英语单词拼读规则表
牛津自然拼读规则表

牛津自然拼读规则表自然拼读是一种通过将字母音素与发音联系起来的教学方法,旨在帮助学生更轻松地学习英语拼读和发音规则。
牛津自然拼读规则表是一份总结了常见英语拼读规则的参考表。
本文将介绍牛津自然拼读规则表的内容和使用方法。
元音规则1. A的发音:A在单词中通常发音为“a”(如cat、hat),但在以后门式拼写时发音为“e”(如gate、late)。
2. E的发音:E在单词中通常发音为“e”(如bed、pen),但在以长元音及辅音后E形式出现时发音为“ee”(如be、sheep)。
3. I的发音:I在单词中通常发音为“i”(如pig、sit),但在以后门式拼写时发音为“ai”(如find、kind)。
4. O的发音:O在单词中通常发音为“o”(如dog、hot),但在以长元音及辅音后O形式出现时发音为“oo”(如go、hope)。
5. U的发音:U在单词中通常发音为“u”(如cup、fun),但在以后门式拼写时发音为“yu”(如mute、tube)。
辅音规则1. C和G的发音:C和G在单词中通常发音为硬音“k”和“g”(如cat、go),但在接元音字母E、I或Y时发音为软音“s”和“j”(如ceiling、gin)。
2. CK和K的发音:CK和K在单词中通常发音相同,即“k”(如black、book)。
3. QU的发音:QU在单词中通常发音为“kw”(如quick、queen)。
4. X的发音:X在单词中通常发音为“ks”或“gz”(如box、exact)。
5. Y的发音:Y在单词中通常发音为元音“i”(如yes、baby),但在以辅音后Y形式出现时发音为“ee”(如happy、party)。
拼读规则1. 辅音字母重叠:当一个单词以两个相同的辅音字母结尾时,通常只读一个辅音字母(如bell、applaud)。
2. E结尾的的拼读规则:当一个单词以E结尾时,通常会影响前面元音的发音(如tub、mice)。
英语单词拼读规则

英语单词拼读规则
英语单词的拼读规则有很多,以下是一些常见的拼读规则:
1.辅音字母加"-e"结尾的单词,一般发音为长音。
例:make [meɪk],like [laɪk]
2.以辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节单词,辅音字母一般发短音。
例:cat [kæt],big [bɪɡ]
3. 以"-er"结尾的单词,一般发[ər]音。
例:teacher [ˈtiːtʃər],four [fɔːr]
4. 以"-le"结尾的单词,辅音字母前一般发[əl]音,元音字母前一般发[l]音。
例:little [ˈlɪtl],able [ˈeɪbl]
5. 以"-ion"结尾的单词,一般发[ʒən]音。
例:action [ˈækʃən],nation [ˈneɪʃən]
6.部分以"-e"结尾的单词,"e"一般不发音。
注意:英语拼读规则并不是绝对的,有些单词可能有特殊发音,拼读规则只是作为一种指导,通常需要通过词典或听力来确定具体发音。
英语单词拼读规则表

many any
ai,ay
ei
在重读音节中
straight,afraid,paint,rain
i
在非重读音节中
Monday,mountain,holiday,captain
weekdayei
birthdayei
air
ε
在重读音节中
repair,chair,hair,stair
al
:
:l
α:
在n./ v. 中
在重读闭音节中
map,practice,that,plan,hand
w+a
watch, what,wash,wallet
water :
α:
a-n,ssspskstthf
answer, grant, class, grasp, basket,fast,bath,after
sand,standlandband
2.在非重读音节中读 音或i
但:yellowsparrowtomorroweverydayei handbag
blackboard :
1.元音字母a及其字母组合的读音
元音字母和字母组合
读 音
说 明
例 词
例 外
a
ei
在重读开音节中
grade,face,table,name
have
operate liberate hibernateeihesitate celebtate
20. laughterA. enoughB. thoughtC. ploughD. through
21. courage A. groundB. doubleC. loudD. mouth
22. brownA. lowB. town C. knowD. knowledge
28条英语自然拼读法基本规则和小窍门(经典收藏)

28条英语自然拼读法基本规则和小窍门(经典收藏)“音标”是英语学习的第一步,你能正确发音吗?下面分享单词自然发音的28条拼读规则,快收藏备用!01 .字母q总是与u在一起,读做/kw/, 此处u不作元音。
02 .字母c在字母e, y, i前读做/s/ (cent, city, cycle), 其他字母前读做/k/(cut, cap, cop)。
03 .字母e, i, y之前的字母g可以读做/j/(page, giant, gym), 其中字母e, i之前的g也可以不读做/j/(get, girl, give); 其它字母之前的g读做/g/(gate, go, gust)。
04 .元音a, e, o, u在音节结尾(开音节)一般读做字母音(长音a, e, o, u), 有助于学生正确划分并拼读元音字母+辅音字母+元音字母的不熟悉单词(report…rather than report)。
05 .字母i和y经常读做/i/(big, gym), 但是也可读做/aɪ/(silent, my, type)。
06 .一个英语单词用字母y而不是i的结尾(my, by)。
07 .有五种情况末尾的字母e不发音.(如me, she, 和he的短单词末尾的字母e 读做e, 较长的单词末尾的e不发音) 尾字母e不发音应该被认为是”having a job”(承担一项工作)7.1 bake gene time / type code cute 使他前面的元音字母发字母音。
7.2 love give blue true 使我们不要以一个v和一个u结束一个单词。
7.3 chance bodice charge allege 使g和c读软音/j/和/s/。
7.4 little castle bottle dabble fiddle 避免一个音节没有一个元音字母。
7.5 are nurse raise bye ewe owe cause 这一条被Spalding女士叫做无工作尾字母e; Sanseri女士叫做老工作尾字母e, 并说前四条之外的不发音尾字母e都叫做老工作尾字母e。
英语发音规则表 详细
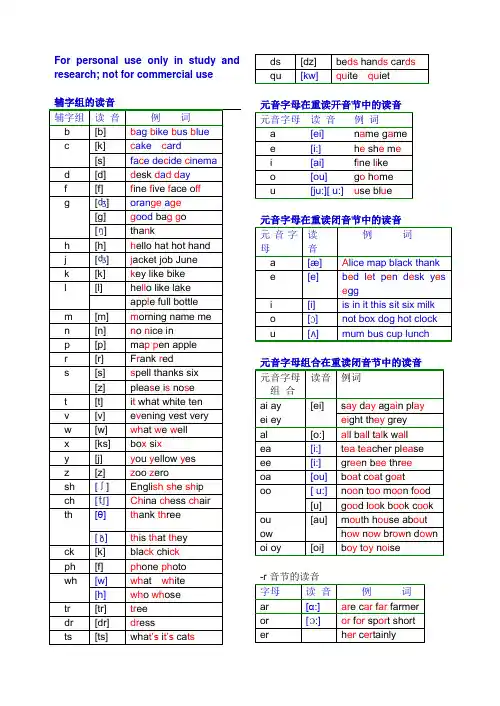
For personal use only in study and research; not for commercial use[[g][][[k][ [ [θ][ [k][ [:]:]英语单词拼读规则表1.单词注音方法推荐在阅读过程中经常需要给一些生词注音,如果把音标写在单词的附近,一是麻烦,二是没有足够的空间来写音标,三是不需要把所有的音标符号都标注出来。
实际上许多字组的发音不需要查字典也知道该读什么音,不知道的信息可能是这个词的重音位置、重读音节中元字组的读音、个别辅音字母的读音等。
所以使用几个符号就可以很完美地给一个单词注音。
使用的符号为:长音符号_ 短音符号 .重音符号´[ ]音符号。
[i]音符号丨哑音符号\其中短音符号 . 和重音符号´也可以充当音节分割符号。
这些符号主要用来标注元音字组的读音。
绝大多数辅音字组无需注音,少数辅音字组的读音还得靠音标来标注。
例如:2.对英语单词可拼读性的认识以整个词为单位,如果词中某个字组读音不规则,或词的重音位置不规则,那么这个词就属于读音不规则的词。
以音节为单位,如果词中某个音节读音不规则,那么这个音节就属于读音不规则的音节。
以字组为单位,如果词中某个字组读音不规则,那么这个字组就属于读音不规则的字组。
3.辅音字母双写的含义辅音字母双写,主要是为了强调双写辅音字母前面的元音字母要发短音,或者说要按元音字母在重读闭音节中的拼读规则读音。
例如:Se attle。
通常ea被看作一个元字组,具有不可分割性,即便是这样,在双写辅音字母前面也被拆分开了。
例外的情况也有:suggestion collapse4.字组的不可分割性不管是元字组还是辅字组都具有不可分割性,所以在给一个词划分音节时,不把字组拆分到两个音节中去。
例如:daugh-ter chil-dren。
但有的词在遇到类似情况时还要考虑到词的来源。
例如:wardroom,dr被划分到不同的音节里,是因为ward和room本来就是两个词。
英语单词拼读规则表

一、元音字母在重读音节中的读音元音字母 读音 例 词编号 开音节[eI ] n a me pl a ne J a ne b a by c a ke 101 a 闭音节[Q ] b a g d a d h a t m a p bl a ck gl a d 102 开音节[iù] h e th e se m e Chin e se 103 e 闭音节[e ] b e d l e t p e n d e sk y e s e gg 104 开音节[aI ] b i ke fl y dr i ve t i me n i ce k i te 105 i/y 闭音节[I ] f i sh b i g dr i nk s i t m i lk sw i m 106 开音节[«U ] th o se cl o se g o h o e h o me n o 107 o 闭音节[•] cl o ck n o t b o x sh o p s o ck 108 开音节[juù] st u dent exc u se d u ty c u te 109 u闭音节[Ã]b u sc u p j u mp m u ch l u nch110在开音节中,元音字母 u 在辅音字母 j l r s 后面时读[uù]音,例如:J u ne bl u e r u ler s u per 。
111二、元音字母在非重读音节中的读音 元音字母 读音 例 词编号[«] Chin a a nother wom a n breakf a st201 a[I ] or a nge vill a ge cabb a ge chocol a te 202 [«] hundr e d stud e nt op e n mom e nt203 e[I ] chick e n pock e t b e gin childr e n 204 [j /«/I /i ] on i on hol i day an i mal bab y per i od205 i/y[aI ] exerc i se crocod i le mob i le 206 [«] sec o nd t o night weap o n welc o me207 o[«U ] als o zer o phot o 208 [«] aut u mn diffic u lt209 u[j U /u (ù)] pop u lar congrat u lation Jan u ary210动词中的a 如果处在开音节位置,字母a 读[eI ]音。
英语单词拼读规则表
英语单词拼读规则表[m] [n] [] [l]a- be- de- re- in- ex--ic或-tion,-sion的词,一、元音字母在重读音节中的读音[][]二、元音字母在非重读音节中的读音[][i][][i][]/[i][ai][][u][]在非重读音节中,许多单词中的元音字母a e i 即可以读作[]音,也可以读作[i]音。
[][]四、-r音节元音字组在重读音节中的读音[:][:][:][:]前面的元音字母不能与音节在非重读音节中通常读[]音,例如:五、-re音节元音字组在重读音节中的读音[ε][i][ai][:][ju]在非重读音节中读[]音节的变体通常发[r]六、元音字组在重读音节中的读音[ε][][:l][:][i][ε][:][i:][i][ei][:][i][u:][u][][:][au][:][ju:i]七、非重读音节中元音字组和字群的读音[]:neighbour serious famous biscuit coffee[n][n][n][][] 八、辅音字母的读音[][][k][][][][] [w][] [k][] [][][] [] [θ] [] [] [tr]ds[dz] ts[ts] ps-[s]辅音字母后加一横线表示这个字组经常出现在音节开头,而不是单词开头。
如:tr-(coun-try) y-(Saw-yer)。
音节开头也不一定就是音节的最前面,如:tr-(street)。
英语单词拼读元音重音规则表
OAR [ɔ:] OOR [ɔ:]
OUR [ɔ:] [auə]
Aor roar hoard coarse board soar hoarse Door doorbell floor flooring 但 poor [puə] Four course source your pour court Our sour hour flour 但 tour [tuə] journey [dʒə: ni:]
后加的元音字母都发非重读的元音。即-r 后的 a o u 发[ə]。当 o 为词尾时发 [əu];-r 后的 i、y 发[i]。
前加元-r 音节的发音
前加元-r 音节及发音 AIR [e ə] AER [e ə] EAR [iə]
[e ə]
[ə:]
EER [iə] EIR [eə]
例词
Air fair pair stairs airing repair hair chair airport upstairs affair Aerial aerobic Ear beard dear near clear hear fear tear rear appear Bear pear wear tear △与 tear[tiə](眼泪)是同形异音词。 辅音前的 ear 发[ə:]: Learn earn early pearl heard earth search research earnest yearn 但 heart [h a: t] beard [biəd] Deer steer queer auctioneer pioneer beer veer engineer electioneer profiteer Heir heirloom their theirs
英语单词自然拼读规则表
英语单词自然拼读规则表Phonics is a great way to help with English pronunciation. Let's start with vowels.The letter "a" can have different sounds. For example, in "cat", it makes the short /æ/ sound. But in "cake", it has the long /eɪ/ sound.The letter "e" often has a short /e/ sound like in "pen". However, in "bee", it makes the long /i: / sound.Now, let's look at the letter "i". In "big", it's the short /ɪ/ sound. In "ice", it's the long /aɪ/ sound.The letter "o" can be short /ɒ/ as in "box" or long /əʊ/ like in "go".The letter "u" has a short /ʊ/ sound in "bus" and a long /ju: / soundin "ruler" (when it follows a consonant).For consonants, the letter "b" always makes the /b/ sound, like in "book".The letter "c" can be /k/ as in "cat" or /s/ when it's followed by "e", "i", or "y", such as in "cent".The letter "d" makes the /d/ sound, for instance in "dog".The letter "f" makes the /f/ sound, like in "fish".The letter "g" can be /g/ as in "go" or /dʒ/ when it's followed by "e", "i", or "y", like in "giant".The letter "h" makes the /h/ sound, for example in "hat".The letter "j" makes the /dʒ/ sound, as in "jump".The letter "k" makes the /k/ sound, like in "kite".The letter "l" makes the /l/ sound, whether it's at the beginning or in the middle of a word, such as in "lion" or "apple".The letter "m" makes the /m/ sound, for example in "map".The letter "n" makes the /n/ sound, like in "no".The letter "p" makes the /p/ sound, for instance in "pen".The letter "q" is always followed by "u" and makes the /kw/ sound, like in "queen".The letter "r" makes the /r/ sound, but in some accents it can be pronounced differently. In American English, it's often a more pronounced /r/ sound as in "red".The letter "s" can be /s/ as in "sun" or /z/ when it's between two vowels or after a voiced consonant, like in "is" or "dogs".The letter "t" makes the /t/ sound, for example in "toy".The letter "v" makes the /v/ sound, like in "van".The letter "w" makes the /w/ sound, for instance in "water".The letter "x" can make the /ks/ sound as in "box" or the /gz/ sound when it's between two vowels, like in "exam".The letter "y" can be a vowel or a consonant. As a vowel, it can make different sounds. As a consonant, it makes the /j/ sound, like in "yes".The letter "z" makes the /z/ sound, for example in "zoo".When two consonants are together, sometimes they keep their individual sounds. For example, in "st" as in "star", we can clearly hear the /s/ and the /t/ sounds.Some letter combinations have special sounds. For example, "ch" usually makes the /tʃ/ sound as in "chair".The combination "sh" makes the /ʃ/ sound, like in "ship".The combination "th" can make the unvoiced /θ/ sound as in "think" or the voiced /ð/ sound as in "this".The combination "ph" usually makes the /f/ sound, like in "phone".Some words don't follow the normal phonics rules exactly. For example, "said" doesn't follow the normal pattern for the letter "a".Words borrowed from other languages might also have different pronunciation rules. For example, "cafe" which is borrowed from French has a different pronunciation compared to a normal English word starting with "c".Silent letters are also a part of English phonics. For example, in "knight", the "k" is silent and the "gh" is also silent.In some words, the stress can change the pronunciation. For example, in "record", when it's a noun, the stress is on the first syllable and the "o" makes a different sound compared to when it's a verb and the stress is on the second syllable.。
英语单词拼读规则表
元音字母
读音
发音规则
例词
a
a在[w]音(quwhw)后面
[ɒ]
want[wɒnt]watch[wɒtʃ]wash[wɒʃ]quality[ˈkwɒləti]
a在w, u前
[ɔ:]
caw[kɔ:]haw[hɔ:]draw[drɔ:]fawn[fɔ:n]
a在(st,ssskspphthghf n m)前
5、双音节词重读规则:双音节词的第一个音节通常是重读音节。例如:`stu-dent`Chi-na`sec-ond`au-tumnin`-deed含有a- be- re- in- ex-等前缀的双音节词往往是在第二个音节上重读。双音节词的重读位置不会因增加前缀或后缀而发生改变。例如:a`boutbe`foreex`cusere`pairfor` get-fulin`-ven-tor
元音字母发短音
clock,big
r音节
一或两个其它元音字母与辅音字母r结合,构成的音节。
发音见r音节表
horse,star
re音节
元音字母与re结合,构成的音节。
发音见re音表
care,here,bore
非重读音节
单词中读得比较弱或模糊的音节。非重读音节在一个词中有一个或一个以上,它是随重读开音节或重读闭音节出现的。不管它在词的开头,结尾或中间音节中,非重读音节本身无开音节和闭音节之说。单音节词为重读音节词,只有两个以上音节的词才有一个是重读音节,一个是非重读音节。例如today,Monbay。
holiday[ˈhɒlədeɪ]beautiful[ˈbju:tɪfl]family[ˈfæməli]animal[ˈænɪml]
闭音节
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
英语单词拼读规则表1.单词注音方法推荐在阅读过程中经常需要给一些生词注音,如果把音标写在单词的附近,一是麻烦,二是没有足够的空间来写音标,三是没有必要把所有的音标符号都标注出来。
实际上许多字组的发音不需要查字典也知道该读什么音,不知道的信息可能是这个词的重音位置、重读音节中元字组的读音、个别辅音字母的读音等。
所以使用几个符号就可以很完美地给一个单词注音。
使用的符号为:长音符号_ 短音符号 .重音符号´[ ]音符号。
[i]音符号丨哑音符号\其中短音符号 . 和重音符号´也可以充当音节分割符号。
这些符号主要用来标注元音字组的读音。
绝大多数辅音字组无需注音,少数辅音字组的读音还得靠音标来标注。
以整个词为单位,如果词中某个字组读音不规则,或词的重音位置不规则,那么这个词就属于读音不规则的词。
以音节为单位,如果词中某个音节读音不规则,那么这个音节就属于读音不规则的音节。
以字组为单位,如果词中某个字组读音不规则,那么这个字组就属于读音不规则的字组。
3.辅音字母双写的含义辅音字母双写,主要是为了强调双写辅音字母前面的元音字母要发短音,或者说要按元音字母在重读闭音节中的拼读规则读音。
例如:Se attle。
通常ea被看作一个元字组,具有不可分割性,即便是这样,在双写辅音字母前面也被拆分开了。
例外的情况也有:suggestion collapse4.字组的不可分割性不管是元字组还是辅字组都具有不可分割性,所以在给一个词划分音节时,不把字组拆分到两个音节中去。
例如:daugh-ter chil-dren。
但有的词在遇到类似情况时还要考虑到词的来源。
例如:wardroom,dr被划分到不同的音节里,是因为ward和room本来就是两个词。
有时辅音字母连缀也有这种现象。
辅音字母双写,一方面可以方便找出音节划分点,另一方面是为了强调双写辅音字母前面的单个元音字母是个闭音节,例如:Seattle ,其中的字母a发短音。
又例如:worry,现在把o读成[ ]音的人多起来了。
5.判断单词读音的三个步骤一、数元字组的个数数一数元字组的数目。
有几个元字组就有几个音节。
二、划分音节划分音节时以元字组为核心。
三、找出重读音节1.单音节词都是重读音节2.双音节词通常是第一个音节重读(前缀不重读)3.多音节词在倒数第三个音节上重读6.如何判断双音节词的重读位置?双音节词的第一个音节通常是重读音节。
例如:´stu-dent ´Chi-na ´sec-ond ´au-tumn in-´deed含有a- be- de- re- in- ex- 等前缀的双音节词往往是在第二个音节上重读。
双音节词的重读位置不会因增加前缀或后缀而发生改变。
例如:a´bout be´fore ex´cuse re´pair for-´get-ful多音节词通常在倒数第三个音节重读。
例如:´el-e-phant con-grat-u´la-tion词尾有-ic或-tion,-sion的词,在-ic或-sion,-tion前的一个音节上重读。
例如:scien´tific im´pression ´nation以上几个词都是开音节词w ag[æ]3-02例外的词a ss[æ]tom a to[α:] 字母a后面是字母t,不符合3-02规则。
这个词也可以按1-01规则来读tomato[t ´meitou]ban ana[α:] 重读音节里的字母a后面有字母n,符合3-02规则。
由于重读音节里的字母a和后面的字母n并不是处在同一音节里,所以banana也可以读成[b ´nein ]3-04例外的词c o st[ ]十、英语语音名词解释1.音节以元音为主体构成的发音单位,一般说来元音发音响亮,可以构成音节,辅音发音不响亮,不能单独构成音节([m] [n] [ ] [l]例外)。
从单词拼写形式上看,有几个元字组就有几个音节。
0-012.音节的划分①在两个音节的相邻处有两个辅字组时,一个辅字组属于前面的音节,一个属于后面的音节。
例如:le t-ter mem-ber chil-dren daugh-ter②在两个音节的相邻处只有一个辅字组时,如果前面音节里的元音是长音则辅字组属于后面一个音节,如果前面一个音节里的元音是短音,则辅字组属于前面一个音节。
例如:长音p a-per st u-dent f a-ther z e-ro m o-tor f ar-ther短音s e v-en st u d-y m o th-er v e r-y m o d-le w ea th-er 0-023.重读音节单词中读音特别响亮的音节。
用音标标记双音节、多音节0-03词的读时,应使用重读符号。
单音节词多数是重读音节,标记读音时不需要使用重读符号。
4.开音节①绝对开音节:单个元音字母后面没有辅字组的重读音节。
例如:n o blue ba-by stu-dent se-cret.0-04②相对开音节:单个元音字母后面加单个辅音字母,再加一个不发音字母e构成的重读音节。
例如:n am e thes e bik e hom e ex-cus e.5.闭音节单个元音字母后面有辅字组(r w y 除外)且以辅字组结尾0-05的重读音节。
例如:b a g e gg fi sh no t cu p6.双音节词重读规则双音节词的第一个音节通常是重读音节。
例如:´stu-dent ´Chi-na ´sec-ond ´au-tumn in-´deed0-06含有a- be- de- re- in- ex- 等前缀的双音节词往往是在第二个音节上重读。
双音节词的重读位置不会因增加前缀或后缀而发生改变。
例如:a´bout be´fore ex´cuse re´pair for-´get-ful in-´ven-tor7.多音节词重读规则多音节词通常在倒数第三个音节重读。
例如:´el-e-phant con-grat-u-´la-tion0-07词尾有-ic 或-tion,-sion 的词,在-ic或-sion,-tion前的一个音节上重读。
例如:scien´tific im´pression ´nation不符合0-02规则的词celebrate(cel-e-brate)划分音节时不能把字组拆分到两个音节中去(chil-dren);br pr bl pl等辅音连缀是不是要当成字组来对待?有时又要考虑到词的来源(ward-room),这时并没有把dr看成是一个字组。
How to divide a word when writing or typingWhen writing or typing it is sometimes neccessary to divide a word at the end of the line because there is not enough space for the complete word. This division is always shown by adding a hyphen(-) immediately after the first part of the divided word at the end of the line. Many people prefer not to divide words at all (especially when writing by hand), but if you do, here are three considerations to help you.1. By syllableThis means dividing the word into syllables or units of sound. For example, the word kind has one syllable, kind·ly has tow, un·kind·ly has three ad un·kind·li·ness has four.2. By structureThis means dividingthe word into the smaller units of meaning such as anti-, dis-, un-, ect(as in anti·sep·tic, dis·ap·pear, un·able) or an ending(a suffix) such as -age, -able, -fully(as in post·age, agree·able, grate·fully).3. By meaningThis means deciding whether each part of the divided word can be understood or spoken so that the complete word is easily recongnised from the two parts. For example, it may be a compound word made up of two different words, such as spot and light in spot·light.All three considerations must be used to decide whether and where you can divide a word. Here are six useful rules to help you:1. Never divide a word within a syllable.2. Never divide an ending (a suffix) of two syllables such as -able, -ably, -fully.3. With the exception of -ly, never divide a word so that an ending of two letters such as -ed, -er, -ic begins the nest line.4. Never divide a word so that one of the parts is a single letter.5. Never divide a word of one syllable.6. Never divide a word of less than five letters.Adapted from OXFORD ADVANCED LEARNER´S DICTIONARY OF CURRENT ENGLISH0-07例外的例词Catholic rhetoric。
