高中英语语法讲义大全
高一英语语法讲义(总结)

第四部分 双枪老太婆 当两个词表示的是一个物体或者一个物体的不同组成部分时就使用一个冠词,否则冠词要分开使用。 解析:the red & white rose; the red &white roses. 第一句 the red & white rose. 当red、white同时表示同一物体rose时,则共用; 当red、white表示为不同物体时,则要分开使用
例题:2、Do you have ____dictionary? A. a English & French B. an English & French C. a English &a French D. an English & a French 解析:由于dictionary本身以单数形式出现,则确定选项中只允许单数形式; 首先就排除C、D;根据a/an之间的区别,可知B项正确。
例题分析:第一步强行填入“这个”,译文为:你见过这只笔吗? 结合Байду номын сангаас文语境,可知不符合逻辑因果关系不成立。
一、 冠词
第一段 快乐大篷车 第三部分 零冠词与冠词 注:但凡遇见复杂的、零散的的知识点时,采用故事记忆法。
故事记忆:——看球痴绝食路
记忆:强调单词Negro 黑人————>black————>African American
高一英语语法突破讲义
Unit 1 冠词
高中英语语法专题讲义_名词

英语语法专题讲义-名词(一)、名词的种类:1、专有名词:1)China, Japan, Beijing, London, Tom, Jack(不加冠词)2)the Great Wall, the Yellow River, the People’s Republic of China, the United States等。
(由普通名词构成的专有名词,要加定冠词。
)2、普通名词1)不可数名词注意:•不可数名词前一般不加冠词,尤不加不定冠词:若加a(an)则使之具体化了。
如:have a wonderful time.‚不可数名词作主语,谓语动词用第三人称单数形式。
ƒ不可数名词一般无复数形式。
部分物质名词在表不同类别时,可用复数形式。
如:fishes, newspapers, waters, snows……| | | |各种各样的鱼各种报纸河湖、海水积雪…有些抽象名词也常用复数,变为可数的具体的事物。
如:times时代,works著作,difficulties 困难…在表数量时,常用“of”词组来表示。
如:a glass of milk, a cup of tea, two pieces of paper….2)可数名词:•可数名词除用复数形式表一类之外,一般都要加冠词:A birdThe frog is a kind of hibernating animal.Vegetables sold at this shop are usually fresh.‚有复数形式:a)规则变化——加“s”或“es”(与初中同,略)b)不规则变化——child (children), foot (feet), tooth (teeth), man (men),woman (women), mouse (mice), goose (geese), Englishman (Englishmen),phenomenon(phenomena)…注意:c)单、复数同形:sheep, deer, Chinese, Japanese, fish(同一种鱼)……。
高中英语重点语法讲义(内部资料).doc
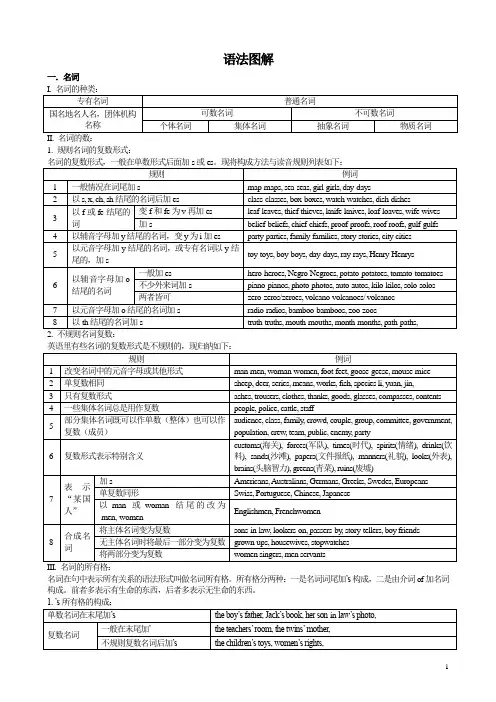
语法图解一.名词1. 规则名词的复数形式:名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。
所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加’s构成,二是由介词of加名词构成。
前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。
用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the first-year students 用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressed二.冠词冠词分为不定冠词(a, an),定冠词(the),和零冠词。
三.代词:1. one, some与any:1) one可以泛指任何人,也可特指,复数为ones。
some多用于肯定句,any多用于疑问句和否定句。
One should learn to think of others.Have you any bookmarks? No, I don’t have any bookmarks.I have some questions to ask.2) some可用于疑问句中,表示盼望得到肯定的答复,或者表示建议,请求等。
W ould you like some bananas? Could you give me some money?3) some 和any修饰可数名词单数时,some表示某个,any表示任何一个。
I have read this article in some magazine. Please correct the mistakes, if any.4) some和数词连用表示“大约”,any可与比较级连用表示程度。
There are some 3,000 students in this school. Do you feel any better today?2. each和every:each强调个别,代表的数可以是两个或两个以上,而every强调整体,所指的数必须是三个或三个以上。
高中英语语法大全全课件非常详细(561张PPT)PPT课件

Two teas, please. 请来两杯茶。
d. 抽象名词有时也可数。
four freedoms 四大自由
the four modernizations 四个现代化
many interests 许多兴趣
精选PPT课件
15
精选PPT课件
16
问题1
The ______ is just around the corner and you won’t miss it. (01北京春季)
有些抽象名词和物质名词也可转化为可数名词,用
来表示某种特定的意义。a knowledge of …表示
“对……有所了解“。又如:
This meeting is a great success.
请看下面的可数与不可数名词的转化:Βιβλιοθήκη 精选PPT课件14
a. 当物质名词转化为个体名词时。
Cake is a kind of food. 蛋糕是一种食物。 (U)
A. a four hour C. a four-hours
B. a four hour's
✓D. a four hours'
精选PPT课件
18
问题3: There are only twelve _____ in the hospital.
✓ A.woman doctors B.women doctors
大多数不可数名词都不可能转化为可数名词,常
见的有:information; news; advice; progress;
fun ……如:
This is not a match. We’re playing chess for _____.
✓ A habit B hobby C fun D game (2001上海春季)
高中英语语法大全(详细)

第一主题英语语法系统全解(一)第1章动词时态 2-4楼第2章被动语态 5-7 楼第3章虚拟语气 9-11 楼第4章情态动词 12-16楼第5章动词不定式 17-20 楼第6章动词的ing形式 21-24楼第7章过去分词 25-27楼第8章独立主格结构 28-30楼第9章名词性从句 31-33楼第10章定语从句 35-40楼第11章状语从句(一) 40-45楼第11章状语从句(二)第12章直接引语和间接引语第13章倒装第14章强调第15章省略第16章主谓一致动词时态--一般时第一章动词时态(一)在英语中,不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,要用不同的动词形式来表示,这就叫做动词的时态。
一、一般时一般时包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和一般过去将来时。
A.一般现在时1.一般现在时的构成一般现在时主要用动词原形来表示。
主语是第三人称单数时,动词后面要加-s或-es。
“我’为开头做称呼的是第一人称‘你’怎么怎么样是第二人称‘他她它’是第三人称第三人称就是第三人称转述。
例:小兰对妈妈说:“我要出去玩了”第三人称:小兰对妈妈说,她要出去玩了。
第三人称,就是说是叙述性质的,没有人的语言,是旁白在记叙!以我的角度说,就是第一人称;以和你说的角度说,就是第二人称;站在事情外说事情,他怎么怎么样,那就是第三人称了They want good jobs.他们想要好的工作。
The coat matches the dress.外衣和裙子很相配。
This work does not satisfy me.这项工作我不满意。
Do you understand?你懂了吗?2.一般现在时的用法①一般现在时的基本用法a. 表示现在习惯性的动作或存在状态He always takes a walk after supper.晚饭后他总是散散步。
Everyone is in high spirits now.现在大家都情绪高涨。
b. 表示客观事实或普遍真理The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.太阳从东方升起在西方落下。
高考英语一轮复习语法总结讲义

一、时态、语态时态、语态需要掌握的要点:1.表达将来时的形式:(1)在时间、条件、让步从句中,一般现在时代替将来时,但要注意区别从句的类型,如:I’ll tell him when you will ring again. 我告诉他你什么时候再来电话。
(宾语从句)比较:I’ll tell him when you ring again.你再打电话时我告诉他。
(状语从句)(2)在make sure, make certain, see (to it) 后的that从句中,谓语动词用一般现在时代替将来时,如:See to it that you include in the paper whatever questions they didn’t know the answer to last time.(include 不能用will include或其他形式) 2.完成时是时态测试的重点,注意与完成时连用的句型和时间状语:(1)by/between/up to/till +过去时间、since、by the time/when +表示过去发生情况的从句,主句用过去完成时。
如:We had just had our breakfast when an old man came to the door.Between 1897 and 1919 at least 29 motion pictures in which artificial beings were portrayed had been produced.(表示1919年时已发生的情况) (2)by +将来时间、by the time/ when +谓语动词是一般现在时的从句,主句用将来完成时。
如:By the time you arrive in London, we will have stayed in Europe for two weeks.I hope her health will have improved greatly by the time we come back next year.(3)by now、since +过去时间、in/during/for/over/the past/last few(或具体数字)years/days/months,主句用现在完成时,如:The changes that had taken place in air travel during the last sixty years would have seemed completely impossible to even the most brilliant scientists at the turn of the 19th century.但在it is +具体时间since/before这一句型中,主句更多的时候不用完成时。
高中英语语法大全ppt课件
2.know nothing about him except that he is from the south.(that引 导的宾语从句作介词宾语时,that不能省略。)对他我一无所知, 只知道他是南方人。 3.That he ever said such a thing I simply don’t believe.(that从句位于 句首时,that不可省略。)我简直不相信他曾说过这样的话。
have been doing/
1)不定式的一般式 不定式的一般式所表示的动作通常与主要谓语的 动作同时或几乎同时发生,或是在它之后发生。如:They invited us to go there this summer.他们邀请我们今年夏天去那儿。He stood aside for me to pass.他站到一边让我通过。
注:从属连词if一般不用来引导表语从句,但 as if却可引导表语从句,如:All this was over twenty years ago , but it's as if it was only yesterday. 这都是20多年前的事了,但宛如昨天一样。
4
能跟表语从句的谓语动词一般为系动词be,seem,look等。 如:It looked as if it was going to rain.看起来天要下雨了。 (3)连接代词who , whom , whose , what , which , whoever , whatever , where ,whichever 连接副词 。如:The problem is who we can get to replace her.问题是我们能找到谁去替 换她呢。The question is how he did it.问题是他是如何做此 事的。That was what she did this morning on reaching the attic.那就是她今晨上了阁楼干的。
高中英语语法大全-精讲教程(最全版)
去年我参观过故宫博物院。 【正】I have visited the Palace Museum.
我参观过故宫博物院。 b. 表示过去经常发生的动作或存在的状态 I wrote home once a week at college. 我上大学时每周给家里写一封信。 He was already in the habit of reading widely in his boyhood. 他童年时就养成了广泛阅读的习惯。 提示: 表示过去的习惯性动作,除了用过去式外,还可以用 used to 或 would 来表示。 She used to study late into the night when she was in Senior Three. 她上高三时经常学习到深夜。 He would sit for hours doing nothing. 过去他常常一坐几个钟头什么事也不做。 c. 表示过去连续发生的一系列动作 She entered the room, picked up a magazine and looked through it carefully. 她走进房间,拿起一本杂志,认真地翻阅了起来。 The students got up early in the morning, did morning exercises and then read English aloud in the open air. 学生们很早起床,做早操,然后在室外朗读英语。 d. 在时间、条件状语从句中表示过去将要发生的动作 We would not leave until the teacher came back. 老师回来我们才会离开。
高中英语语法大全PPT课件
• 形容词→副词 early→early, fast→fast
• 副词→连词 when(什么时候)→(当……时候)
• 介词→副词 in(到……里)→(在里面;在家),on(在…上)→(进行,继续),
第6页/共188页
Chapter 2 名词
• 专有名词 Beijing, Tom, the People’s Republic of China • 普通名词
▲可数名词 ▲不可数名词
第7页/共188页
一、英语可数名词的单复数
• 规则变化 ①在单数名词词尾加s ②s,o,x ,sh,ch结尾的词加es ③以辅音字母加y结尾的名词,变y为i,再加es ④以f或fe结尾的名词,变f或fe为v,再加es。
第15页/共188页
主主格格 宾宾格格
第第一一人人 称称单单数数
第第二二人人 称称单单数数
第第三三人人称称单单数数
男男
女女
II
YYoouu hhee
sshhee
((我我))
((你你))
((他他))
((她她))
mmee
yyoouu
hhiimm
hheerr
((我我))
((你你))
((他他))
((她她))
语或者表语,后面千万不可以跟名词 eg. This is your cup,but where is mine?(这是你的杯子,可我的在哪儿?) • 双重所有格:“of + 名词性物主代词”
第18页/共188页
第一人 第二人 称单数 称单数
第三人称单数
男
女
中性
第一人 第二人 第三人 称复 称复数 称复数 数
高中英语语法讲义大全
高中英语语法一、英语词法1、实词:是指有实在意义,能独立承担句子成分的词名词、代词、形容词、副词、数词、动词2、虚词:没有实在意义,不能独立承担句子成分冠词、介词、连词、感叹词二、英语句法1、简单句2、并列句3、复合句(1)名词性从句◆主语从句◆表语从句◆宾语从句◆同位语从句(2)定语从句◆限定性定语从句◆非限定性定语从句(3)状语从句◆时间状语从句◆条件状语从句◆地点状语从句◆原因状语从句◆方式状语从句◆结果状语从句◆目的状语从句◆比较状语从句◆让步状语从句三、其他句型倒装句强调句省略句It 用法和There be 句型动词时态非谓语动词虚拟语气主谓一致原则反意疑问句第一讲:句子类型与句子成分一、句子种类和类型1、句子种类陈述句;疑问句;祈使句;感叹句2、句子类型简单句:由一个主语加一个谓语构成.并列句:两个或两个以上的简单句用并列连词连在一起构成的句子,叫做并列句,其基本结构是“简单句+并列连词+简单句”。
并列连词有:and, but, or, so, either…or.. neither...nor.. however not only…but also 等.并列句中的各简单句意义同等重要,相互之间没有从属关系,是平行并列的关系。
Hurry up or you'll be late.He is rich while I’m poor.复合句: 由主句和其他从句组成。
并列复合句:含有复合句的并列句.★I asked a man who has a wife and three children who did the cooking in his house and he replied that whoever came home from work first did it.二、句子成分That girl is doing her homework now.主语:主语是句子陈述的对象,说明是谁或什么情况。
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
高中英语语法一、英语词法1、实词:是指有实在意义,能独立承担句子成分的词名词、代词、形容词、副词、数词、动词2、虚词:没有实在意义,不能独立承担句子成分冠词、介词、连词、感叹词二、英语句法1、简单句2、并列句3、复合句(1)名词性从句◆主语从句◆表语从句◆宾语从句◆同位语从句(2)定语从句◆限定性定语从句◆非限定性定语从句(3)状语从句◆时间状语从句◆条件状语从句◆地点状语从句◆原因状语从句◆方式状语从句◆结果状语从句◆目的状语从句◆比较状语从句◆让步状语从句三、其他句型倒装句强调句省略句It 用法和There be 句型动词时态非谓语动词虚拟语气主谓一致原则反意疑问句第一讲:句子类型与句子成分一、句子种类和类型1、句子种类陈述句;疑问句;祈使句;感叹句2、句子类型简单句:由一个主语加一个谓语构成.并列句:两个或两个以上的简单句用并列连词连在一起构成的句子,叫做并列句,其基本结构是“简单句+并列连词+简单句”。
并列连词有:and, but, or, so, either…or.. neither...nor.. however not only…but also 等.并列句中的各简单句意义同等重要,相互之间没有从属关系,是平行并列的关系。
Hurry up or you'll be late.He is rich while I’m poor.复合句: 由主句和其他从句组成。
并列复合句:含有复合句的并列句.★I asked a man who has a wife and three children who did the cooking in his house and he replied that whoever came home from work first did it.二、句子成分That girl is doing her homework now.主语:主语是句子陈述的对象,说明是谁或什么情况。
表示句子说的是"什么人"、“什么事”、“什么东西”、“什么地方”等等。
名词、代词、数词、动名词、To do不定式、一个句子都可以做主语。
All roads lead to Rome.How to do it well is an important question.谓语谓语是对主语动作或状态的陈述或说明,指出“做什么”、“是什么”或“怎么样”. 谓语动词的位置一般在主语之后。
一般由动词或动词短语承担,具有各种时态、语态及语气的变化。
I seldom go to the cinema.He has already left.We are studentsShe fell ill last week宾语宾语,又称受词,是指一个动作(动词)的接受者。
一般而言,及物动词后面最少要有一个宾语,而该宾语通常为直接宾语。
名词、代词、数词、动名词、To do不定式、一个句子都可以做宾语,而to do不定式用于宾语补足语。
We study English at school.He enjoys listening to the music.直接宾语:表示动作的承受者或结果,通常指物。
Lend me your dictionary.间接宾语:动作所向或所为的人或物,通常指人。
Lend your dictionary to me.注意:间接宾语跟在直接宾语之后,间接宾语前要加介词to 或for加介词to的动词:give bring take hand lend pass read tell send show teach write do 等加介词for的动词:fetch find pay sing buy choose find get make等介词宾语:位于介词后面的宾语。
He walked to the office.宾语补足语:及物动词后的,用以补充说明宾语的身份、状态等的词或短语。
这类常用的及物动词有:make consider cause see find call get have let We consider /think the answer (to be) right.Electricity can make a machine run..可做宾语补足语的:名词、形容词及其短语、不定式及其短语、过去分词及其短语、as引出的宾语补足语、介词短语、副词和从句。
Let the enemy inYou mustn’t force him to lend his money to you.We will soon make our community what your community is now.We take English as a useful tool for everyday work.定语定语是用来修饰、限定、说明名词或代词的品质与特征的。
主要有形容词此外还有名词、代词、数词、介词短语、动词不定式(短语)、分词、定语从句或相当于形容词的词、短语或句子都可以作定语。
汉语中常用‘……的’表示。
定语和中心语之间是修饰和被修饰、限制和被限制的关系。
“的”是定语的标志。
He is an interesting man.Have you anything to sayCan you see the car downstairs?He was the one who succeeded in the experiment.状语英语中,状语用来修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。
状语的功用:状语说明地点、时间、原因、目的、结果、条件、方向、程度、方式和伴随状况等。
状语一般由副词、介词短语、分词和分词短语、不定式或相当于副词的词或短语来担当He drove his car carefully.China is developing fast during these year, but, unfortunately,unhealthily.He is very quick to change his mind.To buy a computer, I need money.Seeing his mother, the baby burst into tears.表语表语是用来说明主语的身份、性质、品性、特征和状态的,补充说明主语的意义,也叫主语补足语。
表语常由名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、不定式、动词的-ing、从句来充当,它常位于系动词(be, become, appear, seem, look, sound, feel, get, smell,turn等词)之后。
如果句子的表语也是由一个句子充当的,那么这个充当表语的句子就叫做表语从句。
Our teacher is very strict with us.The book is interesting and I'm interested in it.He looked just as he had looked ten years before.同位语一个名词(或其它形式)对另一个名词或代词进行修饰,限定或说明,这个名词(或其它形式)就是同位语。
We Chinese people are brave and hardworking.Yesterday I met Tom, a friend of my brother's.That is her habit, reading in bed.He gave orders that the work should be started immediately.The question whether to confess or not troubled the girl.三、句子基本结构(简单句)1.主语+谓语这种句型简称为主谓结构,其谓语一般都是不及物动词,例:Things change.事物是变化的。
Nobody went.没有人去。
2.主语+连系动词+表语这种句型称为主系表结构,其实连系动词在形式上也是一种谓语动词,但实质上表语成了谓语,例:Mr. Turner is an artist.特纳先生是位画家。
The milk turned sour.牛奶变酸了。
She became a lawyer.她当了律师。
3.主语+谓语+宾语这种句型可称为主谓宾结构,它的谓语一般多是及物动词,例:We never beat children.我们从来不打孩子。
My sister will fix everything.我姐姐会料理一切。
4.主语+谓语+宾语+宾语这种句型可称为主谓宾宾结构,其谓语应是可有双宾语的及物动词,两个宾语一个是间接宾语,一个是直接宾语,例:He gave the book to his sister.他把这本书给了他的妹妹。
I'll write you a long letter.我将写给你一封长信。
5.主语+谓语+宾语+宾补这种句型可简称为主谓宾补结构,其补语是宾语补语,与宾语一起即构成复合宾语.I found the book easy.我发现这本书不难。
(形容词easy作补语)I'll let him go.我将让他去。
(不定式go用作补语)注意:有时两个或更多的并列主语拥有一个共同的谓语,甚至并列有两个主语和两个谓语,这样的句子仍然是简单句,例:Mr. Wang and I often work together and help each other.王先生和我常在一起工作互相帮助。
第二讲:名词性从句在复合句中起名词作用的从句叫名词从句(Noun Clauses)。
名词从句的功能相当于名词词组, 它在复合句中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语、介词宾语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
1、主语从句在句中起主语作用的句子叫做主语从句。
(1)引导主语从句的关联词有:that(不充当句子成分,仅起引导作用,通常用it作形式主语;分句置于句首时,that绝对不可以省略。
),whether, who, whom, whose, what, which, whoever, whatever, whichever, where, when, how, why。
1 That he will succeed is certain.2 Whether he will go there is not known.3 What he said is not true.4 Where he hid the money is to be found out.5 Whoever comes is welcome.6 How we can help the twins will be discussed at the meeting.7 When they’ll start the project has not been decided yet.(2)为避免主语冗长,句子头重脚轻,经常用it作形式主语,主语从句放在后面作真正的主语.①It + be+形容词(obvious, natural, surprising, wonderful, possible, likely,certain, probable) +that从句.It is certain that he will succeed.②It +be +名词词组(no wonder, an honor, a good thing ,a pity, no surprise )+that 从句.It is a pity that they have to go without her.③It + be+过去分词(said, reported, known, thought, expected, decided, announced, arranged) +that从句.It is not known whether he will go there.④It + seems, happens等不及物动词及短语 +that从句.It seems that Mary is not coming at all.⑤It doesn’t matter (makes no difference)+连接代词或连接副词引导的主语从句.It doesn’t matter whether he comes.(3)注意连接代词whoever, whatever, whichever等引导主语从句的含义。
