern :与.... 相关,涉及到。 6.Skimming also differs from scanning ____ it is an effort to get general information rather than specific facts. (分数: 1.00 ) A. in which B. for that C. in that V
大学英语语法及练习 Last updated at 10:00 am on 25th December 2020
大学英语语法及练习 第一讲虚拟语气 I. 考点分析:分四级语法复习 虚拟语气是动词的特殊形式,用来表达说话人的意愿、建议、请求、意图、惊奇、设想等未能或不可能成为事实的情况,以及在说话人看来实现的可能性很小的情况。 虚拟语气是非常重要的语法考点。考查历届四级试题,我们发现与虚拟语气有关的考题每次至少2题,有时甚至3-4题。虚拟语气的考查要点有: 1. 虚拟语气的形式:分清虚拟时间和主从句的动词形式十分重要,因此我们把所有虚拟语气的不同类型列表归纳并进行对比,以便于同学们记忆掌握。
2. 要注意从句中第一/三人称的过去式was用were代替。 例如:If I were invited, I would come. If she were not ill, she could do a lot of things. 3. if条件句中如谓语动词是were, had, should, could时,可以省略if, 把它们前置。
例如: Had my father a lot of money, he would send me abroad. Could I do it, I would surely do it. Should the Black Death reappear, what should we do?(万一黑死病再次出现,我们该怎么办) 4. 错综时间的条件句是难点,如99年1月第60题: If I hadn’t stood under the ladder to catch you when you fell, you wouldn’t be smiling now.(从句用过去完成时,主句用现在进行时) 又如:If I were you, I would have gone to the film last night.(从句虚拟现在,主句虚拟过去);If we hadn’t got everything ready by now, we should be having a terrible time tomorrow.(从句虚拟过去,主句虚拟将来); If the weather had been more favorable, the crops would be growing still better.(从句虚拟过去,主句虚拟现在) 5. 虚拟句的另一难点是省略if条件句的含蓄条件句,如: I would have written the paper before, but I have been ill.(=If I had not been ill, I would have written the paper before.); A true friend would have acted differently. (=A friend, if he had been true, would have acted differently.) 6. 注意介词短语 without, but for, in the absence等表示虚拟条件。
1.三级语法考点归纳 2.一.虚拟语气 3.1. if 句中虚拟形式 4.if 引导的非真实条件句(纯粹假设或发生的可能性不大): 5.条件从句主句 6.与现在相反 did (be were) would/ should/ might/ could do 与将来相反 did (be were) would/ should/ might/ could do 7.与过去相反 had done would/ should/ might/ could have done 例句 8.If we left (leave) now, we should arrive in time. 9.If they hadn’t gone on vacation, their house wouldn’t have been broken (break) into. 2. 原形虚拟: 10.a. 表命令、决定、要求、建议等词语之后的that-分句中,用动词原形。 11.suggest, demand, advise, propose, order, arrange, insist, command, require, request, desire …… that +(should) do 12.例如 He suggested that we should leave early. My suggestion is that we should tell him. 13.b. It is (was) 形容词/名词that …… (should) do/ 14.例如 It is absolutely essential that all the facts be examined first. 3. 一些句型中的虚拟形式: 15.1. It’s (high, about, the first, etc.) time (that) …动词过去时…例如 It’s time we left. 例如 It is time we went to bed. 2 would rather/sooner 宁愿 as if/ though 好像 16.would rather/sooner 谓语用过去时与现在或者将来相反 as if/ though 谓语用过去完成时与过去相反 4.练习 17.1. I _______ try it again if I_______you. A. will; am B. should; am C. would;were D. would; had been 2. If it _______ not for the water, the plants _______live. 18.A. were; would not B. is; could not C. were; could D. did; could not 3. If I ___ ____ that chance to show my ability, I _______the president of this school. A. have not had; coul d not become B. had not had; would not have become C. did not have; could not become D. doesn’t have; will not become 4. He _______ by that burglar if you _______ to save him. 19.A. might have been killed; hadn’t come B. will be killed; didn’t come C. may be killed; did’t come D. could be killed; haven’t come 5. If it _______for your help, I _______that hard time with so little money. A. were not ; would not spend B. is not; can not spend 20.C. had not been; would not have spent D. have not been; will not spend 6. Where ____ ___ you go if war _______? 21.A. will; breaks out B. do; will break out C. would; were to break out D. will; is to break out 7. She wishes she _______ that humiliating thing. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28.A. doesn’t do B. didn’t do C. haven’t done D. hadn’t done 8. The chairman suggested that the meeting _______ put off. 29.A. can be B. be C. is D. will be 9. It is vital that he _______ immediately.
大学英语 3 级考试真题 一、听力测试(本大题满分25 分,每小题 1 分 ) 做题时,先将答案划在试卷上。录音内容结束后再将试卷上的答案转涂到答题卡上。 第一节 听下面的 8 段短对话。每段对话后有一个小题,从每小题 A 、B 、 C 三个选项中选出一个最佳答案。 听每段对话只读一遍。 1.What color skirt does Linda like? A. Red. B. Green. C. Blue. 2. How is the weather now? A. Sunny. B. Cloudy. C. Rainy. 3. How did they spend their weekend? A. They had a school trip. B. They cleaned up the street. C. They studied for a test. 4. Where will Peter go on vacation? A. To Canada. B. To Australia. C. To Japan. 5. What does Mike’ s father want him to be? A. A soldier. B. A pilot. C. A doctor. 6. Who will repair the bicycle? A. Bill's brother. B. Mrs. Brown's brother. C. Bill. 7. How much is the jacket now? A. 60 dollars. B. 90 dollars. C. 120 dollars. 8. What do we know about Jenny from the conversation? A. She is worried about a coming test. B. She is working hard at physics. C. She didn't pass the recent test. 第二节 下面你将听到 5 段对话或独白。每段对话或独白后有几个小题,从每小题A、B、C 三个选项中,选出一个与你听到的对话或独白内容相符的问题的答案。对话或独白读两遍。 听第一段材料回答 9 至 11 小题。 9. How many people will sit at the table? Xk b https://www.360docs.net/doc/ea17770450.html, A. Two. B. Three. C. Four. 10. What is the restaurant famous for? A. Noodles. B. Chicken soup. C. Dumplings. 11. What would they like to drink? A. Fish soup. B. Beer and coke. C. Milk. 听第二段材料回答第12 至 14 小题。 12. Have the speaker ever seen each other? A. Yes, they have. B. No, they haven't. C. We don't know. 13. How often does Lucy play tennis? A. Twice a week. B. Every morning. C. Never. 14. When may they meet again? A. Next morning. B. Next weekend. C. Next weekday. 听第三段材料回答第15 至 17 小题。 15. What's the relationship ( 关系 ) between the two speakers? A. Friends. B. Teacher and student. C. Father and daughter
三级语法考点归纳 一.虚拟语气 1. if 句中虚拟形式 if 引导的非真实条件句(纯粹假设或发生的可能性不大): 条件从句主句 与现在相反 did (be were) would/ should/ might/ could do 与将来相反 did (be were) would/ should/ might/ could do 与过去相反 had done would/ should/ might/ could have done 例句 If we left (leave) now, we should arrive in time. If they hadn’t gone on vacation, their house wouldn’t have been broken (break) into. 2. 原形虚拟: a. 表命令、决定、要求、建议等词语之后的that-分句中,用动词原形。 suggest, demand, advise, propose, order, arrange, insist, command, require, request, desire …… that +(should) do 例如 He suggested that we should leave early. My suggestion is that we should tell him. b. It is (was) 形容词/名词that …… (should) do/ 例如 It is absolutely essential that all the facts be examined first. 3. 一些句型中的虚拟形式:
大学英语三级语法大全II 倒装:倒装句之全部倒装 全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用于一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有: 1)here,there,now,then,thus等副词置于句首,谓语动词常用be,come,go,lie,run等表示来去或状态的动词。例如: Then came the chairman. 那时总裁来了。 Here is your letter. 你的信。 2)表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。例如: Out rushed a missile from under the bomber. 轰炸机肚底下窜出一枚导弹。 Ahead sat an old woman. 前面坐着一个老妪。 注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。例如: Here he comes. 他来了。 Away they went. 他们走开了。 倒装:以否定词开头作部分倒装 否定词如Not only…but also,Hardly/Scarcely…when,No sooner…than等放在句首,后面要用倒装。例如: Not only did he refuse the gift,he also severely criticized the sender. 他没有收下礼物,还狠狠批评了送礼的人。 Hardly had she gone out when a student came to visit her. 她刚出门,就有个学生来访。 No sooner had she gone out than a student came to visit her. 她刚出门,就有个学生来访。 典型例题 No sooner___ than it began to rain heavily. A. the game began B.has the game begun C. did the game begin D.had the game begun 答案D. 以具有否定意义的副词放在句首时,一般采用倒装句(谓语前置)。这类表示否定意义的词有never,seldom,scarcely,little,few,not,hardly,以及not only…but (also),no sooner…than,hardly…when scarcely…when等等。 注意:只有当Not only…but also连接两个分句时,才在第一个分句用倒装结构。如果置于句首的Not only…but also仅连接两个并列词语,不可用倒装结构,如Not only you but also I am fond of music. 倒装:倒装句之部分倒装 部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态倒装至主语之前。如果句子的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do,does或did,并将其置于主语之前。
大学英语三级考试语法复习要点 一、动词的时态和语态 1. 动词的时态 1.1一般现在时(am/is/are+v-原) 1.1.1在下列从句中,主句如用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时代替一般将来时1)由when, until, the moment, as soon as, after, the next time和if, unless, in case, whether, as long as, once, however,provided that, supposing 等连词引导的时间状语和条件状语从句中。 e.g. If she doesn’t tell him the truth now, he?ll simply keep on asking her until she does. Keep on doing sth继续做某事 He will call you up the moment he finishes the work. You won?t pass the exam unless you study harder. 2)在定语从句中,如,Be quick, or the train will have left by the time we get to the station 3)名词性的wh-, that- 从句中,如:They will be thankful for whatever help you offer him. 4)让步状语从句(从句用一般现在时,主句用一般将来时): e.g.Whether the weather is good or bad,… No matter whether you agree or not… However carefully you drive… 1.1.2 表示客观事实和真理的句子任何时候都用一般现在时。 e.g.In the past many people didn?t believe that the earth is round. 1.1.3 在某些常用的句中表示在一个具体的现在时间所发生的动作或存在的状态。 e.g.Here he comes. There goes the bell. 1.2 一般过去时(was/were+v-原) 1) 当提及过去存在的人或物时,即使句中没有表明过去的时间状语,该句的谓语动词也应该用一般过去时。 e.g.Dickens was a great English writer. When did you write the story? 2) 在表示时间或条件的状语从句中代替过去将来时。 e.g.They said they would let us know if they heard any news about him. I decided to go to the library as soon as I finished what I was doing. 1.3 一般将来时:表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或存在的状态。表示将来 的谓语结构有: shall/will do
大学英语三级词汇表下载: A a,an art.一,任一,每一 abandon v.1.放弃,2.离弃,抛弃 ability n.1.能力 2.才能,能力 able a.1.有能力的,有才干的 2.显示出才华的be~ to V.能,会 aboard ad.在船(飞机,车)上 prep.在(船.飞机.车)上 about prep.1. 在…周围,2.关于,对于 ad.1.周围,附近,到处2.大约 be ~ to V.即将 above prep. 高于,在…之上 a.上面的,上述的 ad.以上,在上面 abroad ad.到国外,在国外 absence n.1.不在,缺席,2.缺乏,没有 absent a.(from)不在的,缺席的 absolute a.完全的,绝对的 absorb vt.吸收 be ~ed in专心于 abstract a. 抽象的 n.摘(提)要 vt. 提(抽)取 abuse n.& v.1.滥用, 2.辱骂 academic a.1.学院的, 2.学术的 accent n.1.口音,腔调 2.重音 accept vt.1.接受,领受 2.同意,承认 acceptable a.可接受的 access n.1.接近. 进入,接近(或进入)的方法 have/gain ~ to 可以获得accident n.事故,意外的事 by ~ 偶然 accompany vt.1.伴随,陪同 2.为……伴奏 accomplish vt.完成 according ~ to 按照,根据 account n.1.账,账户 2叙述,说明 vt.说明 ~ for说明(原因等) on ~ of 因为 take into ~ 考虑 accuracy n.准确(性),精确(性) accurate a.准确的,精确的 accuse vt.(of)控告,谴责 ache vi.痛 n.痛,疼痛 achieve vt.1.完成 2.达到,得到 achievement n.1.完成,达到, 2.成就,成绩 acid n.酸 a.酸的 acquire vt.1.取得,获得 2.学到 across prep.1.横过,穿过 2.在……对面与……交叉 ad. 1.横过,穿过2.宽,阔 act vi.1.行动,做事 2.(on)作用 n.行为,动作 action n.1.行动,行为,活动 2.(on) 作用于 active a.1.有活动力的,积极的,活跃的 2.在活动中的 activity n.1.活动 2.活性,活力 actor n.男演员
三级语法考点归纳 一. 虚拟语气 1. if 句中虚拟形式 if 引导的非真实条件句(纯粹假设或发生的可能性不大) 条件 与现在相反 与将来相反 与过去相反 done 例句 If we left (leave) now, we should arrive in time. If they hadn ' t gone on vacation, their house wouldn 2. 原形虚拟: a. 表命令、决定、要求、建议等词语之后的that-分句中,用动词原形。 suggest, dema nd, advise, propose, order, arran ge, in sist, comma nd, require, request, desire that (should) do 例女口 He suggested that we should leave early. My suggesti on is that we should tell him. b. It is (was)形容词 /名词 that ......... (should) do/ 例女口 It is absolutely essential that all the facts be examined first. 3. 一些句型中的虚拟形式: 1. It ' s (high, about, the first, etc.) time (that)词过去时 … … 例如 It ' s time we left. 2 would rather/so oner as if/ though would rather/sooner 反 as if/ though 4?练习 1. I _______ t ry it agai n if I ______ you. A. will ; am B. should; am would ; had been 2. If it _______ n ot for the water , the pla nts _ A. were ; would not B. is ; could not could not 3. If I school. A. have not had; could not become 从句 did (be > were) did (be * were) had done 主句 would/ should/ might/ could do would/ should/ might/ could do would/ should/ might/ could have 't have been broken (break) into. 例女口 It is time we went to bed. 宁愿 好像 谓语用过去时 与现在或者将来相 谓语用过去完成时 与过去相反 C. would ; were D. live. C. were ; could D. did ; that chanee to show my ability, I the preside nt of this B. had not had ; would not have
C o l l e g e E n g l i s h B a n d T h r e e Part I Listening Comprehension 1. A) To cancel his trip. B) To go to bed early. C) To catch a later flight. D) To ask for a wake-up call. 2. A) They have different opinions as to what to do next. B) They have to pay for the house by installments. C) They will fix a telephone in the bathroom. D) The man’s attitude is more sensible than the woman’s. 3. A) She will save the stamps for the man’s sister. B) She will no longer get letters from Canada. C) She can’t give the stamps to the man’s sister. D) She has given the stamps to the man’s roommates. 4. A) Visiting the Brownings. B) Writing a postcard. C) Looking for a postcard. D) Filling in a form. 5. A) The man should work with somebody else. B) The man should meet his partner’s needs. C) They should come to a compromise. D) They should find a better lab for the project. 6. A) She can’t finish her assignment, either. B) She can’t afford a computer right now. C) The man can use her computer. D) The man should buy a computer right away. 7. A) The visiting economist has given several lectures. B) The guest lecturer’s opinion is different from Dr. Johnson’s. C) Dr. Johnson and the guest speaker were schoolmates. D) Dr. Johnson invited the economist to visit their college. 8. A) She’s never watched a better game. B) Football is-her favorite pastime. C) The game has been canceled. D) Their team played very badly. 9. A) The man should stick to what he’s doing. B) The man should take up a new hobby. C) The man should stop playing tennis. D) The man should find the cause for his failure. 10. A) An invented story. B) A real life experience. C) An imaginary situation. D) A terrible nightmare. Section B Passage 1 11. A) The name of a German town B) A resident of Frankfurt. C) A kind of German sausage. D) A kind of German bread. 12. A) He sold fast food. B) He raised dogs. C) He was A cook. D) He was a Cartoonist. 13. A) Because the Americans found they were from Germany. B) Because people thought they contained dog meat. C) Because people had to get used to their taste. D) Because it was too hot to eat right away. Passage 2 14. A) They give out faint cries. B) They make noises to drive away insects. C) They extend their water pipes. D) They become elastic like rubber bands. 15. A) Quiet plants. B) Well-watered plants. C) Healthy plants. D) Thirsty
