浙大数据结构期末试卷-2012-2013
数据结构(本)期末综合练习(2013年6月)

数据结构(本)期末综合练习2013年6月期末综合练习一1. 在数据结构和算法中,与所使用的计算机有关的是()。
A.数据元数间的抽象关系B.数据的存储结构C.算法的时间复杂度 D.数据的逻辑结构2. 一种逻辑结构在存储时()。
A.只要存储数据元素间的关系 B.只能采用一种存储结构C.可采用不同的存储结构 D.只要存储数据元素的值3 .对顺序表,以下叙述中正确的是 ( )。
A.用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存放线性表的数据元素B.各个数据元素的首地址是连续的C.数据元素不能随机访问D.插入操作不需要移动元素4 .对链表, 以下叙述中正确的是()。
A.不能随机访问任一结点 B.结点占用的存储空间是连续的C.插入删除元素的操作一定要要移动结点 D.可以通过下标对链表进行直接访问5.设有一个长度为25的顺序表,要删除第10个元素(下标从1开始),需移动元素的个数为()。
A.9 B.10 C.15 D.166.线性表在存储后,如果相关操作是:要求已知第i个结点的位置访问该结点的前驱结点,则采用()存储方式是不可行的。
A.单链表 B.双链表 C.单循环链表 D.顺序表7. 设单向链表中,指针p指向结点A,若要删除A的直接后继,则所需修改指针的操作为( )。
A.p->next=p->next->next;B.p=p->next;C.p=p->next->next;D.p->next=p ;8.栈和队列的共同特点是()。
A.都是先进后出 B.元素都可以随机进出C.只容许在端点处插入和删除元素 D.都是先进先出9.元素1,3,5,7按顺序依次进栈,按该栈的可能输出序列依次入队列,该队列的可能输出序列是()。
(进栈出栈可以交替进行)。
A.7,5,3,1 B.7,3,1,5C.7,5,1,3 D.5,1,3,710.元素2,4,6,8按顺序依次进栈,按该栈的的可能输出序列依次入队列,该队列的可能输出序列是()(进栈出栈可以交替进行)。
数据结构期末考试卷试题包括答案

2012 年数据结构期末考试题及答案一、选择题1.在数据结构中,从逻辑上能够把数据结构分为C。
A.动向结构和静态结构B.紧凑结构和非紧凑结构C.线性结构和非线性结构D.内部结构和外面结构2.数据结构在计算机内存中的表示是指A。
A .数据的储存结构B.数据结构C.数据的逻辑结构D.数据元素之间的关系3.在数据结构中,与所使用的计算机没关的是数据的A结构。
A.逻辑B.储存C.逻辑和储存D.物理4.在储存数据时,往常不单要储存各数据元素的值,并且还要储存C。
A.数据的办理方法B.数据元素的种类C.数据元素之间的关系D.数据的储存方法5.在决定选用何种储存结构时,一般不考虑A。
A.各结点的值怎样B.结点个数的多少C.对数占有哪些运算D.所用的编程语言实现这类结构能否方便。
6.以下说法正确的选项是D。
A.数据项是数据的基本单位B.数据元素是数据的最小单位C.数据结构是带结构的数据项的会合D.一些表面上很不同样的数据能够有同样的逻辑结构7.算法剖析的目的是C,算法剖析的两个主要方面是A。
(1)A .找出数据结构的合理性B.研究算法中的输入和输出的关系C.剖析算法的效率以求改良C.剖析算法的易读性和文档性(2)A.空间复杂度和时间复杂度B.正确性和简洁性C.可读性和文档性D.数据复杂性和程序复杂性8.下边程序段的时间复杂度是O(n2)。
s=0;for( I = 0; i < n; i++)for( j=0;j <n;j++)s += B[i][j] ;sum = s ;9.下边程序段的时间复杂度是O(n*m )。
for( i = 0; i <n; i++)for( j=0;j <m;j ++)A[i][j] = 0;10.下边程序段的时间复杂度是O(log3n)。
i = 0;while(i <= n)i = i * 3 ;11.在以下的表达中,正确的选项是B。
A.线性表的次序储存结构优于链表储存结构B.二维数组是其数据元素为线性表的线性表C.栈的操作方式是先进先出D.行列的操作方式是先进后出12.往常要求同一逻辑结构中的全部数据元素拥有同样的特征,这意味着B。
《数据结构》期末考试试卷试题及答案

《数据结构》期末考试试卷试题及答案一、选择题(每题5分,共20分)1. 下列哪个不是线性结构?A. 栈B. 队列C. 图D. 数组2. 下列哪个不是栈的基本操作?A. 入栈B. 出栈C. 查找D. 判断栈空3. 下列哪个不是队列的基本操作?A. 入队B. 出队C. 查找D. 判断队列空4. 下列哪个不是图的基本概念?A. 顶点B. 边C. 路径D. 环二、填空题(每题5分,共20分)5. 栈是一种______结构的线性表,队列是一种______结构的线性表。
6. 图的顶点集记为V(G),边集记为E(G),则无向图G=(V(G),E(G)),有向图G=(______,______)。
7. 树的根结点的度为______,度为0的结点称为______。
8. 在二叉树中,一个结点的左子结点是指______的结点,右子结点是指______的结点。
三、简答题(每题10分,共30分)9. 简述线性表、栈、队列、图、树、二叉树的基本概念。
10. 简述二叉树的遍历方法。
11. 简述图的存储结构及其特点。
四、算法题(每题15分,共30分)12. 编写一个算法,实现栈的入栈操作。
13. 编写一个算法,实现队列的出队操作。
五、综合题(每题20分,共40分)14. 已知一个无向图G=(V,E),其中V={1,2,3,4,5},E={<1,2>,<1,3>,<2,4>,<3,4>,<4,5>},画出图G,并给出图G的邻接矩阵。
15. 已知一个二叉树,其前序遍历序列为ABDCE,中序遍历序列为DBACE,请画出该二叉树,并给出其后序遍历序列。
答案部分一、选择题答案1. C2. C3. C4. D二、填空题答案5. 后进先出先进先出6. V(G),E(G)7. 0 叶结点8. 左孩子右孩子三、简答题答案9. (1)线性表:一个线性结构,其特点是数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系。
2012-2013数据结构
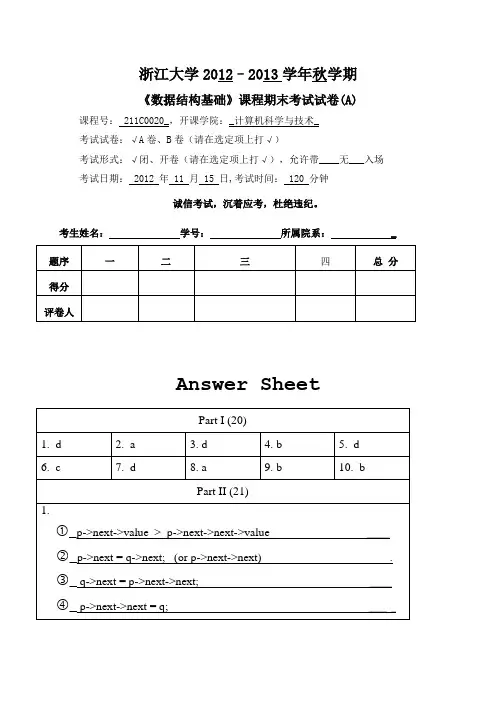
浙江大学2012–2013学年秋学期《数据结构基础》课程期末考试试卷(A) 课程号: 211C0020_,开课学院:_计算机科学与技术_考试试卷:√A卷、B卷(请在选定项上打√)考试形式:√闭、开卷(请在选定项上打√),允许带____无___入场考试日期: 2012 年 11 月 15 日,考试时间: 120 分钟诚信考试,沉着应考,杜绝违纪。
考生姓名:学号:所属院系: _Answer SheetNOTE: Please write your answers on the answer sheet.注意:请将答案填写在答题纸上。
I. Please select the answer for the following problems. (20 points)(1) Which one of the following statements is true as N grows?a. For any x , N x grows faster than !Nb. 2)(log N grows faster than Nc. 2log N grows faster than 2)(log Nd. N grows faster than 2)(log N N(2) What is the time complexity of the following function that computes X N ?long int Pow (long int X, unsigned int N) {if (N == 0) return 1;if (N == 1) return X;if (IsEven(N)) /* IsEven(N) returns 1 if N is even, or 0 otherwise */return Pow(X, N / 2) * Pow (X, N / 2);else return Pow(X * X, N / 2) * X;} a. O(N ) b. O(N log ) c. O(N N log ) d. O(N )(3) Suppose that N integers are pushed into and popped out of a stack. The input sequence is 1, 2, …, N and the output sequence is p 1, p 2, …, p N . If p 2 = 2, then p i (i>2) must be .a. ib. i+2c. N - id. cannot be determined(4) What is the major difference among lists, stacks, and queues? a. Lists use pointers, and stacks and queues use arraysb. Stacks and queues are lists with insertion/deletion constraintsc. Lists and queues can be implemented using circularly linked lists, but stacks cannotd. Stacks and queues are linear structures while lists are not(5) For an in-order threaded binary tree, if the pre-order and in-order traversal sequences are ABCDEF and CBAEDF respectively ,which pair nodes ’ right links are both threads?a. A and Bb. B and Dc. C and Dd. B and E(6) If N keys are hashed into the same slot, then to find these N keys, the minimum number of probes with linear probing is .a. N-1b. Nc. N(N+1)/2d. N+1(7) If an undirected graph with N vertices and E edges is represented by an adjacency matrix. How many zero elements are there in the matrix? a. E b. 2E c. N 2-E d. N 2-2E(8) If a directed graph is stored by an upper-triangular adjacency matrix –- that is, all the elements below the main diagonal are zero. Then its topological order .a. exists and must be uniqueb. exists but may not be uniquec. does not existd. cannot be determined(9)Sort a sequence of nine integers {4, 8, 3, 7, 9, 2, 10, 6, 5} by insertion sort. When 2 is moved to the first position, the number 8 must be at position (start from 1) .a. 4b. 5c. 6d. 7(10)Let T be a tree of N nodes created by union-by-height without path compression, then the depth of the tree isa. N/2b. O(logN)c. O(N2)d. O(1)II. Given the function descriptions of the following two (pseudo-code) programs, please fill in the blank lines. (21 points)(1)Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm. Suppose we have a list of integers and want to sort them in ascending order. Bubble sort repeatedly scans the list from the head to the tail, and swaps two adjacent numbers if they are in the wrong order. Please complete the following program to implement bubble sort. (12 points)struct node{int value;struct node *next;/* some other fields */}struct node BubbleSort (struct node *h){/* h is the head pointer of the list with a dummy head node */struct node *p, *q;int flag_swap;if (!h->next) return h;do{flag_swap = 0;p = h;while (p->next->next){if (① ){flag_swap++;q = p->next;② ;③ ;④ ;}else p = p->next;}} while (flag_swap > 0);return h;}(2)The function is to perform Find as a Union/Find operation with path compression. (9 points)SetType Find ( ElementType X, DisjSet S ){ElementType root, trail, lead;for ( root = X; S[ root ] > 0; ① );for ( trail = X; trail != root; ② ) {lead = S[ trail ] ;③ ;}return root ;}III. Please write or draw your answers for the following problems on the answer sheet. (44 points)(1) A sorting algorithm is stable if for any keys K i = K j for i < j,the corresponding records R i precedes R j in the sorted list.(a)Is Heap Sort stable? Please give a proof if your answer is“YES”, else please provide a counter example. (4 points)(b)Is Quick Sort stable? Please give a proof if your answer is“YES”, else please provide a counter example. (4 points)(2)Given the adjacency list representation of a directed graph.Suppose V1 is always the first vertex being visited. Please list(a)the depth-first search sequence; (5 points)(b)the breath-first search sequence; (5 points) and(c)the strongly connected components. (3 points)(3) A binary search tree is said to be of “type A”if all the keysalong the path from the root to any leaf node are in sorted order(either ascending or descending).(a)Given four keys {1, 2, 3, 4}, please draw all the possiblebinary search trees of type A. (4 points)(b)In general, given N keys {1, 2, …, N}, how many differentbinary search trees of type A can be constructed? (3 points)(4)Given a hash table of size 13 and the hash function H(key) = keymod 13. Assume that quadratic probing is used to solve collisions.Please fill in the hash table with input numbers {2, 15, 3, 16, 6,29, 24, 28}. (4 points)(5)Given eight keys {1, 2, …, 8}. Please do the following:(a)construct a complete binary tree which is also a binary searchtree; (5 points) and(b)construct a min-heap out of the array which stores thecomplete binary tree obtained from (a). Use BuildHeap with asequence of percolate-down’s. (4 points)(c)Observe the keys on each level of the min-heap obtained from(b). Is there a pattern of ordering? Is this true for moregeneral cases? (3 points)IV. Given a tree represented by left-child-right-sibling structure, please describe an algorithm that counts the number of leaf nodes on every level.(15 points)。
大学数据结构期末考试试题(有答案)

“数据结构”期末考试试题一、单选题(每小题2分,共12分)1.在一个单链表HL中,若要向表头插入一个由指针p指向的结点,则执行( )。
A. HL=ps p一>next=HLB. p一>next=HL;HL=p3C. p一>next=Hl;p=HL;D. p一>next=HL一>next;HL一>next=p;2.n个顶点的强连通图中至少含有( )。
A.n—l条有向边B.n条有向边C.n(n—1)/2条有向边D.n(n一1)条有向边3.从一棵二叉搜索树中查找一个元素时,其时间复杂度大致为( )。
A.O(1)B.O(n)C.O(1Ogzn)D.O(n2)4.由权值分别为3,8,6,2,5的叶子结点生成一棵哈夫曼树,它的带权路径长度为( )。
A.24 B.48C. 72 D. 535.当一个作为实际传递的对象占用的存储空间较大并可能需要修改时,应最好把它说明为( )参数,以节省参数值的传输时间和存储参数的空间。
A.整形B.引用型C.指针型D.常值引用型·6.向一个长度为n的顺序表中插人一个新元素的平均时间复杂度为( )。
A.O(n) B.O(1)C.O(n2) D.O(10g2n)二、填空题(每空1分,共28分)1.数据的存储结构被分为——、——、——和——四种。
2.在广义表的存储结构中,单元素结点与表元素结点有一个域对应不同,各自分别为——域和——域。
3.——中缀表达式 3十x*(2.4/5—6)所对应的后缀表达式为————。
4.在一棵高度为h的3叉树中,最多含有——结点。
5.假定一棵二叉树的结点数为18,则它的最小深度为——,最大深度为——·6.在一棵二叉搜索树中,每个分支结点的左子树上所有结点的值一定——该结点的值,右子树上所有结点的值一定——该结点的值。
7.当向一个小根堆插入一个具有最小值的元素时,该元素需要逐层——调整,直到被调整到——位置为止。
数据结构期末试题及答案

《数据结构》期末考试试卷一、选择题(单选题,每小题3分,共33分)1.已知某二叉树的中序、层序序列分别为DBAFCE、FDEBCA,则该二叉树的后序序列为 B 。
A.BCDEAF B.ABDCEF C.DBACEF D.DABECF 2.在11个元素的有序表A[1…11]中进行折半查找(⎣⎦2/)low+),查找元素(highA[11]时,被比较的元素的下标依次是 B 。
A.6,8,10,11 B.6,9,10,11 C.6,7,9,11 D.6,8,9,113.由元素序列(27,16,75,38,51)构造平衡二叉树,则首次出现的最小不平衡子树的根(即离插入结点最近且平衡因子的绝对值为2的结点)为 D 。
A.27 B.38 C.51 D.754.利用逐点插入法建立序列(50,72,43,85,75,20,35,45,65,30)对应的二叉排序树以后,查找元素30要进行 B 次元素间的比较。
A.4 B.5 C.6 D.75.循环链表的主要优点是 D 。
A.不再需要头指针了B.已知某个结点的位置后,很容易找到它的直接前驱结点C.在进行删除后,能保证链表不断开D.从表中任一结点出发都能遍历整个链表6.已知一个线性表(38,25,74,63,52,48),假定采用散列函数h(key)=key%7计算散列地址,并散列存储在散列表A[0…6]中,若采用线性探测方法解决冲突,则在该散列表上进行等概率查找时查找成功的平均查找长度为 C 。
A.1.5 B.1.7 C.2.0 D.2.37.由权值为9,2,5,7的四个叶子结点构造一棵哈夫曼树,该树的带权路径长度为C 。
A.23 B.37 C.44 D.468.在最好和最坏情况下的时间复杂度均为O(nlogn)且稳定的排序方法是 D 。
A.基数排序B.快速排序C.堆排序D.归并排序9.无向图G=(V,E),其中V={a,b,c,d,e,f},E={(a,b),(a,e),(a,c),(b,e),(c,f),(f,d),(e,d)}。
2011-2012第1学期数据结构基础期末考卷 2
诚信应考 考出水平 考出风格浙江大学城市学院2011 — 2012 学年第 一 学期期末考试试卷《 数据结构基础 》开课单位: 计算分院 ;考试形式:闭卷;考试时间: 2012 年 1 月 3 日; 所需时间: 120 分钟一.选择题 (本大题共 15 题,每题 1 分,共 15 分)1.从逻辑上可以把数据结构分成 。
A. 动态结构和静态结构B. 顺序组织和链接组织C. 线性结构和非线性结构D. 基本类型和组合类型 2.执行下面程序段时,执行S 语句的频度为 。
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)S;A. n 2B. n 2/2C. n(n+1)D. n(n+1)/23.若某线性表最常用的操作是在最后一个元素之后插入一个元素和删除第一个元素,则采用下列 存储方式最节省运算时间。
A. 单链表B. 仅有指向表头指针的单循环链表C. 双链表D. 仅有指向表尾指针的单循环链表 4.带头结点的单链表L 为空的判断条件是 。
A. L== NULLB. L->next==NULLC. L->next==LD. L!= NULL 5.允许对队列进行的操作有 。
A. 对队列中的元素排序B. 取出最近入队的元素C. 在队头元素之前插入元素D. 删除队头元素6.在计算递归函数时,如不用递归过程,应借助于 这种数据结构。
A. 线性表 B. 栈 C. 队列 D. 双向队列7.若用一个大小为6的一维数组来实现循环队列,且当前rear和front的值分别为0 和3。
当从队列中删除一个元素,再加入两个元素后,rear和front的值分别是( )。
A. 4 和2B. 2 和4C. 1 和5D. 5 和18.在有n个结点的二叉树的二叉链表表示中,空指针数。
A. 不定B. n+1C. nD. n-19.设x和y是二叉树中的任意两个结点,若在先序遍历中x在y之前,而在后序遍历中x在y 之后,则x和y的关系是。
《数据结构》期末考试试题及答案
《数据结构》期末考试试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 下列哪种数据结构是线性结构?A. 栈B. 树C. 队列D. 图答案:A2. 在计算机科学中,什么是最基本的数据结构?A. 数组B. 链表C. 栈D. 树答案:C3. 下列哪种操作的时间复杂度是O(1)?A. 在链表中插入元素B. 在数组中查找元素C. 在树中删除节点D. 在图中寻找最短路径答案:B4. 下列哪种数据结构常常用于实现栈和队列?A. 数组B. 链表C. 树D. 图答案:A5. 下列哪种数据结构是有序的?A. 栈B. 队列C. 链表D. 图答案:C二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在数据结构中,栈是一种后进先出(____)的数据结构。
答案:线性表2. 队列是一种先进先出(____)的数据结构。
答案:线性表3. 链表是一种____数据结构,由一系列节点组成。
答案:非线性4. 二叉树是一种特殊的树,它的每个节点最多有两个____。
答案:子节点5. 哈希表是通过____函数将关键字映射到表中的位置来访问数据。
答案:哈希三、判断题(每题2分,共20分)1. 树是一种线性结构。
()答案:错误2. 链表的插入和删除操作时间复杂度都是O(1)。
()答案:错误3. 图是一种线性结构。
()答案:错误4. 哈希表是一种基于顺序结构的的数据结构。
()答案:错误5. 在数据结构中,时间复杂度O(n)表示算法随着输入规模的增加而线性增长。
()答案:正确四、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 请简述栈和队列的特点和应用场景。
答案:栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构,应用场景包括函数调用栈、表达式求值等。
队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构,应用场景包括任务队列、缓冲区等。
2. 请简述链表的优缺点。
答案:链表的优点包括动态扩容、插入和删除操作时间复杂度为O(1)、可以方便地实现各种复杂数据结构。
缺点包括占用内存空间较大、不如数组支持随机访问。
2012浙江省数据结构最新考试试题库(完整版)
6、有一个有序表{1,4,6,10,18,35,42,53,67,71,78,84,92,99}。当用二分查找法查找键值为84的结点时,经( B )比较后查找成功。
A) 4 B)3 C)2 D)12
C) 双链表 D) 仅有尾指针的单循环链表
15、链式存储的存储结构所占存储空间( A )。
A)分两部分,一部分存放结点值,另一部分存放表示结点间关系的指针
B)只有一部分,存放结点值
C)只有一部分,存储表示结点间关系的指针
D)分两部分,一部分存放结点值,另一部分存放结点所占单元数
12、对待排序的元素序列进行划分,将其分为左、右两个子序列,再对两个子序列施加同样的排序操作,直到子序列为空或只剩一个元素为止。这样的排序方法是( A )。
A)直接选择排序 B)直接插入排序
C)快速排序 D)起泡排序
13、线索二叉树中某结点D,没有左孩子的条件是( B )。
7、对待排序的元素序列进行划分,将其分为左、右两个子序列,再对两个子序列施加同样的排序操作,直到子序列为空或只剩一个元素为止。这样的排序方法是( A )。
A)直接选择排序 B)直接插入排序
C)快速排序 D)起泡排序
8、n个顶点的强连通图至少有( A )条边。
C)2,4,3,5,1,6 D)4,5,3,6,2,1
27、在一个链队列中,假定front和rear分别为队首和队尾指针,则删除一个结点的操作为( B )。
A) rear=rear->next; B) front=front->next;
C) rear=front->next; D) front=rear->next ;
《数据结构》期末考试试题及答案
《数据结构》期末考试试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 下列哪一个不是线性结构的基本特征?A. 有且只有一个根结点B. 每个结点最多有一个前驱和一个后继C. 有且只有一个叶子结点D. 有序对中第一个元素是根结点答案:C2. 在单链表中,存储元素的数据域称为元素的哪个部分?A. 指针域B. 数据域C. 结点域D. 头结点答案:B3. 在顺序存储结构中,数据元素之间的逻辑关系由哪个因素决定?A. 数据元素的存储顺序B. 数据元素的存储位置C. 数据元素的类型D. 数据元素的大小答案:A4. 下列哪种排序算法的时间复杂度不是O(nlogn)?A. 快速排序B. 归并排序C. 堆排序D. 冒泡排序答案:D5. 在二叉树中,具有度为2的结点的个数是n0,度为0的结点个数是n2,则有()。
A. n0 = n2 - 1B. n0 = n2 + 1C. n0 = n2D. n0 = n2 + 2答案:B6. 在线索二叉树中,哪个结点被称为线索结点?A. 有左子树的结点B. 有右子树的结点C. 既没有左子树也没有右子树的结点D. 具有左右子树的结点答案:C7. 在双向链表中,查找结点的时间复杂度是()。
A. O(1)B. O(n)C. O(nlogn)D. O(n^2)答案:B8. 在栈的操作中,下列哪个操作是非法的?A. 先进先出B. 后进先出C. 可以插入任意元素D. 可以删除任意元素答案:D9. 在顺序表中进行插入操作时,平均移动次数为()。
A. 0B. n/2C. nD. n-1答案:C10. 在下列排序算法中,哪个算法是不稳定的?A. 冒泡排序B. 快速排序C. 插入排序D. 归并排序答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 线性表的顺序存储结构称为顺序表,其基本特点是()。
答案:元素顺序存储2. 在单链表中,每个结点包括两个域:数据域和()。
答案:指针域3. 在二叉树中,度为0的结点称为(),度为2的结点称为()。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
a. E
b. 2E
c. N2-E
d. N2-2E
(8) If a directed graph is stored by an upper-triangular adjacency
matrix –- that is, all the elements below the main diagonal are zero.
but stacks cannot d. Stacks and queues are linear structures while lists are not
(5) For an in-order threaded binary tree, if the pre-order and inorder traversal sequences are ABCDEF and CBAEDF respectively,which pair nodes’ right links are both threads?
struct node{ int value; struct node *next; /* some other fields */
}
struct node BubbleSort (struct node *h) {/* h is the head pointer of the list with a dummy head node */
NOTE: Please write your answers on the answer sheet. 注意:请将答案填写在答题纸上。
I. Please select the answer for the following problems. (20 points)
(1) Which one of the following statements is true as N grows? a. For any x , x N grows faster than N! b. (log N )2 grows faster than N c. log N 2 grows faster than (log N )2
.
a. N-1
b. N
c. N(N+1)/2
d. N+1
(7) If an undirected graph with N vertices and E edges is represented
by an adjacency matrix. How many zero elements are there in the matrix?
Then its topological order
.
a. exists and must be unique
b. exists but may not be unique
c. does not exist
d. cannot be determined
(9) Sort a sequence of nine integers {4, 8, 3, 7, 9, 2, 10, 6, 5} by
a. N/2
b. O(logN)
c. O(N2)
d. O(1)
II. Given the function descriptions of the following two (pseudo-code) programs, please fill in the blank lines. (21 points)
struct node *p, *q; int flag_swap;
if (!h->next) return h;
do{
flag_swap = 0;
p = h;
while (p->next->next){
if (
){
flag_swap++;
q = p->next;
;
;
;
}
else p = p->next;
d. N grows faster than N (log N )2
(2) What is the time complexity of the following function computes XN?
long int Pow (long int X, unsigned int N) { if (N == 0) return 1; if (N == 1) return X; if (IsEven(N)) /* IsEven(N) returns 1 if N is even, or 0 otherwise */ return Pow(X, N / 2) * Pow (X, N / 2); else return Pow(X * X, N / 2) * X;
}
that
a. O( N )
b. O( log N )
c. O( N log N )
d. O( N )
(3) Suppose that N integers are pushed into and popped out of a stack.
The input sequence is 1, 2, …, N and the output sequence is p1, p2, …,
{
ElementType root, trail, lead;
for ( root = X; S[ root ] > 0;
)
;
for ( trail = X; trail != root;
){
lead = S[ trail ] ;
;
}
return root ;
}
III. Please write or draw your answers for the following problems on the answer sheet. (44 points)
诚信考试,沉着应考,杜绝违纪。
考生姓名:
学号:
所属院系:
_
题序
一
二
三
四
总分
得分
评卷人
1.
2.
6.
7.
1.
_ _ _ _
Answer Sheet
Part I (20)
3.
4.
5.
8.
9.
10.
Part II (21)
_____
_
_____ ____ _
2. _
_
__
___
Part III (44)
a. A and B
b. B and D
c. C and D
d. B and E
(6) If N keys are hashed into the same slot, then to find these N keys,
the minimum number of probes with linear probing is
(1) A sorting algorithm is stable if for any keys Ki = Kj for i < j, the corresponding records Ri precedes Rj in the sorted list.
(a) Is Heap Sort stable? Please give a proof if your answer is “YES”, else please provide a counter example. (4 points)
1. (a)
(b)
2. (a) (b) (c)
3. (a)
(b)
4. i 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
H[i]
5.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Part IV (15)
typedef struct TreeNode *Tree; struct TreeNode {
Tree Child; int key; Tree Sibling; }; int Counter[MAX_LEVEL] ; /* Counter[i] stores the number of leaves on the i-th level.*/ /* The root is on the level 0. */ void Count_Leaves( Trቤተ መጻሕፍቲ ባይዱe T )
}
} while (flag_swap > 0);
return h;
}
(2) The function is to perform Find as a Union/Find operation with
path compression. (9 points)
SetType Find ( ElementType X, DisjSet S )
浙江大学 2012–2013 学年秋学期
《数据结构基础》课程期末考试试卷(A)
课程号: 211C0020_,开课学院:_计算机科学与技术_ 考试试卷:√A 卷、B 卷(请在选定项上打√) 考试形式:√闭、开卷(请在选定项上打√),允许带____无___入场 考试日期: 2012 年 11 月 15 日,考试时间: 120 分钟
(a) the depth-first search sequence; (5 points) (b) the breath-first search sequence; (5 points) and (c) the strongly connected components. (3 points)
v1
3
v2 ∧
v3
4
v4 ∧
v5
2
2 5∧ 4
4∧ 1∧
(3) A binary search tree is said to be of “type A” if all the keys along the path from the root to any leaf node are in sorted order (either ascending or descending).
