并列句、复合句大全
简单句并列句复合句(全)

根据句子的结构,英语的句子可分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
1简单句只包含一个主谓结构,He is a doctor.2并列句用并列连词and,but,or把两个的简单句连接而成。
He is a doctor ,andshe is a teacher.I liked the story , but he didn’t like it. Hurry up,or you will be late.3 复合句句型:主句+连词+从句连词+从句+主句(包含一个主句、一个从句的句子叫复合句。
)1).定语从句2).状语从句3).名词性从句I don’t like the wa y (that, in which) he talked to me.Please pass me the book whose cover is green. (of which the cover/the cover of which)二、状语从句1 地点状语从句地点状语从句通常由where, wherever 引导。
Where I live there are plenty of trees.Wherever I am I wil l be thinking of yo u.2 方式状语从句方式状语从句通常由as, (just) as…s o…, as if, as thou gh引导。
1)as, (just) as…s o…引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后,但在(just) as…so…结构中位于句首,这时a s从句带有比喻的含义,意思是"正如…","就像",多用于正式文体,例如:Always do to the others as you would be done by.你希望人家怎样待你,你就要怎样待人。
As water is to fi sh, so air is to man.我们离不开空气,犹如鱼儿离不开水。
并列句复合句讲解

·
·
权
二、宾语从句的四个考点:
感
威
悟
解
中
读
考
考
语
点
法
·
强
名 师
化
精
训
讲
练
课
真
标
题
·
·
权
感
威
悟
解
中
读
考
考
语
点
法
·
强
名 师
化
精
训
讲
练
课
真
标
题
·
·
权
感
威 【提醒】当主句谓语动词为think, suppose, guess, believe等 悟
解
中
读 词,主语为第一人称时,从句表达否定意义时,形式上应否 考
· 感
威 解
叫作并列句。常见分类:
悟 中
读
考
1. 表示同等、平行或承接关系,常用连词and, both. . .
考 点
and, not only. . . but also. . . , neither. . . nor. . . , as well as等。 语
法
· 名 师
2. 表示转折关系,常用连词but, yet(然而), however(然
点击进入相应模块
课
真
标
题
·
·
权
感
威
悟
解
中
读
考
考
语
点
法
·
强
名 师
化
精
训
讲
练
课
真
标
题
(完整)并列句和复合句
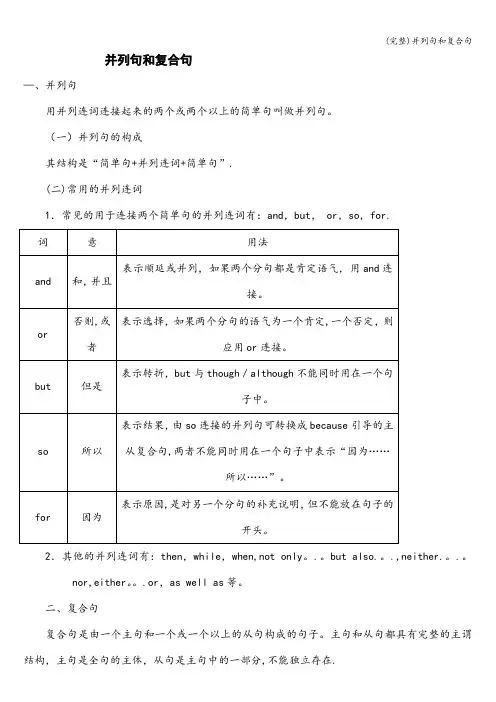
并列句和复合句—、并列句用并列连词连接起来的两个或两个以上的简单句叫做并列句。
(一)并列句的构成其结构是“简单句+并列连词+简单句”.(二)常用的并列连词1.常见的用于连接两个简单句的并列连词有:and,but, or,so,for.2.其他的并列连词有:then,while,when,not only。
.。
but also.。
.,neither.。
.。
nor,either。
.or,as well as等。
二、复合句复合句是由一个主句和一个或一个以上的从句构成的句子。
主句和从句都具有完整的主谓结构,主句是全句的主体,从句是主句中的一部分,不能独立存在.根据从句在全句中的不同作用,从句可分为:宾语从句、定语从句、状语从句、主语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。
在这里重点讲解宾语从句、状语从句和定语从句.(一)宾语从句1.宜语从句的引导词注意:whether和if引导宾语从句时,一般情况下可以互换,但在下列情况下须用whether,不能用if.①具有选择意义,宾语从句中有or或or not时.例如:Eg:We really don't know whether news is true or not.我们真的不知道这消息是否是真的。
②在介词后接宾语从句或不定式时。
例如:Eg:We are talking about whether we’ ll go back to our hometown.我们正在讨论是否回老家去.③作discuss等词的宾语时。
例如:Eg: We discussed whether we should close the shop.我们讨论了是否应该把商店关掉。
2.宾语从句的语序宾语从句无论是陈述句、一般疑问句或特殊疑问句意义,一律用陈述句语序,即“主语+谓语”结构。
句尾标点符号取决于主句。
例如:Are you a student? He asks.→He asks if you are a student.他问你是否是学生。
并列句和复合句

并列句和复合句并列句和复合句是英语中经常使用的两种句子结构。
它们能够使句子更加丰富多样,表达更加准确清晰。
本文将详细介绍并列句和复合句的定义、结构以及使用方法。
一、并列句并列句是由两个或多个独立的句子通过连词连接而成的句子。
它们之间的关系是平等的,没有从属关系。
常见的连词有and、but、or等。
例如:1. I like to play basketball, and my sister prefers swimming.2. The weather is hot today, but we still decided to go hiking.3. You can choose to watch a movie or go shopping.并列句可以通过逗号或者分号来分隔各个句子,也可以通过连词直接连接起来。
需要注意的是,如果句子之间的关系比较紧密,语义上有较强的联系,则使用逗号进行连接;如果句子之间的关系较弱或者需要更强调,则可以使用分号进行连接。
二、复合句复合句是由一个主句和一个或多个从句构成的句子。
主句是一个完整的句子,从句则依附于主句而存在,从属于主句。
从句可以是名词性从句、定语从句或者状语从句。
名词性从句:名词性从句在句子中充当名词的角色,可以作为主语、宾语、表语或者宾补等。
例如:1. What he said is true.(主语从句)2. I believe that you can do it.(宾语从句)3. Her dream is to become a doctor.(表语从句)4. I saw him playing football.(宾补从句)定语从句:定语从句用来修饰前面的名词或代词。
通常由关系代词(who、which、that等)引导。
例如:1. The book that I bought yesterday is very interesting.2. The girl who is sitting next to me is my best friend.状语从句:状语从句表示时间、条件、原因、目的、方式等状况,对主句进行补充说明或解释。
并列复合句

并列复合句并列复合句是指由并列词and, but, or等把两个或者两个以上的简单句连在一起而构成的句子。
1. and 表示并列关系- We provide books, and we set tests every week to check your progress.- Some people like travelling, some like reading and others like staying at home.2. but 表示转折关系- Our teacher is strict, but we all like him.我们的老师很严格,但我们都喜欢他。
- The situation looked desperate, but they didn’t give up hope.情况看起来非常危急,但他们并没有放弃希望。
3. or表示选择关系- Mary can travel with us, or she can stay with her grandparents.玛丽可以跟我们一起旅行,也可以跟她的祖父母呆在一起。
or 否则,要不然- Turn the heat down, or it’ll burn. 把炉火开小些,不然就会烧焦。
4. so 表示因果关系- It was dark, so I couldn’t see what was happening.天很黑,所以我看不见发生了什么事情。
- I can’t speak English well, so I would like to join English Club.5. for表示因果关系- The days were short, for it was now December.白天很短,因为当时是12月份。
6. while连接并列句具有对比转折的含义- Boys like playing computer games, while girls like singing and dancing.- Mary won many prizes, while Lucy won nothing.玛丽赢得了很多奖项,而露西什么也没获得。
中考 并列句和复合句总结

中考并列句和复合句总结一并列句:由两个或两个以上的简单句并列连接起来的句子叫并列句。
1. 并列句的基本句型:简单句+ 并列连词+ 简单句2. 并列句的类型:1) 并列关系(联合关系)。
连接词:and, not only…but (also), neither…nor等例句:I help him and he helps me.我帮助他,他也帮助我。
Not only did we write to her but also we telegraphed her.我们不仅给她写信而且还给她发了电报。
Neither I would consult him nor he would ask me for advice.我不想与他商量,他也不会征求我的意见。
2) 转折关系。
连接词:but, yet, still, while, however, when等例句:He failed many times, but he didn’t despair.他失败多次但并没有气馁。
She has difficulty in learning English, however, she works hard and is making rapid progress. 她学习英语有困难,然后她学习努力,进步很快。
3) 选择关系。
连接词:or, otherwise or else, either…or例句:We must hurry, or we’ll miss the train.我们必须快点,否则会赶不上火车。
Either you come to my place or I go to yours.或者你到我这儿来,或者我到你那去。
4) 因果关系。
连接词:for, so, thus, therefore, and so例句:We had better stay at home, for it was raining.我们最好呆在家里,因为天正在下雨。
简单句及并列句和复合句
一.五种简单句1.主语+不及物动词(主+谓)He laughed.2.主语+及物动词+宾语(主+谓+宾)I like Chinese food.3..主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语(主+谓+宾1+宾2)She taught them physics.4.主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语(主+谓+宾+宾补)We must keep the room warm.5. 主语+连系动词+表语(主+系+表)The weather is very cold.二.并列句He is a worker and I am a worker, too.He is very happy but his mother is very sad.上述两句地位一样,如同湖北的省长和湖南的省长一样,地位相等,称为并列句。
三.主从复合句If you are free, we will go to Beijing to play.前者地位低,为后面的主句服务,叫从句。
后者地位高,为主句。
两句合二为一,为主从复合句。
问题:主句与从句怎么辨别?四.从句种类很多。
句子成分划分:主语,谓语,宾语,定语,状语,补语,表语,同位语。
(8种)(主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句,同位语从句)-----名词性从句(定语从句)------形容词性从句(状语从句)------副词性从句Whether we will go shopping depends on the weather.( )He said that he wanted to go to town. ( )That is what I wanted. ( )Y ou are the man who I am looking for. ( )I will help you although I am not very rich. ( )The news that Mr.Li will be our new English teacher is true. ( )。
高中英语并列句复合句
并列句+ 复合句并列句:由两个或两个以上不分主次、相互独立的简单句构成的句子叫并列句。
并列句通过并列连词、连接副词和分号三种方式连接起来。
基本模式:简单句+并列连词+简单句。
1.表并列关系:and(和),not only...but (also)...(不但…而且…),not...but...(不是…而是…),neither...nor...(既不…也不…),on (the) one hand...on the other (hand)...(一方面…另一方面…),when(这时突然)等。
(1) In my opinion,everyone here is a member of our big family and we learn a lot from each other.就我而言,每一个在这里的人都是我们大家庭里的一员并且我们彼此学到了很多。
(2016·天津)(2) The traffic issue is a hard nut to crack. It not only affects our everyday life,but may also threaten people’s lives.交通问题很难解决。
它不仅影响我们的日常生活,而且威胁人们的生命安全。
(2015·江苏)(3)书籍不仅被分享而且它还能建立一个联系世界各地读者的桥梁。
(2015·重庆)Not only are books shared but also it can build up a bridge connecting readers from different parts of the world as well.(4)我认为,儿子拒绝与他的母亲交流不是因为他没时间而是因为他不愿意。
(2013·重庆)In my opinion,the son refuses to municate with his mother not because he has no time but because he’s unwilling to.(5). 我正在去书店的路上,在一个十字路口等绿灯时,突然一个大约十岁的女孩被一辆过往的汽车撞倒,肇事车辆快速逃逸了。
英语句子结构并列句复合句
两个或两个以上的简单句用并列连词或分号连接而成的句子叫并列句。
Eg.Hurry up;it’s getting late.He has a lot of money and he spent if freely.常见的并列连词:and,not only…but also,or,either…or,but,yet,while,so,for等。
when也可用作并列连词,意为“这时,那时”,常用于以下句型:sb. was doing sth. when…sb. was about to do/going to do/on the point of doing sth. …when…sb. had just done sth. … when…Eg.We were having a meeting______someone broke in.We were about to set off _______it suddenly began to rain.I had just finished my homework_____Tom came to me.Exercises.1.Shall we go to the cinema_____stay at home?2.There are many kinds of sports,______my favorite is swimming.3.Henry is very smart,______many of his classmates like him.4.I was glad to meet Jenny again,_____I didn’t want to spend all day with her.5.Don’t turn off the computer before closing all programs,_____ you could have problems.6.It’s not easy to change habits,______with awareness and self-control,it is possible.7.You have to move out of the way ____the truck cannot get past you.8.At school,some students are active _______ some are shy,yet they can be goods friends with one another.9.Tom was about to close the window_____his attention was caught by a bird.10.Some animals carry weeds from one place to another,______plants can spread to new places.由一个主句和一个或几个从句构成的句子叫做复合句。
并列句和复合句
让步 状语 从句
从句类型 原因
从句引导词
例句
状语
从句
Since everyone is here, let’s because, since, as, begin our meeting. 既然大家都 for 到齐了,我们开始开会吧。 Yao Ming plays basketball so well that many Americans have also become his fans. 姚明篮球打得如此好以至于很 多美国人也成了他的粉丝。
并列句和复合句
十四、并列句和复合句
一、并列句 由并列连词把两个或两个以上的简单句连接起来的句子叫 作并列句。常见分类: 1. 表示同等、平行或承接关系,常用连词and,both. . . and, not only. . . but also. . . ,neither. . . nor. . . ,as well as等。 2. 表示转折关系,常用连词but,yet(然而), however(然而),
连接 词
①that在从句中作宾语时可以省略;作主语时不能省 略 ② what, when, where, how, whatever, whenever, wherever, who, whom, whose等特殊疑问词作连接词 ③当宾语从句由一般疑问句变化而来时,连接词用 whether或if,表示是否 一随主,二随宾,三不变
where 表 示 地 点 , 在 定 语 从 This is the school where we once 句中作地点状语,其先行词 studied. 这就是我们曾经学习过 是表示地点的名词(place, 的学校。 school,room等) why表示原因,在定语从句 Can you tell me the reason why 中作原因状语,其先行词只 he hasn’t come here? 有表示原因的reason一词 你能告诉我他不来这儿的原因吗?
- 1、下载文档前请自行甄别文档内容的完整性,平台不提供额外的编辑、内容补充、找答案等附加服务。
- 2、"仅部分预览"的文档,不可在线预览部分如存在完整性等问题,可反馈申请退款(可完整预览的文档不适用该条件!)。
- 3、如文档侵犯您的权益,请联系客服反馈,我们会尽快为您处理(人工客服工作时间:9:00-18:30)。
并列句,复合句和连词命题规律:并列句和复合句以及连词是中考的重点内容,也是中考的必考题。
期中复合句考察的内容涉及状语从句,宾语从句,定语从句中引导词的运用命题趋势:宾语从句,连词的使用,定语从句的引导词一、并列句用并列连词连接起来的两个或两个以上的简单句叫做并列句。
1. 构成:简单句+ 并列连词+ 简单句2. 常见的用于连接两个简单句的并列连词有:and,but,or,so,for。
(1)and意为“和,并且”,表示顺延、并列等关系。
如:Work hard and you can pass the exam.= If you work hard, you can pass the exam.(2)but意为“但是”表示转折关系。
如:He is rich but he is not happy.(3)or意为“否则,或者,或“表示选择关系。
如:Hurry up, or you’ll be late.=If you don’t hurry up, you’ll be late.(4)so意为“所以,因此,于是”表示因果关系。
如:Kate was i ll so she didn’t go to school.(5)for意为“因为”,表示因果关系。
如:I have to stay up late, for I have a lot of work to do.3. 当连词and连接的并列句前半部分是祈使句,后半部分是将来时的陈述句时,其含义相当于由if引导的条件状语从句。
这种句型还可以用or来连接,但意思不同。
如:Think it over, and you’ll find the answer.=If you think it over, you’ll find the answer.4. 其他的并列句其他的并列连词有then,while,when,yet,not only…but also…, neither…nor…, either…or…, both…and…, as well as。
如:I like English while my brother likes Chinese.二、状语从句状语从句在主从复合句中修饰主句中的动词、形容词或副词等,状语从句由从属连词引导,与主句连接,位于句首时,常用逗号与主句分开,位于句末时,其前一般不用逗号。
状语从句根据其用途可分为时间状语从句、原因状语从句、结果状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句、方式状语从句、目的状语从句等。
的词叫做先行词,通常位于定语从句之前。
引导定语从句的是关系代词that,which,who (whom,whose)和关系副词when,where,why。
关系代词或关系副词位于先行词和定语从句之间,它既起连接作用,又充当从句中的一个成分。
含定语从句的复合句的基本结构为:先行词+ 关系词+ 定语从句1. 关系代词的用法一般情况下,that既可指人又可指物,可以代替who,whom和which,在从句中作主语或谓语动词的宾语,但不能作介词的宾语;which指物,在从句中作主语或谓语动词的宾语;who在从句中作主语;whom在从句中作宾语;whose在从句中作定语;where在从句中通常修饰表示地点的名词,作地点状语;when在从句中通常修饰表示时间的名词,作时间状语;why在从句中作原因状语,先行词通常是reason,有时why也可用“for + which”代替。
(1)下列情况下,只能用that引导,不能用who或which引导:1)当先行词是all,little,much,none,everything,anything,nothing等代词时。
如:❝Is there anything (that) you don’t understand?Tom told her mother all that had happened.2)当先行词前面有the only,the very,the last等修饰时。
如:❝He is the only person that can help you out.(当先行词是人时,也可用关系代词who,whom引导。
)3)当序数词或形容词最高级修饰先行词时。
如:❝This is the best book that I have ever read.4)当先行词前面有only,all,any,no等修饰时。
如:I want to read all the books that were written by Lu Xun.5)当主句是以疑问词who或which开头的特殊疑问句时。
如:❝Who is the boy that is playing football?(2)关系代词的省略。
一般情况下that,which,whom可以省略,但以下情况不能省略:1)关系代词that在从句中作介词的宾语时,不能省略,而且介词不能放在that前面,只能放在从句中有关动词的后面。
如:❝The woman that she talks with is her teacher.2)关系代词which,whom在从句中作介词宾语时,不能省略。
介词可以放在which,whom 之前,也可以放在从句中有关动词的后面,以使关系代词紧跟它所修饰的先行词。
如:❝I’ll never forget the day on which I joined the club.3)that,which,who在从句中作主语时,不能省略。
如:❝Who is the boy that is talking with our teacher?7.【2011湖南湘潭】23.______Zhai Xiaowei has only one leg, he can dance wonderfullyA .Though B.But C. So8.【2011连云港】11.—What shall we do now?—_______it’s raining hard, let’s stay at home.A. SoB. SinceC. ThoughD. If9. (2011贵州毕节)27.We should protect the earth,we will have no water to drink.A.so B.or C.and D.But10.【2013山东济南】29. Sam is a waiter, ____________ he really wants to be a singer.A. orB. ifC. butD. because11.【2013湖南长沙】28. —It’s too late. I have to go now.—Oh, it’s raining outside. Don’t lea ve _____ it stops.A. sinceB. untilC. while12【2013福建泉州】37. — Would you like some milk ?—No, thanks. I don’t like it, _______I know it's good for my health.A. becauseB. thoughC. if13.【2013四川南充】33. Could you tell me ________?A. where do you liveB. where you liveC. you live where14.【2013湖北十堰】35. The new-designed car is on show now. I wonder ___________.A. how much it costB. how much it costsC. how much did it costD. how much does it cost15.【2013湖北孝感】40. —Excuse me, can you tell me _______?—At about 8 o’clock, sir.A what time the plane will reach BeijingB what time will the plane arrive in BeijingC what time the plane will arrive BeijingD what time will the plane get to Beijing16.【2013湖北襄阳】40. —Could you tell me ?—At nine o'clock, in ten minutes.A. how will he leaveB. when he has leftC. why he is leavingD. when he will leave17.【2011浙江杭州】27. It’s too late to invite any more people. ______, you know how Ti m hates parties.A. BesidesB. HoweverC. StillD. Instead18【2011重庆】25. John, work hard_______ you will make much progress.A. orB. norC. butD. an19.【2013甘肃兰州】38. Lily doesn’t know ________ she and her friends can do to help the littleboy_______ parents have left their hometown for making money.A. that; whoseB. how; whoC. what; whoD. what;20.【2013浙江舟山、嘉兴】18. The shops were closed________ I didn't get any milk.A. soB. asC. orD. but21. 【2013浙江台州】20. —Hurry up, ______ you will be late for school.—OK. I’m coming.A. andB. butC. orD. so22【2013四川遂宁】25. He was tired he could not go on walking.A. too, toB. such, thatC. so, that23.【2013四川凉山】28. —Would you like to go shopping with me, Carmen?—I’d love to, you don’t want to go alone.A. untilB. beforeC. if24.【2013浙江绍兴】24.—Do you know ____Jane visits her grandparents?—Once a week. She loves them deeply.A. andB. butC. orD. So。
