中级财务会计分录大全(word)
中级会计师实务分录汇总1

中级会计师实务分录汇总1中级会计师实务中,分录是一项重要的内容。
以下为您汇总了一些常见的中级会计师实务分录,希望能对您的学习和工作有所帮助。
一、货币资金1、库存现金(1)从银行提取现金借:库存现金贷:银行存款(2)将现金存入银行借:银行存款贷:库存现金2、银行存款(1)企业将款项存入银行借:银行存款贷:库存现金/应收账款/主营业务收入等(2)企业从银行支取款项借:库存现金/应付账款/管理费用等贷:银行存款二、存货1、购入存货(1)发票账单与材料同时到达借:原材料/在途物资应交税费——应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款/应付账款/应付票据等(2)发票账单先到,材料后到借:在途物资应交税费——应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款/应付账款/应付票据等材料验收入库时:借:原材料贷:在途物资(3)材料已到,发票账单未到月末暂估入账:借:原材料贷:应付账款——暂估应付账款下月初用红字冲回:借:原材料(红字)贷:应付账款——暂估应付账款(红字)2、发出存货(1)个别计价法按照各种存货逐一辨认各批发出存货和期末存货所属的购进批别或生产批别,分别按其购入或生产时所确定的单位成本计算各批发出存货和期末存货成本。
(2)先进先出法先购入的存货应先发出(销售或耗用),以此确定发出存货和期末存货的成本。
(3)月末一次加权平均法存货单位成本=月初库存存货的实际成本+∑(本月各批进货的实际单位成本×本月各批进货的数量)÷(月初库存存货数量+本月各批进货数量之和)本月发出存货的成本=本月发出存货的数量×存货单位成本本月月末库存存货成本=月末库存存货的数量×存货单位成本(4)移动加权平均法存货单位成本=(原有库存存货的实际成本+本次进货的实际成本)÷(原有库存存货数量+本次进货数量)本次发出存货的成本=本次发出存货数量×本次发货前存货的单位成本本月月末库存存货成本=月末库存存货的数量×本月月末存货单位成本3、存货清查(1)存货盘盈批准前:借:原材料/库存商品等贷:待处理财产损溢——待处理流动资产损溢批准后:借:待处理财产损溢——待处理流动资产损溢贷:管理费用(2)存货盘亏批准前:借:待处理财产损溢——待处理流动资产损溢贷:原材料/库存商品等应交税费——应交增值税(进项税额转出)(管理不善等原因造成的存货盘亏)批准后:借:其他应收款(应由保险公司和过失人赔偿的部分)管理费用(管理不善造成的净损失)营业外支出(自然灾害等非常原因造成的净损失)贷:待处理财产损溢——待处理流动资产损溢三、固定资产1、购入固定资产(1)不需要安装借:固定资产应交税费——应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款等(2)需要安装购入时:借:在建工程应交税费——应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款等支付安装费等:借:在建工程贷:银行存款等安装完毕达到预定可使用状态:借:固定资产贷:在建工程2、固定资产折旧借:制造费用(生产车间计提折旧)管理费用(企业管理部门、未使用的固定资产计提折旧)销售费用(企业专设销售部门计提折旧)其他业务成本(企业出租固定资产计提折旧)研发支出(企业研发无形资产时使用固定资产计提折旧)在建工程(在建工程中使用固定资产计提折旧)贷:累计折旧3、固定资产处置(1)固定资产转入清理借:固定资产清理累计折旧固定资产减值准备贷:固定资产(2)发生的清理费用借:固定资产清理贷:银行存款(3)收回出售固定资产的价款、残料价值和变价收入等借:银行存款原材料贷:固定资产清理应交税费——应交增值税(销项税额)(4)保险赔偿等的处理借:其他应收款贷:固定资产清理(5)清理净损益的处理①属于生产经营期间正常的处理损失借:资产处置损益贷:固定资产清理②属于自然灾害等非正常原因造成的损失借:营业外支出——非常损失贷:固定资产清理③属于生产经营期间正常的处理收益借:固定资产清理贷:资产处置损益④属于自然灾害等非正常原因造成的收益借:固定资产清理贷:营业外收入四、无形资产1、无形资产的取得(1)外购无形资产借:无形资产应交税费——应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款等(2)自行研发无形资产研究阶段支出:借:研发支出——费用化支出贷:银行存款等期末:借:管理费用贷:研发支出——费用化支出开发阶段支出:借:研发支出——资本化支出贷:银行存款等无形资产达到预定用途:借:无形资产贷:研发支出——资本化支出2、无形资产的摊销借:管理费用(自用无形资产的摊销)其他业务成本(出租无形资产的摊销)制造费用(用于产品生产等的无形资产的摊销)贷:累计摊销3、无形资产的处置(1)无形资产的出售借:银行存款累计摊销无形资产减值准备资产处置损益(借方差额)贷:无形资产应交税费——应交增值税(销项税额)资产处置损益(贷方差额)(2)无形资产的报废借:营业外支出——非流动资产报废累计摊销无形资产减值准备贷:无形资产五、投资性房地产1、投资性房地产的取得(1)外购投资性房地产借:投资性房地产应交税费——应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款等(2)自行建造投资性房地产发生建造支出时:借:投资性房地产——在建贷:银行存款等完工达到预定可使用状态时:借:投资性房地产贷:投资性房地产——在建2、投资性房地产的后续计量(1)成本模式计提折旧或摊销:借:其他业务成本贷:投资性房地产累计折旧(摊销)取得租金收入:借:银行存款贷:其他业务收入计提减值准备:借:资产减值损失贷:投资性房地产减值准备(2)公允价值模式不计提折旧或摊销,资产负债表日按公允价值计量,公允价值变动计入当期损益公允价值上升:借:投资性房地产——公允价值变动贷:公允价值变动损益公允价值下降:借:公允价值变动损益贷:投资性房地产——公允价值变动取得租金收入:借:银行存款贷:其他业务收入3、投资性房地产的转换(1)成本模式下的转换①投资性房地产转为自用房地产借:固定资产/无形资产投资性房地产累计折旧(摊销)投资性房地产减值准备贷:投资性房地产累计折旧/累计摊销固定资产减值准备/无形资产减值准备②自用房地产转为投资性房地产借:投资性房地产累计折旧/累计摊销固定资产减值准备/无形资产减值准备贷:固定资产/无形资产投资性房地产累计折旧(摊销)投资性房地产减值准备(2)公允价值模式下的转换①投资性房地产转为自用房地产借:固定资产/无形资产(公允价值)公允价值变动损益(借方差额)贷:投资性房地产——成本——公允价值变动(或借方)②自用房地产转为投资性房地产借:投资性房地产——成本(公允价值)累计折旧/累计摊销固定资产减值准备/无形资产减值准备公允价值变动损益(借方差额)贷:固定资产/无形资产其他综合收益(贷方差额)4、投资性房地产的处置(1)成本模式借:银行存款贷:其他业务收入应交税费——应交增值税(销项税额)借:其他业务成本投资性房地产累计折旧(摊销)投资性房地产减值准备贷:投资性房地产(2)公允价值模式借:银行存款贷:其他业务收入应交税费——应交增值税(销项税额)借:其他业务成本贷:投资性房地产——成本——公允价值变动(或借方)借:公允价值变动损益贷:其他业务成本(或相反分录)借:其他综合收益贷:其他业务成本以上只是中级会计师实务中部分常见的分录汇总,实际工作和学习中还会遇到更多复杂的情况,需要根据具体业务进行准确的会计处理。
中级会计考试会计分录

中级会计考试中,会计分录是一个重要的考点和考核内容。
会计分录是会计师在编制账户记录时,根据经济交易的具体情况,按照借贷原则将交易金额分别记在不同账户中的记录。
以下是一些常见的会计分录示例:
1. 现金收入
借:现金账户
贷:收入账户
2. 销售商品
借:应收账款
贷:销售收入
3. 购买设备
借:设备账户
贷:应付账款或现金账户
4. 预付租金
借:预付账款
贷:现金账户
5. 收到发票
借:应收账款
贷:应交税费(增值税)或其他应交款项
请注意,具体会计分录的设置和账户科目会根据实际情况有所差异,这只是一些常见的例子。
在实际操作中,需要根据具体的交易内容和会计政策,合理设置会计分录。
建议在备考过程中,结合教材和实际练习,加强对会计分录的理解和掌握。
中级财务会计英会计分录汇总

中级财务会计英会计分录汇总考点1调整分录和结账分录Ex. 3-125—Adjusting entries.Present, in journal form, the adjustments that would be made on July 31, 2011, the end ofthe fiscal year, for each of the following.1. The supplies inventory on August 1, 2010 was $7,350. Supplies costing $20,150 wereacquired during the year and charged to the supplies inventory. A count on July 31,2011 indicated supplies on hand of $8,810.2. On April 30, a ten-month, 9% note for $20,000 was received from a customer.*3. On March 1, $12,000 was collected as rent for one year and a nominal account was credited.Solution 3-1251. Supplies Expense ........................................................................ 18,690Supplies ............................................................................. 18,690 2. Interest Receivable . (450)Interest Revenue (450)*3. Rent Revenue .............................................................................. 7,000Unearned Revenue ........................................................... 7,000 Ex. 3-126—Adjusting entries.Reed Co. wishes to enter receipts and payments in such a manner that adjustments at theend of the period will not require reversing entries at the beginning of the next period.Record the following transactions in the desired manner and give the adjusting entry on December 31, 2010. (Two entries for each part.)1. An insurance policy for two years was acquired on April 1, 2010 for $8,000.2. Rent of $12,000 for six months for a portion of the building was received onNovember 1, 2010.Solution 3-1261. Prepaid Insurance .......................................................................... 8,000Cash .................................................................................. 8,000 Insurance Expense ........................................................................ 3,000Prepaid Insurance ............................................................. 3,000 2. Cash ............................................................................................. 12,000Unearned Rent .................................................................. 12,000 Unearned Rent .............................................................................. 4,000Rent Revenue ................................................................... 4,000 Pr. 3-133—Adjusting entries and account classification.Selected amounts from Trent Company's trial balance of 12/31/10 appear below:1. Accounts Payable $ 160,0002. Accounts Receivable 150,0003. Accumulated Depreciation—Equipment 200,0004. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 20,0005. Bonds Payable 500,0006. Cash 150,0007. Common Stock 60,0008. Equipment 840,0009. Insurance Expense 30,00010. Interest Expense 10,00011. Merchandise Inventory 300,00012. Notes Payable (due 6/1/11) 200,00013. Prepaid Rent 150,00014. Retained Earnings 818,00015. Salaries and Wages Expense 328,000(All of the above accounts have their standard or normal debit or credit balance.)Part A. Prepare adjusting journal entries at year end, December 31, 2010, based on the following supplemental information.a. The equipment has a useful life of 15 years with no salvage value. (Straight-linemethod being used.)b. Interest accrued on the bonds payable is $15,000 as of 12/31/10.c. Expired insurance at 12/31/10 is $20,000.d. The rent payment of $150,000 covered the six months from November 30, 2010through May 31, 2011.e. Salaries and wages earned but unpaid at 12/31/10, $22,000.Part B. Indicate the proper balance sheet classification of each of the 15 numbered accounts in the 12/31/10 trial balance before adjustments by placingappropriate numbers after each of the following classifications. If the accounttitle would appear on the income statement, do not put the number in any ofthe classifications.a. Current assetsb. Property, plant, and equipmentc. Current liabilitiesd. Long-term liabilitiese. Stockholders' equitySolution 3-133Part A.a. Depreciation Expense—Equipment ($840,000 – 0) ÷ 15 ..................... 56,000Accumulated Depreciation—Equipment .................................. 56,000 b. Interest Expense ................................................................................... 15,000Interest Payable ....................................................................... 15,000 c. Prepaid Insurance ................................................................................. 10,000Insurance Expense ($30,000 - $20,000) ................................. 10,000 d. Rent Expense ($150,000 ÷ 6) ................................................................ 25,000Prepaid Rent ............................................................................ 25,000 e. Salaries and Wages Expense .............................................................. 22,000Salaries and Wages Payable ................................................... 22,000Pr. 3-134—Adjusting entries.Data relating to the balances of various accounts affected by adjusting or closing entriesappear below. (The entries which caused the changes in the balances are not given.) Youare asked to supply the missing journal entries which would logically account for the changes in the account balances.1. Interest receivable at 1/1/10 was $1,000. During 2010 cash received from debtors forinterest on outstanding notes receivable amounted to $5,000. The 2010 incomestatement showed interest revenue in the amount of $5,400. You are to provide themissing adjusting entry that must have been made, assuming reversing entries arenot made.2. Unearned rent at 1/1/10 was $5,300 and at 12/31/10 was $8,000. The records indicatecash receipts from rental sources during 2010 amounted to $40,000, all of which wascredited to the Unearned Rent Account. You are to prepare the missing adjustingentry.3. Accumulated depreciation—equipment at 1/1/10 was $230,000. At 12/31/10 thebalance of the account was $270,000. During 2010, one piece of equipment was sold.The equipment had an original cost of $40,000 and was 3/4 depreciated when sold.You are to prepare the missing adjusting entry.4. Allowance for doubtful accounts on 1/1/10 was $50,000. The balance in the allowanceaccount on 12/31/10 after making the annual adjusting entry was $65,000 and during2010 bad debts written off amounted to $30,000. You are to provide the missingadjusting entry.5. Prepaid rent at 1/1/10 was $9,000. During 2010 rent payments of $120,000 weremade and charged to "rent expense." The 2010 income statement shows as a generalexpense the item "rent expense" in the amount of $125,000. You are to prepare themissing adjusting entry that must have been made, assuming reversing entries arenot made.6. Retained earnings at 1/1/10 was $150,000 and at 12/31/10 it was $210,000. During2010, cash dividends of $50,000 were paid and a stock dividend of $40,000 wasissued. Both dividends were properly charged to retained earnings. You are to providethe missing closing entry.Solution 3-1341. Interest Receivable ........................................................................ 1,400Interest Revenue ............................................................... 1,400 Interest revenue per books $5,400Interest revenue received related to 2010($5,000 – $1,000) 4,000Interest accrued $1,4002. Unearned Rent Revenue ............................................................... 37,300Rent Revenue ................................................................... 37,300 Cash receipts $40,000Beginning balance 5,300Ending balance (8,000)Rent revenue $37,300Solution 3-134(cont.)3. Depreciation Expense .................................................................. 70,000Accumulated Depreciation—Equipment ........................... 70,000 Ending balance $270,000Beginning balance 230,000Difference 40,000Write-off at time of sale 3/4 × $40,000 30,000$ 70,0004. Bad Debt Expense ......................................................................... 45,000Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ....................................... 45,000 Ending balance $65,000Beginning balance 50,000Difference 15,000Written off 30,000$45,0005. Rent Expense ................................................................................ 5,000Prepaid Rent ..................................................................... 5,000 Rent expense $125,000Less cash paid 120,000Reduction in prepaid rent account $ 5,0006. Income Summary ........................................................................... 150,000Retained Earnings ............................................................. 150,000 Ending balance $210,000Beginning balance 150,000Difference 60,000Cash dividends $50,000Stock dividends 40,000 90,000$150,000Pr. 3-135—Adjusting and closing entries.The following trial balance was taken from the books of Fisk Corporation on December 31,2010.Account DebitCreditCash $ 12,000Accounts Receivable 40,000Note Receivable 7,000Allowance for Doubtful Accounts $ 1,800 Merchandise Inventory 44,000Prepaid Insurance 4,800Furniture and Equipment 125,000Accumulated Depreciation--F. & E. 15,000 Accounts Payable 10,800Common Stock 44,000 Retained Earnings 55,000 Sales 280,000Cost of Goods Sold 111,000Salaries Expense 50,000Rent Expense 12,800Totals $406,600 $406,600 Pr. 3-135 (cont.)At year end, the following items have not yet been recorded.a. Insurance expired during the year, $2,000.b. Estimated bad debts, 1% of gross sales.c. Depreciation on furniture and equipment, 10% per year.d. Interest at 6% is receivable on the note for one full year.*e. Rent paid in advance at December 31, $5,400 (originally charged to expense).f. Accrued salaries at December 31, $5,800.Instructions(a) Prepare the necessary adjusting entries.(b) Prepare the necessary closing entries.Solution 3-135(a) Adjusting Entriesa. Insurance Expense .............................................................. 2,000Prepaid Insurance .............................................................. 2,000b. Bad Debt Expense ...................................................................... 2,800Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ....................................... 2,800c. Depreciation Expense ................................................................. 12,500Accumulated Depreciation--F. & E. .................................... 12,500d. Interest Receivable (420)Interest Revenue (420)*e. Prepaid Rent ................................................................................ 5,400Rent Expense ..................................................................... 5,400f. Salaries Expense ........................................................................ 5,800Salaries Payable ................................................................ 5,800 (b) Closing EntriesSales ................................................................................................... 280,000 Interest Revenue (420)Income Summary ..................................................................... 280,420Income Summary ................................................................................ 191,500Salaries Expense ..................................................................... 55,800Rent Expense ........................................................................... 7,400Depreciation Expense .............................................................. 12,500Bad Debt Expense ................................................................... 2,800Insurance Expense .................................................................. 2,000Cost of Goods Sold .................................................................. 111,000Income Summary ................................................................................ 88,920Retained Earnings .................................................................... 88,920 考点2应收帐款总价净价法,坏账处理,应收票据折价Ex. 7-136—Entries for bad debt expense.A trial balance before adjustment included the following:Debit Credit Accounts receivable $80,000Allowance for doubtful accounts 730Sales $340,000Sales returns and allowances 8,000Give journal entries assuming that the estimate of uncollectibles is determined by taking(1) 5% of gross accounts receivable and (2) 1% of net sales.Solution 7-136(1) Bad Debt Expense ................................................................... 3,270Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ................................ 3,270 Gross receivables $80,000Rate 5%Total allowance needed 4,000Present allowance (730)Adjustment needed $ 3,270Solution 7-136(cont.)(2) Bad Debt Expense ................................................................... 3,320Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ................................ 3,320 Sales $340,000Sales returns and allowances 8,000Net sales 332,000Rate 1%Bad debt expense $ 3,320Ex. 7-137—Accounts receivable assigned.Accounts receivable in the amount of $250,000 were assigned to the Fast Finance Company by Marsh, Inc., as security for a loan of $200,000. The finance company charged a 4% commission on the face amount of the loan, and the note bears interest at9% per year.During the first month, Marsh collected $130,000 on assigned accounts. This amount was remitted to the finance company along with one month's interest on the note.InstructionsMake all the entries for Marsh Inc. associated with the transfer of the accounts receivable,the loan, and the remittance to the finance company.Solution 7-137Cash ...................................................................................................... 192,000Finance Charge ..................................................................................... 8,000 Notes Payable ........................................................................... 200,000 Cash ...................................................................................................... 130,000 Accounts Receivable ................................................................. 130,000 Notes Payable ...................................................................................... 130,000Interest Expense .................................................................................... 1,500 Cash ......................................................................................... 131,500PROBLEMSPr. 7-138—Entries for bad debt expense.The trial balance before adjustment of Risen Company reports the following balances:Dr. Cr.Accounts receivable $100,000Allowance for doubtful accounts $ 2,500Sales (all on credit) 750,000Sales returns and allowances 40,000Instructions(a) Prepare the entries for estimated bad debts assuming that doubtful accounts areestimated to be (1) 6% of gross accounts receivable and (2) 1% of net sales.(b) Assume that all the information above is the same, except that the Allowance forDoubtful Accounts has a debit balance of $2,500 instead of a credit balance. Howwill this difference affect the journal entries in part (a)?Solution 7-138(a) (1) Bad Debt Expense .............................................................. 3,500Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ............................ 3,500 Gross receivables $100,000Rate 6%Total allowance needed 6,000Present allowance (2,500)Bad debt expense $ 3,500(2) Bad Debt Expense .............................................................. 7,100Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ............................ 7,100 Sales $750,000Sales returns and allowances (40,000)Net sales 710,000Rate 1%Bad debt expense $ 7,100(b) The percentage of receivables approach would be affected as follows:Gross receivables $100,000Rate 6%Total allowance needed 6,000Present allowance 2,500Additional amount required $ 8,500The journal entry is therefore as follows:Bad Debt Expense .............................................................. 8,500Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ............................ 8,500 The entry would not change under the percentage of sales method.Pr. 7-140—Accounts receivable assigned.Prepare journal entries for Mars Co. for:(a) Accounts receivable in the amount of $500,000 were assigned to Utley Finance Co.by Mars as security for a loan of $425,000. Utley charged a 3% commission on theaccounts; the interest rate on the note is 12%.(b) During the first month, Mars collected $200,000 on assigned accounts after deducting$450 of discounts. Mars wrote off a $530 assigned account.(c) Mars paid to Utley the amount collected plus one month's interest on the note.Solution 7-140(a) Cash .............................................................................................. 410,000Finance Charge ............................................................................... 15,000Notes Payable ..................................................................... 425,000 (b) Cash .............................................................................................. 200,000Sales Discounts (450)Allowance for Doubtful Accounts (530)Accounts Receivable........................................................... 200,980 (c) Notes Payable ................................................................................. 200,000Interest Expense .............................................................................. 4,250Cash .................................................................................... 204,250 考点三存货盘存方法,折扣Ex. 8-148—Recording purchases at net amounts.Flint Co. records purchase discounts lost and uses perpetual inventories. Prepare journal entries in general journal form for the following:(a) Purchased merchandise costing $900 with terms 2/10, n/30.(b) Payment was made thirty days after the purchase.Solution 8-148(a) Inventory (.98 × $900) (882)Accounts Payable (882)(b) Accounts Payable (882)Purchase Discounts Lost (18)Cash (900)Ex. 8-149—Recording purchases at net amounts.Dill Co. records purchases at net amounts and uses periodic inventories. Prepare entries for the following:June 11 Purchased merchandise on account, $5,000, terms 2/10, n/30.15 Returned part of June 11 purchase, $800, and received credit on account.30 Prepared the adjusting entry required for financial statements.Solution 8-149June 11 Purchases (.98 × $5,000) ................................................... 4,900Accounts Payable ................................................... 4,90015 Accounts Payable (.98 × $800) (784)Purchase Returns and Allowances (784)30 Purchase Discounts Lost (.02 × $4,200) (84)Accounts Payable (84)Pr. 8-159—Accounting for purchase discounts.Otto Corp. purchased merchandise during 2010 on credit for $300,000; terms 2/10, n/30.All of the gross liability except $60,000 was paid within the discount period. The remainderwas paid within the 30-day term. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31, 2010, 90% of the merchandise had been sold and 10% remained in inventory. The company uses a periodic system.Instructions(a) Assuming that the net method is used for recording purchases, prepare the entriesfor the purchase and two subsequent payments.(b) What dollar amounts should be reported for the final inventory and cost of goods soldunder the (1) net method; (2) gross method? Assume that there was no beginninginventory.Solution 8-159(a) Purchases ..................................................................................................... 294,000Accounts Payable ............................................................................ 294,000(To record the purchase at net amount:.98 × $300,000 = $294,000.)Accounts Payable ......................................................................................... 235,200 Cash ................................................................................................. 235,200(To record payment within the discount period:$300,000 – $60,000 = $240,000; .. .98 × $240,000 = $235,200.)Accounts Payable ......................................................................................... 58,800Purchase Discounts Lost .............................................................................. 1,200 Cash ................................................................................................. 60,000(To record the final payment.)考点四,存货减值跌价准备LCMEx. 9-143—Lower-of-cost-or-market.At 12/31/10, the end of Jenner Company's first year of business, inventory was $4,100and $2,800 at cost and at market, respectively.Following is data relative to the 12/31/11 inventory of Jenner:Original NetNet RealizableAppropriateCost Replacement Realizable Value Less InventoryItem Per Unit Cost Value Normal Profit ValueA $ .65 $ .45B .45 .40C .70 .75D .75 .65E .90 .85Selling price is $1.00/unit for all items. Disposal costs amount to 10% of selling price and a "normal" profit is 30% of selling price. There are 1,000 units of each item in the 12/31/11 inventory.Instructions(a) Prepare the entry at 12/31/10 necessary to implement the lower-of-cost-or-marketprocedure assuming Jenner uses a contra account for its balance sheet.(b) Complete the last three columns in the 12/31/11 schedule above based upon thelower-of-cost-or-market rules.(c) Prepare the entry(ies) necessary at 12/31/11 based on the data above.(d) How are inventory losses disclosed on the income statement?Solution 9-143(a) Loss Due to Market Decline of Inventory ........................................ 1,300Allowance to Reduce Inventory to Market .......................... 1,300 Solution 9-143(Cont.)(b) Original NetNet Realizable AppropriateCost Replacement Realizable Value Less InventoryItem Per Unit Cost Value Normal Profit ValueA $ .65 $ .45 $ .90 $ .60 $ .60B .45 .40 .90 .60 .45C .70 .75 .90 .60 .70D .75 .65 .90 .60 .65E .90 .85 .90 .60 .85$3.45 $3.25**$3.25 × 1,000 = $3,250(c) Allowance to Reduce Inventory to Market....................................... 1,300Cost of Goods Sold ............................................................. 1,300 Loss Due to Market Decline of Inventory . (200)Allowance to Reduce Inventory to Market (200)(Cost of inventory at 12/31/07 = $7,250)ORA student can record a recovery of $1,100.(d) Inventory losses can be disclosed separately (below gross profit in operatingexpenses) or they can be shown as part of cost of goods sold.Pr. 9-149—Gross profit method.On December 31, 2010 Felt Company's inventory burned. Sales and purchases for theyear had been $1,400,000 and $980,000, respectively. The beginning inventory (Jan. 1, 2010) was $170,000; in the past Felt's gross profit has averaged 40% of selling price.InstructionsCompute the estimated cost of inventory burned, and give entries as of December 31,2010 to close merchandise accounts.Solution 9-149Beginning inventory $ 170,000Add: Purchases 980,000Cost of goods available 1,150,000Sales $1,400,000Less 40% (560,000) 840,000Estimated inventory lost $ 310,000Sales ...................................................................................... 1,400,000Income Summary ...................................................................... 1,400,000 Cost of Goods Sold ................................................................................ 840,000Fire Loss ................................................................................................ 310,000 Inventory .................................................................................... 170,000 Purchases .................................................................................. 980,000 处置出售捐赠Ex. 10-136—Donated assets.Cheng Company has recently decided to accept a proposal from the City of Bel Aire that publicly owned property with a large warehouse located on it will be donated to Cheng if Cheng will build a branch plant in Bel Aire. The appraised value of the property is $490,000 and of the warehouse is $980,000.InstructionsPrepare the entry by Cheng for the receipt of the properties.Solution 10-136Building (Warehouse) ............................................................................ 980,000Land ....................................................................................................... 490,000 Contribution Revenue................................................................ 1,470,000 Ex. 11-132—Composite depreciation.Kemp Co. uses the composite method to depreciate its equipment. The following totalsare for all of the equipment in the group:Initial Residual Depreciable DepreciationCost Value Cost Per Year$700,000 $100,000 $600,000 $60,000 Instructions(a) What is the composite rate of depreciation? (To nearest tenth of a percent.)(b) A machine with a cost of $18,000 was sold for $11,000 at the end of the third year.What entry should be made?Solution 11-132(a) $60,000———— = 8.6%$700,000(b) Cash ............................................................................................... 11,000Accumulated Depreciation ............................................................. 7,000Equipment ........................................................................... 18,000 Pr. 11-135—Adjustment of Depreciable Base.A truck was acquired on July 1, 2008, at a cost of $216,000. The truck had a six-yearuseful life and an estimated salvage value of $24,000. The straight-line method of depreciation was used. On January 1, 2011, the truck was overhauled at a cost of $20,000, which extended the useful life of the truck for an additional two years beyond that originally estimated (salvage value is still estimated at $24,000). In computing depreciation for annual adjustment purposes, expense is calculated for each month theasset is owned.InstructionsPrepare the appropriate entries for January 1, 2011 and December 31, 2011.Solution 11-135Cost $216,000Less salvage value 24,000Depreciable base, July 1, 2008 192,000Less depreciation to date [($192,000 ÷ 6) × 2 1/2] 80,000Depreciable base, Jan. 1, 2011 (unadjusted) 112,000Overhaul 20,000Depreciable base, Jan. 1, 2011 (adjusted) $132,000January 1, 2011Accumulated Depreciation ..................................................................... 20,000 Cash .......................................................................................... 20,000 December 31, 2011Depreciation Expense ............................................................................ 24,000 Accumulated Depreciation ($132,000 ÷ 5.5 yrs) ....................... 24,000 Ex. 12-130Barkley Corp. obtained a trade name in January 2009, incurring legal costs of $15,000.The company amortizes the trade name over 8 years. Barkley successfully defendedits trade name in January 2010, incurring $4,900 in legal fees. At the beginning of2011, based on new marketing research, Barkley determines that the fair value of thetrade name is $12,000. Estimated total future cash flows from the trade name are$13,000 on January 4, 2011.InstructionsPrepare the necessary journal entries for the years ending December 31, 2009, 2010,and 2011. Show all computations.Solution 12-1302009Dec. 31 Amortization Expense - Trade Name 1,875Trade Name 1,875($15,000 ÷ 8 years)2010Dec. 31 Amortization Expense – Trade Name 2,575Trade Name 2,575[($15,000 - $1,875 + $4,900) ÷7 years]2011Dec. 31 Loss on Impairment 3,450Trade Name 3,450Carrying value = $15,000 - $1,875 + $4,900 - $2,575 = $15,450Total future cash flows= 13,000Therefore, an impairment loss has occurredCarrying value = $15,450。
中财会计分录word格式

1.货币资金和应收账款
monetary capital and account receivable
2.存货
inventory
3.投资
investment
4.固定资产
fixed asset
5.无形资产和其他资产
intangible asset and other assets
6.流动负债
current liabilities
7.非流动负债
non-current liability
8.所有者权益
ower's equity
9.收入、费用、利润
income expenses profit
10.财务报告
financial report
11.
12.
design by Ruby . Jiang
最好的日子,無非是你在鬧,他在笑,如此溫情過一生。
1)货币资金和应收账款monetary capital and account receivable
坏账准备是进行累计的
当期应提取的坏账准备=当期应收款项应提取坏账准备额—坏账准备科目贷余额
2)存货inventory
3)投资investment
4)固定资产fixed asset
5)无形资产和其他资产intangible asset and other assets
6)流动负债current liabilities
7)非流动负债non-current liability
8)所有者权益ower's equity
9)收入、费用、利润income expenses profit
10)财务报告financial report。
典型会计分录Microsoft Word 文档

1、接受投资•借:库存现金、固定资产、原材料•贷:实收资本•2、向银行借款•借:银行存款•贷:短期借款、长期借款•3、发生借款利息:•借:财务费用、在建工程•贷:预提费用、长期借款—应计利息•4、支付利息:•借:预提费用、长期借款—应计利息•贷:银行存款•5、借差旅费:•借:其他应收款•贷:库存现金•6、、报销差旅费:•借:制造费用、管理费用•贷:其他应收款•7、购买材料:•借:在途物资•应缴税费—应交增值税•贷:银行存款、库存现金、应付账款、应付票据、预付账款•8、材料到达入库:•借:原材料•贷:在途物资•9、购买固定资产:•借:固定资产•应缴税费—应交增值税•贷:银行存款、库存现金、应付账款、应付票据、预付账款•10、领用材料:•借:生产成本、制造费用、管理费用•贷:原材料•11、计算工资:•借:生产成本、制造费用、管理费用•贷:应付职工薪酬—工资•12、计提工资福利费:•借:生产成本、制造费用、管理费用•贷:应付职工薪酬—福利费•13、计提折旧:•借:制造费用、管理费用•贷:累计折旧•14、购买办公用品:•借:制造费用、管理费用•贷:银行存款、库存现金•15、预付全年保险费:•借:待摊费用•贷:银行存款、库存现金•16、摊销本月负担的保险费:•借:制造费用、管理费用•贷:待摊费用•17、结转制造费用:•借:生产成本•贷:制造费用•18、产品完工入库:•借:库存商品•贷:生产成本•19、销售产品:•借:银行存款、应收票据、应收账款•贷:主营业务收入•应交税费—应交增值税•20、结转已销产品的销售成本:•借:主营业务成本•贷:库存商品•21、支付广告费、产品的宣传费:•借:销售费用•贷:银行存款、库存现金•22、没收罚款:•借:银行存款、库存现金•贷:营业外收入•23、支付滞纳金:•借:营业外支出•贷:库存现金、银行存款•24、支付广告费、产品的宣传费:•借:销售费用•贷:银行存款、库存现金•25、实现投资收益:•借:应收股利、银行存款•贷:投资收益•26、计算营业税、消费税:•借:营业税金及附加•贷:应缴税费—税种••••••••27、结转本年利润:•借:主营业务收入、其他业务收入•营业外收入•贷:本年利润•借:本年利润•贷:主营业务成本、其他业务成本•销售费用、管理费用、财务费用•营业外支出、营业税金及附加•28、计算所得税:•借:所得税费用•贷:应缴税费—应交所得税•29、将所得税转入本年利润:•借:本年利润•贷:所得税费用•30、将净利润转入利润分配:•借:本年利润•贷:利润分配—未分配利润•31、计提盈余公积金:•借:利润分配•贷:盈余公积—法定、任意•32、计算给投资者分配利润:•借:利润分配•贷:应付股利营业利润=营业收入—营业成本—营业税金及附加—销售费用—管理费用—-财务费用—资产减值损失+公允价值变动收益—公允价值变动损失+投资收益—投资损失利润总额=营业利润+营业外收入—营业外支出净利润=利润总额—所得税费用存货=在途物资+材料采购+原材料+周转材料+委托加工物资+库存商品+生产成本—寻货跌价准备+—材料成本差异+—商品进销差价(借加贷减)。
中级财务会计分录大全(word)资料
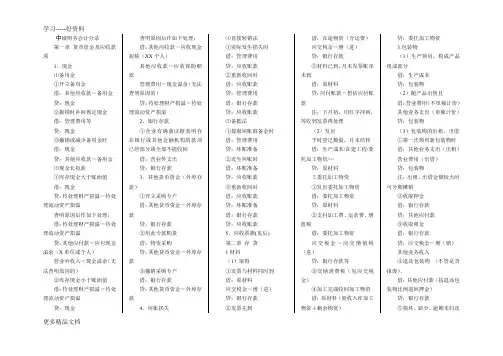
中级财务会计分录第一章货币资金及应收款项1.现金⑴备用金①开立备用金借:其他应收款-备用金贷:现金②报销时补回预定现金借:管理费用等贷:现金③撤销或减少备用金时借:现金贷:其他应收款-备用金⑵现金长短款①库存现金大于账面值借:现金贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢查明原因后作如下处理:借:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢贷:其他应付款-应付现金溢余(X单位或个人)营业外收入-现金溢余(无法查明原因的)②库存现金小于账面值借:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢贷:现金查明原因后作如下处理:借:其他应收款-应收现金短缺(XX个人)其他应收款-应收保险赔款管理费用-现金溢余(无法查明原因的)贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢2.银行存款①企业有确凿证据表明存在银行或其他金融机构的款项已经部分或全部不能收回借:营业外支出贷:银行存款3.其他货币资金(外埠存款)①开立采购专户借:其他货币资金-外埠存款贷:银行存款②用此专款购货借:物资采购贷:其他货币资金-外埠存款③撤销采购专户借:银行存款贷:其他货币资金-外埠存款4.坏账损失⑴直接转销法①实际发生损失时借:管理费用贷:应收账款②重新收回时借:应收账款贷:管理费用借:银行存款贷:应收账款⑵备抵法①提取坏账准备金时借:管理费用贷:坏账准备②发生坏账时借:坏账准备贷:应收账款③重新收回时借:应收账款贷:坏账准备借:银行存款贷:应收账款5.应收票据(见后)第二章存货1材料(1)取得①发票与材料同时到借:原材料应交税金-增(进)贷:银行存款②发票先到借:在途物资(含运费)应交税金-增(进)贷:银行存款③材料已到,月末发票账单未到借:原材料贷:应付账款-暂估应付账款注:下月初,用红字冲回,等收到发票再处理(2)发出平时登记数量,月末结转借:生产成本/在建工程/委托加工物资/…贷:原材料⒉委托加工物资①发出委托加工物资借:委托加工物资贷:原材料②支付加工费、运杂费、增值税借:委托加工物资应交税金-应交增值税(进)贷:银行存款等③交纳消费税(见应交税金)④加工完成收回加工物资借:原材料(验收入库加工物资+剩余物资)贷:委托加工物资3.包装物(1)生产领用,构成产品组成部分借:生产成本贷:包装物(2)随产品出售且借:营业费用(不单独计价)其他业务支出(单独计价)贷:包装物(3)包装物的出租、出借①第一次领用新包装物时借:其他业务支出(出租)营业费用(出借)贷:包装物注:出租、出借金额较大时可分期摊销②收取押金借:银行存款贷:其他应付款③收取租金借:银行存款贷:应交税金-增(销)其他业务收入④退还包装物(不管是否报废),借:其他应付款(按退还包装物比例退回押金)贷:银行存款⑤损坏、缺少、逾期未归还更多精品文档等原因没收押金借:其他应付款其他业务支出(消费税)贷:应交税金-增(销)应交税金-应交消费税其他业务收入(押金部分)⑥不能使用而报废时,按其残料价值借:原材料贷:其他业务支出(出租)营业费用(出借)⑤摊销(略)——一次、五五、分次4.低值易耗品(处理同包装物)5.存货清查⑴盘盈①确认借:原材料贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢②报批转销借:待处理财产损溢贷:管理费用⑵盘亏或毁损①确认借:待处理财产损溢贷:原材料应交税金-增(转出)②报批转销i属于自然损耗产生的定额内损耗借:管理费用贷:待处理财产损溢ii属于收发计量、核算、管理不善造成的损耗借:原材料(残料)其他应收款(保险、责任人赔款)[管理费用]贷:待处理财产损溢iii属于自然灾害或意外事故造成的存货损耗借:原材料(残料)其他应收款(保险、责任人赔款)[营业外支出-非常损失]贷:待处理财产损溢注:待处理财产损溢在结帐前必须将其转平。
中级会计实务必背分录
中级会计实务必背分录一、什么是分录?分录是会计核算中的基本操作,指将经济业务按照一定的规则和格式记录在账簿上的过程。
分录包括借方和贷方两个方向,用于记录资产、负债、所有者权益、收入和费用等会计要素发生的变化。
二、常见的中级会计实务必背分录1. 销售商品销售商品是企业日常经营活动中最为常见的一项。
假设某企业销售了1000元的商品,其中成本为600元,税金为100元,利润为300元。
借方贷方应收账款1000销售收入1000销售成本600库存商品600税金及附加100应交税费100利润3002. 支付货款企业购买货物时需要支付货款。
假设某企业以现金支付了5000元的货款。
借方贷方库存现金5000应付账款50003. 收到货款企业销售商品后,客户会向企业支付货款。
假设某企业收到了2000元的货款。
借方贷方现金2000应收账款20004. 偿还借款企业需要偿还借入的资金。
假设某企业偿还了10000元的借款。
借方贷方银行贷款10000现金100005. 支付工资企业支付员工工资是日常经营活动中的一项重要支出。
假设某企业支付了4000元的工资。
借方贷方工资支出4000应付工资40006. 分红当企业盈利时,可以将部分利润分配给股东。
假设某企业分红1000元。
借方贷方利润分配1000应付股利1000三、如何记忆中级会计实务必背分录?记忆中级会计实务必背分录需要掌握以下几个方法:1. 理解原理分录是根据会计核算的规则和原则进行记录的,因此理解会计核算的原理对记忆分录非常重要。
通过学习会计基础知识和相关法规,掌握借贷记账的基本原则和逻辑。
2. 制定学习计划将所有的中级会计实务必背分录整理成表格或列表,按照不同的类别进行分类。
制定合理的学习计划,每天花一定时间复习和记忆对应的分录。
3. 创造联想利用联想法帮助记忆。
可以将每个分录与具体的场景或实际操作相联系,形成有趣、生动的联想图像。
例如,在销售商品这个分录中,可以想象自己站在店铺里向客户推销商品。
中级财务会计分录总结
中级财务会计分录总结篇一:中级财务会计分录大全中级财务会计分录第一章货币资金及应收款项其他应收款-应收保险赔款管理费用-现金溢余(无法查明原因的)借:管理费用贷:坏账准备⒉委托加工物资①发出委托加工物资1.现金⑴备用金①开立备用金借:其他应收款-备用金贷:现金②报销时补回预定现金借:管理费用等贷:现金③撤销或减少备用金时借:现金贷:其他应收款-备用金⑵现金长短款①库存现金大于账面值借:现金贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢查明原因后作如下处理:借:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢贷:其他应付款-应付现金溢余(X单位或个人)营业外收入-现金溢余(无法查明原因的)②库存现金小于账面值借:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢贷:现金查明原因后作如下处理:借:其他应收款-应收现金短缺(XX个贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢2.银行存款①企业有确凿证据表明存在银行或其他金融机构的款项已经部分或全部不能收回借:营业外支出贷:银行存款3.其他货币资金(外埠存款)①开立采购专户借:其他货币资金-外埠存款贷:银行存款②用此专款购货借:物资采购贷:其他货币资金-外埠存款③撤销采购专户借:银行存款贷:其他货币资金-外埠存款4.坏账损失⑴直接转销法①实际发生损失时借:管理费用贷:应收账款②重新收回时借:应收账款贷:管理费用借:银行存款贷:应收账款⑵备抵法②发生坏账时借:坏账准备贷:应收账款③重新收回时借:应收账款贷:坏账准备借:银行存款贷:应收账款5.应收票据(见后)第二章存货1材料(1)取得①发票与材料同时到借:原材料应交税金-增(进)贷:银行存款②发票先到借:在途物资(含运费)应交税金-增(进)贷:银行存款③材料已到,月末发票账单未到借:原材料贷:应付账款-暂估应付账款注:下月初,用红字冲回,等收到发票再处理(2)发出平时登记数量,月末结转借:生产成本/在建工程/委托加工物资/?借:委托加工物资贷:原材料②支付加工费、运杂费、增值税借:委托加工物资应交税金-应交增值税(进)贷:银行存款等③交纳消费税(见应交税金)④加工完成收回加工物资借:原材料(验收入库加工物资+剩余物资)贷:委托加工物资3.包装物(1)生产领用,构成产品组成部分借:生产成本贷:包装物(2)随产品出售且借:营业费用(不单独计价)其他业务支出(单独计价)贷:包装物(3)包装物的出租、出借①第一次领用新包装物时借:其他业务支出(出租)营业费用(出借)贷:包装物注:出租、出借金额较大时可分期摊销②收取押金借:银行存款贷:其他应付款③收取租金贷:应交税金-增(销)其他业务收入④退还包装物(不管是否报废),借:其他应付款(按退还包装物比例退回押金)贷:银行存款⑤损坏、缺少、逾期未归还等原因没收押金借:其他应付款其他业务支出(消费税)贷:应交税金-增(销)应交税金-应交消费税其他业务收入(押金部分)⑥不能使用而报废时,按其残料价值借:原材料贷:其他业务支出(出租)营业费用(出借)⑤摊销(略)——一次、五五、分次4.低值易耗品(处理同包装物)5.存货清查⑴盘盈①确认借:原材料贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢②报批转销借:待处理财产损溢贷:管理费用⑵盘亏或毁损①确认借:待处理财产损溢应交税金-增(转出)②报批转销i属于自然损耗产生的定额内损耗借:管理费用贷:待处理财产损溢ii属于收发计量、核算、管理不善造成的损耗借:原材料(残料)其他应收款(保险、责任人赔款)[管理费用]贷:待处理财产损溢iii属于自然灾害或意外事故造成的存货损耗借:原材料(残料)其他应收款(保险、责任人赔款)[营业外支出-非常损失]贷:待处理财产损溢注:待处理财产损溢在结帐前必须将其转平。
中级会计职称考试会计实务分录汇总Word版
一、流动资产(一)货币资金1、收到股东投入的股款借:银行存款贷:股本(实收资本)资本公积2、收到实现的主营业务收入借:银行存款贷:主营业务收入应交税费—应交增值税(销项税额)4、因支付内部职工出差等原因所需的现金,按支出凭证所记载的金额借:其他应收款贷:库存现金差旅费剩余款并结算时借:库存现金(按实际收回的现金)管理费用(按应报销的金额)贷:其他应收款(按实际借出的现金)5、每日终了结算现金收支,财产清查等发现的有待查明原因的现金短缺或溢余,属于库存现金短缺借:待处理财产损溢贷:库存现金属于现金溢余:借:库存现金贷:待处理财产损溢待查明原因后作如下处理:如为现金短缺,属于由责任人赔偿的部分:借:其他应收款—应收现金短缺款(个人)库存现金贷:待处理财产损溢属于应由保险公司赔偿的部分:借:其他应收款—应收保险赔款贷:待处理财产损溢属于无法查明的其他原因:借:管理费用—现金短缺贷:待处理财产损溢如为现金溢余,属于应支付给有关人员和单位的:借:待处理财产损溢贷:其他应付款—应付现金溢余(××个人或单位)属于无法查明的现金溢余:借:待处理财产损溢贷:营业外收入—资产盘盈利得6、收到银行存款利息借:银行存款贷:财务费用7、收回备用金和其他应收暂付款项借:银行存款等贷:其他应收款8、收到供应单位因不履行合同而赔偿损失赔款借:银行存款贷:营业外收入9、将款项汇往采购地开立采购专户借:其他货币资金—外埠存款贷:银行存款10、将款项存入银行以取得银行汇票、银行本票和信用卡借:其他货币资金—银行汇票—银行本票—信用卡贷:银行存款11、向银行开立信用证、交纳保证金借:其他货币资金—信用证保证金贷:银行存款12、向证券公司划出资金时借:其他货币资金—存出投资款贷:银行存款购买股票、债券等时借:交易性金融资产等贷:其他货币资金—存出投资款13、将外埠存款、银行汇票、银行本票存款的未用余额转回结算户借:银行存款贷:其他货币资金—外埠存款—银行汇票—银行本票14、交纳税费借:应交税费贷:银行存款15、支付购入材料的价款和运杂费A、采用计划价格核算借:材料采购应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款其他货币资金B、采用实际成本核算支付货款、运杂费、货物已经到达并已验收入库借:原材料库存商品销售费用应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:库存现金银行存款其他货币资金支付货款、运杂费时,货物尚未到达或尚未验收入库借:在途物资销售费用应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:库存现金银行存款其他货币资金16、支付供应单位各种款项借:应付账款应付票据应付内部单位款贷:银行存款17、付委托外单位加工物资加工费和运费借:委托加工物资应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款等18、支付外购动力费借:应付账款贷:银行存款19、支付职工工资借:应付职工薪酬贷:库存现金银行存款20、购入不需安装的固定资产、开发设施借:在建工程贷:银行存款同时借:固定资产油气资产贷:在建工程21、购入工程用物资借:原材料(专用材料、专用设备)贷:银行存款应付账款应付票据为购置大型设备而预付款借:预付账款贷:银行存款收到设备并补付设备价款:借:原材料(专用设备)(设备实际成本)贷:预付账款(预付的价款)银行存款(补付的价款)22、支付探矿权费用、价款,采矿权费用、价款借:油气资产管理费用贷:银行存款应交税费23、拨付备用金借:其他应收款(备用金)贷:库存现金银行存款定期补足备用金借:管理费用等贷:库存现金银行存款24、付待领工资、暂存款和其他应付款项借:其他应付款贷:库存现金银行存款26、支付各项成本、费用借:油气生产成本生产成本输油输气成本在建工程油气勘探支出油气开发支出研发支出制造费用管理费用销售费用财务费用勘探费用营业外支出贷:库存现金银行存款26、发放现金股利借:应付股利贷:库存现金27、按法定程序报经批准减少注册资本的,在实际发还股款或收购股票时借:股本(实收资本)等贷:银行存款(二)交易性金融资产1、企业取得交易性金融资产时借:交易性金融资产—成本(公允价值、不含支付的价款中所包含的、已到付息期但尚未领取的利息或已宣告但尚未发放的现金股利)投资收益(发生的交易费用)(※)应收股利(已宣告发放但尚未发放的现金股利)应收利息(已到付息期尚未领取的利息)贷:银行存款(实际支付的金额)2、持有交易性金融资产期间被投资单位宣告发放现金股利或在资产负债表日按债券票面利率计算利息借:应收股利应收利息贷:投资收益3、收到现金股利或债券利息借:银行存款贷:应收股利应收利息4、资产负债表日,交易性金融资产的公允价值高于账面余额的差额借:交易性金融资产—公允价值变动(公允价值高于账面余额的差额)贷:公允价值变动损益公允价值低于其账面余额的差额借:公允价值变动损益贷:交易性金融资产—公允价值变动(公允价值低于其账面余额的差额)5、出售交易性金融资产时,应按实际收到的金额,借:银行存款(实际收到的金额)投资收益(处置损失)交易性金融资产—公允价值变动(公允价值低于其账面余额的差额)贷:交易性金融资产—成本交易性金融资产—公允价值变动(公允价值高于账面余额的差额)投资收益(处置收益)同时,按原记入“公允价值变动”科目的金额(※)借:公允价值变动损益(公允价值高于账面余额的差额)贷:投资收益或借:投资收益贷:公允价值变动损益(公允价值低于账面余额的差额)(三)存货1、购入物资(1)购入物资在支付价款和运杂费时借:材料采购(采用实际成本法,可使用“在途物资”)应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款库存现金其他货币资金(2)采用商业汇票结算方式的,购入物资在开出、承兑商业汇票时借:材料采购(采用实际成本法,可使用“在途物资”)应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:应付票据2、物资已经收到但尚未办理结算手续的,可暂不作会计分录;待办理结算手续后借:材料采购(采用实际成本法使用“原材料”、“库存商品”)应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款库存现金应付票据应付账款应付内部单位款3、预付物资货款借:预付账款应收内部单位款贷:银行存款收到已经预付货款的物资后借:材料采购(采用实际成本法使用“原材料”“库存商品”)应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:预付账款应收内部单位款补付物资货款借:预付账款应收内部单位款贷:银行存款退回多付的货款借:银行存款贷:预付账款应收内部单位款4、由企业运输部门以自备运输工具,将外购的物资运回企业,计算购入物资应负担的运输费用借:材料采购贷:辅助生产油气辅助生产等5、向供货单位、外部运输机构等收回的物资短缺或其它应冲减材料采购成本的赔偿款项,应根据有关的索赔凭证借:应付账款(或其它应收款)贷:材料采购购入物资运输途中非常损失和尚待查明原因的途中损耗借:待处理财产损溢贷:材料采购6、商品流通企业购入商品抵达仓库前发生的包装费、运杂费、运输存储过程中的保险费、装卸费、运输途中的合理损耗和入库前的挑选整理费用等采购费用借:待摊进货费用贷:银行存款库存现金应付票据应付账款应付内部单位款7、月终,企业应将仓库转来的外购收料凭证,按照材料科目并分别情况进行汇总(1)对于已经付款或已开出、承兑的商业汇票的收料凭证(包括本月付款或开出、承兑商业汇票的上月收料凭证),按计划成本借:原材料包装物低值易耗品贷:材料采购实际成本大于计划成本的差额借:材料成本差异贷:材料采购实际成本小于计划成本的差额借:材料采购贷:材料成本差异采用实际成本法核算的,物资到达入库时借:原材料、库存商品贷:在途物资(2)对于尚未收到发票账单的收料凭证,应当分别材料科目,抄列清单,并按计划成本暂估入账(下月初用红字冲回)借:原材料包装物低值易耗品贷:应付账款—暂估应付账款下月付款或开出、承兑商业汇票后借:材料采购应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:银行存款应付票据(3)对于发票账单已到,但尚未付款或尚未开出、承兑商业汇票的收料凭证,或虽然发票账单未到,但根据合同、随货同行发票等能够计算并确定实际成本的收料凭证,按实际成本借:材料采购应交税费—应交增值税(进项税额)贷:应付账款应付内部单位款同时,按计划成本借:原材料包装物低值易耗品贷:材料采购同时结转材料成本差异。
中级财务会计分录大全word
中级财务会计分录第一章货币资金及应收款项1.现金⑴备用金①开立备用金借:其他应收款-备用金贷:现金②报销时补回预定现金借:管理费用等贷:现金③撤销或减少备用金时借:现金贷:其他应收款-备用金⑵现金长短款①库存现金大于账面值借:现金贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢查明原因后作如下处理:借:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢贷:其他应付款-应付现金溢余(X单位或个人)营业外收入-现金溢余(无法查明原因的)②库存现金小于账面值借:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢贷:现金查明原因后作如下处理:借:其他应收款-应收现金短缺(XX个人)其他应收款-应收保险赔款管理费用-现金溢余(无法查明原因的)贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢2.银行存款①企业有确凿证据表明存在银行或其他金融机构的款项已经部分或全部不能收回借:营业外支出贷:银行存款3.其他货币资金(外埠存款)①开立采购专户借:其他货币资金-外埠存款贷:银行存款②用此专款购货借:物资采购贷:其他货币资金-外埠存款③撤销采购专户借:银行存款贷:其他货币资金-外埠存款4.坏账损失⑴直接转销法①实际发生损失时借:管理费用贷:应收账款②重新收回时借:应收账款贷:管理费用借:银行存款贷:应收账款⑵备抵法①提取坏账准备金时借:管理费用贷:坏账准备②发生坏账时借:坏账准备贷:应收账款③重新收回时借:应收账款贷:坏账准备借:银行存款贷:应收账款5.应收票据(见后)第二章存货1材料(1)取得①发票与材料同时到借:原材料应交税金-增(进)贷:银行存款②发票先到借:在途物资(含运费)应交税金-增(进)贷:银行存款③材料已到,月末发票账单未到借:原材料贷:应付账款-暂估应付账款注:下月初,用红字冲回,等收到发票再处理(2)发出平时登记数量,月末结转借:生产成本/在建工程/委托加工物资/…贷:原材料⒉委托加工物资①发出委托加工物资借:委托加工物资贷:原材料②支付加工费、运杂费、增值税借:委托加工物资应交税金-应交增值税(进)贷:银行存款等③交纳消费税(见应交税金)④加工完成收回加工物资借:原材料(验收入库加工物资+剩余物资)贷:委托加工物资3.包装物(1)生产领用,构成产品组成部分借:生产成本贷:包装物(2)随产品出售且借:营业费用(不单独计价)其他业务支出(单独计价)贷:包装物(3)包装物的出租、出借①第一次领用新包装物时借:其他业务支出(出租)营业费用(出借)贷:包装物注:出租、出借金额较大时可分期摊销②收取押金借:银行存款贷:其他应付款③收取租金借:银行存款贷:应交税金-增(销)其他业务收入④退还包装物(不管是否报废),借:其他应付款(按退还包装物比例退回押金)贷:银行存款⑤损坏、缺少、逾期未归还等原因没收押金借:其他应付款其他业务支出(消费税)贷:应交税金-增(销)应交税金-应交消费税其他业务收入(押金部分)⑥不能使用而报废时,按其残料价值借:原材料贷:其他业务支出(出租)营业费用(出借)⑤摊销(略)——一次、五五、分次4.低值易耗品(处理同包装物)5.存货清查⑴盘盈①确认借:原材料贷:待处理财产损溢-待处理流动资产损溢②报批转销借:待处理财产损溢贷:管理费用⑵盘亏或毁损①确认借:待处理财产损溢贷:原材料应交税金-增(转出)②报批转销i属于自然损耗产生的定额内损耗借:管理费用贷:待处理财产损溢ii属于收发计量、核算、管理不善造成的损耗借:原材料(残料)其他应收款(保险、责任人赔款)[管理费用]贷:待处理财产损溢iii属于自然灾害或意外事故造成的存货损耗借:原材料(残料)其他应收款(保险、责任人赔款)[营业外支出-非常损失]贷:待处理财产损溢注:待处理财产损溢在结帐前必须将其转平。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
中级财务会计分录短缺(XX个人)②重新收回时贷:应付账款-暂估应付账其他业务支岀(单独计价)第一章货币资金及应收款其他应收款-应收保险赔借:应收账款款贷:包装物项款贷:管理费用注:下月初,用红字冲回,(3)包装物的岀租、岀借1 •现金管理费用-现金溢余(无法借:银行存款等收到发票再处理①第一次领用新包装物时⑴备用金查明原因的)贷:应收账款(2)发出借:其他业务支岀(岀租)①开立备用金贷:待处理财产损溢-待处⑵备抵法平时登记数量,月末结转营业费用(岀借)借:其他应收款-备用金理流动资产损溢①提取坏账准备金时借:生产成本/在建工程/委贷:包装物贷:现金 2 •银行存款借:管理费用托加工物资/…注:岀租、岀借金额较大时②报销时补回预定现金①企业有确凿证据表明存贷:坏账准备贷:原材料可分期摊销借:管理费用等在银行或其他金融机构的款项②发生坏账时2.委托加工物资②收取押金贷:现金已经部分或全部不能收回借:坏账准备①发出委托加工物资借:银行存款③撤销或减少备用金时借:营业外支岀贷:应收账款借:委托加工物资贷:其他应付款借:现金贷:银行存款③重新收回时贷:原材料③收取租金贷:其他应收款-备用金 3 •其他货币资金(外埠存借:应收账款②支付加工费、运杂费、增借:银行存款⑵现金长短款款)贷:坏账准备值税贷:应交税金—增(销)①库存现金大于账面值①开立采购专户借:银行存款借:委托加工物资其他业务收入借:现金借:其他货币资金-外埠存贷:应收账款应交税金-应交增值税④退还包装物(不管是否贷:待处理财产损溢-待处款 5 •应收票据(见后)(进)报废),理流动资产损溢贷:银行存款第二章存货贷:银行存款等借:其他应付款(按退还包查明原因后作如下处理:②用此专款购货1材料③交纳消费税(见应交税装物比例退回押金)借:待处理财产损溢-待处借:物资采购(1)取得金)贷:银行存款理流动资产损溢贷:其他货币资金-外埠存①发票与材料同时到④加工完成收回加工物资⑤损坏、缺少、逾期未归还贷:其他应付款-应付现金款借:原材料借:原材料(验收入库加工等原因没收押金溢余(X单位或个人)③撤销采购专户应交税金—增(进)物资+剩余物资)借:其他应付款营业外收入-现金溢余(无借:银行存款贷:银行存款贷:委托加工物资其他业务支出(消费税)法查明原因的)贷:其他货币资金-外埠存②发票先到 3.包装物贷:应交税金—增(销)②库存现金小于账面值款借:在途物资(含运费)(1 )生产领用,构成产品应交税金-应交消费税借:待处理财产损溢-待处 4 .坏账损失应交税金—增(进)组成部分其他业务收入(押金部分)理流动资产损溢⑴直接转销法贷:银行存款借:生产成本⑥不能使用而报废时,按其贷:现金①实际发生损失时③材料已到,月末发票账单贷:包装物残料价值查明原因后作如下处理:借:管理费用未到(2)随产品出售且借:原材料借:其他应收款-应收现金贷:应收账款借:原材料借:营业费用(不单独计价)贷:其他业务支出(出租)营业费用(岀借)故造成的存货损耗贷:短期投资-股票/债券借:应收股利借:长期股权投资-企业-⑤摊销(略)一一一次、五借:原材料(残料)X贷:投资收益-股利收入损益调整五、分次其他应收款(保险、责任人③转让、岀售[长期股权投资-企业]贷:投资收益-股权投资收4.低值易耗品(处理同包装赔款)借:银行存款在实际业务中,因“应收股益物)[营业外支出一非常损失]短期投资跌价准备-股/债禾固定,可先计算“长期股权ii被投资单位宣告分派股5.存货清查贷:待处理财产损溢X投资”,再通过计算即可得岀“投利时⑴盘盈注:待处理财产损溢在结帐贷:短期投资-股票/债资收益”借:应收股利-企业(实际①确认前必须将其转平。
分两种情况:券X(3)权益法数)借:原材料①如果已经董事会等类似权力【应收股利/应收利息】①初始投资或追加投资同贷:长股权投资-企业-损贷:待处理财产损溢-待处机构批准,转入损益等,不用披[投资收益一出售股/债X]上益调整理流动资产损溢露;②如果未经董事会等类似2长期股权投资投资②股权投资差额的处理II净亏损(以股权投资账面②报批转销权力机构批准,应按上述方法结(1)取得i取得时确认余额减至零为限)借:待处理财产损溢平,同时在附注中披露;如果其①以现金资产投资同上借:长股权投资-企业-投借:投资收益-股权投资损贷:管理费用后批准的结果与自行处理不一②以非现金资产投资(见资贷成本失⑵盘亏或毁损致,则要调整当期报表的年初后)贷:银行存款贷:长股权投资-企业-损①确认数。
(2)成本法借:[长期股权投资-企业益调整借:待处理财产损溢8 •存货的期末计价(略)①初始投资或追加投资同-股投差额]注:以后被投资单位又实现贷:原材料第三章投投取得贷:[长股权投资-企业- 利润,先冲减未减记长期股权投应交税金—增(转岀) 1 •短期投资②被投资单位宣告分派利投资成本]资的余额,若还有多余再恢复其②报批转销①购入润或现金股利ii摊销账面价值,恢复时i属于自然损耗产生的定额借:短期投资--股票/债券/ I投资年度以前借:投资收益-股权投资差借:长期股权投资-企业-内损耗基金X借:应收股利-股利收入额摊销损益调整借:管理费用应收股利、应收利息贷:长期股权投资-企业贷:长期股权投资-企业- (确认的损益一未减记的)贷:待处理财产损溢贷:银行存款II投资年度股权投资差额贷:投资收益-股权投资收ii属于收发计量、核算、管其他货币资金i属于投资前的借:长期股权投资-企业- 益理不善造成的损耗注:收到购入时的现金股借:应收股利-股利收入股权投资差额④其他所有者权益变化的借:原材料(残料)利、债券利息贷:长期股权投资-企业贷:资本公积-股权投资准处理其他应收款(保险、责任人借:银行存款ii属于投资后的备i投资单位会计处理赔款)贷:应收股利、应收利息借:应收股利③被投资单位实现净损益借:长股权投资-企业-股[管理费用]②收到持有时期内的股利贷:投资收益-股利收入的处理权投资准备贷:待处理财产损溢或利息III投资年度以后(按公式I净利润贷:资本公积-股权投资准iii属于自然灾害或意外事借:银行存款/现金计算)i被投资单位实现净利润时备(=捐赠物价值* (1-33%)②成本法转换为权益法成本法转换为权益法时初借:资本公积-股权投资准长短,分别在“短期投资”、“长*持股比例)i采用追溯调整法对原成本始投资成本= 200 + 5 + 2 + 302备期债权投资”反映。
注:如被投资单位接受现金法核算进行调整-2贷:资本公积-其他资本公③期末计价(略)捐赠,则不须交税。
借:长期股权投资-企业- 注:投资前与投资后新增股积第四章固定资产ii投资单位岀售该项股权投资成本200权投资差额应分别计算,分别摊注:转增资本时1.增加(如是旧的,则以时,可将原计入资本公积的” 股-企业-股权投资差额1销,前者按投资日算,后者按追借:资本公积-其他资本公净值入帐)权投资准备“转入“其他资本公-企业-损益调整5加投资日算。
但如果追加投资新积①购置积-企业-股权投资准备2形成的股权投资差额不大,可以贷:实收资本/股本I购入不需安装的固定资产(4)成本法与权益法的转贷:长期股权投资-企业并入追溯调整后的股权投资差③尚未摊销的股权投资差借:固定资产换(帐面余额)205额余额,按剩余摊销年限一并摊额也应随同转销贷:银行存款①权益法转换为成本法利润分配-未分配利润(累销。
处置长期股权投资时,未摊借:投资收益-股权投资差II购入需安装的固定资产I转换时计影响数)1销的一并结转额摊销i购入借:长期股权投资-企业资本公积-股权投资准备iv以后分派利润或现金股贷:长期股权投资-企业- 借:在建工程贷:长期股权投资-企业- 2利同权益法股权投资差额贷:银行存款投资成本ii追加投资时(5)短期投资划转为长期 3 •投资的期末计价(略)ii领用安装材料、支付工资长股权投资-企业-损益借:长期股权投资-企业- 投资 4 •委托贷款借:在建工程调整投资成本302借:长期股权/债权投资(成①发放贷款贷:原材料II以后分派利润或现金股贷:银行存款302本与市价孰低者)借:委托贷款-本金应交税金-增-进转岀利时iii再次计算股权投资差额短期投资跌价准备贷:银行存款应付工资i属于已记入投资账面价值成本法转换为权益法时初投资收益②按期计提利息iii交付使用的始投资成本=200 + 5 +2+ 302贷:短期投资借:委托贷款-利息借:固定资产借:应收股利借:长期股权投资-企业- (6)长期股权投资的处置贷:投资收益-委托贷款利贷:在建工程贷:长期股权投资-企业股投差额2①损益的确认息收入②投资者投入ii属于尚未记入投资账面贷:长股权投资-企业-投借:银行存款注:若应收利息到期未收借:固定资产(投资双方确价值的资成本2长期股权投资减值准备至则将已确认的利息收入予以认价)借:应收股利将“损益调整”和“股权投贷:长期股权投资冲回,并在备查薄中登记冲回的贷:实收资本带:投资收益资准备”全部转入“投资成本”[投资收益-股权出售收益/利息金额。
其后,收回该利息,③接受捐赠III对中止采用权益法前被借:长期股权投资-企业- 损失]则冲减委托贷款本金。
借:固定资产(单据金额+ 投资单位实现的净损益,投资单投资成本7应收股利(尚未领取的现金1、科目设置:“委托贷款”税费)位仍按权益法核算。
贷:长期股权投资-企业- 股利或利润)一级科目下设“本金”、“利息”、贷:银行存款(支付的相关借:长期股权投资-企业损益调整5②资本公积准备项目的处“减值准备”二级科目税费)贷:投资收益-企业-股权投资准备2理2、资产负债表中,按期限资本公积-接受捐赠非现金资产准备借:在建工程银行存款(相关费用)贷:固定资产清理策变更应当采用追溯调整,调整递延税款(单据金额X贷:生产成本-辅助生产成2.减少iv岀售后应缴纳的营业税期初留存收益和相关项目。
33%)本只有盘亏不通过“固定资产借:固定资产清理 4 .固定资产的后继续支岀注:接受旧的固定资产捐赠vii工程借款利息支岀(见清理”核算贷:应交税金-应交营业税p113—114或投资,不在账面反映折旧;若借款费用)①投资转岀(售价X 5%)(1)费用化的后续支出接受的捐赠或投资的固定资产viii交付使用借:长期股权投资v结转净损失(或净收益)如果不可能使流入企业的含有原安装成本应从原值中剔借:固定资产贷:固定资产清理(该科目借:营业外支岀-处置固净经济利益超过原先的估计(即通除,新安装成本应加上。
贷:在建工程余额)损失(正常经营)常所说大修和日常修理),应在④经营租入(见后)ix剩余工程物资转作企业银行存款/应交税金(相关营业外支岀-非常损失(非发生时确认为管理费用、制造费⑤融资租入(见后)存货税费)正常原因)用,不再通过待摊费用(长期待⑥自行建造借:原材料②捐赠转岀长期待摊费用(筹建期间发摊费用)、预提费用处理。
