情态动词的基本用法归纳
常见的情态动词及其用法

常见的情态动词及其用法
常见的情态动词有 can,could,will,would,should,may,might 和 must。
以下是每一个情态动词的主要用法:
1. can(could):表示能力和可能性,一般在肯定句中使用。
例如:
- I can swim.
- Can you run fast?
2. will(would):表示意志、愿望和习惯,一般在肯定句中使用。
例如:
- I will go to school tomorrow.
- I would play basketball if I had time.
3. should:表示建议和义务,一般在肯定句和疑问句中使用。
例如:
- You should wear a coat.
- Should we go to the movies?
4. may(might):表示许可和可能性,一般在肯定句和疑问句中使用。
例如:
- You may go now.
- Might you give me a ride to the airport?
5. must:表示义务和必要,一般在肯定句和疑问句中使用。
例如:
- You must clean your room.
- Must we finish this project before Friday?。
情态动词的用法

情态动词的用法情态动词是英语中一类特殊的动词,它们用来表示说话人对某种行为或状态的态度或情感色彩,比如可能性、必要性、愿望、建议等。
情态动词包括can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, ought to等。
它们在句子中通常与动词原形搭配使用,表示不同的意义和语气。
在本文中,我们将探讨情态动词的用法,并举例说明它们在句子中的应用。
1. 表示可能性。
情态动词can, could, may, might用来表示可能性,表明说话人认为某种情况有可能发生。
例如:It may rain tomorrow.(明天可能会下雨。
)。
She could be at home.(她可能在家。
)。
You might be right.(你可能是对的。
)。
2. 表示能力。
情态动词can, could用来表示能力或可能性,表明说话人认为某人有能力或可能做某事。
例如:I can speak English.(我会说英语。
)。
She could run very fast when she was young.(她年轻时跑得很快。
)。
3. 表示请求和允许。
情态动词can, could, may, might用来表示请求或允许,表明说话人请求对方做某事或征求对方的意见。
例如:Can you help me with this?(你能帮我一下吗?)。
Could I use your pen?(我可以用一下你的笔吗?)。
May I come in?(我可以进来吗?)。
4. 表示必要性。
情态动词must, should, ought to用来表示必要性或建议,表明说话人认为某种行为是必要的或值得做的。
例如:You must finish your homework before you go out to play.(你必须在出去玩之前完成作业。
)。
You should apologize to her.(你应该向她道歉。
情态动词用法归纳总结
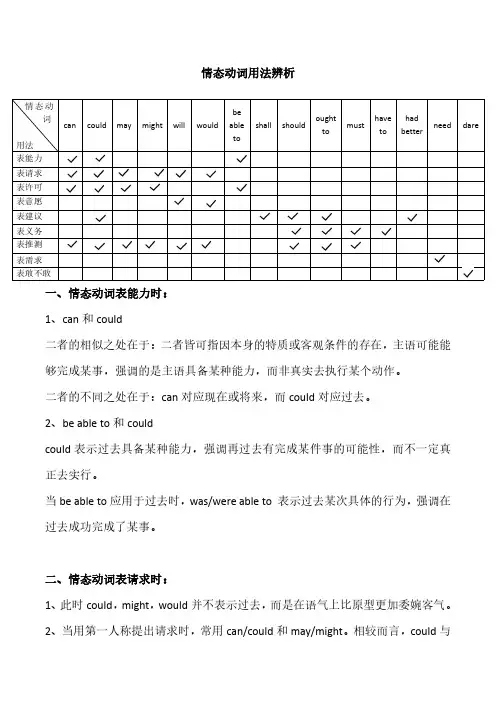
情态动词用法辨析情态动词用法can could may might will would be able to shall should ought to must have to had better need dare表能力表请求表许可表意愿表建议表义务表推测表需求表敢不敢一、情态动词表能力时:1、can 和could二者的相似之处在于:二者皆可指因本身的特质或客观条件的存在,主语可能能够完成某事,强调的是主语具备某种能力,而非真实去执行某个动作。
二者的不同之处在于:can 对应现在或将来,而could 对应过去。
2、be able to 和couldcould 表示过去具备某种能力,强调再过去有完成某件事的可能性,而不一定真正去实行。
当be able to 应用于过去时,was/were able to 表示过去某次具体的行为,强调在过去成功完成了某事。
二、情态动词表请求时:1、此时could ,might ,would 并不表示过去,而是在语气上比原型更加委婉客气。
2、当用第一人称提出请求时,常用can/could 和may/might 。
相较而言,could 与may在表请求的问句中出现的频率最高;might表发请求的语气最为委婉客气,因此反而很少见;而can则常用于熟人间的对话中。
语气强度:can>could/might>might3、当用第二人称提出请求时,常用can/could和will/would。
其中could和would 表达请求的语气更委婉客气;而can与will则常用于熟人对话中。
语气强度:can/will>could/would三、情态动词表许可时:1、与表请求不同,will/would不论前接第几人称,都表示主语本身的意愿,无需得到他人的“许可”,所以will/would不可以用于表请求的句中。
2、can和may二者都可以表示对现在或将来动作的许可,其中can的使用频率更高。
情态动词的基本用法归纳

情态动词的基本用法归纳情态动词有can (could), may (might), must, have to, shall (should, will (would), dare (dared), need (needed), ought to等。
情态动词无人称和数的变化;不能单独使用,必须与其后的动词原形构成谓语。
一、can, could1) 表示能力(体力、知识、技能)。
Can you lift this heavy box?(体力)Mary can speak three languages.(知识)Can you skate?(技能)此时可用be able to代替。
Can只有一般现在时和一般过去式;而be able to则有更多的时态。
I’ll not be able to come this afternoon.当表示“经过努力才得以做成功某事”时应用be able to,不能用Can。
如:He was able to go to the party yesterday evening in spite of the heavy rain.2) 表示请求和允许。
-----Can I go now?----- Yes, you can. / No, you can’t.此时可与may互换。
在疑问句中还可用could,might代替,不是过去式,只是语气更委婉,不能用于肯定句和答语中。
---- Could I come to see you tomorrow?---- Yes, you can. ( No, I’m afraid not. )3) 表示客观可能性(客观原因形成的能力)。
T hey’ve changed the timetable, so we can go by bus instead.This hall can hold 500 people at least.4) 表示推测(惊讶、怀疑、不相信的态度),用于疑问句、否定句和感叹句中。
情态动词的基本用法

1. can的基本用法: ⑴ 表示体力或智力上的能力,即“能够,会”,可与be able to转换。 例:He can speak English. = He is able to speak English. —Can you play basketball? — No, I can’t. 如果表示将来具备的能力,要用will be able to。 例:If I have a good sleep, I will be able to do the problem. ⑵ 表示许可,主要用于口语,书面语一般用may。 例:—Can we go home now, please? — No, you can’t. You can only smoke in this room. You can’t keep the library books for more than a month.
1. can的基本用法: ⑶ 表示“可能”,与may同义,但一般用在疑问句中。 例:What can he possibly want? 在否定句中,否定形式can’t表示推测“不大可能”。 例:Anybody can make mistakes. The news can’t be true. 与第一、二人称连用时,还可以就可能的解决问题的方式或可能的行为 提出建议。在这里,也可用could使语气婉转。 例:Can / Could we meet again next week? 下周我们可以再见面吗? —What shall we do? 我们怎么办呢? — We can / could try asking Lucy for help. ——我们可以请露茜帮忙试试 看。 You can / could help me with the cooking. 你可以帮我做饭。
情态动词用法归纳(全)

情态动词用法归纳(全)情态动词用法归纳情态动词是英语中的一类特殊动词,用于表达情感、态度、能力、推测和义务等。
它们常常用来修饰其他动词,帮助我们表达不同的意思。
在本文中,我们将归纳总结情态动词的用法,帮助读者更好地理解和运用这些动词。
一、态度和情感1. Can (能够)Can用来表示某种态度或情感,常用于表示能力、允许和请求等。
例如:- I can swim. (我会游泳。
)- Can I borrow your pen? (我可以借用你的钢笔吗?)- You can't be serious! (你不可能是认真的!)2. Could (可能)Could用来表示过去的能力、允许和请求等。
它还可以用来表示某种可能性。
例如:- When I was younger, I could run faster. (我年轻的时候跑得更快。
)- Could I ask you a question? (我可以问你一个问题吗?)- It could rain later, so bring an umbrella. (今天后面可能会下雨,所以带上雨伞。
)3. May (可能)May常表示许可、请求和推测等。
它还可以用来表示某种可能性或希望。
例如:- May I use your phone? (我可以用一下你的手机吗?)- It may rain tomorrow. (明天可能会下雨。
)- They may arrive late. (他们可能会迟到。
)4. Might (可能)Might与may的用法类似,但表示的可能性稍微低一些。
例如:- She might be busy. (她可能很忙。
)- I might go to the party, but I'm not sure yet. (我可能会去参加派对,但我还不确定。
)二、能力和推测1. Must (必须)Must用来表示强烈的推断或必要性。
情态动词的用法
情态动词的用法什么是情态动词?在英语中,情态动词(modal verb)是一类特殊的助动词,它们用来表示说话人的态度、意愿、能力、推测、建议、命令等。
常见的情态动词包括can、could、may、might、shall、should、will、would、must、ought to等。
情态动词的基本用法1.表示能力和允许:–can及其过去式could用来表示能力和允许。
例如:I can speak English.(我会说英语。
)Theycould go to the party last night.(他们昨晚能去参加晚会。
)–may及其过去式might用来表示允许和可能性。
例如:May I go to the bathroom?(我可以去洗手间吗?)It might rain tomorrow.(明天可能会下雨。
)2.表示义务和必需:–must用来表示义务和必需。
例如:You must finish your homework before playing games.(你必须在玩游戏之前完成作业。
)–should用来表示应该和建议。
例如:She should eat more vegetables for her health.(她应该多吃蔬菜保护健康。
)3.表示推测和肯定:–will用来表示未来意愿和不可避免的行为。
例如:I will help you with your presentation.(我会帮你做演讲。
)–would用来表示假设和委婉表达。
例如:If I had more time, I would travel around the world.(如果我有更多时间,我会环游世界。
)情态动词的用法注意事项1.情态动词后接不带to的原形动词,即不加动词的第三人称单数-s形式。
例如:He can swim well.(他游泳游得很好。
)They should study hard.(他们应该努力学习。
情态动词的用法
情态动词的用法情态动词是英语中一类具有特殊功能的动词,它们用来表示说话人对某种可能性、能力、意愿、允许或推测的态度。
情态动词包括can、could、may、might、shall、should、will、would、must等。
在本文中,我们将对这些情态动词的用法进行详细介绍。
1. 表示能力情态动词can表示说话人具备某种能力。
例如:He can swim.(他会游泳。
)注意:can在现在时态中表示现在或经常性的能力,在过去时态中表示过去的能力。
2. 表示推测情态动词may、might用于表示推测或猜测的意思。
例如:She may be late for the meeting.(她可能会迟到会议。
)注意:may表示可能性较高,might则表示可能性较低。
3. 表示意愿情态动词will、would表示说话人的意愿、愿望或请求。
例如:I will help you.(我愿意帮助你。
)注意:would常用于表示比较客气的请求。
4. 表示推测的过去情态动词must常用于表示对过去情况的推测或肯定。
例如:He must have missed the bus.(他肯定错过了公交车。
)注意:must用于表示对过去情况的肯定,而might用于表示对过去情况的推测。
5. 表示义务或必要性情态动词must表示对义务、必要性或确定性的肯定。
例如:You must finish your homework.(你必须完成作业。
)6. 表示建议或应该情态动词should表示建议或应该。
例如:You should go to bed early.(你应该早点睡觉。
)注意:should还可以表示对过去情况的推测,例如:He should have arrived by now.(他现在应该已经到达了。
)7. 表示允许或许可情态动词can与may可以用于表示许可或允许。
例如:Can I borrow your pen?(我可以借你的钢笔吗?)8. 表示可能性情态动词could用于表示可能性。
情态动词用法归纳(全)
四、 dare, need
3) dare和 need作实义动词用时, 有人称、时态和数的变化。 在肯定句中,dare后面常接带to的不定式。在疑问句和否 认句中,dare后面可接带to或不带to的不定式。而need后 面只能接带to的不定式。
1. I dare to swim across this river.
----Can it be our teacher? 那个人有可能是我们老师吗?
----No, it can’t be our teacher. He is on a visit to the Great Wall. 不可能。咱们老师正在游览长城精呢品P。PT
例 --- I think Miss Gao must be in the library. She said she would go there. ----- No. She __ be there, I have just been there. A.can’t B.mustn’t C.needn’t D.wouldn’t
精品PPT
六、 will, would
• 3) would表示过去反复发生的动作或某种倾向。would表 示过去习惯时比used to正式,且没有“现已无此习惯〞的 含义。
• 1. During the vacation, he would visit me every other day.
• 2. The wound would not heal.
• 4) 表示估计和猜测。
• It would be about ten o’clock when she left home.
精品PPT
七、should, ought to
1) should, ought to表示“应该〞,ought to表示义务或责任, 比should语气重。
情态动词的用法归纳
情态动词的用法归纳情态动词是一类帮助表达情态、态度、推测、建议和能力等含义的动词。
以下是情态动词的常见用法:1. 表示能力与能力推测:- can例句:I can swim.(我会游泳。
)- could例句:He could swim when he was five.(他五岁时就会游泳了。
)2. 表示许可与禁止:- may例句:You may use my phone.(你可以用我的手机。
)- might例句:I might go to the party tonight.(我可能今晚去参加派对。
)- mustn't例句:You mustn't smoke here.(你不能在这里抽烟。
)3. 表示推测与推测的否定:- may例句:He may be late.(他可能会迟到。
)- might例句:It might rain later.(天后可能会下雨。
)- can't例句:They can't be at home.(他们不可能在家。
)4. 表示义务与责任:- must例句:We must finish our homework.(我们必须完成作业。
)- have to例句:I have to go to work early tomorrow.(我明天必须早点去上班。
)5. 表示愿望与建议:- should例句:You should exercise regularly.(你应该经常锻炼。
)- ought to例句:They ought to help others.(他们应该帮助别人。
)6. 表示推荐与要求:- would like例句:I would like to have a cup of tea.(我想要一杯茶。
)- need例句:You need to finish this report by tomorrow.(你需要在明天之前完成这份报告。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
~情态动词的基本用法归纳情态动词有can (could), may (might), must, have to, shall (should, will (would), dare (dared), need (needed), ought to等。
情态动词无人称和数的变化;不能单独使用,必须与其后的动词原形构成谓语。
一、 can, could1) 表示能力(体力、知识、技能)。
Can you lift this heavy box(体力)Mary can speak three languages.(知识)\Can you skate(技能)此时可用be able to代替。
Can只有一般现在时和一般过去式;而be able to则有更多的时态。
I’ll not be able to come this afternoon.当表示“经过努力才得以做成功某事”时应用be able to,不能用Can。
如:He was able to go to the party yesterday evening in spite of the heavy rain.2) 表示请求和允许。
-----Can I go now----- Yes, you can. / No, you can’t.%此时可与may互换。
在疑问句中还可用could,might代替,不是过去式,只是语气更委婉,不能用于肯定句和答语中。
---- Could I come to see you tomorrow---- Yes, you can. ( No, I’m afraid not. )3) 表示客观可能性(客观原因形成的能力)。
They’ve changed the timetable, so we can go by bus instead.This hall can hold 500 people at least.4) 表示推测(惊讶、怀疑、不相信的态度),用于疑问句、否定句和感叹句中。
Can this be true?This can’t be done by him.How can this be true二、 may, might1) 表示请求和允许。
might比 may语气更委婉,而不是过去式。
否定回答时可用can’t 或mustn’t,表示“不可以,禁止”。
----Might/ May I smoke in this room---- No, you mustn’t.---- May/Might I take this book out of the room---- Yes, you can. (No, you can’t / mustn’t. )》用May I...征徇对方许可时比较正式和客气,而用Can I...在口语中更常见。
2)用于祈使句,表示祝愿。
May you succeed!3) 表示推测、可能性(不用于疑问句)。
might不是过去式,它所表示的可能性比may小。
1.He may /might be very busy now.2.Your mother may /might not know the truth.三、 must, have to:1) 表示必须、必要。
You must come in time.在回答引出的问句时,如果是否定的,不能用mustn’t(禁止,不准),而用needn’t, don’t have to(不必).---- Must we hand in our exercise books today---- Yes, you must.---- No, you don’t have to / you needn’t.2) must是说话人的主观看法,而have to则强调客观需要。
Must只有一般现在时, have to 有更多的时态形式。
1.he play isn’t interesting, I real ly must go now.)2. I had to work when I was your age.3) 表示推测、可能性(只用于肯定的陈述句)1.You’re Tom’s good friend, so you must know what he likes best.2. Your mother must be waiting for you now.四、 dare, need1) dare作情态动词用时, 常用于疑问句、否定句和条件从句中, 过去式形式为dared。
1.How dare you say I’m unfair2.He daren’t speak English before such a crowd, dare he;3. If we dared not go there that day,we couldn’t get the beautiful flowers.2) need 作情态动词用时, 常用于疑问句、否定句。
在肯定句中一般用must, have to, ought to, should代替。
1.You needn’t come so early.2. ---- Need I finish the work today---- Yes, you must. / No, you needn’t.3) dare和 need作实义动词用时,有人称、时态和数的变化。
在肯定句中,dare后面常接带to的不定式。
在疑问句和否定句中,dare后面可接带to或不带to的不定式。
而need后面只能接带to的不定式。
1. I dare to swim across this river.2. He doesn’t dare (to) answer.#五、 shall, should1) shall 用于第一人称,征求对方的意见。
What shall we do this evening2) shall 用于第二、三人称,表示说话人给对方的命令、警告、允诺或威胁。
1. You shall fail if you don’t work hard.(警告)2. He shall have the book when I finish it.(允诺)3. He shall be punished.(威胁)六、 will, would-1) 表示请求、建议等,would更委婉。
Will / Would you pass me the ball, please2) 表示意志、愿望和决心。
1. I will never do that again.2. They asked him if he would go abroad.3) would表示过去反复发生的动作或某种倾向。
would表示过去习惯时比used to正式,且没有“现已无此习惯”的含义。
1. During the vacation, he would visit me every other day.2. The wound would not heal.>4) 表示估计和猜想。
It would be about ten o’clock when she left home.七、 should, ought to1) should, ought to表示“应该”,ought to表示义务或责任,比should语气重。
1. I should help her because she is in trouble.2. You ought to take care of the baby.2) 表示劝告、建议和命令。
should, ought to可通用,但在疑问句中常用should。
1. You should / ought to go to class right away.]2. Should I open the window3) 表示推测should , ought to (客观推测), must(主观推测)。
must be home by now. (断定他已到家)ought to/should be home by now.(不太肯定)3. This is where the oil must be.(直爽)4. This is where the oil ought to/should be.(含蓄)八、情态动词+不定式完成式(have done)~1) can / could + have done在肯定句中表示“本来可以做而实际上能做某事”,是虚拟语气;在疑问句或否定句中表示对过去行为的怀疑或不肯定, 表示推测。
1. You could have done better, but you didn’t try your best. (虚拟语气)2. He can’t have been to that town.(推测)3. Can he have got the book(推测)2) may / might +不定式完成式(have done)表示对过去行为的推测。
不能用于疑问句中,没有虚拟语气的用法。
Might所表示的可能性比may小。
1. He may not have finished the work .2. If we had taken the other road, we might have arrived earlier.,3)must +不定式完成式(have done)用于肯定句中,表示对过去行为的推测。
意为“一定、想必”。
其疑问、否定形式用can,can’t代替。
参看1) can / could + have done表示推测。
1. You must have seen the film Titanic.2. He must have been to Shanghai.4)should +不定式完成式(have done)用于肯定句中,表示对过去行为的推测。
He should have finished the work by now。
表示“本应该做而实际上没有做某事”,其否定式表示某种行为本不该发生却发生了。
可以与ought to +不定式完成式(have done)互换。
1. You ought to / should have helped him. (but you didn’t.)2. She shouldn’t have taken away my measuring tape, for I wanted to use it.5) needn’t +不定式完成式(have done)表示“本来不必做而实际上做了某事”。
