货代英语课后习题 02
货代英语

货代英语练习题。
1.the services that a freight forwarder renders are:a.routine and basic tasksb. a comprehensive package of servicesc.arranging transport of goodsd. a and b (d)2.the freight forwarder may provide services for processing the movement of goods------a.directlyb.trough subcontractors or other agencies employed by himc.utilizing the services of his overseas agentsd.a, b and c (d)3.on behalf of the consignee, the forwarders would1.receive and check all relevant documents relating to the movement of goods;2.deliver the cleared goods to the consignee.3.arrange for customs clearance and pay relevant fees and charges;4.take delivery of the goods from the carrier and pay the freight costs;what’s the order of them?a. 1-4-3-2b.1-3-2-4c. 4-1-3-2d. 3-1-4-2 (a)4.incoterms 2000 include ---------- different international trade terms.a. 10b. 11c. 12d. 13 (d)5.the traditional 3 trade terms area. FOBb. . CPTc. CFRd. CIF (a.c.d)6.FCA, CPT, CIP are suitable for ---------a. any mode for transportb. sea transportc. air transportd. sea and air transport (a)7.under FOB terms, ------- has to bear all costs and risks of loss of or damage to the goods whengoods pass the ship’s rail. The buyer8.the FOB term require ---------to clear the goods for export. The seller9.the CFR term requires -------- to clear the goods for export. The seller10.under FOB term, -------- must pay the freight necessary to bring the goods to the named portof destination. (the buyer)11.CIF means that the seller delivers when the goods ------ at the port of shipment.a. pass the ship’s railb. get delivered on shipc. get delivered on deck (a)12. under CIF term,----- contracts for insurance and pays the insurance premium. The seller13.under FCA, the seller delivers the goods to the carrier nominated by -------at the named place.The buyer 14.under FCA, if delivery occurs at the seller’s premises, ------is responsible for loading.The seller 15.under FCA, if delivery occurs at places other than the seller’s premises, ---------- isresponsible for unloading. The carrier 16.if the buyer nominates a person other than a carrier to receive the goods, the seller is deemednot to have fulfilled his obligation to deliver the goods when they are delivered to that person.(f)17.CFR can be used for sea and inland waterway transport, while CPT can be used for any modeof transport, but not including multi-model transport. ( f )18.FOB,CFR and CIF are followed by the port of shipment of port or port of destination. ( t )19.CPT, CIP and FCA are followed by the place of departure or place of destination. ( t )20.terms of shipment in the contract are compulsory. ( t )21.time of shipment refers to the final time for loading the goods on board the vessel at the portof shipment. ( f )22.the expression “on or about 20 June” means the period –a. from 15 June to 20 Juneb. from 10 to 30 Junec. from 15 June to 25 Juned. from 15 June to 25 June ( end days inclusive) (d)23.the words ---------applying to the period referring to shipment include the date mentioned.a. tob. untilc. tilld. from (a.b.c.d)24.the word “after” will be understood to include the date mentioned. ( f )25.expressions such as ----------- will not be accepted by the bank under L/C.A. prompt b. immediately c. as soon as possible (a.b.c)26.the L/C stipulates an expiry date without a shipment date which means these two dates are thesame. (t) 27.the latest date for shipment can be extended because of the extension of the expiry date andthe date for presentation of documents. (f)28.insurance is a contract between ---a. exporter and insurerb. importer and insurerc. insurer and the insurance companyd. insurance company and the insured (d)29.--------agrees to pay the premium in order to secure the financial assistance of ---------.a. the insured; insurerb. insurer ; the insuredc. the insured ; the insuredd. insurer; the insurance company. (a)30.for freight forwarders, it is not important to advise his clients to insure their cargo. (f)31.Particular Average is partial loss and damages of goods occurred because of natural calamities,for example, stranding, sinking of the vessels, etc. ( f )32.the usual types of cargo insurance coverage are –a. WAb. FPAc. ARd.AR including W and SRCC (a.b.c.d)33.the risks covered in FPA area.total losses resulting from marine perils and other specific accidentsb.total loss in loading, unloading or transshipment operationc.contribution to General Averaged.partial losses incurred as a result of specific casualties (a.b.c.d)34.FPA is not suitable for bulk cargo or unpacked cargo (f)35.FPA is completely suitable for general cargo. (f)36.WA and WPA are different types of coverage (f)37.losses below a specified amount or percentage are --------- under a franchise condition.a. recoverableb. non-recoverable (b)38 under a deductible franchise, in the case of all claims ---------- would bear the loss up to the franchise.a. the insuredb. insurer (a)38.AR is the most comprehensive type of cover. (f)39.War risks are applicable while the goods are in transit by sea or air and also on the land (f)40.loss or damage arising from strikes, riots or civil commotions on land are included. (t)41.marine transportation is the main mode of international transport. (t)42.the types of service provided on the international shipping market are---a conference lines b. non-conference lines c. NOVCC d. tramp services43.the feature of shipping service provided by shipping conference include---a. scheduled serviceb. common tariffc. fixed itinerary of ports of calls44.the main advantages of the conference system to shippers area.stability of freight ratesb. regularity of service.45.like tramp service, liner rates do not fluctuate according to supply and demand. (f)46.an NVOCC is a carrier who operates a regular scheduled service. (t)47.an NVOCC assumes responsibility for ocean carriers, both conference and non-conferencelines. (t)48.an NVOCC provide useful service by providing groupage or consolidation. (t)49.tramp service has no fixed schedule but has fixed itinerary. (f)50.the bill of lading is only signed by ---------. The carrier51.the functions of the bill of lading are :a. evidence of the contract of carriageb. receipt for goods delivered to the carrierc. document of title to the goods52.a sea waybill is the replacement of the traditional ocean bill of lading. (t)53.a sea waybill is non-negotiable document. (t)54.the consignee can only take delivery of goods against presentation of sea waybill. (f)55.a shipping note is issued by -------- to the carrier. The shipper56.a delivery order is issued by -------- or his agent. The carrier57.a mate’s receipt is issued by ------- in the acknowledgement of the goods received on board.The carrier58.chartering shipping and tramp shipping refer to the same term. (t)59.fixed running expenses include:a. employment and wages of crewb. purchase of stores and provisionsc. vessel insuranced. boiler water60.variable running expenses include:a. port chargesb. light duesc. special voyage insuranced. bunker fuel supply61.under voyage chartering, the risk of sudden and alarming rises in the price of bunker fuel fallon the ship-owner. (t) 62.under voyage chartering, the cost and responsibility for loading and discharges are fixed forthe account of the ship-owner. (f)63.the ship-owner receives hire money but not freight under time chartering. (t)64.under time chartering, the ship’s master acts under instructions received from the charterer. (t)65.under time chartering, consular shipping and discharging fees of the crew and charges for portservices pertaining to the crew are –for the account of ---------. Ship-owner66.under time chartering, the charterer shall pay for---a. consular chargesb. commissions and agenciesc. pilotages and towagesd. port charges (a.b.c.d.)67.under time chartering, fumigations ordered because of illnesses of the crew shall be for theaccount of ---------. Ship-owner 68.fumigations ordered because of cargoes carried or ports visited while vessel is employed shallbe for the account of --------. charterer 69.under time chartering, the ship-owner do not allow the charterer to use any dunnage andshifting boards already aboard vessel. (f) 70.under time chartering, the charterer has no involvement in the selection and appointment ofstevedores. (f)71.the possession of a bill of lading is equivalent in law to possession of the goods. (t)72.the terms of the bill of lading contain the terms of the contract. (t)73.straight bill of lading are negotiable and can be transferred to third party. (f)74.most bills of lading forms are printed as Received for shipment Bills of Lading. (f)75.under through B/L, the shipping company, for additional freight, undertake to make allarrangements to get the goods to their destination. (t)76.claused bill of lading is the opposite of clean bill of lading. (t)77.the ship’s port agent may be given the task of drawing up bills of lading. (t)78.the main parties on a bill of lading are :a. shipperb. consignee 千万注意不是发货人c. notify partyd. carrier79. the bill of lading can be signed bya. carrierb. duly authorized agent of carrierc. masterd. duly authorized representative of master (a,b,c,d)79.one of the original B/L must be endorsed by the title holder to the goods in exchange forgoods or the delivery order. (t) 80.a full set of B/L contains at least two original bills of lading. / in practice, a set of threeoriginals is the most common. (t)81.ocean freight rates may be broadly divided into ----a. tramp ratesb. liner freight rates (a, b)82. tramp rates don’t fluctuate with market conditions of supply and demand. (f)83.freight forwarders are mainly concerned with --------a. liner freight ratesb. tramp rates (a)84.the factors for determining the freight rates include:a. stowage factorb. distancec. the principle of “what traffic can bear”d. open market rates (a,b,c,d)85.the principle of “what the traffic can bear” means that commodities which are highly ratedsubsidize those which are rated lower. 什么原理(t)86.in the past, the principle of “what the traffic can bear” was mostly adopted; but at present,“service costs “principle is increasingly adopted. (t) 87.when commodities move in large quantities and are susceptible to charter competition, therates may be left ---a. openb. fixed (a)88. the liners do not need to take into account the surcharges and adjustment factors. (f )89. the vessel can start unloading goods only after the customs authorities grant the necessarypermit, called “entry inwards”. (t)90. the import manifest has to be accompanied by other documents as may be required such as:a. certificate of load lineb. certificate of registryc. port clearance from the last port of calld. crew list (a,b,c,d) 此题还有其他备选答案:safety radio telegraphy and safety equipment; stores list;declaration regarding property of officers and crew)91. export goods can be loaded on to the vessel only if the necessary permit, ”entry inward”, isgiven by the customs authorities. (f) 92. a vessel can leave the port only when written permission, known as ---------, is granted by thecustoms authorities. (port clearance)93. Bill of Entry usually contain particulars particulars such as:a. valueb. quantityc. description of goodsd. name of shipe. port of shipment94. the particulars on the Bill of Entry don’t have to tally with those contained in the importmanifest. (f)95. the examination made by the customs authorities may bea. physical examinationb. documentary examinationc. chemical test (a,b)95. the physical examination made by the customs authorities include:a. visual inspectionb. countingc. weighingd. measuringe. chemical test96. the CMR convention is the convention on contract for international carriage of goods by--------. (road)97. the CMR convention has been ratified by countries in Europe and outside Europe. (f)98. it is no need for the forwarders outside Europe to be aware of the CMR convention. (f)99. under CMR convention, the carrier is responsible for:a.the acts and omissions of his agents and servants or other person whose services hemakes useb.loss of or damage to the goods occurring between the time he takes over the goods andthe time of deliveryc.any delay in delivery (a,b,c) 100. under CMR convention, the carrier is relieved of liability if the loss, damage or delay is due to:a.any wrongful act or neglect of the consignorb.inherent vice of the goodsc.circumstances which he could not avoidd.consequence of the above circumstances he was unable to prevent (a,b,c,d) 101. under CMR convention, the carrier shall not be relieved of liability by reason of :a.the defective condition of the vehicle used by him in order to perform the carriageb.wrongful act or neglect of the person from whom he may have hired the vehiclec.wrongful act or neglect of the agents or servants of the vehicle owner (a,b,c) 102. consolidation and groupage means differently. (f) 103. in consolidation, the individual consignor and consignee can deal directly with the actual carrier. (f) 104. to the individual consignors, the consolidator is the ----------, while in his relationship with the actual carrier, he is the --------.a.carrier, consignor105. the consolidator buys shipping space -------- from the actual carrier and sells it ---------- to theindividual consignors.a.wholesale, retail106. consolidation can benefit:a. exporter and shipperb. carrierc. forwarderd. national economy (a,b,c,d) 107. in groupage, the exporters and shippers get a rate higher than they would have normally paid to the carrier. (f) 108. the advantages of intermodal trasport are:a.minimizing time loss at tran-shipment pointsb.reducing the burden of documentation and formalitiesc.establishing only one agency to deal withd.reducing cost of exports (a,b,c,d)其他备选答案有:providing faster transit of goods; saving costs109. the types of intermodal transport include:a. sea/ airb. air/ roadc. mini-bridge and land bridged. piggybacke. sea train 110.sea/air combines in itself the economy of -------- and the speed of ---------.a.sea transport, air transport111. the combination mode of sea/air favors low value items. (f) 112.both mini-bridge and land bridge involves the movement of containers. (t) 113. in land bridge, the railways are paid a flat rate by the ocean carrier who issues the through bill of lading. (t) 114. --------- is a system of unitized intermodal land transportation of transport by road and rail.(piggyback) 115. piggyback combines in itself the speed and reliability of road transport for collection and delivery with door-to-door flexibility of rail on long trunk hauls. (f) 116. ---------- involves the use of rail and ocean transport, similar to the roll-on, roll-off system except that a rail car is used. (sea train) 117. documentary credit means payment against documents instead of against goods. (t) 118. in documentary credit, the documents transfer title to the goods. (t) 119. by using a documentary credit, -------- can benefit.a. buyerb. sellerc. bank (a,b,c) 120. on settlement of the bill, the whole operation of documentary credit will be regarded as completed. (t) 121. the use of SLI ensures that the shipper’s instructions are complete.122. ---------- is the working document for air cargo acceptance and determines whether shipment can take place as requested. (SLI) 123. when giving the airport of departure, the name of the airport or the city name where the shipper is located are both workable. (t) 124. when giving the airport of destination, the name of the country should be shown. (t) 125. to ensure that the routing/booking requested by the shipper can be adhered to, TACT rules can be checked in. (t) 126. the description of the goods should be correct, since it will determine the rate to be applied to the consignment. (t) 127. the information about gross weight is used toa.calculate the transportation charges of the shipmentb.establish whether the shipment can be handled by available airport facilities.128. when giving measurement, the dimensions must be measured along the smallest length, width and height. (f) 1291. the air waybill is:a. a contract for transportation between a carrier and a shipperb. a receipt and delivery of the shipmented for freight bill calculation, customs declaration.d.Non-negotiable (a,b,c,d) 130. the AWB number comprise ------- parts. ( 3 ) 131. in AWB number, the three-digit prefix identifies -------------. (the carrier) 132. in AWB number, the main portion identifies ----------. (the consignment) 133. the copy of the AWB marked “original 3” is the copy that would normally be presented undera documentary credit. (t) 134. the AWB must be signed and dated by the actual carrier or by the named agent of a named carrier. (f) 135. --------------- is a listing of all AWBs put inside the envelop. (a cargo manifest) 136. the air waybill and cargo manifest are documents going with aircraft. (t) 137. Reception Check List is --------a.document staying on ground used by air terminals.b.the proof of receipt of goodsed to generate the air waybill of the shipment (a,b,c) 138. a premanifest is a document similar to a manifest but sent to an air terminal for cargo build up. (t) 139. General Cargo Rates are applicable to any type of commodity, but are pitched at an extremely high level. (t) 140. the justification for the minimum charge principle is that the costs of documentation and customs clearance are fixed irrespective of consignment size, and small consignments are expensive to handle. (t) 141. under class rating, certain commodities are offered a discount, and many more commodities are surcharged. (t) 142. special commodity rates are set by specific reference to general cargo rates. (f) 143. special commodity rates are always much lower than general cargo rates. (t) 144. Bulk Unitization Rates are available fro all types of freight. (t) 145. Bulk Unitization Rates are only given for freight which is prepackaged into an aircraft ULD that can be loaded directly into the aircraft. (t) 146. Contract FAK Rates are offered to those prepared to sign a contract to give the airline a minimum annual tonnage. (t) 147. FIATA--------a.was founded in Vienna Austria on 31 may 1926b.is the largest non-governmental organization in the field of transportation.c.Is known as the “architects of transport”d.Employing around 8-10 million people in 150 countries. (a,b,c,d) 148. 5 objectives of FIATA:? (理解)149. FIATA has 3 institutes, they are:a. AFIb. CAIc. MTI150. FIATA has 5 advisory bodies:a. ABDGb. ABITc. AGLMd. ABPRe. ABVT151. FIATA has created 8 documents, they are:a. FCPb. FCTc. FWRd. FBLe. FWBf. SDTg. SICh. FFI各单元应掌握的词汇。
货代英语试题及答案讲解

货代英语试题及答案讲解一、选择题1. What does "FOB" stand for in international trade?A. Free On BoardB. Free of BoardB. Free of ChargeD. Full of Benefits答案:A. Free On Board2. The term "LCL" in shipping refers to:A. Less than Container LoadB. Large Container LoadC. Limited Container LoadD. Long Container Load答案:A. Less than Container Load3. Which of the following is NOT a document typically required for exporting goods?A. Commercial InvoiceB. Bill of LadingC. Packing ListD. Receipt of Payment答案:D. Receipt of Payment二、填空题4. The abbreviation "TEU" stands for _______.答案:Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit5. When a shipment is described as "CIF", it means the seller is responsible for _______.答案:Cost, Insurance, and Freight三、简答题6. What are the main responsibilities of a freight forwarder in the logistics process?答案:A freight forwarder is responsible for organizing and managing the transportation of goods from the point of origin to the final destination. This includes arranging for the necessary documentation, booking space on a vessel or aircraft, and ensuring the goods are properly loaded and secured for transport.四、翻译题7. 将以下句子翻译成英文:- 我们提供门到门的物流服务。
国际货运代理考试英语练习题含答案

国际货运代理考试英语练习题含答案2016国际货运代理考试英语练习题(含答案)1. The booking note is issued by the ____ requesting allocation of shipment space. (C)A. carrier to the agentB. carrier to the shipperC. shipper to the carrierD. carrier to consignee2. AN NVOCC is a (n) ____ who operates regular scheduled services. (B)A. shipperB. carrierC. receiverD. charterer3. To the actual shipper, the NVOCC is a ____ while to the actual carrier, he is a ___. (B)A. actual carrier……carrierB. carrier……shipperC. shipper……carrierD. carrier……consignee4. The ____ is issued by the shipper to the carrier requesting allocation of shipment space. (C)A. cargo manifestB. mate’s receiptC. booking noteD. delivery order5. When the goods arrives at the port of destination, the_____ issues an Arrival Notice informing the notify party of the cargo discharge point and other information. (B)B. carrierC. receiverD. consignee6. All bills of lading should be signed either the___ or____. (D)A. notify party……carrierB. carrier……shipperC. consignor……consigneeD. carrier……his agent7. A document signed by the Chief Office acknowledging the receipt of cargo on board ship, and later exchanged for a B/L is called______. (B)A. sea waybillB. mate’s receiptC. booking noteD. delivery order8. Documentary credit means payment against____ instead of against______. (D)A. goods……documentsB. acceptance……confirmationC. documents……acceptanceD. documents……goods9. Detailed provisions dealing with the operation of documentary credit can be found in_____. (B)A. ICCB.UCPC. INCOTERMSD. CMR convention10. In a revocable credit, it is the____ who has the right to revoke the credit. (A)B. sellerC. advising bankD. issuing bank11. The____ bank should ensure that the seller’s documents are drawn up in accordance with the credit terms before such documents are paid for and forwards to the____ bank for final reimbursement. (C)A. issuing……negotiatingB. advising……payin gC. negotiating……issuingD. paying……advising12. _____ published by the ICC contains detailed provisions dealing with the operation of documentary credit. (B)A. Hague RulesB. UCP600C. Incoterms2000D. CMR convention13. In the practice of L/C transaction, the buyer is not required to pay for the goods until the arrival of the relevant____.(C)A. B/LB. invoiceC. documents stipulated by L/CD. L/C14. According to documentary credit, the____, on receipt of letter of credit, will have to prepare shipment of the contract goods within the delivery date. (D)A. agentB. customerD. seller【2016国际货运代理考试英语练习题(含答案)】。
国际货运代理英语(货代英语)forwarderEnglish1to21

Forwarding English (Freight
Forwarding
目录
• Overview of Freight Forwarding Industry • Basic knowledge of freight forwarding English • Import and export business processes and
Oral expression and communication skills
01
Ability to communicate effectively in English with suppliers, customs offices, freight forwarders, and other relevant parties involved in the international freight forwarding process
• International market: The global freight forwarding market is highly concentrated with a few large international players dominating the market These players have extended global networks and advanced technology platforms, enabling them to provide comprehensive services to their clients Additionally, there is a growing trend of collaboration and consolidation among freight forwarders to enhance their competitiveness and meet the changing demands of the market
国际货运代理人《专业英语》练习一及答案-国际货运代理人.doc

2016国际货运代理人《专业英语》练习一及答案-国际货运代理人1UndertheFCATerm,ifthebuyernominatesapersonotherthanacarriertoreceivethe goods,the()is deemed tohave fulfilled his obligation to deliver the goods when theyaredelivered tothat person.AbuyerB consigneesellerDbanker参考答案:C参考解析:采用FCA术语成交时,若买方指定承运人以外的人领取货物,则当卖方将货物交给此人时,即视为已履行了交货义务。
2A document signedbytheChiefOfficer acknowledging thereceiptofcargoonboardship,andlater exchanged foraB/Liscalled ().A.seaway billB.booking noteC.mate’s receiptD.billoflading参考答案:C3Shipsthatdonotsailon regular trade routesorhave regular schedules are called( )AlinersB trampsC chartersD NVOCCs参考答案:B4()meansthattheseller deliversthegoodstothecarrier nominatedbyhim,but the seller mustin addition paythecostof carriage necessary tobring the goodstonamed destination.AFCABFOBCDCPT参考答案:D参考解析:“运费付至(……指定目的地)”是指卖方向其指定的承运人交货,但卖方还必须支付货物运至目的地的运费,亦即买方承担交货之后的一切风险和其他费用。
国际货代专业 英语Unit 2 Scope of Freight Forwarding Service
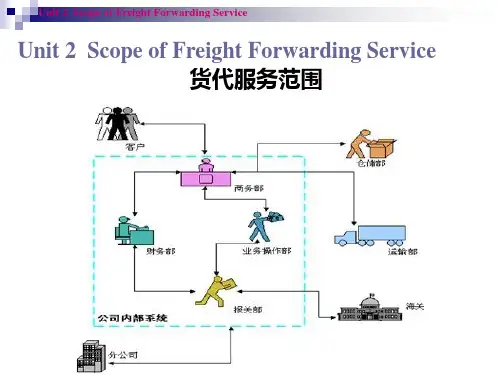
5.Pack the goods, taking into account the route, the mode of transport, the nature of the goods and applicable regulations, if any, in the country of export, transit counties and country of destination. 货物的包装,( 在货物包装时) 要考虑运输路线,运输的方式, 货物的特性,如果有的话还要考虑出口国,中转国和目的地国 家适用的规定。 6.Arrange warehousing of the goods, if necessary. 如果有必要的话,要安排货物的仓储 7.Weight and measure the goods. 测定货物的重量和尺寸。 8.Draw the consignor’s attention to the need for insurance and arrange for the insurance of goods, if required by the consignor. 提醒发货人注意是否需要货物保险,如果发货人需要投保,则 需安排货物的保险。
Unit 2 Scope of Freight Forwarding Service
小练习
1. A freight forwarder is also called ( ) 【单选题】 A. an exporter B. an importer C. a commission agent D. a customer 2. The consignee refers to the ( ) 【单选题】 A. importer B. exporter C. forwarder D. agent 3. That the scope of a forwarder’s service is extended is because of ( ) 【多选题】 A. the forwarder’s willingness to do so B. the expansion of international trade C. the development of different modes of transport D. the improvement of a ship’s structure
国际航运业务英语与函电课后答案
English for International Shipping Business and Correspondence
——课后练习 参考答案
L1 Essentials Qualities of a Good Business Letter EX.Ⅱ
1. We confirm well receipt of your letter.
5. We will consider your request. 6. We have received your letters of the 30th eltimo and 4th
instant.
7. We are sorry to decline your request.
8. We promise there will be no further delay in remitting you $5000 as compensation as per Art.6 of the contract.
Supplementary
1. We would like to receive your specific enquiry at an early date. 望能早日收到你方具体询价单。
2. Our company is ready at any time to give you any assistance. 我公司随时准备给你们提供任何帮助。
2.replenish bunkers
3.settle the account with you 4.quote us your rate
5.frieight rate
6.shipping application/booking note
物流英语习题答案
物流英语习题答案物流英语习题答案在当今全球化的时代,物流行业的发展日益重要。
无论是国内贸易还是国际贸易,物流都扮演着至关重要的角色。
而随着物流行业的发展,掌握一定的物流英语知识也变得越来越重要。
下面是一些常见的物流英语习题及其答案,希望能帮助大家更好地理解和应用物流英语。
习题一:请翻译以下物流相关词汇1. 运输(Transportation)2. 仓库(Warehouse)3. 货物(Cargo)4. 装卸(Loading and unloading)5. 供应链(Supply chain)6. 采购(Procurement)7. 运费(Freight)8. 运输方式(Mode of transportation)9. 物流管理(Logistics management)10. 保险(Insurance)答案:1. Transportation2. Warehouse3. Cargo4. Loading and unloading5. Supply chain6. Procurement7. Freight8. Mode of transportation9. Logistics management10. Insurance习题二:请根据上下文选择正确的词语填空1. We need to find a ________ to transport the goods to the customer.a) vehicleb) warehousec) cargo2. The ________ process involves sorting, packaging, and labeling the products.a) procurementb) loadingc) supply chain3. The ________ company provides insurance coverage for the goods during transportation.a) warehouseb) insurancec) freight4. The most common ________ of transportation for international trade is by sea.a) modec) transportation5. Effective ________ management can help reduce costs and improve efficiency.a) supply chainb) logisticsc) procurement答案:1. a) vehicle2. b) loading3. b) insurance4. a) mode5. b) logistics习题三:请根据给出的定义选择正确的词语1. The process of buying goods and services for a business.a) procurementb) freightc) warehouse2. The cost of transporting goods from one place to another.a) freightb) cargoc) insurance3. A building or facility used for storing goods.b) warehousec) transportation4. The movement of goods from one location to another.a) transportationb) supply chainc) loading and unloading5. The coordination and management of the flow of goods and information.a) logistics managementb) procurementc) mode of transportation答案:1. a) procurement2. a) freight3. b) warehouse4. a) transportation5. a) logistics management习题四:请翻译以下句子1. We need to find a reliable transportation company to ship the products to our customers.答案:我们需要找到一个可靠的运输公司将产品运送给我们的客户。
货代英语
分运单由航空公司签发。 是 否 b
登记货物运价用字母S表示。 是 否 b
在各种航空货物运价中,指定商品运价优先使用。 是 否 b
信用证受益人即B/L上的托运人。 是 否 a
信用证受益人即买卖合同中的卖方。 是 否 a
CIF合同卖方即C/P中的租船人。 是 否 a
A、 已交货完毕 B、发货人责任终止C、收货人有权提货 D、承运人责任已终止
18、到付运费支付时间在(C)。
A、B/L签发前 B、B/L签发后 C、D/O签发前或当时 D、交货后
19、集装箱进出港区时确定箱体交接责任的单证是(D)。
A、提单 B、大副收据 C、提货单 D、设备交接单
2、L/C CFS-CFS,但B/L记载CY-CY,通常可结汇的B/L是(A)。
A、H-B/L B、S-B/L C、M-B/L D、SWBL
3、L/C规定出具全程可转运B/L时,一程船和二程船公司责任划分依据是(D)。
A、全程B/L B、一程B/L C、二程B/L D、MEMO-B/L
C、必须是公路与海运之间D、必须是铁路与公路之间
23、多式联运经营人对货物承担的责任期限是(B)。
A、自己运输区段 B、全程运输 C、实际承运人运输区段D、第三方运输区段
24、卫检对集装箱查验,要求其做到(D)。
A、清洁、干燥B、无味、无尘 C、清洁、无味 D、清洁、干燥、无味、无尘
A、船公司 B、原收货人 C、第三方 D、货运代理人
(4)HBL、SBL哪一张是全程提单?(A)。
A、HBL B、SBL C、HBL、SBL均可作为全程提单 D、根据L/C
(5)HBL、SBL哪一张是结汇提单?(A)。
国际货运代理考试专业英语仿真题及答案(2)
国际货运代理考试专业英语仿真题及答案(2)二、多项选择题1. A shipment of fresh egg is transported to the docks by an exporter on an FOB contract. The eggs are broken by a crane falling them as they are awaiting to be loaded on board. The ___ should be liable for the damage. (A)A. sellerB. buyerC. ship ownerD. freight forwarder2. 100 sewing machines under CIF shanghai are being shipped onto the ship and the rope breaks. The goods finish up at the bottom of the dock and divers are sent down. The recovery and repair of goods costs a great of money. The ___ should be responsible for the damage. (C)A. ship ownerB. buyerC. sellerD. freight forwarder3. According to INCOTERMS 2000, which group of the following trade terms mean that the seller must contract for the carriage of the goods to the named port (or place ) of destination?____ (D)A. FOB/CFR/CIFB. FCA/CPT/CFRC. FOB/FCA/CIPD. CFR/CPT/CIF4. Under the FOB term, the risk of loss or damage to the goods is transferred from the seller to the buyer when goodspass the ship’s rail in the ____. (A)A. port of shipmentB. place of shipmentC. port of destinationD. place of destination5. Under the CFR term, the seller must, in addition, pay the cost of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the ____ , when he delivers the goods to the carrier nominated by him. (D)A. named placeB. named destinationC. any placeD. named port of destination6. According to INCOTERMS 2000, under which group of the following trade terms is the seller required to bear the risk of loss of or damage to the goods when the goods pass the ship’s rail ?(C)A. FCA/CFR/CIPB. FCA/CPT/CFRC. FOB/CFR/CIFD. CFR/CPT/CIF7. When applying to CIF, the expression of ocean bill of lading freight is ____. (A)A. freight prepaidB. freight collectC. freight paidD. freight unpaid8. Which of the following trade terms can be adopted supposing the shipment will be from Chengdu (Sichuan Province) to Hamburg? (CD)A. CIFB. CFRC. FCAD. CPT9. When the goods arrive at the port of destination, _____ issue an Arrival Notice to inform the Notify Party about the cargo discharge point and other information. (B)A. shipperB. carrierC. receiverD. ship owner10. Under FCA, if delivery occurs at the seller’s premises, who is responsible for unloading the goods according to the contract of sale____. (B)A. sellerB. buyerC. carrierD. freight forwarder11. Container freight rates mainly include: ( )A. tramp rateB. liner freight rateC. FAKD. CBR答案:CD12. Logistics is the process of ( ) from point of origin to point of consumption for the purpose of conforming to customer requirements.A. inventoryB. goodsC. informationD. services答案:BCD13. Multimodal transport has the following advantages: ( )A. Minimizing time lossB. Providing faster transit of goodsC. Saving costsD. Reducing cost of exports.答案:ABCD14. Under CMR convention, the carrier is liability of: ( )A. the acts and omissions of his agentsB. any wrongful act or neglect of the consignorC. inherent vice of the goodsD. loss of or damage to the goods during the time he takes the goods答案:AD15. Which of the following trade terms may be used multi-modal transport.A. CIPB. CIFC. FCAD. CPT答案:ACD三、判断题1. In international trade, a country can import goods that make intensive use of the factor of production, instead of importing the factor of production. ( )答案:正确2. Inherent vice or nature of the insured goods are not covered both in WA and All Risks coverage.( )答案:正确3. The date marked on the B/L is the date on which the carriertakes delivery of the goods. ( )答案:错4. The air freight charges may be determined either by weight or weight plus volume. ( )答案:正确5. According UCP600, the words “till”, “after”, “from” applying to any date or period in the credit referring to shipment will be understood to include the date mentioned. ( ) 答案:错6. Tramp service is a carrier who operates a regular scheduled service. The vessels are usually chartered at negotiated rates, particularly when the quantity of cargo is large.( )答案:错7. The air waybill is the document of title for the goods and can be transferred to the third party by endorsement.( ) 答案:错8. The seller must pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination under FOB trade term. ( )答案:错9. The Voyage chartering party includes the payment of dispatch and demurrage. ( )答案:正确10. The standard for examination of documents by the banks is reasonable time not exceeding 7 banking days.( )答案:错11. “unclean on board” is indicated on the B/L means that the goods is not clean.答案:错12. The figure like 11/7/2008 in British English will beunderstood as July 11, 2008, while in American English will be understood as November 7, 2008. ( )答案:正确13. If the goods are in order, but the documents are not correct, the issuing bank has the rights to refuse to pay the seller. ( )答案:正确14. The written permission granted by the customs authorities to allow the vessel which has brought any imports or has loaded exports to leave the port is Entry Inwards. ( ) 答案:错15. The Specific Commodity Rates are higher than General Cargo Rates. ( )答案:错。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
二、多项选择题
3. Which of the following services are performed by the forwarder on behalf of the import . A. Monitor the movement of goods B. check the relevant documents C. Arrange import customs clearance D. Weigh and measure the goods. 4. If there is damage of goods during shipment, the freight forwarder will _______ on behalf of exporter. A. Note damages B. Pay fees to insurer C. Assist exporter in pursuing claims. D. Arrange for the insurance of goods.
四、英汉互译
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 货运代理人 外汇 信用证 清关 委托代理人 转运国 货物的运输 舱位 提单 国际贸易 freight forwarder foreign exchange letter of credit customs clearance commission agent country of transshipment movements of goods shipping space bill of lading International Trade
1.错; 2.对; 3.对; 4.错; 5.对
四、英汉互译
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 transit country trade terms general cargo special cargoes the Forwarders’ Certificate of Receipt the Forwarders’ Certificate of Transport trade contract relevant documents take delivery of the goods mode of transport 转口国 贸易条款 杂货 特殊贸易 货运代理收货证书 货运代理运输证 贸易合同 相关单据 提货 运输方式
1. ABC ; 2. AC ;
三、判断题
1.When freight forwarder pack the goods on behalf of exporter, should take into account the quality of goods. ( ) 2.If necessary, the freight forwarder should pay the fees and other charges including freight for exporter. ( ) 3. The freight forwarder will issue “Forwarders’ Certificate of Receipt” when he take delivery of the goods from exporter. ( ) 4. The freight forwarder can not employ other agency to provide services both for exporter and importer. ( ) 5. The freight forwarder would prepare all necessary documents for exporter if nec of Freight Forwarding Service
一、单项选择题
1.A consignor refers to the person who _______ goods. A. receives B. attends to C. sends D. takes delivery of 2. It is usually the _______ who issues relevant documents such as the Forwarders’ Certificate of Receipt, the Forwarders’ Certificate of Transport, etc. A. consignor B. consignee C. freight forwarder D. carrier 3. Foreign exchange transactions, if any, are usually attended by the _______ as well. A. commission agent B. exporter C. importer D. freight forwarder 4. A freight forwarder originally was a(n) _______ performing on behalf of the exporter/importer routine tasks. A. importer B. exporter C. shipper D. commission agent
1. C ; 2. C ; 3. D ; 4. D
二、多项选择题
1. A freight forwarder shall take into account the route, the mode of transport and applicable regulations, if any, in the _______ A. country of export B. country of destination C. country of transshipment D. transit countries 2. A freight forwarder, on behalf of the exporter, is expected to _______ A. take delivery of the goods B. pay the freight costs C.arrange transit warehousing D.arrange customs clearance
