过程控制复习资料
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEM REVIEW
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1. Typical Controlled Variables
Temperature, Pressure, Flow, Level,Concentration,Physical property
2. Terminology in the process
The Controlled Variable (CV), the Manipulated Variable (MV)
Factors causing CV to deviate from their set points is called the Disturbance or“Load" Variables
3. Two Classes of Process Control
Regulatory control- disturbance change , Servoing control- setpoint change
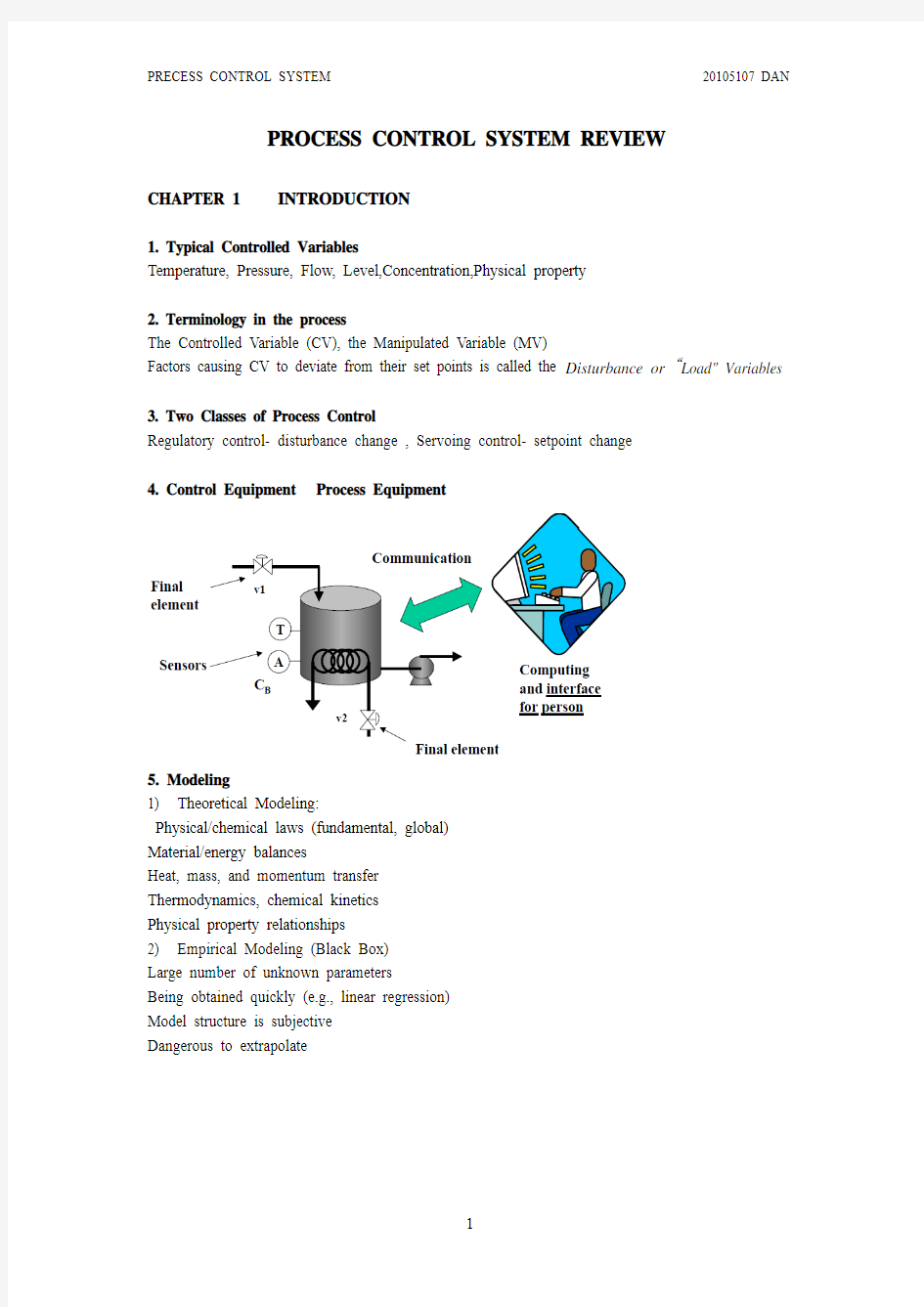
4. Control Equipment Process Equipment
5. Modeling
1) Theoretical Modeling:
Physical/chemical laws (fundamental, global)
Material/energy balances
Heat, mass, and momentum transfer
Thermodynamics, chemical kinetics
Physical property relationships
2) Empirical Modeling (Black Box)
Large number of unknown parameters
Being obtained quickly (e.g., linear regression)
Model structure is subjective
Dangerous to extrapolate
CHAPTER 3 DYNAMIC RESPONSE
1. Analysis of the 1st Order Process
1) Property 1 : y increases from 0 to a new steady state MK, thus self-regulating
(Integrating process: Non-self-regulating )
2) Property 2 : Steady state gain K = y/M, The larger gain K, the more sensitive is the output to the change in the input
3) Property 3 : At t=τ, the output is y =0.632MK
4) Property 4 : The shorter the space time τ, the faster reaches the new steady state
2. Analysis of the 2nd Order Process
)(01222t bx y a dt dy
a dt y d a =++
1) 4 variables
3. Processes with Dead Time
1) Pad é approximation
The 1nd order Pad é approximation
The 2nd order Pad é approximation
2) Two plants have different intermediate variables but have the same input-output behavior!
Steady
state
transfer function
CHAPTER 5 ANALYSIS OF SISO SYSTEM
1. PID Controllers
1) The Proportional Band (PB ) is the inverse of the Gain. In the sense of proportional band PB
The higher PB, the slower (and more stable) control. The lower PB, the faster (and less stable) control.
2) Kc
The higher gain, the faster (less stable) control; The lower gain, the slower (more stable) control. The larger Kc, the faster is the change to a given error; Too large Kc will make the process unstable
3) Integral action makes the process saturation, reset windup
A. Integral term takes on a final nonzero value, thus permitting e s to stay at zero, as time progresses
B. the reset element of the controller continues to increase (or decrease) the controller output
C. even when the change in output does not cause any change in the process measurement (controlled variable).
D. with no resulting decrease in error, the output will continue to increase until it reaches its limit.
4) A small change in error may produce a big controller output occurring in changing set point (derivative kick ) , exhibiting in high-frequency noise
5) The Properties of P, I, D Control: from time standpoint
t = 0 t = t
t = T (T>t)
Proportional Mode
P-Control
Persistent Mode I-Control
Predictive Mode D-Control
Historical period Current Time
Future Time
