句子分类讲解(按使用目的和语法结构划分)
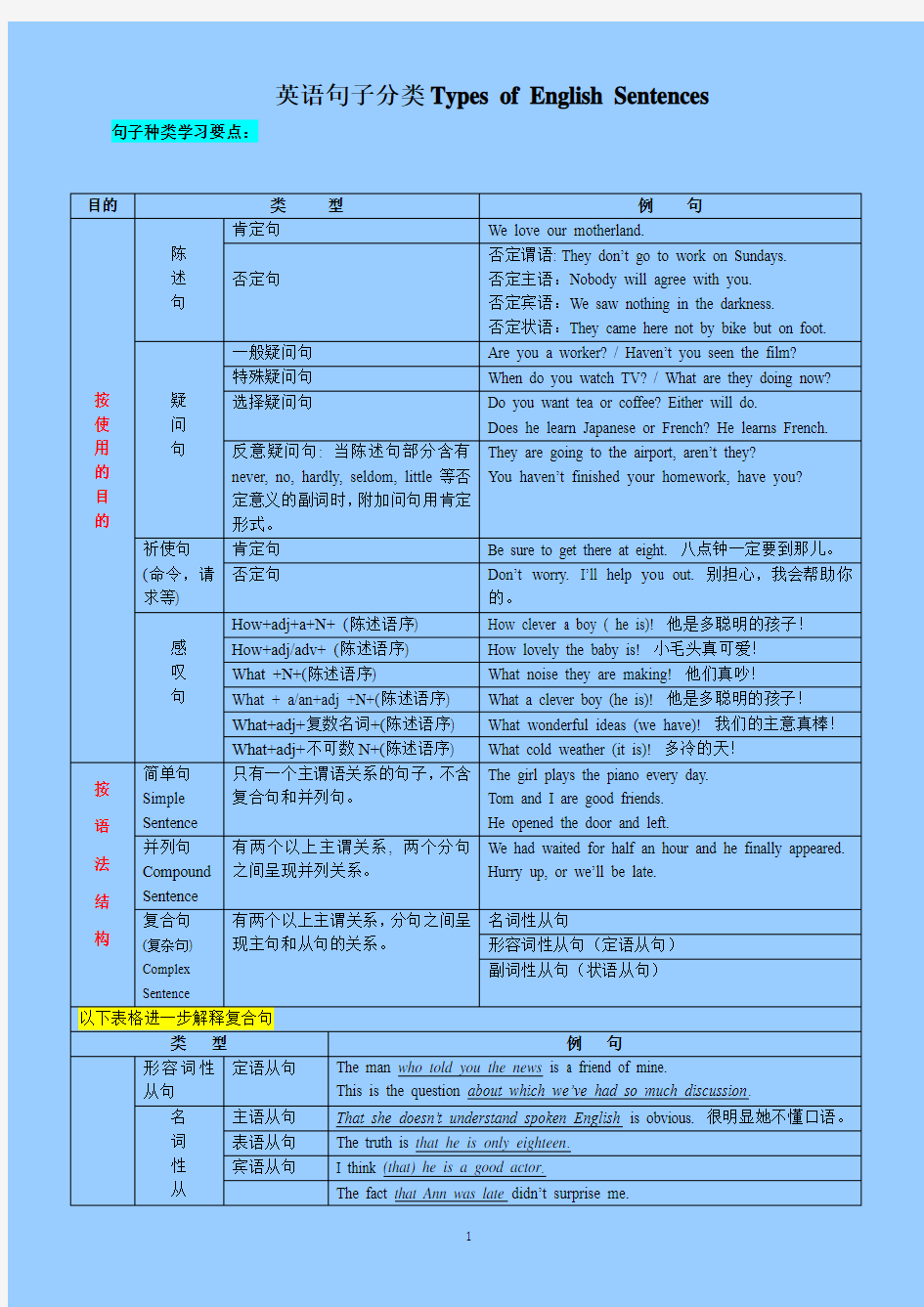

英语句子分类Types of English Sentences 句子种类学习要点:
目的类型例句
按使用的目的
陈
述
句
肯定句We love our motherland.
否定句
否定谓语: They don’t go to work on Sundays.
否定主语:Nobody will agree with you.
否定宾语:We saw nothing in the darkness.
否定状语:They came here not by bike but on foot.
疑
问
句
一般疑问句Are you a worker? / Haven’t you seen the film?
特殊疑问句When do you watch TV? / What are they doing now?
选择疑问句Do you want tea or coffee? Either will do.
Does he learn Japanese or French? He learns French.
反意疑问句: 当陈述句部分含有
never, no, hardly, seldom, little等否
定意义的副词时,附加问句用肯定
形式。
They are going to the airport, aren’t they?
You haven’t finished your homework, have you?
祈使句
(命令,请
求等)
肯定句Be sure to get there at eight. 八点钟一定要到那儿。
否定句Don’t worry. I’ll help yo u out. 别担心,我会帮助你
的。
感
叹
句
How+adj+a+N+ (陈述语序) How clever a boy ( he is)! 他是多聪明的孩子!
How+adj/adv+ (陈述语序) How lovely the baby is! 小毛头真可爱!
What +N+(陈述语序) What noise they are making! 他们真吵!
What + a/an+adj +N+(陈述语序) What a clever boy (he is)! 他是多聪明的孩子!
What+adj+复数名词+(陈述语序) What wonderful ideas (we have)! 我们的主意真棒!
What+adj+不可数N+(陈述语序) What cold weather (it is)! 多冷的天!
按语法结构简单句
Simple
Sentence
只有一个主谓语关系的句子,不含
复合句和并列句。
The girl plays the piano every day.
Tom and I are good friends.
He opened the door and left.
并列句
Compound
Sentence
有两个以上主谓关系, 两个分句
之间呈现并列关系。
We had waited for half an hour and he finally appeared.
Hurry up, or we’ll be late.
复合句
(复杂句)
Complex
Sentence
有两个以上主谓关系,分句之间呈
现主句和从句的关系。
名词性从句
形容词性从句(定语从句)
副词性从句(状语从句)
以下表格进一步解释复合句
类型例句
形容词性从句定语从句The man who told you the news is a friend of mine.
This is the question about which we’ve had so much discussion.
名词性从主语从句That she doesn’t understand spoken English is obvious. 很明显她不懂口语。表语从句The truth is that he is only eighteen.
宾语从句I think (that) he is a good actor.
The fact that Ann was late didn’t surprise me.
复合句\ 复杂句句同位语从句安迟到的事实我不足为奇。
副
词
性
从
句
状
语
从
句
1. 时间状语从句
Can you spare five minutes when it's convenient?
I sent you the news the instant (that) I heard it.
2. 地点状语从句Wuhan lies where the Yangtze and Han River meet.
3. 原因状语从句
We did it because we felt it our duty.
We succeeded by reason that we are better organized.
4. 目的状语从句
She worded so carefully that it might not cause any misunderstanding.
5. 结果状语从句
Everyone lent a hand, so that the work was finished ahead of schedule.
You’d better take more clothes in case the weather is cold.
6. 程度状语从句
It was such good news that I could not believe it at first.
7. 条件状语从句
If you have a complaint, write to the director.
As long as we don't lose heart, we’ll find a way to overcome the difficulty.
8. 让步状语从句
We lost the game although/though/even though we tried our best.
Even if we achieve great success in our work, we should not be proud.
9. 方式状语从句You must try to hold the tool as I do.
10. 比较状语从句
I have always tried to help those who are less fortunate than I.
陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句讲解与练习
一、陈述句
陈述句就是陈述者叙述一件事情后,表达一种看法的句子。
陈述句的分类
陈述句可以分为肯定式和否定式两种。
1.肯定式
第一种:主语+谓语+其他,如
Lucy likes playing sports.
I am singing.
My father went to Beijing last week.
She can ride the bike.
第二种:主语+系动词+表语,如:
This room is empty.
We are good friends .
2.否定式
陈述句的否定式有以下三种:
陈述句的谓语动词
第一种就是Be动词加,后面not 构成否定句。
如:lisa is not a student
There were not at school yesterday.
第二种就是实义动词,而且没有情态动词或助动时,要用“do/dose/did +not 构成否定。
如:I don’t like music.
The farmer did not want to feed the rabbit.
第三种:谓语动词为“助动词、情态动词+实义动词”时,要用“助动词/情态动词+not”构成否定。如:
I am not going to play computer games.
Harry must not go to school at night.
We can not go hiking with you this weekend.
二、疑问句
疑问句分为四种:一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反义疑问句。
1.一般疑问句通常以be, have, 助动词或情态动词开头,回答时用Yes, No, 朗读时要用升调。
2.特殊疑问句是针对句中某一部分的提问。
特殊疑问句的句式是:“特殊疑问词+一般疑问句”。
疑问词有who, whom , whose , what, when, why , where ,how 等。如:
who is our classmate? What does Kate do on Sundays?
Whose cat is it ? which bag will they buy? When did he go out ?
Why don’t we go together? Where were you last night ? How are you today?
3.选择疑问句的结构是提供两种或两种以上的情况,供对方进行选择回答的问句。
选择疑问句的句式是:“一般疑问句+or +可选择部分”。如:
Are the apples red or green ?
Which girl is taller ,Sally or Jessica?
选择疑问句的回答和特殊疑问句一样,不能用yes 或no ,要根据实际情况回答。朗读时,选择疑问句在or 前面的部分要用升调,句末要读降调。
4.反义疑问句(附加疑问句)的句式:
功能:表示对实施或看法提出疑问,或想得到证实。
句型:反义疑问句的句式有两种:
一种是:“肯定句陈述句+否定结构的反意疑问句?”,如:
You know him, don’t you?
另一种是:“否定陈述句+肯定结构的附加疑问句?”。如:
Sandy can’t speaking English, can he?
反义疑问句也要用yes 或No来回答。如果陈述句部分的内容是事实,就用yes 回答,后面相应的用肯定结构;如果陈述句部分的内容不是事实,就用no 来回答,后面跟否定结构。在翻译时要注意yes 和no 的意思。
如:You know him ,don’t you? Yes ,I do . (是,我认识。) No,I don’t ( 不,我不认识)
Sandy can’t speak English, can he ? Yes, he can. (不,他会。)
No,he can’t.(是的,他不会。)
在朗读时,陈述句部分用降调,附加疑问可以升也可以降。
三、祈使句
1.什么是祈使句
用来表示请示、命令、劝告、建议等的句子叫做祈使句。如:Sit down, please. Be careful!
2.祈使句的分类
根据用途和功能,祈使句可以分为以下几类
表请求。如:Close the window , please.
表命令。如Stop talking!
表提醒或警告。如:Look out !The car is coming.
表邀请。如:Help yourself to some fish.
表示禁止。如:Don’t spit ! No parking!
四、感叹句
句型主要有how 和what 引导两种。
1.How感叹句的结构:how +形容词/副词+主语+谓语,如:
How nice the boots are!
3.what 感叹句的结构:What +a/an +形容词+可数名词单数+主语+谓语,如:
What a pretty girl she is !
但是如果是可数名词复数或不可数名词,就可以去掉句中的a/an.
如:What expensive pens these are ! What pleasant weather it is!
巩固练习
基础题
( )1. Where is the man?
A. Under the tree
B. At 10:00
C. Read a book
D. My mother ( )2. How do you go to school?
A. At 8:00
B. I
C. Today
D. By bike
( )3. What’ he?
A. Working
B. His father
C. At home
D. A teacher.
( )4. What time do you get up every day?
A. At home
B. He
C. Clean my bedroom
D. At 7:00 ( )5. What _____ she do this morning?
A. is
B. does
C. do
D. did
( )6. How ______ you do?
A. are
B. is
C. do
D. did
( )7. Which is better, the red one _____ the blue one?
A. and
B. or
C. but
D. so
( )8. ________ are you?
Wonderful!
A. How
B. What
C. Who
D. Where
( )9. _________ is it today?
It’s Monday.
A. What date
B. What day
C. What time
D. What language ( )10. ________ shall we go?
In the morning.
A. When
B. Who
C. Where
D. How
( )11. Excuse me, can you tell me ______ to get to the No. 1 Middle School?
A. where
B. which
C. why
D. how
( )12.____ got the 100th gold metal in the Olympics for China?
- Zhang Yining.
A. Who
B. What
C. When
D. Where
( )13____ are you talking about?
We are talking about the Asia Games in Guangzhou.
A. What
B. Where
C. Why
D. How
( )14.______ do you visit your uncle?
- once a week.
A. How long
B. How many
C. How often
D. How soon ( ) 15. Excuse me! ________ is the nearest bookshop?
Go down the street and turn left at the second corner?
A. how
B. what
C. where
D. who
( ) 16. ______ is a ticker for the film Hacker He?
About forty Yuan.
A. How old
B. How many
C. How much
D. How often ( ) 17. —______ are you going? —I’m going to the library.
A. Who
B. Which
C. What
D. Where ( )1 8. ______? It’s eight.
A. What day is it
B. What’s five and three
C. How old are you
D. What’s your telephone number ( )1 9. ______ shall we meet in the park?
What about half past eight?
A. What
B. When
C. Where
D. Which ( ) 20. ______ a year does your school have sports meetings?
Twice a year.
A. How often
B. How soon
C. How long
D. How many times
提高题
( )1. ______ are you going to be in the future?
I want to be a person _____ Yang Liwei.
A. How, like
B. How, as
C. What, like
D. What, as ( )2.______ will your father be back? .
A. How long
B. how often
C. How soon
D. How wide ( )3. ----________sweater is this?
----I think it’s Peter’s.
A. Who
B. What
C. Which
D. Whose ( )4. ------_____is the Confucian Temple(孔庙) from here?
------It’s about 10 minuters’ walk.
A. How many
B. How long
C. How much
D. How far ( )5. -----______may I keep these book?
-----two weeks.
A. How often
B. How far
C. How long
D. How soon ( )6. ----______is it from here to Yancheng Railway Station?
----About two kilometers.
A. How often
B. How far
C. How soon
D. How long ( )7. ----_______will the foreign students be back from NanJing.
----In two days, I think.
A. How soon
B. How often
C. How far
D. How fast ( )8. ----____________?
---The one behind the tree.
A. Whose girl
B. Who’s that girl
C. Which girl
D. Where’s the girl
( )9. ______the population of china?
A. How many
B. What
C. How’s
D. What’s ( )10. _______ is she?
A. Whom
B. Who
C. Which
D. When ( )11. ________ is the best, Tom, Jack or Tim?
A. Which
B. Who
C. Whom
D. What
( )12 ._______ milk do you need?
- Three cups.
A. How many
B. How much
C. What
D. Where
( ) 13. —______? —I’ve got a headache and a cough.
A. What’s your trouble?
B. What’s wrong with it?
C. Can I help you?
D. How are you?
( ) 14. ______ tea did you have?
Two cups.
A. How many
B. How much
C. How soon
D. Which ( )15. ______?
Behind the tree.
A. Whose girl
B. Who’s that girl
C. Which girl
D. Where’s the girl
( )16. ________ the price of the pen?
It’s two Yuan.
A. What
B. How
C. Which’s
D. What’s ( )17. Whose room is this?
A. He
B. Him
C. Theirs
D. They ( )18. Where ______ you just now?
A. was
B. are
C. do
D. were ( )19. Who ________ best in his class?
A. dance
B. dancing
C. dances D is dance ( )20. How many ________ are there?
A. peoples
B. people
C. sheeps
D. meat ( )21. Could you tell me, how _______ to the bank?
A. go
B. goes
C. went
D. to go
( )22. _______ the weather like?
A. What
B. How
C. How’s
D. What’s
( )23. How much _______ the pen?
A. does
B. are
C. is
D. am
( )24. ________ are you going to have dinner tonight?
A. Who
B. Where
C. When
D. What ( )25. ----_________ do you go to Hong Kong?
----sorry, I’ve never been there.
A. How long
B. How often
C. How far
D. How soon
对划线部分提问
1. My mother goes to work by bike.
2. There are six kites in the sky.
3. Classes begin at eight.
4. It's Sunday today.
5. The cats are running up the tree.
6. He would like five cakes.
7. They play football every Friday.
8. Allan will go back to England by plane next month.
9.He often has lunch in the factory.
10.I got up at six this morning .
11.They were drawing a horse when I came in.
12. Tom comes from Greece.
13.I didn't go to school because I had a bad cold.
14.He comes to China once a year.
15. Ted put his bag in the desk.
16. He is 12 years old.
17. I am fine.
18. They had dinner at home yesterday.
19. She is going to be a nurse in the future.
20. It’s ten minutes’ walk from my home to the school.
Key to
巩固练习
基础题
( )1. Where is the man?
A. Under the tree
B. At 10:00
C. Read a book
D. My mother ( )2. How do you go to school?
A. At 8:00
B. I
C. Today
D. By bike ( )3. What’ he?
A. Working
B. His father
C. At home
D. A teacher. ( )4. What time do you get up every day?
A. At home
B. He
C. Clean my bedroom
D. At 7:00 ( )5. What _____ she do this morning?
A. is
B. does
C. do
D. did
( )6. How ______ you do?
A. are
B. is
C. do
D. did
( )7. Which is better, the red one _____ the blue one?
A. and
B. or
C. but
D. so
( )8. ________ are you?
Wonderful!
A. How
B. What
C. Who
D. Where ( )9. _________ is it today?
It’s Monday.
A. What date
B. What day
C. What time
D. What language ( )10. ________ shall we go?
In the morning.
A. When
B. Who
C. Where
D. How ( )11. Excuse me, can you tell me ______ to get to the No. 1 Middle School?
A. where
B. which
C. why
D. how
( )12.____ got the 100th gold metal in the Olympics for China?
- Zhang Yining.
A. Who
B. What
C. When
D. Where ( )13____ are you talking about?
We are talking about the Asia Games in Guangzhou.
A. What
B. Where
C. Why
D. How ( )14.______ do you visit your uncle?
- once a week.
A. How long
B. How many
C. How often
D. How soon ( ) 15. Excuse me! ________ is the nearest bookshop?
Go down the street and turn left at the second corner?
A. how
B. what
C. where
D. who
( ) 16. ______ is a ticker for the film Hacker He?
About forty Yuan.
A. How old
B. How many
C. How much
D. How often ( ) 17. —______ are you going? —I’m going to the library.
A. Who
B. Which
C. What
D. Where ( )1 8. ______? It’s eight.
A. What day is it
B. What’s five and three
C. How old are you
D. What’s your telephone number ( )1 9. ______ shall we meet in the park?
What about half past eight?
A. What
B. When
C. Where
D. Which
( ) 20. ______ a year does your school have sports meetings?
Twice a year.
A. How often
B. How soon
C. How long
D. How many times
提高题
( )1. ______ are you going to be in the future?
I want to be a person _____ Yang Liwei.
A. How, like
B. How, as
C. What, like
D. What, as ( )2.______ will your father be back? .
A. How long
B. how often
C. How soon
D. How wide ( )3. ----________sweater is this?
----I think it’s Peter’s.
A. Who
B. What
C. Which
D. Whose ( )4. ------_____is the Confucian Temple(孔庙) from here?
------It’s about 10 minuters’ walk.
A. How many
B. How long
C. How much
D. How far ( )5. -----______may I keep these book?
-----two weeks.
A. How often
B. How far
C. How long
D. How soon ( )6. ----______is it from here to Yancheng Railway Station?
----About two kilometers.
A. How often
B. How far
C. How soon
D. How long ( )7. ----_______will the foreign students be back from NanJing.
----In two days, I think.
A. How soon
B. How often
C. How far
D. How fast ( )8. ----____________?
---The one behind the tree.
A. Whose girl
B. Who’s that girl
C. Which girl
D. Where’s the girl
( )9. ______the population of china?
A. How many
B. What
C. How’s
D. What’s ( )10. _______ is she?
A. Whom
B. Who
C. Which
D. When ( )11. ________ is the best, Tom, Jack or Tim?
A. Which
B. Who
C. Whom
D. What
( )12 ._______ milk do you need?
- Three cups.
A. How many
B. How much
C. What
D. Where ( ) 13. —______? —I’ve got a headache and a cough.
A. What’s your trouble?
B. What’s wrong with it?
C. Can I help you?
D. How are you?
( ) 14. ______ tea did you have?
Two cups.
A. How many
B. How much
C. How soon
D. Which ( )15. ______?
Behind the tree.
A. Whose girl
B. Who’s that girl
C. Which girl
D. Where’s the girl
( )16. ________ the price of the pen?
It’s two Yuan.
A. What
B. How
C. Which’s
D. What’s ( )17. Whose room is this?
A. He
B. Him
C. Theirs
D. They ( )18. Where ______ you just now?
A. was
B. are
C. do
D. were ( )19. Who ________ best in his class?
A. dance
B. dancing
C. dances D is dance ( )20. How many ________ are there?
A. peoples
B. people
C. sheeps
D. meat
( )21. Could you tell me, how _______ to the bank?
A. go
B. goes
C. went
D. to go
( )22. _______ the weather like?
A. What
B. How
C. How’s
D. What’s
( )23. How much _______ the pen?
A. does
B. are
C. is
D. am
( )24. ________ are you going to have dinner tonight?
A. Who
B. Where
C. When
D. What
( )25. ----_________ do you go to Hong Kong?
----sorry, I’ve never been there.
A. How long
B. How often
C. How far
D. How soon
对划线部分提问
1. My mother goes to work by bike.
How does your mother go to work?
2. There are six kites in the sky.
How many kites are there in the sky?
3. Classes begin at eight.
When do classes begin?
4. It's Sunday today.
What day is it today?
5. The cats are running up the tree.
What are the cats doing?
6. He would like five cakes.
How many cakes would he like?
7. They play football every Friday.
How often do they play football?
8. Allan will go back to England by plane next month.
How will Allan go back to England next month?
9.He often has lunch in the factory.
Where does he have lunchy?
10.I got up at six this morning .
When did you get up this morning?
11.They were drawing a horse when I came in.
What were they doing when I came in?
12. Tom comes from Greece.
Where does Tom come from?
13.I didn't go to school because I had a bad cold.
Why didn’t you go to school?
14.He comes to China once a year.
How often does he come to China?
15. Ted put his bag in the desk.
What did Ted put in the desk?
16. He is 12 years old.
How old is he?
17. I am fine.
How are you?
18. They had dinner at home yesterday.
Where did they have dinner yesterday?
19. She is going to be a nurse in the future.
What is she going to be in the future?
20. It’s ten m inutes’ walk from my home to the school. How far is it from my home to the school?
英语语法大全 句子成分分析
句子成分分析 在句中起着不同语法作用的成分,叫做句子成分。英语的句子成分有九种: 1、主语(subject)表示句子描述的是“谁”或“什么”,是谓语的陈述对象; 通常由名词、代词、动词不定式、动名词或从句等担任: The sun rises in the east. 日出东方。(名词) He hated to see any bird killed.他讨厌看到鸟儿被杀。(代词) To see is to believe.眼见为实。(动词不定式) Seeing is believing.眼见为实。(动名词) Where we shall hold the party is not decided yet.我们还没有决定在何处举行晚会。(主语从句) It’s human to want something better.精益求精是人类的特性。(不定式) 2、谓语动词(predicate verb)说明主语的动作或状态,由动词或动词短语担任: We study English.我们学习英语。(动词) The car broke down on the way.车在路上抛锚了。(动词短语) Do be quiet,children.孩子们,务必安静点。(助动词+连系动词) We are having a meeting now.我们现在正在开会。(助动词+实义动词) Soldiers must obey orders.军人必须服从命令。(情态动词+实义动词) 3、表语(predicative)说明主语的性质、特征、状态或身份,与连系动词一起构成复合谓语,通常由名词、代词、形容词、数词、副词、介词短语、动词不定式、动名词、分词或从句等担任: The next stop is the zoo.下一站是动物园。(名词) The game is yours.你(们)胜了。(代词) I was first! 我第一名!(数词) I feel terrible.我难受的厉害。(形容词) Is your mother in?你妈妈在家吗?(副词) I’m with you.我站在你这一边。(介词短语) Mary’s task is to set the table.玛丽的任务是摆桌子。(动词不定式) Her hobby is growing roses.她的爱好是种植玫瑰。(动名词) The situation is puzzling.形式令人迷惑不解。(现在分词) Do you feel satisfied with the arrangement?你对这安排满意吗?(过去分词) The fact is that they are cross with each other.事实是他们生彼此的气。(表语从句) That’s where you are wrong.这就是你错的地方(表语从句) He is no longer what he was.他已经不是以前的他了。(表语从句) 4、宾语(object)表示及物动词或及物动词短语的对象或内容,或用于介词后构成介词短语;通常由名词、代词、数词、动词不定式、动名词或从句等担任: May I have your attention ,please.请大家注意。(名词) I want a little.我要一点。(代词) I need two.我需要两个。(数词) Hope to see you soon.希望能很快见到你。(动词不定式) They risk losing everything.他们冒着失去一切的危险。(动名词) He insisted on seeing her home.他坚持送她回家。(动名词作介词的宾语) I’ll do what I can.我将尽力而为。(从句)
英语语法、句式、简单句子结构(透彻分析)
LESSON ONE 句子的三种模式 导言本课的重点是掌握英语的三种基本句型,注意词性和词序,以及定语的位置,同时注意中英文表达上的相同和不相同的地方。三种基本句型虽然简单,但至关重要。掌握好它们,在今后的学习中有一通百通之效。 其实英语只有三种基本句型 ▲主+系动词+表 词序 1 主语 2 系动词 3 表语 即句子的用于连接主语表示主语身份、状态以及主体和表语所处的位置 词性* 名词 代词 Be (is, am, are) * 名词形容词 介词+* 名词(介词短语) 注:*注意该结构中的名词,它们能被定语修饰。 1 这个人是一个老师。The man is a teacher. 主语系表语主语系表语(名词) 2 他(是)很忙。He is busy. 主语系表语主语系表语(形容词)▲注意中文中的系动词经常被省略,而英文中绝不能省。
3 她(是)在教室里。She is in the classroom. 主语系表语主语系表语(介词短语) ▲定语只修饰名词,不破坏句子的基本结构。通常由形容词和介词短语充当,形容词放在所修饰的名词之前,而介词短语放在所修饰的名词之后,请注意英语与汉语词序的不同。看懂中文的定语是翻译好定语的关键。 介词短语 4 幸福是太多和太少之间的一站。--- 英国法学家波洛克 介词短语 Happiness i s a station between too much and too little . -----------Pollock, British jurist 形容词介词短语 5 高个子的男人是从英国来的老师。
形容词介词短语 The tall man is a teacher from England. 介词短语形容词 6. 她在二楼的小教室里。 形容词介词短语 She is i n the small classroom on the second floor. The teacher in the classroom is handsome. My book is o n the deskin the classroom. 表语(介词短语)定语(介词短语)She is in the small classroom on t he second floor.
英语语法 句子成分分析
知识精讲 一、整体把握 成分用法说明位置 主语是执行句子的行为或动作的主 体。 陈述句中放在句首或谓语之前;疑问句或倒装句 中放在动词、助动词、情态动词之后;there be结 构中放在be之后;祈使句中常省 谓语对主语加以陈述,说明主语怎 么样或是什么。必须由动词担 任,其人称和数必须和主语一 致。 通常在主语后(疑问句、倒装句除外)。 表语与系动词连用,一起构成复合 谓语,说明主语的性质、特征、 身份、类别、状态等。 常在系动词之后。 宾语表示动作、行为的对象。一般放在及物动词或介词后。间接宾语通常放在直接宾语之前。直接宾语是人称代词,间接宾语是名词或两个宾语都是人称代词时,间接宾语放在直接宾语之后,并在间接宾语前加to或for。 定语用来修饰名词或代词,说明人 或物的状态、品质、数量及所 属等。 单个词常在被修饰的词前,短语或句子在被修饰 的词之后;副词作定语常放在被修饰的伺候;形 容词修饰不定代词放在被修饰的伺候。 状语修饰动词、形容词、副词,表 示动作发生的时间、地点、目 的、方式等。 位置比较灵活。 补语补充说明宾语或主语的成分。宾语补足语通常置于宾语之后,主语补足语通常置于主语和谓语之后。 同位语对句子中某一成分作进一步解 释、说明,与前面的被修辞成 分在语法上处于同等地位。 常常置于被说明的成分之后。有时可以放在句子 的前面(主语之前),尤其是主语为人称代词时, 为平衡句子的节奏,则把同位语放置于此代词前。 独立成分独立成分是指句子里的一个词 或词组与全局没有语法上的联 系,不属于句子的组成部分; 一般由感叹语、呼语或插入语 等担任。 可放在句首、句中或句末。 二、细讲:主语 表现形式例句
初中英语语法大全之句子的种类
初中英语语法大全之句子的种类 2011-09-24 15:37:42 来源:本站原创进入论坛 句子的种类 (一)按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。 1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。Light travels faster than sound。光比声速度快。(说明事实) The film is rather boring。这部电影很乏味。(说明看法) 2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。有以下四种: a.一般疑问句(General Questions): Can you finish the work in time? 你能按时完成工作吗? b.特殊疑问句(W Questions;H Questions): Where do you live?你住那儿? How do you know that?你怎么知道那件事? c.选择疑问句(Alternative Questions): Do you want tea or coffee? 你是要茶还是要咖啡?
d.反意疑问句(Tag-Questions): He doesn‘t know her,does he? 他不认识她,对不对? 3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如: Sit down,please。请坐。 Don’t be nervous!别紧张! 4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如: What good news it is!多好的消息啊! (二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类: 1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如: She is fond of collecting stamps。她喜欢集邮。 (主)(谓) 2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如: The food was good,but he had little appetite。 (主)(谓)(主)(谓) 食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。 3)复合句(Complex Sentences):包含一个主句从句和一个或几个从句的句子叫复合句,从句由从属连词引导,例如:
初中英语语法 句子的种类
初中英语语法------句子的种类A英语中的句子按其使用目的,句子可分为:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、和感叹句。 Eg: 陈述句:This is a dog. 疑问句:Is this a dog? 祈使句:Open your eyes! 感叹句:What a beautiful building it is! 简单句:I am studying. 并列句:I was born in a small village and I lived there for nearly ten years. 复合句:As soon as I get there, I'll call you. 1 陈述句凡是说明一件事情,提出一个看法,或者是表达一种心情的句子都是陈述句。大多数的句子都是陈述句,陈述句可以用肯定式和否定式。陈述句句末用句号“.”,通常用降调。 Eg:We live in Beijing. We don't live in Beijing. (1) be 动词、一般动词(实义动词)、情态动词的否定句 I am not a student. I don't know him. He can't speak English.
be 动词的否定句句型:主语+ be动词+ not + … I wasn't good at English. They weren't at home yesterday. He isn't my cousin. 进行时和被动语态都有be 动词,它们的否定句与be动词的否定句同形。 Eg:They aren't cleaning the room. The child was not looked after by anybody. 将来时(will,shall)、完成时及情态动词的被动语态不能用be动词否定句型。 They will not be sent to the front. They will be not sent to the front.× 情态动词的否定句 句型:主语+情态动词+ not + 动词原形 Eg:I can't do it myself. You mustn't take the books out. You must not go there alone. 一般动词的否定句. 句型:主语+ do/does/did + not + 动词原形 Eg: They didn't live in Shanghai. He doesn't do his homework every day.
语法汇总(句子结构)
语法汇总(基本句子成分) (本来想手写然后给你照照片的,不过写几个字之后发现自己的中文有点不会写了。个人觉得语法没什么用,可能是中国人比较喜欢系统的总结各种东西,初中高中也学了很多语法,不过等到学到稍高端之后就会发现,他们外国人写东西有语法不过更像是在跟感觉走。 I am never a big fun of grammar. Anyway, let’s get started.) 主语 主语表明这句话说的是谁和什么,主语主要由名词、代词或相当于名词的单词,短语或从句充当。 一、名词作主语 David arrived last night. 大卫昨晚到达。 Pride goes before a fall. 骄必败。 二、代词作主语 Who is speaking, please? (在电话中)请问您是谁? That's OK. 这没问题。 三、数词作主语 Two will be enough. 两个就够了。 Two-thirds of the workers are women. 三分之二的工人是女工。 四、ing形式作主语 Skating is good exercise. 溜冰是很好的运动。 Looking up all the new words in the dictionary took him a lot of time. 从字典里查所有的生词花费了他许多时间。 五、不定式作主语 To translate this ideal into reality needs hard work. 把理想转变成现实需要辛勤的劳动。 六、名词化的形容词作主语 The blind and the lame are well cared for in our country. 在我们国家,盲人和肢残人受到很好的照顾。 The unemployed usually lead a hard life. 失业的人生活一般很困难。 七、短语作主语 How to do well is an important question. 如何把这件事做好是一个重要问题。 Early to bed and early to rise makes a man healthy. 早睡早起身体好。 八、从句作主语 What has happened proves that our policy is right.
初中英语语法——句子成分精讲
一、句子成分精讲 句子成分:主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语、补语等。 主要成分:主语和谓语 1、主语 一个句子中需要加以说明或描述的对象。主语的位置: 一般位于句首,由名词、代词、数词或相当于名词的词、短语等充当。The school is far from here. 名词做主语 She goes to school by bike.代词做主语 Eight is a lucky number.数词做主语 The blind need more help.名词化的形容词做主语 There is a pen on the desk. 名词做主语 Predicting the future is interesting.动名词做主语 To be a doctor is my dream.不定式短语做主语 2、谓语 表示人或事物(主语)的动作和存在的状态. 英语中由动词be、动词have和行为动词来充当谓语动词 句子的时态和语态是通过谓语表现出来。 谓语动词往往由一个或一个以上的助动词或情态动词加上主要动词构成。分析句子的主语和谓语 Mr. Li teaches English. He can play the piano. My parents and I are having dinner. 3、表语 用来说明主语的身份、特征、性质、状态。 表语的位置 用在动词be和系动词的后面。 名词、代词、数词、介词短语、副词等都可以和连系动词一起构成复合谓语。 Y our pen is on the desk. He got very angry. My dream is to have a robot. 常见的系动词
英语语法——英语句子成分分析
英语语法——英语句子成分分析 句子是按照一定的语法规律组成的,表达一个完整的意义。一个句子一般由两部分构成,即主语部分和谓语部分,这两部分也叫做句子的主要成分。句子的次要成分包括宾语,定语,状语,表语等。句子成分是句子中起一定功用的组成部分。 1)主语:是一句的主体,是全句述说的对象,常用名词,数词或代词担任,一般放于句首。如: Students study. (学生学习。) We are friends.(我们是朋友) 这两句话中单词students是个名词,we是代词,它们在句中做主语。 2)谓语:是对主语加以陈述,表示主语的行为或状态,常用动词或者动词词组担任,放在主语的后面。如: Students study. (学生学习。) We are friends. (我们是朋友) 这两句话中单词study和are都是动词,study叫做实意动词,are叫做be 动词,它们在句中作谓语。 3)宾语:表示行为的对象,常由名词或者代词担任。放在及物动词或者介词之后。如: They are teachers. ( 他们是老师。) I play with him. (我和他一起玩。) 这两句话中单词teachers是名词,单词him是带词,它们在句中作宾语。4)定语:是用来说明或者限制名词的成分,常用形容词或者相当于形容词的短语或从句担任。形容词放在名词之前,相当于形容词的短语或从句放在名词的后面。如: This is a red sun.(这是个红太阳.) He is a tall boy.(他是个高个子男孩。) 这两句话中单词red和tall都是形容词,它们作定语。 5)状语是用来说明动词,形容词,副词或整个句子的成分。常由副词担任。修饰动词时可以放在动词之前,也可以放在动词之后;修饰形容词或副词时放在它们之前。如: The students study hard. (这些学生学习努力。) I often write to him. (我常给他写信。) The bag is too heavy. (这个书包太重了。) 这三句话中单词hard 和often修饰的都是动词,第三句话中单词too修饰的是形容词,它们都作状语。 6)表语:用来说明主语的性质或状态。一般由名词或者形容词担任。如:This table is long. (这个桌子是长的。) 通常情况下,主语和宾语前的成分是定语,谓语前的成分是状语,时间词作状语
小学英语语法句子的种类
句子的种类 (1)一般疑问句 用来询问一件事或情况是否属实。用yes 或 no 来回答。 (2)特殊疑问句 特殊疑问句由特殊疑问词加一般疑问句构成,不能用yes来no回答。一般用完整的回答或是直接回答疑问词的提问。Where are you from? I am from Beijing. 或Beijing. (3)选择疑问句 提供两种或两种以上的选项供对方选择,前面的选项之间用逗号分隔开来,后两项之间用or连接,回答时选择一种。 Would you like a pear, an apple or a banana ? I’d like a b anana。 (4)反意疑问句 由陈述句加一个简短问句构成,简短问句对陈述句提出相反的疑问。如果陈述句部分是肯定,后面问句就用否定形式;陈述句部分是否定,简短问句则用肯定形式。 He likes music, doesn’t he? Yes,he does. 是的,他喜欢。No,he doesn’t. 不,他不喜欢。 He doesn’t like music, does he ? Yes,he does. 不,他喜欢。No,he doesn’t. 是的,他喜欢。 即回答应该按实际情况来回答,实际情况是肯定的,就用yes。否定的就用no.
小学英语一般疑问句,否定句以及对划线部分提问的解题指导 改为一般疑问句: 先找am, is, are, was, were或can, would,放在最前面, 如没有则判断是否为过去式,是则动词改为原形,句前加Did,其余照抄; 不是则判断是否为第三人称单数,是则动词改为原形,句前加Does,其余照抄 以上都不是,则句前加Do,其余照抄。 改为否定句: 方法和上面一样, 先找am, is, are, was, were或can, would,再后加not,其余照抄 如没有则判断是否为过去式,是则动词改为原形,人后加didn’t,其余照抄; 不是则判断是否为第三人称单数,是则动词改为原形,人后加doesn’t,其余照抄 以上都不是,则人后加don’t,其余照抄 对划线部分提问: ①用适当的疑问词代替划线部分,②将剩余部分改为一般疑问句 (注:如划线部分为主语,则用who代替,其余照抄;如划线部分为动词或动词短语,则用do代替,句前加what,再改为一般疑问句)例如: He is running now.----- He isn’t ru nning now. ---Is he running now? ---Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t. They are making a puppet.---- They aren’t making a puppet.---Are they making a puppet? ---Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t. I often watch TV in the evening.------ I don’t often watch TV in the evening.---- Do you often watch TV in the evening?-----Yes, I do. No, I don’t. He plays football after school. ---- He doesn’t play football after school. Does he play football after school?----Yes, he does. No,he doesn’t. We began class at 8 o’clock yesterday.------ We didn’t begin class at 8 o’clock yesterday. Did you begin class at 8 o’clock yesterday? ---Yes,we do. No, we don’t. 练一练: 1、填入适当的疑问词。 1) _____wallet is it? It’s mine.2) ____is the Christmas Day? It’s on t he 25th of Decem ber. 3)________is the diary? It’s under the chair. 4) ______is the boy in blue? He’s Mik e.
英语语法基本句子结构
英语语法基本句子结构 课程名称:大学英语语法 学院:电子信息与电气工程学院 学生姓名:王磊 学号:201102010054 专业班级:自动化2011级(1)班 指导教师:李国云 2013年 6 月8 日
英语语法基本句子结构 语法是对现成语言中规则的归纳和总结,以便学习者更快模仿掌握一门外语。所以语法知识很重要,你不能用汉语的语法规则来造英语的句子,那样懂英语的人读不懂,同样不懂英语的语法规则也绝对读不懂英语短文。 不同词类的单词,按照一定的语法规则组合在一起,能够表达一个完整意思的语言单位叫句子,一个句子由各种功能不同的部分组成,这些部分叫做句子成分。 一个句子一般由两部分组成:主语部分和谓语部分。根据各个句子成分在句子中所起得作用,可分为主语、谓语或谓语动词、宾语、表语、定语、补语、状语等。 主语 全句述说的对象,常由名词、代词、名词性短语或分句充当,一般置于句首。下面依次举例: Walls have ears. Football is my favorite. Three plus four equals seven. 谓语或谓语动词 说明主语的动作或状态,主要一般又实义动词或者系动词担任,助动词和情态动词加其他动词的适当形式充当,一般置于主语之后。 They should have finished their work. The chance may never come again.
注意:英语中最基本的原则就是:一句话,只能有一个谓语动词 宾语 宾语表示动作的对象,是动作的承受者。宾语一般放在及物动词之后。英语介词后也会跟宾语。可作宾语的有名词,代词,数词,动名词等,不定时式也可做及物动词的宾语。下面依次举例:She refused to read that terrible book. We haven’t seen her for a long time. He needs a new dictionary. 表语 表述主语的身份、状态、特征,常由名词、代词、形容词、副词、数词、不定式、动名词、介词短语或分句充当。置于联系动词之后。联系动词一般有be,become,turn,get,grow,seem.,appear,look,sound,smell,feel 等。 My father is a professor. The milk has turned sour. Everything here is dear to her. 定语 是修饰名词或代词的词,短语或从句。作定语的有名词,形容词,数词,分词机器短语,不定式及其短语,介词短语以及定语从句等。下面依次举例:
经典英语语法100句
1. Education is the door to freedom. 教育是通向自由之门。[一个简单的主系结构] 2. Challenges make life interesting. 挑战使生活变得有趣。[make+…+:形容词作宾语补足语。] 3. Difficulties make life worth living. 困难让生活有价值。[make+…+介词短语:介词短语作宾语补足语。] 4. Nothing in the world can take the place of persistence. 世界上没有什么可以取代坚持。[否定词作主语。Take the place of:代替。] 5. It’s impossible to defeat a person who never gives up! 打败一个永不放弃的人是不可能的。[动词不定式作主语,“it”为形式主语。“who”引导的定语从句修饰先行词”a person”。] 6. The most important thing in life is to have a great aim and the determination to attain it. 生活中最重要的事情就是有一个远大的目标,并有决心实现它。[动词不定式作表语和定语。] 7. If you can dream it, you can do it. 只要你想得到,人就做得到。[“if”引导的条件状语从句。] 8. Actions speak louder than words. 行动比语言更加强大。[副词比较级] 9. Deeds are more powerful than words. 行为比言语更加强大。[形容语比较级] 10. Mistakes show us what we still need to learn. 从错误中我们知道该学什么。[“what”引导的宾语从句作直接宾语。从句中动词不定式作宾语。]
英语语法词汇句型必背佳句
高中必背句型句句经典(一线优秀教师总结) 1.With the development of economy, more and more families bought private cars, thus leading to much heavier traffic problems and more serious air pollution. 2.What is the most important is that we do not mind what others say so long as we are confident in what we have done. 3.It’s a truth universally acknowledged that a single man in possession of a good fortune must be in want of a wife. However little known the feelings or views of such a man may be on is first entering a neighborhood, this truth is so well fixed in the minds of the surrounding families, that he is considered the rightful property of some one or other of their daughters. 4.We believe we are confident and capable of overcoming the current difficulties and challenges we are faced with. In a word, all we need to do now is plan carefully and act in ways that reflect the reality to assure that we can make full use of our talent and skills. 5.You can take a horse to the water but you can’t make him drink. 强扭的瓜不甜 When everybody is somebody, then nobody is anybody.人人都伟大,世间无豪杰。 6.I love waking up in the morning and not knowing what’s going to happen, or who I’m going to meet, where I’m going to wind up. 泰坦尼克号 7.Your future depends on your dreams. So go to sleep. 加菲猫 8.Teachers are the basis of education and that the best students receive instruction from the best teachers. I t’s of great importance to train and nurture teachers, especially those from impoverished and remote rural areas. 9.what I want to stress is that a harmonious family plays a very important role in our life, therefore, it is up to every family member to contribute to the building of such a family. First of all, parents should be a role model for their children and pay more attention to their own words and behaviour. Being children of the family, we should respect and understand our parents, and share their burdens. Only in this way will our family be always harmonious. 10.In my opinion, it’s high time that our government should take measures to ban farmers from cutting down trees. Besides, various activities should be organized to make it clear that everyone is responsible for the environment. Only in this way can we have a blue day. 11.A recent survey found that walking like a happy person on purpose can lift one’s spirits, according to media report on Wednesday. Walking in a happy style makes people feel happy, while adopting the gait of a depressed person can bring on sadness. 12.when it comes to the current public transport, though it is improving, there still remains something to be done. In the first place, the government should add to the investment in the construction of transport. Additionally, it is better for the festival time to be lengthened. Last but not least, more people should be encouraged to ride home instead of driving a private car. 13.According to the information given above, there is nothing ambiguous about the serious situation and who is at fault. 14.It just can't be denied that it is the fast development that is to blame, but maybe the government should undertake the responsibility. 15.Current situation of pollution is considerably serious. Ranking among top pollution sources are vehicles, coal burning, airborne dust and so on. Reasons behind it go as follows. First of all, economic development are promoted at the expense of environment. Secondly, citizens are not aware of the significance of being careful with protecting the environment.
英语句子结构讲解
学会分析英语句子(语法基础辅导讲义) 第一讲学会判断分析简单句 一、词类和句子成分的关系、动词概说与五种基本句型 1.语法学习和语法学习的方法 1)语法包括哪些内容? 2)怎样学习语法?(死记活用) 关于英语词类的特点的思考题 2.十大词类中,哪种词类是英语中特有而汉语没有的? 3.哪些词和名词有关系? 4.动词有什么特征?动词分为几种类型? 5.什么是不定式?它和谓语动词有什么区别? 6.哪种词类和动词有关?为什么? 二、什么是句子成分?有哪些句子成分? 1.主谓宾定状补主干枝叶分清楚,哪些是主干?哪些是枝叶? 2.什么是状语和定语? 3. 什么是宾语补助语和主语补助语? 英语语法分为句法和词法。 句法就是造句和运用句子的规则,句法是最基本的语法规则;词法就是词的使用规则,如动词时态、语态、助动词、情态动词、形容词和副词的用法等等。要造出一个正确的句子必须有词法和句法知识,比如要弄懂词类和句子成分的关系,比如形容词做定语,副词做装语;又比如代词所有格做定语;主格做主语;宾格做宾语,等等。 动词只能做谓语,十分重要。时态主要体现在动词上,动词做谓语,因此也就是要弄懂谓语的构成,不同的时态有不同的构成,时态有常用的时间状语,要彻底搞清楚。
一个句子必然有时态、语态。对谓语动词要弄清楚其时态和语态,才能进行肯定句、否定句和疑问句的转换。 语态体现在be 动词+ 过去分词上。不管什么语态的句子都有时态,不同时态的被动语态都有固定的结构。 句子必然有其由句子成分构成的句子结构。五种基本句型很重要,但是没有词类和句子成分的知识。例如不懂动词分为及物和不及物两种就不能懂得 主语+ 谓语+ 宾语; 主语+ 谓语+ 间接宾语+ 直接宾语; 主语+ 谓语+ 宾语+ 宾语补助语这三种句型 一个句子或者是简单句或者是并列句,或者是复合句。要弄清楚:是简单句、并列句还是复合句?是复合句,又有什么从句? 每个句子的句子成分是怎么样的?如果不懂什么是宾语,那么就学不懂宾语从句;如果不懂什么是状语,那么就学不懂状语从句;如果不懂什么是定语,那么就学不懂定语从句;如果不懂什么是表语,那么就学不懂表语从句。 要弄清楚句子成分和结构,要学会从简单句、并列句、复合句三个方面分析句子,才能在阅读和造句时不犯错误。 所谓分析英语句子,就是从结构上分析判断它是简单句、并列句还是复合句? 它们是由什么词类词组充当的?并列句有几个分句?是什么从句?这些句子不管主句还是从句又是怎样构成的?这是大结构大框架的分析。还有从局部如谓语的分析,什么时态?什么语态?词法知识都很重要。还有状语定语的分析也是局部分析。 词类和句子成分的关系 十大词类 要搞清楚句子成分必须搞清楚英语的词类,因为句子成分是由一个一个的词或词组充
初中英语语法大全-句子种类
初中英语语法大全-句子的种类 按照英语句子的使用目的和用途,句子可分为四类: 陈述句(Declarative Sentence)、疑问句(Interrogative Sentence)、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)和感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence)。 陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句。 疑问句有一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。 图解语法 1. 陈述句 说明一个事实或陈述一个人的看法,陈述句包括肯定陈述句和否定陈述句 特别提示:
肯定陈述句改成否定句或一般疑问句时,如句中有already,some,something,somebody等词,须分别改成yet,any,anything,anybody 等。 另外,也要注意,too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等。 2. 疑问句
3. 常用的特殊疑问句
4. 特殊的反意疑问句 ①主句是祈使句时,“will you?”意为“请求”,“won’t you?”表示提醒对方注意。 例句: Look at the blackboard, will you / won’t you? Don’t be late again, will you? ②感叹句后的反意疑问,用一般现在时态的否定形式 例句: What fine weather, isn’t it? How beautifully she sings, doesn’t she? ③陈述部分是“I am …”时,用“aren’t I?”而不用“am not I?” 例句: I'm working now, aren’t I?
七年级英语:英语语法大全之句子的种类
七年级英语:英语语法大全之句子的种类 句子的种类 (一)按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。 1)陈述句(Declarative Sentences):说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。 Light travels faster than sound. 光比声速度快。(说明事实) The film is rather boring. 这部电影很乏味。(说明看法) 2)疑问句(Interrogative Sentences):提出问题。有以下四种: a. 一般疑问句(General Questions): Can you finish the work in time? 你能按时完成工作吗? b. 特殊疑问句(W Questions; H Questions): Where do you live? 你住那儿? How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事? c. 选择疑问句(Alternative Questions):
Do you want tea or coffee? 你是要茶还是要咖啡? d. 反意疑问句(Tag-Questions): He doesn’t know her, does he? 他不认识她,对不对? 3)祈使句(Imperative Sentences):提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如: Sit down, please. 请坐。 Don’t be nervous!别紧张! 4)感叹句(Exclamatory Sentences):表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如: What good news it is! 多好的消息啊! (二)句子按其结构可以分为以下三类: 1)简单句(Simple Sentences):只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如: She is fond of collecting stamps. 她喜欢集邮。 (主) (谓) 2)并列句(Compound Sentences):包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如: The food was good, but he had little appetite. (主) (谓) (主)(谓)
