沃尔沃标准VCS 5026,4

STANDARD VCS 5026,4
Volvo Car Corporation
Established Date: Issue: Page: 2016-04 3 1(15)
The English language version is the original and the reference in case of dispute. Den engelska spr?kversionen ?r originalversion och ska ?beropas i h?ndelse av tvist.
Master location system Referenspunktsystem System description and indication Systembeskrivning och skrivs?tt Orientation Orientering
The standard is based on rules for datum targets, as described in ISO 1101 and ASME Y14.5, and is a further development of these rules to meet the needs in connection with positioning and specification of requirements for parts in a vehicle coordinate system. Standarden ?r baserad p? regler f?r lokala referenser i ISO 1101 och ASME Y14.5 och ?r en vidareutveckling av dessa f?r att tillgodose behoven av positionering och kravs?ttning av artiklar i ett vagnskoordinatsystem.
Former practice is described in VCS 5026,29 Master location system. Tidigare praxis beskrivs i VCS 5026,29 Referens-punktsystemet.
This issue differs from issue 2 in that the term “interface system” has been changed to “subordinate system”. Denna utg?va skiljer sig fr?n utg?va 2 genom att ben?mningen ”interface-system” ?ndrats till
”delsystem”.
Contents Inneh?ll
1 Scope and field of application 1 Omfattning och till?mpning
2 The 3-2-1 rule 2 3-2-1-regeln
3 Symbols and indication 3 Symboler och skrivs?tt
4 Description of system 4 Systembeskrivning
5 Selection of master location and support
location points
5 Val av referens- och st?dpunkter
6 Reference in design-engineering
documentation 6 H?nvisning i konstruktionsteknisk
documentation
1 Scope and field of application 1 Omfattning och till?mpning
The system with master location points in accordance with this standard is intended to be applied in order to obtain an effective determination of the position of parts in the vehicle’s coordinate system. It is based on the same – systematically and consistently placed –initial positions being applied throughout the entire production process, that is, in design, production and inspection. Systemet med referenspunkter enligt denna standard ?r avsett att till?mpas f?r en effektiv positionsbest?mning av artiklar i fordonets koordinatsystem. Det bygger p? att samma
utg?ngsl?gen, systematiskt och konsekvent place-rade, till?mpas genom hela framtagningsprocessen, d.v.s. vid konstruktion, produktion och kontroll.
2 The 3-2-1-rule 2 3-2-1-regeln
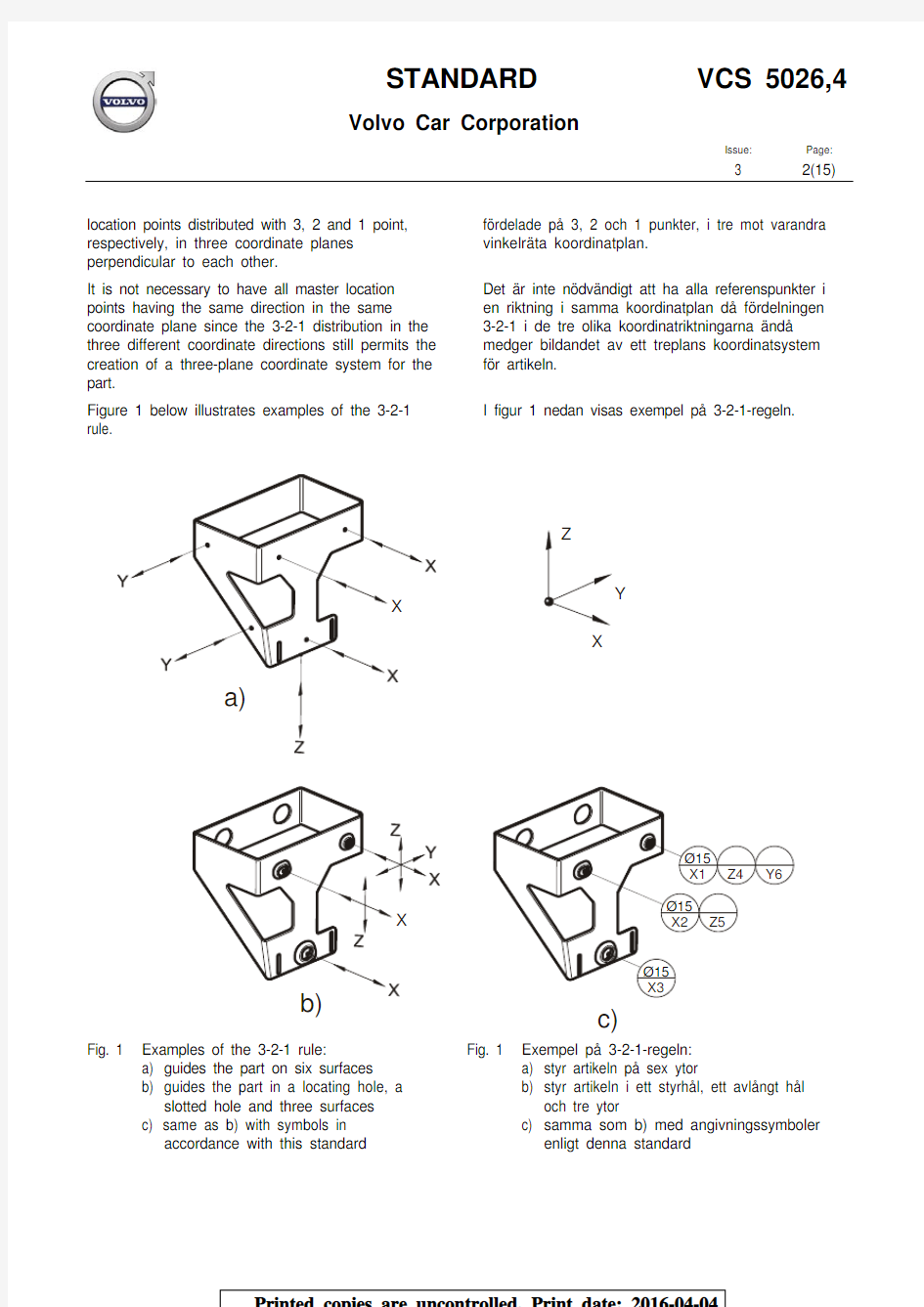
In order for a part (rigid) to be unambiguously located, it must be determined by six master F?r att en artikel (stel) ska vara entydigt lokaliserad m?ste den vara best?md av sex referenspunkter
3 2(15)
location points distributed with 3, 2 and 1 point, respectively, in three coordinate planes perpendicular to each other. f?rdelade p? 3, 2 och 1 punkter, i tre mot varandra vinkelr?ta koordinatplan.
It is not necessary to have all master location points having the same direction in the same coordinate plane since the 3-2-1 distribution in the three different coordinate directions still permits the creation of a three-plane coordinate system for the part. Det ?r inte n?dv?ndigt att ha alla referenspunkter i en riktning i samma koordinatplan d? f?rdelningen 3-2-1 i de tre olika koordinatriktningarna ?nd? medger bildandet av ett treplans koordinatsystem f?r artikeln.
Figure 1 below illustrates examples of the 3-2-1
rule.
I figur 1 nedan visas exempel p? 3-2-1-regeln.
X
c)
Fig. 1 Examples of the 3-2-1 rule:
a) guides the part on six surfaces
b) guides the part in a locating hole, a
slotted hole and three surfaces
c) same as b) with symbols in
accordance with this standard
Fig. 1 Exempel p? 3-2-1-regeln:
a) styr artikeln p? sex ytor
b) styr artikeln i ett styrh?l, ett avl?ngt h?l
och tre ytor
c) samma som b) med angivningssymboler
enligt denna standard
3 3(15)
3 Symbols and indication
3 Symboler och skrivs?tt
= Master location point / Referenspunkt
3.1 Indication
3.1 Skrivs?tt
In the lower section of the circle, the coordinate direction and the sequence number of the master location point shall be indicated. Numbers 1–3 shall be given for the coordinate direction with three master location points, numbers 4–5 shall be indicated for the coordinate direction with two master location points and number 6 for the coordinate direction with one master location point. See figure 1.
I cirkelns nedre del anges koordinatriktningen och ordningsnummer f?r referenspunkten. Nummer 1–3 anges f?r koordinatriktningen med tre referenspunkter, nummer 4–5 anges f?r
koordinatriktningen med tv? referenspunkter och nummer 6 f?r koordinatriktningen med en referenspunkt. Se figur 1.
In the upper section of the circle, the size of the surface used when the master location point is placed on a surface shall be indicated. Se figure 2. I cirkelns ?vre del anges storleken p? ytan som anv?nds d? referenspunkten ?r placerad p? en yta. Se figur 2.
A dashed line from the symbol to the master location point indicates that the datum is on the other side of the material. See figure 3. En streckad linje fr?n symbolen till referens-punkten anger att referensen ligger p? andra sidan materialet. Se figur 3.
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
The size used is usually a diameter value, but in certain cases other sizes can be used. See figure 4.
Som storlek anv?nds oftast en diameter men i vissa fall kan annan storlek anv?ndas. Se figur 4.
3 4(15)
Fig. 4
If the upper portion of the circle is left empty, this means that the datum is a point. Normally,
however, a size is always given, but indication in accordance with figure 5 can be used at the early stages before the size of the surface has been determined.
Om ?vre delen av cirkeln l?mnas tom betyder detta att referensen ?r en punkt. Normalt anges dock alltid en storlek men angivning enligt figur 5 kan anv?ndas i tidiga skeden innan storleken p?
ytan har best?mts.
Fig. 5
3 5(15)
Figure 6 below illustrates examples of master location points in holes. (The same principle applies to, e.g. pins, recesses and projections). I figur 6 nedan visas exempel p? referenspunkter i h?l. (Samma princip g?ller f?r t.ex. tappar, urtag och flikar).
If the upper section of the circle is blank, the axis is referred to.
?r ?vre delen av cirkeln tom avses centrumlinjen.
Fig. 6
When the datum is to be the median value of a feature of size, the symbol shall be placed as shown in figure 7 below. D? referensen ska vara mittv?rdet f?r ett storleksm?tt placeras symbolen enligt figur 7 Fig. 7 Evaluated datum / Utv?rderad referens
3 6(15)
4 Description of system 4 Systembeskrivning
The positioning system with master location points is a basic function in the geometric development process. The master location points are used throughout the entire process and are a design prerequisite that must be decided at an early stage in the process. Positioneringssystemet med referenspunkter ?r en grundfunktion i den geometriska utvecklings-processen. Referenspunkterna anv?nds genom hela processen och utg?r en konstruktions-
f?ruts?ttning som m?ste beslutas i tidigt skede i processen.
Each part has its own fixed master location points, which form the main system of the part. Varje artikel har sina best?mda referenspunkter, vilka bildar artikelns huvudsystem.
When required, subordinate systems with own master location points for openings, hole groups, etc., are also created. See examples in figures 8 and 9. Dessutom skapas vid behov delsystem med egna referenspunkter f?r ?ppningar, h?lgrupper och dylikt. Se exempel i figur 8 och 9.
A subordinate system is a selected represen-tative for the vehicle coordinate system. Ett delsystem ?r en vald representant f?r vagns-koordinatsystemet.
3 7(15)
Fig. 8
3 8(15)
Main system
Subordinate
system
Main system
Subordinate
system
Main system
Huvudsystem
Delsystem
Huvudsystem
Delsystem
Huvudsystem Fig. 9
3 9(15)
4.1 Master location points 4.1 Referenspunkter
For each part, six master location points distributed according to the 3-2-1 rule shall be determined. The master location points are numbered 1–6. F?r varje artikel best?ms sex referenspunkter som ?r f?rdelade enligt 3-2-1-regeln. Referenspunkterna numreras med ordnings-nummer 1 till 6.
The letter indicating the coordinate specifies the principal theoretical coordinate direction but, in practice, they are normal to the real surface. Deras koordinatbokstav anger den huvudsakliga teoretiska koordinatriktningen, men i praktiken ?r de vinkelr?ta mot den verkliga ytan.
4.2 Support location points 4.2 St?dpunkter
For non-rigid parts additional location points can be required, in addition to the six master location points, to provide complete guidance of a part. These are called support location points and numbered 7 and upwards, see figure 10. F?r icke-stela artiklar kan, ut?ver de sex referenspunkterna, ytterligare lokaliseringspunkter erfordras f?r att ge en fullst?ndig uppstyrning av en artikel. Dessa ben?mns st?dpunkter och f?r d? ordningsnummer fr?n 7 och upp?t, se figur 10.
The support location points must not be used to correct the form of the part in such a way that unfavourable stresses arise in the fitted part. Where necessary, the requirement at non-clamped position shall be indicated on the drawing. See figure 10 where requirement at non-clamped position has been indicated for support location point X7. St?dpunkterna f?r ej anv?ndas f?r att korrigera artikelns form s? att ogynnsamma sp?nningar uppst?r i monterad artikel. D?r s? beh?vs ska krav vid ej insp?nt l?ge anges p? ritningen. Se figur 10 d?r krav vid ej insp?nt l?ge angetts f?r st?dpunkten X7.
As an alternative to indication of requirement at non-clamped position, a maximum clamping force can be specified. Som alternativ till att ange krav vid ej insp?nt l?ge kan en max insp?nningskraft specificeras.
Fig. 10
3 10(15)
4.3 Process points
4.3 Processpunkter
In process equipment, master location and location points might have to be supplemented with process points in order to keep the parts together, for example at welding.
I processutrustning kan referens- och st?d-punkter beh?va kompletteras med process-punkter f?r att t ex vid svetsning b?ttre h?lla samman artiklarna.
In some cases there can be a need to indicate process points on the drawing. See figure 11.
I vissa fall kan processpunkter beh?va markeras
p? ritning. Se figur 11.
Fig. 11
Process points must not be used at measuring operations.
Processpunkter f?r inte anv?ndas vid m?toperationer.
4.4 Main system
4.4 Huvudsystem
The main system consists of systematically placed master location points which, where required, are supplemented by support location points.
Huvudsystemet best?r av systematiskt
utplacerade referenspunkter och vid behov ?r dessa kompletterade med st?dpunkter. The datums in the main system position the respective part directly and without tolerance to the coordinate system.
Referenserna i huvudsystemet positionerar respektive artikel direkt och utan tolerans till koordinatsystemet.
4.5 Subordinate systems
4.5 Delsystem
If required, functions on a part in the form of openings, mountings or similar which have functional requirements with respect to a
subsequent assembly part or to each other may form subordinate systems. See figure 9. Funktioner p? en artikel i form av ?ppningar, inf?stningar eller dylikt vilka har funktionskrav mot kommande monteringsartikel eller mot varandra kan vid behov bilda delsystem. Se figur 9.
A subordinate system is a selected represen-tative of the vehicle coordinate system for the purpose of being able to position parts in that system. For subordinate systems, datums are selected in accordance with the 3-2-1 rule and the system then interacts with the assembly part’s main system of the assembly part in order to secure the functional requirements. See figure 15.
Ett delsystem ?r en vald representant f?r vagns-koordinatsystemet i syfte att kunna positionera artiklar mot detta. F?r ett delsystem v?ljs referenser enligt 3-2-1-regeln och systemet samverkar sedan med monteringsartikelns huvudsystem f?r att s?kra funktionskraven. Se figur 15.
3 11(15)
Support location points are not possible in subordinate systems.
St?dpunkter kan ej f?rekomma i delsystem. In subordinate systems, the datums are
considered only as points and, consequently, no size is indicated in the upper portion of the symbol.
I delsystem betraktas referenserna endast som punkter och d?rf?r anges ingen storlek i symbolens ?vre del.
All subordinate systems shall be identified with a designation which shall be indicated adjacent to the lower section of the symbol. See figure 12. Samtliga delsystem ska identifieras med en
beteckning som anges i anslutning till symbolens nedre del. Se figur 12.
The master location points in subordinate
systems can be specified in relation to the main system or to another subordinate system. Figure 13 shows examples of requirement specification in relation to the main system, and figure 14 shows examples of requirement specification in relation to another subordinate system. Referenspunkterna i delsystem kan kravs?ttas mot huvudsystemet eller annat delsystem. Figur 13 visar exempel p? kravs?ttning till huvud-systemet och figur 14 visar exempel p? kravs?ttning till annat delsystem.
Fig. 12
Fig. 13
Fig. 14
3 12(15)
Main system/
Huvudsystem
Main system/
Huvudsystem Fig.15a Main system body side, complete /
Huvudsystem karossida komplett
Fig.15b
Fig.15c Subordinate system window opening/
Delsystem glas?ppning
4.6 Positions of master location and
support location points 4.6 Positioner f?r referens- och
st?dpunkter
The positions of the master location and support location points shall be given in DSM (Digital Shape Model) and CAD the Master. Positionerna f?r referens- och st?dpunkter anges i DSM (Digital Shape Model) och CAD the Master.
For information purposes, a table of coordinate values can be given on the drawing, see the table below. Som information kan ocks? tabell med koordinat-v?rden finnas p? ritningen, se tabell nedan.
When using subordinate systems, the positions of the datums shall be presented in clearly identified separate tables for each subordinate system. D? delsystem anv?nds ska referensernas l?ge ges i tydligt identifierade, separata tabeller f?r varje delsystem.
3 13(15)
All master location and support location points shall also be drawn in views or sections. Exception to this rule can be made when several master location and support location points can be shown with typical views or sections or when the part is defined by a CAD Master. Alla referens- och st?dpunkter ska ?ven ritas i vyer eller snitt. Undantag fr?n denna regel kan
g?ras n?r flera referens- och st?dpunkter kan visas med typiska vyer eller snitt eller n?r artikeln ?r definierad av en CAD the Master.
Coordinate values only for information. Exact definition in digital shape model
Fig. 16
4.7 Sizes representing master
location and support location
points in equipment 4.7 Storlek som representerar
referens- och st?dpunkter i
utrustningar
The size shall be chosen with respect to function and inspection. The size is often a restricted surface, but can also be a point. Storleken v?ljs med h?nsyn till funktion och kontroll. Storleken utg?rs oftast av en begr?nsad yta men kan ocks? vara en punkt.
For sheet metal parts the size ?12 is normally used F?r artiklar i tunnpl?t anv?nds normalt storleken ?12.
The size of the master location and support location surfaces should be the same in process and inspection equipment. In certain cases, process equipment might require a different size. As far as inspection equipment is concerned, the indicated size always applies. Referens- och st?dytornas storlek b?r vara lika i b?de process- och kontrollutrustning. I process-utrustningar kan i vissa fall annan storlek erfordras. I kontrollutrustningen g?ller alltid angiven storlek.
3 14(15)
4.7.1 Locating holes in sheet metal
4.7.1 Styrh?l i tunnpl?t
The hole size and tolerance shall be selected from the tables below.
H?lstorlek och tolerans v?ljs ur nedanst?ende tabeller.
Round locating holes/ Runda styrh?l Slotted holes / Avl?nga styrh?l
+015
,± 0,5
4.8 Part drawings
4.8 Detaljritningar
To illustrate the location of the part’s master location and support location points, an axono-metric view showing the basic shape of the part shall also be included on the drawing. Such an axonometric view shall show all master location and support location points. See figure 17. F?r att ?sk?dligg?ra placeringen av referens- och st?dpunkter p? artikeln ska ritningen ?ven f?rses med en axonometrisk vy som visar artikelns
grundform. S?dan axonometrisk vy ska visa samtliga referens- och st?dpunkter. Se figur 17. The table of coordinate values for master location and support location points shall be placed next to this axonometric view. Tabellen med koordinatv?rden f?r referens- och st?dpunkter ska placeras i anslutning till denna axonometriska vy.
Fig. 17
3 15(15)
4.8 Assembly drawings 4.8 Komplettritningar
On assembly drawings, the position of the coordinates and the guiding direction of all master location and support location points shall be indicated in the same way as on part drawings. P? komplettritningar anges koordinatl?ge och styrriktning f?r samtliga referens- och st?dpunkter p? samma s?tt som p? detaljritningar.
5 Selection of master location
and support location points 5 Val av referens- och
st?dpunkter
The main system for complete vehicle is built up at the same time as master location and support location points are selected for the respective part. Referenssystemet f?r vagn komplett byggs upp samtidigt som referens- och st?dpunkter v?ljs f?r respektive artikel.
The dominating functions of the parts are evaluated and the need for specially manufac-tured features is assessed. The outcome for the points/surfaces selected must be stable. Artiklarnas dominerande funktioner utv?rderas och det bed?ms om speciellt tillverkade element m?ste anv?ndas. Valda punkter/ytor m?ste ha ett stabilt utfall.
The selection of production process affects the construction of the system. Therefore, the selection of master location and support location points shall always be prepared. Valet av produktionsprocess p?verkar systemets uppbyggnad. Val av referens- och st?dpunkter ska d?rf?r alltid beredas.
6 Reference in design-
engineering documentation 6 H?nvisning i konstruktions-
teknisk dokumentation
This standard applies when referred to on the drawing by means of a reference standard or directly by the inclusion of the following note: Denna standard g?ller n?r den ?r h?nvisad till p? ritningen genom en h?nvisningsstandard eller direkt genom f?ljande not:
MASTER LOCATION SYSTEM VCS 5026,4
汽车文化知识试题(选择题)
汽车文化知识试题 宣传部:杨泽 **选择题:(说明:题材选自2005年版的有关资料,如有最新变化请根据05年前的事实回答!)** 1、懂汽车的人通常会说某某汽车的“扭力”多大是体现一款汽车性 能的一个重要因素,请问这个“扭力”具体可以表现在汽车性能的哪一方面( B ) A、该车最高时速300km/h; B、该车百公里加速仅需2.5秒; C、该车百公里油耗仅7.3L; D、该车持续续航可达600km 2、1885年,( A )造出了一台单缸汽油发动机,并将它装在了一辆三轮车上,这也就是世界公认的第一辆汽车。 A、卡尔.本茨 B、戈特利布·戴姆勒 C、道夫·狄塞尔 D、威廉.迈巴赫 3、世界摩托车之父是( B ) A、卡尔.本茨 B、戈特利布·戴姆勒 C、道夫·狄塞尔 D、威廉.迈巴赫 3、前轮驱动汽车的创造者是( A ) A、安德烈.雪铁龙 B、亨利.福特 C、卡尔.本茨 D、戈特利布·戴姆勒 4、以前的轿车从来没有见过这样一里辆十分小巧的车,以至它在
1959年面世时被许多人认为是开玩笑的东西,但它却触发了汽车技术的一场革命。巧妙的重心分布及适当的轴距和轮距。在取得观念上的突破的同时,还在汽车赛中取得成就,其中在蒙特卡洛汽车赛中三次夺魁,在无数次环形路车赛中获胜。这辆车是( B ) A、“甲壳虫”汽车 B、“迷你(Mini)”汽车 C、“高尔夫”汽车 D、大众“帕萨特” 5、汽车的界定:汽车是指自身带有动力装置,能够自行驱动运行的具有四个或四个以上车轮,但车轮不得依靠轨道运行的单车或列车.也包括无轨电车和整车装备质量超过( B )公斤的三轮车. A、300 B、400 C、500 D、600 6、按照新国家标准《汽车和挂车类型的术语和定义》(GB/T3730.1—2001)的规定,汽车分为乘用车和商用车。乘用车为不超过( C )座的车。分为普通乘用车、活顶乘用车、高级乘用车、小型乘用车、敞篷车、仓背乘用车、旅行车、多用途乘用车、短头乘用车、越野乘用车、专用乘用车等11类。 A、5 B、7 C、9 D、11 7、汽车通常由五大系统组成,请问下面哪项不是属于汽车的五大系统( A ) A、电子系统 B、行驶系统 C、转向系统 D、动力系统 8、汽车的传动系统是指将发动机产生的驱动力矩和转速,以一定的关系和要求传递到车轮的系统。其组成为:( A ) A、离合器→变速器→万向节→传动轴→主减速器→差速器→半轴→
沃尔沃标准 VCS 1027,2729-2004 Odour of trim materials in vehicles Organic materials
1 4 Issue Page The English language version is the original and the reference in case of dispute. 此英文版为初始版,如有争议,以英文版为准。 TEST METHOD 试验方法 Odour of trim materials in vehicles汽车装饰材料气味 Organic materials有机材料 Orentation引言 This standard is a further development of standard STD 1027,2712, issue 1, which it replaces and from which it differs in that the requirements under section 3.1 ”Conditioning of test pieces” have been changed.本标准是标准STD 1027,2712,版本1的延伸,该标准在章节3.1:测试件条件做了更改,区别并代替以前版本。 This standard conforms to VDA 270, Versions A2, B2 and C2, with the exception that the test has been extended to include placing a set of test pieces in a test vessel without water. 除了该实验扩展到了在无水试验容器中包含一套试验样件外,本标准和VDA 270, 版本 A2, B2 和 C2是一致的。 Contents 内容 1 Scope and field of application范围和适用性 2 Apparatus 设备 3 Test pieces 测试件 3.1 Conditioning of test pieces测试件条件 3.2 Quantity of materials for testing测试材料数量 4 Testing 测试 5 Evaluation评估 6 Test report 试验报告 1 Scope and field of application 范围和适用性 The purpose of the test is to assess odour under the influence of temperature and moisture. The test is performed on materials from the interior of vehicles and on components that come into contact with the air flow supplied to the interior of vehicles.本试验目的在于在温度和湿度影响下评估气味。本实验在汽车内饰材料和零部件上进行,这些零部件接触了为汽车内部提供的气流。 The expression ‘odour’ is used to denote the suscept ibility of a material, after a specified temperature and moisture cycle, to emit volatile constituents that are accompanied by a perceivable odour.气味odour一词用于一种材料在指定温度和湿度周期后的敏感性,以此发出伴有可感知气味的挥发性化学成分。 2 Apparatus设备 Heating chamber with air circulation in accordance with STD 1027,2231. 依据STD1027.2231,具有空气流通的加热室。
汽车文化
鸳小白 一、填空题 1、当今世界著名的五大车展为:德国法兰克福车展、法国巴黎车展、瑞士日内瓦车展、北_______ 美车展和日本东京车展 2、确切地说汽车是由底盘和车身两大部分组成。而习惯上,常将汽车分为发动机、 底盘、电器禾口车身四部分。 3、我国按照汽车的用途将汽车分为七类:货载汽车、越野汽车、自卸汽车、_专 用汽车、牵引汽车、客车、轿车。 4、国际上通常将汽车车型归并为两大类:乘用车和商用车。 5、目前,电动汽车主要有三种类型:蓄电_______ 、燃料电池电动汽车、混合动力 电动汽车。 6、两位德国人卡尔本茨、 _____ 戈特利布戴姆勒_被誉为现代汽车之父。 7、确定汽车外形有三个因素,包括机械工程学、人体工程学、空气动力学 8、汽车诞生以来,外形经历了马车形、甲鱼形、鱼形、船形、契形、虫形、箱形等演变。 9、LEXUS、Ford、Sabb、FIAT轿车的中文名字分别是雷克萨斯、福特、 ________ 萨博、菲亚特。 10、L EXUS、Volvo、Sabb、Volkswagen、Ford、HUMMER、IVECO 轿车的中文名字分别 是雷克萨斯、沃尔沃、萨博、大众、悍马、依维柯 11、汽车文化包括技术文化、造型文化、车史文化、名人文化、名车文化、车标文化、赛车文化等多个方面。 12、1949年至1965年,我国建成了中国第一汽车制造厂,实现了中国汽车工业零的突破;接着建立了南京汽车制造厂、上海汽车制造厂、济南汽车制造厂、北京汽车制造厂, 形成了五个汽车生产基地。 13、确定汽车外形有三个因素,即机械工程学、人体工程学和空气动力学。汽车外形的演变就是三者协调的发展。
VOLVO英文缩写汇总
英文缩写: PS (Program start) 项目开始 PSC (Program strategy confirmation) 项目策略确定 PTCC (Program Target Compatibility Check point) 项目目标分解 PTC (Program Target Confirmation) 项目目标确定 PA (Program Approval) 项目批准 LR (Launch Readiness) 投产准备就绪 LS (Launch Sign Off) 投产签收 J1 (Job1) 量产 Use for tooling kick off. 用于开模 Purchasing Related Process/ 采购相关的流程 RFQ Request for quotation which include Commercial document and ESOW. Commercial document tells the commercial items and ESOW tells the product information and requirements. 询价书包括了商务文件和产品工程规范和要求( ESOW) ESOW ESOW1 based on first version drawing for quotation ESOW2 based on 2nd version drawings for nomination ESOW3 based on 3rd version drawing for CPA ES0W1基于第一版图纸,用于询价 ES0W2基于第二版图纸,用于确定供应商 ES0W3基于第三版图纸,用于签订CPA CPA CPA is a commercial contract between Volvo and suppliers for the commodities. It is for the commodities price. CPA是沃尔沃和供应商之间的关于零件价格的合同。 Tooling order / 模具订单 Tooling order is an order to kick off suppliers with commercial tooling and engineering perspectives. 模具订单是沃尔沃从工程和商务两 方面来启动供应商的模具工作。 PPAP Refer to STA training later 参考后面STA的培训Purchasing
VOLVO英文缩写汇总
V O L V O英文缩写汇总 Prepared on 24 November 2020
英文缩写: PS (Program start) 项目开始 PSC (Program strategy confirmation) 项目策略确定 PTCC (Program Target Compatibility Check point) 项目目标分解 PTC (Program Target Confirmation) 项目目标确定 PA (Program Approval) 项目批准 LR (Launch Readiness) 投产准备就绪 LS (Launch Sign Off) 投产签收 J1 (Job1) 量产 Use for tooling kick off.用于开模 Purchasing Related Process/采购相关的流程RFQ Request for quotation which include Commercial document and ESOW. Commercial document tells the commercial items and ESOW tells the product information and requirements. 询价书包括了商务文件和产品工程规范和要求(ESOW)ESOW ESOW1 based on first version drawing for quotation ESOW2 based on 2nd version drawings for nomination
ESOW3 based on 3rd version drawing for CPA ESOW1 基于第一版图纸,用于询价 ESOW2 基于第二版图纸,用于确定供应商 ESOW3 基于第三版图纸,用于签订CPA CPA CPA is a commercial contract between Volvo and suppliers for the commodities. It is for the commodities price. CPA是沃尔沃和供应商之间的关于零件价格的合同。 Tooling order / 模具订单 Tooling order is an order to kick off suppliers’ tooling with commercial and engineering perspectives. 模具订单是沃尔沃从工程和商务两方面来启动供应商的 模具工作。 PPAP Refer to STA training later 参考后面STA的培训 Purchasing Drawing related Process/图纸相关流程 V0 1st released version drawing. ESOW1 use it. Design supplier need release V0 drawing to Volvo 第一版图纸用于ESOW1。设计供应商需要发布V0数据到Volvo 系统 V1 2nd released version drawing. ESOW2 use it. Design supplier need release V1 drawing to Volvo 第二版图纸用于ESOW2 。设计供应商需要发布V0数据到Volvo 系统 V2 3rd released version drawing. ESOW3 use it. Can be used for tooling design. Design supplier need release V3 drawing to Volvo 第三版图纸用于ESOW3和模具设计。设计供应商需要发布V2数据到Volvo 系
汽车文化作业
沃尔沃汽车文化发展史 沃尔沃的创始人古斯塔夫·拉尔森 古斯塔夫·拉尔森(Gustav Larson),他生于1887年,学工程,对轿车特别有兴趣,1911年在英国考文垂怀特和波普公司(White&Poppe)工作,1913年回到瑞典,1917年也在SKF 工作,1920年他在斯德哥尔摩的加尔科有限公司(AB Galco)担任技术经理。1924年拉尔森和加比利森在斯德哥尔摩饭店的一次小龙虾宴上相遇,加比利尔森向他建议,一起开发轿车。这时在瑞典市场上每年销售的15000辆轿车,95%是从美国进口的。 古斯塔夫·拉尔森- 人物经历 1887年7月8日出生于厄勒布鲁郡的Vintrosa,拉斯.拉尔森和胡尔达.马格努松的儿子,父亲是农民。1968年7月4日在克里斯蒂安斯塔德的Bastad去世。 1911-1916 英国考文垂怀特和波普公司工人 1913-1917 就读于斯哥德尔摩皇家技术学院 1917-1919 在哥德堡的SKF轴承公司任职 1919-1920 在Katrineholm的SKF轴承公司任职 1920-1926 任职于斯哥德尔摩的加尔科公司 1927与阿瑟·格布尔森一起创立沃尔沃公司 1926-1952 沃尔沃执行副总裁兼技术经理 1952-1958 董事会成员 1952-1968 沃尔沃公司顾问 古斯塔夫·拉尔森- 企业简介 沃尔沃(V olvo)这个名字是拉丁语,意思为“滚滚向前”。在1927年4月14日用于第一辆沃尔沃汽车V4之前,它曾是一个滚珠轴承的品牌名称。沃尔沃汽车的铭牌是钢铁的标志——一个带有斜箭头的圆圈(铁标)。这种标志的设计思路最初源自因耐久性而闻名的瑞典钢铁工业。自那时起,在世界各地,这个钢铁的符号就成了沃尔沃的代表。对沃尔沃而言,这一现代化的企业品牌标志也代表沃尔沃对客户所做出的安全、品质和设计三方面的承诺。 沃尔沃汽车公司成立于1927 年,总部设在瑞典的哥德堡。沃尔沃汽车公司的主要生产厂设在瑞典、比利时和中国,并在全世界超过100 个国家设立了销售和服务网络,拥有2,400 多家展厅。 欧罗夫?佩森被任命为沃尔沃新一任首席执行官 by 沃尔沃集团最新新闻 沃尔沃集团董事会决定任命现年46岁的欧罗夫?佩森(Olof Persson)为沃尔沃的新一任总裁兼首席执行官,欧罗夫?佩森之前的职务是沃尔沃建筑设备公司总裁。欧罗夫将于今年9月1日接替之前宣布8月底退休的雷夫?约翰森,出任沃尔沃集团总裁兼首席执行官。从今年5月1日起,欧罗夫将担任执行副总裁兼副首席执行官,与雷夫?约翰森并肩工作。 欧罗夫?佩森个人简历 欧罗夫?佩森是一名经济学家,研究生学历,曾获得卡尔斯塔德工商管理文学学士学位。职业生涯始于阿西布朗勃法瑞公司,在AdTranz和庞巴迪公司担任过多项管理职务。2006年,担任沃尔沃宇航总裁,同时出任沃尔沃集团管理委员会成员。 生于1964年,获得工商管理文学学士学位。 已婚,育有三个子女。 自2008年起居住于比利时布鲁塞尔(沃尔沃建筑设备公司总部所在地)。 自2006年起担任沃尔沃集团执行委员会成员。 2008年至2011年,任沃尔沃建筑设备公司总裁。
以安全为己任 沃尔沃汽车品牌历史介绍
8888翻页展示 责任编辑:齐天翔 发布时间:2011/7/12 8:00:00 |来源:车168类型:原 创 在80余年前,人们普遍尚未意识到汽车安全的重要性,而今天,能让人立即想到始终致力于安全方面不断创新的汽车品牌,那非VOLVO 沃尔沃莫属。安全车身、三点式安全带、盲点信息系统等,数十种主被动安全技术均出自沃尔沃之手。当然,它在环保等领域也不断努力着。下面,请跟随笔者一同追寻沃尔沃汽车在发展中留下的印记。 沃尔沃车标 VOLVO 的中文名为“沃尔沃”,但之前也曾被叫做“富豪”。Volvo 车标是由三部分组成,圆圈里面有一支箭(箭头呈对角线方向指向右上角)这是铁元素的古老化学符号。沃尔沃之所以在汽车上采用代表铁元素的品牌标志,是为了让人们联想起有着光辉传统的瑞典钢铁工业,以及证明车辆有钢铁般坚强的实力。 以安全为己任 沃尔沃汽车品牌历史介绍
与此同时,在散热器上设置的从左上方向右下方倾斜的一条对角线彩带。该设置原本出于技术上的考虑,用来固定车标在格栅上,后来就逐步演变成为一个装饰性符号而成为Volvo轿车最为明显的标志。当然,在沃尔沃车标中不可缺少的还有“VOLVO”字样(全部采用大写)。 VOLVO的由来 如果提到沃尔沃的历史,那么不得不追溯到1915年。在当时SKF轴承制造商出品的每一组车用滚珠与滚子轴承侧面,都会可有“Volvo”五个字母。随着汽车制造业在工业生产中的位置越发的重要。到了1924年,在SKF公司创始人的脑海中便已经萌生在瑞典建设整车制造公司的想法。直 至1926年,SKF公司董事会最终批准了这个项目,提供所需的资金,并正式创建AB Volvo公司。 20-30年代:沃尔沃发展初期,安全理念已深入人心 1926-1927年:沃尔沃第一款汽车诞生/撞出“安全”
沃尔沃策划书
商务谈判策划书 谈判背景资料 1.双方背景介绍 (1)甲方 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司是一家以汽车及汽车零部件生产经营为主要产业的大型民营企业集团,始建于1986年,经过十八年的建设和发展,在汽车、摩托车、汽车发动机、变速箱、汽车零部件、高等教育、装潢材料制造、旅游和房地产等方面都取得了辉煌业绩,资产总额已经超过50亿元;特别是1997年进入汽车制造领域以来,凭借灵活的经营机制和不断的观念创新,快速成长为中国经济型轿车的主力品牌,2003年企业经营规模列全国500强第331位,列“浙江省百强企业”第25位,被评为“中国汽车工业50年发展速度最快、成长最好”的企业之一,跻身中国国内汽车制造企业“3+6”主流格局。吉利汽车控股有限公司(Geely Automobile Holdings Limited,港交所:00175),是一间于香港交易所上市的公司,集团主席为李书福,主要业务为制造及分销汽车及汽车零部件。2004年被评选为中国汽车工业50年内50家发展速度最快、成长性最好的企业之一,更先后被各国机构,至各级政府评为“亚洲企业500强”、“中国企业500强”、“中国机械500强”、“中国最具生命力百强企业”、“国家创新型企业试点单位”等等荣誉称号。 (2)乙方
乙方:福特汽车公司。福特汽车公司是世界最大的汽车企业之一,1903年由亨利·福特先生创立创办于美国底特律市。现在的福特汽车公司是世界上超级跨国公司,总部设在美国密执安州迪尔伯恩市。2009年7月,由于主要竞争对手通用汽车公司破产重组,出售了8个品牌中的4个,市场份额下降,福特汽车公司成为全美最大汽车制造商,但和全球最大的丰田仍有较大差距。福特公司在2008年爆发的国际金融危机中坚决拒绝了美国联邦政府的注资援助。1999年4月1日,福特汽车公司出资64.5亿美元正式收购沃尔沃轿车。 福特汽车在中国的历史可追溯到1913年,当时第一批T型车销售到中国。1924年孙中山先生致信亨利.福特,请他帮助建立中国的汽车工业。作为首家在新中国开拓业务的外国汽车公司,福特汽车当时的董事长亨利.福特二世于1978年得到了邓小平先生的会见,表达了福特汽车公司与中国汽车工业合作的愿望。福特汽车(中国)有限公司成立于1995年10月25日。程美玮先生为现任董事长兼首席执行官。目前,福特汽车拥有位于江西省南昌市的江铃汽车(股份)有限公司30%的股份。作为上市公司,江铃汽车(股份)有限公司于1997年底成功推出了全顺(Transit) 商用汽车。到目前为止,已成功地推出了多达13种商务车型。 2001年4月25日,福特汽车公司和长安汽车集团共同初期投资9800万美元成立了长安福特汽车有限公司,双方各拥有50%的股份,专业生产满足中国消费者需求的轿车。目前,已经成功推出了福特嘉年华和蒙迪欧两款轿车。2003年10月,福特汽车和长安汽车集团签署了
沃尔沃售后,一个具有高质量高标准的服务体系
沃尔沃售后,一个具有高质量高标准的服务体系 2007 年,一辆1966 年生产的沃尔沃P1800 车型创造了新的行驶里程纪录,该记录超过了418 万公里(260 万英里),大约可以绕地球赤道104 圈!这不仅展现了沃尔沃汽车的高性能,还体现了沃尔沃售后的高质量。 沃尔沃售后团队一心为要消费者带来高质量高标准的服务体系,沃尔沃推出的多款车型服务就证明了这一点。沃尔沃运动型多功能车兼备越野车的性能和跑车的个性,并将动感激情的驾驶乐趣和高度的舒适性集于一身。T6双涡流涡轮增压发动机的澎湃动力和AWD 全轮驱动系统使驾驶者在享受推背感的同时又牢牢地掌握着车辆的稳定性,沃尔沃所有的安全性以及功能性问题沃尔沃售后团队都能够及时地替你分担解决,沃尔沃售后服务团队承诺只要到沃尔沃购车用车整个过程都能让你体验到最安逸最满意最舒适的服务。 沃尔沃汽车操作界面设计简洁大气,驾驶者可以随意采用方向盘上的一键式多功能滚轮或排布在中控台上的快捷键,同步实现对该系统的操作,这项科技配置的推出让沃尔沃在所有豪华车品牌的人车沟通系统的水平上处于绝对领先地位,不单是沃尔沃产品处于领先地位,沃尔沃售后也在所有豪华车品牌中位于领先地位。沃尔沃售后不仅能解决驾驶者在操作上遇到的问题,沃尔沃售后还能替你解决驾驶途中遇到的重大事故问题,因此沃尔沃售后总是能让消费者体验到贴心的服务,这也更充分地体现出沃尔沃汽车在沃尔沃售后方面以人为本理念。 沃尔沃汽车中国销售公司首席执行官施瑞翔(RichardSnijders)表示:“2012款S60是为满足中国豪华车消费者的需求而倾力打造的,它的上市体现了沃尔沃汽车对第二本土市场——中国的重视,反映了沃尔沃汽车中国发展战略在产品引进、品牌打造和销售规划层面的切实进展,同时沃尔沃售后服务也对该款汽车引起了重视,也反映了沃尔沃售后团队对
沃尔沃评审内容(1)
生产现场评估 1.生产过程能力计划 1.1质量体系ISOTS16949/ISO14001等 1.1.1供应商的质量体系需要通过第三方ISO/TS16949和ISO14001体系认证。 1.1.2供应商要对基本政策、质量手册、程序和工艺指导书进行年审,以确保它们都 是及时更新的。 1.2明确规定并经常更新客户和内部期望值、目标值和品质作业系统(QOS)的要求 1.2.1供应商要有一个书面的章程明确规定要定期更新客户和内部期望值、目标值和 品质作业系统要求 1.2.2供应商有明确的组织机构和管理公司的系统性章程,包括: *愿景和战略 *章程需要遵循VSIM(沃尔沃供应商改进矩阵),如PPM、质量关注、8D报告、反应时间、交付等其他目标 *客户满意度调查结果(生产、物流、供应商技术支持、采购人、研发等) *管理层需遵循月度持续改进计划并对各个可度量指标/项目设定责任人 *对于上述表现情况进行月度、年度评估 *行动趋势表可用来说明整改效果。 *人力和设备资源计划的章程 1.2.3供应商对售后情况进行跟踪,并且有一套评估规程来确定售后成本改善以及客 户满意度提高所需的因素。 1.2.4供应商有明确的组织和一个系统性的章程,这个章程必须确保零件符合该零件 领域的合法规定,甚至要符合关于对现存要求的变更和添加条款的要求
(如果没有法定的要求,可使用n/a) 1.3了解VSIM(沃尔沃供应商改进矩阵) 1.3.1供应商能了解PARMA/VSIM,并有章程规定如下: *根据ISO/TS16949和ISO14001及时更新信息 *更新联系信息 *跟踪VSIM要求 1.4关于内审的不符合项 1.4.1供应商要有一个内审的日程安排并依此进行内审 1.4.2内审中的不符合项不能有重复出现的 1.4.3对于内审所发现的所有不符合项,要有根本原因分析以及整改行动计划,避免类似的不符合项再次发生。 2.FMEA(失效模式和有效性分析)/控制计划 2.1FMEA手册和控制计划 2.1.1组织机构要满足AIAG(汽车工业行动小组)的FMEA手册以及ISO/TS16949 Annex A和AIAG APQP中对控制计划的要求 2.1.2所有的零件都要有书面的DFMEA、PFMEA和控制计划 2.1.3为了减少和消除潜在的失效模式,需要有稳健的系统性规程使得这些过程能得到持续发展和改进。 基于以下原则、根据PFMEA得分情况,可以按重要性顺序采取整改行动: 严重度关键度- 严重度和发生频率以及风险顺序数 2.1.4 FMEAs和控制计划至少需每年一次进行审核或者问题出现时进行审核
沃尔沃中国战略
沃尔沃中国战略:成都大庆建厂5年20万销量 来源:中国经营网时间:2011-02-25 15:35 作者:字体:大中小25日,沃尔沃在北京发布未来五年中国战略。沃尔沃表示,未来五年的目标是,到2015年沃尔沃汽车销量超过20万辆,中国豪华车市场份额占20%。 沃尔沃总裁兼首席执行官斯蒂芬·雅克布宣布,沃尔沃将在成都设立在华首个生产基地,成都新厂将于2013年落成并投入生产,届时将达到每年10万辆的生产能力。 除了在成都设立沃尔沃首个国产基地外,雅克布还透露,目前公司已经批准了在大庆建厂的计划。同时,沃尔沃还将在华扩展经销商网络,从现在到2015年,沃尔沃经销商门店数量从现在的106家增加到2015年的220家。此外,今年1月在上海成立沃尔沃中国总部,将成为沃尔沃在中国的研发、设计、采购中心。 雅各布表示,为了执行中国战略,一个全新的中国组织架构也宣布成立。沈晖先生担任全球高级副总裁兼沃尔沃汽车集团中国区董事长;童志远先生担任中国区首席执行官;王召兴先生担任中国区总裁;拉施·丹尼尔森(Lars Danielsson) 先生担任负责生产和质量控制 的中国区副总裁;施瑞翔(Richard Snijders)先生担任沃尔沃汽车集团下属中国销售公司的总裁和首席执行官。
沃尔沃汽车未来五年的商业战略重点包括产品规划和开发,销售与市场、零配件采购、本地化生产及人才战略等几部分。 一、不断调查研究中国市场,在了解中国市场、了解中国客户需求、了解竞争对手的基础上,规划进口产品和国产化的产品,设计满足中国消费者喜好的产品,快速适应中国市场的发展趋势和中国客户的不断变化的需求。 二、上海总部基地是沃尔沃汽车集团中国区的行政中枢,位于上海的沃尔沃汽车中国技术中心的工作重点是高档轿车、电动车和新能源汽车的设计、研究和开发。 三、在成都的沃尔沃汽车西部基地将以覆盖中国西部市场为主,参与和支持中国西部大开发。 四、在大庆的沃尔沃汽车北部基地将以覆盖中国北部市场为主,其地理条件与纬度与瑞典相似,目的是参与和支持东北老工业基地振兴。 五、沃尔沃汽车将加强对销售和市场的管理,4S店将从目前106家增加到220家,培训和优化销售服务人员,改善和提升客户体验和客户服务,大力加强沃尔沃汽车“全球豪华汽车品牌”的品牌建设工作。
VOLVO汽车线束制造标准(中文翻译版)
VOLVO汽车线束制造标准(中文翻译版) 《VCC电线束制造标准》(Rev 19) 目录 1 概述. 2. 零部件要求2.1 零部件要求2.1.1 护套(胶套)2.1.2 连接器与密封件2.1.3 线缆端子2.1.4 光学元件2.1.5 电缆线2.1.5.1 通用线缆规格2.1.5.2 制图代码设置2.1.6 线缆基本颜色代码2.1.7 线缆上的临时颜色代码 3. 关于制造的要求3.1 将线缆端子安装到线缆上3.1.1 线缆端子的压接3.1.2 线缆端子的焊接3.2 电线端子在连接器中的位置3.3 将电缆端子安装到连接器中3.4 电线端子的绝缘3. 4.1 普通端子主干的绝缘3.4.2 防水(WP)环端主干的绝缘3.5 电线端子的绝缘3.6 橡胶件的安装3.7 电线的绞合3.7.1 一般绞线要求3.7.2 常规绞线3.7.3 短距离绞线3.8 电线的布线3.8.1 线缆支架中的线缆布线3.8.2 电气保险盒中的电缆布线3.8.3 定位夹的旋转方向3.9 布线和最大光纤衰减3.10 非屏蔽连接器中使用的屏蔽多芯电缆4. 电子线缆的包裹4.1 包裹到连接器的自由电缆长度4.2 用软管包裹4.3 用开口软管包裹4.4 用拉链软管包裹4.5 用热缩管包裹4.6 用波纹塑料管包裹4.7 用开口的波纹塑料管包裹4.8 用非金属编织线缆套管包裹4.9 用非金属缝合线缆套管包裹,开口并重叠4.10 用粘性PET袖套包裹,开口并重叠4.11 用泡沫管包裹4.12 用PVC片包裹4.13 用PVC胶带包裹4.13.1 胶带缠绕两圈(点缠)4.13.2 胶带松散缠绕(间距缠,花缠)4.13.3 紧密缠绕胶带(全缠,密缠)4.13.4 交叉缠绕胶带(交叉缠)4.14 用其他材料的胶带包裹4.14.1 其他材料的胶带缠绕两次(点缠)4.14.2 4.14.2 其他材料的胶带松散缠绕4.14.3 其他材料的胶带紧密胶带4.14.4 其他材料的胶带交叉缠绕4.14.5 用粘性面对面的其他材料胶带对折4.15 用泡沫胶带包裹4.1 5.1 粘性面对面折叠4.15.2 纵向缠绕,重叠4.16 用线缆扎带包裹4.17 用线缆扎带或胶带缠绕两圈包裹4.18 用铝覆反射热保护包裹4.19 同一点上的几个符号5. 线束标记5.1 零件编号标记5.2 原标识的国家5.3 标识的性能5.4 用记号笔标记5.5 位置标记5.6 功能标记 6. 铰接 6.1 非密封电线铰接点,NWP6.2 密封的电线铰接点,WP6.3 有关铰接点位置的一般要求6.3.1 无尺寸要求的铰接点位置6.3.2 线缆通道外的铰接点位置要求6.3.3 在其他塑料外壳,保险盒或类似物品内铰接点位置的要求6.3.4 靠近胶套的铰接点位置的要求 7.屏蔽标记的末端与性能7.1 7.1 屏幕层的末端,未密封,NWP7.2 7.2 屏蔽层末端,密封的,WP 8.粘接 9.尺寸的定义9.1 概念9.2 主干和分支的定义9.3 分支点9.4 分支长度9.5 原始文件的连接器视图(2D图纸或3D模型)10.长度公差11.原始文件上的表格规范(2D图纸或3D模型)12.结果等级13.公差要求14.端子选择15. 参考原始文档(2D图纸或3D模型) 1.概述 除非在原始文档,2D工程图或3D模型中另有说明,否则本技术法规中规定的所有要求均适用。(可在供应商的“主文件/零件”文件夹中找到有效的原文件的类型) 2.零部件要求 根据本技术法规制造的线束应满足零部件的所有要求以及线束图纸文件和相关文件中规定的要求。对于备件,由于各种原因,线束中较旧的组件可能会被更改或更换。在与VCC EDS零件组的负责零件工程师达成一致之后,仍然可以通过更新文档31814803“售后服务线束偏差电子表格”来满足要求。 2.1 零部件要求线束中包含的所有零件应符合最新有效的“VCC限制物质管理标准”(文件VCS5036,5)确定的要求。使 用的材料之间的兼容性,意味着线束中包含的零件/材料不得以负面的方式相互影响。如果采用新材料/新材料组合,则应始终按照文件31832379线束材料测试标准来进行测试。除非在与VCC,电气架构,EDS设计达成协议之后,可以授予例外情况不进行测试。如果要使用新的聚合物产品和增塑剂,并且没有在VCC上使用10年以上,则必须根据IEC 60068-2-10中的变量1进行真菌学测试。除了DIN IEC 60068 -2-10要求的有机物外,还应使用以下有机物:1. 阿姆斯特丹曲霉;2. 宛氏拟青霉3. 球毛壳霉 ChaetomiumGlobosum.样品应每24小时检查一次霉菌生长。如果检测到霉菌生长,则可以停止测试。要求:不得发霉。绝缘层不得有裂纹,断裂或其他缺陷。 2.1.1 护套(胶套)胶套的密封性能通常来自两个方面,一个是抵靠在车身附件或零部件上的外部密封。该密封对零件等级有要求,并且应由零件文档来满足。另一个密封处就是在胶套与线束之间。如果此密封有密封性能要求,它应在线束图纸上注明,并应采用IP等级与可接受标准字母的形式。可接受标准字母:可接受标准等级IP XX-A:胶套的干区测不允许有水。
汽车文化复习题
汽车文化知识点总结 1、兰博基尼汽车源自意大利,目前是大众汽车公司旗下的品牌。 2、汽车中的贵族是劳斯莱斯品牌。 3、意大利的汽车品牌中被称为跑车中的精品的是法拉利,被誉为气壮如牛的是兰博基尼。 4、萨博和沃尔沃是原自瑞典的汽车品牌。 5、大众汽车公司的创始人是费迪南德.波尔舍。 6至少说明五个以上意大利的知名跑车品牌。 答:法拉利、玛莎拉蒂、兰博基尼、布加迪、阿尔法?罗密欧。 7. 我国的三大汽车集团公司是指一汽、东风、上汽。 8. 汽油机由曲柄连杆机构、配气机构、供给系、润滑系、冷却系、点火系和起动系组成。 9. 福特汽车公司的创始人是亨利?福特。 10. 大众汽车公司的总部设在德国的沃尔夫斯堡市。 11. 中国汽车工业的杰出奠基人和开拓者为饶斌。 12. 德国法兰克福车展、日本东京车展瑞士日内瓦车展、法国巴黎车展、美国北美车展 被誉为当今世界五大车展。 13. 确定汽车外形需要考虑三个因素,即机械工程学、人体工程学和空气动力学。 14. 通用汽车的创始人为威廉.杜兰特 15. 世界汽车制造业中最大的跨国公司是通用公司— 16. 神龙汽车有限公司总部在|湖北武汉 17.2004年一级方程式汽车大赛中国大奖赛在上赛道举行。 18. 汽车底盘由传动系、行使系、转向系、制动系组成。 19. 美国著名的汽车城底特律是通用、福特和克莱斯勒三大汽车公司总部所在地。 20. 上海通用汽车公司由美国通用汽车公司和上海汽车公司出资组建。 21. 世界汽车诞生日是1886年1月29日。
22. 汽油机排气污染主要成分是CO HC和NOX。 23. “VIN车辆识别代号编码”由一组字母和阿拉伯数字组成,共| 17 |位。 24. “当他未来到人世时,这个世界还是马车时代。当他离开人世时,这个世界已成了汽车的世界”这句话使用来形容|亨利福特|的。 25. 日本人称为“日本大批量生产汽车生产之父”是指丰田喜一郎。 不弃的追求; 26.1908年,福特开发了举世闻名的T型车,并首创了汽车大规模流水线生产方式,极大地提高了生产效率。 27. 汽车一般是由发动机、底盘、车身、电气设备四部分组成。 28. CA7180是指一汽公司生产的、排量为1. 8升的小汽车。 29. 宝马是驰名世界的汽车企业,被认为是高档汽车生产业的先导。宝马标志中间的蓝白相间图案,代表蓝天、白云和螺旋桨。 30. 汽油的辛烷值一般表示汽油的抗爆性。 31. 日本丰田公司开创了汽车制造精益生产方式,用精益求精的态度和科学的方法来控制和管理汽车的设计开发、工程技术、采购、制造、储运、销售和销后服务的每一个环节,从而达到以最小的投入创造出最大的价值的目的。 32. 舒马赫总共荣登7次F1世界冠军的宝座。 33. ABS是防抱死制动系统的缩写。 34. GPS是全球定位系统的缩写。 35. 德国奥迪汽车公司原来是由4家公司合并而成。 36. 未来汽车的发展方向是什么?(10分) 答:一、乘用车柴油机化的比例将越来越高。随着柴油机技术的不断发展,特 别是小型高速直喷式柴油机技术的日趋完善,使其较汽油机更为经济、排放更低,因此装用柴油机的车型将越来越受欢迎。二、电动汽车将进入实用阶段。随着低价格、高能量和长寿命新型电池的研究发展,以及人们对环保的强烈呼声,电动汽车将越来越多地在各大城市取代石油能源汽车成为一种代步工具。 37. 流线型车身的大量生产的是甲壳虫车。
VOLVO英文缩写汇总
V O L V O英文缩写汇总 Company Document number:WTUT-WT88Y-W8BBGB-BWYTT-19998
英文缩写: PS (Program start) 项目开始 PSC (Program strategy confirmation) 项目策略确定 PTCC (Program Target Compatibility Check point) 项目目标分解 PTC (Program Target Confirmation) 项目目标确定 PA (Program Approval) 项目批准 LR (Launch Readiness) 投产准备就绪 LS (Launch Sign Off) 投产签收 J1 (Job1) 量产 Use for tooling kick off.用于开模 Purchasing Related Process/采购相关的流程RFQ Request for quotation which include Commercial document and ESOW. Commercial document tells the commercial items and ESOW tells the product information and requirements. 询价书包括了商务文件和产品工程规范和要求(ESOW)ESOW ESOW1 based on first version drawing for quotation ESOW2 based on 2nd version drawings for nomination
Volvo 标准--GPDS Training To Suppliers 20120110
Issue date: 2/15/2012Volvo GPDS Training 沃尔沃GPDS培训 VCTC R&D Miao Weimin 研发缪伟民 2012-01-10
Issue date: 2/15/2012 Training Purpose/培训目的 ?Let suppliers have a initial understanding of Volvo vehicle development process 给供应商一个有关沃尔沃产品开发流程的简单介绍 ?Let suppliers understand all the activities which relate to suppliers 让供应商理解所与供应商有关的活动
Issue date: 2/15/2012 GPDS/GPDS 的定义 ?GPDS: Global Product Development System ?GPDS :全球产品开发体系
Issue date: 2/15/2012 ?GPDS get the engineering, design, purchasing, manufacturing , marketing (customer) and suppliers to work together to deliver a good vehicle. ?GPDS将工程,造型,采购,制造,市场和供应商整合在一起,为客户开发一个好的车型。
Issue date: 2/15/2012 Powertrain / 动力总成Under body / 下车体Upper body /上车体
汽车文化试卷1
《汽车文化》试题一 一、填空题(20分) 1.我国的三大汽车集团公司是指 、 和 。 2.在我国,汽车是指由自身装备的 驱动,一般具有4个或4个以上的车轮,不依靠 或 而在陆地行驶的车辆。 3.汽油机由 、 、供给系、润滑系、冷却系、点火系(柴油机无此系统)和起动系组成。 4.2002年,德国 汽车公司和我国 汽车公司合资生产宝来汽车。 5.福特汽车公司的创始人是 。 6.大众汽车公司的总部设在德国的 市. 7.中国汽车工业的杰出奠基人和开拓者为 。 8.我国著名的车展有 和 。 9.德国法兰克福车展、 、 、 和 被誉为当今五大国际车展。 10.世界上第一条汽车流水线装配线是在 国 二、判断题(20分) ( )1.发动机后置后轮驱动,现在大、中型客车常采用的布置形式。 ( )2.汽车底盘由传动系、行驶系、转向系和制动系4部分组成。 ( )3.戈特利布?戴姆勒制造的是四轮汽车,卡尔?本茨(Karl Benz)发明了三轮汽车,他们二人都被世人尊称为“汽车之父”。 ( )4.在汽车加速行驶时,其阻力由滚动阻力、空气阻力、坡道阻力和加速阻力组成。 ( )5.收缩色就是与同样体积的膨胀色看起来要大一些 。 ( )6.一级方程式赛车的车队由三部分组成:赛车、赛车手和维修人员,一级方程式赛车可以在高速公路正常行驶。 ( )7.只要搞好智能交通系统的建设,交通企业和管理部门的管理水平差点无所谓。 ( )8.中国二汽“东风”牌汽车车标,其中的“二”字寓意于双燕之中,戏跃翻飞的春燕,还象征着东风牌汽车车轮不停地旋转,奔驰在祖国大地,冲出亚洲,奔向世界。 ( )9.汽车耐力赛是一种非场地赛,比如法国勒芒24h 耐力赛。 ( )10.标致----雪铁龙汽车公司在中国的合资企业为上海雪铁龙汽车公司。 三、单选题(30分) ( )1.在下列指标中,可以作为汽车燃料经济性能评价指标的是: A 每小时耗油量 B 有效热效率 C 百公里耗油量 D 有效燃料消耗率 ( ) 2.确定汽车外形需要考虑三个因素,即机械工程学、人体工程学和______.。 A 运动学 B 地面力学 C 仿生学 D 空气动力学 ( )3.一般邮政车采用什么颜色的。 A 红色 B 黄色 C 白色 D 绿色 ( )4.通用汽车的创始人为: A 威廉.杜兰特 B 亨利.福特 C 阿尔弗莱德.斯隆 D 费迪南德.波尔舍 ( ) 5.下列公司属于福特汽车公司的为: A 沃尔沃 B 雪铁龙 C 法拉利 D 宾利 ( )6. SUV 是 汽车。 A 、舒适型休闲汽车 B 、越野比赛用车 C 、运动型多功能 D 以上都不对 ( )7.世界汽车制造业中最大的跨国公司是: A 丰田公司 B 大众公司 C 通用公司 D 雷诺一日产公司 ( )8.高速行驶,箱型汽车并不够理想,因为它的阻力大大妨碍了汽车前进的速度,所以人们又开始研究一种新的车型是: ………………………………装…………………………………订……………………………………线……………………………………
