[精选]高分子材料与工程专业部分翻译--资料
史上最全——高分子材料与工程专业英语词汇大全

全同间同等量聚合物
equitactic polymer
36
共聚物
copolymer
37
二元共聚物
binary copolymer
38
三元共聚物
terpolymer
39
多元聚合物
multipolymer
40
序列共聚物
sequential copolymer
41
多层共聚物
multilayer copolymer
高分子材料与工程专业词汇大全
(包含:一高分子化学二高分子反应三高分子物理四高分子加工技术和应用四大部分的全部词汇~~)
一高分子化学
新序码
汉文名
英文名
注释
1
高分子
macromolecule, polymer
又称“大分子”。
2
超高分子
supra polymer
3
天然高分子
natural polymer
4
73
活[性]高分子
living polymer
74
反应性聚合物
reactive polymer
75
极性聚合物
polar polymer
76
非极性聚合物
non-polar polymer
77
刚性链聚合物
rigid chain polymer
78
半柔性链聚合物
semi- flexible chain polymer
无机高分子
inorganic polymer
5
有机高分子
organic polymer
6
无机-有机高分子
inorganic organic polymer
高分子材料工程专业英语课文翻译 (2)

高分子材料工程专业英语课文翻译Polymer Science and Polymer Engineering are closely related andoften used interchangeably. Polymer Science is concerned with the chemistry and physics of polymers, while Polymer Engineering teaches students how to design and manufacture polymer products. No matter which field you choose, there is constant innovation and new developments in the field of Polymer Science and Engineering.高分子科学和高分子工程密切相关,常常互换使用。
高分子科学研究聚合物的化学和物理学,而高分子工程则教授学生如何设计和制造聚合物产品。
无论您选择哪个领域,高分子科学和工程的领域中都不断有创新和新发展。
Polymers are large molecules that are made up of repeating units called monomers. These molecules are characterized by their high molecular weight, which gives them unique properties such as strength, elasticity, and durability. There are many types of polymers, including plastics, rubbers, and fibers.聚合物是由称为单体的重复单位组成的大分子。
高分子材料工程专业英语课文翻译

Polymer Materials Engineering Professional EnglishText TranslationIntroductionAs an interdisciplinary field incorporating elements of both chemistry and engineering, Polymer Materials Engineering seeks to synthesize, process, and analyze polymers and polymer-based materialsfor a variety of industrial applications. Materials in this field can range from thermoplastics to thermosets, from elastomers to composites, and from gels to liquid crystals. The study of Polymer Materials Engineering is crucial for industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and electronics.To master Polymer Materials Engineering, one must not only have a solid foundation in engineering, chemistry, and physics, but also be proficient in technical English. Therefore, reading and translating English texts related to Polymer Materials Engineering is a vital skill for students and professionals in this field.In this article, we will provide a translation of an English text related to Polymer Materials Engineering, with the m of improving readers’ understanding and usage of specialized vocabulary in this field.Text TranslationOriginal English text:Rightly or wrongly, a connection often is made between themechanical performance of a polymeric material and its degree of crystallinity. The inference, however, can be incorrect as many other factors affect the mechanical response of polymer materials. Simply stated, crystalline regions are usually stronger and stiffer than amorphous regions. Generally, the degree of crystallinity that yields optimum properties depends on the polymer type and on the application.Translated text:通常我们会认为高分子材料的力学性能与其结晶度相关联,这种推论并不总是正确的。
高分子材料专业课程中英文名称与简介

生产实习(Advanced Practicum)本课程是材料科学与工程本科专业的必修课。
课程内容包括带生到工厂和科研院所了解和实践专业知识在实际生产中的应用。
同时配合仿真实习软件掌握化工生产工艺的操作,为学生进社会工作打好基础。
材料学院开课;预修:PSE3840T,PSE3620T。
橡胶工程高等实验(Rubber Engineering Advanced Experiment)本课程开设研制弹性体高分子材料的综合实验,以完成小型科题的训练为教学目标,培养学生的基本科研素质和创新能力。
教师给出科研课题,学生自行设计方案,完成材料选用、配合点、测试表征方案、结果与讨论等步骤。
最后撰写实验和研究报告。
材料学院开课;预修:PSE3620T,PSE3840PSE3421T。
文献查阅(Literature Searching)本课程的特点:是一门实践课;掌握文献检索的基本知识;工具书的使用方法;熟悉图书馆的检索方法;记住必要的专业术语;掌握相关检索工具的网络检索方法。
材料学院秋季开课预修:MSE2022T,MSE2140T,MSE3440T。
聚合物表征(Techniques for Characterization of Polymers)本课程是材料学专业的核心基础课程系统讲授聚合物结构与性能表征的分析方法,主要内容包括:波谱分析,聚合物分子质量及分子质量分布表征,聚合物微结构分析,聚合物热分析,聚合物流变性能分析,聚合物动态力学分析。
材料学院秋季开课;预修:PSE2150PSE2250T,PSE3620T。
橡胶制品及模具设计(Rubber Products and Mold Design)介绍国内外橡胶工业制品种类及生产,讲述橡胶模压制品设计一般要求和规律,讲述橡胶压模类型对制品的影响、结构设计、模具导向与定位、模具的尺寸与强关系、模具材料、热处理及表面处理的要求及模具的尺寸公差与配合、整体设计。
材料学院秋季开课;预修:M1120T,MEE2250T,MEE1640T。
史上最全——高分子材料与工程专业英语词汇大全
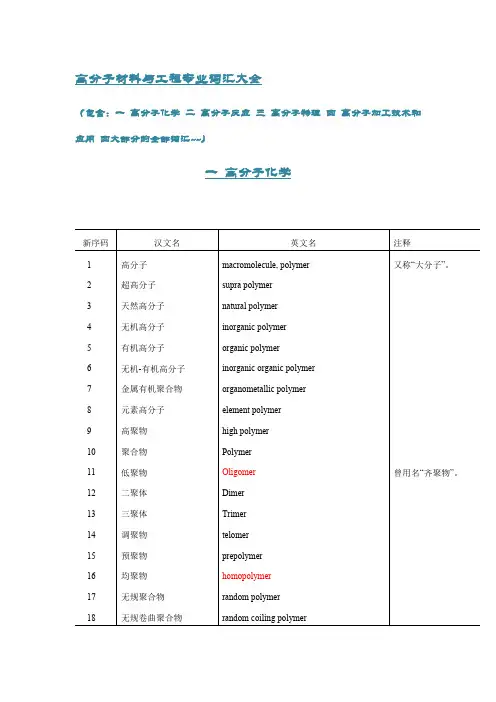
高分子材料与工程专业词汇大全(包含:一高分子化学二高分子反应三高分子物理四高分子加工技术和应用四大部分的全部词汇~~)一高分子化学新序码汉文名英文名注释1高分子macromolecule, polymer又称“大分子”。
2超高分子supra polymer3天然高分子natural polymer4无机高分子inorganic polymer5有机高分子organic polymer6无机-有机高分子inorganic organic polymer7金属有机聚合物organometallic polymer8元素高分子element polymer9高聚物high polymer10聚合物Polymer11低聚物Oligomer曾用名“齐聚物”。
12二聚体Dimer13三聚体Trimer14调聚物telomer15预聚物prepolymer16均聚物homopolymer17无规聚合物random polymer18无规卷曲聚合物random coiling polymer19头-头聚合物head-to-head polymer20头-尾聚合物head-to-tail polymer21尾-尾聚合物tail-to-tail polymer22反式有规聚合物transtactic polymer23顺式有规聚合物cistactic polymer24规整聚合物regular polymer25非规整聚合物irregular polymer26无规立构聚合物atactic polymer27全同立构聚合物isotactic polymer又称“等规聚合物”。
28间同立构聚合物syndiotactic polymer又称“间规聚合物”。
29杂同立构聚合物heterotactic polymer又称“异规聚合物”。
30有规立构聚合物stereoregular polymer, tactic polymer 又称“有规聚合物”。
史上最全——高分子材料与工程专业英语词汇大全 (1)

活[性]高分子
living polymer
74
反应性聚合物
reactive polymer
75
极性聚合物
polar polymer
76
非极性聚合物
non-polar polymer
77
刚性链聚合物
rigid chain polymer
78
半柔性链聚合物
semi- flexible chain polymer
单股聚合物
single-strand polymer
63
双股聚合物
double-strand polymer
64
多股聚合物
multi-strand polymer
65
链型聚合物
chain polymer
66
碳链聚合物
carbon chain polymer
67
杂链聚合物
heterochain polymer
53
多嵌段共聚物
segmented copolymer
54
杂聚物
heteropolymer
55
恒[组]分共聚物
azeotropic copolymer
56
多组分共聚物
multicomponent copolymer
57
单分散聚合物
monodisperse polymer, uniform polymer
58
多分散性聚合物
polydisperse polymer, non-uniform polymer
59
高分子共混物
polyblend, polymer blend
60
聚合物-聚合物配合物
高分子材料专业英语翻译
高分子材料专业英语翻译Polymer materials, also known as macromolecular materials, are a kind of material with high molecular weight composed of repeating structural units. They are widely used in various fields due to their excellent properties such as light weight, high strength, and good corrosion resistance. In recent years, the demand for polymer materials has been increasing, and the study of polymer materials has become a hot topic in the field of materials science. Therefore, it is necessary to have a good understanding of the professional English translation of polymer materials in order to better communicate and exchange ideas with international counterparts.Firstly, let's start with the translation of some basic concepts related to polymer materials. "Polymer" can be translated into "高分子" in Chinese, which refers to the macromolecular compounds formed by the polymerization of monomers. "Polymerization" can be translated as "聚合" or "聚合反应", which specifically refers to the chemical reaction process of monomers forming polymers. "Macromolecule" can be translated as "大分子", which refers to a molecule with a large molecular weight formed by the combination of a large number of atoms. "Monomer" can be translated as "单体", which refers to the small molecules that can polymerize into polymers. "Polymerization degree" can be translated as "聚合度", which refers to the number of monomer units in a polymer molecule.Secondly, it is important to understand the translation of the properties of polymer materials. "Light weight" can be translated as "轻质", which refers to the low density of polymer materials. "High strength" can be translated as "高强度", which refers to the ability of polymer materials to withstand external forces without deformation or fracture. "Corrosion resistance" can be translated as "耐腐蚀性", which refers to the ability of polymer materials to resist chemical or electrochemical corrosion. "Flexibility" can be translated as "柔韧性", which refers to the ability of polymer materials to bend or stretchwithout breaking. "Thermal stability" can be translated as "热稳定性", which refers to the ability of polymer materials to maintain their properties at high temperatures.Furthermore, it is necessary to understand the translation of the processing methods of polymer materials. "Extrusion" can be translated as "挤出", which refers to the process of forcing polymer materials through a die to form continuous shapes. "Injection molding" can be translated as "注塑", which refers to the process of injecting molten polymer materials into a mold to form a desired shape. "Blow molding" can be translated as "吹塑", which refers to the process of inflating molten polymer materials into a mold to form hollow shapes. "Compression molding" can be translated as "压缩成型", which refers to the process of placing polymer materials in a mold and applying pressure and heat to form a desired shape.In conclusion, the professional English translation of polymer materials is essential for researchers, engineers, and professionals in the field of materials science. By mastering the accurate translation of key concepts, properties, and processing methods of polymer materials, we can better communicate and collaborate with international counterparts, promote the exchange of knowledge and technology, and contribute to the development and application of polymer materials on a global scale.。
高分子材料专业英语课文翻译
A 高分子化学和高分子物理UNIT 1 What are Polymer?第一单元什么是高聚物?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt. To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands. These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’are made up of much smaller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds. To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound. Alternatively, individual rings could be of different sizes and materials, and interlinked to represent a polymer from molecules of different compounds.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。
2020年高分子材料与工程专业英语翻译精编版
A 高分子化学和高分子物理UNIT 1 What are Polymer?第一单元什么是高聚物?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt. To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands. These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’are made up of much smaller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds. To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound. Alternatively, individual rings could be of different sizes and materials, and interlinked to represent a polymer from molecules of different compounds.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。
高分子材料工程专业英语翻译全
第一单元什么是高聚物?什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。
与低分子化合物不同的是,普通盐的分子量仅仅是58.5,而高聚物的分子量高于105,甚至大于106。
这些大分子或“高分子〞由许多小分子组成。
小分子互相结合形成大分子,大分子可以是一种或多种化合物。
举例说明,想象一组大小一样并由一样的材料制成的环。
当这些环互相连接起来,可以把形成的链看成是具有同种分子量化合物组成的高聚物。
另一方面,独特的环可以大小不同、材料不同,相连接后形成具有不同分子量化合物组成的聚合物。
许多单元相连接给予了聚合物一个名称,poly意味着“多、聚、重复〞,mer意味着“链节、基体〞〔希腊语中〕。
例如:称为丁二烯的气态化合物,分子量为54,化合将近4000次,得到分子量大约为200000被称作聚丁二烯〔合成橡胶〕的高聚物。
形成高聚物的低分子化合物称为单体。
下面简单地描绘一下形成过程:丁二烯+丁二烯+…+丁二烯——→聚丁二烯〔4000次〕因此可以看到分子量仅为54的小分子物质〔单体〕如何逐渐形成分子量为200000的大分子〔高聚物〕。
本质上,正是由于聚合物的宏大的分子尺寸才使其性能不同于象苯这样的一般化合物。
例如,固态苯,在5.5℃熔融成液态苯,进一步加热,煮沸成气态苯。
与这类简单化合物明确的行为相比,像聚乙烯这样的聚合物不能在某一特定的温度快速地熔融成纯洁的液体。
而聚合物变得越来越软,最终,变成非常粘稠的聚合物熔融体。
将这种热而粘稠的聚合物熔融体进一步加热,不会转变成各种气体,但它不再是聚乙烯〔如图1.1〕。
固态苯——→液态苯——→气态苯加热,5.5℃加热,80℃固体聚乙烯——→熔化的聚乙烯——→各种分解产物-但不是聚乙烯加热加热图1.1 低分子量化合物〔苯〕和聚合物〔聚乙烯〕受热后的不同行为发现另一种不同的聚合物行为和低分子量化合物行为是关于溶解过程。
例如,让我们研究一下,将氯化钠渐渐地添加到固定量的水中。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
Most conveniently, polymers are generally subdivided in three categories, [namely]viz., plastics, rubbers and fibers.
Virtually,实际上,实质上,事实上
而后,这些结晶力实际上以交联方式作用,产生高拉伸强度和高初始模量的材料,如 纤维。
Therefore, a potential fiber polymer will not become a fiber unless subjected to a “drawing” process, i.e., a process resulting in a high degree of intermolecular orientation.
Phase,阶段,状态,方面,侧面; Exc(正如高分子化学的各个部分都可以看到的那样),在高分子化学的所有阶 段,我们都可以发现,这种分类方法有许多例外的情况。
An elastomer (or rubber) results from a polymer having relatively weak interchain forces and high molecular weights.
Modulus, moduli[复数],模量 In terms of…, 根据,借助于,利用,就。。。而言 Range(from)… to…,落在(从)。。。到。。。之间;分布在。。。
到。。。范围内。 Be situated on [at, in]… 处于,位于,坐落在 就初始弹性模量而言,橡胶一般在106到107达因/平方厘米,在尺度的低端,
而纤维具有高的初始模量,达到1010到1011达因/平方厘米,尺度的高端, 塑料的弹性模量一般在108到109达因/平方厘米,在尺度的中间。
UNIT 9 Structure and Properties of
Polymers 聚合物的结构和性质
As is found in all phases of polymer chemistry, there are many exceptions to this categorization.
come under,受。。。的影响(支配) more or less, 近乎,大体上,在不同程度上 permanently,永久地,持久地
因此,当聚合物被高度拉直的时候,取向分子链在不同程度取向的母体中将受强引力 的影响而“永久地结晶”。
These crystallization forces will then act virtually as crosslinks, resulting in a material of high tensile strength and high initial modulus, i.e., a fiber.
However, if the interchain forces are very great, a polymer will make a good fiber.
然而,如果分子链之间的力非常大,聚合物可以用做纤维。
Therefore, when the polymer is highly stretched, the oriented chain will come under the influence of the powerful attractive forces and will “crystallize” permanently in a more or less oriented matrix.
Subdivide, v. 细分,区分。 Subdivide…in…把。。。细分为。。。 Categories[kætigəri], n,种类,类型。Categorization, n, 分类法 很方便地,聚合物一般细分为三种类型,就是塑料,橡胶和纤维。
In terms of initial elastic modules, rubbers ranging generally between 106 to 107dynes/cm2, represent the lower end of the scale, while fibers with high initial moduli [modjulai, modulus的复数] of 1010 to 1011dynes/cm2 are situated on the upper end of the scale; plastics, having generally an initial elastic modulus of 108 to 109dynes/cm2, lie in-between.
straightened out,拉直,打开;stretch,拉直,拉长; extension,n,伸长, 伸展
attraction,引力,吸引;attraction for。。。 对。。。的引力 orient,v,定向,取向; retract,v,收缩
当通过一个拉伸过程将分子链拉直的时候,分子链彼此之间没有足够的相互 吸引力来保持其取向状态,作用力一旦解除,将发生收缩。这是弹性行 为的基础。
Result from…, (作为结果)发生,产生,形成 弹性体是具有相对弱的链之间作用力和高分子量的聚合物。
When the molecular chains are “straightened out” or stretched by a process of extension, they do not have sufficient attraction for each other to maintain the oriented state and will retract once the force is released. This is the basis of elastic behavior.
