Streamlined synaptic vesicle cycle in cone photoreceptor terminals

Neuron,Vol.41,755–766,March 4,2004,Copyright 2004by Cell Press
Streamlined Synaptic Vesicle Cycle in Cone Photoreceptor Terminals
thews,1999;Fuchs et al.,2003).Here we ask whether,in addition to exocytosis and endocytosis,other steps in the vesicle cycle are also specialized for continuous Ruth Rea,1Jian Li,2Ajay Dharia,1Edwin S.Levitan,3Peter Sterling,2and Richard H.Kramer 1,*release in cone photoreceptors.
1
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology At conventional phasic synapses that release trans-Division of Neurobiology
mitter during action potentials,the routes of vesicle re-University of California at Berkeley cycling are often direct.This can include rapid reuse,Berkeley,California 94720where endocytosed vesicles are preferentially rere-2
Department of Neuroscience
leased (Ceccarelli et al.,1973;Murthy and Stevens,University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine 1998;Pyle et al.,2000;Richards et al.,2003),and kiss-Philadelphia,Pennsylvania 19104and-run exocytosis,where docked vesicles release mul-3
Department of Pharmacology tiple times while remaining attached to the plasma mem-University of Pittsburgh
brane (Klingauf et al.,1998;Stevens and Williams,2000;Pittsburgh,Pennsylvania 15261
Gandhi and Stevens,2003;Aravanis et al.,2003).How-ever,there are also detours in the vesicle cycle,where retrieved membrane is stored and perhaps processed Summary
before reuse.For example,during endocytosis,recy-cling can occur through bulk membrane retrieval,re-Cone photoreceptors tonically release neurotransmit-sulting in large vacuoles that eventually give rise to new ter in the dark through a continuous cycle of exo-synaptic vesicles (Takei et al.,1996;Richards et al.,cytosis and endocytosis.Here,using the synaptic vesi-2000;Teng and Wilkinson,2000).Moreover,small inter-cle marker FM1-43,we elucidate specialized features nalized vesicles may be recycled by first fusing with of the vesicle cycle.Unlike retinal bipolar cell termi-intracellular endosomes from which new vesicles are nals,where stimulation triggers bulk membrane re-born (Heuser and Reese,1973;Ryan et al.,1996),espe-trieval,cone terminals appear to exclusively endocy-cially during intense stimulation (Richards et al.,2003).tose small vesicles.These retain their integrity until Finally,at conventional synapses only a small minority exocytosis,without pooling their membranes in endo-of vesicles is “readily releasable”(for review,see Zucker somes.Endocytosed vesicles rapidly disperse through and Regehr,2002).Most are relatively distant from re-the terminal and are reused with no apparent delay.lease sites and immobilized by being tethered to the Unlike other synapses where most vesicles are immo-cytoskeleton by proteins such as synapsin (Hilfiker et bilized and held in reserve,only a small fraction (?15%)al.,1999).These “reserve vesicles”are resistant to re-becomes immobilized in cones.Photobleaching ex-lease and only slowly equilibrate with the readily-releas-periments suggest that vesicles move by diffusion and able pool.Hence,a large fraction of synaptic membrane not by molecular motors on the cytoskeleton and that is side tracked from participating in the vesicle cycle.vesicle movement is not rate limiting for release.The The vesicle cycle at ribbon synapses has been studied huge reservoir of vesicles that move rapidly through-primarily in the retinal bipolar cell,which like photore-out cone terminals and the lack of a reserve pool are ceptors contain hundreds of thousands of synaptic vesi-unique features,providing cones with a steady supply cles and employ graded release (Lagnado et al.,1996;for continuous release.von Gersdorff et al.,1996).However,release from the bipolar cell has a strong phasic component.Step depo-Introduction
larization triggers a transient burst of release (6000vesi-cles released over 200ms)followed by a dramatic slow-Vertebrate photoreceptors tonically release neurotrans-ing,suggesting exhaustion of a readily-releasable pool mitter in the dark.To achieve a continuous cycle of that refills only after tens of seconds (von Gersdorff and exocytosis and endocytosis necessary for tonic release,Matthews,1997,1999).Tracer studies show that actively the photoreceptor terminal has functional and structural cycling vesicles remain within 1?m of the plasma mem-specializations.Exocytosis is unusually sensitive to Ca 2?brane (Lagnado et al.,1996;Paillart et al.,2003).Sus-(Rieke and Schwartz,1996),and vesicles are released tained stimulation eventually labels reserve vesicles in at an unusually high rate in the dark,allowing small the center of the bipolar terminal that appear immobile changes in light intensity to generate significant changes and resistant to release (Lagnado et al.,1996),although in neurotransmitter release (Ashmore and Copenhagen,recent studies challenge this view (Holt et al.,2004).In 1983;Rao-Mirotznik et al.,1998).Endocytosis occurs addition to endocytosis of small vesicles,stimulation with an unusually short delay after a rise in Ca 2?,rapidly triggers bulk membrane retrieval,resulting in large vacu-and accurately retrieving membrane added by exo-oles in the bipolar terminal (Holt et al.,2003;Paillart et cytosis (Rieke and Schwartz,1996).The photoreceptor al.,2003).
terminal has synaptic ribbons,the key structural special-How direct is the vesicle cycle in the cone synapse,ization that allows rapid and coordinated exocytosis and which unlike conventional synapses,tonically release endocytosis (for review,see von Gersdorff and Mat-transmitter?Is there bulk membrane retrieval or recy-cling through endosomes?Is there a large pool of immo-bilized reserve vesicles?Or,does the cone synapse
*Correspondence:rhkramer@https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,
Neuron
756
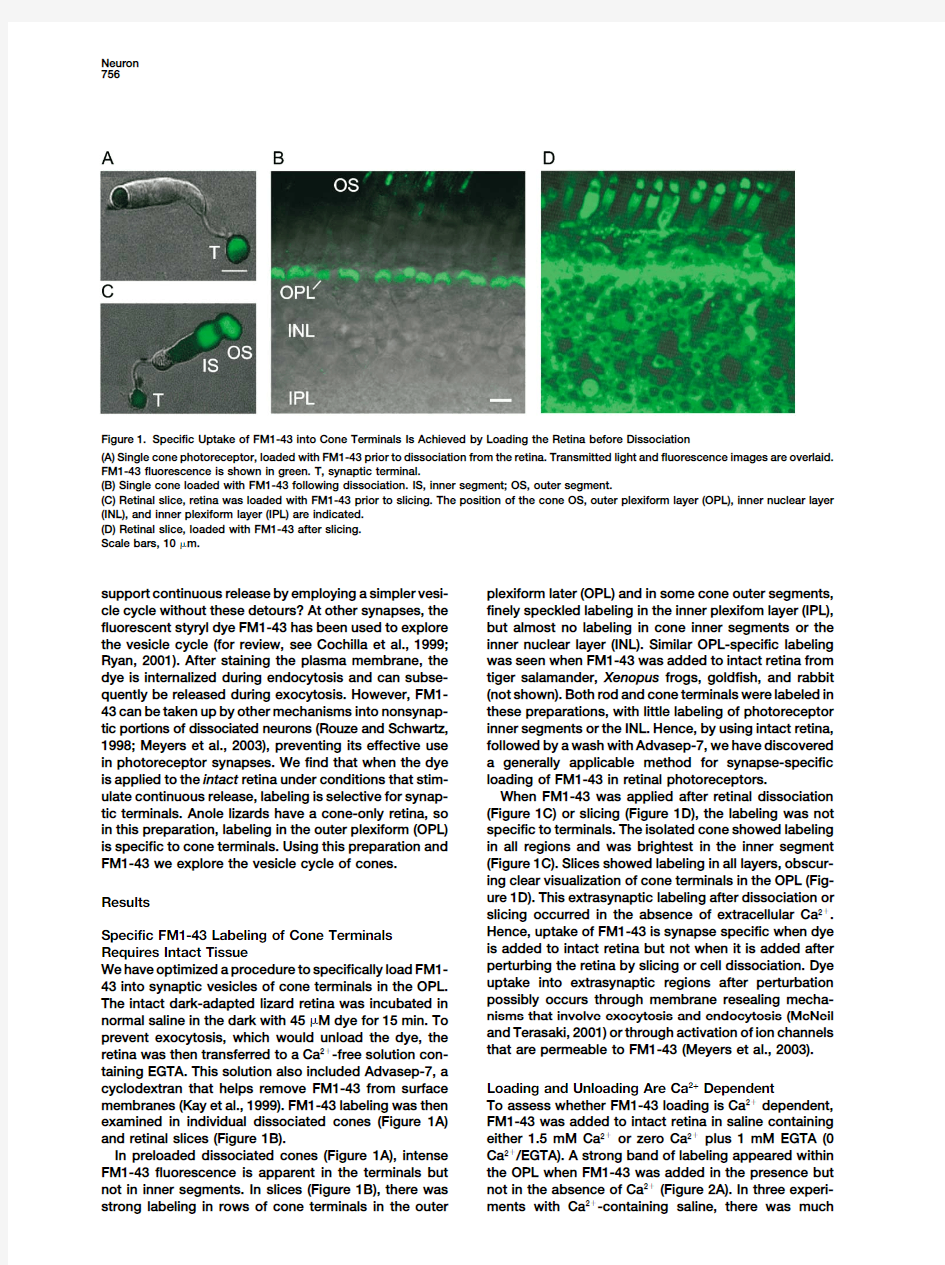
Figure1.Specific Uptake of FM1-43into Cone Terminals Is Achieved by Loading the Retina before Dissociation
(A)Single cone photoreceptor,loaded with FM1-43prior to dissociation from the retina.Transmitted light and fluorescence images are overlaid. FM1-43fluorescence is shown in green.T,synaptic terminal.
(B)Single cone loaded with FM1-43following dissociation.IS,inner segment;OS,outer segment.
(C)Retinal slice,retina was loaded with FM1-43prior to slicing.The position of the cone OS,outer plexiform layer(OPL),inner nuclear layer (INL),and inner plexiform layer(IPL)are indicated.
(D)Retinal slice,loaded with FM1-43after slicing.
Scale bars,10?m.
support continuous release by employing a simpler vesi-plexiform later(OPL)and in some cone outer segments,
finely speckled labeling in the inner plexifom layer(IPL), cle cycle without these detours?At other synapses,the
fluorescent styryl dye FM1-43has been used to explore but almost no labeling in cone inner segments or the the vesicle cycle(for review,see Cochilla et al.,1999;
inner nuclear layer(INL).Similar OPL-specific labeling Ryan,2001).After staining the plasma membrane,the was seen when FM1-43was added to intact retina from dye is internalized during endocytosis and can subse-
tiger salamander,Xenopus frogs,goldfish,and rabbit quently be released during exocytosis.However,FM1-(not shown).Both rod and cone terminals were labeled in
these preparations,with little labeling of photoreceptor 43can be taken up by other mechanisms into nonsynap-
tic portions of dissociated neurons(Rouze and Schwartz,inner segments or the INL.Hence,by using intact retina, 1998;Meyers et al.,2003),preventing its effective use
followed by a wash with Advasep-7,we have discovered in photoreceptor synapses.We find that when the dye a generally applicable method for synapse-specific is applied to the intact retina under conditions that stim-
loading of FM1-43in retinal photoreceptors.
ulate continuous release,labeling is selective for synap-When FM1-43was applied after retinal dissociation
(Figure1C)or slicing(Figure1D),the labeling was not tic terminals.Anole lizards have a cone-only retina,so
in this preparation,labeling in the outer plexiform(OPL)specific to terminals.The isolated cone showed labeling is specific to cone https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,ing this preparation and
in all regions and was brightest in the inner segment FM1-43we explore the vesicle cycle of cones.(Figure1C).Slices showed labeling in all layers,obscur-
ing clear visualization of cone terminals in the OPL(Fig-
ure1D).This extrasynaptic labeling after dissociation or Results
slicing occurred in the absence of extracellular Ca2?.
Hence,uptake of FM1-43is synapse specific when dye Specific FM1-43Labeling of Cone Terminals
is added to intact retina but not when it is added after Requires Intact Tissue
perturbing the retina by slicing or cell dissociation.Dye We have optimized a procedure to specifically load FM1-
uptake into extrasynaptic regions after perturbation 43into synaptic vesicles of cone terminals in the OPL.
possibly occurs through membrane resealing mecha-The intact dark-adapted lizard retina was incubated in
nisms that involve exocytosis and endocytosis(McNeil normal saline in the dark with45?M dye for15min.To
and Terasaki,2001)or through activation of ion channels prevent exocytosis,which would unload the dye,the
that are permeable to FM1-43(Meyers et al.,2003). retina was then transferred to a Ca2?-free solution con-
taining EGTA.This solution also included Advasep-7,a
cyclodextran that helps remove FM1-43from surface Loading and Unloading Are Ca2?Dependent membranes(Kay et al.,1999).FM1-43labeling was then
To assess whether FM1-43loading is Ca2?dependent, examined in individual dissociated cones(Figure1A)FM1-43was added to intact retina in saline containing and retinal slices(Figure1B).
either1.5mM Ca2?or zero Ca2?plus1mM EGTA(0 In preloaded dissociated cones(Figure1A),intense Ca2?/EGTA).A strong band of labeling appeared within FM1-43fluorescence is apparent in the terminals but
the OPL when FM1-43was added in the presence but not in inner segments.In slices(Figure1B),there was not in the absence of Ca2?(Figure2A).In three experi-strong labeling in rows of cone terminals in the outer
ments with Ca2?-containing saline,there was much
Streamlined Vesicle Cycle in Cone Photoreceptors
757
Figure2.Loading and Unloading of FM1-43
Is Ca2?Dependent
(A)Pseudocolor images of slices taken from
retina preloaded with FM1-43in the presence
or absence of Ca2?.Dashed boxes indicate
OPL and INL regions used for analysis of fluo-
rescence intensity,F.Scale bar,20?m.
(B)OPL fluorescence,F OPL,following Ca2?-
dependent and Ca2?-independent loading of
FM1-43.To compensate for differences in
background loading,the fluorescence of a
region of the IPL was subtracted(F OPL?F IPL).
(C)A single slice from retina preloaded with
FM1-43was imaged every30s in high K?,
Ca2?-free solution and1.5mM Ca2?was ap-
plied as indicated.Fluorescence measure-
ments across the OPL are plotted against
time.
(D)Average loss of fluorescence from retina
preloaded with FM1-43after different times
in high K?/Ca2?solutions(n?3–5slices).
(E)Kinetics of FM1-43loading in Ca2?/high
K?saline.Fluorescence measurements were
taken from the OPL of retina that were loaded
for indicated times.Continuous line is a single
exponential fit with??332s.
(F)Kinetics of FM1-43unloading in Ca2?/high
K?saline.Cone terminals in preloaded retina
were visualized in retina slices,and loss of
fluorescence was monitored at10s intervals.
Continuous line is a single exponential fit with
??345s.
greater labeling intensity in this region of the OPL com-slices of retina containing FM1-43-loaded terminals pared to a region of the same size in the INL,whereas
were exposed to Ca2?/high K?saline,and the decline in Ca2?-free saline,there was no difference in OPL ver-in fluorescence was measured at10s intervals(Figure
2F).These experiments showed that unloading also oc-sus INL labeling(Figure2B).Hence,FM1-43loading into
cone terminals is Ca2?dependent.curs over a single exponential time course(??345s; To assess whether un loading of FM1-43is also Ca2?
n?6).Hence,loading and unloading occur over a nearly dependent,retinas were loaded and sliced and then identical time course,consistent with the idea that endo-exposed to saline containing high K?(50mM)to depolar-
cytosis and exocytosis are closely linked in photorecep-ize cones and open voltage-gated Ca2?channels.In tor terminals(Rieke and Schwartz,1996).
an individual slice(Figure2C),FM1-43release could
repeatedly be started by exposure to Ca2?/high K?sa-Loaded FM1-43Is Restricted to Synaptic Vesicles line and stopped by exposure to0Ca2?/EGTA.Analysis
Electron micrographs of thin(90nm)sections showed of FM1-43release from many slices is shown in Figure the cone terminals to be densely packed with small 2D.All slices were incubated for a total period of15min
synaptic vesicles throughout the terminal(Figure3A). and exposed for various periods of time to Ca2?/high The terminals were roughly hemispherical with an aver-K?saline.Dye unloads progressively with increasing
age diameter of6?m,so we estimate from the number time in Ca2?,with more than half unloading within5min.of vesicles in a single section that a terminal contains Hence,unloading of FM1-43is Ca2?dependent.
about250,000synaptic https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,rger membranous To learn more about the kinetics of endocytosis and structures(endosomes or cisternae)were absent.Syn-exocytosis,we carefully examined the time course of
aptic ribbons were also seen at characteristic triad junc-FM1-43loading and unloading(Figures2E and2F).To tions with horizontal and bipolar cell dendrites,and there measure the kinetics of loading,intact retinas were ex-
were also a few mitochondria.
posed to dye in Ca2?/high K?saline for a variable time FM1-43inserts into plasma membrane and becomes (2–20min)before washing with0Ca2?/EGTA,slicing,
internalized upon endocytosis of vesicles(Betz et al., and analyzing fluorescence in cone terminals.Data from1992).However,FM1-43can also enter some cells 40retinas(n?3–6per time point)showed that dye
through ion channels,including the vanilloid receptor accumulation could be fit with a single exponential time(TRPV1)and a purinergic receptor(P2X2)(Meyers et al., course(??332s)that reached steady state within about
2003).Hence,under certain conditions,FM1-43loading 10min(Figure2E).To measure the rate of unloading,in retinal bipolar cells(Rouze and Schwartz,1998)and
Neuron
758
Figure3.AM1-43Is Localized to Synaptic
Vesicles
(A)Electron micrograph of a lizard cone termi-
nal filed with thousands of synaptic vesicles
dispersed throughout.Also shown are synap-
tic ribbons(r),postsynaptic dendrites from
horizontal and bipolar cells(hc and bc),and
mitochondria(mit).
(B)Photobleaching of AM1-43in the pres-
ence of DAB.The blue rectangle indicates the
region centered on the OPL that was exposed
to photobleaching laser light.Fluorescence
and transmitted light images are overlaid to
show AM1-43fluorescence(green)and DAB
reaction product(black)following photocon-
version.Scale bar,10?m.
(C)Semithin section of a slice photocon-
verted as in(B).The blue rectangle indicates
the photobleached region.DAB reaction
product in cone terminals appears brown.
The tissue was counterstained with Toluidine
blue.Scale bar,25?m.
(D and E)Electron micrographs of an AM1-
43photoconverted(D)and control(E)cone
terminal.Dense DAB reaction product is lo-
calized to synaptic vesicles in(D).Scale bar,
250nm.
cochlear hair cells(Meyers et al.,2003)does not require Movement of Endocytosed Vesicles
extracellular Ca2?and is not readily unloaded by promot-
Where do vesicles go after endocytosis in cone termi-ing Ca2?entry.Since some TRP channels are activated nals?To answer this question,cone terminals in intact by Ca2?(Launay et al.,2002),it seemed possible that
retina were loaded with FM1-43in the dark.The retina such channels could contribute to Ca2?-dependent up-was then washed with Advasep-7,to remove dye from take of FM1-43in cone terminals.To test whether load-
surface membranes,plus0Ca2?/EGTA,to prevent un-ing in cone terminals results exclusively from endocyto-loading.Then,in the continued presence of0Ca2?/
EGTA,we applied FM4-64to selectively stain surface sis,we used AM1-43,a structural analog of FM1-43that
can be crosslinked to proteins by fixation with glutaral-membranes.FM4-64is chemically similar to FM1-43,but dehyde.Intense illumination of AM1-43,in the presence
it has a different emission spectrum,allowing labeling by of diaminobenzidine(DAB),results in“photoconversion”the two dyes to be distinguished.Thus,green FM1-43 of the DAB to form an electron-dense reaction product
fluorescence appeared in the interior of cone terminals that is visible with electron microscopy(EM)(Henkel(Figure4A)with red FM4-64on the surface membranes
of cone terminals and other cells in the vicinity(Figure4B). et al.,1996a;Harata et al.,2001).Figure3B shows a
fluorescence image of a slice with AM1-43-loaded termi-Superimposing the two images(Figure4C)shows nals that had been photobleached by prolonged illumi-
FM1-43entirely filling the cone terminal,suggesting that nation with strong488nm light.Transmitted light images endocytosed vesicles are not restricted to specific re-from this slice show the brown reaction product local-
gions and that no additional structures external to the ized in cone terminals(Figure3C).EM images from pho-cone terminal are labeled with FM1-43.A density profile toconverted(Figure3C)and control regions(Figure3D)
taken through a terminal(Figure4D)shows that Ca2?-of the slice show that a large proportion(?80%)of dependent labeling with FM1-43and Ca2?-independent synaptic vesicles in the photoconverted region were
labeling with FM4-64show no overlap except within1 filled with electron-dense material,whereas in the con-?m of the membrane,near the limit of our spatial resolu-trol region,?1%of the vesicles were electron dense.
tion.Hence endocytosed vesicles disperse throughout Similar results were obtained in three experiments.cone terminals,and these are the only structures in the About50%of photoconverted vesicles had electron-
OPL that incorporate appreciable amounts of FM1-43. dense“coats,”suggesting a role for clathrin in endocy-How rapidly do endocytosed vesicles disperse?To tosis(Brodin et al.,2000;Slepnev and De Camilli,2000).
address this,we loaded with AM1-43in the dark,wash-Notably,photoconversion did not raise the background ing with Advasep-7and0Ca2?/EGTA,and then fixed density of cytoplasm,suggesting that AM1-43was re-
with glutaraldehyde.Fluorescence distributed nearly stricted to the lumen of vesicles.Hence,dye loading of evenly through the terminal,either with a2min or15 cone terminals occurs specifically through endocytosis
min loading period(Figures5A and5B).The normalized of vesicles.density profiles in Figure5C show that,even though
Streamlined Vesicle Cycle in Cone Photoreceptors
759
Figure4.FM1-43Fills the Entire Cone Terminal and No Other Structures in the OPL
(A)Confocal image of two cone terminals in a slice previously loaded with green FM1-43with Ca2?and then placed in red FM4-64without Ca2?.A500–550nm emission filter was used to pass only the FM1-43fluorescence.Scale bar,5?m.
(B)The same region imaged through a650LP filter to pass only FM4-64fluorescence.Gain settings were previously adjusted to remove bleedthrough of FM1-43fluorescence(about20%of the total signal).
(C)Overlay of images in(A)and(B),showing localization of the two dyes.Green labeling is in synaptic vesicles inside the terminals and red labeling is on surface membranes.
(D)Average fluorescence measured across one terminal,showing the intensity profile of both dyes.The region used for analysis is indicated in(C)(white dotted rectangle).
less total fluorescence is present,terminals loaded for the FM1-43such that vesicles within the region were ?2min show the same fluorescence profile as terminals
no longer fluorescent(Figure6A).Over time,the fluores-loaded for15min.cence within the bleached region recovered and fluores-After dispersal,do labeled vesicles remain mobile?To
cence in the remainder of the terminal decreased as address this question,loaded terminals were exposed to vesicles redistributed within the terminal.In control ex-Ca2?/high K?saline previously.Fluorescence remained
periments,application of high K?/Ca2?saline was effec-nearly uniform across the terminal,both after a short2tive in unloading the FM1-43that remained after local min unloading period(Figure5D)and a long15min
photobleaching,indicating that the procedure had not unloading period(Figure5E).Again,a density profile functionally damaged the terminal.Fluorescence inten-through the terminal shows that the distribution of fluo-
sity profiles across the terminal including the bleached rescence remains remarkably similar both at the begin-region show how the fluorescence has redistributed at ning and the end of the unloading period(Figure5F).
different times after the bleach(Figure6B).The mobility Hence,during unloading,labeled vesicles redistribute of vesicles in the terminal can be assessed by comparing rapidly and are drained from the entire terminal,leaving
the recovery of fluorescence in the bleached region to no local areas devoid of vesicles.the fluorescence across the whole terminal at each time To quantify vesicle mobility in cone terminals,we used
point.The fluorescence recovery can be fitted to a biex-Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching(FRAP)ponential function with time constants of?2s and9s (Figure6)in FM1-43-loaded terminals where vesicle cy-
(Figure6C).However,recovery is incomplete,such that cling had been stopped with0Ca2?/https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,ing a con-even after recovery reaches steady state(25s)the ratio focal scanning microscope,a small area(2?m2)in the
of fluorescence in the bleached to unbleached regions center of a cone terminal was scanned with an Argon is87%?2%(n?10).This suggests that about87% laser(488nm)at full power for about1.5s.This bleached
of vesicles are sufficiently mobile to exchange between
Neuron
760
Figure5.Vesicles Disperse Rapidly during FM1-43Loading and Remain Evenly Dispersed during Unloading
(A and B)Vesicles disperse evenly and rapidly during loading.FM1-43fluorescence in terminals following a2min(A)or15min(B)load with AM1-43.Slices were fixed with glutaraldehyde immediately after loading to prevent unloading during image acquisition.
(C)Very similar fluorescence profiles across the terminals loaded for2and15min.Average fluorescence,F,was normalized to peak average fluorescence,F peak.Analysis regions are indicated in(A)and(B)(red rectangles).
(D and E)Vesicles remain evenly dispersed during unloading.Retina was preloaded with FM1-43for15min and then unloaded in high K?solution for2(D)or15min(E).
(F)Very similar fluorescence profiles across the terminals unloaded for2and15min.
Scale bars,1?m.
the unbleached and bleached region(the mobile frac-applying a Ca2?ionophore.Adding5?M ionomycin in tion).This stands in stark contrast to the neuromuscular
conjunction with normal(1.5mM)external Ca2?in-junction,where FRAP measurements have shown that creased internal Ca2?from?50nM to?0.5?M within little recovery occurs even1hr after FM1-43photo-
2min(Rea et al.,unpublished data),but had no effect bleaching,indicating that vesicles are immobile(Henkel on the mobile fraction of vesicles(n?27)(Figure6D). et al.,1996b).
Neither adding1?M forskolin to activate adenylate cy-The position of the bleached region within the terminal clase and trigger cAMP production(n?26)nor adding
50?M8-Br-cAMP(n?13)affected vesicle mobility. did not substantially affect the rate or extent of FRAP.
This applied even to areas at the base of the terminal Hence,vesicle mobility does not appear to be regulated that should contain synaptic ribbons.However,differ-
by intracellular Ca2?or cAMP.Treatment with1?M ences in the mobility of free vesicles and those residing okadaic acid(OA),a protein phosphatase inhibitor,de-on ribbons may be difficult to resolve considering that
creased the percentage of mobile vesicles to74%?our EM evidence shows that less than1%of vesicles11%(n?8),slightly less than control(p?0.1).Okadaic reside on ribbons.
acid slows the spread of FM1-43fluorescence in bipolar Further analysis of the FRAP results provides an esti-cell terminals but has no effect on the kinetics of release
(Guatimosim et al.,2002).Together with these results, mate of the diffusion coefficient(D)for mobile synaptic
vesicles.To determine the rate of vesicle movement,our findings suggest that protein phosphorylation may we fitted the FRAP time course to the solution of the
play some role in regulating vesicle mobility,but it is diffusion equation based on a fit of the photobleach unlikely to have a large impact on vesicles cycling at profile with a Fourier expansion(Berk et al.,1993).This
ribbon synapses.
solution takes the form of an infinite series of exponen-
tials,but the first two terms are sufficient to describe Endocytosed Vesicles Retain Their Integrity
the FRAP time course.Hence,FRAP data were fitted
Throughout the Vesicle Cycle
with a double exponential function.By using the time To determine whether endocytosed vesicles retain their constant for the slowest component(9s),which was
identity or whether they fuse with other vesicles or endo-best resolved with our data acquisition,it was possible somes in cone terminals,we compared simultaneous
versus sequential loading of FM1-43and FM4-64.The to estimate D for synaptic vesicles within photoreceptor
terminals.This yielded a value of1.1?10?9cm2/s.Be-absorbance spectrum of FM4-64overlaps with the emis-cause D?(distance)2/6(time)for diffusion in three di-
sion spectrum of FM1-43,so when they are mixed mensions,a synaptic vesicle will on average move1?m together,FM4-64can quench FM1-43fluorescence in1.5s.
(Rouze and Schwartz,1998).To test whether vesicular Is the mobility of vesicles modulated by intracellular membranes intermingle during the vesicle cycle,we messengers that regulate the release rate?We tested
used the four protocols illustrated in Figure7.First,cone whether elevated intracellular Ca2?influences FRAP by terminals were loaded for15min in the dark with45?M
Streamlined Vesicle Cycle in Cone Photoreceptors
761
Figure6.FRAP Experiments Reveal Rapid Vesicle Mobility
(A)Series of images taken from a single terminal in a slice preloaded with FM1-43,showing fluorescence before and after photobleaching of a2?m2region(white square).Confocal section thickness was1.7?m.Scale bar,1?m.
(B)Profiles of average fluorescence,F,across the terminal.The white dotted rectangles in(A)indicate the profile region,and the shaded rectangle indicates the bleached region.
(C)Time course of FRAP for terminals in Ca2?-free saline.Photobleaching at time?0s.Average fluorescence in the bleached region was divided by average fluorescence over the whole terminal for each image.These ratios were then normalized to the ratio before the bleach (time??2s).Continuous line shows fit to a double exponential function with time constants of1.4and9s.
(D)The size of the mobile fraction of vesicles is unaffected by intracellular messengers.The mobile fraction was estimated from the percentage of FRAP measured at25s after bleach in slices incubated for30min with0Ca2?saline alone or saline also containing50?M8-Br cAMP,1?M forskolin,5?M ionomycin(with1.5mM Ca2?for15min),or1?M OA.Data are from three to five experiments in each case.
FM1-43alone(protocol1).This served as a reference To control for the possibility that the extra FM4-64added for the next experiment,in which the same concentration
in protocol2reduced FM1-43fluorescence not by of FM1-43was loaded for15min,but this time in the quenching but by saturating the uptake of the dye,we presence of90?M FM4-64(protocol2).Since FM1-43
examined terminals loaded with135?M FM1-43alone and FM4-64should label the same vesicles,protocol2for15min.The fluorescence signal in these terminals should establish the maximal amount of quenching
was1.4?0.02times larger than terminals loaded with when FM1-43and FM4-64are maximally intermixed in45?M FM1-43(n?6),a significant increase(p?0.01). the same internalized membranes.Third,we loaded45
Hence,dye uptake was not saturating in these experi-?M FM1-43for15min and then added90?M FM4-64ments.
for5min(protocol3).If the vesicles loaded with FM1-
Figure7(bottom)compares the results of protocols 43coalesce with vesicles containing FM4-64,there3and4.Loading sequentially with FM1-43for15min should be some quenching.Finally,FM1-43was loaded
and then FM4-64for5min results in a FM1-43produced for15min,followed by5min with neither dye(protocol fluorescence that was not significantly different(86%?4).This controlled for the unloading of FM1-43that
15%)from that obtained by loading with FM1-43for would occur during the5min of loading FM4-64in proto-15min followed by5min unloading(n?3).Hence, col3.
sequential loading does not allow quenching of FM1-43 Figure7(top)compares the results of protocols1and by FM4-64,suggesting that vesicles loaded separately 2.Simultaneous loading with FM1-43and FM4-64for
with one dye or the other do not intermix.
15min results in a69%?4%reduction in the FM1-43It is possible that,rather than fusing with an internal fluorescence(n?4),suggesting substantial quenching.
endosome after fission from the plasma membrane,
Neuron
762
Figure7.Vesicles Retain Their Integrity
Throughout the Vesicle Cycle
Retinas were loaded with four different proto-
cols.Protocol1(independent loading):FM1-
43was loaded for15min in the presence of
Ca2?and then transferred to Ca2?-free solu-
tion for imaging.Protocol2(simultaneous
loading):FM1-43and FM4-64were mixed to-
gether and then loaded for15min in the pres-
ence of Ca2?.Orange color indicates mixing
of the two dyes in the vesicle membrane.Pro-
tocol3(sequential loading):retina were
loaded with FM1-43for15min,washed in
Ca2?-free saline,and then loaded further with
FM4-64for5min.Diagram indicates the pos-
sibility that FM1-43and FM4-64may mix,if
vesicles individually containing one dye fuse
with endosomes,eventually producing vesi-
cles containing both dyes(orange).Note that
some FM1-43vesicles unload during the sec-
ond loading step.Protocol4:FM1-43was
loaded for15min and then unloaded in Ca2?
for5min to estimate the extent of FM1-43
unloading in the second step of protocol3.
Bar charts show the average FM1-43fluores-
cence,F,measured from terminals under
each condition,normalized to the fluores-
cence of terminals loaded by Protocol1,F1.
large vesicles are endocytosed and then subdivide to lizard cones,even when they have been strongly depo-form smaller synaptic vesicles.Evidence for endocyto-
larized with Ca2?/high K?saline.
sis of ferritin into large structures in retinal bipolar cells
has been obtained from EM observations(Paillart et Discussion
al.,2003)and using a tetrarhodamine-labeled40kDa
dextran(TAMRA-40K-DEX)which is also preferentially Activity-Dependent Loading of FM1-43
into Cone Terminals
taken up into large vacuoles(Holt et al.,2003).EM stud-
ies on chick photoreceptors also show that extracellular FM1-43is an important tool for studying presynaptic horseradish peroxidase tracer appears in large vacuoles
function and membrane trafficking in neurons and other in some photoreceptor terminals in a dark-dependent cell types(for review,see Cochilla et al.,1999;Ryan, manner(Cooper and McLaughlin,1983).To test whether
2001).It has been particularly useful for exploring synap-large vacuoles form in lizard cone terminals,we incu-tic function in ribbon synapses of retinal bipolar cells bated slices in Ca2?/high K?saline with TAMRA-40K-
(Lagnado et al.,1996;Rouze and Schwartz,1998;Mack DEX for15min(n?2)or30min(n?2).Subsequent et al.,2000;Zenisek et al.,2002;Guatimosim et al.,2002). examination of cone terminals with confocal microscopy
However,Ca2?-independent extrasynaptic labeling has showed TAMRA-40K-DEX internalization in26%(15precluded its use in dissociated photoreceptors.We
have shown that simply by applying the dye while the min)and18%(30min)of terminals as compared
to?95%when terminals were loaded with FM1-43.Ter-retina is still intact and then washing with Advasep-7, minals that did take up TAMRA-40K-DEX showed dif-
photoreceptor terminals are loaded selectively without fuse rather than punctate labeling,suggesting uptake labeling neighboring structures such as horizontal and into relatively small structures.Examination of EM im-
bipolar cell terminals.Loading and unloading are Ca2?ages also failed to show large vacuoles in any of20dependent,and electron microscopy shows that the dye cone terminals examined.Therefore,it is unlikely that
is located specifically in synaptic vesicles.Thus,even bulk membrane retrieval is a part of the vesicle cycle in though FM1-43can enter cells through routes other than
Streamlined Vesicle Cycle in Cone Photoreceptors
763
endocytosis(Rouze and Schwartz,1998;Meyers et al.,
2003),dye uptake into cone terminals in intact retina
occurs primarily through endocytosis of surface mem-
brane.
The synapse-specific loading of FM1-43has enabled
us to explore the vesicle cycle in cones.Moreover,activ-
ity-dependent loading and unloading opens the oppor-
tunity to explore how light and other stimuli regulate
transmitter release.Most of what we know about how
release is regulated comes indirectly from recordings
of postsynaptic responses from retinal bipolar and hori-
zontal cells.However,these responses are determined
not only by the rate of photoreceptor exocytosis but also
by diffusion in the synaptic cleft,the rate of glutamate
reuptake(Gaal et al.,1998),the properties of postsynap-
Figure8.The Steps in the Vesicle Cycle of Cones
tic glutamate receptors,and the effects of electrical
(1)Fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma membrane;(2a) and/or chemical feedback from HCs onto cone terminals retrieval by endocytosis of small vesicles;(3)dispersal of vesicles (Kamermans and Spekreijse,1999).It was established throughout the cone terminal;(4a)binding to a synaptic ribbon; long ago that cone terminals accumulate markers,such
(5)movement along the ribbon,priming,and docking to plasma
membrane;(1)fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma mem-as horseradish peroxidase,in small vesicles in the dark
brane.Our evidence suggests that step2b(bulk membrane re-(Ripps et al.,1976;Schacher et al.,1976;Schaeffer and
trieval),step4b(immobilization of vesicles by tethering to the cy-Raviola,1978).However,these experiments required
toskeleton),and step4c(fusion with an intracellular endosome)are long incubation times(hours)and labeling could not be not usual parts of the vesicle cycle.
observed in real time,but only after permeabilizing the
tissue.FM1-43allows direct measurement of how light
affects cone exocytosis in real time(Rea et al.,unpub-The vesicle cycle of cones does not seem to involve lished data).Moreover,measurements can be made not bulk membrane retrieval or an endosomal intermediate only on isolated cells but also on arrays of cone terminals step.When endocytosed vesicles are retrieved from the in retinal slices or retinal flat mounts(Rea et al.,unpub-plasma membrane,they must recoup important lipid lished data),allowing release to be evaluated as it occurs and protein constituents needed for the next round of in the intact system.Even though the OPL contains exocytosis.By avoiding the mixing of membrane con-horizontal,bipolar,and Mu¨ller glial cells along with pho-stituents that could occur in vacuoles formed by bulk toreceptor terminals,the only structures exhibiting con-membrane retrieval or by fusing vesicles with an endo-siderable membrane cycling in the dark,and therefore somal intermediate,cone terminals avoid the extra step FM1-43loading,are rod and cone terminals.Since anole of sorting and parsing out of these constituents as new lizards possess cones but no rods,we have discovered vesicles are born.Perhaps conventional synapses with a way to understand synaptic information transfer in a a large reserve pool can afford to side track at least defined synaptic layer of the CNS from a homogenous some of their vesicles through an endosomal intermedi-population of cells.ate(Heuser and Reese,1973;Ryan et al.,1996;Richards
et al.,2000).However,even at these synapses there is The Vesicle Cycle in Cones
evidence that many cycling vesicles retain their integrity Figure8shows our proposed sequence of events in the and are reused(Ceccarelli et al.,1973;Murthy and Ste-
vens,1998)and that endosomes may only be important vesicle cycle.After fusion of synaptic vesicles with the
membrane and release of the neurotransmitter gluta-with intense stimulation(Richards et al.,2003).Most mate(1),membrane is retrieved by endocytosis of small
conventional synapses are remote from neuronal so-vesicles(2a).Unlike other synapses,endocytosis does mata.These synapses might use an intermediate endo-not appear to involve bulk membrane retrieval(2b).En-
somal step in the vesicle cycle as a quality control mech-docytosed vesicles diffuse from their site of origin anism for extensively reused synaptic vesicle proteins. throughout the terminal(3)and eventually encounter
Perhaps the relatively close proximity of cone terminals and bind to a synaptic ribbon(4a).Steps4b and4c to inner segments makes such a step unnecessary. illustrate events that are common in many synapses but
Our diagram of the vesicle cycle does not include are,at most,of minor significance to the vesicle cycle much shorter cycles that might occur,including multiple of cones.Only a small proportion of vesicles become
rounds of kiss-and-run exocytosis,the shortest vesicle tethered to the cytoskeleton(4b),and there is no evi-cycle possible.Recent studies on hippocampal syn-dence for vesicles fusing and intermingling their mem-
apses in culture suggest that many fusion events are of branes with other vesicles in endosomes(4c).In con-the kiss-and-run variety(Aravanis et al.,2003;Gandhi trast,the high mobility of synaptic vesicles is important
and Stevens,2003),characterized by repeated transient for increasing the likelihood that vesicles will encounter and incomplete fusion of vesicles with the plasma mem-and bind to a synaptic ribbon(4a).Vesicles then move
brane.FM1-43is,at best,incompletely released during along the synaptic ribbon,are primed for release,and these events,because fusion pore openings are too dock to the plasma membrane(5).Elevated intracellular
brief to allow rapid release of the dye,which dissociates Ca2?triggers fusion of docked synaptic vesicles(1),slowly from membranes.However,FM2-10is more hy-completing the cycle.
drophilic,dissociates more rapidly,and therefore is fully
Neuron
764
released even during kiss-and-run exocytosis(Klingauf have no effect on mobility.Okadaic acid,a protein phos-
et al.,1998).We find no difference in the unloading rate
phatase inhibitor,slightly decreases vesicle mobility in
of FM1-43and FM2-10during application of high K?/cones,suggesting that there might be some other phos-
Ca2?saline(Rea et al.,unpublished data).Therefore,the
phoprotein that can regulate interactions between syn-
vesicle cycling revealed by FM1-43may account for aptic vesicles and other structures in the cytoplasm.
nearly all of the transmitter release from the cone termi-
However,it appears that the mobility of vesicles and
nal,without involving kiss-and-run exocytosis.presumably their delivery to synaptic ribbons is largely
unregulated in cones.The average time required for a
synaptic vesicle to traverse a6?m diameter cone termi-Synaptic Vesicle Mobility
nal is seven times faster than the time constant of re-FM1-43-containing vesicles disperse evenly through
lease(48s versus345s),indicating that vesicle mobility cone terminals within2min after uptake.Even many
is not rate limiting for release.Therefore,subsequent minutes after dye uptake,vesicles remain mobile,sug-
steps in the vesicle cycle,for example,movement along gesting that most vesicles do not become tethered to
the ribbon,docking to the plasma membrane,or fusion the cytoskeleton.The percentage of vesicles that are
itself,must be rate limiting for continuous release.More-mobile and the diffusion rate of mobile vesicles are both
over,small changes in the size of the mobile fraction of unaffected by elevating Ca2?.This is in contrast to neu-
vesicles or in the rate of their movement should have romuscular and hippocampal synapses,where the mo-
little effect on release from cones.
bility of vesicles is highly restricted both before and
Most synaptic terminals,including those of retinal bi-during stimulation(Henkel et al.,1996b;Kraszewski et
polar cells(Lagnado et al.,1996;von Gersdorff et al., al.,1996).We have calculated the diffusion coefficient
1996),contain a large reserve pool of synaptic vesicles of synaptic vesicles in cones,which we measure as
that are relatively immobile and cannot easily be re-having an average diameter of about50nm(unpublished
leased.Strong and prolonged stimulation depletes the data).Assuming that the cytoplasmic viscosity and den-
readily-releasable pool,resulting in depression of the sity of the cytoskeletal matrix in cone terminals are simi-
rate of vesicle fusion and therefore synaptic transmis-lar to those of fibroblasts,the measured diffusion coeffi-
sion.With intense stimulation at phasic synapses,vesi-cient of synaptic vesicles(0.11?m2/s)is similar to the
cles are mobilized from the reserve pool to help replen-rate that an inert particle of similar diameter(50nm)
ish the readily-releasable pool(Hilfiker et al.,1999; would diffuse passively(0.15?m2/s)(Luby-Phelps et al.,
Zucker and Regehr,2002).In contrast,our results sug-1987).This suggests that synaptic vesicles in cones
gest that there is almost no reserve pool in cones.About diffuse without binding to structures that could hinder
87%of labeled vesicles remain mobile1hr after dye their movement.Consistent with this,synaptic vesicles
loading,the majority of vesicles in loaded terminals ap-in cones appear to move randomly with no particular
pear electron dense after photoconversion,and most directionality,for example,toward release sites at the
of the loaded dye can be released upon depolarization base of the terminal.
with high K?.
In bipolar cells,indirect measurements have sug-
The lack of a reserve pool and the huge number of gested that peripheral vesicles are mobile,but central
highly mobile vesicles insures that synaptic ribbons in vesicles are not(Lagnado et al.,1996).However,a recent
cones remain fully charged with synaptic vesicles.This study using more direct measures of mobility suggests
limits the extent of synaptic depression,even in the that most vesicles throughout the bipolar terminal are
face of a high tonic release rate in the dark.Intense mobile and that this is also unaffected by raising intracel-
stimulation of cochlear hair cells,which also have tonic lular Ca2?(Holt et al.,2004).These features of vesicle
synapses,depletes the number of docked vesicles and mobility are qualitatively similar to those in cone termi-
vesicles in the cytoplasm,but to a lesser extent the nals.Yet,vesicles move ten times more quickly in cone
number associated with ribbons(Lenzi et al.,2002).This terminals than in bipolar terminals.Thus,mobility seems
suggests that ribbons have a relatively high affinity for to correlate with the capacity for tonic release,with
vesicle binding.We propose that cytoplasmic vesicles conventional phasic terminals having immobile vesicles,
are kept highly mobile to help keep ribbons saturated tonic cone terminals having maximally mobile vesicles,
with vesicles.This should minimize fluctuations in the and phasic-tonic bipolar terminals having vesicles of
number of vesicles that are immediately available for intermediate mobility.
release,allowing changes in Ca2?-dependent exocy-At nearly all synapses,synaptic vesicles are tethered
tosis to accurately represent changes in illumination. to the cytoskeleton through the membrane-associated
protein synapsin,which binds to actin(Hilfiker et al.,
Experimental Procedures
1999).Intracellular Ca2?and cAMP,via CaMKII and PKA,
respectively,can trigger the phosphorylation of synap-
Retinal Preparation and FM Loading
sin,decreasing its affinity for actin.Synapsin phosphor-Anolis segrei lizards maintained on a12:12hr light:dark cycle were
ylation,and consequently mobilization of tethered vesi-used for all experiments.The care and use of these animals was
cles,is one of several Ca2?-and cAMP-mediated events
approved by the UC Berkeley Animal Care and Use Committee.
Eyes were removed following decapitation and pithing,and dark-that have been implicated in modulation of secretion
adapted on ice for30min in normal lizard saline(in mM:NaCl149; from presynaptic terminals.Remarkably,vertebrate
KCl4;CaCl21.5;MgCl21.5;HEPES10;glucose10;pH7.5)before rods and cones from nearly all species lack synapsin
removal of the retina.Enucleation was carried out in normal saline (Von Kreigstein et al.,1999;Morgans,2000).This may in the dark under infrared light,using IR viewers attached to a
account for the high mobility of synaptic vesicles in dissecting microscope.The retina was separated manually from the
cones and may also help explain why Ca2?and cAMP
retinal pigment epithelium(RPE)and loaded with dye(FM1-43,FM4-
Streamlined Vesicle Cycle in Cone Photoreceptors
765
64,or AM1-43)in normal saline for15min in the dark.Unless other-References
wise stated,loading was followed by washing in0Ca2?/EGTA solu-
tion(same as normal saline,but with1mM EGTA substituted for Aravanis,A.M.,Pyle,J.L.,and Tsien,R.W.(2003).Single synaptic 1.5mM Ca2?).FM or AM dyes were removed from external mem-
vesicles fusing transiently and successively without loss of identity. branes by washing with1mM Advasep-7(Kay et al.,1999)for15Nature423,643–647.
min.About1/3of the retina was cut from a position lateral to the Ashmore,J.F.,and Copenhagen,D.R.(1983).An analysis of trans-optic nerve and fovea and prepared for imaging.For retinal slices,mission from cones to hyperpolarizing bipolar cells in the retina of the piece of retina was flattened onto nitrocellulose paper with the the turtle.J.Physiol.340,569–597.
photoreceptor side uppermost and cut into300?m thick slices
Berk,D.A.,Yuan,F.,Leunig,M.,and Jain,R.K.(1993).Fluorescence using a tissue chopper.In experiments examining the distribution
photobleaching with spatial Fourier analysis:measurement of diffu-of dye at given time points of endocytosis,the tissue was fixed in
sion in light-scattering media.Biophys.J.65,2428–2436.
2.5%glutaraldehyde before slicing,within2min after dye loading.
Betz,W.J.,Mao,F.,and Bewick,G.S.(1992).Activity-dependent For dissociated cell preparations,the piece of retina was treated
fluorescent staining and destaining of living vertebrate motor nerve with10U/ml papain plus1mg/ml cysteine for15min,transferred
terminals.J.Neurosci.12,363–375.
to10mg/ml BSA for2min,and finally triturated gently five to ten
Brodin,L.,Low,P.,and Shupliakov,O.(2000).Sequential steps in times using a narrow glass pipette(0Ca2?/EGTA solution used for
clathrin-mediated synaptic vesicle endocytosis.Curr.Opin.Neuro-all three stages).A suspension of dissociated cones was then trans-
biol.10,312–320.
ferred onto a coverslip for imaging.
Ceccarelli,B.,Hurlbut,W.P.,and Mauro,A.(1973).Turnover of trans-
mitter and synaptic vesicles and the frog neuromuscular junction. Imaging
J.Cell Biol.57,499–524.
Images were obtained with a Zeiss Axioplan2upright microscope
Cochilla,A.J.,Angleson,J.K.,and Betz,W.J.(1999).Monitoring and Zeiss510confocal system equipped with a488nm argon laser.
secretory membrane with FM1–43fluorescence.Annu.Rev.Neu-Fluorescence was imaged with a63?achroplan,0.9NA water-
rosci.22,1–10.
immersion objective.Additional magnification,time series,and pho-
Cooper,N.G.,and McLaughlin,B.J.(1983).Tracer uptake by photo-tobleach protocols were controlled by Zeiss LSM acquisition soft-
receptor synaptic terminals.I.Dark-mediated effects.J.Ultrastruct. ware.For FRAP experiments,a2?m2region of the terminal was
Res.84,252–267.
continually scanned five times at maximum laser power(total pho-
tobleach time1.5s).For examination of dye localization within a Fuchs,P.A.,Glowatzki,E.,and Moser,T.(2003).The afferent syn-single terminal and for FRAP experiments,images were acquired apse of cochlear hair cells.Curr.Opin.Neurobiol.13,452–458. with a spatial resolution of33pixels per micron and optical section Gaal,L.,Roska,B.,Picaud,S.A.,Wu,S.M.,Marc,R.,and Werblin, thickness of1.7?m(?1Airy unit).Scion Image software(Scion F.S.(1998).Postsynaptic response kinetics are controlled by a gluta-Corporation,Frederick,MD)was used for image analysis.FM1-43mate transporter at cone photoreceptors.J.Neurophysiol.79, (or AM1-43)and FM4-64dyes were excited using the488nm laser190–196.
line,and emitted light was collected through a500-550BP or650LP
Gandhi,S.P.,and Stevens,C.F.(2003).Three modes of synaptic filter,respectively.In experiments examining FM4-64fluorescence
vesicular recycling revealed by single-vesicle imaging.Nature in double-loaded tissue,FM1-43bleedthrough into the650LP chan-
423,607–613.
nel was first assessed by imaging a sample loaded with FM1-43
Guatimosim,C.,Hull,C.,Von Gersdorff,H.,and Prado,M.A.(2002). alone,and the gain settings then reduced to below the threshold
Okadaic acid disrupts synaptic vesicle trafficking in a ribbon-type for FM1-43fluorescence.Variability among data is expressed as
synapse.J.Neurochem.82,1047–1057.
mean?SEM.Student’s t test was used to assess statistical signifi-
cance at p?0.05unless stated otherwise.Harata,N.,Ryan,T.A.,Smith,S.J.,Buchanan,J.,and Tsien,R.W.
(2001).Visualizing recycling synaptic vesicles in hippocampal neu-
rons by FM1–https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,A98, Electron Microscopy12748–12753.
Slices were prepared from retina previously loaded with45?M
Henkel,A.W.,Lubke,J.,and Betz,W.J.(1996a).FM1–43dye ultra-AM1-43.Slices were then fixed in2.5%glutaralydehyde in0.1M
structural localization in and release from frog motor nerve terminals. phosphate buffer(PBS)overnight at4?C.After fixation,slices were
https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,A93,1918–1923.
washed in100mM glycine solution for1hr to reduce glutaraldehyde
Henkel,A.W.,Simpson,L.L.,Ridge,R.M.,and Betz,W.J.(1996b). autofluorescence.Slices were then incubated in1mg/ml diamino-
Synaptic vesicle movements monitored by fluorescence recovery benzidine(DAB)solution(sonicated and filtered)in PBS at21?C for
after photobleaching in nerve terminals stained with FM1–43.J. 30min,before exchanging for fresh DAB solution.Photoconversion
Neurosci.16,3960–3967.
of DAB was achieved using a confocal microscope by focusing high
power,488nm light from an argon laser onto a60?m2region of Heuser,J.E.,and Reese,T.S.(1973).Evidence for recycling of synap-the slice to include a row of AM1-43-loaded terminals for8min.
tic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuro-Following photoconversion,the slice was trimmed to enable location muscular junction.J.Cell Biol.57,315–344.
of the photoconverted region and prepared for electron microscopy Hilfiker,S.,Pieribone,V.A.,Czernik,A.J.,Kao,H.T.,Augustine,G.J., by dehydration and embedding as described previously(von Gers-and Greengard,P.(1999).Synapsins as regulators of neurotransmit-dorff et al.,1996).ter release.Philos.Trans.R.Soc.Lond.B Biol.Sci.354,269–279.
Holt,M.,Cooke,A.,Wu,M.M.,and Lagnado,L.(2003).Bulk mem-
brane retrieval in the synaptic terminal of retinal bipolar cells.J. Acknowledgments
Neurosci.23,1329–1339.
We thank Sue Yeon Choi for help with TAMRA-40K-DEX experi-
Holt,M.,Cooke,A.,Neef,A.,and Lagnado,L.(2004).High mobility ments and Fred Lanni and Diek Wheeler for assistance with FRAP of vesicles supports continuous exocytosis at a ribbon synapse. analysis.This work was supported by NIH grants to R.H.K.
Curr.Biol.14,173–183.
(EY12608),E.S.L.(NS32385),and P.S.(EY08124)and a Fight for Kamermans,M.,and Spekreijse,H.(1999).The feedback pathway Sight grant(to R.H.K.).E.S.L.was a Miller Visiting Professor at from horizontal cells to cones.A mini review with a look ahead. UC Berkeley.Vision Res.39,2449–2468.
Kay,A.R.,Alfonso,A.,Alford,S.,Cline,H.T.,Holgado,A.M.,Sak-
mann,B.,Snitsarev,V.A.,Stricker,T.P.,Takahashi,M.,and Wu, Received:September24,2003
L.G.(1999).Imaging synaptic activity in intact brain and slices with Revised:January23,2004
FM1–43in C.elegans,lamprey,and rat.Neuron24,809–817. Accepted:February10,2004
Published online:February12,2004Klingauf,J.,Kavalali,E.T.,and Tsien,R.W.(1998).Kinetics and regu-
Neuron
766
lation of fast endocytosis at hippocampal synapses.Nature394,Stevens,C.F.,and Williams,J.H.(2000).“Kiss and run”exocytosis at 581–585.
hippocampal https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,A97,12828–12833.
Takei,K.,Mundigl,O.,Daniell,L.,and De Camilli,P.(1996).The Kraszewski,K.,Daniell,L.,Mundigl,O.,and Decamilli,P.(1996).
synaptic vesicle cycle:a single vesicle budding step involving Mobility of synaptic vesicles in nerve endings monitored by recovery
clathrin and dynamin.J.Cell Biol.133,1237–1250.
from photobleaching of synaptic vesicle-associated fluorescence.
J.Neurosci.16,5905–5913.Teng,H.,and Wilkinson,R.S.(2000).Clathrin-mediated endocytosis
near active zones in snake motor boutons.J.Neurosci.20,7986–Lagnado,L.,Gomis,A.,and Job,C.(1996).Continuous vesicle cy-
7993.
cling in the synaptic terminal of retinal bipolar cells.Neuron17,
957–967.von Gersdorff,H.,and Matthews,G.(1997).Depletion and replen-
ishment of vesicle pools at a ribbon-type synaptic terminal.J.Neu-Launay,P.,Fleig,A.,Perraud,A.L.,Scharenberg,A.M.,Penner,R.,
rosci.17,1919–1927.
and Kinet,J.P.(2002).TRPM4is a Ca2?-activated nonselective cat-
ion channel mediating cell membrane depolarization.Cell109,von Gersdorff,H.,and Matthews,G.(1999).Electrophysiology of 397–407.synaptic vesicle cycling.Annu.Rev.Physiol.61,725–752.
Lenzi,D.,Crum,J.,Ellisman,M.H.,and Roberts,W.M.(2002).Depo-von Gersdorff,H.,Vardi,E.,Matthews,G.,and Sterling,P.(1996). larization redistributes synaptic membrane and creates a gradient Evidence that vesicles on the synaptic ribbon of retinal bipolar neu-of vesicles on the synaptic body at a ribbon synapse.Neuron36,rons can be rapidly released.Neuron16,1221–1227.
649–659.Von Kriegstein,K.,Schmitz,F.,Link,E.,and Sudhof,T.C.(1999). Luby-Phelps,K.,Castle,P.E.,Taylor,D.L.,and Lanni,F.(1987).Distribution of synaptic vesicle proteins in the mammalian retina Hindered diffusion of inert tracer particles in the cytoplasm of mouse identifies obligatory and facultative components of ribbon synapses. https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,A84,4910–4913.Eur.J.Neurosci.11,1335–1348.
Mack,A.F.,Behrens,U.D.,and Wagner,H.J.(2000).Inhibitory con-Zenisek,D.,Steyer,J.A.,Feldman,M.E.,and Almers,W.(2002).A trol of synaptic activity in goldfish Mb bipolar cell terminals visual-membrane marker leaves synaptic vesicles in milliseconds after ized by FM1–43.Vis.Neurosci.17,823–829.exocytosis in retinal bipolar cells.Neuron35,1085–1097. McNeil,P.L.,and Terasaki,M.(2001).Coping with the inevitable:how Zucker,R.S.,and Regehr,W.G.(2002).Short-term synaptic plastic-cells repair a torn surface membrane.Nat.Cell Biol.3,E124–E129.ity.Annu.Rev.Physiol.64,355–405.
Meyers,J.R.,MacDonald,R.B.,Duggan,A.,Lenzi,D.,Standaert,
D.G.,Corwin,J.T.,and Corey,D.P.(2003).Lighting up the senses:
FM1–43loading of sensory cells through nonselective ion channels.
J.Neurosci.23,4054–4065.
Morgans,C.W.(2000).Presynaptic proteins of ribbon synapses in
the retina.Microsc.Res.Tech.50,141–150.
Murthy,V.N.,and Stevens,C.F.(1998).Synaptic vesicles retain their
identity through the endocytic cycle.Nature392,497–501.
Paillart,C.,Li,J.,Matthews,G.,and Sterling,P.(2003).Endocytosis
and vesicle recycling at a ribbon synapse.J.Neurosci.23,4092–
4099.
Pyle,J.L.,Kavalali,E.T.,Piedras-Renteria,E.S.,and Tsien,R.W.
(2000).Rapid reuse of readily releasable pool vesicles at hippocam-
pal synapses.Neuron28,221–231.
Rao-Mirotznik,R.,Buchsbaum,G.,and Sterling,P.(1998).Transmit-
ter concentration at a three-dimensional synapse.J.Neurophysiol.
80,3163–3172.
Richards,D.A.,Guatimosim,C.,and Betz,W.J.(2000).Two endo-
cytic recycling routes selectively fill two vesicle pools in frog motor
nerve terminals.Neuron27,551–559.
Richards,D.A.,Guatimosim,C.,Rizzoli,S.O.,and Betz,W.J.(2003).
Synaptic vesicle pools at the frog neuromuscular junction.Neuron
39,529–541.
Rieke,F.,and Schwartz,E.A.(1996).Asynchronous transmitter re-
lease:control of exocytosis and endocytosis at the salamander rod
synapse.J.Physiol.493,1–8.
Ripps,H.,Shakib,M.,and MacDonald,E.D.(1976).Peroxidase up-
take by photoreceptor terminals of the skate retina.J.Cell Biol.
70,86–96.
Rouze,N.C.,and Schwartz,E.A.(1998).Continuous and transient
vesicle cycling at a ribbon synapse.J.Neurosci.18,8614–8624.
Ryan,T.A.(2001).Presynaptic imaging techniques.Curr.Opin.Neu-
robiol.11,544–549.
Ryan,T.A.,Smith,S.J.,and Reuter,H.(1996).The timing of synaptic
vesicle https://www.360docs.net/doc/8411067227.html,A93,5567–5571.
Schacher,S.,Holtzman,E.,and Hood,D.C.(1976).Synaptic activity
of frog retinal photoreceptors.A peroxidase uptake study.J.Cell
Biol.70,178–192.
Schaeffer,S.F.,and Raviola,E.(1978).Membrane recycling in the
cone cell endings of the turtle retina.J.Cell Biol.79,802–825.
Slepnev,V.I.,and De Camilli,P.(2000).Accessory factors in clathrin-
dependent synaptic vesicle endocytosis.Nat.Rev.Neurosci.1,
161–172.
高中生自我评价8
高中生自我评价 下面是由提供的关于高中生自我评价的文章,欢迎阅读 1、基于下面的学习项目描述,您认为老师应该选择教授和评价哪些21世纪技能? 同学沉浸于中世纪时代,每个同学选择一个人物角色,例如国王或王后,并通过口头报告的形式来研究和扮演这个角色,包括了解这个角色在当时生活中的各个方面,此外,这个项目还包括设计和建造一个梦想城堡,并为国王准备一场盛宴。 A、信息素养 B、创造力 C、自主学习 D、解决问题 答案:AB 注通过角色扮演、口头陈述、建行梦想城堡和准备宴会,这个学习项目将为同学提供很多显示创造力的机会。同学还将通过调研中世纪的一个国王或王后来锻炼信息素养技能。 2、在一节数学课上,同学正在为设计操场进行以下活动,可以用哪些活动来作评价? A、为操场设施拍摄照片作为收集的数据。 B、与老师会面说明他们如何选择特定图片上传到上。 C、在社区成员中做问卷调查。
D、完成操场设计,填写项目计划书。 答案:BD 注老师可以通过师生讨论会来了解同学的思考过程,同学可以通过项目计划书来监督自己的工作。图片拍摄和问卷调查在此则不用作评价目标。 3、下面哪些是有关形成性评价的描述? A、形成性评价的目标是评定分数 B、形成性评价是持续进行的评价 C、形成性评价贯穿于整个课堂活动中 D、形成性评价由老师和同学共同完成 答案:BCD 注形成性评价贯穿于整个课堂活动中,并由老师和同学共同完成,可以给同学和老师提供反馈,而不仅用于评定分数。 4、下面哪些是关于终结性评价的正确描述? A、可以包括小测验和考试,也可以是关于技能或过程的展示 B、发生在一个学习项目或单元的中间 C、贯穿于整个项目,用于改善学习和改进教学 D、测试对一项技能的掌握情况 答案:AD 注终结性评价在学习结束阶段使用。
生化 期末复习
第二章蛋白质的结构与功能 蛋白质元素组成:C、H、O、N、S。 特点:各种蛋白质含氮量接近,平均为16% 100克样品中蛋白质含量(g%)=每克样品含氮克数×6.25×100 氨基酸:蛋白质的基本组成单位,蛋白质是高分子化合物,可以受酸、碱或蛋白酶作用水解为氨基酸。 分类:①非极性侧链氨基酸 ②极性中性侧链氨基酸 ③酸性氨基酸(含有两个羧基)(谷氨酸、天冬氨酸) ④碱性氨基酸(含有两个以上氨基)(精氨酸、赖氨酸、组氨酸) 通式:组成人体的氨基酸均为L构型(L—α—氨基酸,氨基在左侧) D构型(D—α—氨基酸,氨基在右侧) 氨基酸之间通过肽键连接。 蛋白质的一级结构:在蛋白质分子中,从N—端至C—端的氨基酸排列顺序称为蛋白质的一级结构。 胰岛素一级结构:胰岛素由51个氨基酸残基组成,3个二硫键(在A6与A11、A20与B19、A7与B7号半胱氨酸之间)。 蛋白质二级结构连接键:氢键。 形式:α—螺旋:①多肽链主链以肽单元为单位。 ②螺旋每圈含3.6个氨基酸残基。 ③螺旋中的每个肽键的亚氨基氢和第四个肽键的酰基氧相互靠近形成氢键。 ④各氨基酸残基的R集团伸向螺旋外侧。 Β—折叠:①多肽链呈伸展状态。 ②两段以上的β—折叠结构平行排列,它们之间靠链间肽键的酰基氧与亚氨基氢形成氢键。 ③两条肽链的走向可以相同,也可以相反。 ④R基团交错伸向锯齿状结构的上下方。 Β—转角和无规则卷曲。 蛋白质三级结构:由一条多肽链构成的蛋白质,具有三级结构才能发挥生物学火性。 连接键:次级键。 蛋白质四级结构:指蛋白质分子中各亚基的空间排布及亚基接触部位的相互作用。 亚基:每一条多肽链都有完整的三级结构,称为亚基,亚基与亚基之间呈特定的三维空间排布,并以非共价键相连接。 等电点:净电荷为零,呈兼性离子状态,此时溶液的pH值称为该蛋白质的等电点。 蛋白质胶体性质的稳定因素:蛋白质表面的水化膜和电荷的排斥作用使蛋白质不易聚沉,稳定地分散在水中,成为稳定的亲水胶体。 蛋白质变性:在某些物理或化学因素作用下,蛋白质的空间结构受到破坏,从而导致其理化性质的改变和生物学活性的丧失(主要是二硫键和非共价键的破坏,不涉及一级结构的改变)。 改变:溶解度降低,黏度增加,结晶能力消失,生物学活性丧失,易被蛋白酶水解,光吸收性增加,分子不对称性增加。 因素:加热、乙醇等有机溶剂、强酸、强碱、重金属离子及生物碱试剂等。
高中生自我评价评语(共5篇)
篇一:高中生个人评价评语 1.一直来你总是孜孜不倦地认真学习,积极工作,尽自己的努力把学习和工作做好。由于目标明确、态度认真,因此成绩也不错。但工作时要注意方法,并要持之以恒,有始有终,以身作则,这样就会有更多的同学信任你、支持你。加油干吧,你一定会更加出色。 2.你性情敦厚,诚实可信,尊敬师长,团结同学,行为举止文明,你擅长足球,绿茵场上洒下了你的汗水。愿你打下扎实的文化基础,使你能在足球王国里腾飞,我愿做你最忠实的球迷! 3.这一学期你的成绩有点下降,并非你不努力,而是方法上有问题,我想这可能和你性格有关,你性格过于内向,思维的灵活性受到影响,平时也不敢发问。其实,你只要上课认真听,课后认真复习,有什么不懂的及时向别人请教,成绩是会跟上来的。努力吧! 4.在所有男同学中,我最喜欢批改你的作业了,清楚、整洁!平时讲文明、讲礼貌,但在学习上,你时而积极,时而又有些人偷懒,让老师很担心,希望你能严格要求自己,努力!再努力,争取更大的进步! 5.虽然平日你默默无闻,却看得出你样样要强。打扫卫生时,你把瓷砖擦得干干净净;学习时,你总是专心致志,勤学苦练,决不放过一个疑难问题;同学有困难时,你总能及时伸出温暖的手。愿你亲手培育的花儿更美丽! 6.默默无闻、踏踏实实、勤恳为大家的工作精神是大家所钦佩的,你是具有这种品质的孩子。娟秀的小字,干净的卷面都说明确你是一个认真仔细的好孩子。老师真为有你这样的学生而自豪,望你今后与书交朋友,做个知识渊博的人 7.你是我们班上的“小才女”,优秀的成绩,逼真的绘画,优美的字迹赢得了同学们的青睐。但你一定要记住:“天才出于勤奋”,老师希望你更加严格要求自己,不断进取,成为一个更出色的你。 8.你是我们班一位挺出色的学生,你画的画,形象逼真;你写的字,工整娟秀;你积极动脑,大胆发言;学习成绩好,工作能力强,是老师信得过的得力助手。不过更让大家佩服的是你还经常牺牲掉休息时间主动帮助学习有困难的同学。若能戒骄戒躁,持之以恒,你会更加优秀,更加可爱! 9.你活泼乐观,自信心强,尊敬老师,是你的最大优点,作业能按时完成,有强烈的好奇心,可惜的是你上课管不住自己,不守纪律,老师提出问题不经过深思熟虑,只想发表自己的见解,也不爱听同伴的发言,因此,问题回答不全面,希望你扬长避短,做个人见人爱的好学生。 10.课堂上,你的回答常给老师惊喜,你的口头表达能力很强,但由于平时不够勤奋,练笔不多,你的写作水平提高不快,希望思维独特的你,要正视自己的缺点,虚心好学,认真作业,把你的聪明才智发挥出来,做生活、学习中的强者。 13.在老师的眼里,你是一位很乖巧可爱的女孩,你的嗓音细嫩甜美,你的字迹潇洒漂亮。看你平时不多言多语,课堂上你却专心听讲,认真完成作业,常常受到同学和老师的赞赏。如果课堂上你也能把手举得高高的,让同学听听你那独到的见解,那就更好了!老师期待着…… 14.你生性好动,聪明活泼,是人见人爱的“小精灵”。老师最喜欢听到你响亮而又有感情的回答。对待学习一丝不苟。希望你更加努力,不断拓宽自己的知识面,取得更加辉煌的成绩。 15.当你一次次主动地帮助同学打扫教室时,当你为一道难题凝神沉思时,当你单薄的身体奔跑在运动场上时,不发你弯腰拾起地上的纸屑时……作为老师的我,是多么的高兴!我为你的热心、勤奋和勇敢而高兴!今后学习应多思多问,多花点时间掌握基础知识。 16.每当遇到什么事,老师总是能看到你那很有主见的身影,忽闪的眼睛代表了你的智慧。可是,为什么你上课总是心不在焉,做作业时马虎粗心呢?老师在期待:你高高举起的双手、
三羧酸循环-河北科技大学大学英语精品课
第 22 次课 2 学时 注:本页为每次课教案首页 2,4,6,7,8 《生物化学》科学出版社 现代生物学精要速览中文版 王镜岩等译 高等教育出版社 罗纪盛等
第十章糖代谢(2) Glycometabolism 二、柠檬酸循环(TCA,1953年获得诺贝尔奖) ?EMP:G--------→2丙酮酸(在细胞浆中) ?丙酮酸进线粒体--→乙酰CoA ?TCA:乙酰CoA进入TCA(在线粒体基质中) ?电子传递水平磷酸化(在线粒体内膜上) 1.EMP G--------→2丙酮酸 ●净得2ATP ●得2NADH+H+ 2. TCA(柠檬酸循环、三羧酸循环第92页) tricarboxylic acid cycle) Krebs循环 有氧条件下,将酵解作用产生的丙酮酸氧化脱羧成乙酰CoA,再经一系列氧化和脱羧,最终 生成二氧化碳和水并产生能量。 2 丙酮酸 + 2 GDP + 2 Pi + 4 H2O + 2 FAD + 8 NAD --------→6 CO2 + 2 GTP + 2 FADH2 + 8 NADH+H+ ?化学历程 ?能量计量 ?调控 ?生物学意义 三羧酸循环的发现历史 Albert Szent Gyorgyi观察用丙酮酸与肌肉组织一起在有氧条件下保温,丙酮酸可以被彻底氧化,生成二氧化碳和水。因此认为葡萄糖或糖原的有氧分解也循着糖酵解途径,有氧分解可以说是无氧分解的继续。 H. Krebs通过总结大量的实验结果,认为糖的氧化过程不是直线进行的,而是以循环方式进行。于是他于1937年提出了三羧酸循环假设并用实验证明了三羧酸循环的存在。 (1)化学历程 TCA循环的准备阶段:丙酮酸--→乙酰CoA TCA循环阶段: ①准备阶段(丙酮酸进入线粒体--→乙酰CoA) 丙酮酸 + CoA-SH + NAD+→ Acetyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+ 丙酮酸脱氢酶复合体系 有三种酶组成:三种酶均以二聚体的形式存在。 ?E1——丙酮酸脱氢酶(24条肽链) ?E2 ——二氢硫辛酸转乙酰基酶(24条肽链) ?E3——二氢硫辛酸脱氢酶(12条肽链) 砷化物:可与E2-SH共价结合,使酶失去活性。 练习题 ●糖酵解的终产物是丙酮酸 ●糖酵解的脱氢步骤反应是 ( )
高中生自我评价6篇
高中生自我评价6篇 【高中生的自我评价100字一】 本人在校热爱祖国,尊敬师长,团结同学,乐于助人,是老师的好帮手,同学的好朋友。我学习勤奋,积极向上,喜欢和同学讨论并解决问题,经常参加班级学校组织的各种课内外活动。 在家尊老爱幼,经常帮爸爸妈妈做家务是家长的好孩子,邻居的好榜样。 高中以来我学到了很多知识,思想比以前有了很大的提高,希望以后 能做一个有理想,有抱负,有文化的人,为建设社会主义中国做出自己的 努力。 【高中生的自我评价100字二】 本人遵纪守法,积极参加社会实践和文体活动。集体观念强,劳动积 极肯干。尊敬师长,团结同学,严于律己。学习目的明确,学习刻苦努力,能独立完成各科作业,学习成绩优秀。一年来,坚持出满勤,注重德、智、体全面发展,具有较好的综合素质。 【高中生的自我评价100字三】 本人自入学以来,一直遵守学校的各项规章制度,具有良好的思想道 德品质,各方面表现优秀。有强烈的集体荣誉感和工作责任心,坚持实事 求事的原则。思想端正,能吃苦耐劳,有崇高的理想和伟大的目标,注重 个人道德修养,养成良好的生活作风,乐于助人,关心国家大事。 【高中生的自我评价100字四】
本人认真遵守学校的规章制度,积极参加社会实践和文体活动,集体 观念强,劳动积极肯干。尊敬师长,团结同学。学习态度认真,能吃苦, 肯下功夫,成绩稳定上升。 希望能成为有理想有抱负,基础扎实,心理素质过硬、全面发展的优 秀学生。 【高中生的自我评价100字五】 本人能自觉遵守中学生守则,积极参加各项活动,尊敬师长,与同学 和睦相处,关心热爱集体,乐于帮助别人,劳动积极肯干,自觉锻炼身体,经常参加并组织班级学校组织的各种课内外活动。 【高中生的自我评价100字六】 本人品德兼优、性格开朗、热爱生活,有较强的实践能力和组织能力 学习之余,走出校门,本人珍惜每次锻炼的机会,与不同的人相处, 让自己近距离地接触社会,感受人生,品味生活的酸甜苦辣。
生化简答题(附答案)
1.简述脂类的消化与吸收。 2.何谓酮体?酮体是如何生成及氧化利用的? 3.为什么吃糖多了人体会发胖(写出主要反应过程)?脂肪能转变成葡萄糖吗?为什么? 4.简述脂肪肝的成因。 5.写出胆固醇合成的基本原料及关键酶?胆固醇在体内可的转变成哪些物质? 6.脂蛋白分为几类?各种脂蛋白的主要功用? 7.写出甘油的代谢途径? 8.简述饥饿或糖尿病患者,出现酮症的原因? 9.试比较生物氧化与体外物质氧化的异同。 10.试述影响氧化磷酸化的诸因素及其作用机制。 11.试述体内的能量生成、贮存和利用 12.试从蛋白质营养价值角度分析小儿偏食的害处。 13.参与蛋白质消化的酶有哪些?各自作用? 14.从蛋白质、氨基酸代谢角度分析严重肝功能障碍时肝昏迷的成因。 15.食物蛋白质消化产物是如何吸收的? 16.简述体内氨基酸代谢状况。 17.1分子天冬氨酸在肝脏彻底氧化分解生成水、二氧化碳和尿素可净生成多少分子ATP?简述代谢过程。 18.简述苯丙氨酸和酪氨酸在体内的分解代谢过程及常见的代谢疾病。 19.简述甲硫氨酸的主要代谢过程及意义。 20.简述谷胱甘肽在体内的生理功用。 21.简述维生素B6在氨基酸代谢中的作用。 22.讨论核苷酸在体内的主要生理功能
23.简述物质代谢的特点? 24.试述丙氨酸转变为脂肪的主要途径? 25.核苷、核苷酸、核酸三者在分子结构上的关系是怎样的? 26.参与DNA复制的酶在原核生物和真核生物有何异同? 27.复制的起始过程如何解链?引发体是怎样生成的? 28.解释遗传相对保守性及其变异性的生物学意义和分子基础。 29.什么是点突变、框移突变,其后果如何? 30.简述遗传密码的基本特点。 31.蛋白质生物合成体系包括哪些物质,各起什么作用。 32.简述原核生物基因转录调节的特点。阻遏蛋白与阻遏机制的普遍性。33.简述真核生物基因组结构特点。 34.同一生物体不同的组织细胞的基因组成和表达是否相同?为什么?35.简述重组DNA技术中目的基因的获取来源和途径。 36.作为基因工程的载体必须具备哪些条件? 37.什么叫基因重组?简述沙门氏菌是怎样逃避宿主免疫监视的?38.简述类固醇激素的信息传递过程。 39.简述血浆蛋白质的功能。 40.凝血因子有几种?简述其部分特点? 41.简述红细胞糖代谢的生理意义。 42.试述维生素A缺乏时,为什么会患夜盲症。 43.简述佝偻病的发病机理。 44.维生素K促进凝血的机理是什么?
高中生综合素质自我评价
高中生综合素质自我评价 高中生综合素质自我评价怎样写?下文是自我评价网提供参考的范文: 自我评价范文一 三年来,我遵纪遵法,尊敬师长,热心助人,与同学相处融洽。我有较强的集体荣誉感,努力为班为校做好事。作为一名团员,我思想进步,遵守社会公德,积极投身实践,关心国家大事。在团组织的领导下,力求更好地锻炼自己,进步自己的思想觉悟。 性格活泼开朗的我积极参加各种有益活动。高一年担任语文科代表,协助老师做好各项工作。参加市演讲比赛获三等奖。主持校知识竞赛,任小广播员。高二以来任班级文娱委员,组织同学参加各种活动,如:课间歌咏,班级联欢会,集体舞赛等。在校文艺汇演中任领唱,参加朗诵、小提琴表演。在校辩论赛在表现较出色,获“最佳辩手”称号。我爱好运动,积极参加体育锻炼,力求德、智、体全面发展,校运会上,在800米、200米及4×100米接力赛中均获较好名次。 自我评价范文二 三年的高中生活,使我增长了知识,也培养了我各方面的能力,为日后我成为社会主义现代化建设的接班人打下了坚实的基础。但是,通过三年的学习,我也发现了自己的不足,也就是吃苦精神不够,具体就体现在学习上“钻劲”不够、“挤劲”不够。当然,在我
发现自己的不足后,我会尽力完善自我,培养吃苦精神,从而保证日后的学习成绩能有较大幅度的提高。 作为跨世纪的一代,我们即将告别中学时代的酸甜苦辣,迈入高校去寻找另一片更加广阔的天空。在这最后的中学生活里,我将努力完善自我,提高学习成绩,为几年来的中学生活划上完美的句号,也以此为人生篇章中光辉的一页。 自我评价范文三 本人,热爱祖国,遵纪守法,以自己是一个中国人而感到自豪,祖国的每一点变化,都牵动着我的心,香港回归的日子,神州五号发射的日子,申奥成功的日子,都是我最难忘,最让我激动的日子,我和每一位热爱祖国的中国人一样,为那一时刻的到来而欢呼雀跃。 我从小养成了一个习惯。每当在电视里看到国旗升起的时候,就情不自禁地起立敬礼。曾经当过学校护旗手,也一直是我自豪和荣耀的经历。当国旗升起,国歌奏响后,我的内心就充满了自豪感,每天的新闻联播是我必看的内容。 学习之余,坐在车里,观看家乡的夜景,是让我最放松的一件事,这几年家乡的变化太大了,立交桥,景观大道,休闲广场,人们的生活环境越来越好了,我热爱祖国,热爱家乡,一定努力学习,争取为祖国和家乡的发展多做一份贡献。 自我评价范文四
食品添加剂的现状和发展趋势
食品添加剂的现状和发展趋势 食品添加剂是指在食品或食品加工中使用的各种微量的物质,通常其添加量不超过食品质量的2%。添加目的为:①改进和保持食品的营养价值;②延长食品的货架期;③方便食品的加工;④增强食品的风味,改变食品的色泽;⑤确保微生物的安全性;⑥保持食品品质的连续性和统一性。 1、食品添加剂市场 据统计,目前全球开发的食品添加剂总数已达1.4万多种,其中直接使用的品种有300o余种,常的有680余种。美国是世界上食品添加剂便用量最大、使用品种最多的国家.目前允许直接使用的有230o种以上,消费量已超过14o万吨(不包括淀粉及其衍生物、香精/香料和调味料);西欧消费量已近50075~,其中淀粉及其衍生物的数量高达40万吨。 食品添加剂已.成为医药、农用化学品及饲料添加剂之后的第四类倍受人们关注的精细化工行业。目前食品添加剂的世界市场价值为200亿美元,其中,调味品占30~,4、氢化胶体占17%、酸化剂占13%、调味增强剂占12%、甜味剂占6%、色素占5%、乳化剂占5%、维生素和矿物质占5%、酶占4%、化学防腐剂占2%、抗氧化剂占1%。j负计禾来5年内冥年增长率为2%-3%。全球调味品和香料的市场价值为12o亿美,其中调味品约占49%(59亿美元)。调味品市场中,饮料占31%、佐料占23%、奶制品占14%、其他占32%。需求增长最强劲的食品添加剂将是维生素、矿物质、调味增强剂和脂肪代用品。
罗氏(R.h)和巴斯夫公司是世界上重要的食品添加剂和精细化学品生产商。维生素是罗氏公司维生素和精细化学品部最大的业务部门,几乎占全球销售额的50%,其次是精细化学品占30%、类胡萝卜素占20%。罗氏新上市的营养药品包括用于眼科保健的玉米黄质、番茄红素和叶黄素,以及供功能饮料用的水溶性维生素E制品等。罗氏公司也加快投资中国市场,与上海新亚药业公司合资兴建了1000吨/年维生素B工厂,还有罗氏泰山(上海)维生素A新厂,以及在无锡兴建4万吨/年柠檬酸工厂。巴斯夫公司在全球维生素市场上约占25%的份额,该公司在韩国Gunsan建成3000吨/年维生素B 工厂和世界规模的维生素C及维生素B的工厂。 我国食品添加剂的生产随食品加工业的发展而不断发展壮大,目前已批准使用的添加剂共有21类1474种,产品门类齐全,基本可以满足食品工业的需要。我国各类食品添加剂的年产品量已超过200万吨,其中味精达60万吨以上,柠檬酸的产量近20万吨。表1列出我国主要的食品添加剂生产企业和产量。我国食品添加剂的总量已可以满足市场需求,但由于我国多数食品添加剂企业生产规模小,技术水平低,因此产品质量方面尚存在一些差距。因此少数用量少、档次高的食品添加剂仍依赖进El。一些合资的食品加工企业和引进的食品加工生产线为了保证其产品的质量,仍以较高的价格购买国外的同类产品。 2、营养添加剂 牛磺酸近年来,国内外研究表明,牛磺酸是一种具有多种生理功
生物化学
第一部分核酸 一、填空 1.核酸最初是从中分离出来的一种含磷较多的酸性物质。 2.核酸按组成不同分为和。RNA主要存在于中,功能是;DNA主要存在于,功能是。 3.核酸完全水解的产物有、、。 4.核酸中戊糖有和两种,在RNA中含,在DNA中含。核酸中的嘌呤碱有、两种,嘧啶碱有、和三种。 5.RNA中含有、、和四种含氮碱,DNA中含、、和四种含氮碱。 6.组成核酸的基本单位是,它由、和各一分子缩合而成。 7.1953年、提出DNA分子具有双螺旋结构假说。 8.DNA的二级结构为结构。RNA据其功能不同分为、、。 9.维持DNA双螺旋结构的维系力主要是和。 10.、、、是组成DNA的基本单位,、、、是组成RNA的基本单位。 二.名词 1、Tm 2、增色效应 3、DNA的复性 三、选择 1.已知一段DNA一条链为5'AGCTGACCTAGA3',其另一条互补链为()。 A 5'TCTAGGTCAGCT3' B 5'CUCAGGUCAGCU3' C 5'CACATTGAUTAT3' D 5'UCACUCGGGAUC3' 2.DNA变性后的特征变化是()。 A 磷酸二酯键断裂 B A260增高 C A280增高 D 分子量变小 3.已知某双链DNA的一条链中A=30%、G=24%,其互补链的碱基组成正确的是 A T和C 46% B A和T 46% C A和G 54 % D T和C 54% 4.作为第二信使的核苷酸是( ) A cAMP B cCMP C AMP D cUMP
5.DNA的T m值的叙述正确的是() A 与溶液浓度无关 B与分子大小无关 C 无种属特异性 D G—C碱基对含量高,T m值也高。 6.核酸分子中,储存遗传信息的关键部分是( ) A 戊糖磷酸的骨架 B 碱基序列 C 戊糖构象 D 磷酸二酯键 7.参与构成DNA分子的单糖是( ) A 核糖 B 脱氧核糖 C 葡萄糖 D 果糖 8.只存在于RNA而不存在于DNA的碱基是( ) A 尿嘧啶 B 腺嘌呤 C 鸟嘌呤 D 胞嘧啶 9.DNA是( ) A 核糖核苷酸 B 核糖核酸 C 脱氧核糖核酸 D 核蛋白体10.DNA的二级结构是() A 超螺旋 B 双螺旋 C 局部双螺旋 D 发夹式结构11.关于DNA和RNA彻底水解产物的叙述,正确的是() A 碱基相同,戊糖相同 B 碱基相同,戊糖不同 C 碱基不同,戊糖相同 D 部分碱基相同,戊糖不同 12.核酸最初是从()分离出的呈酸性的物质。 A 线粒体 B 细胞核 C 叶绿体 D 细胞质 13.DNA分子中碱基配对规律是();RNA分子中碱基配对规律是()。 A A-T,G-C B G-C,A-U C A-U,A-C D A-C,G-A 14.核酸一级结构的维系力是() A 氢键 B 磷酸二酯键 C 范德华力 D 碱基堆积力 15. 核酸分子中,碱基配对主要依赖于()化学键 A 氢键 B 糖苷键 C 磷酸二酯键 D 碱基堆积力 16.DNA的T m叙述正确的是() A 20%的DNA解链时的温度 B 40%的DNA解链时的温度 C 50%的DNA解链时的温度 D 60%的DNA解链时的温度 17.关于tRNA的叙述不正确的是() A 通常由70—90个核苷酸组成 B 含有较多稀有碱基
高中生综合自我评价-自我评价
高中生综合自我评价-自我评价 好好学习,天天向上,这句话无论在哪个时刻都是非常适用的。已经是一名高中生的你就要学会自我评价,这样才能够更好的成长起来。下面给大家分享的高中生综合自我评价,希望能够给大家一些帮助。 高中生综合自我评价 转眼间,一学期就快过去了,在这一学期中,我多次参加学校组织的集体活动和雏鹰小队校外活动,在课内更加努力地学习功课,与同学们团结友爱、互相帮助,自己各方面能力有了很大的进步。 在学校里,我有了很大的进步。比如关心同学,和同学互帮互助。在同学没有记作业时热情地帮助他,在值日生有事没法干值日时主动和他换班;同学在学校运动受伤时,陪他去医务室治疗;同学生病住院时,和老师、同学们一起去探望。数学作业的书写也有所提高,口算能力更是进了一大步。但是,语文作业的书写还需要努力,把“凤舞龙翔”改成“正楷端庄”。有时在学习的时候比较浮躁,这点也应该纠正。 在课外,我参加了学校组织的才艺展示:英语书法和篮球投篮的比赛。通过这些比赛,我不仅发现了自己的优点,还看到了自己的不足,找到了继续努力的方向。遗憾的是我没有作为班级篮球队成员参加学校的篮球比赛,没能和同学们一起去对抗强大的对手,但是在场
下,我仍然使劲地为他们加油;我还积极向“xx晚报校园周刊”投稿,《有趣的机器人课》成功的刊登在了报纸上。这些都使我为班级集体的荣誉尽到自己的努力。 我还参加了同学家长组织的“雏鹰小队活动”如:去千佛山和同学们一起讲一讲自己的国庆见闻,然后和同学们一起在草坪上欢乐地玩耍;和同学们在赛场下一起切磋切磋羽毛球……。这些都开阔了我的眼界,提高了自己的语言表达水平,增加了与别人沟通的能力。 这学期我有了新的优点,但同时也有缺点,我要保持优点,改正不足。 高中生综合自我评价2 宝剑锋从磨砺出,梅花香自苦寒来”,本人坚信通过不断地学习和努力,使自己成为一个有理想、有道德、有文化、有纪律的学生,以优异的成绩迎接挑战,为社会主义建设贡献我毕生的力量。 时光如梭,转眼即逝,当毕业在即,回首三年学习生活,历历在目: 三年来,学习上我严格要求自己,注意摸索适合自己情况的学习方法,积极思维,分析、解决问题能力强,学习成绩优良。 我遵纪守法,尊敬师长,热心助人,与同学相处融洽。我有较强的集体荣誉感,努力为班为校做好事。作为一名团员,我思想进步,遵守社会公德,积极投身实践,关心国家大事。在团组织的领导下,力求更好地锻炼自己,提高自己的,提高自己的思想觉悟。 性格活泼开朗的我积极参加各种有益活动。高一年担任语文科代
生物化学的发展
生物化学是一门较年轻的学科,在欧洲约在160年前开始,逐渐发展,一直到1903年才引进“生物化学”这个名词而成为一门独立的学科,但在我国,其发展可追溯到远古。我国古代劳动人民在饮食、营养、医、药等方面都有不少创造和发明,生物化学的发展可分为:叙述生物化学、动态生物化学及机能生物化学三个阶段。 (一)叙述生物化学阶段 1.饮食方面:公元前21世纪,我国人民已能造酒,相传夏人仪狄作酒,禹饮而甘之,作酒必用曲,故称曲为酒母,又叫做酶,与媒通,是促进谷物中主要成分的淀粉转化为酒的媒介物。现在我国生物化学工作者将促进生物体内化学反应的媒介物(即生物催化剂)统称为酶,从《周礼》的记载来推测,公元前12世纪以前,已能制饴,饴即今之麦芽糖,是大麦芽中的淀粉酶水解谷物中淀粉的产物。《周礼》称饴为五味之一。不但如此,在这同时,还能将酒发酵成醋。醋亦为五味之一。《周礼》上已有五味的描述。可见我国在上古时期,已使用生物体内一类很重要的有生物学活性的物质——酶,为饮食制作及加工的一种工具。这显然是酶学的萌芽时期。 2.营养方面:《黄帝内经·素问》的“藏气法时论”篇记载有“五谷为养,五畜为益,五果为助,五菜为充”,将食物分为四大类,并以“养”、“益”、“助”、“充”表明在营养上的价值。这在近代营养学中,也是配制完全膳食的一个好原则。谷类含淀粉较多,蛋白质亦不少,宜为人类主食,是生长、发育以及养生所需食物中之最主要者;动物食品含蛋白质,质优且丰富,但含脂肪较多,不宜过多食用,可用以增进谷类主食的营养价值而有益于健康,果品及蔬菜中无机盐类及维生素较为丰富,且属于粗纤维,有利食物消化及废物的排出;如果膳食能得到果品的辅助,蔬菜的充实,营养上显然是一个无可争辩的完全膳食。膳食疗法早在周秦时代即已开始应用,到唐代已有专书出现。盂诜(公元7世纪)著《食疗本草》及昝殷(约公元8世纪)著《食医必鉴》等二书,是我国最早的膳食疗法书籍。宋朝的《圣济总录》(公元前12世纪)是阐明食治的。元朝忽思慧(公元14世纪)针对不同疾患,提出应用的食物及其烹调方法,并编写成《饮膳正要》。由此可看出我国古代医务工作者应用营养方面的原理,试图治疗疾患的一些端倪。 3.医药方面:我国古代医学对某些营养缺乏病的治疗,也有所认识,如地方性甲状腺肿古称“瘿病”,主要是饮食中缺碘所致,有用含碘丰富的海带、海藻、紫菜等海产品防治。公元4世纪,葛洪著《肘后百一方》中载有用海藻酒治疗瘿病的方法。唐·王焘(公元8世纪)的《外台秘要》中载有疗瘿方36种,其中27种为含碘植物。而在欧洲直到公元1170年才有用海藻及海绵的灰分治疗此病者。脚气病是缺乏维生素B1的病。孙思邈(公元581~682年)早有详细研究,认为是一种食米区的疾病,分为“肿”、“不肿”及“脚气入心”三种,可用含有维生素B1的车前子、防风、杏仁、大豆、槟榔等治疗。酿酒用的曲及中药中的神曲(可生用)均含维生素B1较丰富,且具有水解糖类的酶,可用以补充维生素B1的不足,亦常用以治疗胃肠疾患。夜盲症古称“雀目”,是一种缺乏维主素A的病症。孙思邈首先用含维生素A较丰富的猪肝治疗。我国最早的眼科专著《龙木论》记载用苍术、地肤子、细辛、决明子等治疗雀目。这些药物都是含有维生素A原的植物。 我国研究药物最早者据传为神农。神衣后世又称炎帝,是始作方书,以疗民疾者。《越绝书》上有神农尝百草的记载。自此以后,我国人民开始用天然产品治疗疾病,如用羊靥(包括甲状腺的头部肌肉)治甲状腺肿,紫河车(胎盘)作强壮剂,蟾酥(蟾蜍皮肤疣的分泌物)
第二章 细胞生物学汇总
一、独立的生命单位 细胞是包含了全部生命信息和体现所有基本特点的独立的生命单位。 细胞包含3个体系: ●遗传信息的复制、维持和表达体系 ●新陈代谢体系 ●构成维持生命结构有序性体系,如细胞骨架系统 真核细胞是如何进化来的? 共生假说:认为真核细胞是一种复合体,它是若干原核细胞与真核细胞祖先的胞质共生 的结果 渐进式进化:认为原核细胞到真核细胞是一种渐进、直接进化的过程。 根据分子分类研究结果,却认为真核细胞、原核细胞和古细菌细胞同属于由共同祖先平行 进化而来的种类。 二、限制细胞大小的自然规律 ● Relationship Between Cells Volume(细胞体积) 一个生活细胞要维持正常的独立生活功能,最低限度需要容纳下为自身生存和繁殖 所必须的足够的DNA、蛋白质分子以及其他内部结构的空间(最低限度需要500~1000种不 同类型的酶和蛋白质)。 ● Cell Surface Area(表面积) 细胞必须有足够的表面积才能从环境中获得充足的营养和水分。 ◆细胞维持体积的相对恒定 1~10μm之间,而真核细胞的直径平均为3~30μm; ,如人的卵细胞直径只有0.1mm,而鸵鸟的卵细胞的直 径则有5cm; ,不依生物个体的大小而增大或缩小。如人、牛、马、 鼠、象的肾细胞、肝细胞的大小基本相同; ,与细胞的数量成正比,而与细胞的大小无关,把这种 现象为“细胞体积的守恒定律”。 细胞化学成分 水:85% 无机盐:1.5% 蛋白质:10% 脂质:2% 糖类:0.4% DNA: 0.4% RNA : 0.7% 三、原核细胞 主要特点 1.遗传物质仅一个环状DNA 2.无核膜,有细胞壁 3.无细胞器, 无细胞骨架 4.以无丝分裂或出芽繁殖 代表生物:支原体、细菌、蓝藻 四、真核细胞 三大结构体系 生物膜系统质膜、内膜系统(细胞器) 遗传信息表达系统染色质(体)、核糖体、mRNA、tRNA等等 细胞骨架系统胞质骨架、核骨架
高中生年度自我评价
高中生年度自我评价 高中生年度自我评价(一) 春去秋来,日复一日,高中上学期就如白驹过隙,转眼间过去了。蓦然回首,过去的一切深深地烙在我这颗心上了。刚来到望中报到 的那一天还历历在目,怪不得人们常说日月如梳!初一上学期生活, 虽然短暂,但我过得并不充实,成绩一落千丈。在此总结我这次的 考试情况以及这学期的学习态度: 这次考试不理想,一塌糊涂… 在我的学习成绩上,一直并不优秀,上学总是在伪装,在发呆,因为,当时在我的思想里完全找不到认真读书的念头,也没有意识 到读书的得益与不学习的后果。直到面临严峻的期末考试的前段时间,“无知”的我才意识到学习的重要性,我所意识的重要并不是 为考试而学习、为老师为家长而学习,而是为自己为未来为今后的 我而学习,学习就是我未来的基矗虽然我开始养成一种谦虚、勤问 的学习态度,我知道学习上的东西来不了弄虚作假,是不懂就不懂,绝不能不懂装懂!要想在学问上有所成就,古今中外所有的成功例子 都证明了只要保持这两种学习态度才行。所以,我一有问题就问同学,直到弄懂为止。即使是对待很差成绩的人我也是这样,其道理 就在孔夫子说过“三人行,必有我师”,但是,觉得我常常都是“得 过扯过”马马虎虎的混日子。 在娱乐上,我实施了每天给自己体育锻炼,每天二百个俯卧撑(标准、分次)、步行上学(早上跑步),在路程遥远的早上路途中, 不但长度跋涉还坚持至少跑一圈广常但为什么我在体育考试中这么 失败?原因是我当天过度疲劳,辛苦劳累的我在当时没有发挥基本水平。 纵上所述,虽然我在这个学期没有了一定的进步,而且还一落千丈,但是我最终也认识了自己的错误,并为之改正,我决定给自己
(发展战略)食品添加剂状态和发展方向
食品添加剂现状和发展趋势 食品添加剂是指在食品或食品加工中使用的各种微量的物质,通常其添加量不超过食品质量的2%。添加目的为:①改进和保持食品的营养价值;②延长食品的货架期;③方便食品的加工;④增强食品的风味,改变食品的色泽;⑤确保微生物的安全性;⑥保持食品品质的连续性和统一性。 l、食品添加剂市场 据统计,目前全球开发的食品添加剂总数已达1.4万多种,其中直接使用的品种有300o余种,常的有680余种。美国是世界上食品添加剂便用量最大、使用品种最多的国家.目前允许直接使用的有230o种以上,消费量已超过14o万吨(不包括淀粉及其衍生物、香精/香料和调味料);西欧消费量已近50075~,其中淀粉及其衍生物的数量高达40万吨。 食品添加剂已.成为医药、农用化学品及饲料添加剂之后的第四类倍受人们关注的精细化工行业。目前食品添加剂的世界市场价值为200亿美元,其中,调味品占30~,4、氢化胶体占17%、酸化剂占13%、调味增强剂占12%、甜味剂占6%、色素占5%、乳化剂占5%、维生素和矿物质占5%、酶占4%、化学防腐剂占2%、抗氧化剂占1%。j 负计禾来5年内冥年增长率为2%-3%。全球调味品和香料的市场价值为12o亿美,其中调味品约占49%(59亿美元)。调味品市场中,饮料占31%、佐料占23%、奶制品占14%、其他占32%。需求增长最强劲的食品添加剂将是维生素、矿物质、调味增强剂和脂肪代用品。
罗氏(R。h)和巴斯夫公司是世界上重要的食品添加剂和精细化学品生产商。维生素是罗氏公司维生素和精细化学品部最大的业务部门,几乎占全球销售额的50%,其次是精细化学品占30%、类胡萝卜素占20%。罗氏新上市的营养药品包括用于眼科保健的玉米黄质、番茄红素和叶黄素,以及供功能饮料用的水溶性维生素E制品等。罗氏公司也加快投资中国市场,与上海新亚药业公司合资兴建了1000吨/年维生素B工厂,还有罗氏泰山(上海)维生素A新厂,以及在无锡兴建4万吨/年柠檬酸工厂。巴斯夫公司在全球维生素市场上约占25%的份额,该公司在韩国Gunsan建成3000吨/年维生素B工厂和世界规模的维生素C及维生素B的工厂。
专升本生物化学问答题答案(A4)解读
专升本生物化学问答题答案(A4)解读
温医成教专升本《生物化学》思考题参考答案 下列打“*”号的为作业题,请按要求做好后在考试时上交 问答题部分:(答案供参考) 1、蛋白质的基本组成单位是什么?其结构特征是什么? 答:组成人体蛋白质的氨基酸仅有20种,且均属L-氨基酸(甘氨酸除外)。 *2、什么是蛋白质的二级结构?它主要形式有哪两种?各有何结构特征? 答:蛋白质分子中某一段肽链的局部空间结构,即该段肽链主链骨架原子的相对空间位置,并不涉及氨基酸残基侧链的构象。 α-螺旋、β-折叠。 α-螺旋:多肽链的主链围绕中心轴做有规律的螺旋上升,为右手螺旋,肽链中的全部肽键 都可形成氢键,以稳固α-螺旋结构。 β-折叠:多肽链充分伸展,每个肽单元以Cα为旋转点,依次折叠成锯齿状结构,肽链间形成氢键以稳固β-折叠结构。 *3、什么是蛋白质变性?变性的本质是什么?临床上的应用?(变性与沉淀的关系如何?)(考过的年份:2006 答:某些理化因素作用下,使蛋白质的空间构象遭到破坏,导致其理化性质改变和生物活性的丢失,称为蛋白质变性。 变性的本质:破坏非共价键和二硫键,不改变蛋白质的一级结构。 变性的应用:临床医学上,变性因素常被应用来消毒及灭菌。此外, 防止蛋白质变性也是有效保存蛋白质制剂(如疫苗等)的必要条件。 (变性与沉淀的关系:变性的蛋白质易于沉淀,有时蛋白质发生沉淀,但并不变性。) 4、简述细胞内主要的RNA及其主要功能。(同26
题) 答:信使RNA(mRNA):蛋白质合成的直接模板; 转运RNA(tRNA):氨基酸的运载工具及蛋白质物质合成的适配器; 核蛋白体RNA(rRNA):组成蛋白质合成场所的主要组分。 *5、简述真核生物mRNA的结构特点。 答:1. 大多数真核mRNA的5′末端均在转录后加上一个7-甲基鸟苷,同时第一个核苷酸的C′2也是甲基化,形成帽子结构:m7GpppNm-。 2. 大多数真核mRNA的3′末端有一个多聚腺苷酸(polyA)结构,称为多聚A尾。 6、简述tRNA的结构特点。 答:tRNA的一级结构特点:含10~20% 稀有碱基,如DHU;3′末端为— CCA-OH;5′末端大多数为G;具有T C 。 tRNA的二级结构特点:三叶草形,有氨基酸臂、DHU环、反密码环、额外环、TΨC环组成。tRNA的三级结构特点:倒L形。 7、试述酶与一般催化剂相比有哪些异同点。 答:酶与一般催化剂的共性:1.本身反应前后无变化,2.不改变化学反应平衡常数,3.降低反应的活化能 酶的催化特性:1. 高度的催化效率,2.高度专一性,3.高度的不稳定性,酶易失活,4.酶的催化活性的可调节性。 *8、何谓酶的竞争性抑制作用,其动力学特点如何?并以此解释磺胺药抑制细菌在体内繁殖的机理。 (举例说明酶的竞争性抑制作用及其实际应用意义)(考过的年份:2012、2011、2010、2009、2008 答:抑制剂与底物结构相似(1分),共同竞争酶的活
期末高中生自我评价及评定
---------------------------------------------------------------范文最新推荐------------------------------------------------------ 期末高中生自我评价及评定 期末高中生自我评价及评定 春去秋来,日复一日,初中上学期就如白驹过隙,转眼间过去了。蓦然回首,过去的一切深深地烙在我这颗心上了。刚来到望中报到的那一天还历历在目,怪不得人们常说日月如梳!初一上学期生活,虽然短暂,但我过得并不充实,成绩一落千丈。在此总结我这次的考试情况以及这学期的学习态度: 这次考试不理想,一塌糊涂 在我的学习成绩上,一直并不优秀,上学总是在伪装,在发呆,因为,当时在我的思想里完全找不到认真读书的念头,也没有意识到读书的得益与不学习的后果。直到面临严峻的期末考试的前段时间,无知的我才意识到学习的重要性,我所意识的重要并不是为考试而学习、为老师为家长而学习,而是为自己为未来为今后的我而学习,学习就是我未来的基矗虽然我开始养成一种谦虚、勤问的学习态度,我知道学习上的东西来不了弄虚作假,是不懂就不懂,绝不能不懂装懂!要想在学问上有所成就,古今中外所有的成功例子都证明了只要保持这两种学习态度才行期末高中生自我 1 / 17
评价及评定。所以,我一有问题就问同学,直到弄懂为止。即使是对待很差成绩的人我也是这样,其道理就在孔夫子说过三人行,必有我师,但是,觉得我常常都是得过扯过马马虎虎的混日子。 在生活上,我基本上都可以和同学们友好相处,和睦共处,互帮互爱,自己的事情自己做,形成独立自理自立的良好品德- ---最我觉得自豪的是,光明2年期间,我从来没有一次光顾洗衣部,即使是在寒冷的冬天,我也坚持自己洗衣服,不给自己偷懒的机会期末高中生自我评价及评定。因为我知道惰性这样东西是培养出来的,只要不给它一次机会,它就永远没有可能成为现实中的东西了。还有的是,我在生活中,始终保持干净的作风,做到勤清洁,勤洗手,养成良好的卫生习惯 在娱乐上,我实施了每天给自己体育锻炼,每天二百个俯卧撑(标准、分次)、步行上学(早上跑步),在路程遥远的早上路途中,不但长度跋涉还坚持至少跑一圈广常但为什么我在体育考试中这么失败?原因是我当天过度疲劳,辛苦劳累的我在当时没有发挥基本水平。纵上所述,虽然我在这个学期没有了一定的进步,而且还一落千丈,但是我最终也认识了自己的错误,并为之改正,我决定给自己制定一些措施,以便更好的
生物化学(简答题、问答题)
简答题、问答题 1.组成蛋白质的氨基酸有多少种?其结构特点是什么? 答:组成蛋白质的氨基酸有20种。结构特点:(1)除脯氨酸是α-亚氨基酸外,所有氨基酸均为α-氨基酸;(2)除甘氨酸外,其它氨基酸的α-碳原子(分子中第二个碳,Cα)均为不对称碳原子,D-型和L-型两种立体异构体,但天然蛋白质中的氨基酸都是L-型氨基酸;(3)氨基酸之间的不同,主要在于侧链R 的不同。 2.蛋白质分子结构可分为几级?维持各级结构的化学键是什么? 答:蛋白质分子结构分为一、二、三、四级;维持各级结构的化学键分别是肽键、二硫键,氢键,次级键(疏水键),次级键(疏水键)。 3、酶作为一种生物催化剂有何特点? 答:酶具有高效性、专一性、活性可调性。 4、解释酶的活性部位、必需基团二者之间的关系。 答: 必需基团 5、说明米氏常数的意义及应用。 答:米氏常数等于酶促反应速度为最大反应速度一半时的底物浓度。 应用: (1)米氏常数是酶的特征性常数,每一种酶都有它的Km 值,与酶的性质、催化的底物和酶促反应条件(如温度、pH 、有无抑制剂等)有关,而与酶浓度无关。 (2)K m 值可用于表示酶和底物亲和力的大小。 (3)当使用酶制剂时,可以根据K m 值判断使酶发挥一定反应速度时需要多大的底物浓度;在已规定底物浓度时,也可根据K m 值估算出酶能够获得多大的反应速度。 6、什么是竞争性和非竞争性抑制?试用一两种药物举例说明不可逆抑制剂和可逆抑制剂对酶的抑制作用? 答:竞争性抑制:抑制剂结构与底物的结构相似,它和底物同时竞争酶的活性中心,因而妨碍了底物与酶的结合,减少了酶分子的作用机会,从而降低了酶的活性。非竞争性抑制:抑制剂和底物不在酶的同一部位结合,抑制剂与底物之间无竞争性,酶与底物结合后,还可与抑制剂结合,或者酶和抑制剂结合后,也可再同底物结合,其结果是形成了三元复合物(ESI)。可逆抑制剂:增效联磺的杀菌作用:增效联磺抑制细菌的二氢叶酸合成酶、二氢叶酸还原酶德活性,使细菌体内四氢叶酸的合成受到双重抑制,使细菌因核酸的合成受阻而死亡。不可逆抑制剂:有机磷农药能共价结合胆碱酯酶活性中心上的羟基,使胆碱酯酶失活。临床药物解磷定(PAM )可解除有机磷化合物对胆碱酯酶的抑制。 7、简述糖酵解的生理意义。 答:(1)糖酵解是机体在缺氧情况下迅速获得能量的重要方式。例如剧烈{ 活性中心内 活性中心外 维持酶活性中心的空间构象 { 结合基团:能与底物结合 催化基团:催化底物发生化学反应
